Number Concentration Measurements of Polystyrene Submicrometer Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)—Particle Sizing
2.2. Dry Mass (DM)—Number Concentration
2.3. Flow Cytometry (FCM)
2.3.1. Submicrometer Particle Concentration Measurement Using TruCount (TC) Microspheres as an Internal Counting Standard
2.3.2. Particle Concentrations Measured Volumetrically
2.3.3. Submicrometer Sphere Size Distribution—Mie Scattering Calculation
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy (FM)—Number Concentration
2.5. Particle Tracking Analysis (PTA)
2.6. Microfluidic Resistive Pulse Sensing (MRPS)
2.7. Particle Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation–Multi-Angle Light Scattering (AF4-MALS)
2.8. Reengineered Non-Sorting Analytical Flow Cytometer—Virus Counter (VC)
3. Results
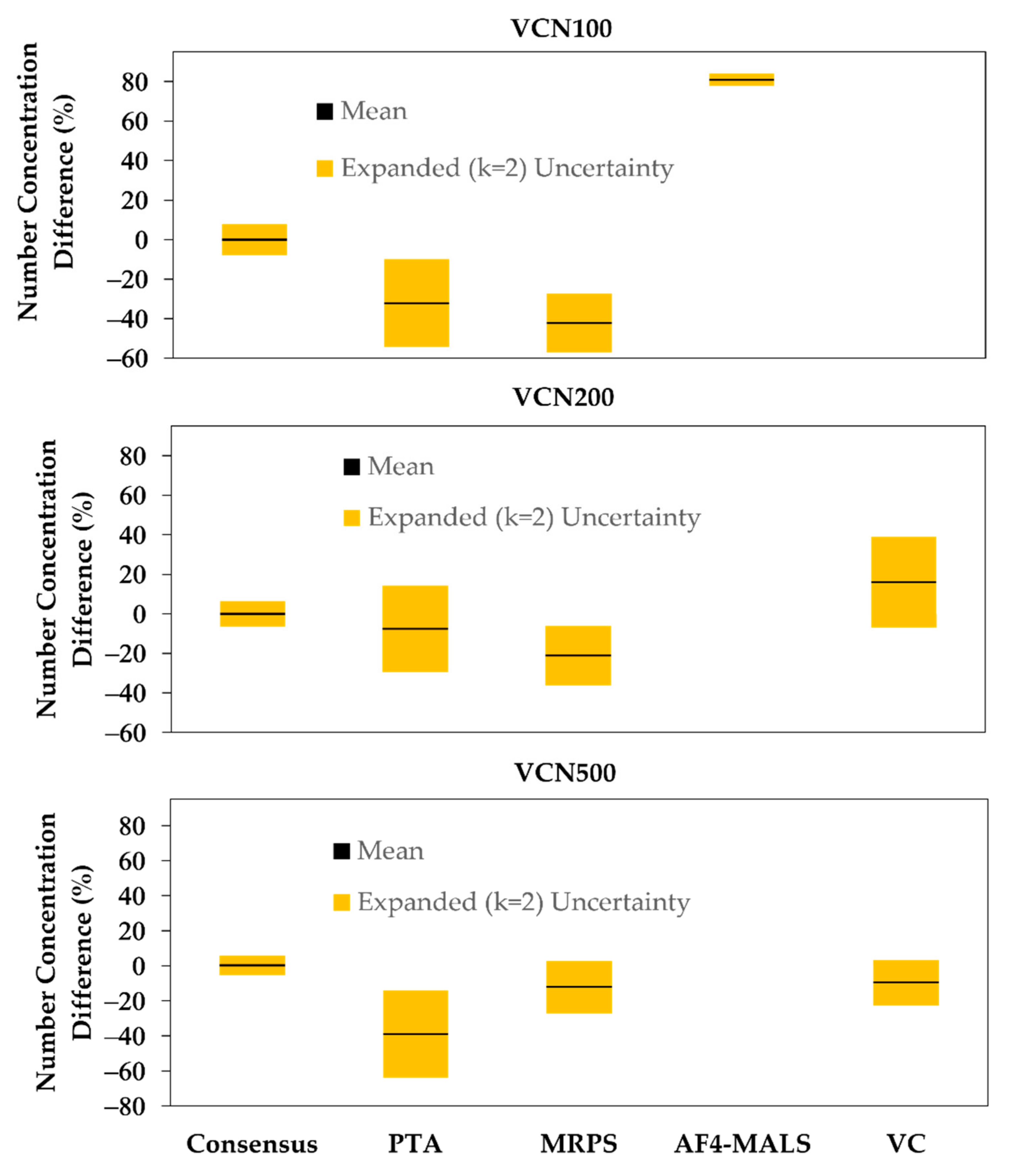
3.1. Number Concentration
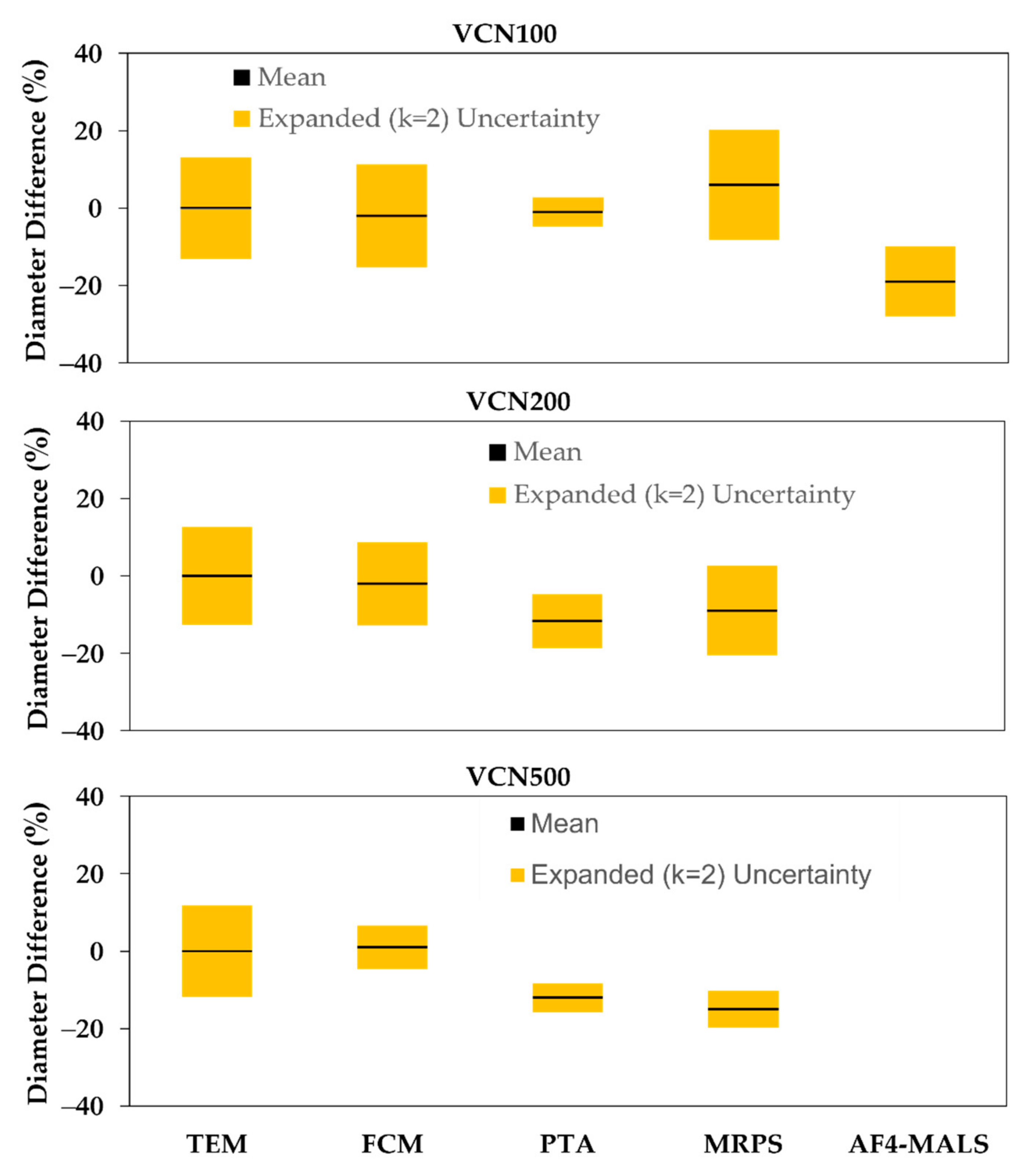
3.2. Diameter
4. Discussion
4.1. Number Concentration
4.2. Diameter
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
NIST Disclaimer
References
- Gaudin, R.; Barteneva, N. Sorting of Small Infectious Virus Particles by Flow Virometry Reveals Distinct Infectivity Profiles. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, G.; Minsker, K.; Kapish, A.; Osborn, J.; Ha, S.; Davide, J.; Califano, J.P.; Sehlin, D.; Rustandi, R.R.; Dick, L.W.; et al. Flow Virometry for Process Monitoring of Live Virus Vaccines—Lessons Learned from ERVEBO. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, B.; Maragh, S.; Ghiran, I.; Jones, J.; DeRose, P.; Elsheikh, E.; Vreeland, W.N.; Wang, L. Measurement and Standardization Challenges for Extracellular Vesicle Therapeutic Delivery Vectors. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2149–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, J.; Annel, P.; Noverini, P.; Hooper, S. GMP Implementation of Online Water Bioburden Analyzers. Pharma. Eng. 2021, 41, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Benkstein, K.; Da Silva, S.; Lin, N.; Ripple, D. Evaluating changes to Ralstonia pickettii in high-purity water to guide selection of potential calibration materials for online water bioburden analyzers. J. Ind. Microbio. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, M.; Yang, D.; Kwok, S.; Rios, A.; Das, T.; Patel, A.; Wuchner, K.; Antochshuk, V.; Junge, F.; Bou-Assaf, G.M.; et al. A Multicompany Assessment of Submicron Particle Levels by NTA and RMM in a Wide Range of Late-Phase Clinical and Commercial Biotechnology-Derived Protein Products. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, H.; Harazono, A.; Kiyoshi, M.; Ishii-Watabe, A. Quantitative Evaluation of Insoluble Particulate Matters in Therapeutic Protein Injections Using Light Obscuration and Flow Imaging Methods. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrling, M.P.; Rychen, P. Review of Nanoparticles in Ultrapure Water: Definitions and Current Metrologies for Detection and Control. Ultrapure Micro 2017, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, E.; Montoro Bustos, A.; Blaza Toman, B.; Johnson, M.; Ellefson, M.; Caceres, G.; Mader, B. Determining what really counts: Modeling and measuring nanoparticle number concentrations. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2876–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammel, M.; Kummrow, A.; Neukammer, J. Reference measurement procedures for the accurate determination of cell concentrations: Present status and future developments. J. Lab. Med. 2012, 36, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Neukammer, J.; Kammel, M.; Höckner, J.; Kummrow, A.; Ruf, A. Reference Procedure for the Measurement of Stem Cell Concentrations in Apheresis Products. PTB Mitt. 2015, 125, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ripple, D.C.; DeRose, P.C. Primary Determination of Particle Number Concentration with Light Obscuration and Dynamic Imaging Particle Counters. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stan. Technol. 2018, 123, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeRose, P.; Tian, L.; Elsheikh, E.; Urbas, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Expanding NIST Calibration of Fluorescent Microspheres for Flow Cytometry to More Fluorescence Channels and Smaller Particles. Materials 2020, 13, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Ehara, K. Primary Standard for the Number Concentration of Liquid-borne Particles in the 10 to 20 μm Diameter Range. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruma, Y.; Sakagucchi, T.; Sakurai, H. Primary Standard for the Number Concentration of Liquid-Borne Particles: Extension of the Diameter Range from the Micrometer to the Sub-Micrometer Level and Reduction of Measurement Uncertainty. Metrologia 2021, 58, 0450007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, K.; Kurokawa, A. Measurement of the Number Concentration of Gold Nanoparticle Suspension by Scanning Electron Microscopy. Metrologia 2019, 56, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkstein, K.D.; Balakrishnan, G.; Bhirde, A.; Chalus, P.; Das, T.K.; Do, N.; Duewer, D.L.; Filonov, N.; Cheong, F.C.; Garidel, P.; et al. An Interlaboratory Comparison on the Characterization of a Sub-micrometer Polydisperse Particle Dispersion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ViroCheck Nanoparticle Reference Kit. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/V10425?SID=srch-hj-V10425 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- ApogeeMix. Available online: http://www.apogeeflow.com/apogee-mix.php (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Clinical Applications of Flow Cytometry: Quality Assurance and Immunophenotyping of Lymphocytes: Approved Guideline; NCCLS-H42-A; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 1998.
- Stebbings, R.; Wang, L.; Sutherland, J.; Kammel, M.; Gaigalas, A.K.; John, M.; Roemer, B.; Neukammer, J. Determination of CD4+ Cell Count per µL in Reconstituted Lyophilized Human PBMC Pre-labelled with Anti-CD4 FITC Antibody. Cytometry 2015, 87A, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; van der Pol, E.; Bettin, B.A.; Carter, D.R.; Hendrix, A.; Lenassi, M.; Langlois, M.A.; Llorente, A.; van de Nes, A.S.; Nieuwland, R.; et al. Towards Defining Reference Materials for Measuring Extracellular Vesicle Refractive Index, Epitope Abundance, Size and Concentration. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1816641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupert, D.L.M.; Mapar, M.; Shelke, G.V.; Norling, K.; Elmeskog, M.; Lötvall, J.O.; Block, S.; Bally, M.; Agnarsson, B.; Höök, F. Effective Refractive Index and Lipid Content of Extracellular Vesicles Revealed Using Optical Waveguide Scattering and Fluorescence Microscopy. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8522–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Macko, P.; Curran, J.; Whelan, M.; Worth, A.; Patterson, E. Settling Dynamics of Nanoparticles in Simple and Biological Media. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caicedo, J.; Cooper, S.; Heigwer, F.; Cooper, S.; Heigwer, F.; Warchal, S.; Qiu, P.; Molnar, C.; Vasilevich, A.S.; Barry, J.D.; et al. Data-analysis Strategies for Image-based Cell Profiling. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-source Platform for Biological-image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, P. Particle Tracking Analysis. In Characterization of Nanoparticles; Hodoroaba, V., Unger, W.E.S., Shard, A.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Fraikin, J.; Teesalu, T.; McKenney, C.; Ruoslahti, E.; Cleland, A. A High-throughput Label-free Nanoparticle Analyser. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulst, H.C.; van de Hulst, H.C. Light Scattering By Small Particles; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, C.A.; Kearney, B.J.; Olschner, S.P.; Williams, P.L.; Robinson, C.G.; Heinrich, M.L.; Zovanyi, A.M.; Ingram, M.F.; Norwood, D.A.; Schoepp, R.J. Evaluation of ViroCyt® Virus Counter for Rapid Filovirus Quantitation. Viruses 2015, 7, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepke, A.; Lafarge, T.; Possolo, A.; Toman, A. Consensus Building for Interlaboratory Studies, Key Comprisons and Meta-Analysis. Metrologia 2017, 54, S34–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possolo, A.; Koepke, A.; Newton, D.; Winchester, M.R. Decision Tree for Key Comparisons. J. Res. NIST 2021, 126, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defante, A.; Vreeland, W.; Benkstein, K.; Ripple, D. Using Image Attributes to Assure Accurate Particle Size and Count Using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schavkan, A.; Gollwitzer, C.; Garcia-Diez, R.; Krumrey, M.; Minelli, C.; Bartczak, D.; Cuello-Nuñez, S.; Goenaga-Infante, H.; Rissler, J.; Sjöström, E.; et al. Number Concentration of Gold Nanoparticles in Suspension: SAXS and spICPMS as Traceable Methods Compared to Laboratory Methods. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, P.J.; Weida, M.J. Method and Apparatus for Determining Absolute Number Densities of Particles in Suspension. US Patent No. US6774994B1, 10 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kestens, V.; Bozatzidis, V.; De Temmerman, P.-J.; Ramaye, Y.; Roebben, G. Validation of a Particle Tracking Analysis Method for the Size Determination of Nano- and Microparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, P.J. Submicrometer Particle Sizing by Multiangle Light Scattering following Fractionation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 197, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Technique | 100 nm Sphere | 200 nm Sphere | 500 nm Sphere | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size nm | Concentration mL−1 | Size nm | Concentration mL−1 | Size nm | Concentration mL−1 | |
| TEM and DM | 107 ± 14 | (4.0 ± 1.6) × 109 | 189 ± 24 | (1.0 ± 0.4) × 109 | 492 ± 58 | (2.5 ± 0.9) × 109 |
| FCM | 105 ± 14 | (4.4 ± 0.3) × 109 TruCount standard | 186 ± 20 | (0.90 ± 0.06) × 109 TruCount standard | 498 ± 28 | (2.6 ± 0.2) × 109 TruCount standard |
| (3.9 ± 0.3) × 109 Volumetric | (0.88 ± 0.06) × 109 Volumetric | (2.5 ± 0.2) × 109 Volumetric | ||||
| FM | N/A | (3.8 ± 0.3) × 109 | N/A | (0.8 ± 0.2) × 109 | N/A | (2.7 ± 0.2) × 109 |
| PTA | 106 ± 4 | (2.7 ± 0.6) × 109 | 175 ± 4 | (0.8 ± 0.2) × 109 | 433 ± 16 | (1.6 ± 0.4) × 109 |
| MRPS | 113 ± 16 | (2.3 ± 0.3) × 109 | 172 ± 20 | (0.7 ± 0.1) × 109 | 419 ± 20 | (2.3 ± 0.3) × 109 |
| AF4-MALS | 87 ± 8 | (7.2 ± 0.2) × 109 | ||||
| VC | N/A | (1.0 ± 0.2) × 109 | N/A | (2.4 ± 0.3) × 109 | ||
| Component | Type | d = 100 nm | d = 200 nm | d = 500 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | ||||
| Repeatability | A | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| TruCount number concentration | B | 3.0% | 3.0% | 3.0% |
| Gate choice | B | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| Background counts | B | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| Combined rel. standard uncertainty | 3.5% | 3.5% | 3.5% | |
| (b) | ||||
| Repeatability | A | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| Volume determination | B | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| Gate choice | B | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| Background counts | B | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| Other counting errors | B | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% |
| Combined rel. standard uncertainty | 3.2% | 3.2% | 3.2% | |
| (c) | ||||
| Repeatability | A | 3.3% | 12.6% | 2.9% |
| Sample cell height | B | 1.3% | 1.3% | 1.3% |
| Pixel size | B | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% |
| Background counts | B | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% |
| Combined rel. standard uncertainty | 3.6% | 12.7% | 3.3% | |
| (d) | ||||
| Diameter repeatability | A | 0.3% | 0.2% | 0.3% |
| Diameter accuracy | B | 6.5% | 6.3% | 5.9% |
| Particle segmentation | B | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% |
| Combined rel. standard uncertainty | 6.5% | 6.3% | 5.9% | |
| (e) | ||||
| Propagated diameter uncertainty | B | 20.0% | 19.0% | 18.0% |
| Mass repeatability | A | 0.5% | 1.1% | 0.4% |
| Mass accuracy | B | 1.4% | 0.4% | 0.7% |
| Combined rel. standard uncertainty | 20.1% | 19.0% | 18.0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeRose, P.C.; Benkstein, K.D.; Elsheikh, E.B.; Gaigalas, A.K.; Lehman, S.E.; Ripple, D.C.; Tian, L.; Vreeland, W.N.; Welch, E.J.; York, A.W.; et al. Number Concentration Measurements of Polystyrene Submicrometer Particles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183118
DeRose PC, Benkstein KD, Elsheikh EB, Gaigalas AK, Lehman SE, Ripple DC, Tian L, Vreeland WN, Welch EJ, York AW, et al. Number Concentration Measurements of Polystyrene Submicrometer Particles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183118
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeRose, Paul C., Kurt D. Benkstein, Elzafir B. Elsheikh, Adolfas K. Gaigalas, Sean E. Lehman, Dean C. Ripple, Linhua Tian, Wyatt N. Vreeland, Eric J. Welch, Adam W. York, and et al. 2022. "Number Concentration Measurements of Polystyrene Submicrometer Particles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183118
APA StyleDeRose, P. C., Benkstein, K. D., Elsheikh, E. B., Gaigalas, A. K., Lehman, S. E., Ripple, D. C., Tian, L., Vreeland, W. N., Welch, E. J., York, A. W., Zhang, Y.-Z., & Wang, L. (2022). Number Concentration Measurements of Polystyrene Submicrometer Particles. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183118






