Influence of Chymosin on Physicochemical and Hydrolysis Characteristics of Casein Micelles and Individual Caseins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Skim Milk, Individual Caseins, and Chymosin
2.2. Preparation of Skim Milk and Individual Casein Samples with/without Chymosin
2.3. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.4. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.5. Particle Size Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
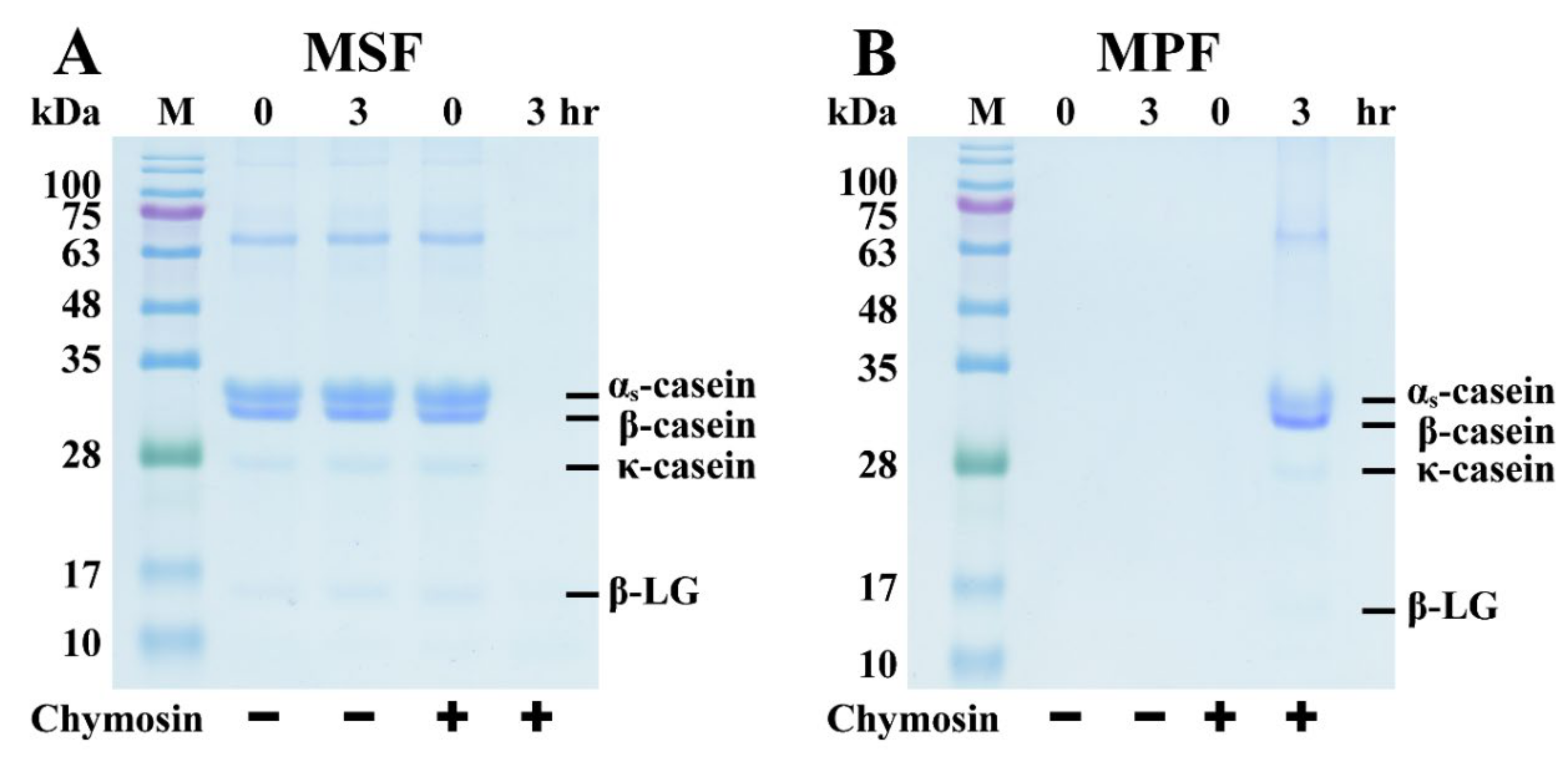
3.1. SDS-PAGE Analysis of Chymosin’s Effect on the Coagulation of Milk Proteins
3.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis of Chymosin’s Effect on the Hydrolysis of Individual Milk Proteins
3.3. MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis of Chymosin’s Effect on the Hydrolysis of Individual Milk Proteins
3.4. Particle Size Analysis of Milk Proteins and Individual Milk Proteins Treated with Chymosin
3.5. Hydrolysis Reaction Scheme on Casein Micelles and Individual Caseins Induced by Chymosin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Getaneh, G.; Mebrat, A.; Wubie, A.; Kendie, H. Review on goat milk composition and its nutritive value. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2016, 3, 401. [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish, D.G. On the structural models of bovine casein micelles-review and possible improvements. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.B.; Poulsen, N.A.; Andersen, K.K.; Hammershøj, M.; Poulsen, H.D.; Larsen, L.B. Distinct composition of bovine milk from Jersey and Holstein-Friesian cows with good, poor, or noncoagulation properties as reflected in protein genetic variants and isoforms. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6905–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, T.; Fox, P.F.; Kelly, A.L. The Caseins: Structure, Stability, and Functionality. In Proteins in Food Processing; Yada, R.Y., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 49–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.F.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Enzymatic Coagulation of Milk. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science; Fox, P.F., Guinee, T.P., Cogan, T.M., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 185–229. [Google Scholar]
- Gamlath, C.J.; Leong, T.S.H.; Ashokkumar, M.; Martin, G.J.O. The inhibitory roles of native whey protein on the rennet gelation of bovine milk. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, A.; Visentin, G.; De Marchi, M.; Berry, D.P.; Fenelon, M.A.; O’Connor, P.M.; Kenny, O.A.; McParland, S. Prediction of individual milk proteins including free amino acids in bovine milk using mid-infrared spectroscopy and their correlations with milk processing characteristics. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3171–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimutis, W.R. Bioactive properties of milk proteins with particular focus on anticariogenesis. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 989S–995S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Hsieh, J.F. Propylene glycol alginate-induced coacervation of milk proteins: A proteomics approach. Food Hydrocolloid. 2016, 53, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Chen, S.T.; Hsieh, J.F. Proteomic analysis of polysaccharide-milk protein interactions induced by chitosan. Molecules 2015, 20, 7737–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureşan, C.C.; Marc, R.A.V.; Anamaria Semeniuc, C.; Ancuţs Socaci, S.; Fărcaş, A.; Fracisc, D.; Rodica Pop, C.; Rotar, A.; Dodan, A.; Mureşan, V.; et al. Changes in physicochemical and microbiological properties, fatty acid and volatile compound profiles of Apuseni cheese during ripening. Foods 2021, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Cogan, T.M.; Guinee, T.P. General Aspects. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Cogan, T.M., Guinee, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1–617. [Google Scholar]
- Rayanatou, I.A.; Mahamadou, E.G.; Garric, G.; Harel-Oger, M.; Leduc, A.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Cauty, C.; Adakal, H.; Grongnet, J.F.; et al. Physico-chemical characterization of dairy gel obtained by a proteolytic extract from Calotropis procera-A comparison with chymosin. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budelli, E.; Bernal, M.; Lema, P.; Fink, M.; Negreira, C.; Tanter, M.; Gennisson, J.L. Use of shear wave elastography for monitoring enzymatic milk coagulation. J. Food Eng. 2014, 136, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.D.T.; Silva, M.Z.R.; Oliveira, J.P.B.; Silva, A.F.B.; Ramos, M.V.; de Sousa, J.S. Study of milk coagulation induced by chymosin using atomic force microscopy. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Corredig, M. Effects of pH-modification on the rennet coagulation of concentrated casein micelles suspensions. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, A.B.; Ozer, B. Nondestructive monitoring of renetted whole milk during cheese manufacturing. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, K.; Abdelghani, A.; Burleigh, S.; Johansen, L.B.; Lindmark-Månsson, H.; Paulsson, M.; Glantz, M. An investigation of the enzymatic cleavage of κ-casein in non-coagulating milk. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 109, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Sahingil, D.; Gokce, Y.; Hayaloglu, A.A. Effect of blends of camel chymosin and microbial rennet (Rhizomucor miehei) on chemical composition, proteolysis and residual coagulant activity in Iranian Ultrafiltered White cheese. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.F.; Pan, P.H. Proteomic profiling of the coagulation of milk proteins induced by chymosin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, D.S. Casein micelle structure: Models and muddles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijl, E.; van Valenberg, H.; Sikkes, S.; Jumelet, S.; Sala, G.; Olieman, K.; Hooijdonk, T.V.; Huppertz, T. Chymosin-induced hydrolysis of caseins: Influence of degree of phosphorylation of alpha-s1-casein and genetic variants of beta-casein. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 39, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusu, Y.; Şentürk, S.B.; Kuduğ, H.; Gökçe, İ. Expression, purification, and characterization of bovine chymosin enzyme using an inducible pTOLT system. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredig, M.; Salvatore, E. Enzymatic Coagulation of Milk. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; McSweeney, P.L.H., O’Mahony, J.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 287–307. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.; Corredig, M.; Alexander, M. Investigation of the colloidal interactions at play in combined acidification and rennet of different heat-treated milks. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4915–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Gunasekaran, S.; Olson, N.F. Combined use of chymosin and protease from Cryphonectria parasitica for control of meltability and firmness of cheddar cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Chemistry and Biochemistry of Cheese. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Fox, P.F., Uniacke-Lowe, T., McSweeney, P.L.H., O’Mahony, J.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 499–546. [Google Scholar]
- Horneffer, V.; Linz, N.; Vogel, A. Principles of laser-induced separation and transport of living cells. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 054016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haginaka, J. Enantiomer separation of drugs by capillary electrophoresis using proteins as chiral selectors. J. Chromatogr. A. 2000, 875, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, C.G.; Holt, C. Casein Micelle Structure, Functions and Interactions. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry-1 Proteins; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 233–276. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-C.; Chen, L.-Y.; Li, W.-T.; Chang, K.-L.; Kuo, M.-I.; Chen, C.-J.; Hsieh, J.-F. Influence of Chymosin on Physicochemical and Hydrolysis Characteristics of Casein Micelles and Individual Caseins. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102594
Chen C-C, Chen L-Y, Li W-T, Chang K-L, Kuo M-I, Chen C-J, Hsieh J-F. Influence of Chymosin on Physicochemical and Hydrolysis Characteristics of Casein Micelles and Individual Caseins. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102594
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chun-Chi, Liang-Yu Chen, Wen-Tai Li, Ken-Lin Chang, Meng-I Kuo, Chao-Jung Chen, and Jung-Feng Hsieh. 2021. "Influence of Chymosin on Physicochemical and Hydrolysis Characteristics of Casein Micelles and Individual Caseins" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102594
APA StyleChen, C.-C., Chen, L.-Y., Li, W.-T., Chang, K.-L., Kuo, M.-I., Chen, C.-J., & Hsieh, J.-F. (2021). Influence of Chymosin on Physicochemical and Hydrolysis Characteristics of Casein Micelles and Individual Caseins. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102594











