Antibacterial Surgical Sutures Developed Using Electrostatic Yarn Wrapping Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
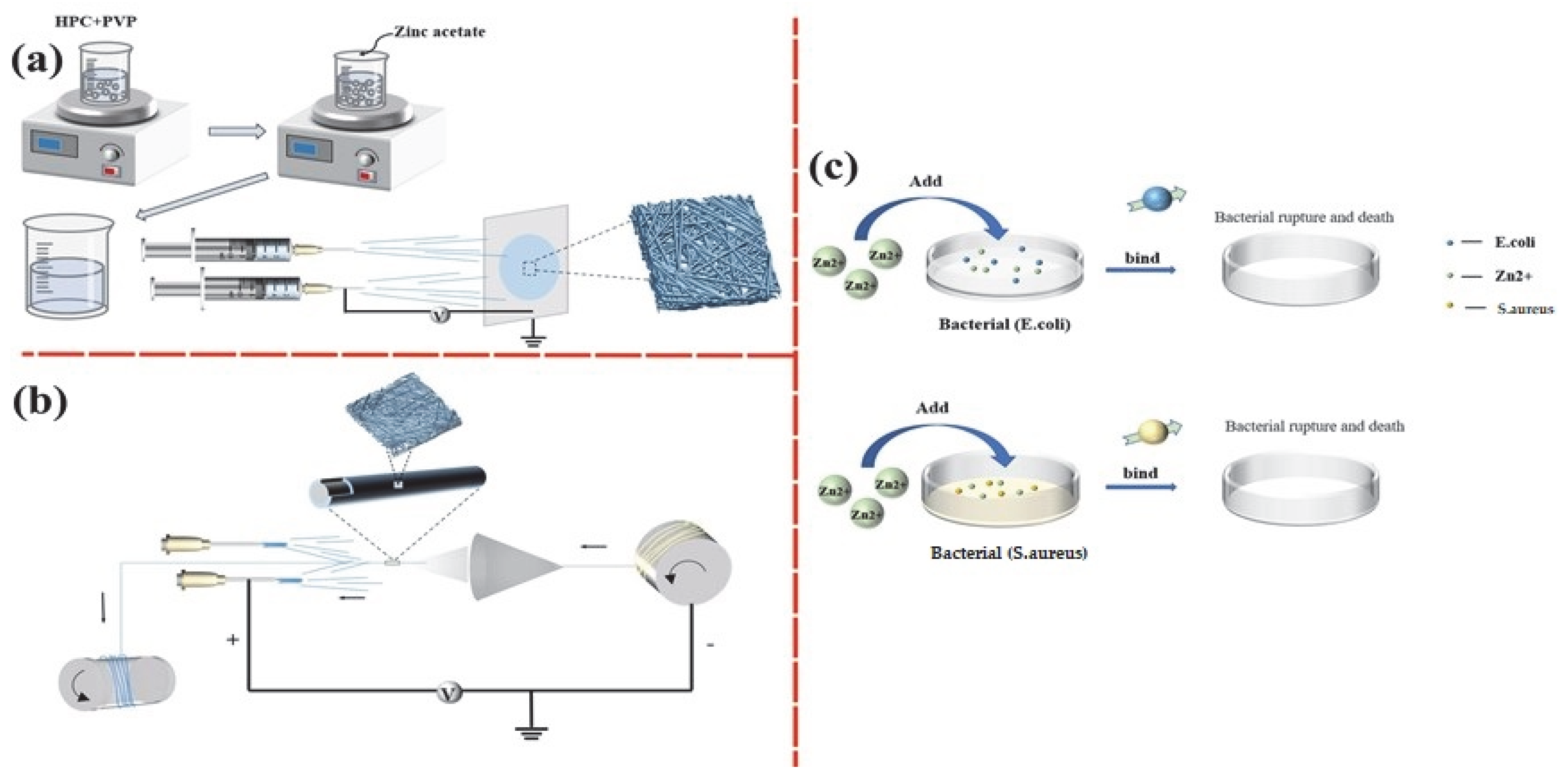
2.2. Preparation of HPC/PVP/Zn Nanofiber Membranes
2.3. Bacterial Biology Experiment
2.3.1. Bacterial Culture
2.3.2. Antibacterial Test
2.4. Cell Biology Experiment
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology Analysis of Nanofibers
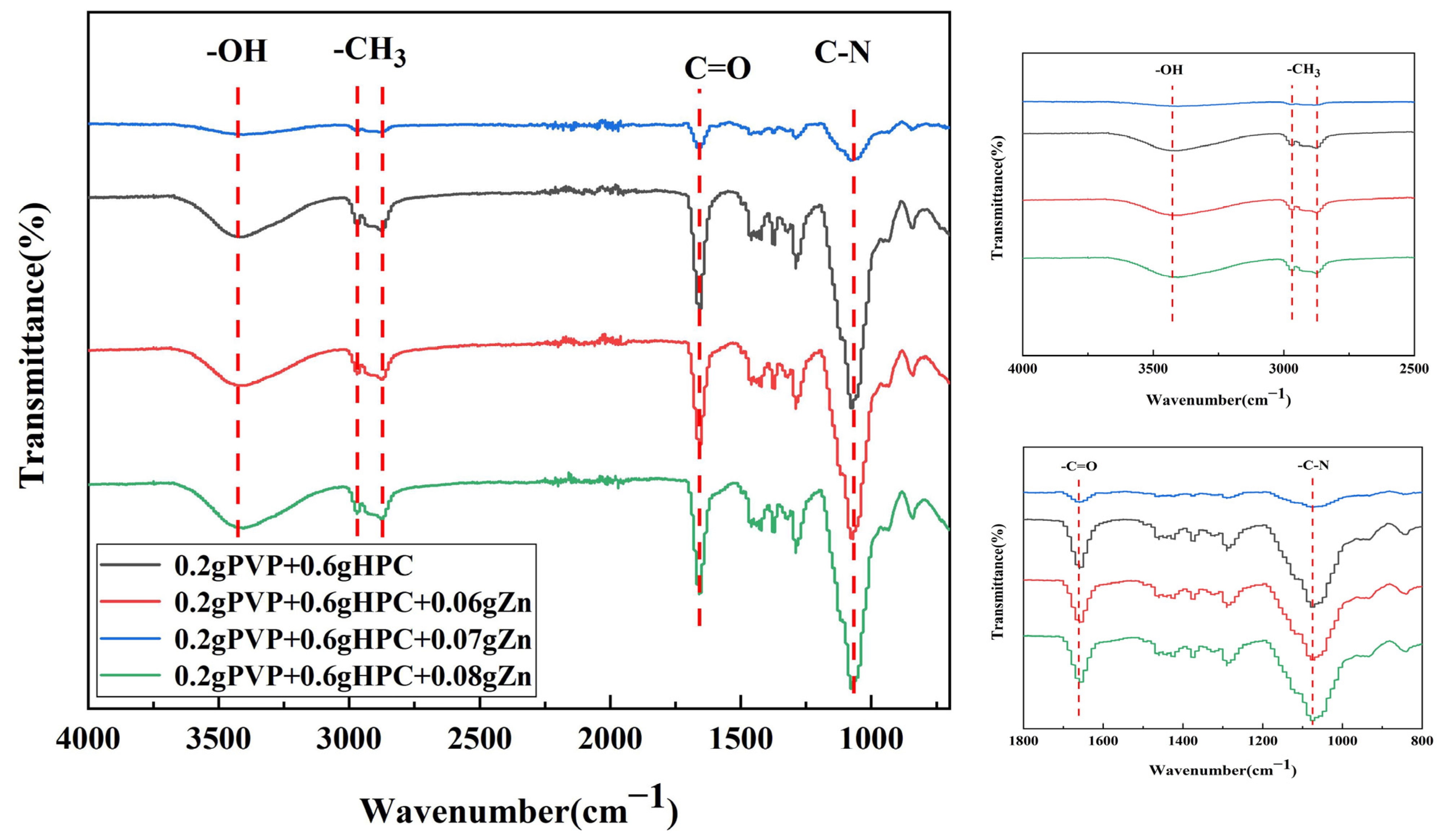
3.2. FTIR and EDS Analyses
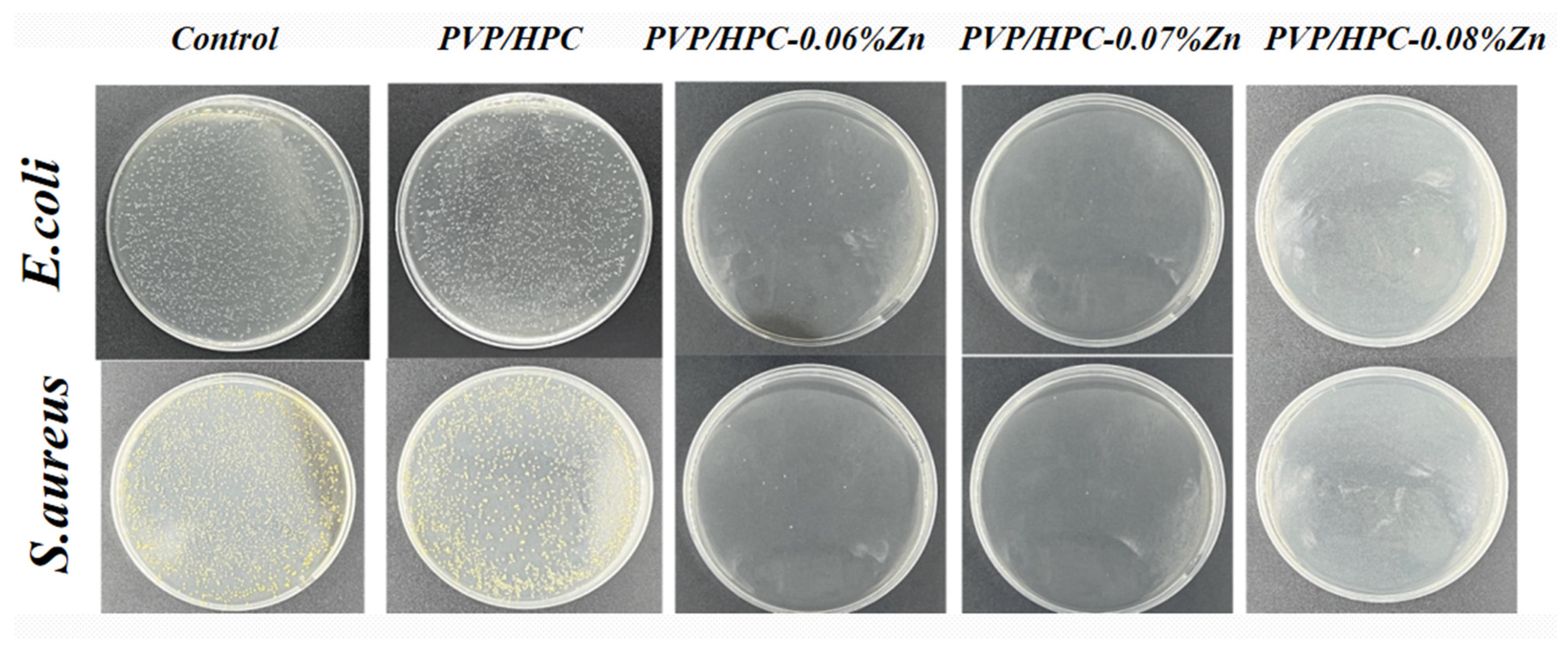
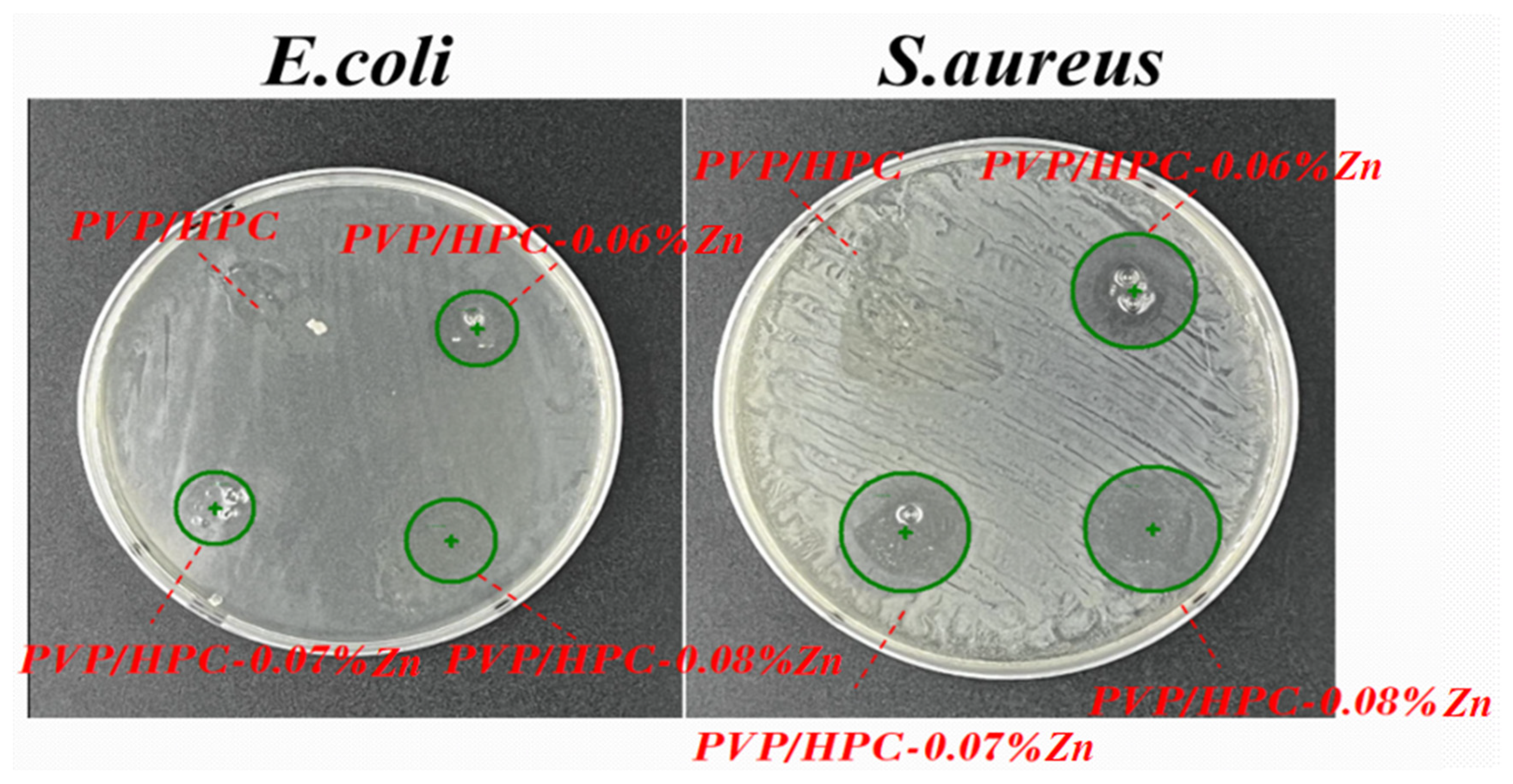
3.3. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szabo, P.; Kallai-Szabo, B.; Kallai-Szabo, N.; Sebe, I.; Zelko, R. Preparation of hydroxypropyl cellulose microfibers by high-speed rotary spinning and prediction of the fiber-forming properties of hydroxypropyl cellulose gels by texture analysis. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4419–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, N.; Gupta, P.M.; Naithani, S. Hydroxypropyl cellulose from alpha-cellulose isolated from Lantana camara with respect to DS and rheological behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.H.; Gray, D.G.; Pieranski, P. Revisiting (hydroxypropyl) cellulose (HPC)/water liquid crystalline system. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 2108–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nau, M.; Trosien, S.; Seelinger, D.; Boehm, A.K.; Biesalski, M. Spatially Resolved Crosslinking of Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Esters for the Generation of Functional Surface-Attached Organogels. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappert, M.F. Contributions to the chemistry of carbenemetal chemistry. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 5467–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.Y.; Xiong, Q.Z.; Zhou, H.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, G.Z.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhao, H.J. Oxoacetohydrazide-Functionalized Cellulose with Enhanced Adsorption Performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.42950 (accessed on 9 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Nau, M.; Seelinger, D.; Biesalski, M. Functional surface coatings from tailor-made long-chain hydroxypropyl cellulose ester nanoparticles. Cellulose 2018, 25, 5769–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcuende, M.; Parra, C.; Marco, E.; Garrido, A.; Martinez, E.; Canoves, J. Influence of limestone filler and viscosity-modifying admixture on the porous structure of self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.P.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Q.H.; Wu, X.J. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose derivatives prepared in NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Lei, Q.; Luo, J.H.; Wang, P.M.; Xiao, P.W.; Ye, Y.Z.; Wu, X.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.Z. Application of Nanocellulose in Oilfield Chemistry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 20833–20845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazsoki, A.; Szabo, P.; Zelko, R. Prediction of the hydroxypropyl cellulose-poly(vinyl alcohol) ratio in aqueous solution containing papaverine hydrochloride in terms of drug loaded electrospun fiber formation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.N.; Lopes, L.F.; Godinho, M.H. Recent advances in the manipulation of circularly polarised light with cellulose nanocrystal films. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenborn, E.; Braunschweig, B. Hydroxypropyl cellulose as a green polymer for thermo-responsive aqueous foams. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 2876–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.J.; Lee, H.K.; Jeong, E.H.; Park, W.H.; Youk, J.H. Preparation of polymer nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles by using poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddheswaran, R.; Sankar, R.; Babu, M.R.; Rathnakumari, M.; Jayavel, R.; Murugakoothan, P.; Sureshkumar, P. Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanofibers by electrospinning. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2006, 41, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Fang, D.W.; Wang, N.N.; Jiang, S.; Nie, J.; Yu, Q.; Ma, G.P. Preparation of PVDF/PVP core-shell nanofibers mats via homogeneous electrospinning. Polymer 2014, 55, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Cortez, I.E.; Alvarado-Castaneda, A.; Garcia-Gutierrez, D.F.; Garcia-Gomez, N.A.; Sepulveda-Guzman, S.; Garcia-Gutierrez, D.I. Core-shell PEDOT:PSS-PVP nanofibers containing PbS nanoparticles through coaxial electrospinning. Synth. Met. 2016, 220, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edikresnha, D.; Suciati, T.; Munir, M.M.; Khairurrijal, K. Polyvinylpyrrolidone/cellulose acetate electrospun composite nanofibres loaded by glycerine and garlic extract with in vitro antibacterial activity and release behaviour test. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26351–26363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yu, W.J.; Qian, X.D.; Li, X.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Ji, J. Dissolving microneedles with a biphasic release of antibacterial agent and growth factor to promote wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardi, M.; Kossyvaki, D.; Picone, P.; Summa, M.; Guo, X.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Giacomazza, D.; Carzino, R.; Goldoni, L.; Scoponi, G.; et al. Electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) hydrogels containing hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives as potential wound dressings. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Akbari, A.; Rahimkhoei, V.; Lighvani, Z.M.; Jafari, H. Halloysite nanotubes/carbohydrate-based hydrogels for biomedical applications: From drug delivery to tissue engineering. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 4497–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alborzi, S.; Lim, L.T.; Kakuda, Y. Encapsulation of folic acid and its stability in sodium alginate-pectin-poly(ethylene oxide) electrospun fibres. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.Y.; Gao, Y.L.; Zhai, Y.L. Electrospun nanofibers as a wound dressing for treating diabetic foot ulcer. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Ghayour, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Nur, H.; Berto, F. Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Biomedical and Tissue Engineering Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2020, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamizi, E.; Azizi, M.; Dorraji MS, S.; Dusti, Z.; Panahi-Azar, V. Stabilized core/shell PVA/SA nanofibers as an efficient drug delivery system for dexpanthenol. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sali, M.; Buonsenso, D.; D’Alfonso, P.; De Maio, F.; Ceccarelli, M.; Battah, B.; Palucci, I.; Chiacchio, T.; Goletti, D.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. Combined use of Quantiferon and HBHA-based IGRA supports tuberculosis diagnosis and therapy management in children. J. Infect. 2018, 77, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; McDonough, W.G.; Dunkers, J.P.; Wight, S.A.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Forster, A.L.; Rice, K.D.; Holmes, G.A. X-ray scattering study on the damage in fibers used in soft body armor after folding. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaoglu, B.; Ulku, T.K.; Gereli, A.; Karahan, M.; Turkmen, M. Evaluation of Absorbable and Nonabsorbable Sutures for Repair of Achilles Tendon Rupture with a Suture-Guiding Device. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethinam, S.; Nallathambi, G.; Vijayan, S.; Basaran, B.; Mert, A.; Bayraktar, O.; Wilson, A.A. A new approach for the production of multifilament suture—In vitro and in vivo analysis. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 70, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmakumar, S.; Joseph, J.; Neppalli, M.H.; Mathew, S.E.; Nair, S.V.; Shankarappa, S.A.; Menon, D. Electrospun Polymeric Core-sheath Yarns as Drug Eluting Surgical Sutures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6925–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.; Aly, A. The Surgical Suture. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2019, 39, S67–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rethinam, S.; Parvathaleswara, S.T.; Nandhagobal, G.; Alagumuthu, T.; Robert, B. Preparation of absorbable surgical suture: Novel approach in biomedical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, D.A.; Chan, D.W. The clinical application of proteomics. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 357, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Kharaziha, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, S.; Razzaghi, M.; Rama, K.S.; Berto, F. Antimicrobial Synthetic and Natural Polymeric Nanofibers as Wound Dressing: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.T.; Shiu, B.C.; Lin, J.H.; Lou, C.W. Two methods for constructing ZIF-8 nanomaterials with good bio compatibility and robust antibacterial applied to biomedical. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.T.; Peng, H.K.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Two-step strategy for constructing hierarchical pore structured chitosan-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, D.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, S.J.; Hwang, E.T.; Maharjan, A.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, D.; Joo, J.H. Origin of Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles: The Roles of Protonic and Electronic Conductions. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36, 1900141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.R.; He, J.H.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.Y. Effect of solution concentration on diameter and morphology of PVA nanofibres in bubble electrospinning process. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Number of Samples | Strength of Solution | Voltage (KV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP (w/v) | HPC (w/v) | Zn (w/v) | ||
| 1 | 1% | 5% | - | 19 |
| 2 | 1% | 6% | - | 19 |
| 3 | 1% | 7% | - | 19 |
| 4 | 2% | 6% | 0.6% | 19 |
| 0.7% | ||||
| 0.8% | ||||
| 5 | 2% | 7% | - | 19 |
| 6 | 2% | 8% | - | 19 |
| 7 | 2% | 10% | - | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, C.-W.; Hung, C.-Y.; Wei, M.; Li, T.; Shiu, B.-C.; Lin, J.-H. Antibacterial Surgical Sutures Developed Using Electrostatic Yarn Wrapping Technology. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14050248
Lou C-W, Hung C-Y, Wei M, Li T, Shiu B-C, Lin J-H. Antibacterial Surgical Sutures Developed Using Electrostatic Yarn Wrapping Technology. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(5):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14050248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Ching-Wen, Chun-Yu Hung, Mengdan Wei, Tingting Li, Bing-Chiuan Shiu, and Jia-Horng Lin. 2023. "Antibacterial Surgical Sutures Developed Using Electrostatic Yarn Wrapping Technology" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 5: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14050248
APA StyleLou, C.-W., Hung, C.-Y., Wei, M., Li, T., Shiu, B.-C., & Lin, J.-H. (2023). Antibacterial Surgical Sutures Developed Using Electrostatic Yarn Wrapping Technology. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(5), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14050248









