Inhalable Microparticles Embedding Biocompatible Magnetic Iron-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FeCaP NPs Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Analysis of FeCaP NPs Biocompatibility with Human Alveolar Lung Cells
2.2.1. Semi-Quantitative Evaluation of Internalization of FeCaP NPs
2.2.2. Cell Metabolism/Viability Assay
2.2.3. Lactase Dehydrogenase Assay (LDH); Reduced Cell Membrane Integrity and Necrotic Cell Death
2.2.4. Determination of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.2.5. Measurement of Interleukin 8 (IL-8) Mediator Release
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.3. dp-FeCaPs Preparation
2.4. dp-FeCaPs Characterizations
2.5. Restoration of FeCaPs NPs from dpFeCaPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of FeCaP NPs
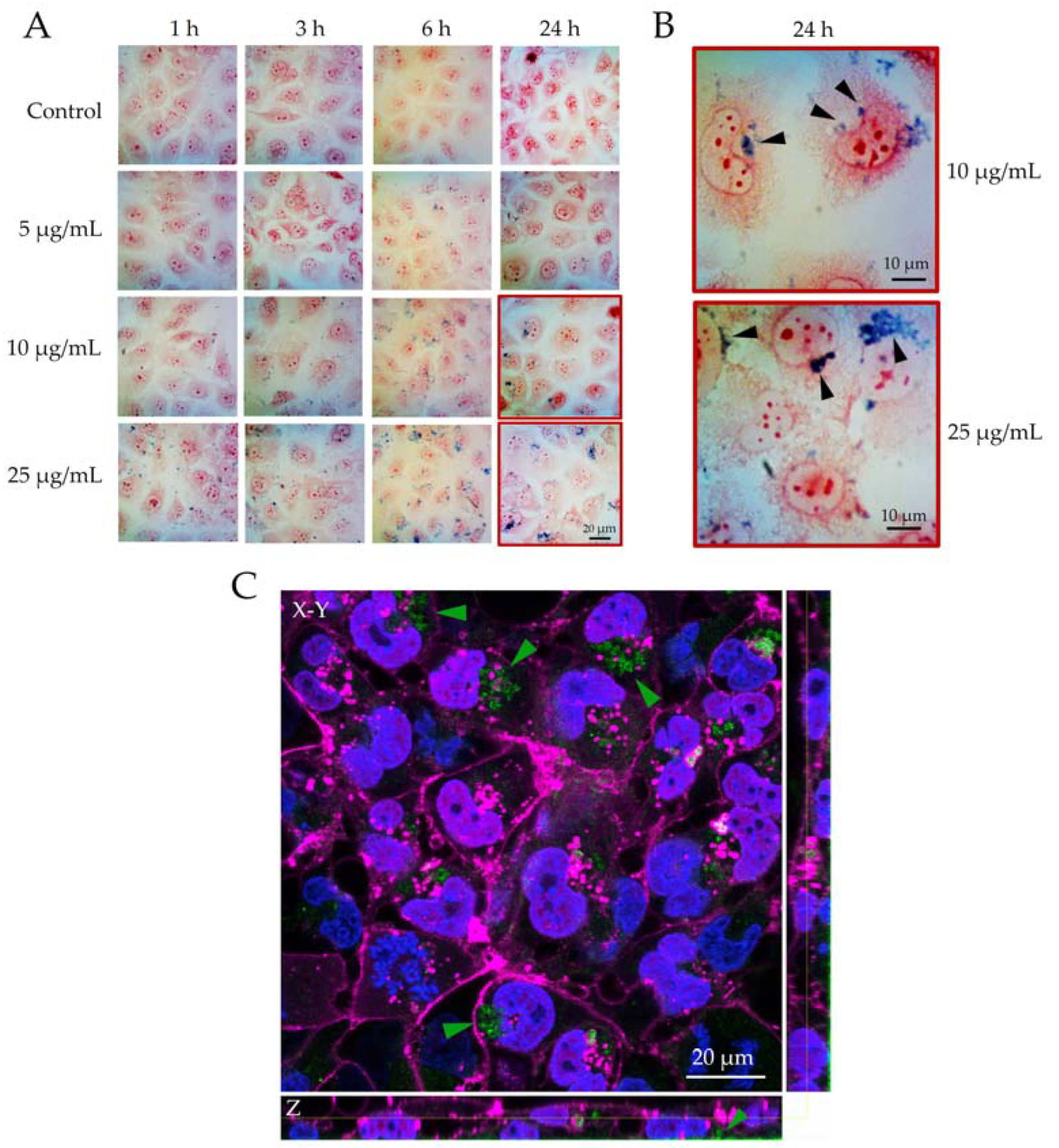
3.2. Biocompatibility of FeCaP NPs towards Lung Tissue Cells
3.3. Preparation and Characterizations of dp-FeCaPs
3.4. Release of FeCaP NPs by dp-FeCaPs Dissolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.; Chan, J.; Wang, A.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O. Nanoparticles in medicine: Therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarmi, S.; Roa, W.H.; Löbenberg, R. Targeted delivery of nanoparticles for the treatment of lung diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, E.; Jadhav, K.; Sirsath, N.; Dudhe, P.; Verma, R.K.; Chatterjee, A.; Naik, J. Nanotherapeutics for pulmonary drug delivery: An emerging approach to overcome respiratory diseases. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapis, N.; Bennett, D.; Jackson, B.; Weitz, D.A.; Edwards, D. Trojan particles: Large porous carriers of nanoparticles for drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12001–12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilcer, G.; Amighi, K. Formulation strategy and use of excipients in pulmonary drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 392, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, E.; Sonvico, F.; Bettini, R.; De Luca, C.; Dotti, A.; Catalucci, D.; Iafisco, M.; Degli Esposti, L.; Colombo, G.; Trevisi, G. Inhalable Microparticles Embedding Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles for Heart Targeting: The Formulation Experimental Design. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuberger, T.; Schöpf, B.; Hofmann, H.; Hofmann, M.; von Rechenberg, B. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Possibilities and limitations of a new drug delivery system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Celi, N.; Zhang, D.; Cai, J. Magnetic biohybrid microrobot multimers based on chlorella cells for enhanced targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6320–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.K.; Richey, J.; Strand, M.; Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Flask, C.A.; Labhasetwar, V. Magnetic nanoparticles with dual functional properties: Drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiano, A.; Wu, V.M.; Carella, F.; Lamura, G.; Canepa, F.; Tampieri, A.; Iafisco, M.; Uskoković, V. Magnetic calcium phosphates nanocomposites for the intracellular hyperthermia of cancers of bone and brain. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1267–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocke, N.A.; Meenach, S.A.; Arnold, S.M.; Mansour, H.M.; Hilt, J.Z. Formulation and characterization of inhalable magnetic nanocomposite microparticles (MnMs) for targeted pulmonary delivery via spray drying. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewes, F.; Ehrhardt, C.; Healy, A.M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs)-loaded Trojan microparticles for targeted aerosol delivery to the lung. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.N.; Stromberg, L.R.; Kunda, N.K.; Muttil, P. In vivo pulmonary delivery and magnetic-targeting of dry powder nano-in-microparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4741–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.S.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Domingues, R.M.; Costa, R.R.; Paz, E.; Rodríguez-Abreu, C.; Freitas, P.; Almeida, B.G.; Carvalho, M.A.; Gonçalves, C. Development of inhalable superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) in microparticulate system for antituberculosis drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Jenkins, G.J.; Asadi, R.; Doak, S.H. Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.-T.; Kim, D.-S.; Minai-Tehrani, A.; Hwang, S.-K.; Chang, S.-H.; Lee, E.-S.; Xu, C.-X.; Lim, H.T.; Kim, J.-E.; Yoon, B.-I. Inhaled fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles induced extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen of mice. J. Occup. Health 2009, 51, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalay, B.; Tátrai, E.; Nyírő, G.; Vezér, T.; Dura, G. Potential toxic effects of iron oxide nanoparticles in in vivo and in vitro experiments. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, F.; Mao, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhou, Q. Iron overload by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles is a high risk factor in cirrhosis by a systems toxicology assessment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampieri, A.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Sprio, S.; Landi, E.; Bertinetti, L.; Panseri, S.; Pepponi, G.; Goettlicher, J.; Bañobre-López, M.; et al. Intrinsic magnetism and hyperthermia in bioactive Fe-doped hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannotti, V.; Adamiano, A.; Ausanio, G.; Lanotte, L.; Aquilanti, G.; Coey, J.M.D.; Lantieri, M.; Spina, G.; Fittipaldi, M.; Margaris, G. Fe-doping-induced magnetism in nano-hydroxyapatites. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafisco, M.; Drouet, C.; Adamiano, A.; Pascaud, P.; Montesi, M.; Panseri, S.; Sarda, S.; Tampieri, A. Superparamagnetic iron-doped nanocrystalline apatite as a delivery system for doxorubicin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiano, A.; Iafisco, M.; Sandri, M.; Basini, M.; Arosio, P.; Canu, T.; Sitia, G.; Esposito, A.; Iannotti, V.; Ausanio, G. On the use of superparamagnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as an agent for magnetic and nuclear in vivo imaging. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Montesi, M.; Sandri, M.; Iafisco, M.; Adamiano, A.; Ghetti, M.; Cenacchi, G.; Tampieri, A. Magnetic labelling of mesenchymal stem cells with iron-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as tool for cell therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjoerup, J.; Hilberg, O.; Bendstrup, E. Inhaled mannitol in the treatment of non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in adults. Respirology 2012, 17, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.J.; Thorley, A.J.; Gorelik, J.; Seckl, M.J.; O’Hare, M.J.; Arcaro, A.; Korchev, Y.; Goldstraw, P.; Tetley, T.D. Immortalization of human alveolar epithelial cells to investigate nanoparticle uptake. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riss, T.; Moravec, R.; Niles, A.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.; Worzella, T.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. In Assay Guidance Manual; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company: Rockville, MD, USA; the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, A. Topas Academic V5. Coelho Softw. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.M.; Cameron, M.; Crowley, K.D. Structural variations in natural F, OH, and Cl apatites. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 870–876. [Google Scholar]
- Fronczek, F.R.; Kamel, H.N.; Slattery, M. Three polymorphs (α, β, and δ) of D-mannitol at 100 K. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2003, 59, o567–o570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley, A.J.; Ruenraroengsak, P.; Potter, T.E.; Tetley, T.D. Critical determinants of uptake and translocation of nanoparticles by the human pulmonary alveolar epithelium. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11778–11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruenraroengsak, P.; Chen, S.; Hu, S.; Melbourne, J.; Sweeney, S.; Thorley, A.J.; Skepper, J.N.; Shaffer, M.S.; Tetley, T.D.; Porter, A.E. Translocation of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes across human pulmonary alveolar epithelium: Dominant role of epithelial type 1 cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5070–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Liu, R.-B.; Meng, C.-G.; Yu, F.-Y.; Ji, S.-H.; Tan, Z.-C. Heat capacities and nonisothermal thermal decomposition reaction kinetics of D-mannitol. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehring, R. Pharmaceutical particle engineering via spray drying. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechanteur, A.; Evrard, B. Influence of composition and spray-drying process parameters on carrier-free DPI properties and behaviors in the lung: A review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, T.C.; Peters, J.I.; Williams III, R.O. Influence of particle size on regional lung deposition–what evidence is there? Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, T.M.; Rosati, J.A.; Schroeter, J.D.; Hickey, A.J.; Martonen, T.B. Fundamental effects of particle morphology on lung delivery: Predictions of Stokes’ law and the particular relevance to dry powder inhaler formulation and development. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisgaard, H.; O’Callaghan, C.; Smaldone, G.C. Drug Delivery to the Lung; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tomoda, K.; Ohkoshi, T.; Hirota, K.; Sonavane, G.S.; Nakajima, T.; Terada, H.; Komuro, M.; Kitazato, K.; Makino, K. Preparation and properties of inhalable nanocomposite particles for treatment of lung cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 71, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample | Nominal Mannitol Content (wt.%) | Water (wt.%) | Mannitol (wt.%) | Residual at 450 °C (FeCaP NPs) (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dp-FeCaP without mannitol | - | 8.7 ± 0.9 | - | 89.4 ± 9.0 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:0.2 | 16.7 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 21.7 ± 2.0 | 73.1 ± 7.0 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:4 | 80 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 81.2 ± 8.0 | 17.2 ± 2.0 |
| Sample | Dv10 (μm) | Dv50 (μm) | Dv90 (μm) | EF (%) | FPF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dp-FeCaP without mannitol | 1.20 ± 0.02 | 3.32 ± 0.01 | 7.22 ± 0.05 | 75.2 ± 0.3 | 34.5 ± 01 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:0.2 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 2.70 ± 0.01 | 6.91 ± 0.04 | 75.6 ± 0.2 | 44.6 ± 0.2 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:2 | 0.65 ± 0.01 | 2.27 ± 0.01 | 6.60 ± 0.05 | 75.4 ± 0.1 | 60.3 ± 0.1 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:4 | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 2.22 ± 0.02 | 5.68 ± 0.09 | 76.3 ± 0.1 | 65.7 ± 0.1 |
| Sample | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | PdI | ζ-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original FeCaP NPs | 179 ± 3 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | −21 ± 1 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:0.2 | 1105 ± 24 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | −22 ± 1 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:2 | 243 ± 4 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | −23 ± 1 |
| dp-FeCaP 1:4 | 212 ± 1 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | −31 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quarta, E.; Chiappi, M.; Adamiano, A.; Tampieri, A.; Wang, W.; Tetley, T.D.; Buttini, F.; Sonvico, F.; Catalucci, D.; Colombo, P.; et al. Inhalable Microparticles Embedding Biocompatible Magnetic Iron-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040189
Quarta E, Chiappi M, Adamiano A, Tampieri A, Wang W, Tetley TD, Buttini F, Sonvico F, Catalucci D, Colombo P, et al. Inhalable Microparticles Embedding Biocompatible Magnetic Iron-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(4):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040189
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuarta, Eride, Michele Chiappi, Alessio Adamiano, Anna Tampieri, Weijie Wang, Teresa D. Tetley, Francesca Buttini, Fabio Sonvico, Daniele Catalucci, Paolo Colombo, and et al. 2023. "Inhalable Microparticles Embedding Biocompatible Magnetic Iron-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 4: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040189
APA StyleQuarta, E., Chiappi, M., Adamiano, A., Tampieri, A., Wang, W., Tetley, T. D., Buttini, F., Sonvico, F., Catalucci, D., Colombo, P., Iafisco, M., & Degli Esposti, L. (2023). Inhalable Microparticles Embedding Biocompatible Magnetic Iron-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(4), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040189











