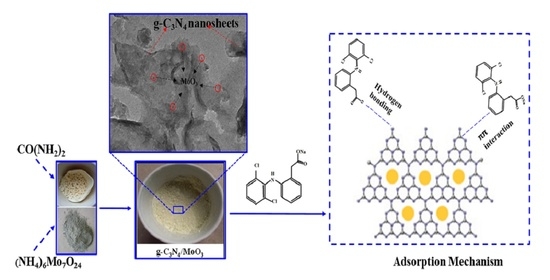
Facile Synthesis of g-C3N4/MoO3 Nanohybrid for Efficient Removal of Aqueous Diclofenac Sodium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Nanohybrid (g-C3N4 (1-x)/MoO3(x))
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Assays
3. Results and Discussion
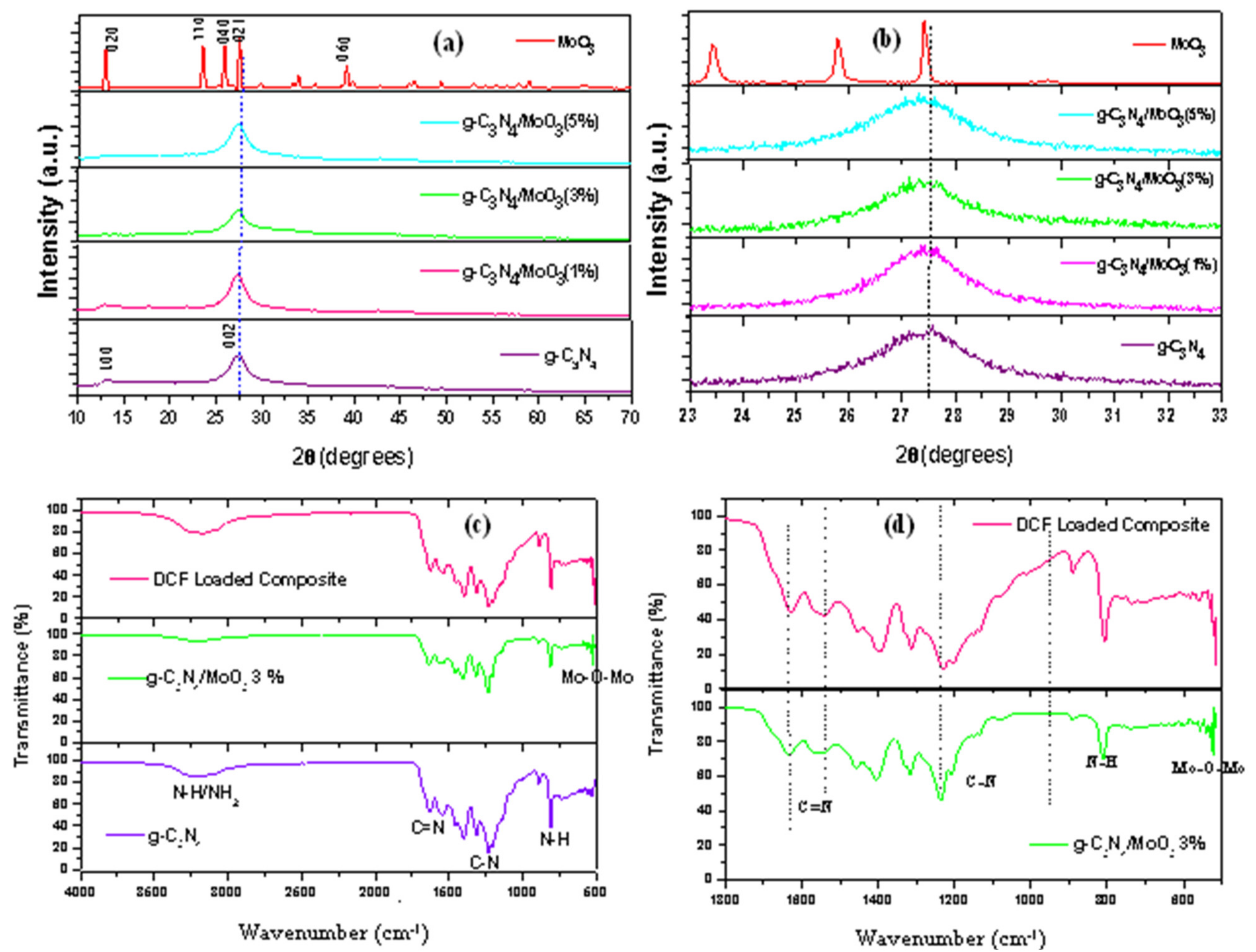
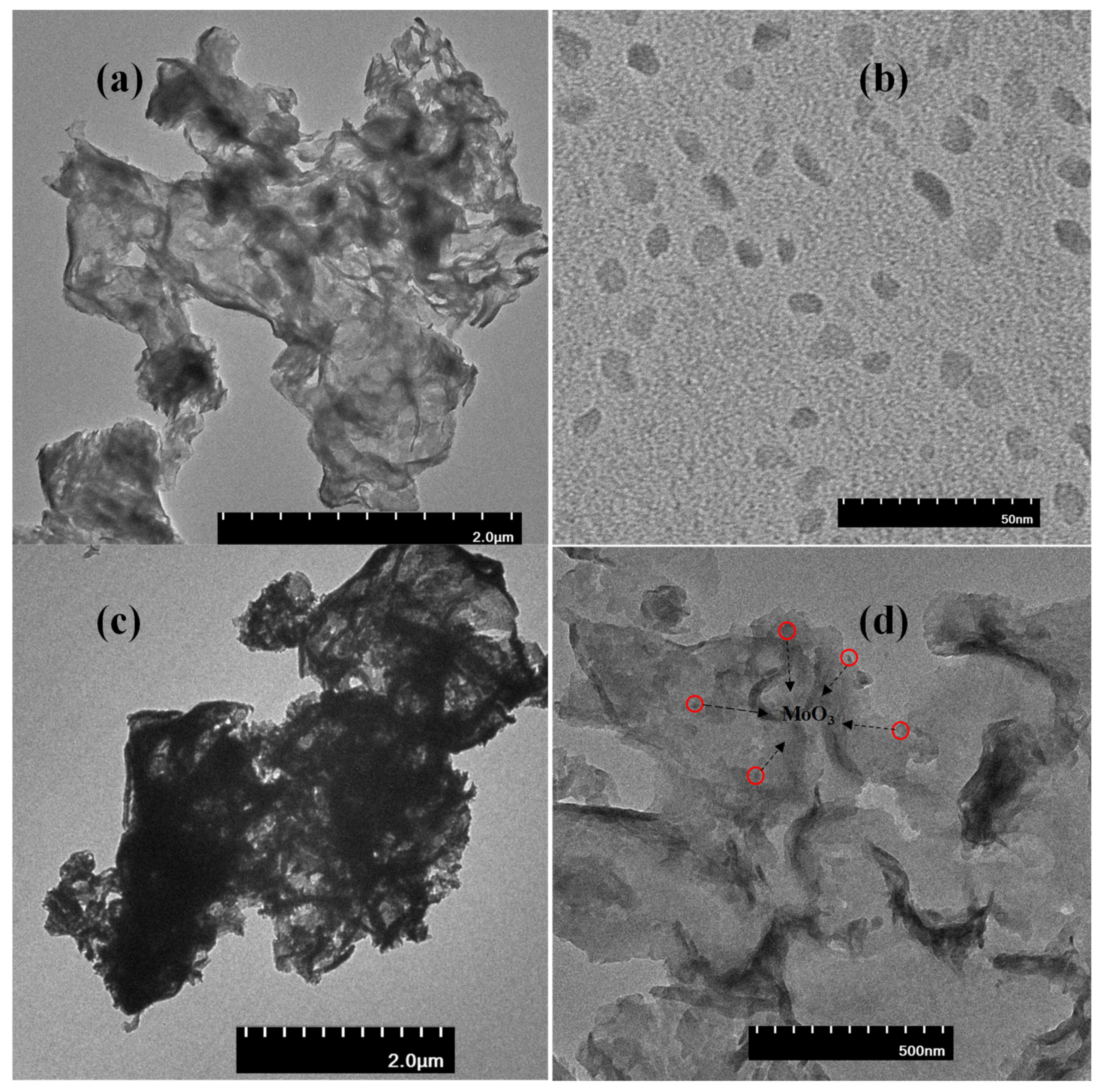
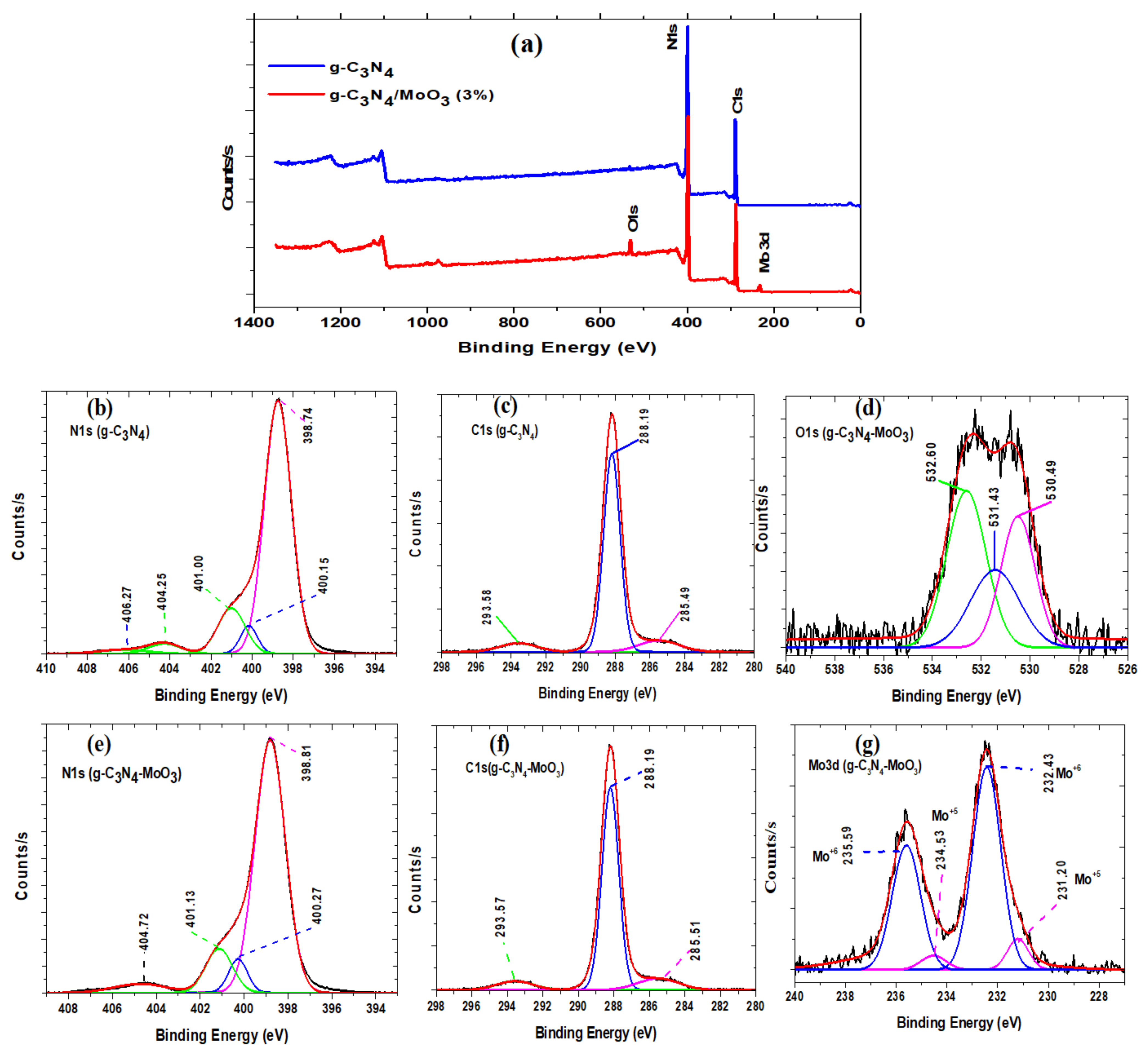
3.1. Material Characterizations
3.2. Adsorption Activities
3.2.1. Effect of g-C3N4 Modification on Diclofenac Removal
3.2.2. Diclofenac Concentration and Solution pH Effect on Adsorption
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dose and Temperature
3.2.4. Reaction Kinetics
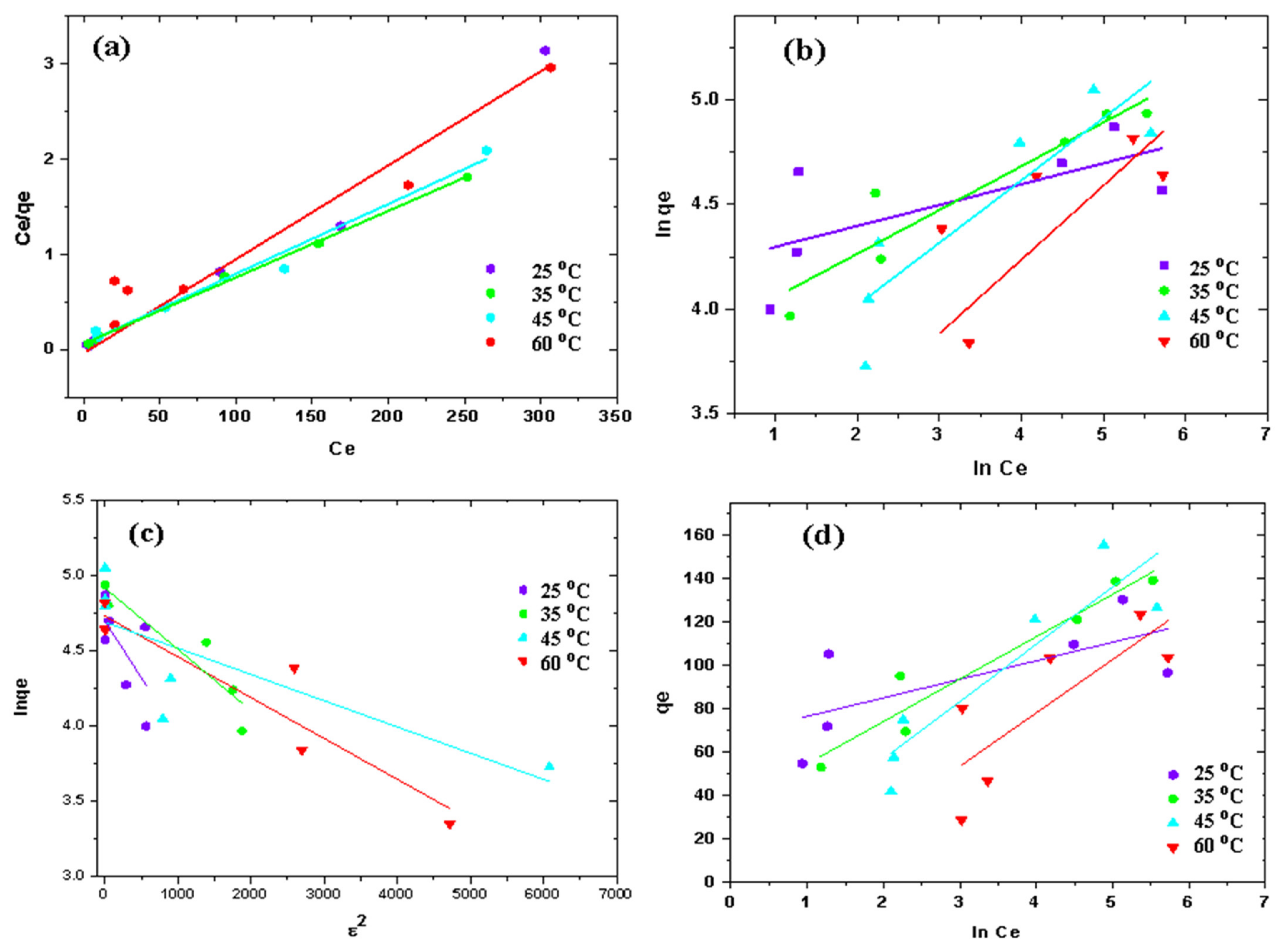
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Reusability of g-C3N4/MoO3 (3%) Nanohybrid
3.5. Comparison of g-C3N4/MoO3 (3%) with Other Literature Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lonappan, L.; Brar, S.K.; Das, R.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Diclofenac and its transformation products, Environmental occurrence and toxicity-A review. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGettigan, P.; Henry, D. Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that elevate cardiovascular risk, an examination of sales and essential medicines lists in low-, middle-, and high-income countries. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuna, V.; Ginebreda, A.; Mor, J.R.; Petrovic, M.; Sabater, S.; Sumpter, J.; Barcelo, D. Balancing the health benefits and environmental risks of pharmaceuticals, Diclofenac as an example. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, U.; Nicell, J. Human health relevance of pharmaceutically active compounds in drinking water. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 558–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serna, R.; Jurado, A.; Vázquez-Suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence of 95 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in urban ground waters underlying the metropolis of Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozinski, J.M.; Lahti, M.; Meierjohann, A.; Oikari, A.; Kronberg, L. The anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, naproxen and ibuprofen are found in the bile of wild fish caught downstream of a wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, R.J.; Taggart, M.A.; Prakash, V.; Chakraborty, S.S.; Deori, P.; Galligan, T.; Shringarpure, R. Avian scavengers and the threat from veterinary pharmaceuticals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2014, 369, 20130574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.J.I.; Ogada, D.L.; Malik, R.N.; Virani, M.Z.; Giovanni, M.D. First evidence that populations of the critically endangered Long-billed Vulture Gyps indicus in Pakistan have increased following the ban of the toxic veterinary drug diclofenac in south Asia. Bird Conserv. Int. 2012, 22, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Bishwakarma, M.C.; Chaudhary, A.; Cuthbert, R.; Dave, R.; Kulkarni, M.; Green, R.E. The population decline of Gyps vultures in India and Nepal has slowed since veterinary use of diclofenac was banned. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaks, J.L.; Gilbert, M.; Virani, M.Z.; Watson, R.T.; Meteyer, C.U.; Rideout, B.; Mahmood, S. Diclofenac residues as the cause of vulture population decline in Pakistan. Nature 2004, 427, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BirdLife International. Gyps indicus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Dumont, E.; Williams, R.J.; Oldenkamp, R.; Cisowska, I.; Sumpter, J.P. Do concentrations of ethinylestradiol, estradiol, and diclofenac in European rivers exceed proposed EU environmental quality standards? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12297–12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoisheer, N.; Alseroury, A.; Kumar, R.; Almeelbi, T.; Barakat, M.A. Synthesis of graphene oxide/silica/carbon nanotubes composite for removal of dyes from wastewater. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Laskar, M.A.; Hewaidy, I.F.; Barakat, M.A. Modified adsorbents for removal of heavy metals from aqueous environment, a review. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, F.; Qin, X. Adsorption of diclofenac onto goethite, Adsorption kinetics and effects of pH. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.E.; Wan, J.C.; Kim, H.; Liang, C.H.; Dai, Y.D.; Chiang, P.C. Adsorption of selected pharmaceutical compounds onto activated carbon in dilute aqueous solutions exemplified by acetaminophen, diclofenac, and sulfamethoxazole. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 186501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshia, U.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Ahmed, M.J. Adsorption of endocrine disrupting compounds and other emerging contaminants using lignocellulosic biomass-derived porous carbons, A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, V.; Sanchis, J.; Abad, J.L.; Ginebreda, A.; Farre, M.; Perez, S.; Barcelo, D. Investigating the formation and toxicity of nitrogen transformation products of diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole in wastewater treatment plants. J. Hazard Mater. 2016, 309, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, I.; Hapeshi, E.; Osorio, V.; Perez, S.; Petrovic, M.; Zapata, A.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Solar photocatalytic treatment of trimethoprim in four environmental matrices at a pilot scale, Transformation products and eco-toxicity evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmelek, S.B.; Greaves, J.; Ishida, K.P.; Cooper, W.J.; Song, W. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products from reverse osmosis retentate using advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3665–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouei, F.; Noorizadeh, H.; Nekouei, S.; Asif, M.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Removal of malachite green from aqueous solutions by cuprous iodide–cupric oxide nano-composite loaded on activated carbon as a new sorbent for solid phase extraction, Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, H.T.; Wang, X.; Xue, B.; Li, Y.X.; Cao, Y. A new and environmentally benign precursor for the synthesis of mesoporous g C3N4 with tunable surface area. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4510–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A.; Alseroury, F.A. Oxidized g-C3N4/polyaniline nanofiber composite for the selective removal of hexavalent chromium. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Ai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. β-Cyclodextrin modified graphitic carbon nitride for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solution, experimental and theoretical calculation study. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14170–14179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, M.; Morales-Luna, M.; Santoyo-Salazar, J.; Crotte-Ledesma, H.; García-Tinoco, P.E.; Tomás, S.A. Improved adsorption and photocatalytic removal of Methylene Blue by MoO3 thin films, Role of the sputtering power, film thickness, and sputtering working pressure. Catal. Today 2021, 360, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakass, S.; Hassani, H.O.; Abboudi, M.; Kooli, F.; Mohmoud, A.; Aljuhani, A.; Al Wadaani, F. Molybdenum trioxide, efficient nanosorbent for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. Molecules 2018, 23, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, X.; Zuo, Y.; Cui, L. Synthesis of Mo-doped graphitic carbon nitride catalysts and their photocatalytic activity in the reduction of CO2 with H2O. Catal. Commun. 2016, 74, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Beltrán, M.; Paraguay-Delgado, F.; García, R.; Antúnez-Flores, W.; Ornelas-Gutiérrez, C.; Santos-Beltrán, A. Fast methylene blue removal by MoO3 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 28, 2935–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; He, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Kong, L. A 2D-g-C3N4 nanosheets as an eco-friendly adsorbent for various environmental pollutants in water. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Reis, R.A.; Rossa, V.; Reis, M.M.; Costa, A.L.; Veloso, C.O.; Chiaro, S.S. Silica–alumina impregnated with cerium, nickel, and molybdenum oxides for adsorption of sulfur and nitrogen compounds from diesel. Mater. Lett. 2012, 83, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Xia, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, H. Synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4/MoO3 photocatalyst with improved visible-light photoactivity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyki, M.H.; Mohammadirad, M.; Shemirani, F.; Saboury, A.A. Magnetic cellulose ionomer/layered double hydroxide, an efficient anion exchange platform with enhanced diclofenac adsorption property. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 157, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gao, S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Dai, Y.; Lu, J. In-situ-reduced synthesis of Ti3+ self-doped TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunctions with high photocatalytic performance under LED light irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9023–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H. Crosslinked g-C3N4/rGO nanocomposites with tunable band structure and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Small 2013, 9, 3336–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W. One-pot synthesis of K-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible-light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zeng, X.; Gao, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Dai, Y.; Lu, J. Ultrasonic-assisted pyrolyzation fabrication of reduced SnO2–x/g-C3N4 heterojunctions, enhance photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic activity under visible LED light irradiation. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Lv, W.; Liu, G. Construction of carbon dots modified MoO3/g-C3N4 Z-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for the degradation of tetracycline. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 229, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Taoufik, N.; García, A.M.; Korili, S.A. Comparative removal of emerging contaminants from aqueous solution by adsorption on an activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, C.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Lu, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, J. Enhanced adsorption of pharmaceuticals onto core-brush shaped aromatic rings-functionalized chitosan magnetic composite particles, Effects of structural characteristics of both pharmaceuticals and brushes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, A.R.; Tsyshevsky, R.V.; Trotochaud, L.; Yu, Y.; Kyhl, L.; Lu, O.K.; Kuklja, M.M.; Bluhm, H. Adsorption of dimethyl methylphosphonate on MoO3, the role of oxygen vacancies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 29077–29088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirbazari, A.E.; Saberikhah, E.; Badrouh, M.; Emami, M.S. Alkali treated Foumanat tea waste as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 6, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, K.Y.; Chee, J.M.C.; Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Saint, C.; Poh, P.E.; Aryal, R. Evaluation of physicochemical methods in enhancing the adsorption performance of natural zeolite as low-cost adsorbent of methylene blue dye from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 118, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomao, G.R.; Pinheiro, J.H.P.A.; Isique, W.D.; Torres, N.H.; Cruz, I.A.; Ferreira, L.F.R. Diclofenac removal in water supply by adsorption on composite low-cost material. Environ. Technol. 2019, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.S.M.; Ramos, R.L.; Ortega, E.P. Sorption of diclofenac from aqueous solution on an Organobentonite and adsorption of cadmium on organobentonite saturated with diclofenac. Clay Clay Miner. 2018, 66, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Huang, L.; Shuai, Q. Facile synthesis of porous carbon for the removal of diclofenac sodium from water. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15051–15060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, Z. Removal of diclofenac from aqueous solution with multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified by nitric acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.Y.A.; Yang, H.; Lee, W.D. Enhanced removal of diclofenac from water using a zeolitic imidazole framework functionalized with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81330–81340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larous, S.; Meniai, A.H. Adsorption of Diclofenac from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from olive stones. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 10380–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, M.; Suresh, S.; Garg, A. Tea waste derived activated carbon for the adsorption of sodium diclofenac from wastewater, adsorbent characteristics, adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2018, 25, 32210–32220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, V.O.; Pereira, M.C.; Aquino, S.F.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Correa, S.; Ramalho, T.C.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Silva, A.C. Adsorption of diclofenac on a magnetic adsorbent based on maghemite, experimental and theoretical studies. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.A.E.; Carvalho, C.B.; Bonetto, M.M.; Soares, R.P.; Feris, L.A. Diclofenac removal from water by adsorption using activated carbon in batch mode and fixed-bed column, isotherms, thermodynamic study and breakthrough curves modelling. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, H. Adsorption of diclofenac and triclosan in aqueous solution by purified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
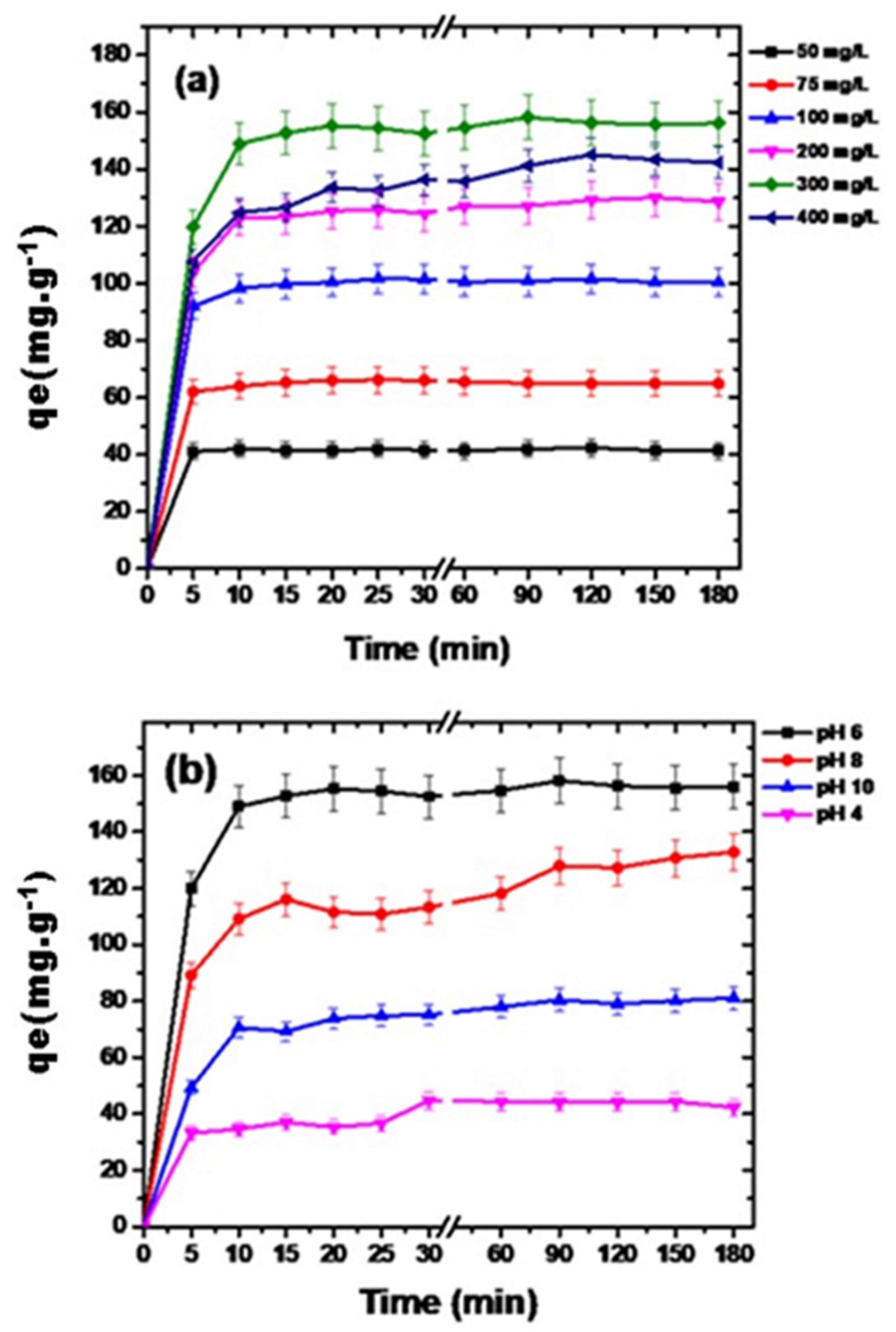
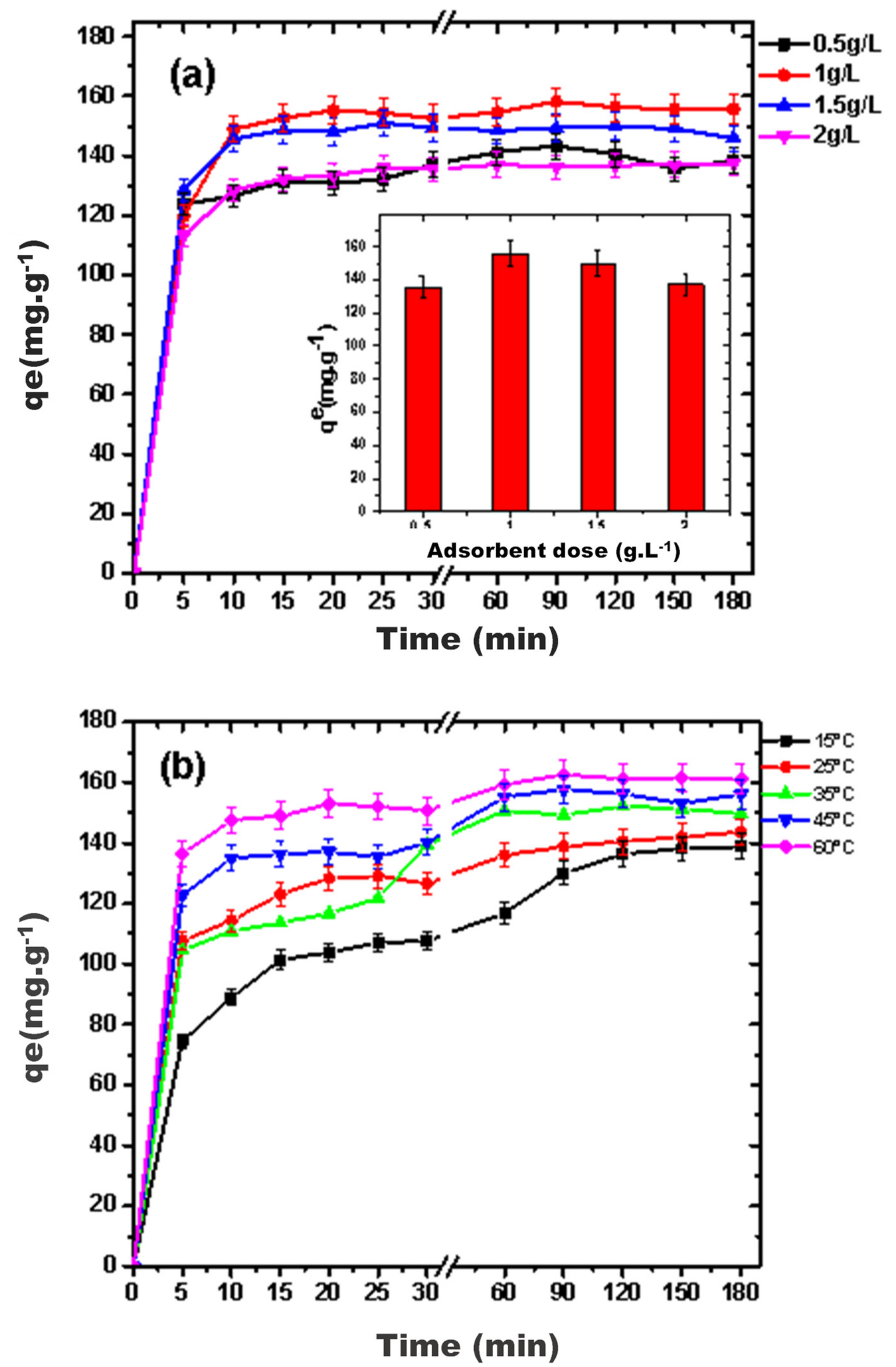
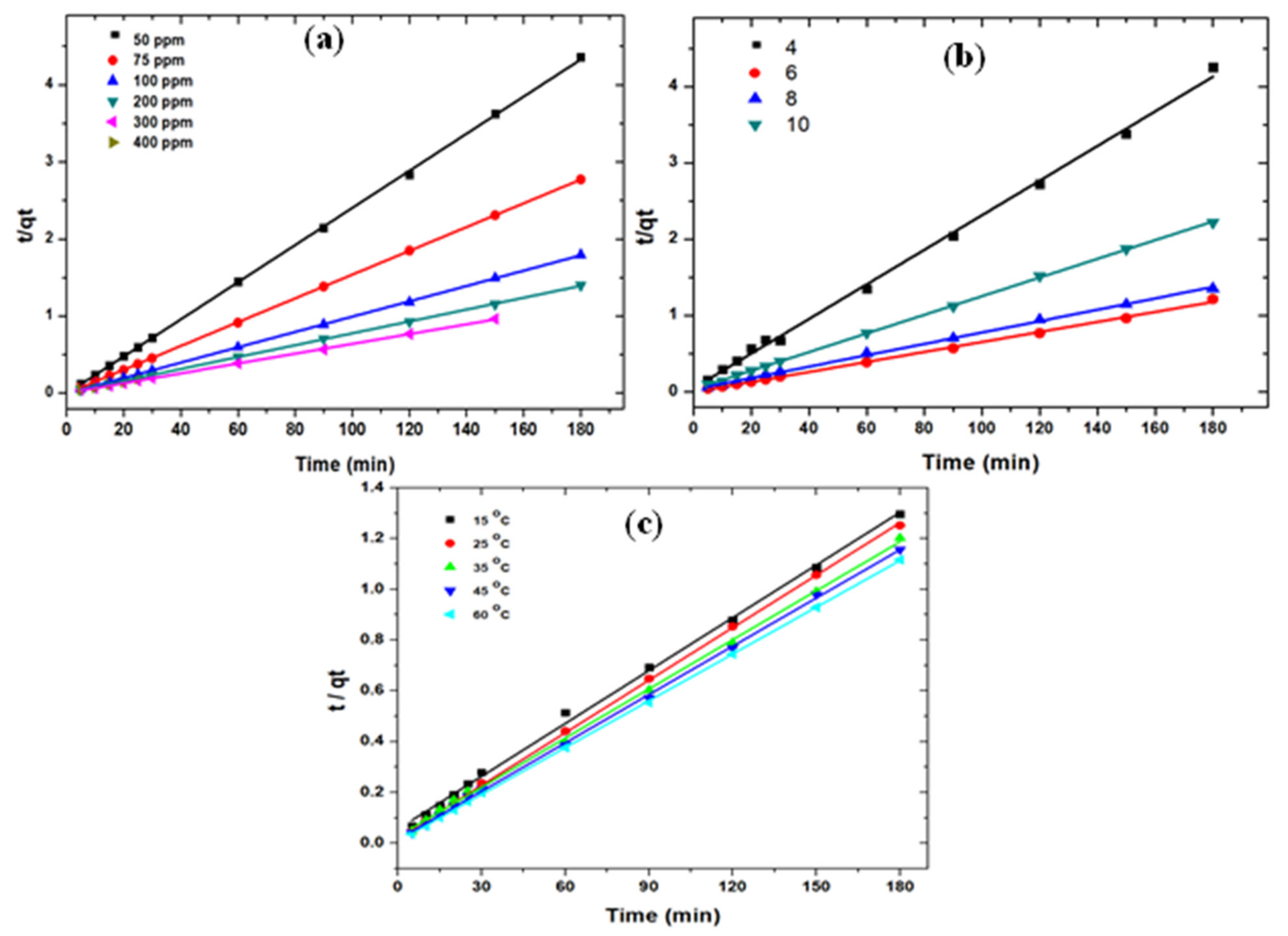
| Pseudo 1st Order Kinetics | Pseudo 2nd Order Kinetics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCF (mg L−1) | qe (exp) (mg g−1) | qe (cal) (mg g−1) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe (cal) (mg g−1) | K2 (min−1) | R2 |
| Effect of initial pollutant concentration | |||||||
| 50 | 41.96 | 1.11 | 0.0062 | 0.0784 | 42.43 | 0.0241 | 0.9999 |
| 75 | 66.1 | 39.4 | 0.0547 | 0.9472 | 67.00 | 0.0154 | 1 |
| 100 | 101.61 | 48.1 | 0.1029 | 0.8777 | 99.11 | 0.0096 | 1 |
| 200 | 130 | 17.51 | 0.0049 | 0.5967 | 130.3 | 0.0077 | 0.999 |
| 300 | 158.2 | 26.6 | 0.0093 | 0.4501 | 155.00 | 0.0062 | 0.9977 |
| 400 | 145.10 | 36.88 | 0.0053 | 0.6345 | 147.00 | 0.0070 | 0.9993 |
| Effect of pH Change | |||||||
| 4 | 44.75 | 23.68 | 0.010204 | 0.5871 | 44.96 | 0.0228 | 0.998 |
| 6 | 158 | 26.64 | 0.009379 | 0.4501 | 165 | 0.0066 | 0.9987 |
| 8 | 132.86 | 41.5 | 0.003734 | 0.8179 | 132.40 | 0.0075 | 0.9987 |
| 10 | 81.12 | 18.42 | 0.004386 | 0.7094 | 80.94 | 0.0123 | 0.9997 |
| Effect of solution temperature | |||||||
| 15 | 138.81 | 80.96 | 0.005558 | 0.9548 | 134.88 | 0.007 | 0.9972 |
| 25 | 143.71 | 38.58 | 0.004168 | 0.8408 | 142.5 | 0.0069 | 0.9996 |
| 35 | 152.1 | 75.56 | 0.008728 | 0.826 | 150.4 | 0.0065 | 0.9988 |
| 45 | 157.69 | 68.41 | 0.010421 | 0.8403 | 159 | 0.0064 | 0.9994 |
| 60 | 162.58 | 43.1 | 0.009336 | 0.6885 | 163.89 | 0.0062 | 0.9999 |
| Temperature | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isotherms | 25 °C | 35 °C | 45 °C | 60 °C |
| LangmuirIsotherm | ||||
| qm (mg g−1) | 101 | 142 | 137 | 123 |
| b (L mg−1) | 0.25 | 0.121 | 0.124 | 0.030 |
| R2 | 0.9786 | 0.9978 | 0.9838 | 0.9474 |
| FreundlichIsotherm | ||||
| Kf | 66.54 | 46.84 | 30.63 | 16.8 |
| nf | 10 | 4.8 | 3.4 | 2.83 |
| R2 | 0.477 | 0.8879 | 0.7936 | 0.5498 |
| Dubinin-RadushkevichIsotherm | ||||
| qm (mg g−1) | 114 | 115 | 137 | 107 |
| β (mol2 kJ−2) | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0016 |
| E (kJ mol−1) | 70.71 | 70.71 | 31.62 | 17.67 |
| R2 | 0.7239 | 0.6976 | 0.931 | 0.5662 |
| TemkinIsotherm | ||||
| B | 8.5666 | 19.596 | 26.47 | 24.681 |
| A (L mg−1) | 36.124 | 69.6 | 35.63 | 74.77 |
| b (J mol−1) | 24.26 | 14.85 | 14.134 | 20.2 |
| R2 | 0.4748 | 0.9303 | 0.8283 | 0.6401 |
| Adsorbent | Solution pH | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4/MoO3 (3%) | 6 | 162 | This study |
| Goethite | 5.23 | 0.046 | [15] |
| Chitosan/Fe3O4 composite | 6 | 151 | [41] |
| Functionalized sugarcane bagasse ash | 7 | 0.57 | [44] |
| Organobentonite (OBHDTMA) | 7 | 388 | [45] |
| Porous carbon prepared at 1000 °C (PC-1000) | 6.5 | 392 | [46] |
| Porous Carbon (PC-800) | 6.5 | 186 | [46] |
| CNT/HNO3 | 7 | 24 | [47] |
| CTAB-ZIF-67 | 6.5 | 61 | [48] |
| Activated carbon prepared from olive stones | 2 | 8.8 | [49] |
| Tea waste derived activated carbon | 6.47 | 62 | [50] |
| γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles | 7 | 261 | [51] |
| Granular activated carbon | 5.5 | 46.22 | [52] |
| Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes | 6 | 19.9 | [53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, J.; Saleemi, F.; Akram, B.; Wang, L.; Hussain, N.; Xu, M. Facile Synthesis of g-C3N4/MoO3 Nanohybrid for Efficient Removal of Aqueous Diclofenac Sodium. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061564
Rashid J, Saleemi F, Akram B, Wang L, Hussain N, Xu M. Facile Synthesis of g-C3N4/MoO3 Nanohybrid for Efficient Removal of Aqueous Diclofenac Sodium. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061564
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Jamshaid, Faryal Saleemi, Bilal Akram, Lin Wang, Naveed Hussain, and Ming Xu. 2021. "Facile Synthesis of g-C3N4/MoO3 Nanohybrid for Efficient Removal of Aqueous Diclofenac Sodium" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061564
APA StyleRashid, J., Saleemi, F., Akram, B., Wang, L., Hussain, N., & Xu, M. (2021). Facile Synthesis of g-C3N4/MoO3 Nanohybrid for Efficient Removal of Aqueous Diclofenac Sodium. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061564