Mapping the Infodemic: Geolocating Reddit Users and Unsupervised Topic Modeling of COVID-19-Related Misinformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Volume and Impact of COVID-19 Misinformation
2.2. Methods for Detecting Fake News
2.3. Topic and Sentiment Analysis Approaches
2.4. Geolocation and Regional Dynamics
3. Methodology
3.1. Phase 1: Data Collection
3.2. Phase 2: Geolocation Analysis
3.3. Phase 3: Data Preprocessing and Labeling
Data Cleaning and Transformation
3.4. Phase 4: Topic Modeling and Unsupervised Learning
3.4.1. Key Findings from Topic Modeling
3.4.2. Distribution of Misinformation Across Topics
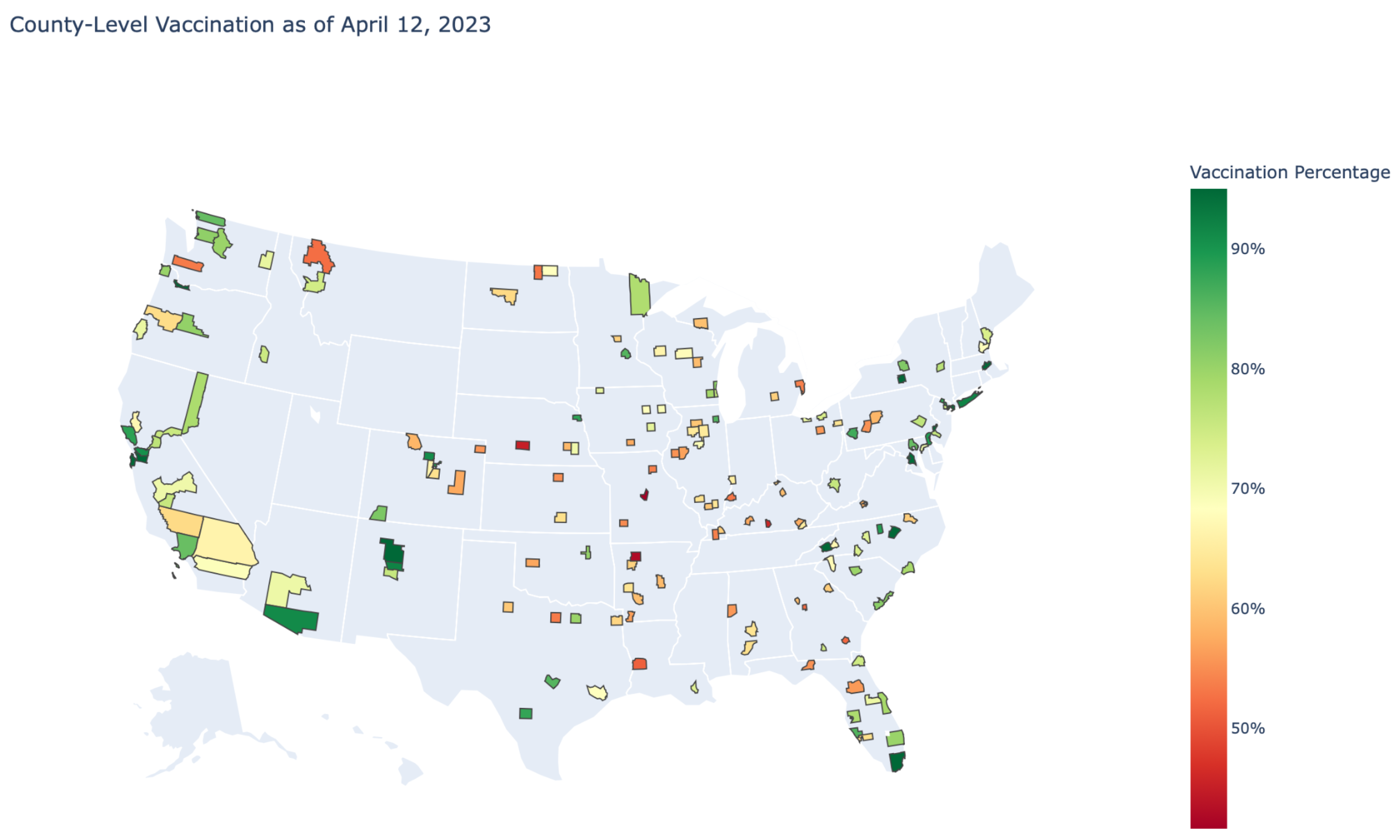
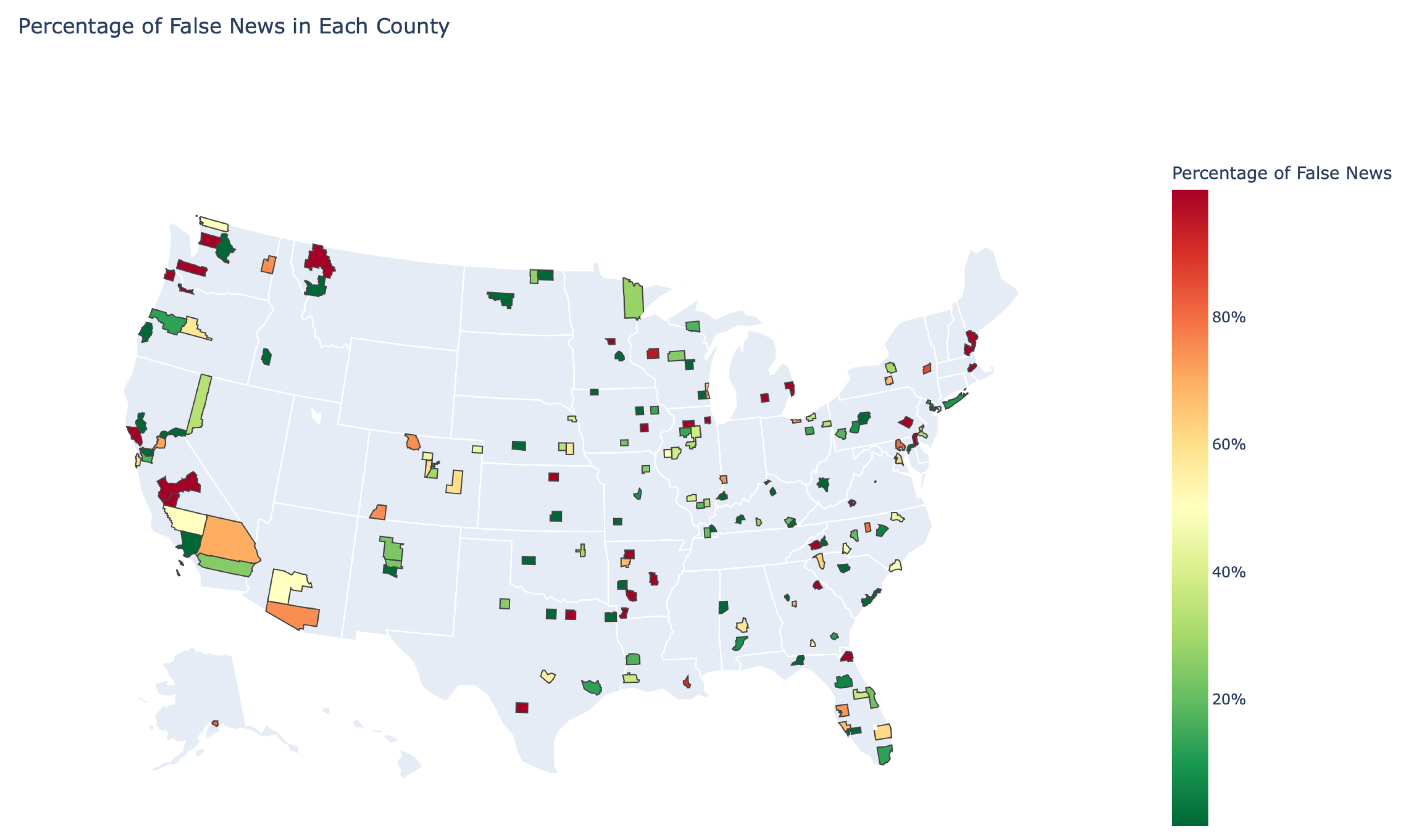
3.5. Phase 5: Visualization, Mapping, and Insights
4. Discussion and Analysis
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Managing the COVID-19 Infodemic: Promoting Healthy Behaviors and Mitigating the Harm from Misinformation and Disinformation. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/23-09-2020-managing-the-covid-19-infodemic-promoting-healthy-behaviours-and-mitigating-the-harm-from-misinformation-and-disinformation (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Cinelli, M.; Quattrociocchi, W.; Galeazzi, A.; Valensise, C.M.; Brugnoli, E.; Schmidt, A.L.; Zola, P.; Zollo, F.; Scala, A. The COVID-19 social media infodemic. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Sarkar, T.; Khan, S.I.; Kamal, A.H.M.; Hasan, S.M.M.; Kabir, A.; Yeasmin, D.; Islam, M.A.; Chowdhury, K.S.K.; Anwar, I.; et al. COVID-19–Related Infodemic and Its Impact on Public Health: A Global Social Media Analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, C.A.; Olusanya, O.A.; Ammar, N.; Shaban-Nejad, A. Public Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modeling Regarding COVID-19 Vaccines on the Reddit Social Media Platform: A Call to Action for Strengthening Vaccine Confidence. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, L.; Fu, X.; Yang, J. Early Detection of Fake News on Social Media Through Propagation Path Classification with Recurrent and Convolutional Networks. Inf. Sci. 2019, 493, 298–315. [Google Scholar]
- Patwa, P.; Sharma, S.; Pykl, S.; Guptha, V.; Kumari, G.; Akhtar, M.S.; Chakraborty, T. Fighting an Infodemic: COVID-19 Fake News Dataset. In Proceedings of the Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages During Emergency Situations: First International Workshop, CONSTRAINT 2020, Virtual, 8 February 2021; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Amjad, M.; Sidorov, G.; Zhila, A.; Gómez-Adorno, H.; Voronkov, I.; Gelbukh, A. Bend the Truth: Benchmark Dataset for Fake News Detection in Urdu Language and Its Evaluation. Data Brief 2020, 31, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, W. Using Deep Learning Models to Detect Fake News About COVID-19. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Yadav, K.; Yadav, N.; Ferdinand, K.C. Covid-19 on Social Media: Analyzing Misinformation in Twitter Conversations. J. Med Syst. 2020, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, M.A.; Madria, S.K. CoronaVis: A Real-Time COVID-19 Tweets Data Analyzer and Data Repository. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 104515–104525. [Google Scholar]
- Valdez, D.; Ten Thij, M.; Bathina, K.; Rutter, L.A.; Bollen, J. Social Media Insights Into US Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Longitudinal Analysis of Twitter Data. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e21418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayank, M.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, R. DEAP-FAKED: Knowledge Graph-Based Approach for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Istanbul, Turkey, 10–13 November 2022; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Oyebode, O.; Ndulue, C.; Mulchandani, D.; Suruliraj, B.; Adib, A.; Orji, F.A.; Orji, R. COVID-19 Pandemic: Identifying Key Issues Using Social Media and Natural Language Processing. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2022, 6, 174–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsudias, L.; Rayson, P. COVID-19 and Arabic Twitter: How Can Arab World Governments and Public Health Organizations Learn From Social Media? In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for COVID-19 at ACL 2020, Online, 5–10 July 2020.
- Ajao, O.; Garg, A.; Da Costa-Abreu, M. Exploring Content-Based and Meta-Data Analysis for Detecting Fake News Infodemic: A Case Study on COVID-19. In Proceedings of the 2022 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Systems (ICPRS), Saint-Etienne, France, 7–10 June 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jlifi, B.; Sakrani, C.; Duvallet, C. Towards a Soft Three-Level Voting Model (Soft T-LVM) for Fake News Detection. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.J. Establishing Legitimacy Through the Media and Combating Fake News on COVID-19: A Case Study of Taiwan. Chin. J. Commun. 2022, 15, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, U.; Imran, M.; Ofli, F. GeoCoV19: A Dataset of Hundreds of Millions of Multilingual COVID-19 Tweets With Location Information. SIGSPATIAL Spec. 2020, 12, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.A.; Qazi, A.; Zahid, M.; Syed, T.A. Temporal analysis and detection of COVID-19 misinformation on Twitter using ensemble machine learning models. J. Comput. Soc. Sci. 2023, 6, 101–123. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Mishra, S.; Mukherjee, A. A hybrid BERT-LDA model for topic-wise fake news detection during COVID-19. Online Soc. Netw. Media 2024, 36, 100762. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.H.; Madanu, H.; Lavu, S.; Mansourifar, H.; Alsagheer, D.; Shi, W. Detecting Conspiracy Theory Against COVID-19 Vaccines. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindelöf, G.; Aledavood, T.; Keller, B. Vaccine Discourse on Twitter During the COVID-19 Pandemic. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SimpleMaps. United States Cities Database. 2024. Available online: https://simplemaps.com/data/us-cities (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Mehta, V.; Valkunde, T.; Moustakas, E. Topics, Trends, and Sentiments of Tweets About the COVID-19 Pandemic: Temporal Infoveillance Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e22624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifrah, S.; Benlahmar, E.H. Topic Modeling Coherence: A Comparative Study between LDA and NMF Models using COVID-19 Corpus. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 5756–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozarth, L.; Budak, C. Keyword expansion techniques for mining social movement data on social media. EPJ Data Sci. 2022, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, H.; Nithyanand, R. Exploring the magnitude and effects of media influence on Reddit moderation. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, online, 15 May–15 July 2022; Volume 16, pp. 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Gozzi, N.; Chinazzi, M.; Dean, N.E.; Longini, I.M.; Halloran, M.E.; Perra, N.; Vespignani, A. Estimating the impact of COVID-19 vaccine inequities: A modeling study. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozarth, L.; Quercia, D.; Capra, L.; Šćepanović, S. The role of the big geographic sort in online news circulation among US Reddit users. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Techniques | Features/Gaps Addressed |
|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. [5] | Recurrent, convolutional neural networks | Early detection of fake news on social media |
| Patwa et al. [6] | Logistic regression, decision trees | Benchmark dataset for COVID-19 fake news detection |
| Amjad et al. [7] | Logistic regression | Fake news detection in low-resource languages |
| Chen et al. [8] | CNN, LSTM networks | Deep learning models for COVID-19 fake news detection |
| Sharma et al. [9] | Keyword filtering, manual coding | Misinformation patterns, geographical variability |
| Kabir and Madria [10] | NLP | Real-time analysis of COVID-19 tweets |
| Melton et al. [4] | Topic modeling, sentiment analysis | Addressing misinformation in Reddit discussions |
| Valdez et al. [11] | Longitudinal analysis | Impact of misinformation on mental health |
| Mayank et al. [12] | Knowledge graphs | Knowledge-driven approach for fake news detection |
| Oyebode et al. [13] | NLP | Extracting key insights from user-generated content |
| Alsudias and Rayson [14] | Linguistic analysis | Regional nuances in misinformation dissemination |
| Ajao et al. [15] | Content/meta-data analysis | Improved detection methods |
| Jlifi et al. [16] | Soft T-LVM | Novel model combining language and contextual factors |
| Lin [17] | Case study | Media’s role in combating fake news |
| Qazi et al. [18] | Dataset creation, multilingual geotagging | Cross-regional public health and misinformation analysis using geolocated tweets |
| Wani et al. [19] | Ensemble machine learning (XGBoost, RF) | Temporal modeling of COVID-19 misinformation spread on Twitter |
| Das et al. [20] | BERT + LDA hybrid model | Detection of topic-wise fake news clusters and misinformation intent classification |
| Topic | Description | Top Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 0 | Humorous/Informal Vaccine Discussions | booster, vaccine, covid, dose, second, shot, people, card, months, day |
| Topic 1 | Conspiracy Theories | vaccine, booster, dude, thank, microchips, tracking, control, gave, run, right |
| Topic 2 | Public Debates on Vaccination | vaccine, people, covid, vaccines, vaccinated, virus, time, unvaccinated, spread, point |
| Topic 3 | Brand Skepticism and Technical Concerns | booster, vaccine, moderna, shot, microchips, covid, pfizer, phone, yes, activation |
| Topic | Description | Top Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 0 | Public Health Concerns | people, vaccinated, unvaccinated, virus, time, spread, point, cases, risk, health |
| Topic 1 | Discussions Around Booster Shots/vaccine brands | booster, moderna, shot, pfizer, shots, second, dose, months, day, thanks |
| Topic 2 | Conspiracy Theories | vaccine, microchips, chips, gates, tracking, right, chip, government, lol, thought |
| Topic 3 | Confusion and Misinformation Blend | covid, vaccines, chips, flu, work, reception, prevent, tower, shot, vax |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alarfaj, L.; Blackburn, J.; Amjad, M.; Patel, J.; Ertem, Z. Mapping the Infodemic: Geolocating Reddit Users and Unsupervised Topic Modeling of COVID-19-Related Misinformation. Information 2025, 16, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090748
Alarfaj L, Blackburn J, Amjad M, Patel J, Ertem Z. Mapping the Infodemic: Geolocating Reddit Users and Unsupervised Topic Modeling of COVID-19-Related Misinformation. Information. 2025; 16(9):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090748
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlarfaj, Lulu, Jeremy Blackburn, Maaz Amjad, Jay Patel, and Zeynep Ertem. 2025. "Mapping the Infodemic: Geolocating Reddit Users and Unsupervised Topic Modeling of COVID-19-Related Misinformation" Information 16, no. 9: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090748
APA StyleAlarfaj, L., Blackburn, J., Amjad, M., Patel, J., & Ertem, Z. (2025). Mapping the Infodemic: Geolocating Reddit Users and Unsupervised Topic Modeling of COVID-19-Related Misinformation. Information, 16(9), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090748







