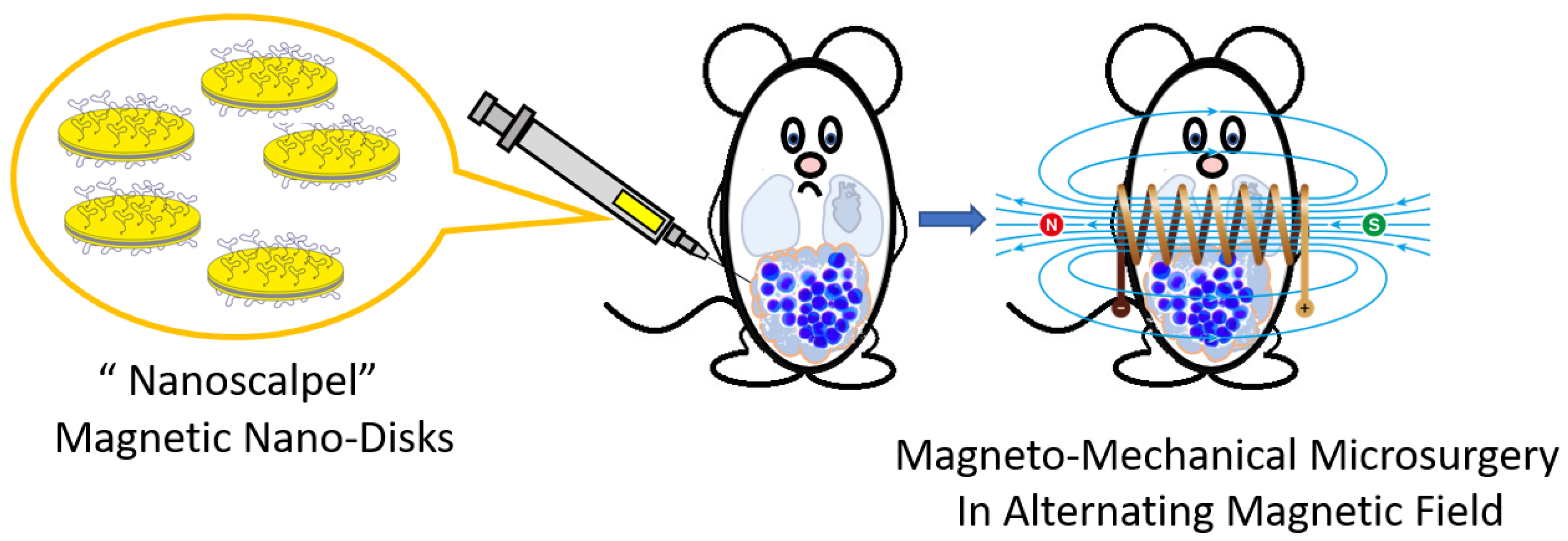
Magnetic Nanoscalpel for the Effective Treatment of Ascites Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
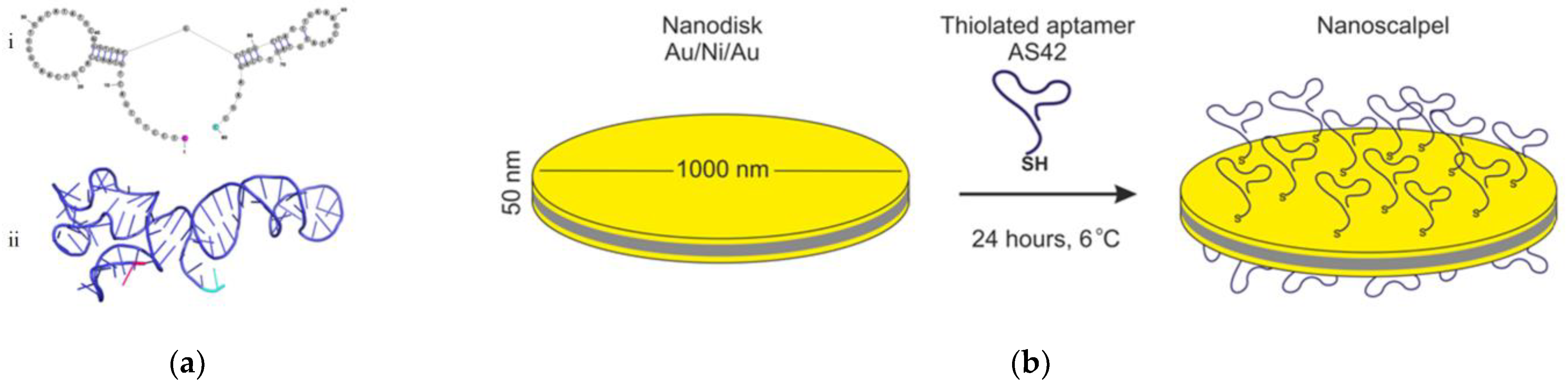
2.2. MNDs and Their Functionalization with the Aptamers
2.3. Determining MNDs Concentration
2.4. Magnetic Coil
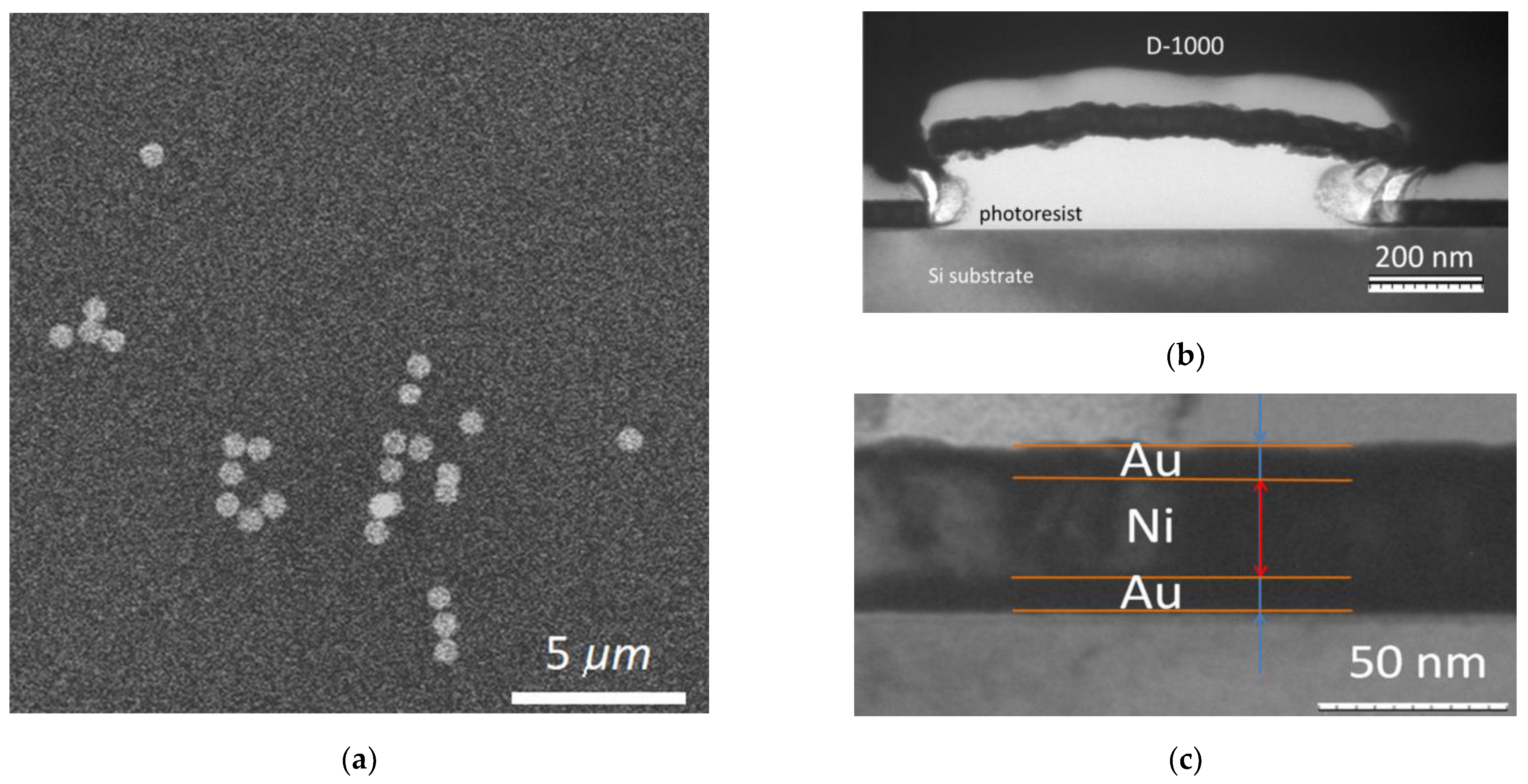
2.5. Morphological and Magnetic Characterization of MNDs
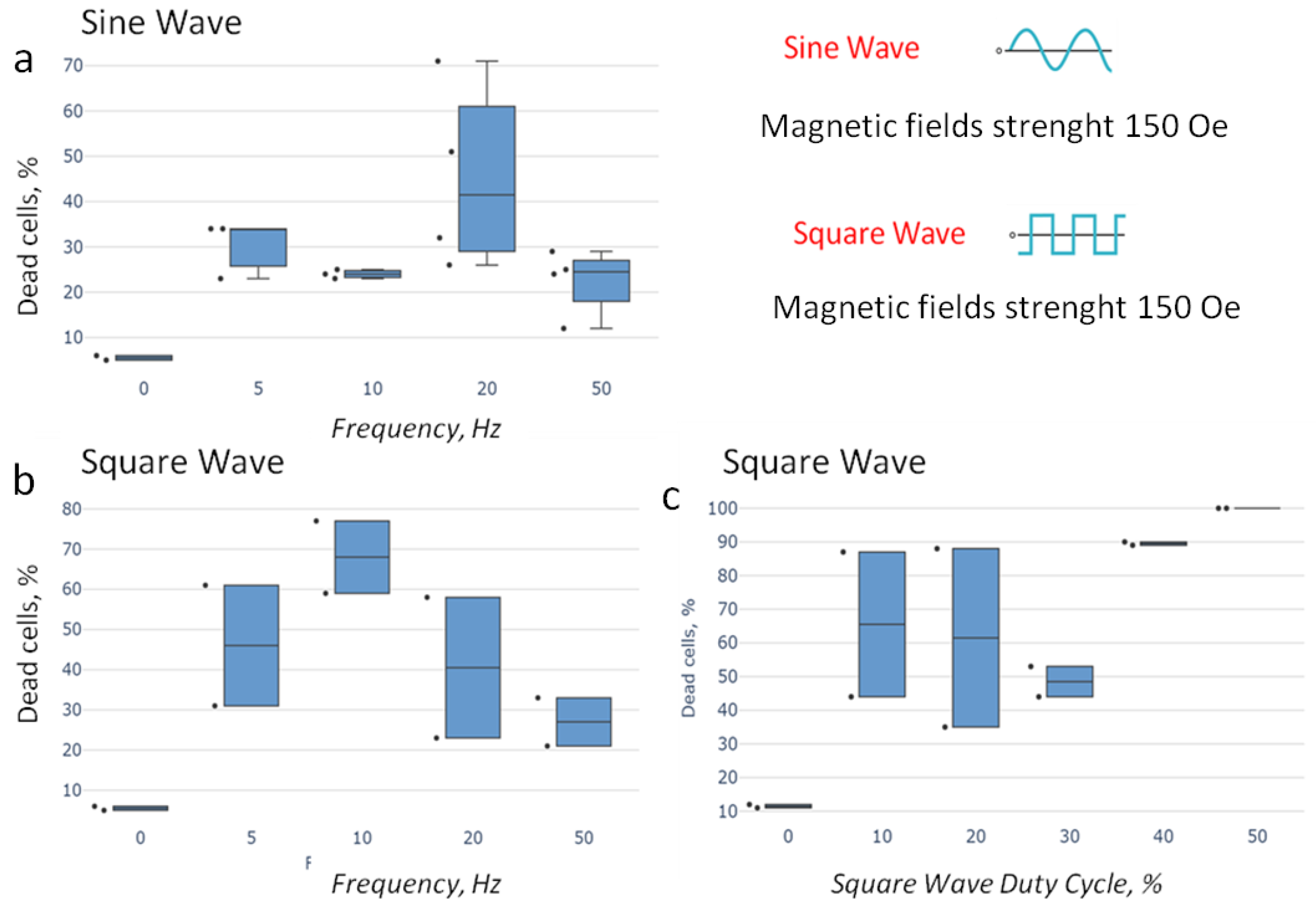
2.6. Searching for the Optimal Parameters of the AMF Destructing Tumor Cells with AS42–MNDs
- (1)
- 5, 10, 20, and 50 Hz of a sine-shaped AMF (strength 150 Oe);
- (2)
- 5, 10, 20, and 50 Hz frequencies of a rectangular-shaped AMF (strength 150 Oe) and a duty cycle of 0.5;
- (3)
- A duty cycle of 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 at a frequency of 10 Hz of a rectangular-shaped AMF (strength 150 Oe).
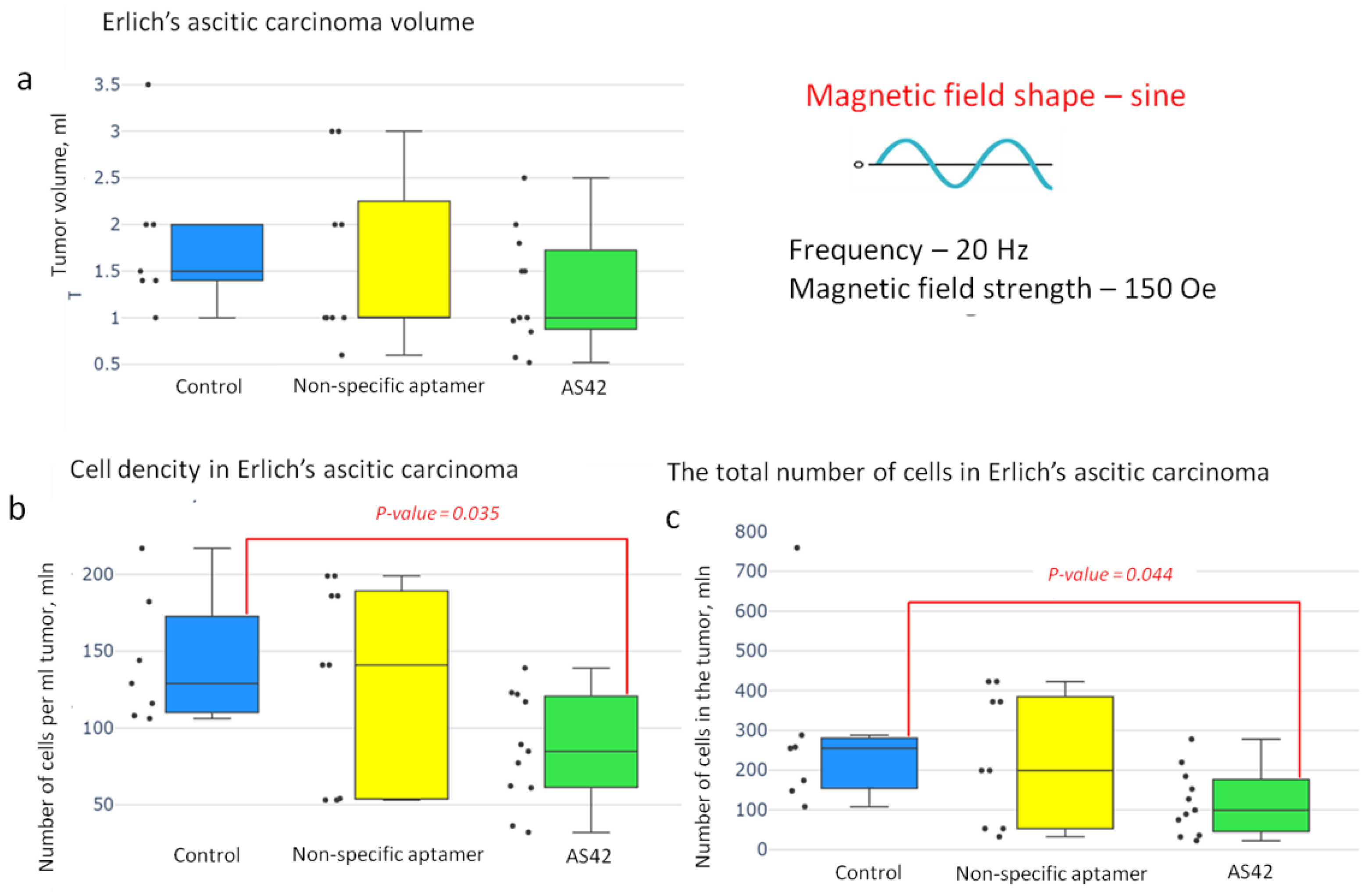
2.7. MMM In Vivo
- The control group without treatment (injected intraperitoneally with 200 µL of phosphate buffer);
- MMM with NO-MNDs injected intraperitoneally with (69 million MNDs modified with nonspecific aptamers in 200 µL of phosphate buffer per mouse);
- MMM with AS42–MNDs (69 million MNDs modified with AS42 in 200 µL of phosphate buffer per mouse).
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nanodiscs
3.1.1. Structural Characterization of Nanodiscs
3.1.2. Magnetic Characteristics of MNDs
3.2. In Vitro Effect of MMM with AS42–MNDs on Ascites Cells
3.3. Optimization of Parameters for AS42–MND-Based MMM In Vitro
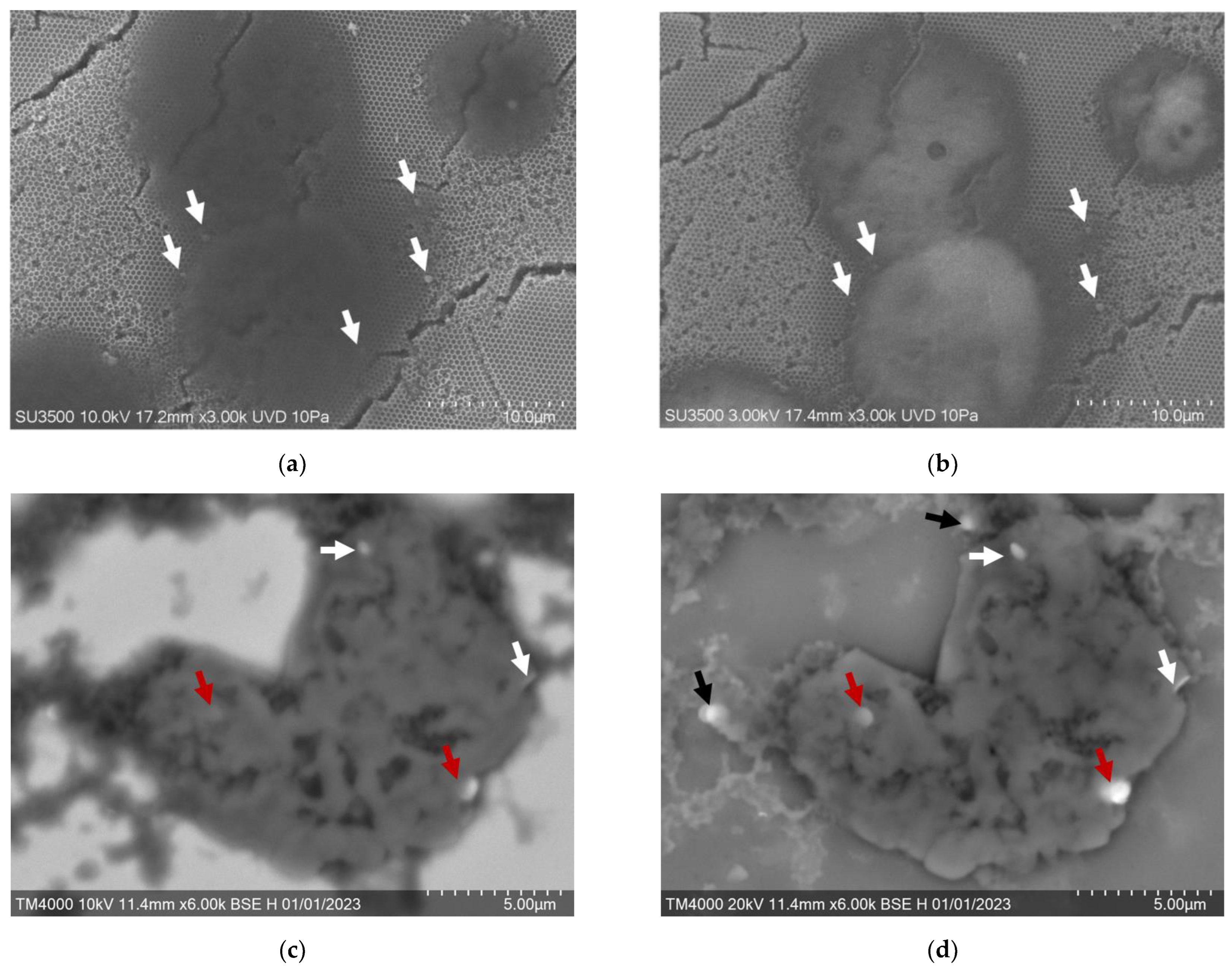
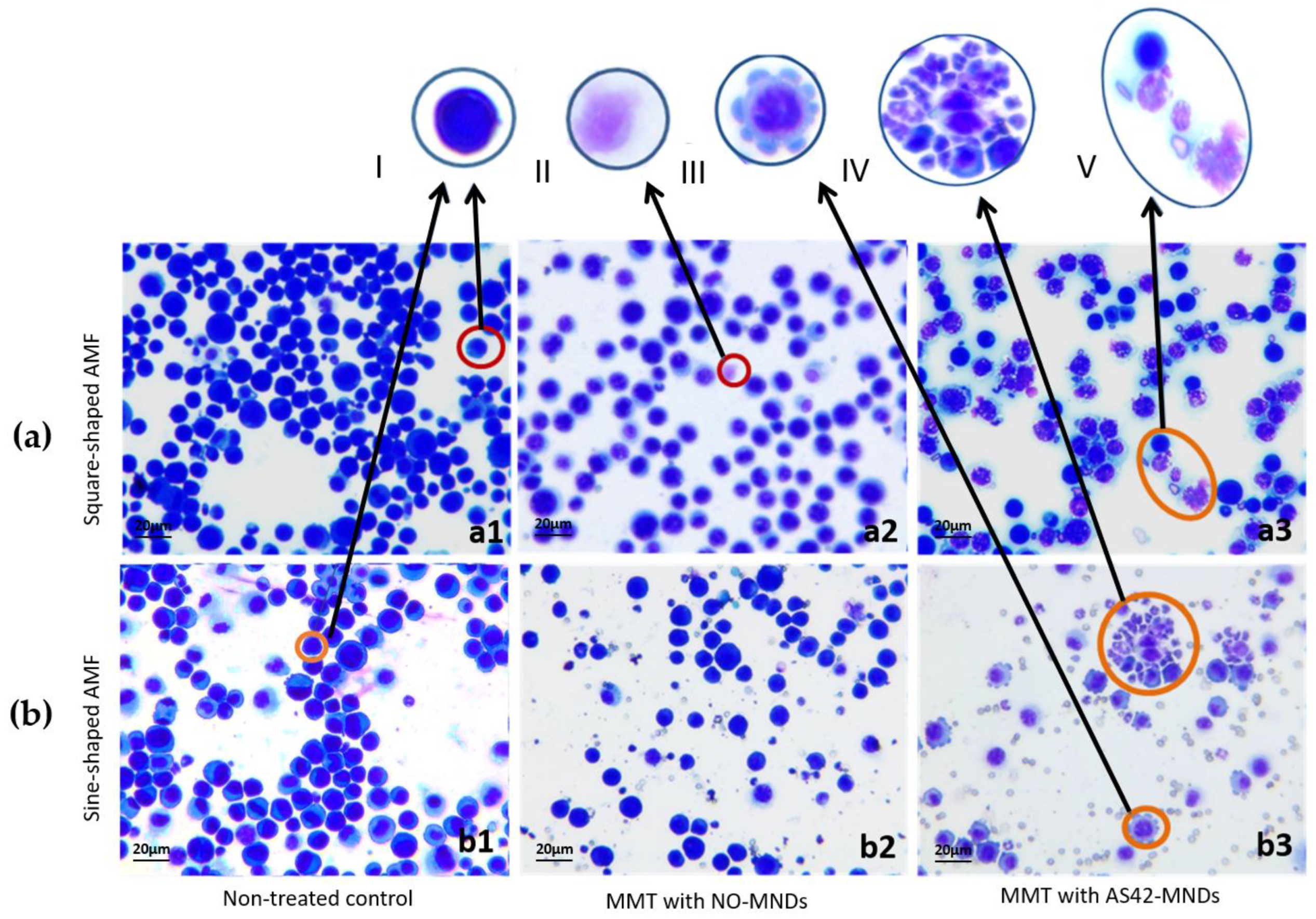
3.4. Destruction of EAC by MNDs in an AMF In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bettio, M.; Gavin, A.; Visser, O.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 103, 356–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisio, M.A.; Fu, L.; Goyeneche, A.; Gao, Z.H.; Telleria, C. High-grade serous ovarian cancer: Basic sciences, clinical and therapeutic standpoints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szender, J.B.; Emmons, T.; Belliotti, S.; Dickson, D.; Khan, A.; Morrell, K.; Khan, A.N.M.N.; Singel, K.L.; Mayor, P.C.; Moysich, K.B.; et al. Impact of ascites volume on clinical outcomes in ovarian cancer: A cohort study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 146, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Nunes, D.L.; Mendes-Frias, A.; Silvestre, R.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.; Ricardo, S. Immune Tumor Microenvironment in Ovarian Cancer Ascites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangisetty, S.l.; Miner, T.J. Malignant ascites: A review of prognostic factors, pathophysiology, and therapeutic measures. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2012, 4, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naud, C.; Thebault, C.; Carriere, M.; Hou, Y.; Morel, R.; Berger, F.; Dienya, B.; Joisten, H. Cancer treatment by magneto-mechanical effect of particles, a review. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 26, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichot, S.L.; Bentouati, S.; Ahmad, S.S.; Sotiropoulos, M.; Jena, R.; Cowburn, R. Versatile magnetic microdiscs for the radio enhancement and mechanical disruption of glioblastoma cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8161–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Rojas, G.G.; López-Saucedo, F.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Mendizabal, E.; Bucio, E. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Medical Applications: Updated Review. Macromolecules 2022, 2, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, R.; Vemulkar, T.; Petit, D.C.M.C.; Cheng, Y.; Murphy, J.; Lesniak, M.S.; Cowburn, R.P. Magnetic particles with perpendicular anisotropy for mechanical cancer cell destruction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, D.W.; Gan, W.L.; Liu, N.; Lew, W.S. Magneto-actuated cell apoptosis by biaxial pulsed magnetic field. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrés, V.M.; Costo, R.; Roca, A.G.; Marco, J.P.; Goya, G.F.; Serna, C.J.; Morales, M.P. Uniform and water stable magnetite nanoparticles with diameters around the monodomain–multidomain limit. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 134003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.M.; Zheng, W.T.; Jiang, Q. Saturation Magnetization of Ferromagnetic and Ferromagnetic Nanocrystals at Room Temperature. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials. Addison-Wesley Pub. Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1972; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugazagoitia, J.; Guedes, C.; Ponce, S.; Ferrer, I.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Paz-Ares, L. Current challenges in cancer treatment. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Ulasov, I.; Bader, S.D.; Rajh, T.; Lesniak, M.S.; Novosad, V. Biofunctionalized magnetic-vortex microdiscs for targeted cancer-cell destruction. Nature Mater. 2010, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wilson, G.; Hebbard, L.; Duan, W.; Liddle, C.; George, J.; Qiao, L. Aptamers: A promising chemical antibody for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13446–13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.; Xiang, J. Aptamers, the Nucleic Acid Antibodies, in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.R.; Jimenez, R.M.; Chaput, J.C. Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.; Szostak, J. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljohani, M.M.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Chinnappan, R.; Al-Kattan, K.; Zourob, M. Aptamers: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents for Blood Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Pal, R.; Sharma, T.K.; Sarkar, S. Identification and Engineering of Aptamers for Theranostic Application in Human Health and Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Belyanina, I.V.; Zamay, S.S.; Denisenko, V.V.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Ivanchenko, T.I.; Grigorieva, V.L.; Garanzha, I.V.; Veprintsev, D.V.; et al. Noninvasive Microsurgery Using Aptamer-Functionalized Magnetic Microdiscs for Tumor Cell Eradication. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, A.S.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Spivak, E.A.; Zubkova, O.A.; Kadkina, A.V.; Erkaev, E.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Savitskaya, A.G.; et al. DNA-aptamer/protein interaction as a cause of apoptosis and arrest of proliferation in Ehrlich ascites adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 2014, 8, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Babkin, V.A.; Medvedeva, E.N.; Neverova, N.A.; Kirichenko, A.K.; Zamay, S.S.; Lapin, I.N.; Morozov, E.V.; et al. Aptamer-Conjugated Superparamagnetic Ferroarabinogalactan Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetodinamic Therapy of Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamay, T.N.; Starkov, A.K.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zamay, G.S.; Veprintsev, D.V.; Luzan, N.; Nikolaeva, E.D.; Lukyanenko, K.A.; Artyushenko, P.V.; Shchugoreva, I.A.; et al. Nucleic Acid Aptamers Increase the Anticancer Efficiency and Reduce the Toxicity of Cisplatin-Arabinogalactan Conjugates in Vivo. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2022, 32, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhizhchenko, A.; Kuchmizhak, A.; Vitrik, O.; Kulchin, Y.; Juodkazis, S. On-demand concentration of an analyte on laser-printed polytetrafluoroethylene. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21414–21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanova, O.V.; Nemtsev, I.V.; Shabanov, A.V. Development of SEM method for analysis of organ-containing objects using inverse opals. Sib. Aerosp. J. 2020, 21, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metlov, K.L. Equilibrium large vortex state in ferromagnetic disks. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 113, 223905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuzzi, P.; Godin, B.; Tanaka, T.; Lee, S.Y.; Chiappini, C.; Liu, X.; Ferrari, M. Size and shape effects in the biodistribution of intravascularly injected particles. J. Control. Release 2010, 141, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goiriena-Goikoetxea, M.; Muñoz, D.; Orue, I.; Fernández-Gubieda, M.L.; Bokor, J.; Muela, A.; García-Arribas, A. Disk-shaped magnetic particles for cancer therapy. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamay, T.; Zamay, S.; Luzan, N.; Fedotovskaya, V.; Masyugin, A.; Zelenov, F.; Koshmanova, A.; Nikolaeva, E.; Kirichenko, D.; Veprintsev, D.; et al. Magnetic Nanoscalpel for the Effective Treatment of Ascites Tumors. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040179
Zamay T, Zamay S, Luzan N, Fedotovskaya V, Masyugin A, Zelenov F, Koshmanova A, Nikolaeva E, Kirichenko D, Veprintsev D, et al. Magnetic Nanoscalpel for the Effective Treatment of Ascites Tumors. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(4):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040179
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamay, Tatiana, Sergey Zamay, Natalia Luzan, Victoriya Fedotovskaya, Albert Masyugin, Fyodor Zelenov, Anastasia Koshmanova, Elena Nikolaeva, Daria Kirichenko, Dmitry Veprintsev, and et al. 2023. "Magnetic Nanoscalpel for the Effective Treatment of Ascites Tumors" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 4: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040179
APA StyleZamay, T., Zamay, S., Luzan, N., Fedotovskaya, V., Masyugin, A., Zelenov, F., Koshmanova, A., Nikolaeva, E., Kirichenko, D., Veprintsev, D., Kolovskaya, O., Shchugoreva, I., Zamay, G., Lapin, I., Lukyanenko, A., Borus, A., Sukhachev, A., Volochaev, M., Lukyanenko, K., ... Kichkailo, A. (2023). Magnetic Nanoscalpel for the Effective Treatment of Ascites Tumors. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(4), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040179








