Abstract
Over the years, several bone regeneration procedures have been proposed using natural (autografts, allografts, and xenografts) and synthetic (i.e., metals, ceramics, and polymers) bone grafts. In particular, numerous in vitro and human and animal in vivo studies have been focused on the discovery of innovative and suitable biomaterials for oral and maxillofacial applications in the treatment of severely atrophied jaws. On this basis, the main objective of the present narrative review was to investigate the efficacy of innovative collagenated porcine bone grafts (OsteoBiol®, Tecnoss®, Giaveno, Italy), designed to be as similar as possible to the autologous bone, in several bone regeneration procedures. The scientific publications were screened by means of electronic databases, such as PubMed, Scopus, and Embase, finally selecting only papers that dealt with bone substitutes and scaffolds for bone and soft tissue regeneration. A total of 201 papers have been detected, including in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. The effectiveness of over 20 years of translational research demonstrated that these specific porcine bone substitutes are safe and able to improve the biological response and the predictability of the regenerative protocols for the treatment of alveolar and maxillofacial defects.
1. Introduction
Bone regeneration procedures are surgical techniques developed to restore the jaw defects provoked by tissue damage, infections, tooth loss, neoplasms, or local trauma [1,2,3]. Many different protocols have been adopted in accordance with the defect type (horizontal/vertical augmentation) [4,5,6,7], the local anatomy (anterior/posterior region of maxilla/mandibula) [8,9,10,11], the defect extension, and the planned rehabilitation [4,12,13,14]. The rationale of these procedures is to obtain a durable regeneration of the hard/soft tissue interface after the organization of a blood clot, which promotes the local new bone formation [15,16,17]. The use of xenografts and alloplastic bone substitutes represents a useful and safe technique that takes advantage of the high manageability of these products, avoiding the need for a donor site for autologous graft retrieving [17,18,19]. The effectiveness of these products has been evaluated by different studies conducted in various research centers around the world. These studies have been developed on a progressive scale, starting from in vitro studies on cell cultures, proceeding with in vivo studies on animal models, and finally with human studies, which allow for strengthening the 20-year work experience in translational research activity. In particular, both the histological and histomorphometric investigations performed at the microscopic level are able to reveal the bone response to the graft, providing strong knowledge about the bone scaffold behavior, the resorption process, the local bone neoformation, and the long-term persistent response of the regenerated tissues. Moreover, these methodologies have been associated with other techniques, such as Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and Synchrotron Micro-CT, in order to improve the biomaterial surface characterization and information about the physicochemical and biological compositions. This methodological approach steers clinicians towards the correct choice of the scaffold shape (i.e., particulate/block), the surgical procedure, and the graft manipulation and stabilization techniques, in order to increase the predictability of the procedure. In these terms, the aim of the present review was to describe the effectiveness of several protocols for the alveolar/maxillofacial bone and soft tissue regeneration using different OsteoBiol® innovative collagenated porcine bone grafts.
2. Materials and Methods
The screening of the studies was performed using the electronic databases PubMed, Scopus, and Embase, through the research of specific keywords: Piattelli A AND porcine bone biomaterials; Piattelli A AND porcine bone biomaterials AND jawbone regeneration; Piattelli A AND porcine granules; Piattelli A AND porcine bone blocks; Piattelli A AND porcine collagen bone barriers; Piattelli A AND porcine collagen membranes; OsteoBiol® AND porcine bone biomaterial; OsteoBiol® AND jawbone regeneration; OsteoBiol® AND maxillofacial regeneration; OsteoBiol® AND porcine granules; OsteoBiol® AND porcine bone blocks; OsteoBiol® AND porcine collagen bone barriers; OsteoBiol® AND porcine collagen membranes.
The manuscripts were then evaluated through a qualitative synthesis.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
The studies published up to January 2021 were evaluated with no language restrictions. The identified studies were limited to papers that dealt with collagenated porcine bone substitutes and scaffolds for bone and soft tissue regeneration during the last 20 years. No restrictions about the use of barrier membranes were applied to the systematic research process. The inclusion criteria considered human studies, in vitro research and reports, and animal model investigations. The off-topic publications were excluded from the investigation. The articles were then classified in accordance with the surgical procedure and the study design.
2.2. Selection of the Studies
The screening of the study data and papers was performed independently by two calibrated and expert reviewers (M.T. and A.P.). After a first check, all the abstracts of the identified papers were evaluated as the 1st level of screening. The reviews and book chapters were excluded from the qualitative analysis. A description of the reasons for exclusion was drafted, concerning not considered articles. The full text of the included papers was obtained, and then, they were classified for the qualitative synthesis. For this purpose, a specially designed data form was used (Excel Office Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA).
A total of 1375 manuscripts have been detected by the electronic database research. A total of 266 duplicates have been removed, and 1109 papers have been considered for the full-text eligibility evaluation. A total of 44 literature reviews, five book chapters, 87 papers written in non-English grammar, and 772 off-topic manuscripts were excluded. In the end, a total of 201 papers have been included in the final analytical synthesis (Figure 1).
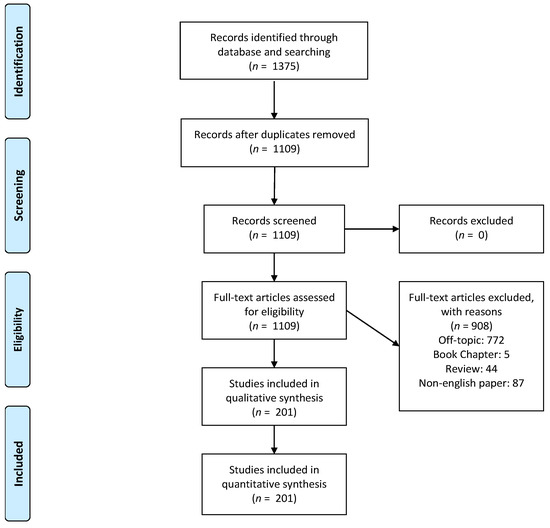
Figure 1.
PRISMA Flowchart of the study design and manuscript-selection process.
2.3. Description of the Porcine Grafts
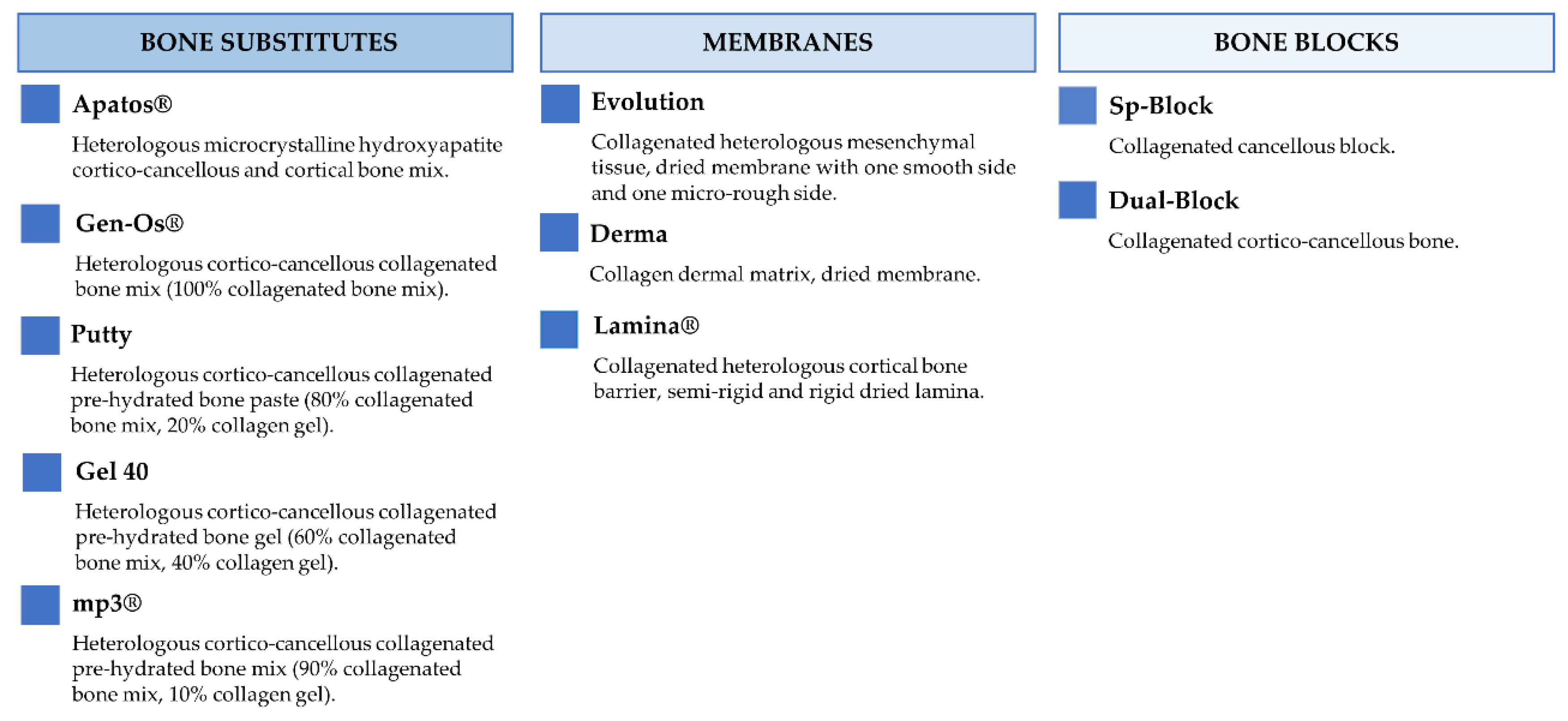
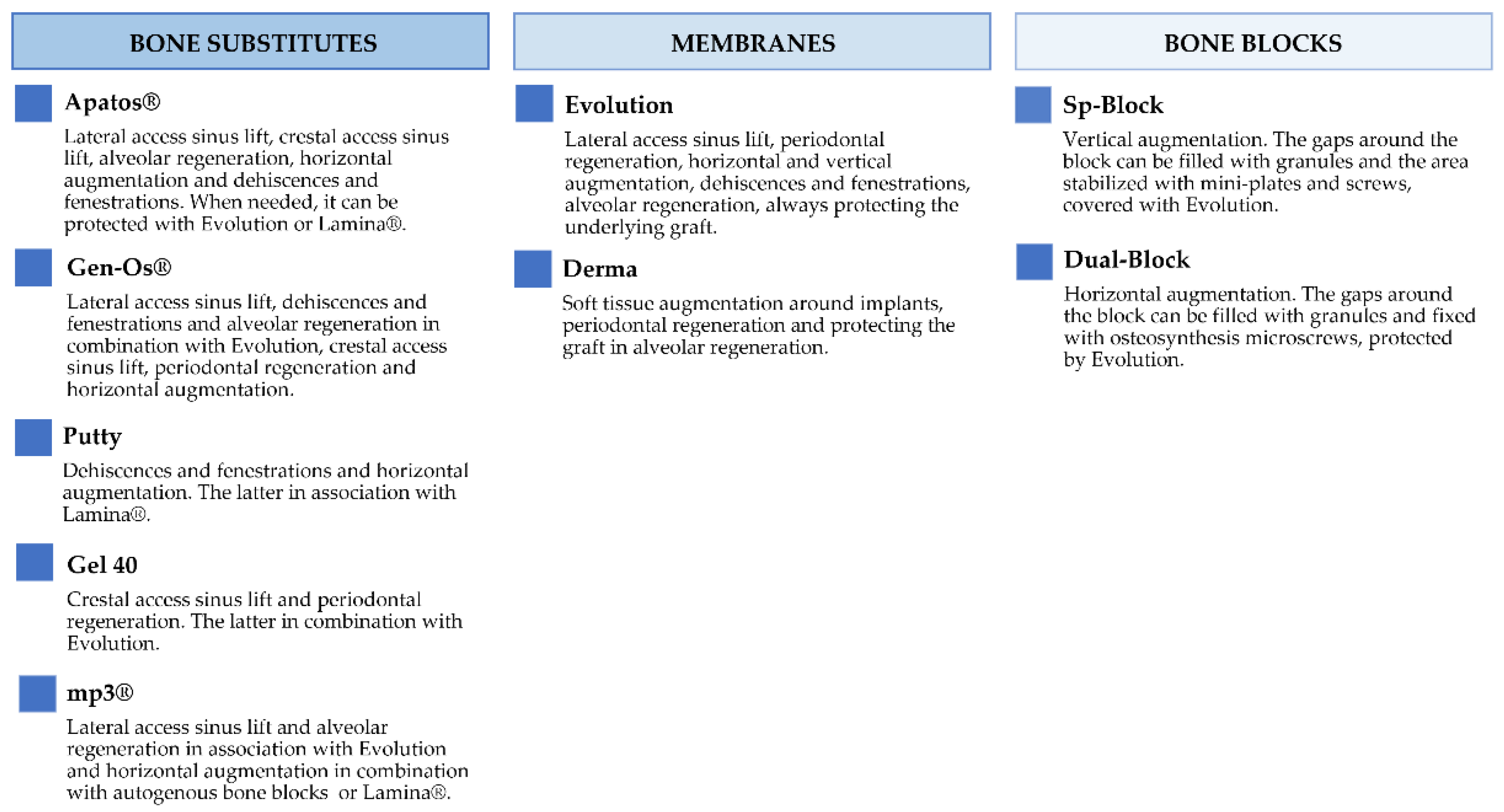
Figure 2 and Figure 3 report the characteristics and the clinical applications of the different biomaterials (OsteoBiol®, Tecnoss®, Giaveno, Italy) used and cited in the selected papers. All of them are porcine collagenated xenografts and show high biocompatibility and osteoconductive properties [20,21]. A dedicated product has been developed for every clinical indication, trying to provide the best handling, granulometry, and consistency, in order to achieve ideal regenerative results [22]. In particular, the dual-phase heterologous bone matrix granules are composed of a mineral phase and a xenogenic collagen phase, which is able to provide the best biocompatibility, a chemical composition similar to autogenous bone, gradual resorption of the bone matrix with the replacement by the newly formed bone at re-entry time, and a high angiogenic potential [23,24,25,26]. These elements are critical for a successful bone regeneration procedure that sometimes can be further improved with the association of some of these xenografts.
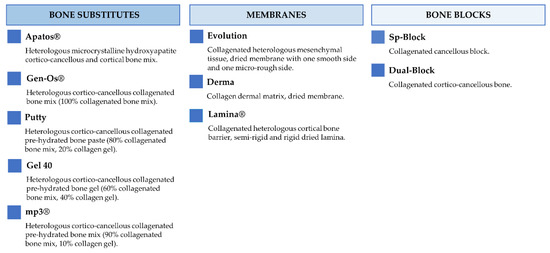
Figure 2.
Description of the characteristics regarding OsteoBiol® products.
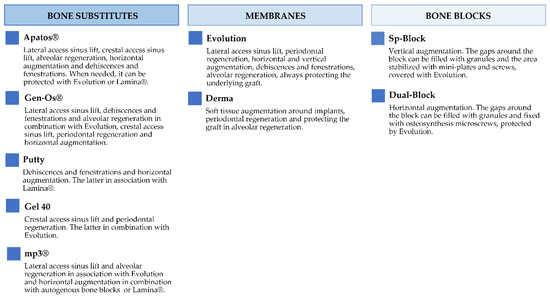
Figure 3.
Description of the clinical applications of OsteoBiol® products.
3. Results
The main effective results for each biomaterial used alone or in combination have been schematically divided and summarized in the tables below [Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8], on the basis of the clinical indication they have been specifically designed for.

Table 1.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Alveolar Regeneration (ALR) and Alveolar Regeneration/Dehiscences and Fenestrations (ALR/DEH).

Table 2.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Dehiscences and Fenestrations (DEH) and Dehiscences and Fenestrations/Lateral Access Sinus Lift (DEH/LASL).

Table 3.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Crestal Access Sinus Lift (CASL), Lateral Access Sinus Lift (LASL) and Lateral Access Sinus Lift/Horizontal Augmentation (LASL/HOR).

Table 4.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Horizontal Augmentation (HOR), Vertical Augmentation (VER), Horizontal and Vertical Augmentation (HOR/VER) and Vertical Augmentation/Lateral Access Sinus Lift (VER/LASL).

Table 5.
Bone regeneration procedures with porcine xenografts: Maxillofacial (MAX).

Table 6.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Periodontal Regeneration (PER) and Soft Tissue Augmentation (TIS).

Table 7.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Laboratory Tests (in vitro studies) (LAB), Laboratory Tests/Experimental Studies (LAB/EXP) and Laboratory Tests/Lateral Access Sinus Lift (LAB/LASL).

Table 8.
Bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine xenografts: Experimental Studies (EXP).
In summary, all the in vitro, experimental, and clinical results described in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8 suggested that, during the last 20 years, the OsteoBiol® collagenated biomaterials have shown reliable outcomes in terms of biocompatibility, morbidity, new bone formation, and bone and soft tissue regeneration, according to expert surgeons’ experience.
4. Discussion
The number of studies reporting surgical techniques for bone regeneration and the clinical effectiveness of bone substitutes and xenografts has greatly increased over the last years, with high predictability and stability of the regenerated alveolar bone ridges [9,18,219]. The treatment of bone defects represents a clinical occurrence that requires optimal management of the three-dimensional stability of the grafts and regenerative spaces. In this way, blood-clot stability plays a key role in new bone formation and the morphological restoration of the atrophied bone ridge [220].
The effectiveness of graft implantation is affected by a biunivocal biological relationship between the host tissue and the bone substitutes that has been investigated by numerous histological studies on retrieved biopsies [221].
In many ex vivo studies conducted by using porcine graft specimens, the histologic and histomorphometric evaluations reported newly formed bone in contact with the scaffolds and an evident presence of cells in the osteocyte lacunae [7,24,25,27,222].
This evidence has been corroborated by the clinical success of these biomaterials, which confirmed the histologic and histomorphometric findings and showed an intimate apposition of newly formed bone in contact with the porous porcine-derived biomaterials, especially in maxillary sinus augmentation procedures [28,85,89,90,93,97,99,100,101,110,111,116,117,119].
In addition, the results obtained from ex vivo and clinical data have been supported by in vitro studies, which demonstrated the osteoblast differentiation and bone regeneration capabilities together with the angiogenic potential of the OsteoBiol® bone matrix [21,23,26,178,183,184,185,194,197].
With reference to graft resorption, many studies revealed the nearly complete substitution of membranes and the ongoing resorption of collagenated bone particles within 6 months. Especially, Wachtel et al. [123] reported that the biodegradation of the cortical bone Lamina® was almost complete after 6 months, with varying degrees of residual graft particles. Cardaropoli et al. [30] confirmed the presence of a marginal residual graft rate (24.5%) of Gen-Os® biomaterial, covered by Evolution® collagen membrane to preserve the bone socket, just after 4 months from implant insertion. Additionally, another clinical study [95] reported a high resorption rate of mp3®, with 13.55% of residual grafting material after 5 months, that reached 12.3% within 12 months [24]. Considering that the limit for the residual volume of bone grafts for successful implant placement is set at 40% [223], these values are considerably lower.
Regarding the aforementioned residual graft limit, it should be considered that only Apatos Cortical® showed a higher residue percentage (around 30%) after many years from the surgery, although it stayed within 40%, comparable to the different types of xenografts present in the market [96,224].
However, these histological findings allow for adequate preservation of the grafted volume and do not appear to negatively affect the predictability of regenerative procedures and the survival rate of the dental implant in regenerated sites [225].
Overall, based on the data discussed, it appears clear that, due to the unique properties of these xenografts, an adequate preservation of graft volume and an improved new bone formation have been achieved.
In addition, the literature proved that OsteoBiol® materials could be used alone or in combination both for the regeneration of bone defects and soft tissue augmentation. For example, in the latter case, membranes, such as Derma, can be used alone as an alternative to connective tissue graft to improve the quality of keratinized tissues [166,171,172,173,174]. Apatos®, instead, is a universal filler that can be employed to treat peri-implant defects and two-wall defects [68,74]. Moreover, thanks to its granulometry, Apatos® fits well in big sockets, e.g., after molar extractions [41]. For this reason, sinus lift procedures (with crestal or lateral access) [85,91] can be performed with Apatos® as a bone substitute, as well as surgeries for horizontal regenerations. Finally, as an example of a combination of materials, Apatos® grafts can be protected with Evolution membrane [59] to reach a better ridge preservation compared to non-preserved size.
Although the effectiveness of using these biomaterials has been summarized in the results (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8) and discussed in this section, it is necessary to recognize that this narrative review has potential weaknesses. The main limitations include: (i) the manuscript does not contain all the reports in the field of “effectiveness of bone regeneration procedures with collagenated porcine grafts”, but only some selected publications that concern OsteoBiol® biomaterials; (ii) the collected articles come from studies not only conducted by the authors of this review, but also by several other authors; (iii) the manuscript describes the individual works but does not quantify the results, and no statistical analysis is performed here; (iv) the manuscript does not compare the effectiveness of OsteoBiol® products with other competitors, which are also successfully used for bone and soft tissue regeneration within the craniofacial area. However, our main goal was to summarize the achievements of these specific materials over the years.
Despite these limitations, we can conclude that the 20-year translational research experience showed the safety of these specific porcine bone substitutes and demonstrated their capability to improve the biological response and predictability of regenerative protocols for the treatment of alveolar and maxillofacial defects. For future perspectives, it will certainly be useful to extend the number of included studies, analyze and compare the success rate of each product, and perform longer-term histological and histomorphometric studies in order to better understand the resorption times of all these biomaterials. In this way, a systematic review could be performed to better highlight the advantages of using OsteoBiol® collagenated porcine bone grafts with respect to other porcine substitutes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P. and N.D.P.; validation, G.I. and L.M.; investigation, M.T., G.I. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, T.R., N.D.P., F.I. and M.T.; writing—review and editing, M.P. and P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data supporting reported results regarding publications cited in this review are available contacting the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kanczler, J.M.; Oreffo, R.O.C. Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis: The Potential for Engineering Bone. Eur. Cells Mater. 2008, 15, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Piñas, L.; Murias, A.; Prado, R.; Tejero, R. Effects of Calcium Ions on Titanium Surfaces for Bone Regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Simancas-Pallares, M.; Marincola, M.; Chuang, S.K. Grafting and Dental Implantation in Patients with Jawbone Cavitation: Case Series and 3-Year Follow-Up. Implant Dent. 2017, 26, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malchiodi, L.; Scarano, A.; Quaranta, M.; Piattelli, A. Rigid Fixation by Means of Titanium Mesh in Edentulous Ridge Expansion for Horizontal Ridge Augmentation in the Maxilla. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1998, 13, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Roccuzzo, A.; Schwarz, F. A Systematic Review on the Influence of the Horizontal Distance between Two Adjacent Implants Inserted in the Anterior Maxilla on the Inter-Implant Mucosa Fill. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, S.; Levin, L. Human Studies of Vertical and Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Comparing Different Types of Bone Graft Materials: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 44, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Carinci, F.; Assenza, B.; Piattelli, M.; Murmura, G.; Piattelli, A. Vertical Ridge Augmentation of Atrophic Posterior Mandible Using an Inlay Technique with a Xenograft without Miniscrews and Miniplates: Case Series. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moraissi, E.A.; Alkhutari, A.S.; Abotaleb, B.; Altairi, N.H.; del Fabbro, M. Do Osteoconductive Bone Substitutes Result in Similar Bone Regeneration for Maxillary Sinus Augmentation When Compared to Osteogenic and Osteoinductive Bone Grafts? A Systematic Review and Frequentist Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Lorusso, F.; de Oliveria, P.S.; Padmanabhan, S.K.; Licciulli, A. Hydroxyapatite Block Produced by Sponge Replica Method: Mechanical, Clinical and Histologic Observations. Materials 2019, 12, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G.; Degidi, M.; Marchetti, C. Reconstruction of an Atrophied Posterior Mandible with the Inlay Technique and Inorganic Bovine Bone Block: A Case Report. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2010, 30, 582–591. [Google Scholar]
- Felice, P.; Piana, L.; Checchi, L.; Corvino, V.; Nannmark, U.; Piattelli, M. Vertical Ridge Augmentation of an Atrophic Posterior Mandible with an Inlay Technique and Cancellous Equine Bone Block: A Case Report. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Assenza, B.; di Cerbo, A.; Candotto, V.; de Oliveira, P.S.; Lorusso, F. Bone Regeneration in Aesthetic Areas Using Titanium Micromesh. Three Case Reports. ORAL Implantol. 2017, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Mazón, P.; del Fabbro, M.; Tumedei, M.; Aramburú, J.; Pérez-Díaz, L.; de Aza, P.N. Histological and Histomorphometric Analyses of Two Bovine Bone Blocks Implanted in Rabbit Calvaria. Symmetry 2019, 11, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, V.K.L.; Shinagawa, A.; da Graça Naclério-Homem, M. Bone Healing of Mandibular Criticalsize Defects in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Braz. Oral Res. 2013, 27, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isacco, C.G.; Nguyen, K.C.D.; Ballini, A.; Paduanelli, G.; Pham, V.H.; Aityan, S.K.; Schiffman, M.; Tran, T.C.; Huynh, T.D.; Filgueira, L.; et al. Innovative Scaffold Solution for Bone Regeneration Made of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Granules, Autologous Fibrin Fold, and Peripheral Blood Stem Cells. In Regenerative Medicine and Plastic Surgery; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulghani, S.; Mitchell, G.R. Biomaterials for in Situ Tissue Regeneration: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumedei, M.; Savadori, P.; del Fabbro, M. Synthetic Blocks for Bone Regeneration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testori, T.; Wallace, S.S.; Trisi, P.; Capelli, M.; Zuffetti, F.; del Fabbro, M. Effect of Xenograft (ABBM) Particle Size on Vital Bone Formation Following Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Clinical Histomorphometric Trial. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Vijfeijken, S.E.C.M.; Münker, T.J.A.G.; Spijker, R.; Karssemakers, L.H.E.; Vandertop, W.P.; Becking, A.G.; Ubbink, D.T.; Becking, A.G.; Dubois, L.; Karssemakers, L.H.E.; et al. Autologous Bone Is Inferior to Alloplastic Cranioplasties: Safety of Autograft and Allograft Materials for Cranioplasties, a Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.; Henriques, J.; Martins, G.; Guerra, F.; Judas, F.; Figueiredo, H. Physicochemical Characterization of Biomaterials Commonly Used in Dentistry as Bone Substitutes-Comparison with Human Bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, G.; Sollazzo, V.; Carinci, F.; Palmieri, A.; Girardi, A.; Monguzzi, R. Osteobiol® Influences Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose Derived Stem Cells. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2011, 9, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Checchi, V.; Felice, P.; Zucchelli, G.; Barausse, C.; Piattelli, M.; Pistilli, R.; Grandi, G.; Esposito, M. Wide Diameter Immediate Post-Extractive Implants vs Delayed Placement of Normal-Diameter Implants in Preserved Sockets in the Molar Region: 1-Year Postloading Outcome of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeanneau, C.; le Fournis, C.; About, I. Xenogeneic Bone Filling Materials Modulate Mesenchymal Stem Cell Recruitment: Role of the Complement C5a. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, A.; Iezzi, G.; Mazzoni, S.; Piattelli, A.; Perrotti, V.; Barone, A. Regenerative Properties of Collagenated Porcine Bone Grafts in Human Maxilla: Demonstrative Study of the Kinetics by Synchrotron Radiation Microtomography and Light Microscopy. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannmark, U.; Sennerby, L. The Bone Tissue Responses to Prehydrated and Collagenated Cortico-Cancellous Porcine Bone Grafts: A Study in Rabbit Maxillary Defects. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2008, 10, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, C.; Jeanneau, C.; Camilleri, J.; Laurent, P.; About, I. Characterization and Angiogenic Potential of Xenogeneic Bone Grafting Materials: Role of Periodontal Ligament Cells. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Covani, U.; Ameri, S.; Crespi, R.; Barone, A. Preservation of the Alveolar Process with Heterologous Bone. Histological Considerations. Ital. Oral Surg. 2004, 3, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Arcuri, C.; Cecchetti, F.; Germano, F.; Motta, A.; Santacroce, C. Clinical and Histological Study of a Xenogenic Bone Substitute Used as a Filler in Postextractive Alveolus. Minerva Stomatol. 2005, 54, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Aldini, N.N.; Fini, M.; Giardino, R.; Calvo Guirado, J.L.; Covani, U. Xenograft Versus Extraction Alone for Ridge Preservation after Tooth Removal: A Clinical and Histomorphometric Study. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardaropoli, D.; Cardaropoli, G. Preservation of the Postextraction Alveolar Ridge: A Clinical and Histologic Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2008, 28, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, R.; Capparè, P.; Gherlone, E. Dental Implants Placed in Extraction Sites Grafted with Different Bone Substitutes: Radiographic Evaluation at 24 Months. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Morales, R.S.; Frascaria, M.; Benzi, R.; Squadrito, N. Planning Implants in the Esthetic Zone Using a New Implant 3D Navigation System. Eur. J. Esthet. Dent. 2010, 5, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crespi, R.; Capparè, P.; Romanos, G.E.; Mariani, E.; Benasciutti, E.; Gherlone, E. Corticocancellous Porcine Bone in the Healing of Human Extraction Sockets: Combining Histomorphometry with Osteoblast Gene Expression Profiles in Viv. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Festa, V.M.; Addabbo, F.; Laino, L.; Femiano, F.; Rullo, R. Porcine-Derived Xenograft Combined with a Soft Cortical Membrane versus Extraction Alone for Implant Site Development: A Clinical Study in Humans. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Orlando, B.; Cingano, L.; Marconcini, S.; Derchi, G.; Covani, U. A Randomized Clinical Trial to Evaluate and Compare Implants Placed in Augmented versus Non-Augmented Extraction Sockets: 3-Year Results. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Ricci, M.; Tonelli, P.; Santini, S.; Covani, U. Tissue Changes of Extraction Sockets in Humans: A Comparison of Spontaneous Healing vs. Ridge Preservation with Secondary Soft Tissue Healing. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Borgia, V.; Covani, U.; Ricci, M.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Flap versus Flapless Procedure for Ridge Preservation in Alveolar Extraction Sockets: A Histological Evaluation in a Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Ricci, M.; Romanos, G.E.; Tonelli, P.; Alfonsi, F.; Covani, U. Buccal Bone Deficiency in Fresh Extraction Sockets: A Prospective Single Cohort Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttarello GM, L.G. Case Report: Implant Placement and Immediate Loading with Simultaneous Bone Regeneration Following Jaw Odontogenic Cyst Enucleation. Dentistry 2015, 5, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmair, T.; Fickl, S.; Schneider, D.; Hinze, M.; Wachtel, H. Dimensional Alterations of Extraction Sites after Different Alveolar Ridge Preservation Techniques—A Volumetric Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Quaranta, A.; Alfonsi, F.; Cucchi, A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Negri, B.; di Felice, R.; Covani, U. Volumetric Analysis of Remodelling Pattern after Ridge Preservation Comparing Use of Two Types of Xenografts. A Multicentre Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, e105–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Zucchelli, G.; Cannizzaro, G.; Barausse, C.; Diazzi, M.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Esposito, M. Immediate, Immediate-Delayed (6 Weeks) and Delayed (4 Months) Post-Extractive Single Implants: 4-Month Post-Loading Data from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 9, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Marconcini, S.; Derchi, G.; Saverio, M.; Covani, U. Esthetic Outcome of Implants Placed in Fresh Extraction Sockets by Clinicians with or without Experience: A Medium-Term Retrospective Evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2016, 31, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Quaranta, A.; Alfonsi, F.; Cucchi, A.; Negri, B.; di Felice, R.; Marchionni, S.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Covani, U.; et al. Clinical and Histological Changes after Ridge Preservation with Two Xenografts: Preliminary Results from a Multicentre Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonsi, F.; Borgia, V.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; Covani, U.; Tonelli, P.; Barone, A. Molecular, Cellular and Pharmaceutical Aspects of Filling Biomaterials during the Management of Extraction Sockets. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Zucchelli, G.; Cannizzaro, G.; Checchi, L.; Barausse, C.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Felice, P. Immediate, Immediate-Delayed (6 Weeks) and Delayed (4 Months) Post-Extractive Single Implants: 1-Year Post-Loading Data from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A. Traditional Postextractive Implant Site Preparation Compared with Pre-Extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation in the Mandibular Molar Region, Using an Ultrasonic Device: A Randomized Pilot Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Derchi, G.; Marconcini, S.; Covani, U. Extra Oral Digital Scanning and Imaging Superimposition for Volume Analysis of Bone Remodeling after Tooth Extraction with and without 2 Types of Particulate Porcine Mineral Insertion: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, R.; Capparè, P.; Gherlone, E. Comparison of Magnesium-Enriched Hydroxyapatite and Porcine Bone in Human Extraction Socket Healing: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Corbella, S.; Taschieri, S.; Francetti, L.; Weinstein, R.; del Fabbro, M. Histomorphometric Results after Postextraction Socket Healing with Different Biomaterials: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, A.; Ataol, M. How Effective Is Collagen Resorbable Membrane Placement after Partially Impacted Mandibular Third Molar Surgery on Postoperative Morbidity? A Prospective Randomized Comparative Study. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, G.; Zhurakivska, K.; lo Muzio, L.; Laino, L.; Cicciù, M.; lo Russo, L. Combination of Bone Graft and Resorbable Membrane for Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. J. Periodontol. 2017, 89, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.; Longo, E.; Mijiritsky, E. A New Interpretation of Guided Implant Surgery to Achieve an Optimal Result in the Esthetic Zones. Med. Res. Arch. 2017, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Lorusso, F.; Santos De Oliveira, P.; Murmura, G.; Carinci, F. Dental Implants Displaced into the Mandibular Corpus: Clinical Note. J. Dent. Oral Care 2018, 89, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G.; Mesa, N.F.; Ferri, M.; Botticelli, D. Influence of the Presence of Alveolar Mucosa at Implants: A Histological Study in Humans. Implant Dent. 2018, 27, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Suresh, N.; Muthusamy, S. Platelet-Rich Fibrin with Bone Grafts for Regeneration of Bony Defect Following Extraction of Supernumerary Teeth: A Case Report. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 20, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G.; Derchi, G.; Covani, U. Extraction Socket Healing in Humans after Ridge Preservation Techniques: Comparison Between Flapless and Flapped Procedures in a Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivovics, M.; Szabó, B.T.; Németh, O.; Tari, N.; Dőri, F.; Nagy, P.; Dobó-Nagy, C.; Szabó, G. Microarchitectural Study of the Augmented Bone Following Ridge Preservation with a Porcine Xenograft and a Collagen Membrane: Preliminary Report of a Prospective Clinical, Histological, and Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, S.; Giammarinaro, E.; Derchi, G.; Alfonsi, F.; Covani, U.; Barone, A. Clinical Outcomes of Implants Placed in Ridge-Preserved versus Nonpreserved Sites: A 4-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Borges, T.; Almeida, B.L.; Correia, A. Dental Implant Outcomes in Grafted Sockets: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2019, 10, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria-Almeida, R.; Astramskaite-Januseviciene, I.; Puisys, A.; Correia, F. Extraction Socket Preservation with or without Membranes, Soft Tissue Influence on Post Extraction Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2019, 10, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Buti, J.; Gessaroli, M.; Esposito, M. Immediate, Early (6 Weeks) and Delayed (4 Months) Single Post- Extractive Implants: 3-Year Post-Loading Data from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Buti, J.; Pistilli, R.; Esposito, M. Posterior Jaw Rehabilitation Using Partial Prostheses Supported by Implants 4.0 × 4.0 mm or Longer: Three-Year Post- Loading Results of a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 1, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Barausse, C.; Bonifazi, L.; Piattelli, M.; Pistilli, R.; Ferri, A.; Felice, P. Wide-Diameter Immediate Postextraction Implants Versus Socket Preservation and Delayed Placement of Normal-Diameter Implants in the Molar Region: 5-year postloading Outcome of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2021, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Th Elaskary, A.; Gaweesh, Y.; el Tantawi, M.; Maebed, M. Vestibular Socket Therapy: A Novel Approach for Implant Placement in Defective Fresh Extraction Sockets with or without Active Socket Infection (One-Arm Cohort Study). Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2021, 36, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarico, M.; Xhanari, E.; Pisano, M.; de Riu, G.; Tullio, A.; Meloni, S.M. Single Post-Extractive Ultra-Wide 7 Mm-Diameter Implants versus Implants Placed in Molar Healed Sites after Socket Preservation for Molar Replacement: 6-Month Post-Loading Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 9, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Tallarico, M.; Xhanari, E.; Pisano, M.; Gatti, F.; Meloni, S.M. Molar Replacement with 7 Mm-Wide Diameter Implants: To Place the Implant Immediately or to Wait 4 Months after Socket Preservation? 1 Year after Loading Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Ameri, S.; Covani, U. Immediate Postextraction Implants: Treatment of Residual Peri-Implant Defects. A Retrospective Analysis. Eur. J. Implant Prosthodont. 2006, 2, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Covani, U.; Barone, A.; Cornelini, R.; Crespi, R. Clinical Outcome of Implants Placed Immediately after Implant Removal. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covani, U.; Cornelini, R.; Barone, A. Buccal Bone Augmentation around Immediate Implants with and without Flap Elevation: A Modified Approach. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2008, 23, 841–846. [Google Scholar]
- Covani, U.; Marconcini, S.; Crespi, R.; Barone, A. Immediate Implant Placement after Removal of a Failed Implant: A Clinical and Histological Case Report. J. Oral Implantol. 2009, 35, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotte, C.; Lindfors, N.; Nannmark, U. Surgical Reconstruction of Peri-Implant Bone Defects with Prehydrated and Collagenated Porcine Bone and Collagen Barriers: Case Presentations. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassetta, M.; Ricci, L.; Iezzi, G.; Dell’Aquila, D.; Piattelli, A.; Perrotti, V. Resonance Frequency Analysis of Implants Inserted with a Simultaneous Grafting Procedure: A 5-Year Follow-up Study in Man. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent 2012, 32, 581–589. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Quaranta, A.; Derchi, G.; Covani, U. The Clinical Outcomes of Immediate Versus Delayed Restoration Procedures on Immediate Implants: A Comparative Cohort Study for Single-Tooth Replacement. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Marconcini, S.; Giammarinaro, E.; Mijiritsky, E.; Gelpi, F.; Covani, U. Clinical Outcomes of Implants Placed in Extraction Sockets and Immediately Restored: A 7-Year Single-Cohort Prospective Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstein, J.; Tandelich, M.; Nart, J.; Calvo Guirado, J.L.; Shapira, L. Marginal Bone Level around Conical Connection Tapered Implants with Platform Switching: A Multicenter Retrospective Study at 14 Months Follow-Up. J. Osseointegration 2016, 8, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Covani, U.; Canullo, L.; Toti, P.; Alfonsi, F.; Barone, A. Tissue Stability of Implants Placed in Fresh Extraction Sockets: A 5-Year Prospective Single-Cohort Study. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, e323–e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliuzzi Michele, M. Postextractive Implants in Aesthetic Areas: Evaluation of Perimplant Bone Remodeling over Time. Ann. Di Stomatol. 2015, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zita Gomes, R.; de Vasconcelos, M.R.; Lopes Guerra, I.M.; de Almeida, R.A.B.; de Campos Felino, A.C. Implant Stability in the Posterior Maxilla: A Controlled Clinical Trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6825213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Cornelini, R.; Ciaglia, R.; Covani, U. Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sockets and Simultaneous Osteotome Sinus Floor Elevation: A Case Series. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2008, 28, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Santagata, M.; Guariniello, L.; Rauso, R.; Tartaro, G. Immediate Loading of Dental Implant after Sinus Floor Elevation with Osteotome Technique: A Clinical Report and Preliminary Radiographic Results. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 36, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.A.; Lico, S.; Casale, M.; Ormanier, Z.; Carinci, F. The Use of Various Biomaterials in Computer-Guided Crestal Sinus Lift Procedures. A Report on Two Case Studies with Volume Comparison. ORAL Implantol. 2016, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Crespi, R.; Aldini, N.N.; Fini, M.; Giardino, R.; Covani, U. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Histologic and Histomorphometric Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2005, 20, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Santini, S.; Sbordone, L.; Crespi, R.; Covani, U. A Clinical Study of the Outcomes and Complications Associated with Maxillary Sinus Augmentation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2006, 21, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orsini, G.; Scarano, A.; Piattelli, M.; Piccirilli, M.; Caputi, S.; Piattelli, A. Histologic and Ultrastructural Analysis of Regenerated Bone in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using a Porcine Bone–Derived Biomaterial. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Santini, S.; Marconcini, S.; Giacomelli, L.; Gherlone, E.; Covani, U. Osteotomy and Membrane Elevation during the Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Procedure: A Comparative Study: Piezoelectric Device vs. Conventional Rotative Instruments. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Piattelli, M.; Carinci, F.; Perrotti, V. Removal, after 7 Years, of an Implant Displaced into the Maxillary Sinus. A Clinical and Histologic Case Report. J. Osseointegration 2009, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Piattelli, A.; Assenza, B.; Quaranta, A.; Perrotti, V.; Piattelli, M.; Iezzi, G. Porcine Bone Used in Sinus Augmentation Procedures: A 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Evaluation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Piattelli, A.; Perrotti, V.; Manzon, L.; Iezzi, G. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation in Humans Using Cortical Porcine Bone: A Histological and Histomorphometrical Evaluation After 4 and 6 Months. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2011, 13, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, M.; Vrielinck, L.; Thalmair, T.; Wachtel, H.; Bolz, W. Zygomatic Implant Placement in Conjunction with Sinus Bone Grafting: The “Extended Sinus Elevation Technique.” a Case-Cohort Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2013, 28, e376–e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iezzi, G.; Degidi, M.; Piattelli, A.; Mangano, C.; Scarano, A.; Shibli, J.A.; Perrotti, V. Comparative Histological Results of Different Biomaterials Used in Sinus Augmentation Procedures: A Human Study at 6 Months. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Ricci, M.; Grassi, R.F.; Nannmark, U.; Quaranta, A.; Covani, U. A 6-Month Histological Analysis on Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with and without Use of Collagen Membranes over the Osteotomy Window: Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Fernández, M.P.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Maté-Sánchez del Val, J.E.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Negri, B.; Barona-Dorado, C. Ultrastructural Study by Backscattered Electron Imaging and Elemental Microanalysis of Bone-to-Biomaterial Interface and Mineral Degradation of Porcine Xenografts Used in Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassetta, M.; Ricci, L.; Iezzi, G.; Calasso, S.; Piattelli, A.; Perrotti, V. Use of Piezosurgery during Maxillary Sinus Elevation: Clinical Results of 40 Consecutive Cases. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2012, 32, e182–e188. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, M.; Martegani, P.; D’Avenia, F.; Farneti, M.; Capri, D.; Paolantoni, G.; Landi, L. Simultaneous Sinus Augmentation with Implant Placement: Histomorphometric Comparison of Two Different Grafting Materials. A Multicenter Double-Blind Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2013, 28, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traini, T.; Piattelli, A.; Caputi, S.; Degidi, M.; Mangano, C.; Scarano, A.; Perrotti, V.; Iezzi, G. Regeneration of Human Bone Using Different Bone Substitute Biomaterials. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, M.; Perrotti, V.; Calasso, S.; Piattelli, A.; Sinjari, B.; Iezzi, G. Bone Formation in Sinus Augmentation Procedures Using Autologous Bone, Porcine Bone, and a 50:50 Mixture: A Human Clinical and Histological Evaluation at 2 Months. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falisi, G.; Galli, M.; Vittorini-Velasquez, P.; Gallegos-Rivera, J.C.; Minasi, R.; de Biase, A.; di Paolo, C. Use of 3D Cartilage Scaffolds for the Stabilization of Implants and Bone Regeneration with the Fit-Lock Technique. Acta Odontológica Lat. AOL 2013, 26, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G.; Varvara, G. Spontaneous Bone Formation on the Maxillary Sinus Floor in Association with Surgery to Remove a Migrated Dental Implant: A Case Report. Minerva Stomatol. 2014, 63, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Corbella, S.; Taschieri, S.; Weinstein, R.; del Fabbro, M. Histomorphometric Outcomes after Lateral Sinus Floor Elevation Procedure: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.A.; Manzulli, N.; Casale, M.; Ormianer, Z.; Carinci, F. The Use of Resorbable Heterologous Cortical Lamina as a New Sinus Lift Floor: A Technical Note. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; Giuliani, A.; Mangano, C.; Barone, A.; Manzon, L.; Degidi, M.; Scarano, A.; Filippone, A.; Perrotti, V. Molecular, Cellular and Pharmaceutical Aspects of Bone Grafting Materials and Membranes during Maxillary Sinus-Lift Procedures. Part 2: Detailed Characteristics of the Materials. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Davó, R.; Marti-Pages, C.; Ferrer-Fuertes, A.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Ippolito, D.R.; Felice, P. Immediately Loaded Zygomatic Implants vs Conventional Dental Implants in Augmented Atrophic Maxillae: 4 Months Post-Loading Results from a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Forabosco, A.; Gheno, E.; Spinato, S.; Garuti, G.; Forabosco, E.; Consolo, U. Concentrated Growth Factors in Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: A Preliminary Clinical Comparative Evaluation. Int. J. Growth Factors Stem Cells Dent. 2018, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Davó, R.; Felice, P.; Pistilli, R.; Barausse, C.; Marti-Pages, C.; Ferrer-Fuertes, A.; Ippolito, D.R.; Esposito, M. Immediately Loaded Zygomatic Implants vs Conventional Dental Implants in Augmented Atrophic Maxillae: 1-Year Post-Loading Results from a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Bechara, S.; Kubilius, R.; Veronesi, G.; Pires, J.T.; Shibli, J.A.; Mangano, F.G. Short (6-Mm) Dental Implants versus Sinus Floor Elevation and Placement of Longer (≥10-Mm) Dental Implants: A Randomized Controlled Trial with a 3-Year Follow-Up. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirilă, L.; Rotaru, C.; Filipov, I.; Săndulescu, M. Management of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis after Sinus Bone Grafting Procedures with Simultaneous Dental Implants Placement—A Retrospective Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noami, S.; Elmosy, K.; Askar, N. Evaluation of Pre-Hydrated Collagenated Cortico- Cancellous Granules (Mp3®) in Augmentation of the Maxillary Sinus (Preliminary Study). J. Dent. Oral Disord. Ther. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, C.; Bösch, T. Implantology and Prothodontics at Crossroads-Classic vs. Modern Treatment Concepts. Mod. Treat. Concepts. JSM Dent. Surg. 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, S.; Lang, N.P.; Iida, T.; Ferri, M.; Apaza Alccayhuaman, K.A.; Botticelli, D. Influence of the Position of the Antrostomy in Sinus Floor Elevation Assessed with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, e12362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; de Oliveira, P.S.; Traini, T.; Lorusso, F. Sinus Membrane Elevation with Heterologous Cortical Lamina: A Randomized Study of a New Surgical Technique for Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation without Bone Graft. Materials 2018, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Murmura, G.; Mastrangelo, F.; Lorusso, F.; Greco Lucchina, A.; Carinci, F. A Novel Technique to Prevent Sinus Membrane Collapse during Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation without Bone Graft: Technical Note. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, S.; Lang, N.; Ferri, M.; Alccayhuaman, K.; Botticelli, D. Influence of the Height of the Antrostomy in Sinus Floor Elevation Assessed by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, A.; Lang, N.P.; Ferri, M.; Fortich Mesa, N.; Apaza Alccayhuaman, K.A.; Botticelli, D. Tomographic Evaluation of the Influence of the Placement of a Collagen Membrane Subjacent to the Sinus Mucosa during Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; Ferri, M.; Mesa, N.F.; Apaza Alccayhuaman, K.A.; Botticelli, D. Sinus Floor Elevation and Antrostomy Healing: A Histomorphometric Clinical Study in Humans. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiloglu, S.; Giray, C.B.; Kulac, I.; Usubutun, A.; Aktas, A. Clinical and Histopathological Comparative Study of Two Equine-Derived Bone Graft: A Human Study. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, R.; Sgaramella, N.; Traini, T.; Bugea, C. Graftless Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation with Simultaneous Porcine Bone Layer Insertion: A 1- to 5-Year Follow-up Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2020, 35, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Davó, R.; Pistilli, R.; Marti-Pages, C.; Ferrer-Fuertes, A.; Ferri, A.; Esposito, M. Immediately loaded zygomatic implants versus conventional dental implants in augmented atrophic maxillae: Three-year post-loading results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 2, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliani, L.; Andersson, P.; Lanza, M.; Nappo, A.; Verrocchi, D.; Volpe, S.; Sennerby, L. A Collagenated Porcine Bone Substitute for Augmentation at Neoss Implant Sites: A Prospective 1-Year Multicenter Case Series Study with Histology. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, M.; Calasso, S.; Vozza, I.; Dell’Aquila, D. Rehabilitation of Atrophic Alveolar Crests with Cylindrical Sandblasted and Acid Etched Implants: A Pilot Study. Eur. J. Implant Prosthodont. 2005, 3, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Covani, U. Maxillary Alveolar Ridge Reconstruction with Nonvascularized Autogenous Block Bone: Clinical Results. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, M.; Guariniello, L.; Tartaro, G. A Modified Edentulous Ridge Expansion Technique for Immediate Placement of Implants: A Case Report. J. Oral Implantol. 2011, 37, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachtel, H.; Fickl, S.; Hinze, M.; Bolz, W.; Thalmair, T. The Bone Lamina Technique: A Novel Approach for Lateral Ridge Augmentation—A Case Series. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodriguez, J.G.; Eldibany, R.M. Vertical Splitting of the Mandibular Body as an Alternative to Inferior Alveolar Nerve Lateralization. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Murmura, G.; Sinjiari, B.; Assenza, B.; Sollazzo, V.; Spinelli, G.; Carinci, F. Expansion of the Alveolar Bone Crest with Ultrasonic Surgery Device: Clinical Study in Mandible. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Piattelli, A.; Murmura, G.; Iezzi, G.; Assenza, B.; Mancino, C. Delayed Expansion of the Atrophic Mandible by Ultrasonic Surgery: A Clinical and Histologic Case Series. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.; Andreasi Bassi, M.; Confalone, L.; Carinci, F. Regeneration of Atrophic Crestal Ridges with Resorbable Lamina: Technical Note. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, M.A.; Bassi, M.A.; Confalone, L.; Carinci, F.; Ormianer, Z.; Lauritano, D. The Use of Resorbable Cortical Lamina and Micronized Collagenated Bone in the Regeneration of Atrophic Crestal Ridges: A Surgical Technique. Case Series. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Amr, A.; Abdel, G.K.; Abuel-Ela, H.; Abd Elhamid, E. Xenogenic Flexible Bone Lamina Graft: A Successful Alternative to the Autogenous Onlay Bone Block Graft in Alveolar Ridge Augmentation: A Clinical, Radiographic and Histological Evaluation. J. Dent. Treat. Oral Care 2017, 1, 104. [Google Scholar]
- del Corso, M.; Ehrenfest, D.M.D. Immediate Implantation and Peri-Implant Natural Bone Regeneration (NBR) in the Severely Resorbed Posterior Mandible Using Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF): A 4-Year Follow-Up. Poseido J. 2013, 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Checchi, V.; Gasparro, R.; Pistilli, R.; Canullo, L.; Felice, P. Clinical Classification of Bone Augmentation Procedure Failures in the Atrophic Anterior Maxillae: Esthetic Consequences and Treatment Options. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4386709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Conti, A.; Bertazzo, D.; Pilloni, A. Horizontal Ridge Augmentation with the Cortical Lamina Technique: A Case Report. Mod. Res. Dent. 2019, 4, 000591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Ciccarese, S.; Amuso, D.; Mortellaro, C.; Lorusso, F. Cortical Bone Lamina Approach for Mandibular Large Cystic Defect: A Case Report. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Bellini, P.; Buti, J.; Felice, P. Immediate loading of 3 mm-diameter implants as an alternative to horizontal bone augmentation for placing 4 mm-diameter implants: One-year post-loading results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 2, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, G.; Perrotti, V.; Piattelli, A.; D’arcangelo, C.; Altieri, F.; Cassetta, M. Split Crest Technique for Implant Treatment of Agenesis of the Upper Lateral Incisors: Results of a Randomized Pilot Histological and Clinical Study at 24-Month Follow-Up. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, P.; Piana, L.; Checchi, L.; Pistilli, R.; Pellegrino, G. Vertical Ridge Augmentation of the Atrophic Posterior Mandible with a 2-Stage Inlay Technique: A Case Report. Implant Dent. 2012, 21, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Felice, P.; Marchionni, S.; Covani, U. Early Volumetric Changes after Vertical Augmentation of the Atrophic Posterior Mandible with Interpositional Block Graft versus Onlay Bone Graft: A Retrospective Radiological Study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Barone, A.; Zucchelli, G.; Piattelli, M.; Pistilli, R.; Ippolito, D.; Simion, M. Interpositional Augmentation Technique in the Treatment of Posterior Mandibular Atrophies: A Retrospective Study Comparing 129 Autogenous and Heterologous Bone Blocks with 2 to 7 Years Follow-Up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, S.; Covani, U.; Giammarinaro, E.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; de Santis, D.; Alfonsi, F.; Barone, A. Clinical Success of Dental Implants Placed in Posterior Mandible Augmented with Interpositional Block Graft: 3-Year Results from a Prospective Cohort Clinical Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Gatto, R.; Severino, M.; Botticelli, G.; Caruso, S.; Rastelli, C.; Lupi, E.; Quiroz Roias, A.; Iacomino, E.; Falisi, G. Short versus Longer Implants in Mandibular Alveolar Ridge Augmented Using Osteogenic Distraction: One-Year Follow-up of a Randomized Split-Mouth Trial. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 44, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheno, E.; Palermo, A.; Rodella, L.F.; Buffoli, B. The Effectiveness of the Use of Xenogeneic Bone Blocks Mixed with Autologous Concentrated Growth Factors (CGF) in Bone Regeneration Techniques: A Case Series. J. Osseointegration 2014, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, R.; Rancitelli, D.; Poli, P.P.; Rasia Dal Polo, M.; Nannmark, U.; Maiorana, C. The Use of a Collagenated Porcine Cortical Lamina in the Reconstruction of Alveolar Ridge Defects. A Clinical and Histological Study. Minerva Stomatol. 2016, 65, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.; Foce, E.; Scolavino, S. The Cortical Lamina Technique: A New Option for Alveolare Ridge Augmentation. Procedure, Protocol and Case Report. J. Leban. Dent. Assoc. 2017, 52, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Polis-Yanes, C.; Cadenas-Sebastián, C.; Gual-Vaqués, P.; Ayuso-Montero, R.; Marí-Roig, A.; López-López, J. Guided Bone Regeneration of an Atrophic Maxilla Using Heterologous Cortical Lamina. Case Rep. Dent. 2019, 2019, 481827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.; Foce, E. Reconstruction of a Horizontal and Vertical Bone Defect Using The Cortical Lamina Technique. Med. Res. Arch. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, R.; Ghezzi, C.; Tomecek, M. Cortical Lamina: A New Device for the Treatment of Moderate and Severe Tridimensional Bone and Soft Tissue Defects. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2020, 15, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Cannizzaro, G.; Soardi, E.; Pistilli, R.; Piattelli, M.; Corvino, V.; Felice, P. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 6 Mm-Long, 4 Mm-Wide Implants or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. Preliminary Results from a Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felice, P.; Pistilli, R.; Piattelli, M.; Soardi, E.; Corvino, V.; Esposito, M. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 5 × 5 Mm Implants with a Novel Nanostructured Calcium-Incorporated Titanium Surface or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. Preliminary Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Pistilli, R.; Felice, P.; Piattelli, M.; Gessaroli, M.; Soardi, E.; Barausse, C.; Buti, J.; Corvino, V.; Esposito, M. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 5 × 5 Mm Implants with a Novel Nanostructured Calcium-Incorporated Titanium Surface or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. One-Year Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 6, 343–357. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Zucchelli, G.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Felice, P. Four Mm-Long versus Longer Implants in Augmented Bone in Atrophic Posterior Jaws: 4-Month Post-Loading Results from a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 9, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolle, C.; Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Esposito, M. Four Mm Long vs Longer Implants in Augmented Bone in Posterior Atrophic Jaws: 1-Year Post-Loading Results from a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial-PubMed. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gastaldi, G.; Felice, P.; Pistilli, V.; Barausse, C.; Ippolito, D.; Esposito, M. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 5 × 5 Mm Implants with a Nanostructured Calcium-Incorporated Titanium Surface or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. 3-Year Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Orlal Implantol. 2018, 11, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pistilli, R.; Felice, P.; Cannizzaro, G.; Piattelli, M.; Corvino, V.; Barausse, C.; Buti, J.; Soardi, E.; Esposito, M. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 6 Mm Long 4 Mm Wide Implants or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. One-Year Post-Loading Results from a Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 6, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, V.; Piattelli, M.; Ippolito, D.; Esposito, M. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 6 Mm Long × 4 Mm Wide Implants or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. 3-Year Post-Loading Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Piattelli, M.; di Simone, S.; Ippolito, D.R.; Felice, P. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 5 × 5 Mm Implants with a Nanostructured Calcium-Incorporated Titanium Surface or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. Five-Year Results from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 12, 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Felice, P.; Pistilli, R.; Barausse, C.; Piattelli, M.; Buti, J.; Esposito, M. Posterior Atrophic Jaws Rehabilitated with Prostheses Supported by 6-Mm-Long 4-Mm-Wide Implants or by Longer Implants in Augmented Bone. Five-Year Post-Loading Results from a within-Person Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 12, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Kalemaj, Z. Four-mm-Long Versus Longer Implants in Augmented Bone in Atrophic Posterior Jaws: Three-Year Post-Loading Results from a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 2, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinna, C.; Ungari, C.; Saltarel, A.; Cassoni, A.; Reale, G. Orbital Floor Restoration. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2005, 16, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenga, P.L.; Reale, G.; Cofone, C.; Meduri, A.; Ceruti, P.; Grenga, R. Hess Area Ratio and Diplopia: Evaluation of 30 Patients Undergoing Surgical Repair for Orbital Blow-out Fracture. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 25, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinna, C.; Reale, G.; Foresta, E.; Mustazza, M.C. Medial Orbital Wall Reconstruction with Swine Bone Cortex. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2009, 20, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, B.; Findikcioglu, K.; Sezgin, B.; Guney, K.; Barut, I.; Ozmen, S. A New Option for the Reconstruction of Orbital Floor Defects with Heterologous Cortical Bone. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, P.; Vellone, V.; Ramieri, V.; Basile, E.; Tarsitano, A.; Marchetti, C. Reconstruction of the Adult Hemifacial Microsomia Patient with Temporomandibular Joint Total Joint Prosthesis and Orthognathic Surgery. Case Rep. Surg. 2018, 2018, 2968983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senese, O.; Boutremans, E.; Gossiaux, C.; Loeb, I.; Dequanter, D. Retrospective Analysis of 79 Patients with Orbital Floor Fracture: Outcomes and Patient-Reported Satisfaction. Arch. Craniofacial Surg. 2018, 19, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Corso, M. Soft Tissue Response to Platelet Rich Fibrin: Clinical Evidences. Cosmet. Dent. 2008, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cardaropoli, D.; Cardaropoli, G. Healing of Gingival Recessions Using a Collagen Membrane with a Hemineralized Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2009, 29, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Fickl, S.; Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Lincke, T.; Bechtold, M.; Fischer, K.R.; Schlagenhauf, U. Porcine Dermal Matrix for Covering of Recession Type Defects: A Case Series. Quintessence Int. 2013, 44, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Lambert, F.; Matos, S.; Pietruska, M.; Rossi, R.; Salhi, L.; Buti, J. The Effectiveness of a Resorbable Bone Substitute with a Resorbable Membrane in the Treatment of Periodontal Infrabony Defect—A Multicenter Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Attia, A.M. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of cortico-cancellous bone mix xenograft (osteobiol gen-os®) in the treatment of human periodontal intrabony defects. Egypt. Dent. J. 2017, 63, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aslan, S.; Buduneli, N.; Cortellini, P. Entire Papilla Preservation Technique in the Regenerative Treatment of Deep Intrabony Defects: 1-Year Results. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, S.; Buduneli, N.; Cortellini, P. Entire Papilla Preservation Technique: A Novel Surgical Approach for Regenerative Treatment of Deep and Wide Intrabony Defects. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Fickl, S.; Mardas, N.; Bozec, L.; Donos, N. Stage-Two Surgery Using Collagen Soft Tissue Grafts: Clinical Cases and Ultrastructural Analysis. Quintessence Int. 2014, 45, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoh, U.; Petelin, M.; Gašperšič, R. Split-Mouth Comparison of Coronally Advanced Flap with Connective Tissue Graft or Collagen Matrix for Treatment of Isolated Gingival Recessions. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2019, 39, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Testori, T.; Wachtel, H.; Mühlemann, S.; Happe, A.; del Fabbro, M. Soft Tissue Augmentation Applying a Collagenated Porcine Dermal Matrix during Second Stage Surgery: A Prospective Multicenter Case Series. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verardi, S.; Orsini, M.; Lombardi, T.; Ausenda, F.; Testori, T.; Pulici, A.; Oreglia, F.; Valente, N.A.; Stacchi, C. Comparison between Two Different Techniques for Peri-Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: Porcine Dermal Matrix Graft versus Tenting Screw. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, N.; Buti, J.; Mensi, M.; Alfonsi, F.; Cinquini, C.; Tonelli, P.; Barone, A. Xenogeneic dermal matrix versus autologous connective tissue graft versus no graft at abutment connection for improving aesthetics: 6 month outcomes of a randomised controlled trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubiani, O.; Scarano, A.; Orsini, G.; di Iorio, D.; D’Arcangelo, C.; Piccirilli, M.; Sigismondo, M.; Caputi, S. The Performance of Human Periodontal Ligament Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Xenogenic Biomaterials. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2007, 20, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmas, J.; Szwaja, M.; Kolodziejski, W. Solid-State NMR and IR Characterization of Commercial Xenogeneic Biomaterials Used as Bone Substitutes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 61, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manescu, A.; Giuliani, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Tromba, G.; Mazzoni, S.; Diomede, F.; Zini, N.; Piattelli, A.; Trubiani, O. Osteogenic Potential of Dualblocks Cultured with Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells: In Vitro and Synchrotron Microtomography Study. J. Periodontal. Res. 2016, 51, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Funel, N.; Campani, D.; Covani, U. Expression of SP7, RUNX1, DLX5, and CTNNB1 in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cultured on Xenogeneic Bone Substitute as Compared with Machined Titanium. Implant Dent. 2014, 23, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marco, P.; Zara, S.; de Colli, M.; Radunovic, M.; Lazović, V.; Ettorre, V.; di Crescenzo, A.; Piattelli, A.; Cataldi, A.; Fontana, A. Graphene Oxide Improves the Biocompatibility of Collagen Membranes in an in Vitro Model of Human Primary Gingival Fibroblasts. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radunovic, M.; de Colli, M.; de Marco, P.; di Nisio, C.; Fontana, A.; Piattelli, A.; Cataldi, A.; Zara, S. Graphene Oxide Enrichment of Collagen Membranes Improves DPSCs Differentiation and Controls Inflammation Occurrence. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2017, 105, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Naenni, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Masuda, K.; Mussano, F. Plasma of Argon Enhances the Adhesion of Murine Osteoblasts on Different Graft Materials. Ann. Anat. 2018, 218, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, G.; Carinci, F.; Girardi, A.; Palmieri, A.; Caccianiga, G.; Sollazzo, V. OsteoBiol® Effect on Dental Pulp Derived Stem Cells. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2012, 10, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Tromba, G.; Diomede, F.; Piattelli, A.; Trubiani, O.; Giuliani, A. Role of Cortico-Cancellous Heterologous Bone in Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Xeno-Free Culture Studied by Synchrotron Radiation Phase-Contrast Microtomography. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, D.; Carinci, F.; Zollino, I.; Hassanipour, A.; Saggese, V.; Palmieri, A.; Girardi, A.; Cura, F.; Piras, A.; Zamboni, P.; et al. OsteoBiol® Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation in Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cells. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2012, 10, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Maté Sánchez de Val, J.; Mazón, P.; Piattelli, A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.; Mareque Bueno, J.; Granero Marín, J.; de Aza, P. Comparison among the Physical Properties of Calcium Phosphate-Based Bone Substitutes of Natural or Synthetic Origin. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2018, 15, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genova, T.; Pesce, P.; Mussano, F.; Tanaka, K.; Canullo, L. The Influence of Bone-Graft Bio-Functionalization with Plasma of Argon on Bacterial Contamination. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2019, 107, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Carlo, R.; Zara, S.; Ventrella, A.; Siani, G.; da Ros, T.; Iezzi, G.; Cataldi, A.; Fontana, A. Covalent Decoration of Cortical Membranes with Graphene Oxide as a Substrate for Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballé-Serrano, J.; Munar-Frau, A.; Delgado, L.; Pérez, R.; Hernández-Alfaro, F. Physicochemical Characterization of Barrier Membranes for Bone Regeneration. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 97, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrożewicz, E.; Muszyńska, M.; Tokajuk, G.; Grynkiewicz, G.; Žarković, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Beneficial Effects of Vitamins K and D3 on Redox Balance of Human Osteoblasts Cultured with Hydroxyapatite-Based Biomaterials. Cells 2019, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Rakic, M.; Sculean, A.; Miron, R.; Muzzi, M.; Carossa, S.; Mussano, F. Effects of Argon Plasma Treatment on the Osteoconductivity of Bone Grafting Materials. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2611–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, M.; Asady, S.; Toledano-Osorio, M.; García-Godoy, F.; Serrera-Figallo, M.A.; Benítez-García, J.A.; Osorio, R. Differential Biodegradation Kinetics of Collagen Membranes for Bone Regeneration. Polymers 2020, 12, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettorre, V.; de Marco, P.; Zara, S.; Perrotti, V.; Scarano, A.; di Crescenzo, A.; Petrini, M.; Hadad, C.; Bosco, D.; Zavan, B.; et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Characterization of Graphene Oxide Coated Porcine Bone Granules. Carbon 2016, 103, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijiritsky, E.; Ferroni, L.; Gardin, C.; Bressan, E.; Zanette, G.; Piattelli, A.; Zavan, B. Porcine Bone Scaffolds Adsorb Growth Factors Secreted by MSCs and Improve Bone Tissue Repair. Materials 2017, 10, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, F.; D’Aurora, M.; Gugliandolo, A.; Merciaro, I.; Orsini, T.; Gatta, V.; Piattelli, A.; Trubiani, O.; Mazzon, E. Biofunctionalized Scaffold in Bone Tissue Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, F.; Zini, N.; Gatta, V.; Fulle, S.; Merciaro, I.; D’Aurora, M.; la Rovere, R.M.L.; Traini, T.; Pizzicannella, J.; Ballerini, P.; et al. Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Cultured onto Cortico-Cancellous Scaffold Drive Bone Regenerative Process. Eur. Cells Mater. 2016, 32, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diomede, F.; D’Aurora, M.; Gugliandolo, A.; Merciaro, I.; Ettorre, V.; Bramanti, A.; Piattelli, A.; Gatta, V.; Mazzon, E.; Fontana, A.; et al. A Novel Role in Skeletal Segment Regeneration of Extracellular Vesicles Released from Periodontal-Ligament Stem Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Jeanneau, C.; Giraud, T.; Richard, G.; About, I. Complement Activation Links Inflammation to Dental Tissue Regeneration. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 4185–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.P.R.; Mazón, P.; Gehrke, S.A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; de Aza, P.N. Comparison of Two Xenograft Materials Used in Sinus Lift Procedures: Material Characterization and in Vivo Behavior. Materials 2017, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.P.R.; Gehrke, S.A.; Martinez, C.P.A.; Guirado, J.L.C.; de Aza, P.N. SEM-EDX Study of the Degradation Process of Two Xenograft Materials Used in Sinus Lift Procedures. Materials 2017, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannmark, U.; Azarmehr, I. Short Communication: Collagenated Cortico-Cancellous Porcine Bone Grafts. A Study in Rabbit Maxillary Defects. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2010, 12, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.; Coimbra, P.; Cabrita, A.; Guerra, F.; Figueiredo, M. Comparison of a Xenogeneic and an Alloplastic Material Used in Dental Implants in Terms of Physico-Chemical Characteristics and in Vivo Inflammatory Response. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3506–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickl, S.; Nannmark, U.; Schlagenhauf, U.; Hürzeler, M.B.; Kebschull, M. Porcine Dermal Matrix in the Treatment of Dehiscence-Type Defects—An Experimental Split-Mouth Animal Trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Stavropoulos, A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Schneider, D.; Fickl, S. Influence of Local Administration of Pamidronate on Extraction Socket Healing—A Histomorphometric Proof-of-Principle Pre-Clinical in Vivo Evaluation. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, M.; Karaca, I.R.; Firat, A.; Kaymaz, F.; Bozkaya, S. Experimental Evaluation of the Effects of Ankaferd Blood Stopper and Collagenated Heterologous Bone Graft on Bone Healing in Sinus Floor Augmentation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, e63–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Lorusso, F.; Ravera, L.; Mortellaro, C.; Piattelli, A. Bone Regeneration in Iliac Crestal Defects: An Experimental Study on Sheep. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4086870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Crincoli, V.; di Benedetto, A.; Cozzolino, V.; Lorusso, F.; Podaliri Vulpiani, M.; Grano, M.; Kalemaj, Z.; Mori, G.; Grassi, F.R. Bone Regeneration Induced by Bone Porcine Block with Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in a Minipig Model of Mandibular “Critical Size” Defect. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9082869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Carneiro Martins Neto, E.; Botticelli, D.; Apaza Alccayhuaman, K.A.; Lang, N.P.; Xavier, S.P. Influence of a Collagen Membrane Positioned Subjacent the Sinus Mucosa Following the Elevation of the Maxillary Sinus. A Histomorphometric Study in Rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, Y.; Ricardo Silva, E.; Botticelli, D.; Apaza Alccayhuaman, K.A.; Lang, N.P.; Xavier, S.P. Reposition of the Bone Plate over the Antrostomy in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Histomorphometric Study in Rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Develioğlu, H.; Özcan, G.; Gültekin, S.E.; Sengüven, B.; Yildirim, A. The Short-Term Effects of Various Xenografts on Bone Healing in Rats Cranial Defects. Biomed. Res. 2018, 29, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemtoi, A.; Danila, V.; Dragan, E.; Pasca, S.; Nemtoi, A.; Constantin, M.; Sava, A.; Haba, D. The Effects of Insulin and Strontium Ranelate on Guided Bone Regeneration in Diabetic Rats. Rev. De Chim. 2017, 68, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Silva, E.R.; Lang, N.P.; Apaza Alccayhuaman, K.A.; Botticelli, D.; Xavier, S.P. Histological and Micro-Computed Tomography Evaluations of Newly Formed Bone after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using a Xenograft with Similar Density and Mineral Content of Bone: An Experimental Study in Rabbits. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2018, 4, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diker, N.; Sarican, H.; Cumbul, A.; Kilic, E. Effects of Systemic Erythropoietin Treatment and Heterogeneous Xenograft in Combination on Bone Regeneration of a Critical-Size Defect in an Experimental Model. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilaslan, S.; Karabuda, Z.C.; Olgac, V. The Effect of Concentrated Growth Factor on Calvarial Bone in Diabetic Healing. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 31, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favero, G.; Viña-Almunia, J.; Carda, C.; Martín de Llano, J.J.; García-Mira, B.; Soto-Peñaloza, D.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Botticelli, D. Influence of the Use of Autogenous Bone Particles to Close the Access Window after Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: An Experimental Study in Rabbits. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Sena, G.; Tromba, G.; Mazzon, E.; Fontana, A.; Diomede, F.; Piattelli, A.; Trubiani, O. Could the Enrichment of a Biomaterial with Conditioned Medium or Extracellular Vesicles Modify Bone-Remodeling Kinetics during a Defect Healing? Evaluations on Rat Calvaria with Synchrotron-Based Microtomography. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.R.; Götz, W.; Kauffmann, F.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Friedmann, A. Ridge Preservation of Compromised Extraction Sockets Applying a Soft Cortical Membrane: A Canine Proof-of-Principle Evaluation. Ann. Anat. 2020, 231, 151524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragoneses, J.; Suárez, A.; Rodríguez, C.; Aragoneses, J.M. Clinical and Histological Differences between Guided Tissue Regeneration with Acellular Dermal Matrix of Porcine Origin and Autologous Connective Tissue: An Animal Study. Materials 2021, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumedei, M.; Piattelli, A.; Degidi, M.; Mangano, C.; Iezzi, G. A Narrative Review of the Histological and Histomorphometrical Evaluation of the Peri-Implant Bone in Loaded and Unloaded Dental Implants. A 30-Year Experience (1988–2018). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, R.; Jones, E.; McGonagle, D.; Giannoudis, P.V. Bone Regeneration: Current Concepts and Future Directions. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumbras, A.; Krukis, M.M.; Januzis, G.; Juodzbalys, G. Regenerative Bone Potential after Sinus Floor Elevation Using Various Bone Graft Materials: A Systematic Review. Quintessence Int. 2019, 50, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Degidi, M.; Iezzi, G.; Pecora, G.; Piattelli, M.; Orsini, G.; Caputi, S.; Perrotti, V.; Mangano, C.; Piattelli, A. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Different Biomaterials: A Comparative Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in Man. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmagnola, D.; Adriaens, P.; Berglundh, T. Healing of Human Extraction Sockets Filled with Bio-Oss®. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simion, M.; Dahlin, C.; Trisi, P.; Piattelli, A. Qualitative and Quantitative Comparative Study on Different Filling Materials Used in Bone Tissue Regeneration: A Controlled Clinical Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1994, 14, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolpak, H.A.; Gönen, Z.B.; Özdamar, S.; Alkan, A.; Kütük, N. Vertical Ridge Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Procedure and Dental Pulp Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Simultaneous Dental Implant Placement: A Histologic Study in a Sheep Model. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).