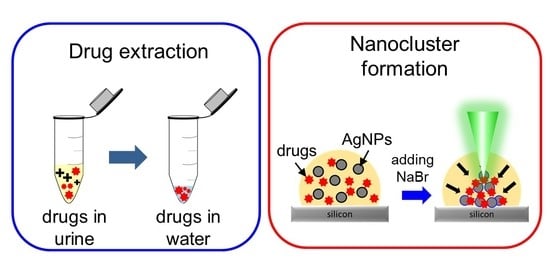
Rapid Formation of Nanoclusters for Detection of Drugs in Urine Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of AgNPs
2.3. Urine Sample Pretreatment
2.4. SERS Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formation of SERS-Active Nanoclusters
3.2. Detection of MC and 4-MMC in Water
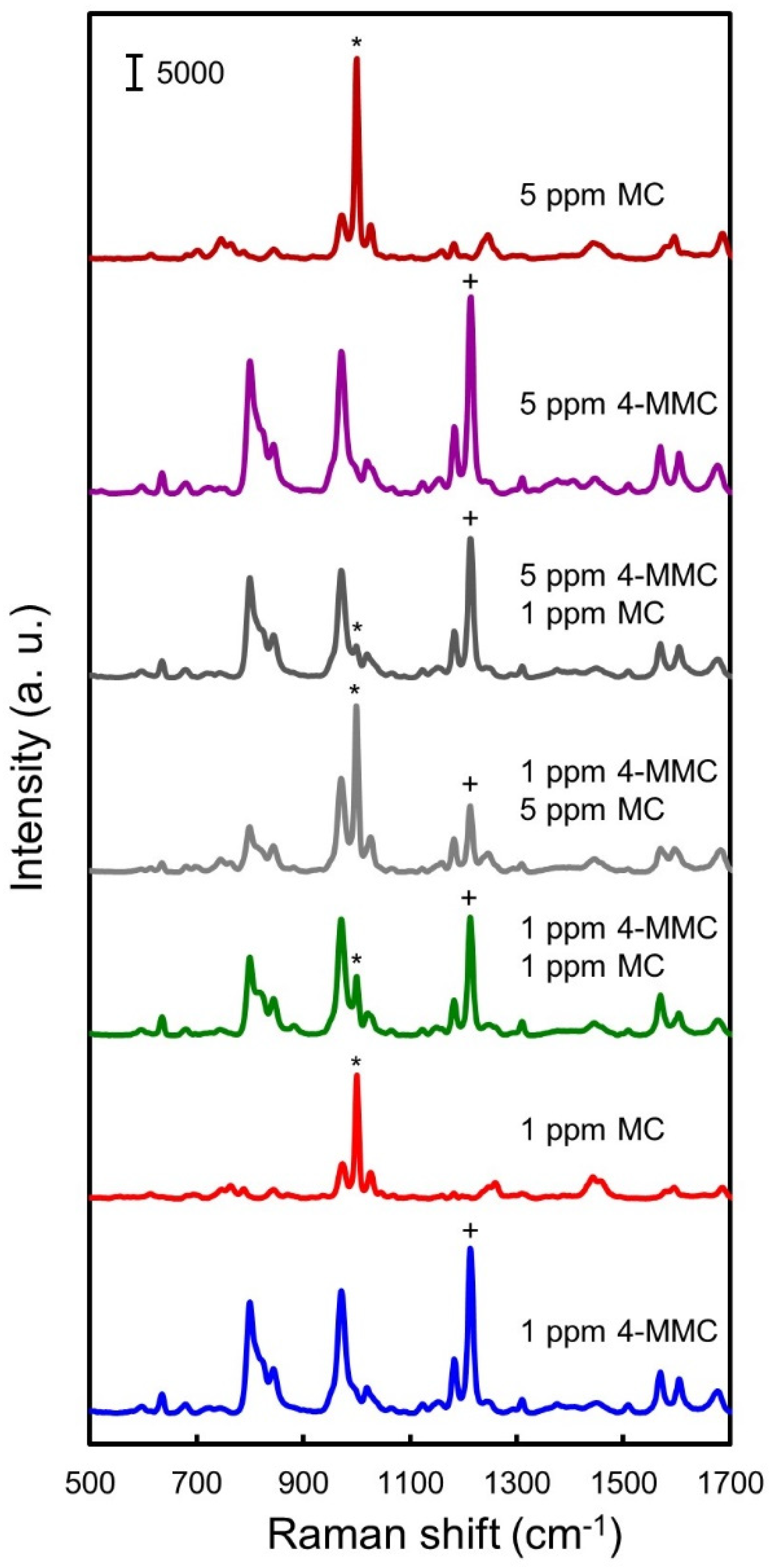
3.3. Simultaneous Detection of MC and 4-MMC in Water
3.4. Urine Sample Pretreatment
3.5. Simultaneous Detection of MC and 4-MMC in Urine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Dai, I.; Harmon, T.; Bernert, J.T. Simultaneous determination of multiple drugs of abuse and relevant metabolites in urine by LC-MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2007, 31, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Lechago, J. Rapid and simultaneous determination of multiple classes of abused drugs and metabolites in human urine by a robust LC-MS/MS method—Application to urine drug testing in pain clinics. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentin, T.R.; Fogarty, M.; Limberger, R.P.; Logan, B.K. Determination of cutting agents in seized cocaine samples using GC-MS, GC-TMS and LC-MS/MS. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 295, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitman, A.; Park, H.D.; Fitzgerald, R.L. False-positive interferences of common urine drug screen immunoassays: A review. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 38, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelini, D.J.; Biggs, T.D.; Prugh, A.M.; Smith, J.A.; Hanburger, J.A.; Llano, B.; Avelar, R.; Ellis, A.; Lusk, B.; Naanaa, A.; et al. Detection of fentanyl and derivatives using a lateral flow immunoassay. Forensic Chem. 2021, 23, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruperez, A.; Montes, R.; Laserna, J.J. Identification of stimulant-drugs by surface-enhanced Raman-spectrometry on colloidal silver. Vib. Spectrosc 1991, 2, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, L.; Garcia-Ramos, J.V.; Domingo, C.; Sanchez-Cortes, S. Sensing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with dithiocarbamate-functionalized Ag nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-A.; Li, W.-E.; Lin, D.-Z.; Chen, Y.-F. Three-dimensional SERS substrates formed with plasmonic core-satellite nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugandzic, V.; Kupfer, S.; Jahn, M.; Henkel, T.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J. A SERS-based molecular sensor for selective detection and quantification of copper(II) ions. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 279, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, A.; Giovannozzi, A.M.; Mandrile, L.; Sacco, A.; Rossi, A.M.; Taglietti, A. In situ seed-growth synthesis of silver nanoplates on glass for the detection of food contaminants by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Talanta 2020, 216, 120936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriu, C.; Conticello, I.; Mebel, A.M.; McCord, B. Micro solid phase extraction surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (μ-SPE/SERS) screening test for the detection of the synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 in oral fluid. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4780–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Lei, C.; Zhang, S. Proximity-dependent isothermal cycle amplification for small-molecule detection based on surface enhanced Raman scattering. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 51, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, N.D.; Tripathi, A.; Mirsafavi, R.; Pardoe, I.; Moskovits, M.; Meinhart, C.; Guicheteau, J.A.; Christesen, S.D.; Fountain, A.W. Optimization of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy conditions for implementation into a microfluidic device for drug detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10513–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Tang, X.H.; Zhou, B.B.; Xie, Q.W.; Yang, L.B. Designing of ordered two-dimensional gold nanoparticles film for cocaine detection in human urine using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2017, 164, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Chong, X.; Squire, K.; Wang, A.X. Microfluidic diatomite analytical devices for illicit drug sensing with ppb-Level sensitivity. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 259, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameku, W.A.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Ataide, V.N.; Ferreira Santos, M.S.; Gutz, I.G.R.; Araki, K.; Paixão, T.R.L.C. Combined colorimetric and electrochemical measurement paper-based device for chemometric proof-of-concept analysis of cocaine samples. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masterson, A.N.; Hati, S.; Ren, G.; Liyanage, T.; Manicke, N.E.; Goodpaster, J.V.; Sardar, R. Enhancing nonfouling and sensitivity of surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates for potent plasma via fabrication of a flexible plasmonic patch. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2578–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, H.; Fukuoka, T.; Itoh, T.; Imai, Y.; Iwata, Y.T.; Yamamuro, T.; Kuwayama, K.; Tsujikawa, K.; Kanamori, T.; Inoue, H. Rapid detection of hypnotics using surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on gold nanoparticle co-aggregation in a wet system. Analyst 2019, 144, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, P.; Zhou, B.; Tang, X.; Li, X.; Weng, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Optimal hotspots of dynamic surfaced-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for drugs quantitative detection. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4875–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dies, H.; Raveendran, J.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. Rapid identification and quantification of illicit drugs on nanodendritic surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 257, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tanemura, M.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, F.; Nogami, M. Controlled fabrication of silver nanoneedles array for SERS and their application in rapid detection of narcotics. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2663–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Cao, C.; Li, P.; Mao, M.; Xie, Q.; Yang, L. Sensitive and simple determination of zwitterionic morphine in human urine based on liquid-liquid micro-extraction coupled with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 186, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Qiu, G.; Ye, W.; Li, Y.; Harris, R.A.; Jiang, C. Group-targeting SERS screening of total benzodiazepines based on large-size (111) faceted silver nanosheets decorated with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3403–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, C.; Hoonejani, M.R.; Barmi, M.R.; Moskovits, M.; Meinhart, C.D. Rapid detection of drugs of abuse in saliva using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and microfluidics. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7157–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Z.; Liu, H.L.; Meng, J.; Yang, L.B.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.H. Portable kit for identification and detection of drugs in human urine using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9500–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Weng, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Detection and direct readout of drugs in human urine using dynamic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and support vector machines. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Weng, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Three-dimensional surface-enhanced Raman scattering hotspots in spherical colloidal superstructure for identification and detection of drugs in human urine. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Mao, M.; Meng, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on liquid interfacial nanoparticle arrays for multiplex detecting drugs in urine. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8145–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuntawong, N.; Eiamchai, P.; Somrang, W.; Denchitcharoen, S.; Limwichean, S.; Horprathum, M.; Patthanasettakul, V.; Chaiya, S.; Leelapojanaporn, A.; Saiseng, S. Detection of methamphetamine/amphetamine in human urine based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and acidulation treatments. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2017, 239, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, B.; Han, F.Y.; Qin, Z.N.; Feng, Y.Q.; Hu, J.M.; Shen, A.G. On-site and quantitative detection of trace methamphetamine in urine/serum samples with a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active microcavity and rapid pretreatment device. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13539–13549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulds, K.; Smith, W.E.; Graham, D.; Lacey, R.J. Assessment of silver and gold substrates for the detection of amphetamine sulfate by surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Analyst 2002, 127, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turzhitsky, V.; Zhang, L.; Horowitz, G.L.; Vitkin, E.; Khan, U.; Zakharov, Y.; Qiu, L.; Itzkan, I.; Perelman, L.T. Picoanalysis of drugs in biofluids with quantitative label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Small 2018, 14, 1802392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Bell, S.E.J. Modification of Ag nanoparticles with mixed thiols for improved SERS detection of poorly adsorbing target molecules: Detection of MDMA. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4523–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.W.Y.; Silverson, V.A.D.; Jones, L.E.; Ho, Y.C.; Fletcher, N.C.; McNaul, M.; Peters, K.L.; Speers, S.J.; Bell, S.E.J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of novel psychoactive substances using polymer-stabilized Ag nanoparticle aggregates. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muhamadali, H.; Watt, A.; Xu, Y.; Chisanga, M.; Subaihi, A.; Jones, C.; Ellis, D.I.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Goodacre, R. Rapid detection and quantification of novel psychoactive substances (NPS) using Raman spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquharson, S.; Lee, Y.H. Trace drug analysis by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Proc. SPIE 2000, 4200, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, W.S.; Laserna, J.J.; Angebranndt, M.J.; Winefordner, J.D. Surface-enhanced Raman analysis of sulfa drugs on colloidal silver dispersion. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Yang, L.B.; Liu, J.H. Three-dimensional SERS hot spots for chemical sensing: Towards developing a practical analyzer. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lee, Y.H.; Phang, I.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Ling, X.Y. Hierarchical 3D SERS substrates fabricated by integrating photolithographic microstructures and self-assembly of silver nanoparticles. Small 2014, 10, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Yang, Z.L.; Meng, L.Y.; Sun, Y.D.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.B.; Liu, J.H.; Tian, Z.Q. Three-dimensional and time-ordered surface-enhanced Raman scattering hotspot matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5332–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Fang, J.M.; Xu, J.F.; Wang, F.; Sun, B.; He, S.N.; Sun, G.P.; Liu, H.L. A hanging plasmonic droplet: Three-dimensional SERS hotspots for a highly sensitive multiplex detection of amino acids. Analyst 2015, 140, 2973–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.D.; Han, Z.Z.; Liu, H.L.; He, S.N.; Yang, L.B.; Liu, J.H. Three-dimensional hotspots in evaporating nanoparticle sols for ultrahigh Raman scattering: Solid-liquid interface effects. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6619–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.K.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.F. Glycerol-assisted construction of long-life three-dimensional surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot spot matrix. Langmuir 2019, 35, 15795–15804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, S.; Praharaj, S.; Basu, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Jana, S.; Pande, S.; Vo-Dinh, T.; Jiang, H.; Pal, T. Self-assembly of silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, optical properties, and application in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 13436–13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.W.; Chan, S.; Sun, L.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.W.; Berlin, A.A. Specific chemical effects on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for ultra-sensitive detection of biological molecules. Appl. Spectrosc. 2004, 58, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Metters, J.P.; Khreit, O.I.G.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Banks, C.E. Forensic electrochemistry applied to the sensing of new psychoactive substances: Electroanalytical sensing of synthetic cathinones and analytical validation in the quantification of seized street samples. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9985–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-C.; Hong, S.-W.; Wu, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-F. Rapid Formation of Nanoclusters for Detection of Drugs in Urine Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071789
Chen Y-C, Hong S-W, Wu H-H, Wang Y-L, Chen Y-F. Rapid Formation of Nanoclusters for Detection of Drugs in Urine Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071789
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yun-Chu, Shang-Wen Hong, Huang-Hesin Wu, Yuh-Lin Wang, and Yih-Fan Chen. 2021. "Rapid Formation of Nanoclusters for Detection of Drugs in Urine Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071789
APA StyleChen, Y.-C., Hong, S.-W., Wu, H.-H., Wang, Y.-L., & Chen, Y.-F. (2021). Rapid Formation of Nanoclusters for Detection of Drugs in Urine Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071789