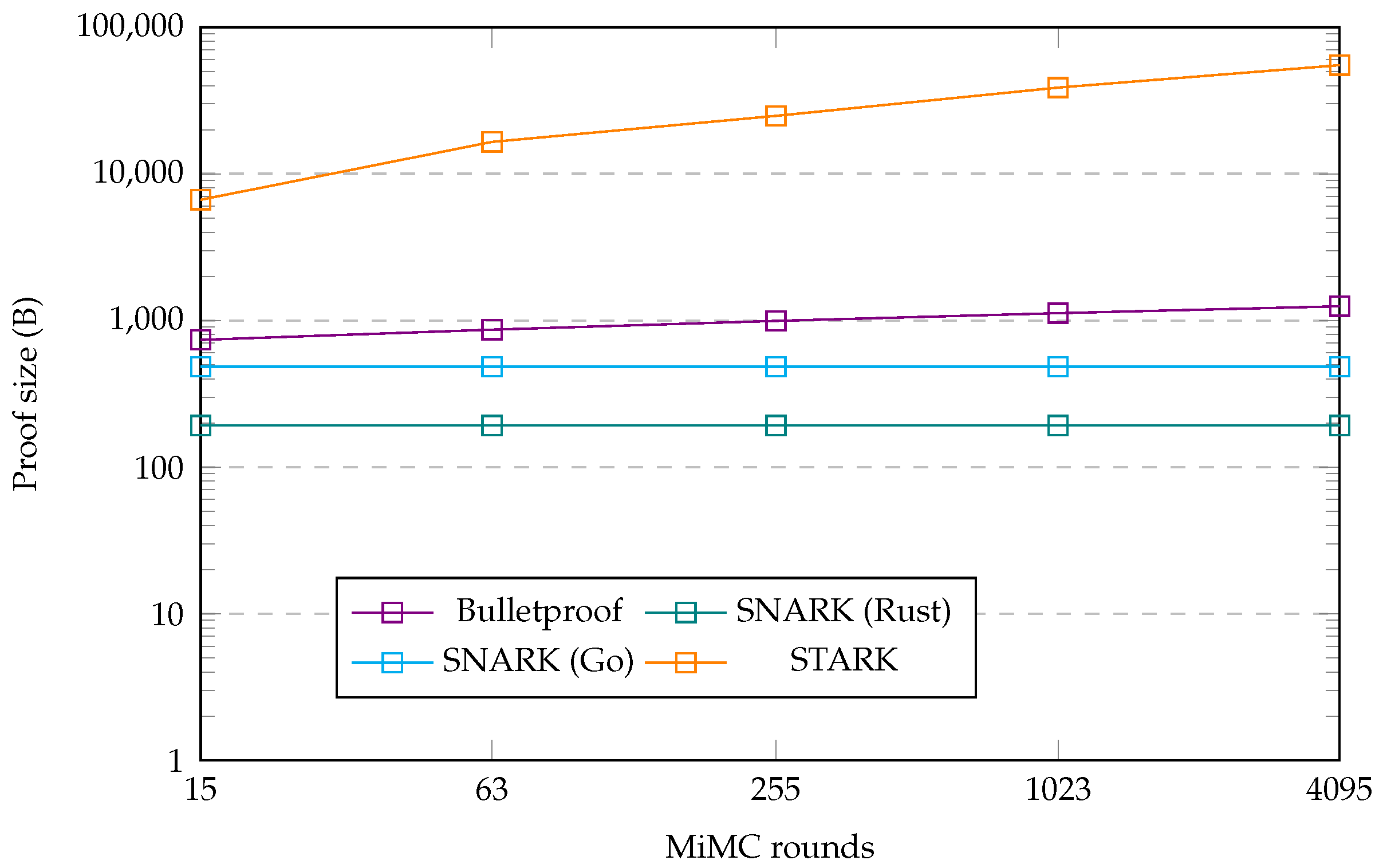Abstract
This study builds on our previous systematic literature review (SLR) that assessed the applications and performance of zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof non-interactive zero-knowledge proof (NIZKP) protocols. To address the identified research gaps, we designed and implemented a benchmark comparing these three protocols using a dynamic minimized multiplicative complexity (MiMC) hash application. We evaluated performance across four general-purpose programming libraries and two programming languages. Our results show that zk-SNARK produced the smallest proofs, while zk-STARK generated the largest. In terms of proof generation and verification times, zk-STARK was the fastest, and Bulletproof was the slowest. Interestingly, zk-SNARK proofs verified marginally faster than zk-STARK, contrary to other findings. These insights enhance our understanding of the functionality, security, and performance of NIZKP protocols, providing valuable guidance for selecting the most suitable protocol for specific applications.
1. Introduction
In everyday life, individuals often need to prove statements to others. The simplest method is by plainly stating, explaining, or showing evidence that can be verified. For instance, when purchasing age-restricted goods, a customer might show an identity document to prove their age to a cashier. However, this process can expose more information than necessary, such as the customer’s exact birth date and other personal details. In digital environments, the risk is even higher as servers can store copies of sensitive information. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), first introduced in a work by Goldwasser et al. [1], are a recent technology that could solve these problems. ZKPs allow a prover to prove a given statement, the proof of which a verifier can subsequently verify without being able to obtain any knowledge apart from the facts induced by the correctness of the statement itself. However, traditional ZKPs are interactive, meaning that they require multiple interactions between the prover and verifier before the verifier can trust or reject the statement. Additionally, other parties cannot verify the same proof afterward since this would require additional interactions. This limits the practicality of standard ZKPs. To this end, Blum et al. proposed non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs (NIZKPs) [2]. NIZKPs enable a verifier to verify a claim in a single interaction while also allowing other verifiers to verify the truth of the proven statement at another point in time.
Notably, ZKPs, especially the non-interactive variants, have gained prominence in cryptocurrencies like Zcash [3] and Ethereum [4]. In these contexts, they facilitate transaction verification without disclosing sensitive transaction details, thereby preserving privacy. Although cryptocurrencies have been the main source of interest in ZKPs due to their surge in popularity next to other blockchain technologies, the utility of ZKPs extends far beyond this domain. In our previous systematic literature review (SLR) [5], a summary of which we detail later, we collected applications of the three main NIZKP protocols relating to privacy-preserving authentication. Notably, we investigated applications and the performance of the zk-SNARK (zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge) [6,7], zk-STARK (zero-knowledge succinct transparent argument of knowledge) [8], and Bulletproof [9] protocols. In the SLR, we examined a total of 41 works that applied NIZKP protocols in a diverse set of applications. However, we found high variability in protocol performance metrics between the several applications, which we believed to be attributable in large part to the difference in applications and benchmarking procedures. This result indicated that a research gap exists for a comparison of the three main NIZKP protocols benchmarked in an equal, real-world applicable, use case.
Our aim in this work is to satisfy the observed research gap by performing a benchmark of the three main NIZKP protocols implemented in an equal, real-world privacy-preserving related, application. The relevance of this lies mostly with researchers and application designers obtaining a meaningful overview of the main NIZKP protocols, the situations in which they excel, and their implied performance characteristics. Insights from this work can furthermore guide researchers to the main aspects of concern when applying NIZKP protocols to real-world applications. This, in turn, can incite research into mathematical improvements and newly designed NIZKP protocols that reduce the deficiencies of existing protocols.
To define our aims and objectives for this research, we first outline the key research questions that we intend to address as a result of this research work. These questions serve to guide the main direction of this research investigating the differences between the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols:
- What are the performance differences between the three included NIZKP protocols, as observed from a real-world implementation of each protocol in an application that is as equal as possible, expressed in efficiency and security level?
- What use case contexts are the most beneficial for each NIZKP protocol, given the unique combination of its features and performance metrics?
In our previous SLR [5], the applications described in the included research works were each implemented with a single protocol. This meant that the research works were hard to compare on common grounds because of the dissimilar applications, benchmark procedures, and results. Therefore, the objective of this research is to implement a single application for the three protocols in a manner that is as similar as possible, with the direct purpose of making comparisons between the three protocols more straightforward. As a result, the comparison outcomes should be more informative. This objective is deeply embedded in the previously stated research questions, meaning that these questions will guide us toward a deep exploration of the three NIZKP protocols in a manner that aims to expose and clarify their associated differences.
We now reflect on the objectives we set for our overall research, specifying those we were unable to fully meet as outlined in the SLR. These objectives included filling the research gap by comparing the three most used NIZKP protocols and providing recommendations on the settings in which each protocol is most advantageous. The goals we aim to achieve in this research are as follows:
- To implement and evaluate the protocols in a practical setting, using a common benchmark for a real-world use case.
- To compare the efficiency and security of these three protocols, including their trade-offs between efficiency and security.
- To provide recommendations for the use of these protocols in different applications, based on their strengths and weaknesses.
While we made advances on these objectives in our previous SLR, we intend to further progress in the development of understanding related to these aims. Therefore, this specific research work aims to more comprehensively achieve the stated objectives to determine conclusive answers to the research questions from the previous section. To conclude, our aims and objectives for this research are to further detail the performance characteristics of the three most prevalent NIZKP protocols. We aim to do so by more comprehensively comparing those protocols in a benchmark, where we implemented each protocol in an application that is as equal as possible between the three implementations. We can then thoroughly answer which aspects of each NIZKP protocol should be considered when choosing a protocol to be applied in a particular environment.
The scope of our research is twofold. First, we briefly describe the mathematical and cryptographic primitives underlying each of the three main NIZKP protocols, the intention of which is to provide a concise understanding of the fundamental techniques that differentiate them. We do not, however, aim to accomplish a comprehensive mathematical and cryptographic manual that can be used as the basis for implementing the protocol itself in code or to create a new protocol from scratch. Furthermore, we describe the security model of each protocol, next to some vulnerabilities that have surfaced in at least some of the NIZKPs included in this work. The intention is, again, not to be comprehensive; instead, the information should serve as a general overview of security aspects and security vulnerabilities to consider when choosing a NIZKP protocol. Second, this work designs and performs a benchmark comparing the three NIZKP protocols zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproofs on their performance and security level. In the benchmark, each protocol is implemented in a privacy-preserving, authentication-related application using general-purpose programming libraries designed for each protocol. There are several limitations to this part of our scope. First, we intend to implement each protocol in an application to enable straightforwardly comparing their performance. For this, the application should be as equal as possible. The application, however, does not need to consider and implement every aspect that a production-ready real-world application would, as long as the benchmark results are representative. Secondly, we implement each protocol within a single application. We do not create multiple application benchmarks, nor will we implement the benchmark application across an exhaustive selection of programming languages and NIZKP protocol libraries. Provided that our benchmark implements the application using at least each of the NIZKP protocols, we have achieved this scope. Finally, while we aspire to benchmark the security level of each protocol, we will not allocate time for an in-depth attempt to breach the security of each protocol. We leave this to other researchers, as it is more meaningful to perform such tests in the context of an actual production-ready application rather than in our representative benchmark application.
As mentioned before, the relevance of this work lies mostly in providing other researchers and application designers with a meaningful overview of the three most prevalent NIZKP protocols and the situations in which they excel. The description of their mathematical and cryptographic primitives, as well as their security aspects and trade-offs, should provide researchers with a concise reference for understanding each protocol. Next, the benchmark results should provide researchers and application designers with a novel comparison of the three NIZKP protocols in an equal setting. This, in turn, should help them make informed decisions about which protocols to apply in which real-world applications, given the performance characteristics we detailed. While our previous SLR was a first step in achieving this, this research takes it a step further, helping researchers and application designers to choose the best-fitting NIZKP protocol for their requirements.
Therefore, we believe that our work benefits multiple entities. First, it serves as additional work for researchers just entering the field of NIZKPs next to our previous SLR [5]. Second, it should help individuals and organizations interested in applying NIZKP protocols to real-world applications by providing them with insights into each protocol’s performance and suitability in privacy-preserving related applications. Ultimately, we believe that our work will benefit academia, industry, and society as a whole by advancing the understanding and application of NIZKP protocols.
We organized this work as follows. First, we summarize our previous SLR, detailing its findings and the rationale for this follow-up research. Second, we describe our methodology for performing a benchmark comparison of NIZKP protocols, including the design and approach used for analyzing our results. Third, we provide a brief overview of the mathematical and cryptographic primitives for each of the three NIZKP protocols. Fourth, we detail the setup used for the benchmark, including the software, hardware, and specifics of our implementation. Fifth, we present the results from our benchmark and analyze them. Sixth, we discuss our results by answering our research questions and detailing the strengths and limitations of this research. Finally, we conclude this research with the main findings and recommendations, as well as a description of potential future research directions.
2. Related Work
In our previous SLR, we analyzed a broad spectrum of research works that described diverse use cases related to authentication. All included works were related because of our requirement that the use case applied at least one of the three NIZKP protocols, zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, or Bulletproofs, for privacy-preserving use within the application context. Ultimately, we examined 41 research works that surfaced from our collection and filtering criteria, discussing their implementation of the NIZKP protocol, and comparing these implementations on their use case. Furthermore, we discussed the performance and security of the NIZKP in the application when a work included benchmarked figures for these. For anyone interested in a more detailed description of our SLR intentions, collection and filtering process, results, and discussion, amongst other things, we recommend consulting the full research document [5]. We limit the remainder of this section to highlight the key findings from the SLR.
To start, 31 of the 41 works included in our SLR employed the zk-SNARK protocol in their described application, whereas the other 10 works utilized the Bulletproof protocol. This indeed means that our work did not end up including any works that based their application on the zk-STARK protocol. While this prevented us from drawing definitive conclusions on the proportionate use of the zk-STARK protocol compared to the other protocol, we did remark that this finding signifies the zk-STARK protocol was not commonly deployed in privacy-preserving authentication-related applications. More specifically, applications adhering to the search and filtering criteria from the SLR do not seem to utilize the zk-STARK protocol. We exert confidence in the notion that the reason for this will be more evident by the end of this work.
We also want to recite the observation that all but two works did not mention the quantum resistance of their implementation. We find this interesting especially since none of the 41 included works applied the only quantum-resistant protocol, zk-STARK. This clearly emphasizes a lack of consideration regarding this security aspect, despite quantum computing and quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols having been ongoing important topics for the past few years [10].
Of the 41 works included in the SLR, 30 works included some form of performance analysis of the implementation. Among those, 22 employed the zk-SNARK protocol, with the remaining 8 works utilizing Bulletproofs. In the SLR, we discussed the performance results in several categories, although here we will only review the overall performance differences between all works. We observed highly varying measures in multiple categories of performance metrics, including proof size, proof generation time, and proof verification times. These variations were significant, with several orders of magnitude performance differences between the same protocol applied in different works. Considering this extreme variance in observed metrics, we concluded that it was impossible to draw any definitive conclusions from comparing the performance between applications. The research works would have to specifically perform their benchmarks in a related way to another research work for us to draw any revealing conclusions from the comparison.
We had to draw a similar conclusion to that of the performance comparison for the security comparison, which proved to be even more complex to perform and accomplish a reasonable comparison. The main reason for this difficulty involved the diverse ways researchers used to describe the security of each implementation. Some works described the security by proving mathematical theorems in either natural language or as mathematical statements, whereas others described the security requirements of their application and mentioned either how they were achieved or how attacks were mitigated through implemented security measures, just to name a few of the encountered possibilities. Altogether, our SLR had a particularly challenging time inferring any reliable security comparison outcomes from the 31 works that included some form of security analysis.
2.1. Research Gaps
To remediate the current impossibilities of comparing different applications and their applied protocols on their performance and security, as described in Section 2, we suggested future research into a benchmarking standard. More concretely, we stated that the following actionable question arose from our SLR: “How can future security analyses of non-interactive zero-knowledge proof application implementations be standardized to facilitate better comparison?” If every research work utilizing NIZKP protocols would follow such a standard, this would facilitate a more uniform benchmarking procedure that enables an equitable and in-depth performance comparison between works. Yet, as our SLR found multiple research gaps stemming from limitations in current research works, this is not the research direction that we took for this work.
The research gap that we intend to address in this work involves the lack of availability, to the best of our knowledge, of a comprehensive applied performance comparison on the three main NIZKP protocols. Such benchmarks should utilize each of the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols in an identical application to allow anyone to extract meaningful metrics from the benchmark. In the next section, we explain how we will approach addressing this research gap.
2.2. Addressing Research Gaps
This work intends to perform the benchmark described in Section 2.1 to fill the previously stated research gap. This means that we will describe, in detail, the design and implementation of a benchmark application that we implemented as equally as possible for each of the three NIZKP protocols. To achieve such implementation, we select at least one programming library for each of the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols, and use these libraries to implement an identical application design. We can then conduct the benchmarking procedure, which we meticulously define in this document and, thereby, obtain metrics on the performance of each protocol implementation. We then use the data to compare the protocols based on their performance facets. This analysis helps us to draw conclusions and provide recommendations on which situations warrant the usage of each protocol, given their features, performance, and security characteristics.
The design of our benchmark will inherently incur some limitations on the results that we obtain, in turn, limiting the indications we can provide from a comparison using these metrics. We, however, express our conviction that the benchmark results will be beneficial for improving scientific knowledge of the NIZKP protocols regardless of the limitations and that the comparison will furthermore help many researchers obtain knowledge of the performance and security aspects embedded in each protocol.
Overall, we considered the stated knowledge gap to be important to fill given the rise in popularity of NIZKPs, which we previously observed in our SLR from the increasing number of published research works by year utilizing NIZKP protocols (see Figure 5 in our SLR [5]). Being well-informed on the performance and security characteristics of each protocol is an important first aspect in selecting the right protocol for a given application. A comparison between the three main NIZKP protocols implemented in an identical application, as proposed by this work, could strengthen the current corpus of scientific knowledge on this topic.
3. Methodology
In this section, we detail the methodology that we applied to obtain an answer to the research questions. We define an approach in which we describe how we aimed to achieve the defined objective in Section 3.1. Then, in Section 3.2, we describe in a detailed manner the design of our benchmark, as well as the application on which we benchmark the three NIZKP protocols. Finally, we outline the results that we intend to obtain from the benchmark and the analyses that we will conduct on the acquired data in Section 3.3 and provide a schematic overview of our work in Section 3.4.
3.1. Approach
As we previously stated, the main approach of this research was to design a benchmark that implements the same application, or one as close as possible, for each of the NIZKP protocols. For this, we used general-purpose programming libraries that implemented the three types of NIZKPs of interest: zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproofs. This gave us the ability to directly compare the metrics collected from the benchmark between the protocols, or at minimum, the metrics available for all three. The benchmark should preferably use a full-featured, stable programming library to implement the NIZKP application, as this provided us with the most options, stable performance, and a hopefully somewhat optimized codebase. Additionally, we prefer to use the same programming language for all three protocol libraries, as this eliminates the variable of differing performance and options associated with various programming languages. We also express a preference for low-level compiled languages over higher-level interpreted languages to minimize runtime overhead and reduce performance variability. We required the NIZKP libraries to be intended for general-purpose use, meaning that they were usable for all kinds of proofs in various application settings. While it would have technically been possible to implement a custom NIZKP protocol implementation for one specific application, enabling optimizations for that specific application, we wanted our benchmark to be representative of all kinds of different applications. Furthermore, while we only implemented a single application in our benchmark, by using general-purpose NIZKP libraries for each protocol, the performance differences between the protocols can be generalized for many other applications. We implemented the benchmark in code using the same programming language that the NIZKP libraries were written in, which enabled us to perform benchmarks directly on individual parts of the code. This was a requirement for us because we needed to benchmark the separate phases of the protocol, namely the setup, proving, and verification phases. Implementing the benchmark in this manner furthermore allowed us to access the size and security level metrics provided by the programming languages and NIZKP libraries. Both metrics would have been harder to benchmark accurately when running a benchmark using just compiled binaries as input.
3.2. Design
As outlined in our approach, our goal was to design an application, preferably related to privacy-preserving authentication, which could be equally implemented across three NIZKP protocols. This allowed us to benchmark their performance differences effectively. Initially inspired by Cloudflare’s concept of using hardware security keys (HSKs) for the attestation of personhood [11], further elaborated by Whalen et al. [12], our design aimed to replace CAPTCHAs with HSK-based signature validation. This concept evolved into ZKAttest by Faz-Hernández et al. [13], using sigma-protocol ZKPs to attest to personhood while preserving HSK certificate privacy. Due to implementation constraints and time limitations, we simplified our benchmark application to a hash function across all protocols, reflecting foundational performance insights despite not directly targeting privacy-preserving authentication scenarios. This approach allowed scalable benchmarking, offering crucial insights into protocol performance across varying computational loads.
3.3. Results Analysis
Now that we have defined our approach for the benchmark, we conclude the methodology by outlining the metrics we aimed to collect and the analyses we intended to conduct on those metrics.
Regarding the metrics, it is important to note that they varied between the protocols. For instance, the zk-SNARK protocol necessitates a trusted setup, unlike zk-STARK and Bulletproofs. Therefore, for zk-STARK, we focused on the size of the CRS, a metric not applicable to the other protocols. Common metrics across all three protocols included proof size, proof generation time, proof verification time, and the theoretical security levels of the proofs, although achieving uniform data across all protocols proved challenging, as clarified in Section 5.3.
Additionally, certain metrics were contingent on how each library implemented the ZKP protocol, such as additional compilation requirements or the inclusion of commitments in the proof. Our aim was to provide comprehensive metrics relevant to each protocol, enabling a robust comparison of data transfer, storage size, and computation times.
In terms of analysis, we evaluated several key aspects across the protocols:
- Setup requirements and time: What are the trusted setup requirements for each protocol? How long does setup take, and what is the data size involved?
- Proof generation: How long does it take to generate a proof? What is the resulting data size necessary for proof verification?
- Verification: What is the verification time for the proofs?
- Security aspects: How do the security levels differ between protocols? How does altering security levels impact other metrics?
Furthermore, we provided qualitative insights into aspects of the protocols and their library implementations that transcend exact metrics. Specifically, we discussed practical considerations where certain implementations may excel or falter based on situational demands.
3.4. Overview
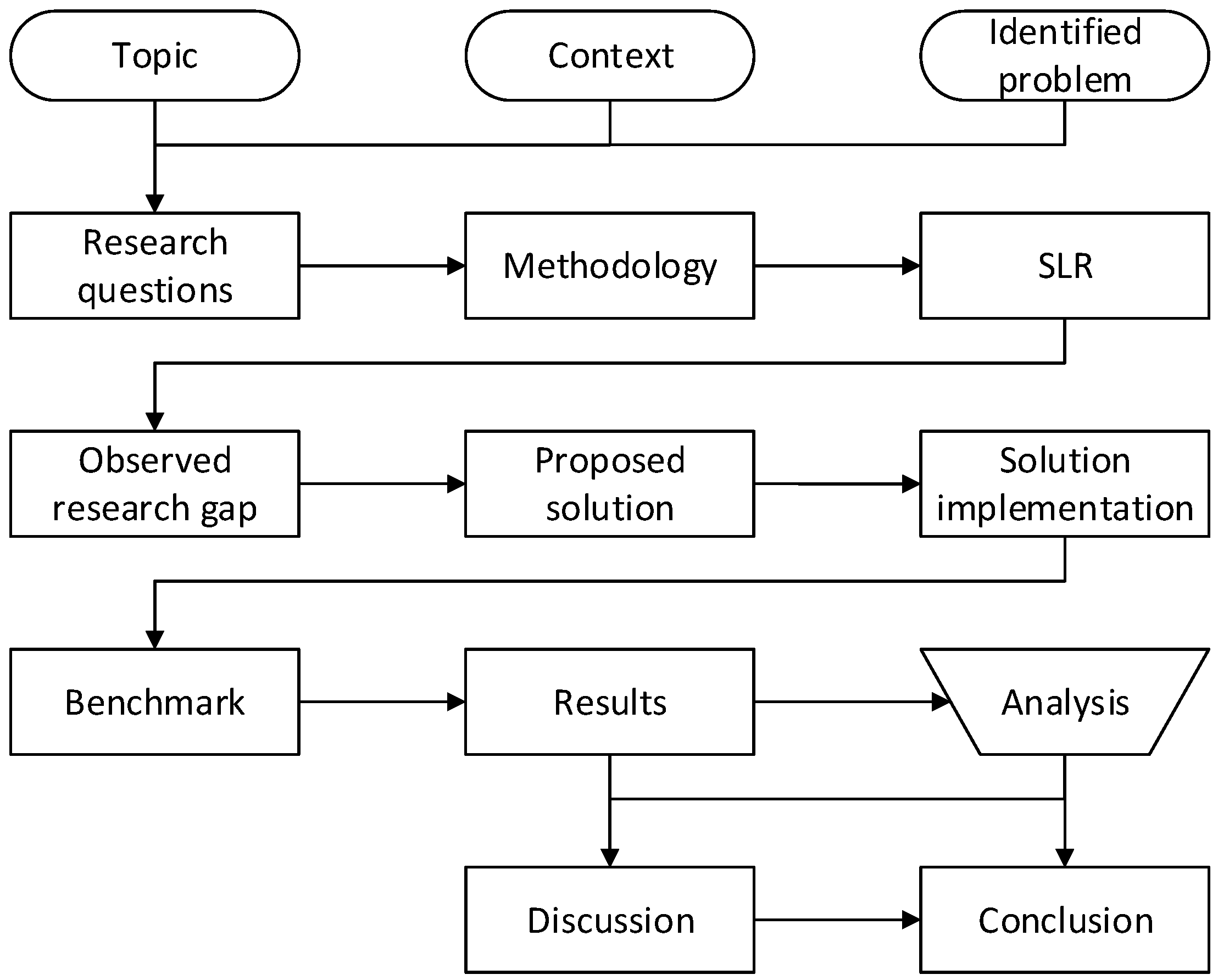
To conclude this section, we provide a schematic overview of the entire process for our research work, including the previously performed SLR, in Figure 1.
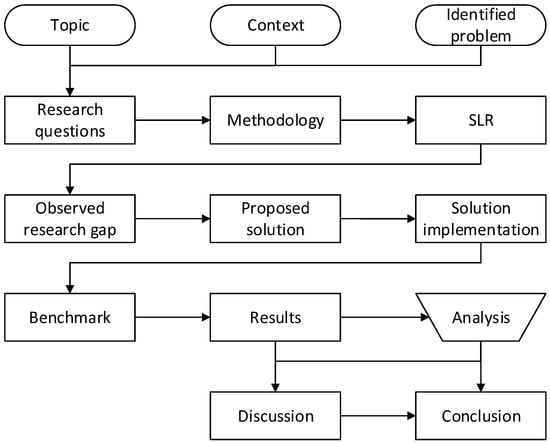
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the research work.
4. Protocol Comparison
To start this section, we emphasize the inclusion of this comparison to understand the origins of performance and security differences among the various protocols. The mathematical and cryptographic primitives underlying a NIZKP protocol not only enable the functionality of proving statements succinctly and with privacy but also define their core features, strengths, and limitations. These foundational elements significantly influence the performance and security characteristics of each protocol. Therefore, comprehending these underlying differences is crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of this study, including the benchmarks performed and the subsequent conclusions drawn. In addition to the performance primitives, this section also briefly touches upon the security models and assumptions inherent to each protocol. Understanding these models and assumptions is essential for anyone integrating NIZKPs into their applications. Deviations from these models can compromise the expected security levels, posing risks in critical scenarios such as medical data protection or financial transaction integrity. Hence, familiarity with these aspects is vital for informed protocol selection and implementation. Furthermore, we underscore the importance of understanding the historical implementation pitfalls of NIZKP protocols. By outlining past vulnerabilities—describing their nature, affected protocols, and remedial measures—we aim to prevent recurrent errors and enhance overall implementation security. This highlights the necessity for implementers to possess a foundational understanding of the mathematical and cryptographic underpinnings of NIZKPs. Such knowledge mitigates the risks associated with flawed implementations and contributes to the robustness of applications leveraging zero-knowledge proofs. Given these considerations, we argue that a grasp of NIZKP protocol primitives is advantageous, especially for readers less versed in the field. To aid comprehension, this section includes a concise overview of these primitives, facilitating a clearer understanding of subsequent discussions and analyses. We summarize the defining characteristics of the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols. Table 1 shows this comparison. Additionally, we briefly describe how we obtained the values listed in that table.

Table 1.
Comparison of zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols.
First, for zk-SNARK, the values for “Proof size”, “Proof generation”, and “Proof verification” were obtained from the introduction section of the Pinocchio paper by Parno et al. [6] and the Groth16 SNARK paper by Groth et al. [7]. They emphasize that the proof size is constant and the generation and verification times are linear, relative to the computation size. Second, for zk-STARK, Ben-Sasson et al. [8] provided details on the complexities of “Proof generation” and “Proof verification” in their paper. The proof size complexity, stated to be polylogarithmic, was confirmed through references and documentation from StarkWare [14]. Third, for Bulletproofs, the proof size complexity was obtained from Bünz et al. [9], where it is stated to be logarithmic in the number of multiplication gates. The linear complexities for proof generation and verification were confirmed through their detailed explanations in the Bulletproof paper. The values for “Trusted setup”, “Quantum secure”, and “Assumptions” were collected based on the comprehensive overview of the mathematical foundation and security assumptions of the three protocols. It is important to note that the complexities of proof size, generation, and verification may vary slightly due to the specific implementations and details of each protocol. For precise details, we recommend consulting the cited works directly.
5. Proposed Solution
In this section, we describe the proposed solution according to the methodology as described in Section 3. First, in Section 5.1, we restate our implementation for the proposed solution and link this to the research gap observed in our SLR. In Section 5.2, we then describe in detail the software and hardware that were used to perform the benchmark, while in Section 5.3 we comprehensively describe the implementation of the benchmark design as outlined in Section 3.2. After that, we detail the benchmark procedure that we followed to obtain the actual results from our implementation in Section 5.4. Finally, we justify our proposed solution where we briefly state how our proposed solution will address our research questions in this work in Section 5.5 and present a schematic overview of our proposed solution in Section 5.6.
5.1. Solution
In Section 2.1, we previously stated which of the research gaps observed in our previous SLR we intend to address in this work. To summarize in a single sentence, we intend to address the lack of a comprehensive applied performance comparison on the three main NIZKP protocols in existing research works. We described our methodology and how we intend to resolve our chosen research gap, in Section 3. Specifically, in Section 3.2, we implement a hash function application using each of the three protocols. Using these equivalent application implementations utilizing several NIZKP protocols, we can benchmark the performance and subsequently compare the resulting metrics between the protocols. To link our implementation back to the observed research gap, by implementing each of the three protocols of interest we provide the comparison between the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols that are absent in the current literature. We additionally go one step further by implementing these protocols in an equivalent application, which means that we remove the difficulty of comparing the performance between different protocol use cases, which was a significant limitation to the protocol comparison in our SLR. By benchmarking each protocol utilized in an identical application, we provide the closest possible comparison between the NIZKP protocols.
5.2. Software and Hardware
This section describes our use of software and hardware in implementing and performing the benchmark. Knowing the exact version of each piece of software that we used is important, because different software, and even different software versions of the same software, can induce vastly different implementations which exhibit vastly different performance characteristics. By providing the exact version of each used piece of software, we strive to make our benchmark repeatable by other researchers. Likewise, knowing the hardware used in a benchmark is important because using different hardware can manifest in vastly differing benchmark results. While we would expect different hardware to produce metrics that are proportionate to the speed of the hardware, where the metrics for each protocol change according to the performance of the hardware, this is undoubtedly not guaranteed. Such expectations may particularly not hold when using different processor designs, including different implemented instruction sets (e.g., AVX, AVX2) or an entirely different processor architecture (e.g., ARM instead of x86–64). For this reason, we list the hardware that we used to perform the benchmark, intending to make the benchmark repeatable for other researchers. Alternatively, the list of hardware allows other researchers to explain observed performance differences in the reproduced benchmarks when they use different hardware.
5.2.1. Software
For the software, the most important components in the benchmark are, of course, the ZKP libraries used to implement the three protocols. For this reason, these libraries were the first software that we decided on.
Initially, we started looking at ZKP libraries implemented in the Go language since this was the language with which we were most familiar. It also satisfied our requirement of being a compiled and performant language. However, we found that only a full-featured zk-SNARK library named gnark [15] was available in Go. Because of the requirements we set in Section 3.1, we should preferably choose a library for each protocol in the same programming language, this would not work. However, we noticed that the gnark package was well documented and had implemented more primitive building blocks than other libraries we found for the three protocols. For this reason, we found this package interesting to use for initial proof of concept implementations for ideas we thought of. Additionally, we expected that it would be useful to implement our benchmark application in the gnark package as well, next to the zk-SNARK implementation in the language of the other two protocol libraries. This SNARK implementation in Go could then indicate, when compared to the other SNARK implementation, what potential performance differences a library implementation in a different programming language can make.
This led us to perform a more general cursory search for ZKP libraries, through which we found that Rust had a well-implemented Bulletproof library [16]. We also found and examined several JavaScript libraries, but these did not fulfill our requirement of being written in a compiled and high-performance language. For example, the Bulletproof-js library [17] includes a benchmark comparison to other Bulletproof libraries in their documentation, including a comparison to the aforementioned Rust Bulletproof library. This comparison demonstrated that the performance of the Bulletproof-js library is several orders of magnitude lower than that of the comparable Rust Bulletproof library, which indicated to us that Rust might be a suitable candidate language to find an implementation for the other ZKP protocols. We also noticed that—by not finding any STARK libraries written in either Go or JavaScript—a full-featured zk-STARK library would be the most difficult to find. Therefore, we focused our attention on finding a good STARK library first. We found a library called libSTARK [18], which is a STARK implementation in C++ by the authors of the original STARK paper. However, our initial impression was that it seemed that this library uses a special notation to design circuits and that we would not be able to freely implement it with the main programming language. Furthermore, we found the Rust Winterfell crate [19], which seemed well-implemented, provided documentation, and was in active development. There were some limitations to this library though, including that it does not implement perfect zero-knowledge and focuses on succinctly proving computations instead of knowledge. We will describe these limitations in more detail in Section 5.3. However, even with these limitations in mind, it was the best option we found. We already identified the Rust Bulletproof crate earlier, which meant that we only had to find a SNARK library to discover a library for each protocol in the Rust language. We found this in the Rust Bellman crate [20]. With us unearthing a full-featured library implementation for all three protocols written in Rust, we implemented our benchmark in Rust. Apart from having a library implementing each protocol, the libraries were each well-implemented, at least somewhat documented, and well-known. In summary, we found that implementing the ZKP application in Rust using the Bellman, Bulletproof, and Winterfell crates was the best option for our benchmark.
To summarize, we ended up using four ZKP libraries written in two different programming languages. Since our benchmark implementation depended on these ZKP protocol libraries, we included those as our main dependencies. We additionally depended on several cryptographic libraries required for using the mentioned NIZKP libraries. We detail the full list of (direct) dependencies by language in Table 2.

Table 2.
Programming dependencies used to implement the benchmark.
Because of our chosen ZKP libraries, we required the usage of the two programming languages Go and Rust, as well as the Rust package manager Cargo. The software versions used are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Software used to implement the benchmark.
5.2.2. Hardware
As for the used hardware, we performed the benchmarks on a desktop computer with the following specifications:
- AMD Ryzen 9 5900x processor.
- 32 GB DDR4 3600 MHz memory (2 × 16 GB in dual channel).
The computer ran Windows 10 version 22H2 as the operating system and we configured it to run in the better performance power mode. The D.O.C.P. (direct overclock profile) setting was enabled in the motherboard settings to attain the intended speeds as specified for the memory modules. We did not apply any further overclock or undervolt, meaning that the processor ran at stock speeds.
5.3. Implementation
Now that we have determined which software and dependencies we want to use to implement the benchmark, we will describe the actual implementation of the benchmark using the chosen NIZKP libraries.
Our initial idea for the implementation, as described in Section 3.2, comprised of a zero-knowledge proof, which proved that a given public elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) key verified a signature and is included on a list of trusted keys. The intention for such proof was to prove that the user utilized a hardware security key from a trusted manufacturer to sign a message, without leaking the manufacturer details or batch information of the hardware security key. Our benchmark application would have implemented such proof for each of the three NIZKP protocols, albeit without communicating to a real hardware security key, generating the public keys in code instead. Our first step in creating the implementation was to create a proof of concept using the gnark zk-SNARK library. We implemented the proof of concept in gnark because of the great documentation, familiarity with the language, and numerous existing cryptographic primitives that the codebase contained. We started with an implementation using the Edwards-curve digital signature algorithm (EdDSA) to become familiar with the gnark library since creating a gnark circuit for proving the verification of an EdDSA signature was explained in a tutorial [21]. We expanded this proof to additionally verify that the used public key was included in a provided list of trusted public keys. We defined the public key as a secret input to the circuit, while we set the message, signature, and trusted key list as public inputs. The code for this implementation can be found in the Git repository for this research [22]. With a working implementation for EdDSA, we re-implemented the same approach in gnark for ECDSA. This process was more involved, because we had to use more primitive cryptographic building blocks, yet eventually we obtained the ECDSA-proof circuit working identically to the EdDSA circuit. We should note though that, since we ended up not using this implementation, we did not fully implement some aspects of the proof that did not impact functionality but would have impacted security in any real use cases. The corresponding code can be found in our Git repository [22].
Since we had a working zk-SNARK implementation using the gnark library, we knew that the idea would technically be possible to implement. With that said, we had to implement the same application for each of the three ZKP protocol libraries in Rust, which is where we hit some difficulties. First, while we implemented the proof-of-concept idea in gnark because it provided a tutorial, documentation, and many cryptographic primitives, this was not the case for the Rust ZKP libraries. This meant that we would have had to implement these primitives ourselves, leading to more opportunities for security issues. More importantly, we expected that this would take more time than we had available for the research. Even more critically, their creators geared the zk-STARK library toward succinctly proving computations, as opposed to knowledge like the zk-SNARK and Bulletproof libraries. This meant that the application would require a completely different approach in the STARK implementation compared to the other two protocols. On top of this, at the time of implementation, the STARK library did not provide perfect zero-knowledge. This meant that there was no option for us to provide the used public key to the circuit, as required in our proof of concept since the proof would not keep this key private. While it sounds strange to have to keep a public key secret, we reiterate that openly providing this key would reveal some privacy-sensitive information about the used hardware security key. As a result, doing so would invalidate the entire reason for utilizing a NIZKP in the application in the first place. For these reasons, we decided to abandon this idea for our benchmark application. Instead, we opted to use a more rudimentary application.
For the basic ZKP application idea that we could implement more equally for all three protocols, we implemented a hash function. Our application would ensure this hash either had a variable number of rounds or would use the hash as part of a hash chain, to enable some way to increase the required amount of work in the proof. After some deliberation between the MiMC [23], Poseidon [24], and rescue [25] hashes, we eventually chose the MiMC hash function. Namely, this hash function is well-optimized for zero-knowledge proofs [26] and has a simple algorithm that is easy to implement in proof circuits; moreover, example implementations we could adapt and build on were available for the SNARK and Bulletproof Rust ZKP libraries. The number of rounds used in the MiMC hash can be varied in our benchmark, where each round requires a different round constant for security. This enabled us to implement the hash for all three protocols, since, at least for our intents and purposes, proving knowledge of the pre-image of a public hash is the same as proving the computation of calculating the required hash from a pre-image provided by the prover. However, in the latter case, applicable to the STARK implementation, the pre-image would not necessarily remain private. Therefore, for equality reasons, we did not focus on these variables remaining private in the other protocols either. This is a limitation of our benchmark, for which we decided that the most important aim was to keep the proof as similar as possible. Since this limitation is important to consider for real-world implementations using ZKPs, we further discuss this limitation in Section 7.4.
The MiMC hash, named for its minimal complexity multiplication, is optimal for use in zero-knowledge proofs due to its simplicity and minimal multiplication requirements. While this simplicity limits the complexity of the proof, potentially making MiMC less directly applicable to more sophisticated cryptographic hash functions or complex computational problems, it is crucial to note that our benchmark intends to assess the core performance characteristics of the underlying protocols rather than specific applications.
The benchmark’s equivalence to more complex applications is ensured by adjusting the number of rounds in the MiMC hash, simulating increased computational effort akin to more sophisticated use cases. The approach is representative of complex applications since all statements, regardless of their complexity, are transformed into simple proof circuits with a varying number of gates before being processed into the proof. This method provides a foundational understanding of protocol behavior under varied computational loads, irrespective of specific hash functions or applications.
Although the MiMC application may not generalize directly to all scenarios, its purpose here is to offer a controlled environment to evaluate the protocol implementations. The focus is on the protocols’ handling of computational complexity, with the MiMC hash serving as a scalable proxy. The differences observed in performance metrics are primarily attributed to the NIZKP library’s implementation intricacies rather than the inherent limitations of the MiMC hash itself. Thus, while specific hash functions may yield different absolute performance results, the relative performance insights provided by our benchmark remain robust and informative.
To summarize, our actual implementation existed of a proof that verifies that the prover knows a pre-image to a certain MiMC hash image. The MiMC hash had a variable number of rounds, and we provided the round constants as input to the circuit. We implemented this application in each of the three chosen Rust protocol libraries. Our implementation adapted and built upon example implementations for both the Rust SNARK library [27] and Bulletproof library [28], while we created the Winterfell STARK library implementation from scratch. Moreover, we implemented the application in the Go gnark zk-SNARK library as well, for comparison reasons described in Section 5.2. We conjecture that this implementation provided the best possible comparison between the three protocols. Where significant for such real-world implementations, we provide additional protocol-specific context in Section 6 and Section 7. We also present additional justification for our implementation idea in Section 3.2. The code for all implementations can be found in the Git repository for this research [22].
An important consideration for the Bulletproof implementation was that we did not apply any form of batch verification, even though this is one of the beneficial aspects of the Bulletproof protocol that the Bulletproof library implements. While such batching verification could reduce the total verification time compared to performing each proof verification separately, it required an application where such batching is viable. In this work, we benchmarked the process of generating and verifying a single proof, which means that batching did not apply to our benchmark. We will discuss the implications of this in Section 7.
Finally, when inspecting our implementation, one should consider that we used seeded randomness for our benchmark. This means that the randomness we used in our implementation is not secure. Any real-world implementation should at minimum replace the seeded randomness with a cryptographically secure randomness source.
5.4. Benchmark Procedure
With the implementation code completely written, we commenced the benchmark procedure. First, we restarted the hardware which we performed the benchmark on to clear as many resources as possible. After this restart, we waited a minute for the operating system and all initiated startup processes to settle. We then opened a separate terminal window in the Rust and Go implementation directories.
The first benchmark we performed was the benchmark comparing the protocols on several numbers of rounds. For the number of rounds, we settled on the numbers corresponding to with , since this formula is a requirement for the zk-STARK implementation as described in Section 5.3. This gave us the set of MiMC rounds , which we believe provided a nice range to represent the performance differences between the NIZKP protocols for various amounts of required work. We ensured that we applied the correct default configurations and had set the desired number of MiMC rounds in the benchmark code. We then issued the ‘cargo bench‘ command, which compiled the Rust code as a release target for the best performance and used this compiled binary to run the benchmark for each of the three protocols sequentially. When the benchmark for the Rust implementations was complete, we logged the benchmark results and other metric outputs in an Excel sheet for each protocol under the set number of MiMC rounds. With the Rust benchmark results recorded, we switched to the other terminal for the Go implementation and repeated the process, only using the ‘go test -bench . ./internal/hash/.’ command instead. This command, like the ‘cargo bench‘ command for Rust, compiled the Go SNARK MiMC implementation and ran the benchmark outputting the results. When we performed all benchmarks for a given number of MiMC rounds, we repeated the process for each other number of rounds, noting down all the results in the same Excel sheet. We additionally ran a benchmark comparing the performance of the zk-STARK implementation for different options. The process for this benchmark resembled the procedure described above, yet instead of using fixed option parameters with a dynamic number of rounds, we fixed the number of rounds and modified the default option parameters by a single option at a time. By initiating the ‘cargo bench stark‘ command, we conducted the benchmark for just the zk-STARK implementation and obtained the performance difference caused by a single option parameter change. We then recorded the benchmark results and metrics in the Excel sheet and subsequently reverted the option parameter to the default, repeating this process for all options and several parameters for each option. Finally, we performed one final benchmark for the STARK, in which we set the option parameters to a combination of values that provided the best performance according to the individual parameter benchmarks. Now that we performed all benchmarks, we processed the metrics in the Excel sheet into the benchmark result tables and graphs found in Section 6.1. The code that we wrote to implement all benchmarks can be found in the Git repository corresponding to this work [22].
5.5. Justification
Now that we depicted our proposed solution in-depth, we succinctly justify how this proposed solution addresses the research questions as stated in Section 1. We address the first research question, “What are the performance differences between the three included NIZKP protocols, as observed from a real-world implementation of each protocol in an application that is as equal as possible, expressed in efficiency and security level?”, with our proposed solution. By implementing the identical MiMC hash application utilizing a real-world library implementation for each of the three included NIZKP protocols, we will be able to observe the performance metrics related to the efficiency and security level for each. While the performance and security metrics available in each protocol will limit our scope, we can compare the metrics that we were able to obtain for each protocol to provide an answer to this first research question. By extracting the strengths of each included NIZKP protocol from the performance metrics and cross-referencing these with the unique requirements of various applications, we can distill knowledge about the use case contexts that are most beneficial for each protocol. Using this extracted knowledge, we will then be able to answer the second research question, which should provide researchers with recommendations on the situations in which a given NIZKP protocol is best applied. To conclude, we express our confidence that by implementing the proposed application we will be able to provide a comprehensive answer to the research questions stated at the start of this work. We consider this to constitute sufficient justification to implement our proposed solution.
5.6. Overview
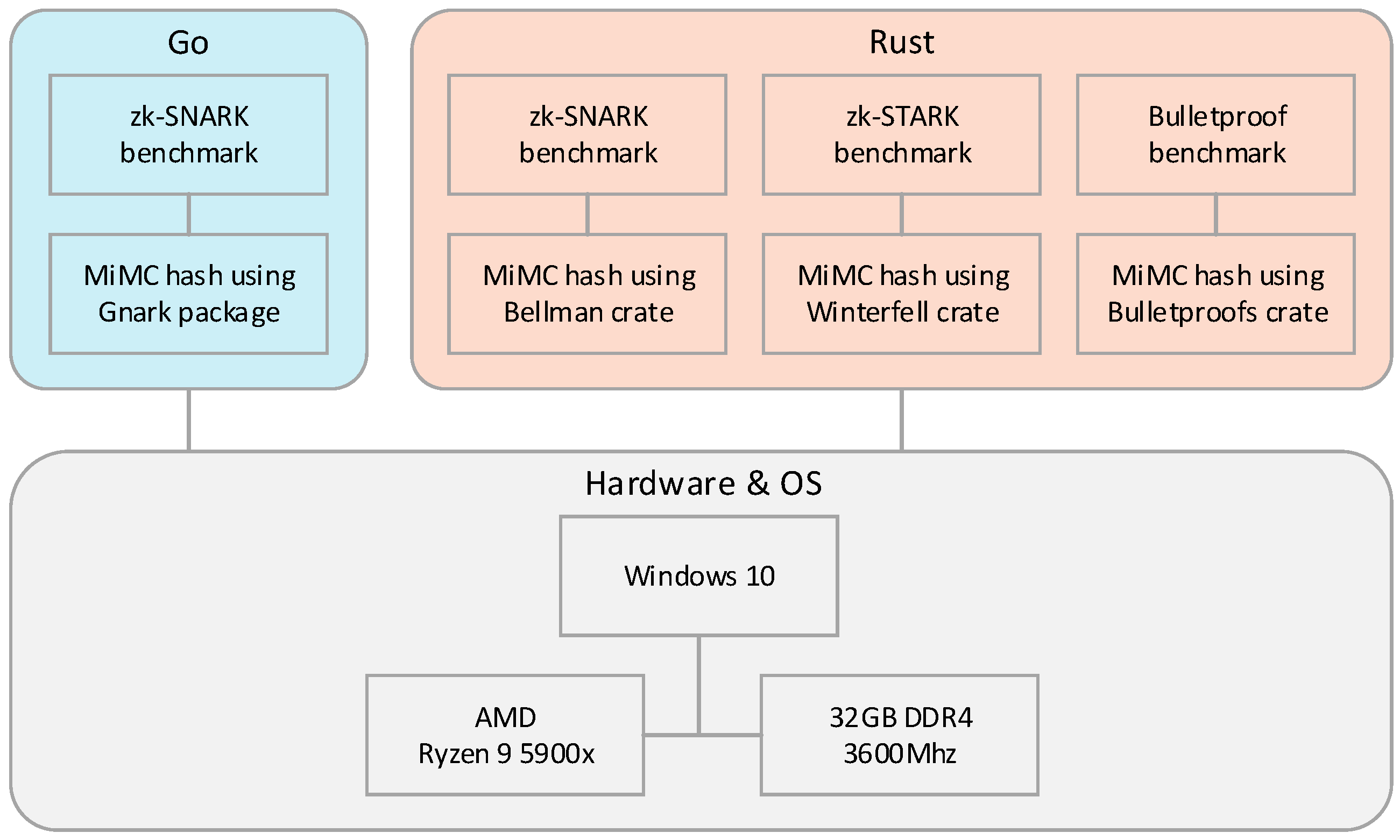
To conclude this section, we will provide a schematic overview of our proposed solution in Figure 2.
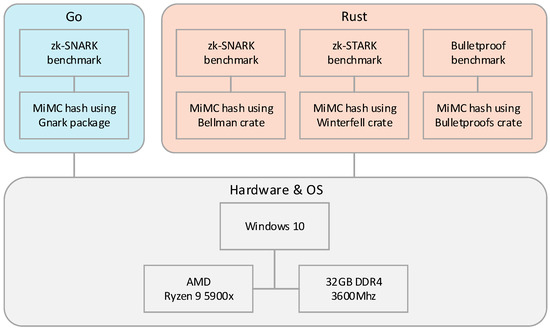
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of our proposed solution.
6. Results
In this section, we detail and analyze the findings collected from our benchmark. In Section 6.1, we list the benchmark results in the form of tables, with some explanations and complementary context for the metrics. In addition, we provide graphs as an alternative way to compare the performance differences between the ZKP protocols. Subsequently, we analyze the raw benchmark data and provide more context on the data in Section 6.2. In this analysis, we dive deeper into the differences between the ZKP protocols and any anomalous results we obtained from our benchmark.
6.1. Benchmark Results
In this section, we present the results from the benchmark that we implemented as described in Section 5.3 and subsequently performed according to the procedure described in Section 5.4. Before listing the results, however, we first provide some context on the abbreviations used to list the results, next to the configuration we used for each protocol.
6.1.1. Abbreviations
Within Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, the following abbreviations are used to save space, which enabled us to fit the tables on a single page:

Table 4.
Size results of the protocols benchmark.

Table 5.
Time and security level results of the protocols benchmark.

Table 6.
Results for option parameter changes in the STARK benchmark.
- Rnds—rounds; the number of rounds used in the MiMC hash.
- Protocol—The NIZKP protocol and corresponding programming library.
- –
- Bulletproof—Used the Rust Bulletproofs crate v4.0.0 [16,29].
- –
- SNARK (R)—Used the Rust Bellman crate v0.14.0 [20,30].
- –
- SNARK (G)—Used the Go gnark package v0.9.1 [31,32].
- –
- STARK—Used the Rust Winterfell crate v0.8.1 [19,33].
- CRS (B)—Common reference string; the size of the CRS (without verification key) in bytes.
- VK (B)—Verification key; the size of the verification key in bytes.
- W (B)—Witness; the size of the full witness in bytes.
- PW (B)—Public witness; the size of the public witness part in bytes.
- C (B)—Commitments; the size of the commitments in bytes.
- P (B)—Proof; the size of the proof in bytes.
- CT (ms)—Compile-time; the time required to compile the circuit in milliseconds.
- ST (ms)—Setup time; the time required to perform the setup in milliseconds.
- PT (ms)—Proof time; the time required to generate the proof in milliseconds.
- VT (ms)—Verification time; the time required to verify the proof in milliseconds.
- SC (b)—Security conjectured; the conjectured security level in bits.
- SP (b)—Security proven; the proven security level in bits.
- Option—The option for which the parameter was changed from the default. If (D) is appended to one of the option names, then this parameter is our chosen default.
- –
- NQ—NUM_QUERIES; the number of queries performed to verify correctness.
- –
- BF—BLOWUP_FACTOR; the factor that determined the probability of detecting a false proof in each query.
- –
- GF—GRINDING_FACTOR; the factor that impacted the security of the proof by requiring a certain number of leading zeros in specific hashes, resembling a proof-of-work.
- –
- FFF—FRI_FOLDING_FACTOR; the factor by which each iterative round reduces the degree of the polynomial.
- –
- FRMD—FRI_REMAINDER_MAX_DEGREE; the maximum degree of the remainder polynomial.
- –
- Hash—Hasher; the algorithm we set to calculate hashes within the protocol.
- –
- FE—FIELD_EXTENSION; field extensions enabled higher proof security than possible with just the finite field.
6.1.2. Configurations
For the main benchmarks, we chose a default configuration for each of the three protocols. In the Bulletproof protocol implementation, there were not a lot of configuration options. The protocol implementation depended on the curve25519_dalek_ng crate [34], which means that the protocol used the Curve25519 elliptic curve in combination with the Ristretto group [35]. This group enabled the construction of prime-order elliptic curve groups that had the special property of a non-malleable encoding. Furthermore, the Bulletproof protocol implementation depended on the Merlin crate [36], implementing proof transcripts and automating the Fiat–Shamir transform [37]. Apart from the dependencies, we used the following configuration for the Bulletproof implementation:
- Bulletproof generator capacity: This number had to be larger than the number of multipliers in the circuit, rounded to the next power of two. We accordingly set the Bulletproof generator’s capacity to , where m is the set number of MiMC rounds.
- Pedersen commitment generators: We used the default option provided by the library, meaning that we configured the usage of the ristretto255 base point and SHA3-512 hash of the same base point for the blinding.
The zk-SNARK implementation libraries, similarly, did not provide a wide range of configuration options. We configured both the Rust and Go implementations to use the BLS12-381 pairing-friendly elliptic curve [38] for the scalar field and pairings. For the Go code, we used the BLS12-381 implementation in the gnark-crypto package, while we used the bls12_381 crate for the Rust code. Additionally, both implementations used the Groth16 [7] proof system to implement the zk-SNARK proof, a system that both protocol libraries had built in. We did not select any further configuration parameters. Where required, we generated any other parameter randomly.
Finally, the zk-STARK library provided the most options for the configuration of all protocols and implementing libraries. Considering that the STARK implementation did not have any dependencies outside of the Winterfell crate itself, we only had to choose the default STARK configuration parameters:
- Number of queries (NQ): 42.
- Blowup factor (BF): 8.
- Grinding factor (GF): 16.
- FRI folding factor (FFF): 8.
- FRI remainder maximum degree (FRMD): 31.
- Hasher (Hash): Blake3_256.
- Field extension (FE): None.
We explain the meaning of these configuration options in Section 6.1.1. We chose these configuration parameters because they provided a good security level and were reasonable options near the middle of possible configurations in most cases. However, as described in Section 5.4, we also performed a benchmark for different configuration parameters for the zk-STARK protocol. This further compared the performance difference that the configuration parameters can make since configuration options were numerous enough that using just one configuration could have displayed a distorted view of the protocol performance. The results of the configuration parameter benchmark can be found in Section 6.1.3.
6.1.3. Results
Now that we described the abbreviations and configurations used for the benchmarks, we can start listing the benchmark results.
The results from the benchmark for each protocol, using the default configuration as described in Section 6.1.2, can be found in Table 4 and Table 5. Table 4 lists the sizes in bytes of different data, provided as inputs and outputs. As one can observe, the proof size was the only metric available for all three protocols and all four implementations. The CRS, because of the trusted setup requirement that is only applicable to the SNARK protocol, was only available for the two SNARK implementations. Similarly, the witness was only available for the Go zk-SNARK implementation because that library generated the witness in a separate step. After creation, the library used the witness as input to the proof-generating function, next to the proving key and the constraint circuit. The proof-generating function in the Rust implementation, on the other hand, only accepted the circuit and CRS as input. The library presumably generated the witness internally, which we could not directly measure in our benchmark. Lastly, the commitment size was only available in the Bulletproof protocol yet served a similar purpose to the witness in the SNARK protocol.
Table 5 lists the proof generation and verification times, in milliseconds, next to the security level in bits. In this table as well, we only list the results that we could obtain from each protocol implementation. As shown, only the proving-time and verification time metrics were available for all three protocols and all four implementations. Just like for the size benchmarks, the setup time metric corresponding to the trusted setup was only available for protocols that require a trusted setup, meaning just the two zk-SNARK implementations. The compile-time, only available to the Go SNARK implementation, was a separate step in the Go SNARK implementation. For this reason, we recorded it separately. The Rust SNARK library was written such that other steps include the compile-time; the compilation is not a separate step. Since at one point the circuit had to be transformed in a constraint system, and unlike in the Go implementation the Rust implementation took the non-compiled circuit as input to the proof-generating function, we expect the burden of the compile-time from the Go implementation was included in the proving-time for the Rust implementation. We consider this in our analysis in Section 6.2 and discussion in Section 7.
Finally, the conjectured and proven security levels of the proof in bits were only available from the protocol in the STARK implementation. The other protocols, sadly, did not implement any functionality to obtain the security of the proof as configured. While Section 4 outlines the cryptographic assumptions made for each protocol, and notes that only the zk-STARK protocol is considered quantum-resistant due to its security depending on the underlying cryptographic protocols, the proof circuit, and e.g., the security of the input, this does not specify the exact security level of each proof we created. Addressing this limitation, while possible, would require an extraordinary amount of time, extensive theoretical knowledge of the protocols, and a practical understanding of the library implementations. Therefore, we consider this to be outside of the scope of this research work and will elaborate on this limitation in Section 7.4. This means that we were unable to provide a full picture, but we will endeavor to provide a security level comparison in Section 6.2 by collecting security level metrics from works by other researchers. For theoretical security comparisons, we refer the reader to Section 4.
We then performed the configuration benchmark for the zk-STARK protocol implementation, in which we changed a single configuration parameter at a time to measure the performance impact. Table 6 lists the performance metrics obtained from that benchmark for the metrics available to the STARK implementation. The first column, “Option”, denotes the configuration parameter that we changed the default value of. We grouped the options by different values for the same parameter and marked the default parameter with (D). There are a few things to note in this table. First, the GF 32 benchmark does not have a listed result. This is due to the benchmark for this parameter not finishing a single iteration after a few minutes. Second, the FE Cubic benchmark, equally, does not have any results. This absence came as the result of the library not implementing the cubic field extension for our use, as specified by the library in a returned error.
Finally, with the results for the zk-STARK implementation configuration benchmark in hand, we wondered what would happen if we combined all the best-performing parameters together. Would the performance differ significantly from our configured default? To investigate this, we configured the zk-STARK implementation with the following ’best’ parameters, where we made sure the conjured security level did not go below 100 bits:
- Number of queries: 41; lower tested numbers showed better performance, at least for proof size and verification time, but reduced the security level below our set threshold.
- Blowup factor: 16; slightly increased the proof size and verification time, but strongly reduced the proof generation time. Blowup factors of 8 or lower demonstrated even better performance, yet they reduced the security level to a value below our set threshold.
- Grinding factor: 8; had the best proof size, a proof time equivalent to lower values, and a proof verification time equivalent to grinding factor 24.
- FRI folding factor: 4; showed the best proof and verification time metrics, while the proof size was only slightly larger than for the default FRI folding factor of 8.
- FRI remainder maximum degree: 255; the highest possible maximum remainder degree for the FRI had the best performance in all three metrics of proof size, proof time, and verification time, while not appearing to have impacted the security level.
We changed neither the hasher nor the field extension from the default. The Blake3_192 hasher, as expected, showed better performance than the Blake3_256 hasher for proof size and time, with a similar verification time. The quadratic field extension, while almost halving the proof time, significantly increased the proof size and verification time. Apart from displaying worse metrics, we worried that a different field extension would have an impact that would make it hard to compare the performance of the optimized parameters against the performance of the default values. Therefore, we did not alter this setting. We note that, while in most cases the conjured security level remained the same or at least above our stated threshold of 100 bits of security, the proven security level was usually affected negatively when choosing more performant configuration parameter values. When configured with the stated optimized parameters, we obtained the metrics as shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
zk-STARK combined configuration values benchmark.
6.2. Analysis
Now that we have detailed all the obtained benchmark results, we start with our analysis of those results.
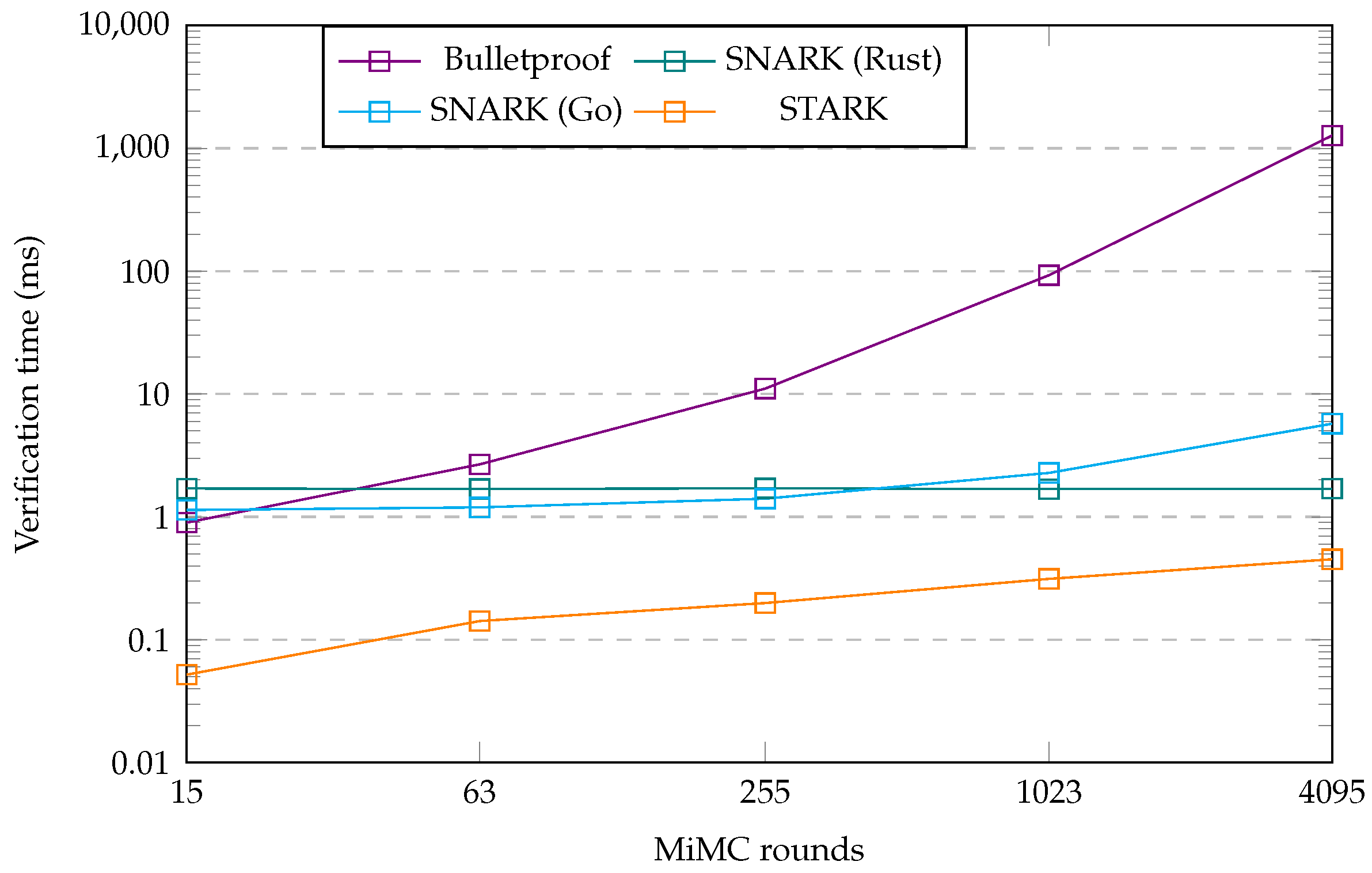
First, we analyzed the differences between the Bulletproof, zk-SNARK, and zk-STARK protocols. To this end, we created some additional graphs that show the obtained metrics as a plot for each protocol, which also shows the change in this metric for different numbers of MiMC rounds. Figure 3 shows the size of the proof generated by each protocol implementation and the difference that an increasing number of MiMC rounds makes for this metric. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show a similar plot for the proof generation time and proof verification time metrics, respectively.
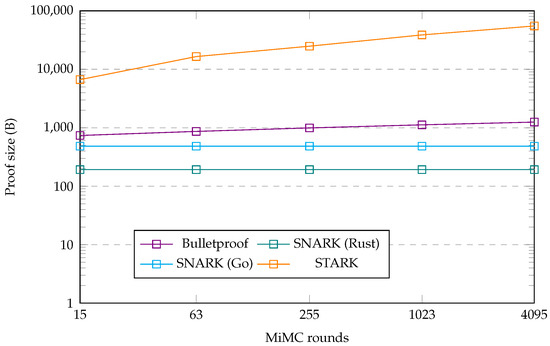
Figure 3.
Proof size benchmark plot.
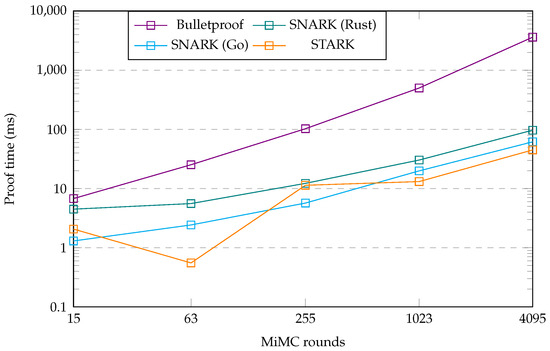
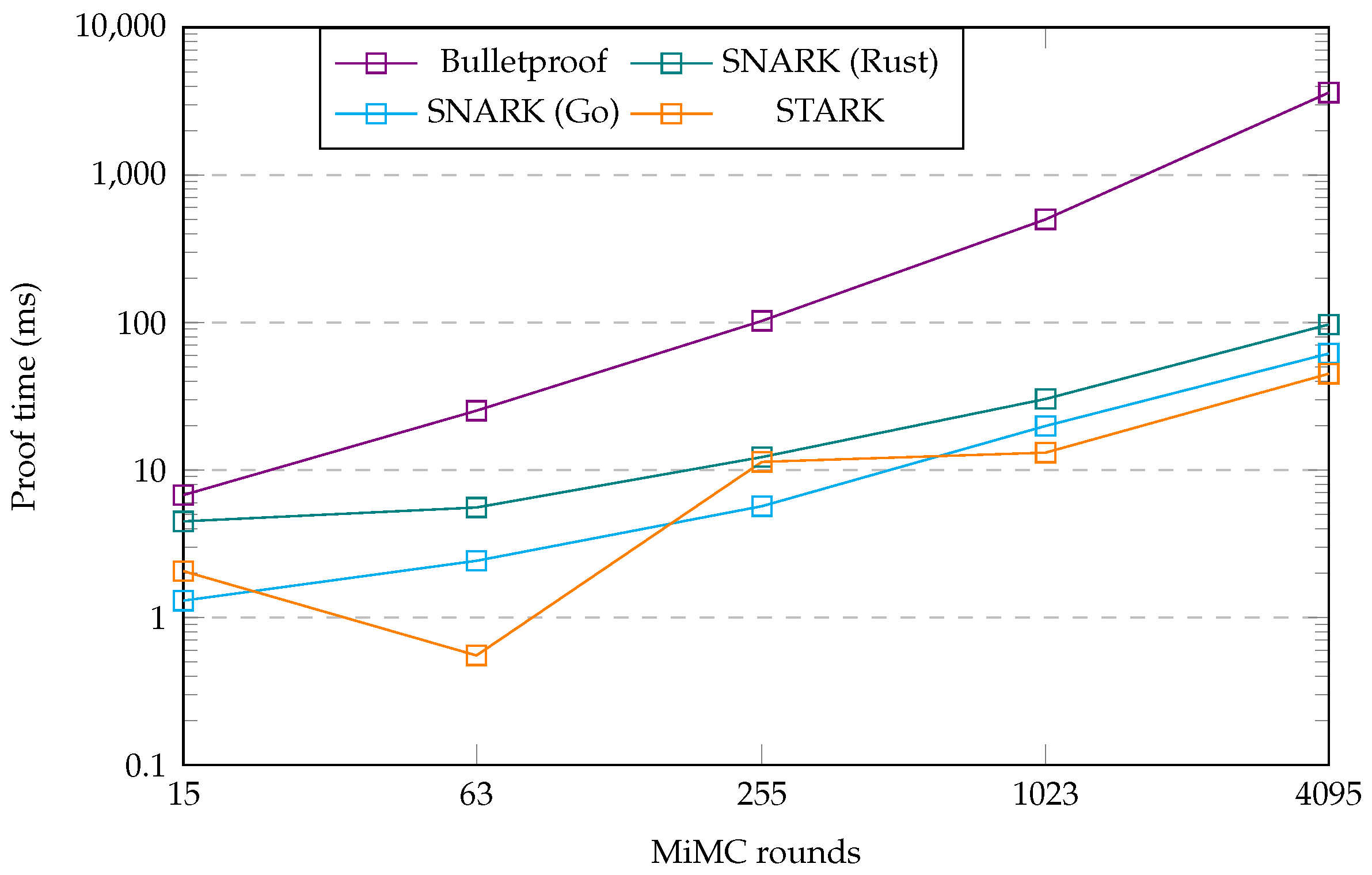
Figure 4.
Proof time benchmark plot.
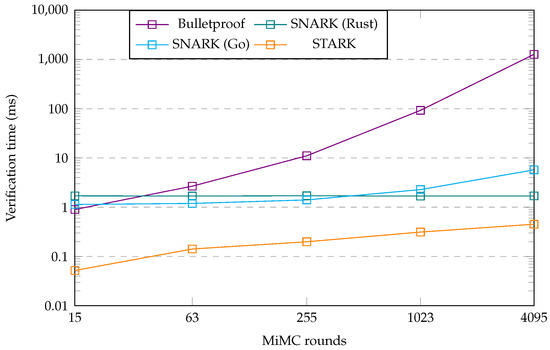
Figure 5.
Verification time benchmark plot.
As one can see from the metrics in Table 4 and the plot in Figure 3, there is a clear distinction between the proof sizes in the four implementations. The SNARK protocol implementations had the smallest proofs, with a size of 192 bytes for the Rust implementation and 484 bytes for the Go implementation. The proof size was also constant for both, meaning that the size of the proof remained the same, independent of the number of MiMC rounds. This was different for the Bulletproof and zk-STARK implementations, which both displayed a proof size that increased with the number of MiMC rounds. The proof size of the STARK protocol was larger than that of the Bulletproof protocol and additionally grew more rapidly in size with the number of MiMC rounds than the Bulletproof proof. This observation, however, fails to capture the broader perspective of data that needs to be transferred. The two SNARK protocol implementations may have had the lowest proof sizes, they additionally required the verifier to obtain the verification key. This key involved a constant additional 528 bytes for the Rust implementation, or an incrementally increasing size starting at 1448 bytes for the Go implementation. For us to obtain the total data size as required by the verifier, we summed these figures. This resulted in the data size from the Rust SNARK implementation, a total of 720 bytes, suddenly being just shy of the Bulletproof implementation data size. Having said that, the size of the Rust SNARK implementation was nonetheless still constant, whereas the data size for the Bulletproof implementation grew with the number of hash rounds. At the same time, the combined data size of the Go SNARK implementation grew even faster in the number of MiMC rounds. Moreover, the combined amount of data was already larger than for the Bulletproof, even without the public witness the verifier required to verify a proof in this implementation. By 1023 MiMC rounds, the amount of data from the combined verification key and proof size in the Go SNARK implementation was higher than for the STARK implementation. This showed a clear contrast between the two zk-SNARK implementations, an aspect which we will deliberate on in Section 7.
We will now examine the proof generation times, as detailed in Table 5 and plotted in Figure 4. As one can see, the Bulletproof protocol implementation demonstrated the slowest proof-generating time, followed from a distance by the two SNARK implementations. Additionally, even though all protocol implementations showed the proof generation times to be increasing with the number of MiMC rounds, the Bulletproof implementation proving-time increased faster than the other three implementations. The two SNARK implementations performed similarly in this metric, and performance between the two converged at higher numbers of MiMC rounds. In particular, at lower round numbers, however, the Go implementation performed better than the Rust implementation. Having said that, the Go SNARK implementation required a separate compile-time, which the Rust implementation did not need. For a lower number of MiMC rounds, the compile-time was negligible; however, as the number of rounds increased, this compile-time grew and became significant. When added to the proof-generating time, the Go implementation converged with the Rust implementation at 1023 rounds. Beyond this point, the combined compile-time and proving-time in the Go library exceeded that of the Rust library. The zk-STARK implementation’s proof time metrics showed some intriguing fluctuations. These fluctuations made it beat the Go SNARK implementation for some numbers of MiMC rounds while losing out to it in others. In particular, the 63 MiMC rounds benchmark metric is perplexing since the proof generating time was much faster than at 15 MiMC rounds. At first, we suspected this result to be a fluke in our benchmark. Re-running the same benchmark multiple times, however, provided us with consistent results throughout each attempt. This indicated that the performance fluctuation was caused by something other than a problem in our benchmark. Therefore, we attribute the performance fluctuation to some number internal to the protocol, related to the number of MiMC rounds, being optimal for the FRI process at 63 MiMC rounds, especially compared to the same number for the 15 rounds benchmark. We elaborate on this topic in our discussion in Section 7. In general, the data and graphs showed that the zk-STARK and two zk-SNARK implementations had proof times within the same order of magnitude, while the Bulletproof protocol was slower in generating proofs. Additionally, the proof time for the Bulletproof implementation increased more rapidly with the number of rounds compared to the other implementations.
We now change our focus from the proof generation times to the proof verification times, which we plot in Figure 5 from the data in Table 5. Our first observation is that the rankings between the protocols were like those for the proof generation times. The Bulletproof protocols showed the slowest proof generation times, whereas the two zk-SNARK implementations demonstrated a comparable proof verification time. The zk-STARK implementation demonstrated the fastest proof verification times throughout. Upon closer inspection, though, there are several more differences. First, the Bulletproof implementation temporarily had a faster proof verification time than the two STARK implementations for the lowest number of benchmarked MiMC rounds. Second, unlike the Go SNARK implementation, which showed slightly increasing verification times for larger numbers of MiMC rounds, the Rust implementation verification times were constant within the margin of expected variability of a benchmark. As for the proof generation times, this means that the Rust implementation became faster than the Go implementation at higher numbers of MiMC rounds. Third, especially at low round numbers, the zk-STARK protocol was around an order of magnitude faster than the two zk-SNARK implementations. Given that the verification times for the STARK increased though, while those of the Rust STARK implementation remained constant, it is conceivable that the STARK implementation would have lost this advantage for even larger numbers of MiMC rounds. This observation involves us extrapolating the data though, it is not something we can conclude from our benchmark data.
The final analysis for the comparing benchmark is the security level of each protocol. As specified in Section 6.1.3 and reflected in Table 5, we could only obtain the conjured and proven security level in bits from a function in the zk-STARK implementation library. This made it hard to directly compare the security levels for each implementation, which we will indicate as a limitation in Section 7.4. However, we could obtain an expected security level for the protocol implementations from referential works by others. In [39], the authors surveyed several elliptic curves for proof systems, including the BLS12-381 curve. They specified the BLS12-381 curve, the curve used in both our SNARK implementations, to have a 127- or 126-bit security for the group and prime field, respectively. While they likewise discussed curve25519 as used in the Bulletproof implementation, they did not mention any security level. Because the only configuration option for the zk-SNARK implementation was the used elliptic curve, as discussed in Section 6.1.2, we assume that the curve alone decided most of the protocol security in the SNARK implementation. This would give the two SNARK implementations the same (almost 128-bit level) security as stated for the BLS12-381 curve, which we expect to be a conjured security level and not a proven one. Similarly, because the Bulletproofs paper [9] only mentioned the security of the protocol in the context of the libsecp256k1 curve, we expect the curve to define the burden of the security level of the protocol. Since our Bulletproof protocol benchmark implementation used Curve25519, which provides an approximately 128-bit security level [40], we hypothesize this to be the conjured security level of the Bulletproof implementation as well. This is not the case for the zk-STARK, for which Ben-Sasson et al. described the proven security bounds in their work [41]. As they demonstrated, the conjured security level for zk-STARK is the minimum between a number calculated from the number of queries and grinding factor, the collision resistance of the used hash, and a number calculated from the field extension and trace length [42]. The lack of direct numbers for the security level of each protocol implementation in our benchmark resulted in uncertainty, though from the hypothesized numbers that we obtained from a spectrum of sources, the best we could infer was that the security level for the three protocols feature a comparable conjured security level. Yet, for this conclusion, we admittedly did not consider several practical factors in the SNARK and Bulletproof protocols. For this reason, we state that the conclusion does not provide a comprehensive view.
At last, we analyzed the benchmark comparing the different configuration parameter values in the zk-STARK protocol implementation. First, we dissected the obtained metrics for changing each configuration parameter, starting with the number of queries. As can be seen in Section 6.1.2, the proof size and verification time increased with the number of queries. This makes sense since the more queries, i.e., checks in the protocol, the protocol had to perform, the more work had to be included in the proof and verified. This can be observed clearly in the results, in that the number of queries determined a large part of the security level. The one metric that behaved anomalously to the expectation in this regard was the proof time metric. Even when the prover did not have to perform any additional work for a larger number of queries, this does not explain why the benchmark results drastically differ between even small value changes. Furthermore, these metrics neither consistently go up nor down, which is explicitly visible when looking at the sixfold increase in the proof time between 41 and 42 queries. We currently do not have an explanation for this phenomenon, yet the results for this metric were intriguing. Next up is the blowup factor. For this parameter, we could see a clear increase in the proof size and verification time. Apart from some fluctuation, the proof time also seemed to increase with a larger blowup factor, especially toward higher values. This observation can be accounted for by an increasing blowup factor leading to a higher likelihood that a verifier detects a false proof. In turn, this can be observed in the security level increasing with the blowup factor and the additional work that this required. We now look at the grinding factor, which determined a specific number of leading zeros in hashes, resembling a proof-of-work-like concept. This would require extra work from the prover for larger grinding factor values, which is indeed what we observed. In return for this extra work, the proof demonstrated a higher proven security level, though the conjured security level remained identical. The verification time, furthermore, did not significantly shift outside of the variation expected from a benchmark. The proof size, on the other hand, fluctuated in a manner that we cannot explain with benchmark variation. Instead, the small variation of a few thousand bytes indicated an expected proof size difference, initiated by fluctuations in parameters internal to the protocol that the proof had to include. The FRI folding factor did not show a clear increase or decrease in the proof size, proof time, and verification time metrics with the size of the parameter value. Instead, it seems that the optimum balance was somewhere in the middle. Whereas a folding factor set to 8 provided an optimal proof size, a value of 4 provided optimal proof generation and verification times. These optimum values were consistent with the impact that the FRI folding factor had, namely that it determined how much each iterative round reduced the degree of the polynomial. Therefore, large values would mean that each iterative round had to reduce the polynomial degree by a large amount, requiring a lot of work. Small FRI folding factor values, on the contrary, would require a lot of iterations to reduce the polynomial to the desired degree. The FRI folding factor did not seem to influence the security level. Lastly, there was the FRI remainder maximum degree parameter, an increase that generally led to a smaller proof size and lower proof verification time. The proof time overall showed the same trend, though as it did for the number of queries and the blowup factor, it fluctuated significantly. The observation that the proof size and verification times went down with a higher maximum remainder degree makes sense given that this value allowed a polynomial to have a higher maximum remainder degree. This enabled the protocol to not reduce the degree of the polynomial as much, which removed the need for the proof to include these additional iterations. This further reduced the work required for the verification. From our benchmark results, we observed that a reduced maximum FRI remainder degree did not impact the security level.
The final benchmark results, which collected the metrics for the STARK protocol when configured using a combination of the best-performing parameters, produced some disappointing results. The outcomes of this benchmark can be seen in Table 7. Each metric, except for the conjured security level, showed an improvement over the default configuration. While this is true, a closer examination reveals that the achieved metrics were worse than those achieved by just changing the FRI remainder maximum degree to 255. Only the proven security level improved when using this ’optimal’ configuration as opposed to choosing the default configuration and altering the FRI remainder maximum degree to 255. We further reflect on this finding in Section 7.
7. Discussion
In this section, we discuss the research and benchmark performed as described in previous sections. Starting in Section 7.1, we discuss the results achieved from the benchmark, including a discussion of our findings as well as a general discussion on the implementation and the used ZKP protocol libraries. With the achieved results discussed, we aim to answer our research questions from Section 1 in Section 7.2. We conclude the discussion by talking about the strengths of our research in Section 7.3, and subsequently contrast these strengths by examining the limitations of our work in Section 7.4.
7.1. Achieved Results
In our work, we benchmarked four general-purpose NIZKP libraries implementing the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof protocols for real applications. We benchmarked these libraries in an equivalent application related to the privacy-preserving authentication context. From the benchmark results, detailed in Section 6, we observed the following ordering between the protocols regarding proof size, proof generation time, and proof verification time:
- Proof size: We found that the SNARK protocol produced the smallest proofs, with the zk-STARK protocol producing the largest proofs. The Bulletproof implementation produced proofs that were somewhere in the middle, yet closer to the proof size from the SNARK. The Bulletproof proof size was within one order of magnitude from the two SNARK implementations, while the STARK implementation proof was at least one order of magnitude larger than the two other protocols. We note that this observation considers just the proof size, not including the verifying key size in the SNARK protocol.
- Proof generation time: Though with some fluctuations in the duration metrics, we overall observed the STARK implementation to be the fastest in generating proof. The two SNARK implementations came in second place, with the proof times for these three implementations remaining within a one-order-of-magnitude difference. Generating a proof using the Bulletproof implementation took longer than the other protocols, with a proof time that was more than an order of magnitude larger for the upper MiMC round numbers.
- Proof verification time: When verifying a proof, the STARK protocol performed the verification fastest. The Bulletproof proof verified the slowest, except at the lowest number of MiMC rounds where the proof verified slightly faster than the two SNARK proofs. Interestingly, the verification times for the STARK and Bulletproof proofs increased much more rapidly with the number of MiMC rounds than the SNARK proofs. While the STARK implementation was well over an order of magnitude faster at lower MiMC round numbers, this difference had shrunk to just around or even within an order of magnitude difference compared to the Go or Rust SNARK implementations, respectively, at the largest number of MiMC rounds. In the same way, the Bulletproof proof went from verifying slightly faster than the SNARK proofs at the lowest number of MiMC rounds to verifying more than two orders of magnitude slower than the SNARK proof by the largest number of benchmarked MiMC rounds.
We included these metrics for reference in Table 8. Assuming the found metrics are valid, and disregarding that the hardware used to perform the benchmark is unknown, we cross-referenced the metrics to our results obtained from the benchmark to observe that our results indicated a corresponding performance ordering for most metrics. The ordering for the proof size matched, and even the exact figures were comparable to the ones we obtained at higher numbers of MiMC rounds. We remark that it is not exactly meaningful that the exact metrics match, though since we expect the found comparison to be obtained from an entirely different application benchmarked on different hardware. Therefore, we expect this correspondence to be coincidental. For the proof time, the ordering of the best-performing protocols also matched, even with the SNARK and STARK metrics being much closer to each other than to the Bulletproof at higher MiMC round numbers. Only for the verification time, the ordering in our benchmark was different from the cross-reference source. Whereas in our benchmark the STARK implementation verified faster than the SNARK implementations, the cross-referenced comparison stated the inverse. What did match, however, was that the SNARK and STARK times were much closer together, with the Bulletproof proof verifying significantly slower. At least, when considering the results we obtained for larger numbers of MiMC rounds.

Table 8.
Found external protocol comparison.
Regarding the cross-check for the proof size, this only included the actual proof size. When we included the verification key as well, as required by the verifier to verify proof in the two SNARK protocol implementations, the outcome changed. Not only did the Rust implementation, in that case, have a combined size almost as large as the proof size for the Bulletproof protocol, but for lower MiMC round numbers, the total data size for the Go SNARK implementation became larger than the Bulletproof proof. Not only that, but the combined size also furthermore became so large at higher numbers of MiMC rounds that the Go SNARK implementation had a larger combined verification key and proof size than the size of the STARK implementation proof. That was the case without even including the witness size, which the verifier additionally required in the Go SNARK implementation. Not only would including the verifying key in the comparison alter the performance ordering between the different protocols, but it also furthermore unveiled a clear contrast between the performance of two implementations of the same protocol. A contrast that manifested itself to a significantly smaller degree in the time-based metrics. We found this difference, a verifying key constant in size or almost increasing exponentially in size with the number of MiMC rounds, intriguing at the very least. While we aimed to limit such contrast between the different implementations of the three different protocols by using libraries written in the same programming language for each protocol, these observations not only tell us that that was the right thing to do but also show the importance of optimized protocol libraries. The libraries implementing the protocol can significantly impact the final performance, just like the programming language they were written in. Libraries can improve performance for example by using efficient computations and taking into account memory management and hardware bottlenecks. Such optimization can make a substantial difference in the performance, even when both library implementations use the same Groth16 backend [7] underneath. So, libraries implementing cryptographic protocols play a crucial role in determining the efficiency and performance of these protocols. By leveraging optimized computations, efficient memory management, and hardware acceleration, libraries can significantly enhance the speed and reliability of cryptographic operations. The impacts of the libraries on performance are as follows:
- Efficient computations:
- Algorithm optimization: Libraries can optimize the underlying algorithms used in cryptographic protocols. This includes implementing efficient mathematical operations, such as fast modular arithmetic, which can significantly reduce computation time.
- Data structures: The choice of data structures within a library can affect performance. Efficient data structures can lead to faster data access and manipulation, improving overall speed and responsiveness.
- Memory Management:
- Memory allocation: Libraries that efficiently manage memory allocation and deallocation can reduce allocation performance overhead. This is crucial in resource-constrained environments where memory is limited.
- Cache utilization: Libraries that are designed to take advantage of CPU cache can reduce latency by minimizing the need to access slower main memory. Optimizing data locality and access patterns can lead to substantial performance gains.
- Hardware bottlenecks:
- Parallelism and concurrency: Libraries that support parallel processing can leverage multi-core processors to execute multiple operations simultaneously, reducing execution time for complex cryptographic tasks.
- Hardware acceleration: Some libraries are optimized to use hardware accelerators, such as GPUs or FPGAs, which can perform specific cryptographic operations much faster than general-purpose CPUs.
- Programming language influence:
- Language features: The programming language in which a library is written can influence performance. Languages that support low-level memory access and fine-grained control over hardware resources, like C or Rust, can enable highly optimized implementations.
- Compiler optimizations: The choice of compiler and its optimization settings can also impact performance. Compilers for languages like C++ or Rust can apply aggressive optimizations that improve the efficiency of compiled code.
- Impact on protocol performance:
- Proof and verification sizes: As mentioned, the size of the proof and verification key can vary significantly depending on the library implementation. This affects not only storage requirements but also the time required for verification.
- Time-based metrics: The execution time of cryptographic operations can vary based on library optimizations. Differences in computation speed, memory usage, and data handling can lead to noticeable variations in performance metrics.
Lastly, we want to discuss the results achieved in the benchmark comparing the configuration parameter values for the zk-STARK protocol implementation. We examined the performance when configured using the settings that individually provided optimal performance, as described in Section 5.4. We found that this improved the performance compared to our default configuration for all metrics except the conjured security level. We could argue that this means that we initially chose the wrong default configuration parameters. However, as mentioned in Section 6.2, we achieved even better performance metrics when using the default configuration adjusting only the FRI maximum remainder degree. This demonstrated that the ’optimal’ configuration parameter values when combined are not necessarily ’optimal’ at all and the combination of different parameters forms a complex system of trade-offs. To truly inspect the impact of each parameter and the best-performing configuration, in that case, would require more than benchmarking all combinations of parameters. Just to benchmark all combinations of our selected individual parameter changes would require benchmarking configurations. Considering all parameter values would significantly increase this value. Even then, we would have benchmarked for just a single number of MiMC rounds, which as seen from our benchmark can significantly influence the performance of the STARK protocol implementation. And even at that point, we still would have only performed the benchmarks on a single hardware configuration, while different hardware configurations may benefit from different software configuration settings. Because of this, we still consider our approach of choosing the initial configuration using parameter values somewhere in the middle to be a safe choice, which enabled us to inspect the impact each parameter has on the protocol performance. In addition, we observed that the proof size, verification time, and conjured security level were not extremely different. Even the proof time, for which our default number of queries of 42 was a bad pick, was reduced only six times by choosing 41 as the number of queries. While such performance improvement is not negligible, it is sufficiently within an order of magnitude difference even though it constitutes a larger improvement than the threefold improvement achieved by the combination benchmark. Given that the zk-STARK protocol had a proof size more than an order of magnitude larger than the second-largest proof size created by the Bulletproof protocol, not to mention that the STARK implementation already showed the best performance for the proof time and proof verification time, a more optimal configuration would ultimately not have altered our conclusions. Therefore, we conclude that our findings are still valid, despite the sub-optimal default configuration that we used for the zk-STARK protocol.
7.2. Research Question Answers
Based on the achieved results, we can now attempt to answer the research questions from Section 1. The two research questions stated for this work are as follows:
- What are the performance differences between the three included NIZKP protocols, as observed from a real-world implementation of each protocol in an application that is as equal as possible, expressed in efficiency and security level?
- What use case contexts are most beneficial for each NIZKP protocol, given the unique combination of its features and performance metrics?
The first question we can conveniently answer for the performance by using Table 9, which includes the average performance for each protocol over the five benchmarks with different numbers of MiMC rounds. We calculated the average using the original, exact numbers and then rounded the average proof and verification times to three decimal places.

Table 9.
Protocol comparison using the average performance over the five default benchmarks with different MiMC rounds.
From this table, we can observe that the SNARK protocol generates the smallest proofs, whereas the generated proofs from the Bulletproof and STARK protocols are slightly larger or significantly larger, respectively. This proved to be a significant disparity with the proof and verification times, for which we observed the shortest average proof generation and verification times from the STARK protocol. The SNARK and Bulletproof protocols took longer to create and verify their proofs. This observation answers the research question regarding the performance aspect, yet it is not a comprehensive perspective on its own. The SNARK protocol, as implemented in our benchmark, required a trusted setup. There exist situations where this is not desirable, as it requires trust in the party that performs the setup. Similarly, the STARK protocol in our benchmark involved limitations in using private data in the proofs, whereas for the Bulletproof protocol, we did not apply some specific benefits not found in other protocols. We refer the reader to other sections in this section for more discussion on this aspect. Given the limited availability of security level metrics from the libraries we used to implement the benchmark applications, we were unfortunately, as likewise discussed in other sections in this section, unable to answer the security level component of this question. While other sources for these metrics indicated that the security level was comparative for the used configurations, this was no guarantee and would require additional research and implementation work to confirm.
The second research question we answer in detail through our recommendations in Section 8.2. To summarize: The zk-SNARK protocol is a good overall choice for performance, granted that a trusted setup is conceivable for the specific use case. The small proof sizes make the protocol particularly beneficial for Internet of Things (IoT) usage, where notable storage, bandwidth, or processing power limitations apply. The Bulletproof protocol is a viable alternative for the zk-SNARK in these applications when a trusted setup is unacceptable and can furthermore be a great option for applications that require proofs that values lie within a pre-determined range. This suitability, however, comes at the cost of much larger proof creation and verification times, though the latter can be reduced significantly when the application allows the batching of proof verifications. The zk-STARK protocol, finally, is currently best applied to succinctly prove the correctness of computations. This makes the STARK protocol for example applicable to cloud computing and distributed learning applications. The STARK protocol allows quickly generating the proof for large statements, and is even quicker in verifying the generated proofs, though there exists a significant trade-off in the substantial size of the generated proofs. Finally, the zk-STARK protocol is the only viable option when the quantum resistance of the protocols is an important requirement, given that the other two protocols use cryptographic primitives that are not quantum-resistant.
With the research questions answered, we reflect on the aims and objectives mentioned in Section 1:
- To implement and evaluate the protocols in a practical setting, using a common benchmark for a real-world use case.
- To compare the efficiency and security of these three protocols, including their trade-offs between efficiency and security.
- To provide recommendations for the use of these protocols in different applications, based on their strengths and weaknesses.
Regarding the first objective, we fully achieved it by considering that our benchmark evaluated the protocols in a practical setting for a real-world use case. Regarding the second objective, while we were able to compare the efficiency of the three NIZKP protocols, including their efficiency trade-offs, we were insufficiently able to do the same for the security aspects of the protocols. Given the limitations of the libraries that we used to benchmark the three protocols, we could only obtain the security level metrics from a single protocol. While this work did include an attempt to complement these metrics using expertise from works by other authors, this did not satisfy the comparison for the actual implementations that we had in mind. Somewhat consoling is our inclusion of the security primitives and limitations for each protocol in Section 4, which provided alternative insights into the security of each protocol that should partly offset the limited security comparison in the practical setting. This aspect constitutes a potential direction for future research. As for the third objective—we adequately look at this in Section 8.2. While it was inconceivable to enumerate all potential applications best suited to each protocol, we believe that we provided a fair number of categories and applications that constitute a thriving environment for each protocol. We leave the ideation of other applications up to other researchers, which they can derive from the information conveyed in this work, with the potential for them to unearth entirely new, unprecedented, application categories.
7.3. Strengths
The main strength of this work lies in the benchmark procedure performed on the three main NIZKP protocols: zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproofs. The benchmark application that we implemented for this procedure was relevant to real-life applications focusing on privacy preservation and authentication. Additionally, we performed the benchmark using four existing general-purpose NIZKP libraries that allowed for general applicability in all kinds of zero-knowledge-proof applications. This is an important aspect of our work since these libraries enable using ZKPs in all kinds of applications without the extensive knowledge that would be required to securely realize a custom implementation for one of the NIZKP protocols. Altogether, this means that our benchmark provides a helpful indication of the performance differences between each ZKP protocol when utilized. To the best of our knowledge, our work constitutes the first research that directly compares the three main NIZKP protocols using results from an equivalent benchmark implemented with existing general-purpose ZKP programming libraries. We argue that our decision to use general-purpose NIZKP libraries increases the relevance of the obtained benchmark results for researchers aiming to implement an application since the libraries allow researchers to implement a ZKP into their application faster and more securely without deep knowledge of the cryptography behind each protocol. In situations where the overhead of general-purpose NIZKP libraries is known to be unacceptable, the exact ZKP protocol that one should use is undoubtedly known. In the unlikely event that this statement does not apply, the relative speed by which the general purpose NIZKP libraries allow for the implementation of a ZKP will quickly surface this requirement from the proof-of-concept implementation. Affected researchers can then pivot to a custom NIZKP implementation, or different protocol altogether, without having wasted too much research time.
In Section 7.1, we detailed some metrics that float around on the internet comparing the three main NIZKP protocols, but we were unable to find the source of these metrics. As a result, we could not determine which application they benchmarked and which hardware and software they used in the process. This left us with uncertainty regarding how the metrics were obtained. In contrast, one of the main strengths of our work is the detailed documentation of the benchmarking procedure. Not only does this enable other researchers to reproduce our efforts, but it also allows them to extend this research to fill additional knowledge gaps and advance understanding of ZKPs.
Another strength of our work is that it not only provides a comparison benchmark between the three main NIZKP protocols but also describes the cryptographic primitives forming each protocol in Section 4. This not only allows researchers to gain insights into the right ZKP protocol to use in their application regarding performance but also provides them with a source for knowledge of the cryptographic primitives behind each of the ZKP protocols. From our perspective, this makes our work an ideal starting point for any researcher to obtain more knowledge of the three NIZKP protocols, especially when they have the intent to utilize one of the three discussed NIZKP protocols for a privacy-preserving application.
7.4. Limitations
In view of the strengths as discussed in Section 7.3, it is just as important to discuss the many limitations of this work. Discussing these limitations accentuates where our work leaves something to be desired, and where other researchers can step in to fill the knowledge gaps. Most of the limitations described in this section were a direct result of the scoping of the work and the decisions we made in the process. Some of these decisions were a compromise, where we deliberately accepted a limitation mentioned in this section to further increase one of the strengths of this work as mentioned in Section 7.3.
The main limitation of this work is that the results obtained from the benchmark do not necessarily indicate the performance of only the protocol. The metrics partially reflect the performance of the ZKP implementation library, which may or may not be well optimized, and to a lesser degree that of the programming language in which it is written. This is a direct trade-off from our aim to benchmark a real-world implementation of an application using zero-knowledge proofs, which necessarily involves an implementation of each NIZKP protocol that can impact the performance. We further increased the impact of the implementation on the protocol performance through our decision to benchmark general-purpose NIZKP libraries. While we justified this decision by stating that this is how most applications will implement ZKPs, through a general-purpose NIZKP library that removes the extensive knowledge requirement for a custom implementation, it meant that the obtained performance metrics were even further removed from the theoretical performance that the protocol could provide. We observed this impact firsthand when inspecting and discussing the performance differences between the Rust and Go implementations of the zk-SNARK protocol. These two libraries showed vastly different performances, even while we ensured both used BLS12-381 elliptic curve [38] and the Groth16 backend [7]. To reduce the impact of this limitation, we decided early on to implement the benchmark using a library for each ZKP protocol written in the same programming language. As discussed in Section 5, we chose the Rust language for this, while we also included a single library in another language as a means for comparison. The comparison enabled us to show, with numbers, how the library can impact the performance of a protocol, as discussed in Section 7.1. While we expect this decision to have benefited the conclusiveness of the obtained benchmark results, we also admit that we cannot guarantee this. There are simply not enough libraries that implement zero-knowledge proof protocols to include multiple libraries written in the same programming language for the same ZKP protocol in this research. This is another limitation of our work, which other researchers have the potential to rectify in the future when alternative NIZKP libraries have emerged for each protocol. The comparison with metrics for each protocol circulating on the internet which we used to show that our benchmark achieved comparable results, however, contributed to our confidence that the overall performance observations from our benchmark were accurate despite these limitations. It is crucial to address the limitations of our work, which highlight areas for potential improvement and further research. These limitations often stem from the scoping decisions made during this study, frequently as trade-offs to enhance certain strengths.
Table 10 presents the primary limitations of our work and potential mitigations in Table 11 that could be explored in future research.

Table 10.
Primary limitations and potential mitigations.

Table 11.
Potential mitigations.
Table 11 Outlines the potential mitigations for the identified limitations.
8. Conclusions
In this section, we conclude our research in which we performed a benchmark for the zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof ZKP protocols. First off, in Section 8.1, we recollect the results from Section 6 and reiterate our key findings. Following our key findings, we provide some recommendations on the utilization of NIZKPs that follow our benchmark in Section 8.2. Subsequently, we provide some promising future research directions on all kinds of NIZKP aspects that we would like to see realized in section Section 8.3. In drawing things to a close, we finalize our work by providing a conclusion with some final remarks in Section 8.5.
8.1. Key Findings
In this section, we concisely reiterate the key takeaways from our NIZKP protocol benchmark. For more in-depth findings, we refer the reader to Section 6 and Section 7, corresponding to the results and discussion sections. We first recollect the results of the performance metrics found for all three NIZKP protocols, averaged over the five benchmarks on different numbers of hash rounds, listed in Table 9. From this table, we clearly observed that the SNARK protocol generated the smallest proofs, while the STARK protocol generated by far the largest proofs. Regarding the proof generation and verification times, the STARK protocol was faster in both metrics than the two SNARK protocol implementations, while the Bulletproof protocol turned out to be by far the slowest for these metrics. Furthermore, we observed these findings to be analogous to the externally found protocol comparison for which we could not determine how they were benchmarked, included for reference in Table 8. The exception to this equivalence was the protocol ordering in the proof verification times between the SNARK and STARK, which switched places in our results. Given that the absolute difference between these reversed metrics was small for both our results and the external results, especially compared to the difference with the Bulletproof protocol, this does not constitute an alarming difference.
With all configuration settings in the zk-STARK protocol library, we found it sensible to benchmark the performance differences between these configurations. While we discovered that our default configuration may not have been optimal, we remarked that this realistically did not impact the conclusion from the comparisons between the protocols. Furthermore, we observed that the configuration parameter values which were individually optimal did not exactly provide the best possible performance when combined. We claimed this to be a result of the complexity of the inner workings of the protocol. We suggested evaluating several configurations that fit the context when utilizing zk-STARKs in an application use case.
Regarding the security level of the protocols, we identified evidence that the performance on this aspect between the protocols did not deviate from our chosen configurations. With that said, this finding was inconclusive given that three of the four protocol-implementing libraries did not include a method to obtain such a security-level metric. As such, we had to supplement our findings with complementary data from research works by other authors.
Benchmarking Considerations and Variability
In conducting performance benchmarks for cryptographic protocols, several factors can influence the results, which must be carefully considered to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the findings. Two critical aspects that can introduce variability in benchmarking results are the optimization levels of different implementations and the hardware/software platforms on which the benchmarks are executed.
- Implementation Variability:Different implementations of the Minimized Multiplicative Complexity (MiMC) hash function, or any cryptographic algorithm, may exhibit significant differences in performance due to variations in optimization strategies. Implementations may be optimized for specific hardware architectures, programming languages, or software environments, leading to discrepancies in performance metrics. For instance, optimizations such as loop unrolling, parallel processing, or efficient memory access patterns can impact the speed and resource utilization of the MiMC function. Consequently, benchmarks conducted using different implementations of the same algorithm might yield varying results, making it crucial to evaluate the specific characteristics and optimizations employed by each implementation.To address this issue, we have implemented a comprehensive evaluation framework that includes multiple implementations of equivalent MiMC hash function algorithm implementations. By benchmarking these implementations under controlled conditions and examining their performance characteristics, we aim to provide a more nuanced understanding of how optimization impacts the results. We acknowledge that while our benchmarks offer valuable insights, they may still be influenced by the inherent differences in implementation approaches. Future research should focus on standardizing benchmarks across a broader range of implementations and exploring the impact of different optimization techniques on performance metrics.
- Hardware and Software Platform Variability: Benchmark results can also be significantly affected by the hardware and software platforms on which they are executed. Variations in processor architecture, memory hierarchy, and system load can introduce discrepancies in performance measurements. For example, benchmarks conducted on different types of processors (e.g., CPUs vs. GPUs) or across different operating systems may exhibit divergent results due to differences in computational capabilities, memory access speeds, and system overhead.To mitigate the impact of platform variability, we have standardized our benchmarking environment as much as possible. We conducted our benchmarks on a consistent hardware setup and used a uniform software configuration to minimize external influences on the results. However, given the inherent variability of hardware and software platforms, it is challenging to achieve absolute comparability across all possible configurations. Therefore, it is essential for future research to include a broader range of hardware and software environments in benchmarking studies and to report detailed platform specifications to enable more accurate comparisons.
By addressing these considerations, we aim to provide a more robust and comprehensive analysis of the performance of the cryptographic protocols under investigation. We encourage further research to explore the impact of implementation optimizations and platform variability on benchmarking results to enhance the reliability and applicability of performance evaluations in cryptographic research.
8.2. Recommendations
Reflecting on the obtained results from Section 6, and the discussion that subsequently ensued in Section 7, in this section we strive to provide some recommendations on which application contexts we would recommend utilizing each protocol.
We start with the zk-SNARK protocol. The two implementations for this protocol showed the smallest proof sizes, in addition to the proof size itself being constant. The small proof size makes this protocol a great contender for applications where either storage space is limited, or where the network connection has a restricted capacity or transfer speed. An example of a situation where storage space is limited is in blockchain systems, for which we can see the zk-SNARK protocol already in use, e.g., in Zcash [43]. Limited network connections, on the other hand, are a reality for Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs), often used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications and sensor networks where the devices are in a remote location and have low power requirements [44]. The small and constant size of the SNARK proofs, especially those created by the Rust implementation, make the zk-SNARK protocol a good protocol to consider for these kinds of applications. Furthermore, as the benchmark, creating a SNARK proof is not much more compute-intensive than creating a STARK proof, which is beneficial for the IoT application where devices and sensors are often low-powered devices with little computing power. The most important consideration to make before applying the zk-SNARK protocol, even for these applications, is whether the requirement for a trusted setup is acceptable. There are sparks of hope to apply the zk-SNARK protocol in situations where a trusted setup is unacceptable. Researchers have recently created new SNARK backend techniques, including Supersonic [45] and Halo [46], which do not require a trusted setup in certain situations. Zcash currently uses a Halo 2 zk-SNARK backend [46] in their network, which according to them eliminates the trusted setup requirement. As it currently stands, however, the trusted setup is a definite requirement in the Groth16 backend implementation used by both the Rust and Go zk-SNARK protocol libraries benchmarked in this work. Therefore, we recommend investigating the use of the zk-SNARK protocol for applications where the proof size is a key factor, including blockchain and IoT applications, yet to ensure that the trusted setup requirement to obtain a CRS is not a hindrance in said application.
For applications in which a trusted setup is not an option, the Bulletproof protocol offers a viable alternative. Bulletproof proofs are not considerably larger than SNARK proofs, especially when compared to STARK proofs. Unlike the SNARK proofs, though, the size of the Bulletproof proofs is not constant. A further downside for the applicability of the Bulletproof protocol is the much larger proof creation and verification times than in the two other protocols, which furthermore increase more rapidly as well with the size of the computation. At present, this makes the Bulletproof protocol less suitable to apply to low-compute IoT environments. In applications where aggregation of proof and batch verification, as discussed in Section 7.4, is possible, the proof size and especially the verification times can however be significantly reduced. This is beneficial in situations where a single prover must create the proof, but many verifiers need to verify that proof. This applies for example when proving and verifying transactions in blockchains, for which e.g., the Monero network [47] already applies the Bulletproof protocol. The Bulletproof protocol has yet another benefit, not visible in our benchmark since we use R1CS proofs, in that it specializes in range proofs. This allows the Bulletproof protocol to be especially beneficial and performant in applications that use ZKPs to prove that a certain value lies within a pre-determined interval. In general, applications that benefit from such a range of proofs include financial transactions, income checks, and age verification. There are, however, many more specialized uses for range proofs, including genomic range queries [48]. In brief, we recommend that the Bulletproof protocol could be a viable alternative to the SNARK protocol in situations where a trusted setup is undesirable, where the proof creation cost is not a limiting factor, or where proof is verified frequently after it is created once. Furthermore, we recommend investigating the use of the Bulletproof protocol specifically where the proof must prove that a value is inside of a pre-determined range, a use case in which Bulletproof range proofs are particularly good.
Finally, there is the zk-STARK protocol. Given the proof size which, in our benchmark, was at least an order of magnitude larger than that for the other two protocols, we can only recommend the use of the STARK protocol for applications where the proof size is not important. An example where the proof size is unlikely to be important is in the context of cloud computing, data centers, or machine learning. In that application context, ample storage space and network capacity are available, and datasets used as input to calculations can be extremely large to begin with. In return for the large proof sizes, we observed a low proof creation time and especially short proof verification time compared to the other protocols in our benchmark. These small proof and verification times become especially useful when applied to large computations as performed in data centers and machine learning. This applicability factors into the zk-STARK protocol in general, and to an even greater degree for the Winterfell library used in our benchmark. Currently, this library does not implement perfect zero-knowledge, instead, the library aims to enable succinctly proving computations. This makes it hard to securely implement applications where the proof proves a statement on confidential data, as the generated proof could leak the data. This is a significant distinction from the Bulletproof and zk-SNARK protocol implementations, which do intend to guard against the verifier obtaining confidential information. For the reasons listed above, we recommend considering the zk-STARK protocol, and specifically the Winterfell library, in situations where the application uses ZKPs to ensure the correct execution of a computation in a succinct manner. This includes but is not limited to, machine learning, distributed or multi-party computations, and verifiable computing applications, e.g., in the cloud.
This brings us to our final advice when contemplating which NIZKP protocol and library to use for a given application context. We recommend, where possible, creating a proof of concept for the desired application using multiple libraries implementing the same protocol. When in doubt between multiple protocols, try them all in a way that is representative yet does not cost a lot of time. This recommendation stems from two observations: first, the challenges we had in applying the three protocols to a single, equivalent, application. Second, the Rust and Go libraries both implement the same Groth16 SNARK protocol [7], yet exhibit different performance metrics, particularly regarding the size of the proving and verifying keys in the CRS. Furthermore, we not only recommend trying out multiple protocols and multiple libraries for the same protocol, but we also advocate attempting different methods to utilize ZKPs in the application. Specifically, when using the STARK protocol, Furthermore, we recommend evaluating the performance for several configurations to see which best achieves a pre-determined set of objectives for the application. All these tests can lead to vastly different performance metrics, which could make or break the usability of NIZKPs in an application context. While we understand that this recommendation requires a considerable time investment, we hope that our work can reduce this time investment by serving as a knowledge base to limit the amount of experimentation required to find the right NIZKP protocol that best fits the application needs. Table 12 provides protocol-specific recommendations, while Table 13 summarizes which protocols we would consider optimal for several applications. In addition to protocol-specific recommendations, we provide general recommendations in Table 14.

Table 12.
Protocol-Specific Recommendations.

Table 13.
Comparison of applications and the optimal protocol to use.

Table 14.
General recommendations.
8.3. Future Directions
With the results, discussion, strengths, limitations, and recommendations out of the way, we will now provide some suggestions for future research directions.
First, we would like to suggest research that compares many different programming libraries implementing the same NIZKP protocol. These libraries could be written in different programming languages, as long as the implemented protocol is the same. This would not only better indicate the differences between several libraries than we did in our comparison since that was not our main goal, but it would also provide a nice overview for anyone wanting to implement a given protocol in an application using a library. The comparison could not only compare the performance of the protocols but also the features that each implementation includes. In addition, a comparison of different libraries implementing an identical protocol would have an easier time implementing a more detailed and interesting application for the benchmark. The direct result of such a benchmark would be that it provides visibility to the specialization of the protocol more than our benchmark did. We believe that research performing the described comparison is valuable to read for anyone who has the goal to utilize that specific NIZKP protocol in any given application.
Second, we think it would be interesting for future researchers to examine whether our initial benchmark application idea of implementing ZKAttest, as introduced by Faz-Hernández et al. [13], for all three NIZKP protocols, would be doable after all. Our research as described did not have the capacity to implement this application, yet any research could easily extend our current benchmark with the results of a benchmark for such an application. Such an addition would provide an even better idea of the real-world performance to expect from each protocol and matching libraries.
Third, we believe there is room for more research into new and improved NIZKP protocols. Researchers have performed vast amounts of research on NIZKP protocols in the past few years, with the Bulletproof protocol [9] and FRI underlying the STARK protocol [49] originating only in 2017. Work on the zk-SNARK protocol has not been dormant either, with the introduction of Sonic [50], Supersonic [45], Halo [46], and Halo 2. Zcash currently uses a Halo 2 zk-SNARK backend in their network, which, according to them, eliminates the trusted setup requirement [46]. Even the Groth16 SNARK scheme [7], which originated in 2016 and is widely implemented in SNARK libraries, is continuously improved upon; for example, see Section 7. Section 7.4 mentions work by Gailly et al. [51] from 2021, which introduced aggregation for Groth16 proofs. As we found in this research, however, in practice, implementations understandably lag research. Furthermore, there is still a vast number of limitations and performance implications that anyone utilizing NIZKPs to prove knowledge or computations in their application must deal with. We expect that future research works can resolve more of these limitations, which would open opportunities to gain benefits from using the ZKP protocols in applications without the current downsides. For this reason, we argue that more research on NIZKP protocol improvements would benefit the ZKP ecosystem.
Fourth, as mentioned in the limitations to our work in Section 7, our work was unable to compare in detail the actual security level of most of the benchmarked protocol implementations. This leaves us with questions on which of the three protocols is most secure. Therefore, we indicate this aspect could be researched in-depth in future work.
Fifth and last, we recommend a future research direction into the establishment of benchmarking standards for ZKP applications. We anticipate that introducing such a standard would make it easier to compare research on applications implementing ZKPs when the authors of these works benchmarked their application and followed the set standard while doing so. Furthermore, we anticipate that an established benchmark standard would entice implementing libraries to implement functionality to obtain the metrics defined in this benchmarking standard, which would make it even easier for researchers who implement an application using such a library to include the standardized ZKP metrics for comparison. While we do not expect a standard to be all-encompassing, nor do we expect every researcher to embrace it, we would still consider it an improvement over the current situation in which comparing the performance of ZKP protocols in applications is a complex endeavor.
Alternative Zero-Knowledge Proof Protocols
In addition to zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproofs, other non-interactive zero-knowledge proof implementations offer various advantages depending on application requirements. All proof systems, except for zk-SNARG, are considered to be alternative zk-SNARK constructions to the Groth16 implementation benchmarked in this work. This section provides a detailed comparison of these alternatives, including their strengths, weaknesses, quantum resistance, and preferred applications. Table 15 summarizes the key characteristics of these systems.

Table 15.
Comparison of alternative zero-knowledge proof protocols.
Table 15 provides a comprehensive comparison of various zero-knowledge proof protocols, integrating quantum resistance to give a complete overview of each protocol’s characteristics and suitability for different applications. Future research should consider these aspects to identify and develop more resilient cryptographic solutions.
8.4. Quantum Resistance of NIZKP Protocols
The advent of quantum computing poses a significant challenge to the field of cryptography. As quantum computers become more powerful, they could potentially break many of the cryptographic assumptions that current cryptographic protocols rely on. NIZKPs are no exception. This section discusses the quantum resistance of the three primary NIZKP protocols analyzed in this study: zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproof.
8.4.1. zk-SNARK Protocol
The zk-SNARK protocol, while efficient in terms of proof size and verification time, relies on cryptographic assumptions that are vulnerable to quantum attacks. Specifically, zk-SNARKs are built upon elliptic curve cryptography and the hardness of certain problems, such as the discrete logarithm problem. Quantum computers have the potential to solve these problems efficiently using Shor’s algorithm, thereby compromising the security of zk-SNARKs.
Key points:
- Elliptic curve cryptography: zk-SNARKs often use elliptic curves, which are susceptible to quantum attacks due to Shor’s algorithm.
- Discrete logarithm problem: The security of zk-SNARKs is partially based on the difficulty of solving the discrete logarithm problem, which can be efficiently solved by quantum computers.
- Current mitigations: While zk-SNARKs are not quantum-resistant, research is ongoing into post-quantum cryptographic methods that could be used to secure these protocols in the future.
8.4.2. zk-STARK Protocol
In contrast to zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs are designed to be quantum-resistant. zk-STARKs leverage hash functions and other cryptographic primitives that are not vulnerable to known quantum algorithms, such as Shor’s algorithm. This inherent resistance to quantum attacks makes zk-STARKs a promising choice for future-proof applications.
Key Points:
- Hash functions: zk-STARKs use hash functions, which are currently believed to be resistant to quantum attacks.
- No trusted setup: Unlike zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs do not require a trusted setup, adding another layer of security.
- Future-proofing: The quantum resistance of zk-STARKs makes them suitable for long-term security considerations.
8.4.3. Bulletproof Protocol
The Bulletproof protocol is specifically optimized for efficient range proofs, even though it can also generate general proofs for any rank-one constraint system (R1CS) without a trusted setup. While the Bulletproof protocol is susceptible to quantum attacks using Shor’s algorithm, this breaks the anonymity of the protocol while the soundness of the protocol is expected to remain intact.
Key Points:
- Anonymity: Bulletproofs use a sophisticated version of calculating inner proofs which allows them to reduce the number of times a commitment needs to be opened when creating range proofs. This provides it with performance benefits in range proofs while being able to generate general proofs for any R1CS as well as using the same inner proofs. However, the algorithms used in the Bulletproof protocol will not protect and be able to hide the data inside the proofs against quantum attacks, leaving the anonymity of the proof system vulnerable to quantum attacks.
- No trusted setup: Bulletproofs have an advantage over zk-SNARKs in that they do not require a trusted setup in order to generate a common reference string (CRS).
- Use cases: Bulletproofs are suitable for applications but may not be useful in situations where the anonymity of data must remain guaranteed in a future where sufficiently powerful quantum computers are widely available. Even so, the verifier can rest assured that the soundness of the proof system remains valid.
8.4.4. Future Proof
Given the potential of quantum computing to disrupt current cryptographic protocols, it is essential to consider quantum resistance in the selection of NIZKP protocols for future applications. Future research should focus on the following areas:
- Post-quantum cryptography: Investigate the development of post-quantum cryptographic methods that can be integrated into zk-SNARKs to enhance their resistance to quantum attacks.
- Protocol adaptation: Explore adaptations of existing protocols to improve their quantum resistance without significantly compromising their efficiency.
- Standards development: Support the development of standards for quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols to guide the industry toward future-proof solutions.
- Benchmarking quantum resistance: Establish benchmarking methods to assess the quantum resistance of various cryptographic protocols, including NIZKPs.
As quantum computing technology advances, it is crucial to ensure that cryptographic protocols remain secure against these emerging threats. By focusing on quantum resistance, researchers and practitioners can develop more robust and future-proof cryptographic solutions.
8.5. Last Word
In this research, we designed and implemented a benchmark to compare the three NIZKP protocols, zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and Bulletproofs, in a real-world setting. To achieve this, we designed a single benchmark application that incorporates privacy-preserving authentication uses. The application we decided on, after deliberating some other options, was to implement a MiMC hash with a variable number of rounds. After describing the methodology for this work, we provided a concise description of the mathematical primitives underlying each protocol. This description included the security assumptions they made, as well as the vulnerabilities and limitations present in each. By providing this information we aimed to supply readers with sufficient information to understand the basic workings that enabled their functionality and established their characteristics. By additionally describing previous ZKP vulnerabilities and how to prevent or resolve them, we strengthened the idea that deciding which protocol to use is not always a performance-related proposition. Our intention for this was to reinforce the notion that security and privacy are central to implementing NIZKP protocols in actual production-ready applications. With the primitives clarified, we commenced by implementing the benchmark application. We implemented the application equally for each protocol using existing general-purpose NIZKP libraries, namely Bellman [30] for the SNARK protocol, Winterfell [33] for the STARK protocol, and Bulletproofs [29] for the Bulletproof protocol. All three libraries were written in the Rust programming language. On top of that, we implemented the same application using the gnark zk-SNARK library [43] written in the Go programming language. We decided on this additional implementation to compare the performance differences between two NIZKP libraries implementing the same protocol yet written in a different programming language. We benchmarked all implementations using a default configuration. Afterward, we benchmarked just the zk-STARK protocol, altering a single configuration parameter at a time. Inspecting the results then allowed us to determine the performance impact of altering this parameter. The results from conducting the benchmark indicated the following performance characteristics: The SNARK protocol proofs were the smallest, in addition to being constant. The Bulletproof proofs were slightly larger, whereas the STARK protocol created by far the largest proofs. Neither the Bulletproof nor the STARK proofs were constant in size, and both increased with the number of hash rounds. The proof times for the SNARK and STARK protocols were comparable, with the STARK creating a proof faster overall. The Bulletproof protocol was much slower in creating proofs, which only worsened with an increasing number of hash rounds. We observed a similar pattern to the proof creation for the verification times, with the remark that we did not apply any form of batch verification in our benchmark. In the subsequent sections, we discussed the collected results and described the strengths and limitations of our research. While our research had several limitations, we argued that these resulted from the choices we had to make for our benchmark and that these limitations did not invalidate the results. Moreover, the strengths resulting from those decisions outweighed the induced limitations. In the last section of this work, we wrapped up our research by providing recommendations on the strengths of each benchmarked protocol and described the application contexts in which each protocol would prosper. We explained that the SNARK protocol would be the best protocol for applications that benefit from small proofs when the requirement for a trusted setup is not a critical issue. In situations where a trusted setup is undesirable, the Bulletproof protocol provides similarly sized proofs, at the cost of a higher proof creation and verification time. The Bulletproof protocol is furthermore beneficial for its specialization in range proofs, though we only benchmarked Bulletproof R1CS proofs in this work. Finally, we found the zk-STARK protocol to be most advantageous in application categories where large proof sizes are not a problem, whereas quick proof generation and verification times are convenient. We indicated that verifiable computation and machine learning are examples of such application categories, which the Winterfell library cemented by focusing on succinct proofs of computation, unlike the other two protocol libraries.
Ultimately, we expect our research to be useful for anyone looking into the use of non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs for an application. We consider our work to be an excellent starting point from which to obtain knowledge about the mathematical and cryptographic primitives that formed the three main NIZKP protocols and their analogous real-world performance aspects to consider.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.O.R.; methodology, M.E.-H.; software, B.O.R.; validation, B.O.R.; formal analysis, B.O.R.; resources, B.O.R.; data curation, B.O.R.; writing—original draft, M.E.-H. and B.O.R.; writing—review and editing, M.E.-H. and B.O.R.; visualization, B.O.R.; supervision, M.E.-H.; project administration, M.E.-H.; funding acquisition, M.E.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Goldwasser, S.; Micali, S.; Rackoff, C. The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems. In Roviding Sound Foundations for Cryptography: On the Work of Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 18, pp. 186–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Feldman, P.; Micali, S. Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge and Its Applications. In Proceedings of the Twentieth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC ’88, Chicago, IL, USA, 2–4 May 1988; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biryukov, A.; Feher, D.; Vitto, G. zkChannels: Privacy-Preserving Off-Chain Payments for Decentralized Economies. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 1813–1830. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, E.S. Preserving privacy in ethereum blockchain. Ann. Data Sci. 2022, 9, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Roelink, B.; El-Hajj, M.; Sarmah, D. Systematic review: Comparing zk-SNARK, zk-STARK, and bulletproof protocols for privacy-preserving authentication. Secur. Priv. 2024, e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parno, B.; Gentry, C.; Howell, J.; Raykova, M. Pinocchio: Nearly Practical Verifiable Computation. Commun. ACM 2016, 59, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, J. On the Size of Pairing-based Non-interactive Arguments. In Advances in Cryptology—EUROCRYPT 2016: 35th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Vienna, Austria, 8–12 May 2016; Proceedings, Part II 35; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sasson, E.; Bentov, I.; Horesh, Y.; Riabzev, M. Scalable, transparent, and post-quantum secure computational integrity. Cryptol. Eprint Arch. 2018, 2018/046. [Google Scholar]
- Bünz, B.; Bootle, J.; Boneh, D.; Poelstra, A.; Wuille, P.; Maxwell, G. Bulletproofs: Short Proofs for Confidential Transactions and More. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy 2018, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Post-Quantum Cryptography | CSRC | CSRC—csrc.nist.gov. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/Projects/post-quantum-cryptography (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Meunier, T. Humanity Wastes about 500 Years per Day on CAPTCHAs. It’s Time to End This Madness. 2021. Available online: https://blog.cloudflare.com/introducing-cryptographic-attestation-of-personhood (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Whalen, T.; Meunier, T.; Kodali, M.; Davidson, A.; Fayed, M.; Faz-Hernández, A.; Sullivan, N.; Wolters, B.C.; Guerreiro, M.; Galloni, A. Let The Right One In Attestation as a Usable CAPTCHA Alternative. In Proceedings of the 18th Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security (SOUPS 2022), Boston, MA, USA, 8–9 August 2022; pp. 599–612. [Google Scholar]
- Faz-Hernández, A.; Ladd, W.; Maram, D. ZKAttest: Ring and Group Signatures for Existing ECDSA Keys. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Selected Areas in Cryptography, Virtual Event, 29 September–1 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- STARK—starkware.co. Available online: https://starkware.co/stark/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Ernstberger, J.; Chaliasos, S.; Kadianakis, G.; Steinhorst, S.; Jovanovic, P.; Gervais, A.; Livshits, B.; Orru, M. zk-Bench: A Toolset for Comparative Evaluation and Performance Benchmarking of SNARKs. Cryptol. Eprint Arch. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub—Dalek-Cryptography/Bulletproofs: A Pure-Rust Implementation of Bulletproofs Using Ristretto—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/dalek-cryptography/bulletproofs (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Bulletproof-js—npmjs.com. Available online: https://www.npmjs.com/package/bulletproof-js (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- GitHub—Elibensasson/libSTARK: A Library for Zero Knowledge (ZK) Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge (STARK)—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/elibensasson/libSTARK (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- GitHub—Facebook/Winterfell: A STARK Prover and Verifier for Arbitrary Computations—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/facebook/winterfell (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- GitHub—zkcrypto/Bellman: zk-SNARK Library—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/zkcrypto/bellman (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- EdDSA | Gnark—docs.gnark.consensys.io. Available online: https://docs.gnark.consensys.io/Tutorials/eddsa (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- Bjornouderoelink. NIZKP-Benchmark. Available online: https://github.com/bjornouderoelink/NIZKP-Benchmark (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Albrecht, M.; Grassi, L.; Rechberger, C.; Roy, A.; Tiessen, T. MiMC: Efficient Encryption and Cryptographic Hashing with Minimal Multiplicative Complexity. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Guangzhou, China, 4–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, L.; Khovratovich, D.; Rechberger, C.; Roy, A.; Schofnegger, M. Poseidon: A New Hash Function for Zero-Knowledge Proof Systems. In Proceedings of the 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21), Virtual Event, 11–13 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Szepieniec, A.; Ashur, T.; Dhooghe, S. Rescue-Prime: A Standard Specification (SoK). Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sasson, E.; Goldberg, L.; Levit, D. STARK Friendly Hash—Survey and Recommendation. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bellman-Examples/src/sharkmimc.rs at Master · Lovesh/Bellman-Examples—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/lovesh/bellman-examples/blob/master/src/sharkmimc.rs (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- bulletproofs-r1cs-gadgets/src/gadget_mimc.rs at Master · lovesh/bulletproofs-r1cs-gadgets—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/lovesh/bulletproofs-r1cs-gadgets/blob/master/src/gadget_mimc.rs (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Bulletproofs—crates.io: Rust Package Registry. Available online: https://crates.io/crates/bulletproofs/4.0.0 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Bellman Crates.io: Rust Package Registry. zk-SNARK Library. Available online: https://crates.io/crates/bellman/0.14.0 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Gnark Package—github.com/Consensys/Gnark—Go Packages—v0.9.1. Available online: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/consensys/gnark@v0.9.1 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- GitHub—Consensys/Gnark: Gnark Is a Fast zk-SNARK Library That Offers a High-Level API to Design Circuits. The Library Is Open Source and Developed under the Apache 2.0 License—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/Consensys/gnark (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Prover, W.S. Verifier. Winterfell—crates.io: Rust Package Registry. Available online: https://crates.io/crates/winterfell/0.8.1 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- curve25519_dalek_ng—Rust—docs.rs. Available online: https://docs.rs/curve25519-dalek-ng/latest/curve25519_dalek_ng/ (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Ristretto—The Ristretto Group—ristretto.group. Available online: https://ristretto.group/ristretto.html (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Merlin—Rust—docs.rs. Available online: https://docs.rs/merlin/latest/merlin/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Fiat, A.; Shamir, A. How To Prove Yourself: Practical Solutions to Identification and Signature Problems. In Proceedings of the Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO’ 86, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 11–15 August 1986; Odlyzko, A.M., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BLS12-381: New zk-SNARK Elliptic Curve Construction—electriccoin.co. Available online: https://electriccoin.co/blog/new-snark-curve/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Aranha, D.F.; El Housni, Y.; Guillevic, A. A survey of elliptic curves for proof systems. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 2023, 91, 3333–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, Y.; Josefsson, S. Curve25519 and Curve448 for the Internet Key Exchange Protocol Version 2 (ikev2) Key Agreement; Technical Report; RFC Edito: Fremont, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sasson, E.; Carmon, D.; Ishai, Y.; Kopparty, S.; Saraf, S. Proximity Gaps for Reed–Solomon Codes. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 61st Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), Durham, NC, USA, 16–19 November 2020; pp. 900–909. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub—starkware-libs/ethSTARK—github.com. Available online: https://github.com/starkware-libs/ethSTARK?tab=readme-ov-file#7-Measuring-Security (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Banerjee, A.; Clear, M.; Tewari, H. Demystifying the Role of zk-SNARKs in Zcash. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Application, Information and Network Security (AINS), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 17–19 November 2020; pp. 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Puluckul, P.P.; Berkvens, R.; Weyn, M. Energy Consumption Analysis of LPWAN Technologies and Lifetime Estimation for IoT Application. Sensors 2020, 20, 4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bünz, B.; Fisch, B.; Szepieniec, A. Transparent SNARKs from DARK Compilers. In Advances in Cryptology—EUROCRYPT 2020: 39th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Zagreb, Croatia, 10–14 May 2020; Proceedings, Part I 39; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bowe, S.; Grigg, J.; Hopwood, D. Recursive Proof Composition without a Trusted Setup. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moneropedia: Bulletproofs—getmonero.org. Available online: https://www.getmonero.org/resources/moneropedia/bulletproofs.html (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Hwang, S.; Ozturk, E.; Tsudik, G. Balancing Security and Privacy in Genomic Range Queries. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM Workshop on Privacy in the Electronic Society, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; Volume 26, pp. 23:1–23:28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Sasson, E.; Bentov, I.; Horesh, Y.; Riabzev, M. Fast Reed-Solomon Interactive Oracle Proofs of Proximity; Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik: Wadern, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Maller, M.; Bowe, S.; Kohlweiss, M.; Meiklejohn, S. Sonic: Zero-Knowledge SNARKs from Linear-Size Universal and Updateable Structured Reference Strings. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gailly, N.; Maller, M.; Nitulescu, A. Snarkpack: Practical Snark Aggregation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security, Grenada, 2–6 May 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).