Partial Oxidation Strategy to Synthesize WS2/WO3 Heterostructure with Enhanced Adsorption Performance for Organic Dyes: Synthesis, Modelling, and Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
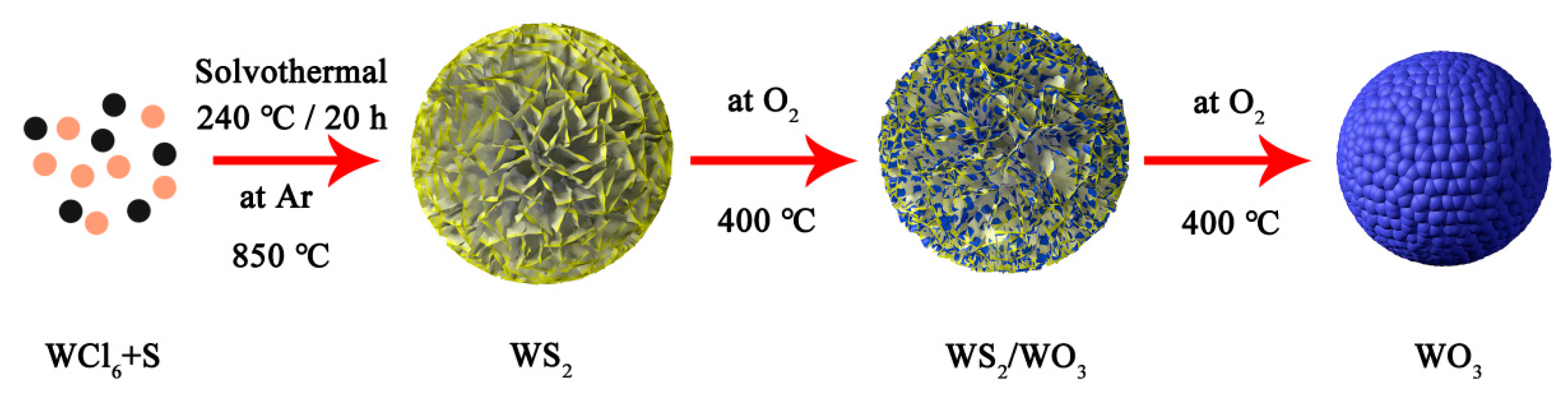
2.2. Synthesis of WS2, WS2/WO3 Heterostructures and WO3
2.3. Material Characterizations
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
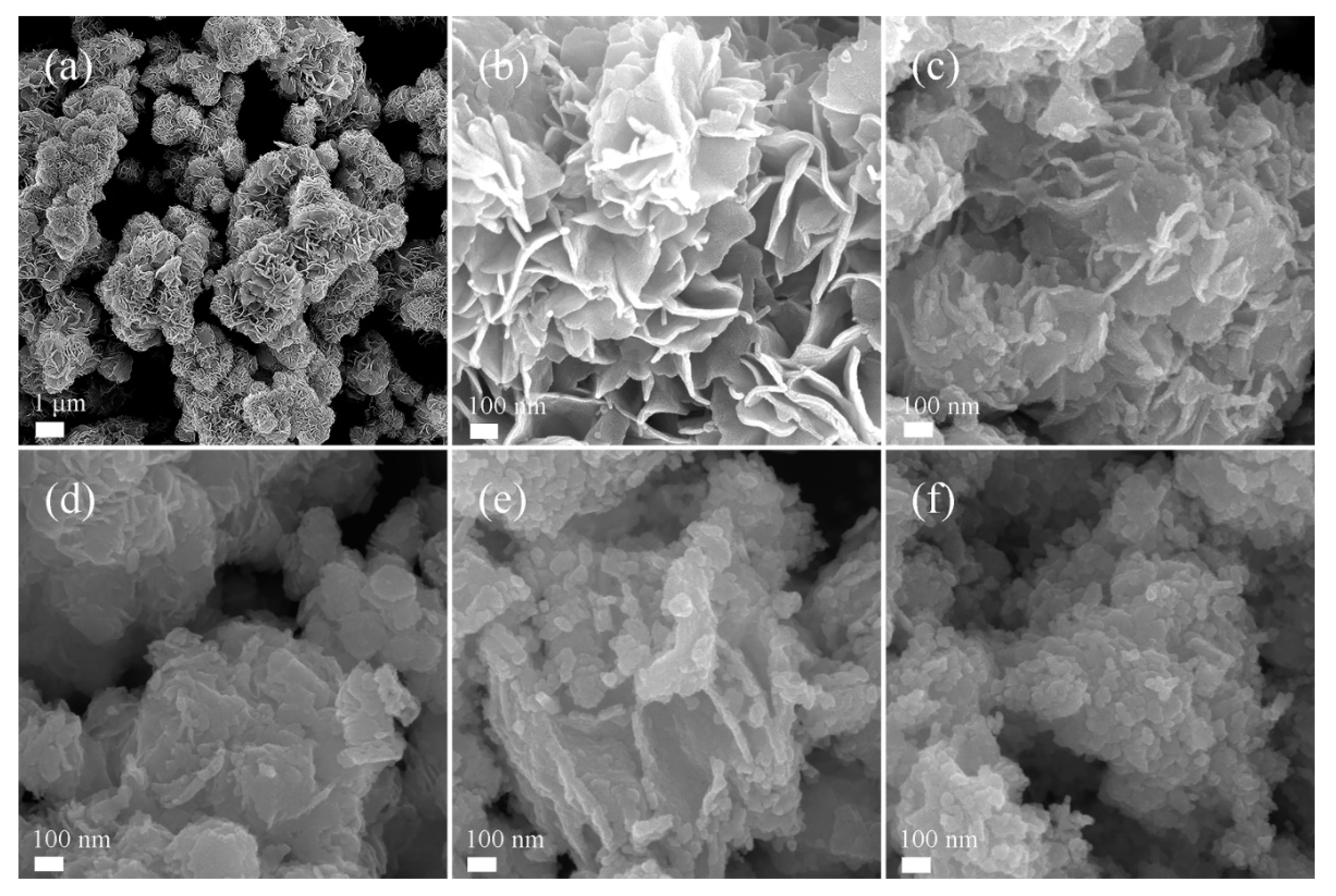
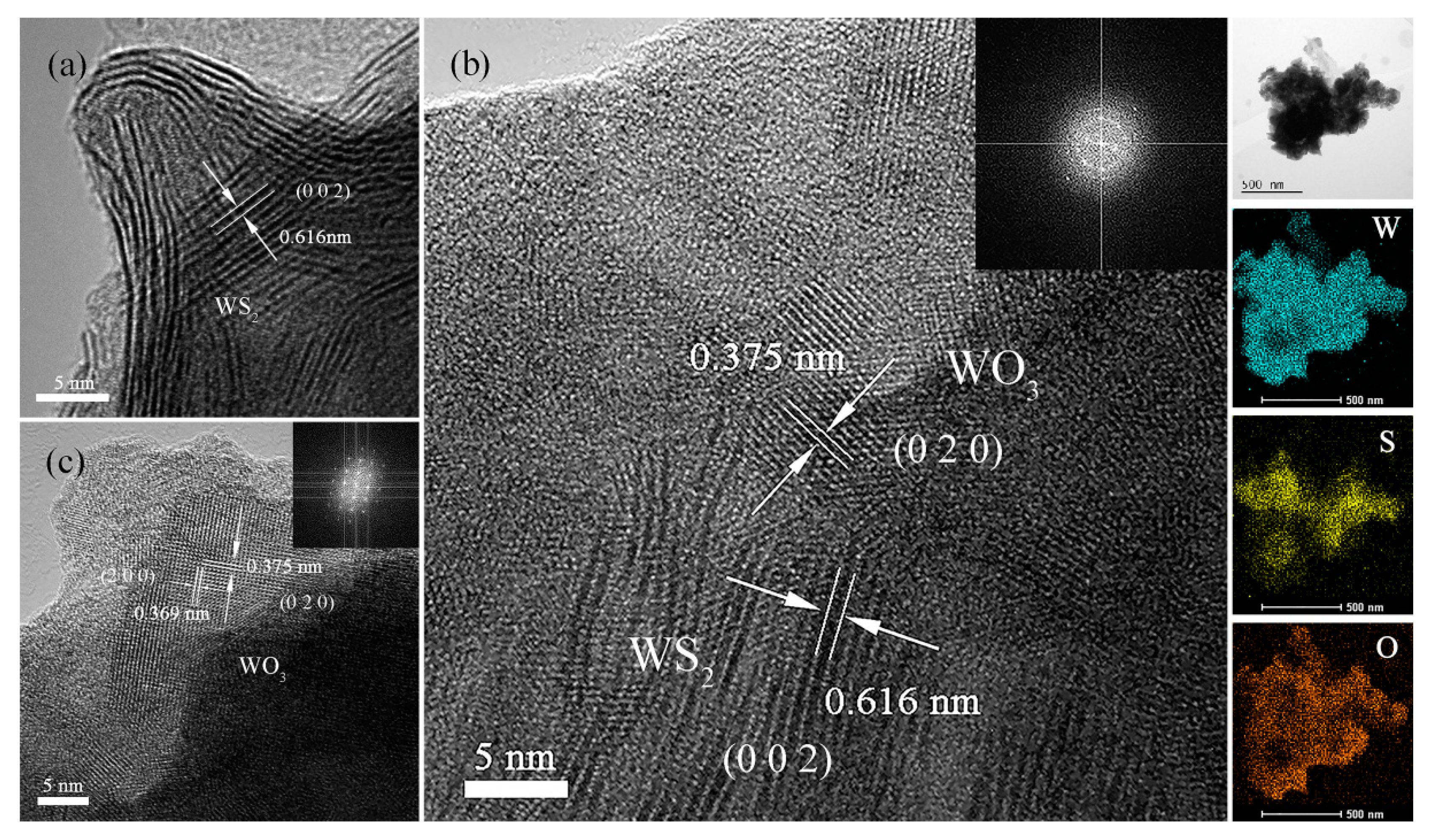
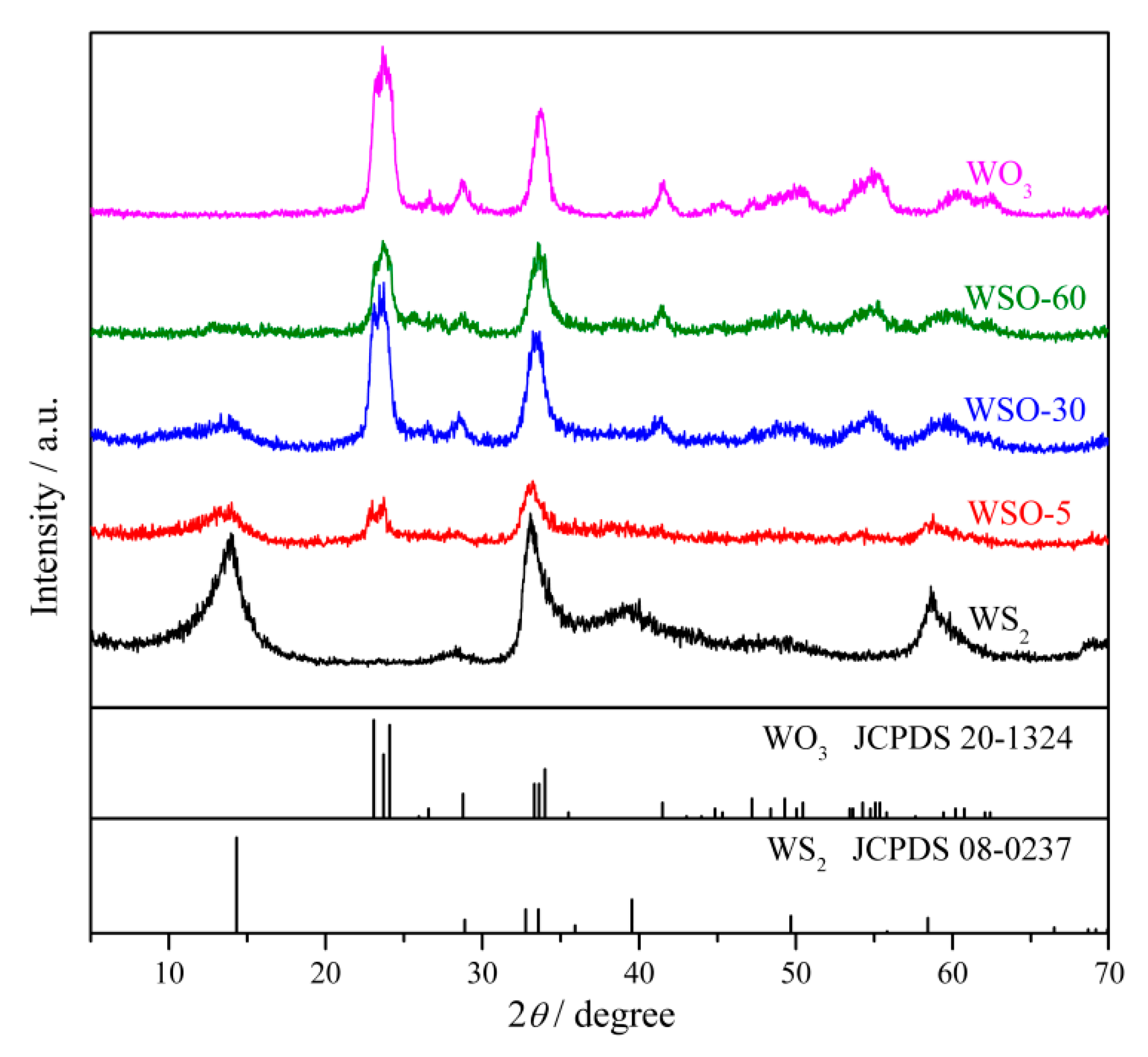
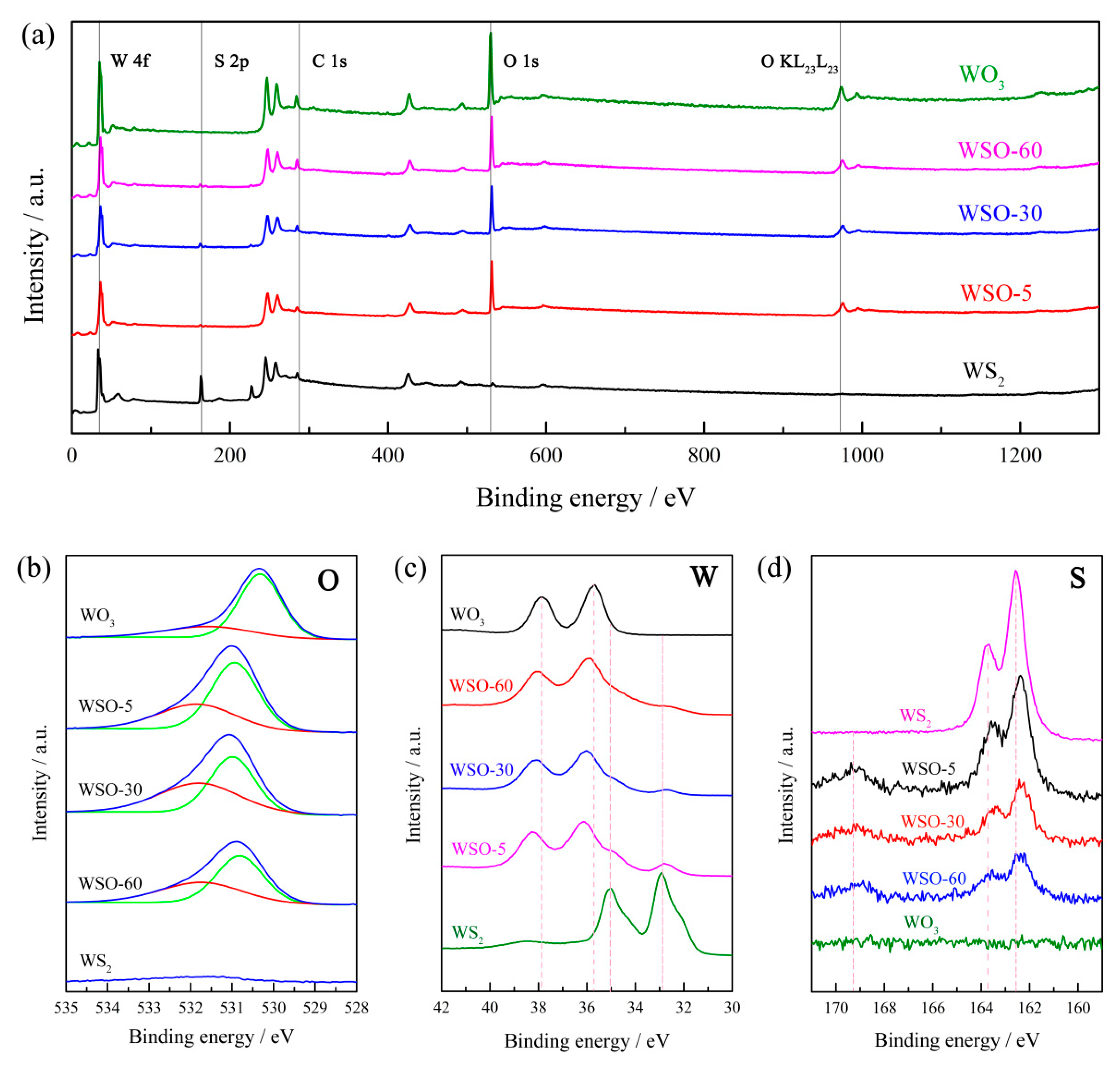
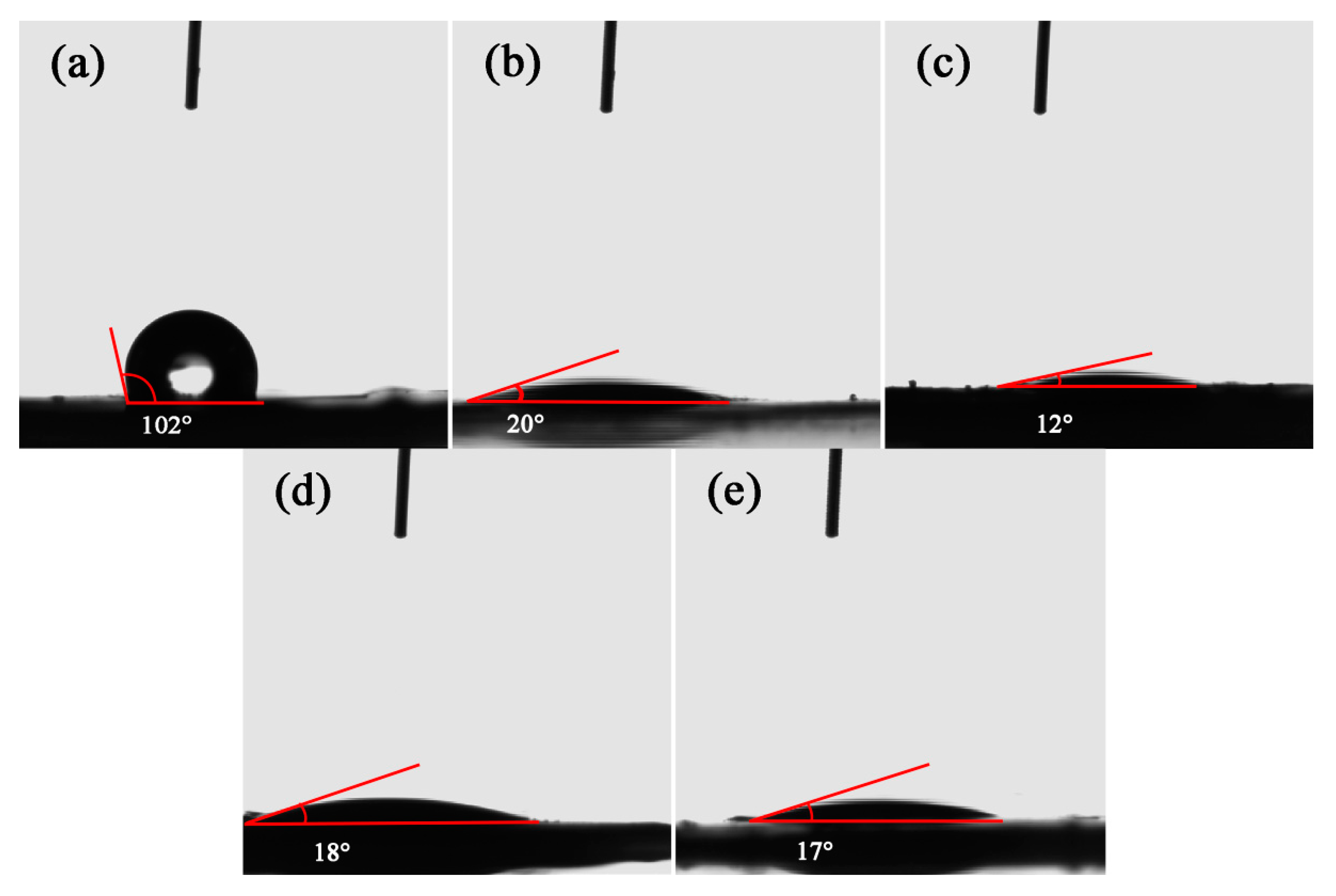
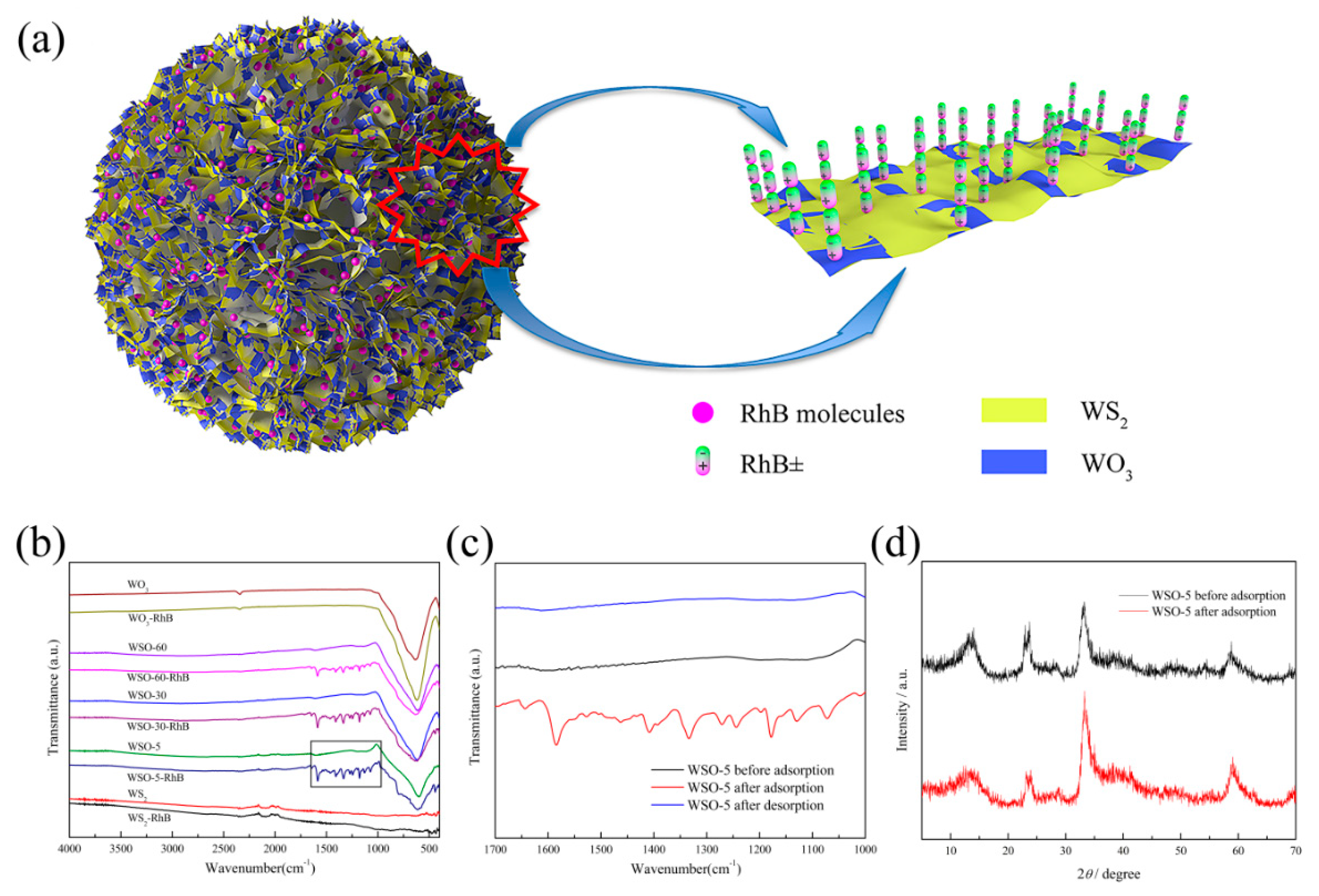
3.1. Characterizations
3.2. Adsorption Knetics
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage and Solution pH
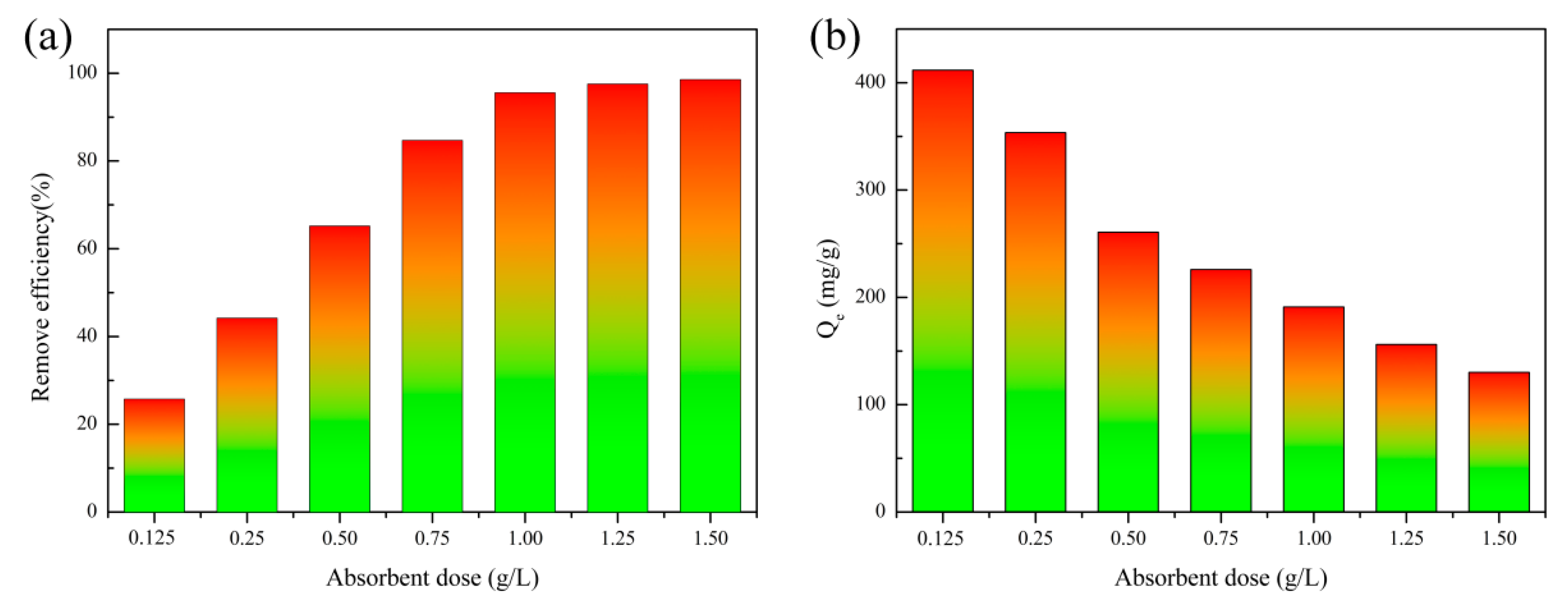
3.4.1. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.4.2. Effect of Solution pH
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
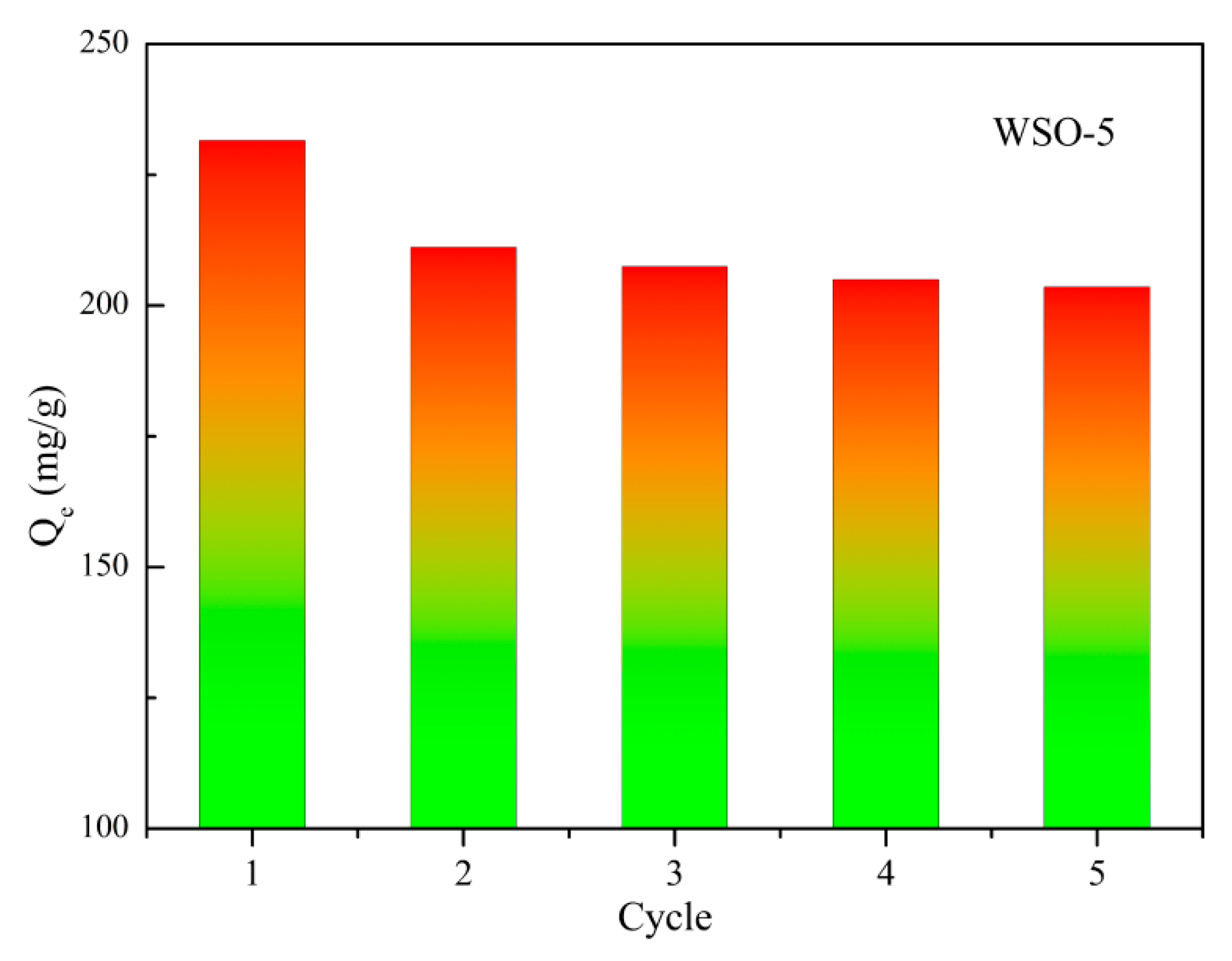
3.6. Recyclability
3.7. Comparison with Other Adsorption Materials
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okesola, B.O.; Smith, D.K. Applying low-molecular weight supramolecular gelators in an environmental setting self-assembled gels as smart materials for pollutant removal. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4226–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, H.; Hao, H. Oil-phase cyclic magnetic adsorption to synthesize Fe3O4@C@TiO2-nanotube composites for simultaneous removal of Pb(II) and Rhodamine B. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.B.; Vakili, M.; Horri, B.A.; Poh, P.E.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Salamatinia, B. Adsorption of dyes by nanomaterials: Recent developments and adsorption mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pu, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, J.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, K. Synthesis of a novel nanosilica-supported poly β-cyclodextrin sorbent and its properties for the removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 538, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Hu, X.; Feng, R.; Zhou, M. Direct carbonization of Zn/Co zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for efficient adsorption of Rhodamine B. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Magnetic Porous Carbonaceous Material Produced from Tea Waste for Efficient Removal of As(V), Cr(VI), Humic Acid, and Dyes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Huang, X.; Tian, B.; Hao, H. Highly Efficient and Reusable Montmorillonite/Fe3O4/Humic Acid Nanocomposites for Simultaneous Removal of Cr(VI) and Aniline. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Bi, J.; Xie, C.; Hao, H. Design and synthesis of core–shell Fe3O4@PTMT composite magnetic microspheres for adsorption of heavy metals from high salinity wastewater. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X.; Guan, G.; Abudula, A. Facile Preparation of Ion-Imprinted Composite Film for Selective Electrochemical Removal of Nickel(II) Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9543–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körbahti, B.K.; Artut, K.; Geçgel, C.; Özer, A. Electrochemical decolorization of textile dyes and removal of metal ions from textile dye and metal ion binary mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Zou, C.; Xu, Y. Iron(III)–Alginate Fiber Complex as a Highly Effective and Stable Heterogeneous Fenton Photocatalyst for Mineralization of Organic Dye. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 4199–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Mukherji, S.; Garg, A. Removal of Chemical Oxygen Demand and Color from Simulated Textile Wastewater Using a Combination of Chemical/Physicochemical Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10063–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Meng, X.; Huang, X.; Hao, H. Co–Cu–Al Layered Double Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalyst for Enhanced Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater by Activating Peroxymonosulfate: Performance and Synergistic Effect. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 8699–8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thung, W.-E.; Ong, S.-A.; Ho, L.-N.; Wong, Y.-S.; Ridwan, F.; Lehl, H.K.; Oon, Y.-L.; Oon, Y.-S. Biodegradation of Acid Orange 7 in a combined anaerobic-aerobic up-flow membrane-less microbial fuel cell: Mechanism of biodegradation and electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Nagatsu, M.; Wang, X. Carbon nanotubes as adsorbents in environmental pollution management: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X. Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Oxidized Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 9144–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Luo, X. Hierarchically mesostructured MIL-101 metal–organic frameworks with different mineralizing agents for adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Xie, S.; Quan, H.; Luo, X.; Guo, L. Adsorption Behaviors of Organic Micropollutants on Zirconium Metal–Organic Framework UiO-66: Analysis of Surface Interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41043–41054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Few-Layered Graphene Oxide Nanosheets As Superior Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ion Pollution Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.B.; Jing, C.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, X.; Dong, F.; Dong, B.; Zhang, Y.X. 2D-2D growth of NiFe LDH nanoflakes on montmorillonite for cationic and anionic dye adsorption performance. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, P.; Shi, J.; Xu, G. Easy-separative MoS2-glue sponges with high-efficient dye adsorption and excellent reusability for convenient water treatment. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 540, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Shi, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, G. Flower-Like Molybdenum Disulfide for Polarity-Triggered Accumulation/Release of Small Molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36431–36437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.M.; Chang, W.E.; Chang, Y.T.; Chang, C.-K. Piezo-Catalytic Effect on the Enhancement of the Ultra-High Degradation Activity in the Dark by Single- and Few-Layers MoS2 Nanoflowers. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3718–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, H.B.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Lou, X.W. Hierarchical MoS2 microboxes constructed by nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium storage and water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3302–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Yao, S.; Wu, X.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Geng, B. High supercapacitor and adsorption behaviors of flower-like MoS2 nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 15958–15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, F.; Li, W.; Fahlman, B.D.; Chen, M.; Li, W. Preparation and adsorption capacity of porous MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105222–105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Jing, X.; Wang, D.; Meng, L. Controlled preparation of high quality WS2 nanostructures by a microwave-assisted solvothermal method. Crystengcomm 2018, 20, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fang, B.; Bonakdarpour, A.; Sun, A.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Wang, D. WS2 nanosheets as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Meng, S.; Fu, X. Study on the separation mechanisms of photogenerated electrons and holes for composite photocatalysts g-C3N4-WO3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 150–151, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Shi, W.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Feng, P.; Cheng, P. Metal–Organic Framework-Derived ZnO/ZnS Heteronanostructures for Efficient Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpak, A.P.; Korduban, A.M.; Medvedskij, M.M.; Kandyba, V.O. XPS studies of active elements surface of gas sensors based on WO3−x nanoparticles. J. Electron Spectrosc. 2007, 156–158, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-L.; Wei, K.-H.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Li, L.-J. Comparative study on MoS2 and WS2 for electrocatalytic water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 12302–12309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K. Fabrication of Two-Dimensional Lateral Heterostructures of WS2/WO3·H2O Through Selective Oxidation of Monolayer WS2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15226–15230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, E.; Yan, H. The modifications of the surface wettability of amorphous carbon films. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 335, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Wettability of natural superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 210, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Wen, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Hydrogen-Bonding-Driven Wettability Change of Colloidal Crystal Films: From Superhydrophobicity to Superhydrophilicity. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4984–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Hao, J. Reversibly switchable wettability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.-R.; Yan, L.-G.; Yang, K.; Yu, S.-J.; Hao, Y.-F.; Yu, H.-Q.; Du, B. Magnetic Fe3O4/MgAl-LDH composite for effective removal of three red dyes from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azha, S.F.; Sellaoui, L.; Shamsudin, M.S.; Ismail, S.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Ben Lamine, A.; Erto, A. Synthesis and characterization of a novel amphoteric adsorbent coating for anionic and cationic dyes adsorption: Experimental investigation and statistical physics modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J.; Ben Lamine, A.; Erto, A. Insights on the statistical physics modeling of the adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions on bentonite-chitosan composite in single and binary systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Guedidi, H.; Knani, S.; Reinert, L.; Duclaux, L.; Ben Lamine, A. Application of statistical physics formalism to the modeling of adsorption isotherms of ibuprofen on activated carbon. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2015, 387, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Tao, Q.; Lu, H.; Luo, L.; Li, G.; Hao, H. Self-assembly of immobilized titanate films with different layers for heavy metal ions removal from wastewater: Synthesis, modeling and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Sellaoui, L.; Bedia, J.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Belver, C. Adsorption of ibuprofen on organo-sepiolite and on zeolite/sepiolite heterostructure: Synthesis, characterization and statistical physics modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zong, P.; Hu, J.; Sheng, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic HNT/iron oxide composite for high-efficient decontamination of U(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Shen, T.; Yu, M.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, J. Insights into the efficient adsorption of rhodamine B on tunable organo-vermiculites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandkumar, J.; Mandal, B. Adsorption of chromium(VI) and Rhodamine B by surface modified tannery waste: Kinetic, mechanistic and thermodynamic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Removal of Rhodamine B with Fe-supported bentonite as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst under visible irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 178, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Hao, P.; Leng, Y.; Liu, H. From UV to Near-Infrared, WS2 Nanosheet: A Novel Photocatalyst for Full Solar Light Spectrum Photodegradation. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.-Q.; Hu, F.-C.; Tian, F.-Y.; Hou, D.-F.; Li, D.-S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on MB adsorption by ultrathin 2D MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11631–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, K.; Hu, L.; Teng, F.; Yu, P.; Zhu, Y. Superior Adsorption and Regenerable Dye Adsorbent Based on Flower-Like Molybdenum Disulfide Nanostructure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.J.; You, S.; Jia, X.H.; Yang, J. MoS2 nanosheets decorated with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their ultrafast adsorption for wastewater treatment. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 13896–13902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

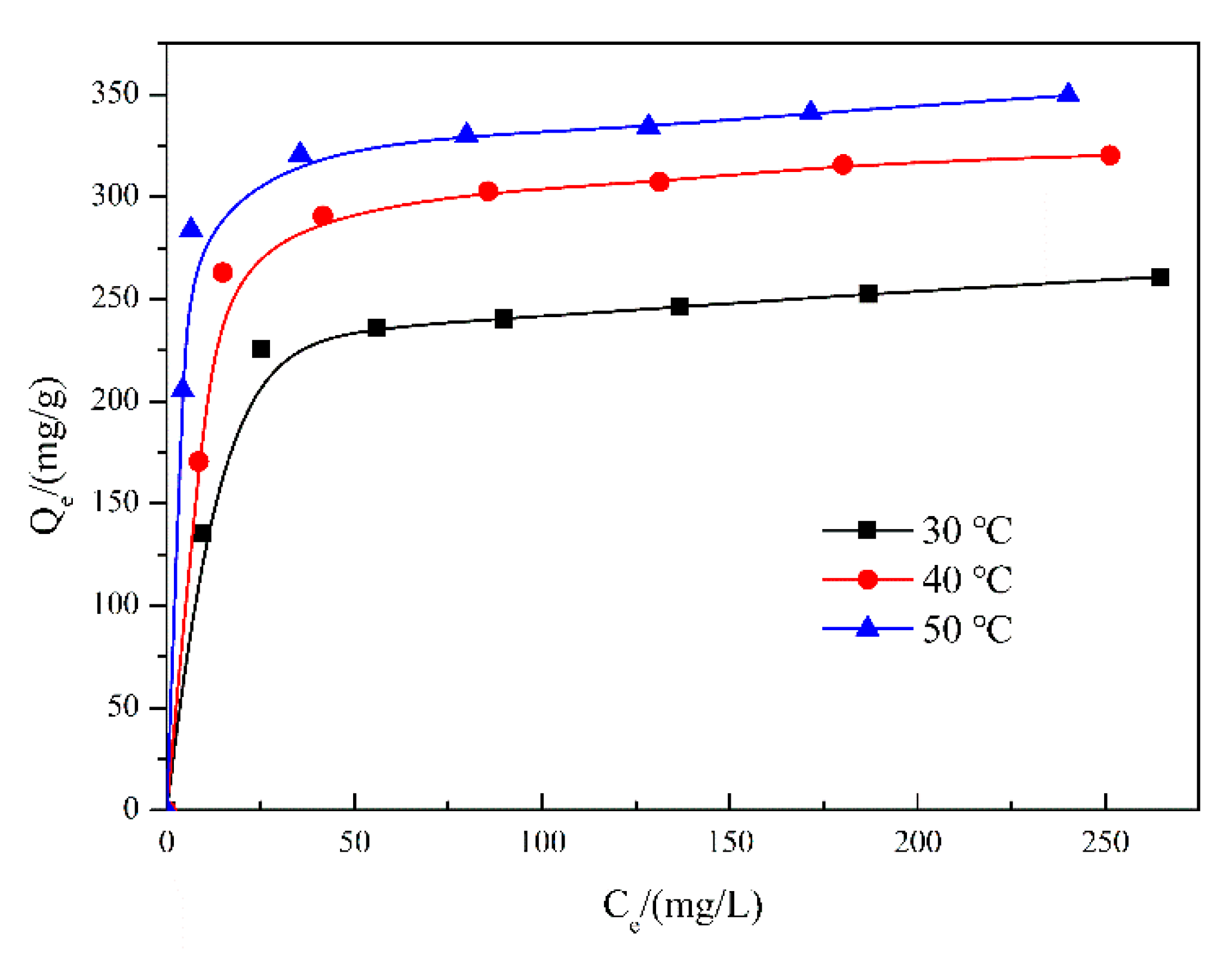


| (°C) | (mg/g) | (mg/g) | (kJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 1.840 | 136.3 | 250.8 | 5.901 | 0.9993 |
| 40 | 2.495 | 123.9 | 309.1 | 6.336 | 0.9992 |
| 50 | 2.922 | 114.8 | 335.4 | 8.575 | 0.9993 |
| Adsorbents | Dyes | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Adsorption Time (min) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2 nanosheets | RhB | 163 | 420 | [27] |
| 2D MoS2 nanosheets | MB | 146 | 5 | [50] |
| Flower-like MoS2 | RhB | 55.0 | 180 | [51] |
| MoS2-glue sponges | RhB | 127 | 60 | [22] |
| Fe3O4/MoS2 | RhB | 22.0 | 30 | [52] |
| Flower-like WS2 | RhB | 16.4 | 100 | This work |
| WO3 particles | RhB | 30.4 | 100 | This work |
| Flower-like WSO-5 | RhB | 237 | 100 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Mao, Y.; Luo, L.; Hao, H. Partial Oxidation Strategy to Synthesize WS2/WO3 Heterostructure with Enhanced Adsorption Performance for Organic Dyes: Synthesis, Modelling, and Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020278
Li G, Wang Y, Bi J, Huang X, Mao Y, Luo L, Hao H. Partial Oxidation Strategy to Synthesize WS2/WO3 Heterostructure with Enhanced Adsorption Performance for Organic Dyes: Synthesis, Modelling, and Mechanism. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020278
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guiping, Yongli Wang, Jingtao Bi, Xin Huang, Yafei Mao, Liang Luo, and Hongxun Hao. 2020. "Partial Oxidation Strategy to Synthesize WS2/WO3 Heterostructure with Enhanced Adsorption Performance for Organic Dyes: Synthesis, Modelling, and Mechanism" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020278
APA StyleLi, G., Wang, Y., Bi, J., Huang, X., Mao, Y., Luo, L., & Hao, H. (2020). Partial Oxidation Strategy to Synthesize WS2/WO3 Heterostructure with Enhanced Adsorption Performance for Organic Dyes: Synthesis, Modelling, and Mechanism. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020278








