Can Intelligence Affect Alcohol-, Smoking-, and Physical Activity-Related Behaviors? A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Population
2.2. Variables and Data Sources
2.3. Instrumental Variables (IVs) Selection
2.4. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Control and Pleiotropy Diagnosis
3.2. MR Estimation
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Alcohol Behaviors
4.2. Smoking Behaviors
4.3. Physical Activity Behaviors
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, Emma L., Laura D. Howe, Kaitlin H. Wade, Yoav Ben-Shlomo, W. David Hill, Ian J. Deary, Eleanor C. Sanderson, Jie Zheng, Roxanna Korologou-Linden, Evie Stergiakouli, and et al. 2020. Education, intelligence and Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence from a multivariable two-sample Mendelian randomization study. International Journal of Epidemiology 49: 1163–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstey, Kaarin J., Lee-Fay Low, Helen Christensen, and Perminder Sachdev. 2009. Level of cognitive performance as a correlate and predictor of health behaviors that protect against cognitive decline in late life: The path through life study. Intelligence 37: 600–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, Rosalind, Michelle Luciano, Ian J. Deary, Chandra A. Reynolds, Nancy L. Pedersen, Brenda L. Plassman, Matt McGue, Kaare Christensen, and Peter M. Visscher. 2016. The association between intelligence and lifespan is mostly genetic. International Journal of Epidemiology 45: 178–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhouse, Ellen V., Caroline A. McHutchison, Vera Cvoro, Susan D. Shenkin, and Joanna M. Wardlaw. 2017. Early life risk factors for cerebrovascular disease. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis 88: 976–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, G. David, Ian J. Deary, Ingrid Schoon, and Catharine R. Gale. 2007. Childhood Mental Ability in Relation to Food Intake and Physical Activity in Adulthood: The 1970 British Cohort Study. Pediatrics 119: e38–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, G. David, Ian J. Deary, Ingrid Schoon, Carol Emslie, Kate Hunt, and Catharine R. Gale. 2008. Childhood Mental Ability and Adult Alcohol Intake and Alcohol Problems: The 1970 British Cohort Study. American Journal of Public Health 98: 2237–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, Derrick A., and Michael V. Holmes. 2017. Mendelian randomisation in cardiovascular research: An introduction for clinicians. Heart 103: 1400–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, Jack, and Michael V. Holmes. 2019. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Research Synthesis Methods 10: 486–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, Jack, Fabiola Del Greco M., Cosetta Minelli, George Davey Smith, Nuala A. Sheehan, and John R. Thompson. 2016b. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: The role of the I2 statistic. International Journal of Epidemiology 45: 1961–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, Jack, George Davey Smith, and Stephen Burgess. 2015. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. International Journal of Epidemiology 44: 512–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, Jack, George Davey Smith, Philip C. Haycock, and Stephen Burgess. 2016a. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genetic Epidemiology 40: 304–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, Stephen, and Simon G. Thompson. 2017. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. European Journal of Epidemiology 32: 377–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, Stephen, Dylan S. Small, and Simon G. Thompson. 2015. A review of instrumental variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 26: 2333–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, Stephen, George Davey Smith, Neil M. Davies, Frank Dudbridge, Dipender Gill, M. Maria Glymour, Fernando P. Hartwig, Michael V. Holmes, Cosetta Minelli, and Caroline L. Relton. 2019. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations. Wellcome Open Research 4: 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, Stephen, Neil M. Davies, and Simon G. Thompson. 2016. Bias due to participant overlap in two-sample Mendelian randomization. Genetic Epidemiology 40: 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, Stephen, Sonja A. Swanson, and Jeremy A. Labrecque. 2021. Are Mendelian randomization investigations immune from bias due to reverse causation? European Journal of Epidemiology 36: 253–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvin, Catherine M., G. David Batty, Geoff Der, Caroline E. Brett, Adele Taylor, Alison Pattie, Iva Čukić, and Ian J. Deary. 2017. Childhood intelligence in relation to major causes of death in 68 year follow-up: Prospective population study. BMJ 357: j2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvin, Catherine M., Ian J. Deary, Candida Fenton, Beverly A. Roberts, Geoff Der, Nicola Leckenby, and G. David Batty. 2011. Intelligence in youth and all-cause-mortality: Systematic review with meta-analysis. International Journal of Epidemiology 40: 626–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Guoqing, Qiuling Wang, Ranran Xue, Xia Liu, and Hao Yu. 2021. Examining the Causal Inference of Leptin and Soluble Plasma Leptin Receptor Levels on Schizophrenia: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Frontiers in Psychiatry 12: 753224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Jinyu, Ting Xu, and Min Wu. 2022a. Depression in systemic lupus erythematosus: Modifiable or inheritable? a two-sample mendelian randomization study. Frontiers in Genetics 13: 988022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Xiong, Xiaosi Hong, Wenjing Gao, Shulu Luo, Jiahao Cai, Guochang Liu, and Yinong Huang. 2022b. Causal relationship between physical activity, leisure sedentary behaviors and COVID-19 risk: A Mendelian randomization study. Journal of Translational Medicine 20: 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Yu, Alfredo Spagna, Tingting Wu, Tae Hyeong Kim, Qiong Wu, Caiqi Chen, Yanhong Wu, and Jin Fan. 2019. Testing a Cognitive Control Model of Human Intelligence. Scientific Reports 9: 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom, Roberto, and Paul M. Thompson. 2011. Understanding human intelligence by imaging the brain. In The Wiley-Blackwell Handbook of Individual Differences. Hoboken: Wiley Blackwell, pp. 330–52. [Google Scholar]
- Colom, Roberto, Sherif Karama, Rex E. Jung, and Richard J. Haier. 2010. Human intelligence and brain networks. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 12: 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, Alex J., Philip J. Law, Maria Timofeeva, Kimmo Palin, Susan M. Farrington, Claire Palles, Mark A. Jenkins, Graham Casey, Hermann Brenner, Jenny Chang-Claude, and et al. 2020. Modifiable pathways for colorectal cancer: A mendelian randomisation analysis. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology 5: 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, Antonio, Leonardo Bonetti, Teppo Särkämö, Marina Kliuchko, and Elvira Brattico. 2019. On the Association Between Musical Training, Intelligence and Executive Functions in Adulthood. Frontiers in Psychology 10: 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, Gail, Albert Tenesa, Antony Payton, Jian Yang, Sarah E. Harris, David Liewald, Xiayi Ke, Stephanie Le Hellard, Andrea Christoforou, Michelle Luciano, and et al. 2011. Genome-wide association studies establish that human intelligence is highly heritable and polygenic. Molecular Psychiatry 16: 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, Neil M., Michael V. Holmes, and George Davey Smith. 2018. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 362: k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, Neil Martin, W. David Hill, Emma L. Anderson, Eleanor Sanderson, Ian J. Deary, and George Davey Smith. 2019. Multivariable two-sample Mendelian randomization estimates of the effects of intelligence and education on health. eLife 8: e43990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, Ian J. 2001. Human intelligence differences: Towards a combined experimental—Differential approach. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 5: 164–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, Ian J., Frank M. Spinath, and Timothy C. Bates. 2006. Genetics of intelligence. European Journal of Human Genetics 14: 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, Ian J., Lars Penke, and Wendy Johnson. 2010. The neuroscience of human intelligence differences. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 11: 201–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deary, Ian J., Martha C. Whiteman, John M. Starr, Lawrence J. Whalley, and Helen C. Fox. 2004. The impact of childhood intelligence on later life: Following up the Scottish mental surveys of 1932 and 1947. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 86: 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, Ian J., Sarah E. Harris, and W. David Hill. 2019. What genome-wide association studies reveal about the association between intelligence and physical health, illness, and mortality. Current Opinion in Psychology 27: 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deary, Ian J., Wendy Johnson, and Lorna M. Houlihan. 2009. Genetic foundations of human intelligence. Human Genetics 126: 215–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Ruoyang, Mengnan Lu, Jiawen Xu, Feng Zhang, Mingyi Yang, Pan Luo, Ke Xu, and Peng Xu. 2022. Pulmonary embolism and 529 human blood metabolites: Genetic correlation and two-sample Mendelian randomization study. BMC Genomic Data 23: 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, Meredith C., and Douglas K. Detterman. 2004. Scholastic assessment org? The relationship between the scholastic assessment test and general cognitive ability. Psychological Science 15: 373–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfredson, Linda S. 1997. Mainstream science on intelligence: An editorial with 52 signatories, history, and bibliography. Intelligence 24: 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, Jozo, Dorothea Dumuid, Enrique Garcia Bengoechea, Nipun Shrestha, Adrian Bauman, Timothy Olds, and Zeljko Pedisic. 2018. Health outcomes associated with reallocations of time between sleep, sedentary behaviour, and physical activity: A systematic scoping review of isotemporal substitution studies. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 15: 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, Stephani L., Peter B. Jones, Diana Kuh, Rebecca Hardy, Michael E. J. Wadsworth, and Marcus Richards. 2007. Childhood cognitive ability and adult mental health in the British 1946 birth cohort. Social Science & Medicine 64: 2285–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, Gibran, Jie Zheng, Benjamin Elsworth, Kaitlin H. Wade, Valeriia Haberland, Denis Baird, Charles Laurin, Stephen Burgess, Jack Bowden, Ryan Langdon, and et al. 2018. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 7: e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, Gibran, Kate Tilling, and George Davey Smith. 2017. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genetics 13: e1007081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horička, Pavol, Jaromir Šimonek, and Ľubomír Paška. 2020. Relationship between reactive agility, cognitive abilities, and intelligence in adolescents. Journal of Physical Education and Sport 20: 2263–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Hua, Daojun Hu, Jun Wang, Bo Zhang, Chiyi He, and Jiyu Ning. 2022. Adiponectin and the risk of gastrointestinal cancers in East Asians: Mendelian randomization analysis. Cancer Medicine 11: 2397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, Satoshi, and Josephine E. E. U. Hellberg. 2010. Intelligence and Substance Use. Review of General Psychology 14: 382–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koellinger, Philipp D., and Ronald de Vlaming. 2019. Mendelian randomization: The challenge of unobserved environmental confounds. International Journal of Epidemiology 48: 665–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornilova, Tatiana V., Sergey A. Kornilov, and Maria A. Chumakova. 2009. Subjective evaluations of intelligence and academic self-concept predict academic achievement: Evidence from a selective student population. Learning and Individual Differences 19: 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, Debbie A. 2016. Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: Opportunities and challenges. International Journal of Epidemiology 45: 908–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Gloria Hoi-Yee, Stanley Kam-Ki Lam, Ian Chi-Kei Wong, Jody Kwok-Pui Chu, and Ching-Lung Cheung. 2021. Education Attainment, Intelligence and COVID-19: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine 10: 4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Yifei, Yong Yang, Tingting Fu, Ling Lin, Xingming Zhang, Qiong Guo, Zhenglong Chen, Banghua Liao, and Jin Huang. 2022. Impairment of kidney function and kidney cancer: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Cancer Medicine. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Hui-Min, Qin Hu, Qiang Zhang, Guan-Yue Su, Hong-Mei Xiao, Bo-Yang Li, Wen-Di Shen, Xiang Qiu, Wan-Qiang Lv, and Hong-Wen Deng. 2019. Causal effects of genetically predicted cardiovascular risk factors on chronic kidney disease: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Frontiers in Genetics 10: 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, Sharon M., Ann Chen Wu, John E. Hokanson, Stijn Vansteelandt, and Christoph Lange. 2021. Caution against examining the role of reverse causality in Mendelian Randomization. Genetic Epidemiology 45: 445–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, Sharon M., Kirsten Voorhies, Ann Chen Wu, John Hokanson, Stijn Vansteelandt, and Christoph Lange. 2022. The influence of unmeasured confounding on the MR Steiger approach. Genetic Epidemiology 46: 139–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, Jean, Nicholas Knoblauch, Joseph H. Marcus, Matthew Stephens, and Xin He. 2020. Mendelian randomization accounting for correlated and uncorrelated pleiotropic effects using genome-wide summary statistics. Nature Genetics 52: 740–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, Laust H., Thorkild I. A. Sørensen, and Morten Grønbæk. 2005. Intelligence in relation to later beverage preference and alcohol intake. Addiction 100: 1445–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, Christoph, and Johan Ärnlöv. 2018. A Mendelian randomization study of the effects of blood lipids on breast cancer risk. Nature Communications 9: 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohi, Kazutaka, Kentaro Takai, Ayumi Kuramitsu, Shunsuke Sugiyama, Midori Soda, Kiyoyuki Kitaichi, and Toshiki Shioiri. 2021. Causal associations of intelligence with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: A Mendelian randomization analysis. European Psychiatry 64: e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, Jue-Sheng, and Stuart MacGregor. 2019. Implementing MR-PRESSO and GCTA-GSMR for pleiotropy assessment in Mendelian randomization studies from a practitioner’s perspective. Genetic Epidemiology 43: 609–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, Brandon L., and Stephen Burgess. 2013. Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: Subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. American Journal of Epidemiology 178: 1177–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, Shaun, Benjamin Neale, Kathe Todd-Brown, Lori Thomas, Manuel A. R. Ferreira, David Bender, Julian Maller, Pamela Sklar, Paul I. W. De Bakker, and Mark J. Daly. 2007. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. The American Journal of Human Genetics 81: 559–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, Rebecca C., and George Davey Smith. 2022. Mendelian randomization: Concepts and scope. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 12: a040501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, Stuart J., and Elliot M. Tucker-Drob. 2018. How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological Science 29: 1358–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, Mickael, Arnaud Chignon, Zhonglin Li, Marie-Chloé Boulanger, Benoit J. Arsenault, Yohan Bossé, Sébastien Thériault, and Patrick Mathieu. 2019. A Mendelian randomization study of IL6 signaling in cardiovascular diseases, immune-related disorders and longevity. NPJ Genomic Medicine 4: 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salber, Eva J., Brian MacMahon, and Barbara Welsh. 1962. Smoking Habits of High School Students Related to Intelligence and Achievement. Pediatrics 29: 780–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, Eleanor, George Davey Smith, Jack Bowden, and Marcus R. Munafò. 2019. Mendelian randomisation analysis of the effect of educational attainment and cognitive ability on smoking behaviour. Nature Communications 10: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, Jeanne E., Philip R. Jansen, Sven Stringer, Kyoko Watanabe, Julien Bryois, Christiaan A. de Leeuw, Mats Nagel, Swapnil Awasthi, Peter B. Barr, Jonathan R. I. Coleman, and et al. 2018. Genome-wide association meta-analysis in 269,867 individuals identifies new genetic and functional links to intelligence. Nature Genetics 50: 912–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxe, Glenn N., Daniel Calderone, and Leah J. Morales. 2018. Brain entropy and human intelligence: A resting-state fMRI study. PLoS ONE 13: e0191582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekula, Peggy, M. Fabiola Del Greco, Cristian Pattaro, and Anna Köttgen. 2016. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 27: 3253–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölund, Sara, Peter Allebeck, and Tomas Hemmingsson. 2012. Intelligence quotient (IQ) in adolescence and later risk of alcohol-related hospital admissions and deaths—37-year follow-up of Swedish conscripts. Addiction 107: 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, George Davey, Debbie A. Lawlor, Roger Harbord, Nic Timpson, Ian Day, and Shah Ebrahim. 2007. Clustered environments and randomized genes: A fundamental distinction between conventional and genetic epidemiology. PLoS Medicine 4: e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, Siti Shazwani Ahmad, Nik Ahmad Sufian Burhan, Abdul Razak Abdul Rahman, and Mohd Najmi Daud. 2019. Populations with Higher Average Intelligence Are Healthier, but Do They Smoke Fewer Cigarettes? The Mankind Quarterly 59: 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teumer, Alexander. 2018. Common methods for performing Mendelian randomization. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 5: 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Tobacco and Genetics Consortium. 2010. Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nature Genetics 42: 441–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Xiaoyu, Hua Xie, Nancy Carlisle, Gregory A. Fonzo, Desmond J. Oathes, Jing Jiang, and Yu Zhang. 2022. Transdiagnostic connectome signatures from resting-state fMRI predict individual-level intellectual capacity. Translational Psychiatry 12: 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, Adam J., Niall Ramsbottom, Magdalena Kowal, and Mark J. Campbell. 2020. Converging Evidence Supporting the Cognitive Link between Exercise and Esport Performance: A Dual Systematic Review. Brain Sciences 10: 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, Marie, Chia-Yen Chen, Benjamin Neale, and Ron Do. 2018. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 50: 693–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, Mark, Salman Zarka, Nomi Werbeloff, Efrat Kravitz, and Gad Lubin. 2010. Cognitive test scores in male adolescent cigarette smokers compared to non-smokers: A population-based study. Addiction 105: 358–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wraw, Christina, Geoff Der, Catharine R. Gale, and Ian J. Deary. 2018. Intelligence in youth and health behaviours in middle age. Intelligence 69: 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Gui, Hu Wang, Jiaji Hu, Li Liu, Tingting Zhang, Mengjia Zhou, Xingxing Li, and Chunxiang Qin. 2022a. Estimating the causal effect of frailty index on vestibular disorders: A two-sample Mendelian randomization. Frontiers in Neuroscience 16: 990682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Gui, Qingnan He, Li Liu, Tingting Zhang, Mengjia Zhou, Xingxing Li, Yijun Chen, Yanyi Chen, and Chunxiang Qin. 2022b. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Journal of Translational Medicine 20: 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Haoran, and Wei Pan. 2020. Inferring causal direction between two traits in the presence of horizontal pleiotropy with GWAS summary data. PLoS Genetics 16: e1009105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Yik Weng, Marie Loh, Steven Tien Guan Thng, and John C. Chambers. 2020. Investigating causal relationships between Body Mass Index and risk of atopic dermatitis: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Scientific Reports 10: 15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Shuai, Honghui Yao, and Susanna C. Larsson. 2020. Associations of cigarette smoking with psychiatric disorders: Evidence from a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Scientific Reports 10: 13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Jie, Denis Baird, Maria-Carolina Borges, Jack Bowden, Gibran Hemani, Philip Haycock, David M. Evans, and George Davey Smith. 2017. Recent Developments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Current Epidemiology Reports 4: 330–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Zhihong, Zhili Zheng, Futao Zhang, Yang Wu, Maciej Trzaskowski, Robert Maier, Matthew R. Robinson, John J. McGrath, Peter M. Visscher, Naomi R. Wray, and et al. 2018. Causal associations between risk factors and common diseases inferred from GWAS summary data. Nature Communications 9: 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| GWAS ID | N | Item |
|---|---|---|
| ebi-a-GCST006250 | 269,867 | Intelligence |
| finn-b-AUD | 218,792 | Alcohol use disorder (based on the International Classification of Diseases) |
| finn-b-F5_ALCOHOL | 216,759 | Mental and behavioral disorders due to alcohol |
| finn-b-F5_ALCOHOL_DEPENDENCE | 211,535 | Alcohol dependence |
| finn-b-KRA_PSY_ALCOH | 218,792 | Alcohol abuse |
| finn-b-SMOKING | 138,088 | Smoking |
| finn-b-SMOKING_DEPEND | 218,433 | Smoking dependence |
| ieu-a-961 | 68,028 | Smoking quantity (cigarettes smoked per day) |
| ieu-a-963 | 70,675 | Smoking cessation (former vs. current smoker) |
| ukb-b-4886 | 454,783 | Walking frequency |
| ukb-b-16998 | 395,831 | Walking duration |
| ukb-b-4710 | 440,266 | Moderate PA frequency |
| ukb-b-151 | 440,512 | Vigorous PA frequency |
| Outcome | MR-PRESSO (Global Test) | MR-Egger | |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | Intercept | p | |
| Alcohol use disorder | 0.682 | −0.005 | 0.557 |
| Mental and behavioral disorders due to alcohol | 0.854 | −0.0008 | 0.916 |
| Alcohol dependence | 0.845 | −0.012 | 0.236 |
| Alcohol abuse | 0.774 | 0.010 | 0.462 |
| Smoking | 0.976 | −0.006 | 0.768 |
| Smoking dependence | 0.907 | −0.004 | 0.862 |
| Smoking quantity | 0.965 | −0.007 | 0.876 |
| Smoking cessation | 0.842 | 0.001 | 0.894 |
| Walking frequency | 0.089 | −0.002 | 0.399 |
| Walking duration | 0.910 | −0.0008 | 0.461 |
| Moderate PA frequency | 0.068 | −0.002 | 0.509 |
| Vigorous PA frequency | 0.403 | −0.002 | 0.294 |
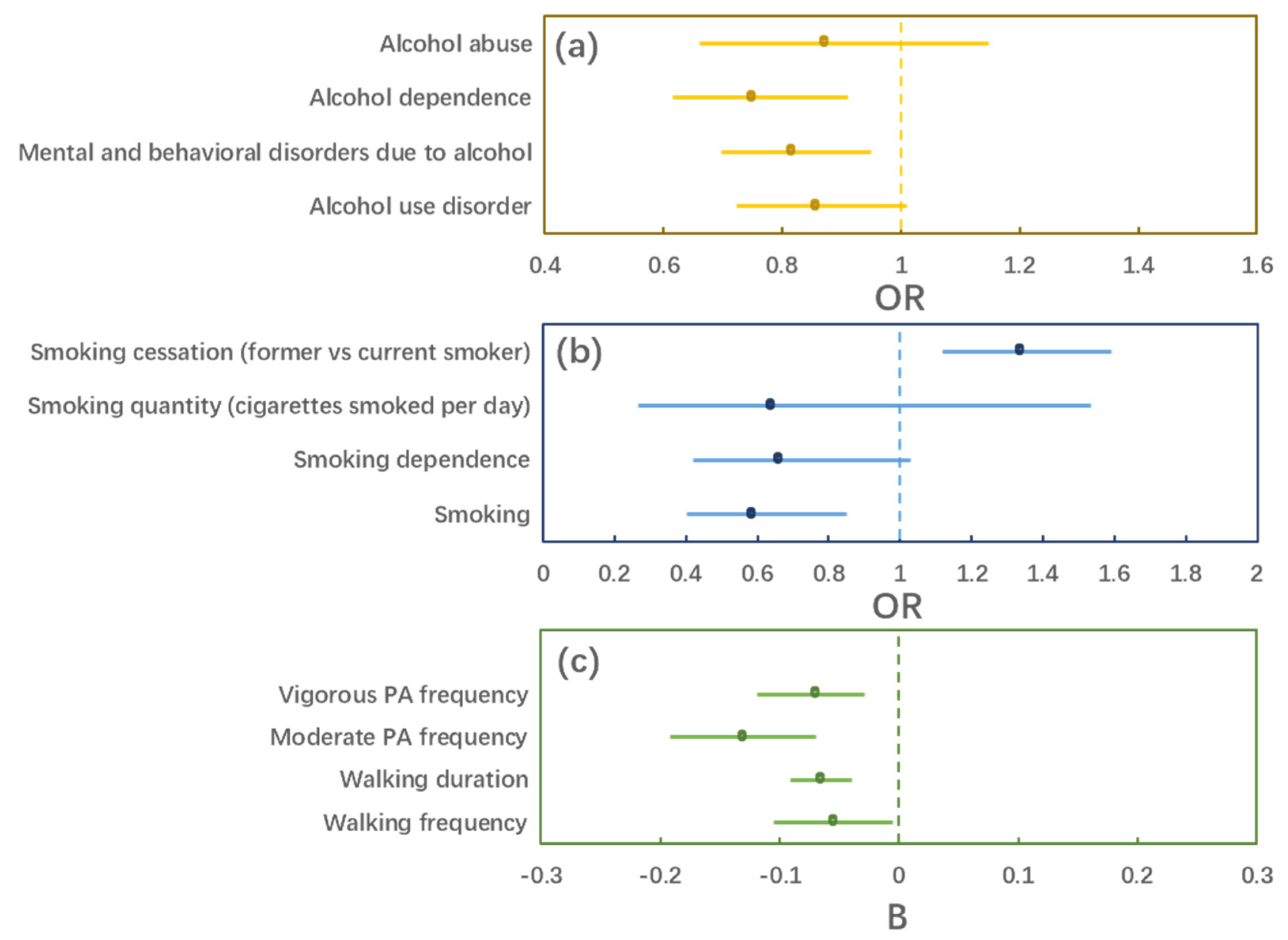
| Outcome | OR/B | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol use disorder | 0.855 | (0.724, 1.011) | 0.066 |
| Mental and behavioral disorders due to alcohol | 0.814 | (0.697, 0.950) | 0.009 |
| Alcohol dependence | 0.749 | (0.615, 0.911) | 0.003 |
| Alcohol abuse | 0.870 | (0.660, 1.147) | 0.323 |
| Smoking | 0.585 | (0.402, 0.851) | 0.005 |
| Smoking dependence | 0.658 | (0.421, 1.029) | 0.066 |
| Smoking quantity (cigarettes smoked per day) | 0.638 | (0.265, 1.535) | 0.316 |
| Smoking cessation (former vs. current smoker) | 1.334 | (1.118, 1.593) | 0.001 |
| Walking frequency | −0.055 | (−0.105, −0.005) | 0.031 |
| Walking duration | −0.066 | (−0.091, −0.040) | <0.001 |
| Moderate PA frequency | −0.131 | (−0.192, −0.070) | <0.001 |
| Vigorous PA frequency | −0.070 | (−0.119, −0.029) | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhang, G. Can Intelligence Affect Alcohol-, Smoking-, and Physical Activity-Related Behaviors? A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Intell. 2023, 11, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11020029
Li H, Zhang X, Zhang X, Wang Z, Feng S, Zhang G. Can Intelligence Affect Alcohol-, Smoking-, and Physical Activity-Related Behaviors? A Mendelian Randomization Study. Journal of Intelligence. 2023; 11(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hansen, Xing Zhang, Xinyue Zhang, Zhenhuan Wang, Siyuan Feng, and Guodong Zhang. 2023. "Can Intelligence Affect Alcohol-, Smoking-, and Physical Activity-Related Behaviors? A Mendelian Randomization Study" Journal of Intelligence 11, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11020029
APA StyleLi, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Feng, S., & Zhang, G. (2023). Can Intelligence Affect Alcohol-, Smoking-, and Physical Activity-Related Behaviors? A Mendelian Randomization Study. Journal of Intelligence, 11(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11020029





