An AI-Assisted and Self-Powered Smart Robotic Gripper Based on Eco-EGaIn Nanocomposite for Pick-and-Place Operation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Soft Robotic Gripper
2.2. Fabrication of Sensors
3. Results and Discussion
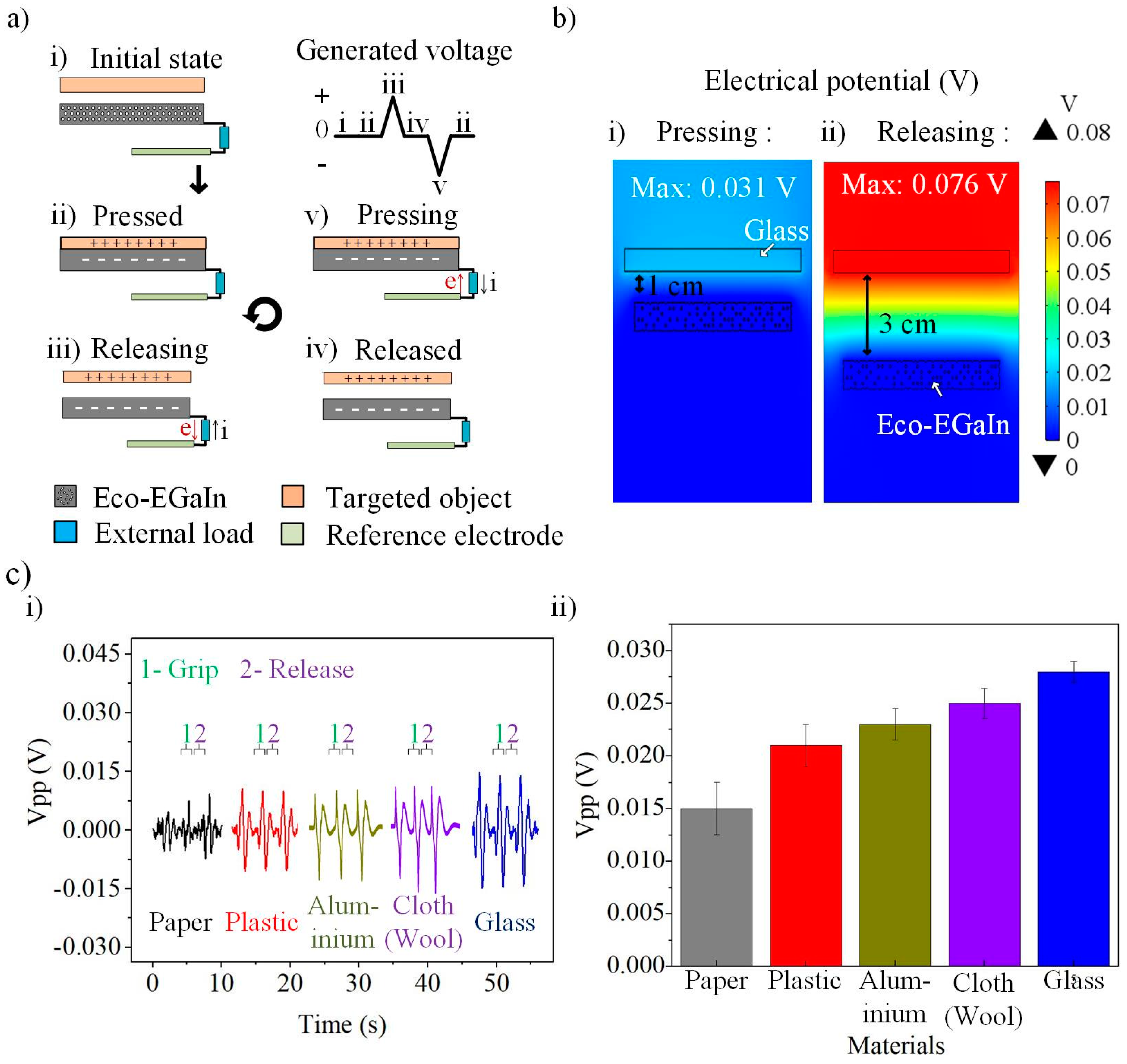
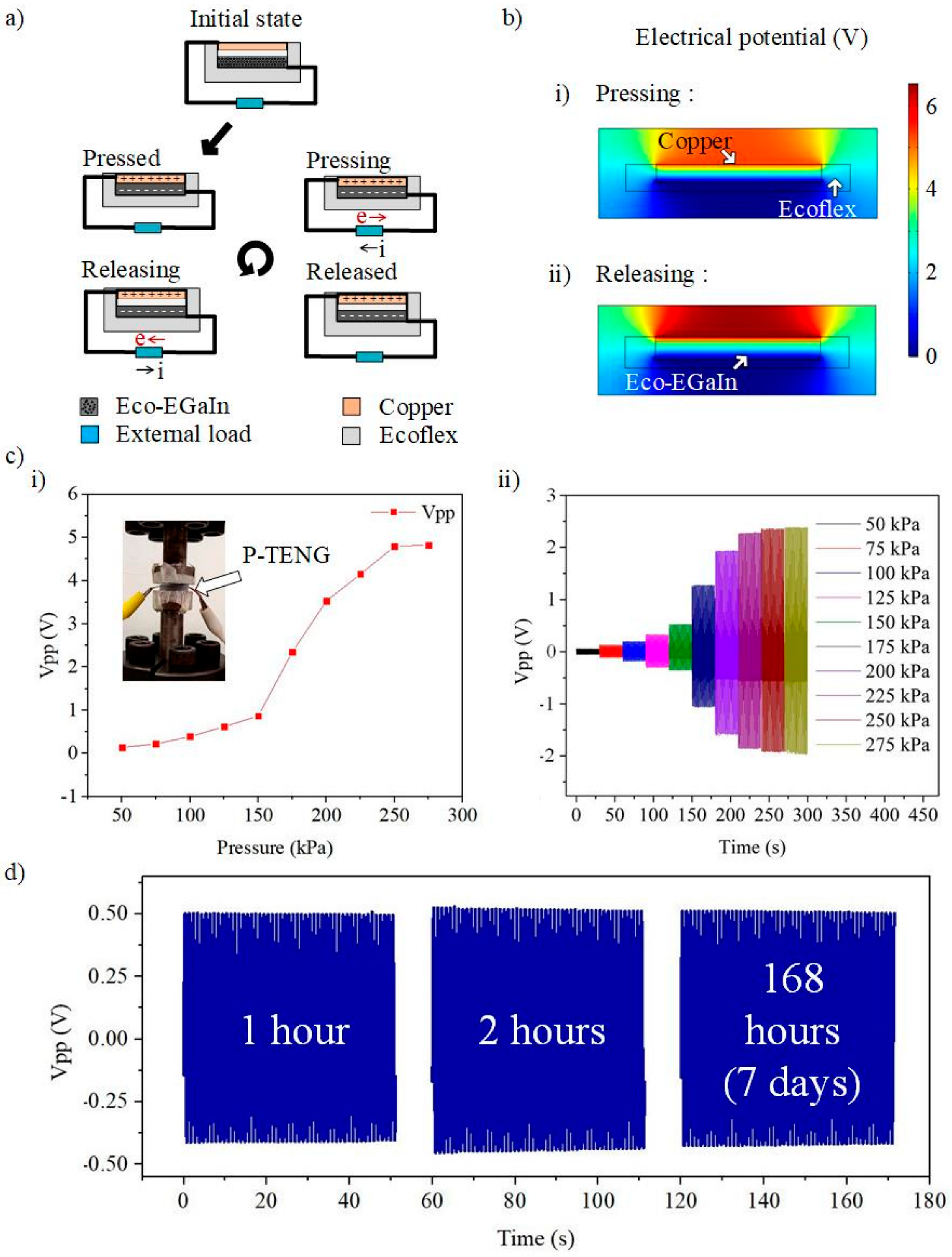
3.1. Single-Electrode Mode P-TENG Sensor
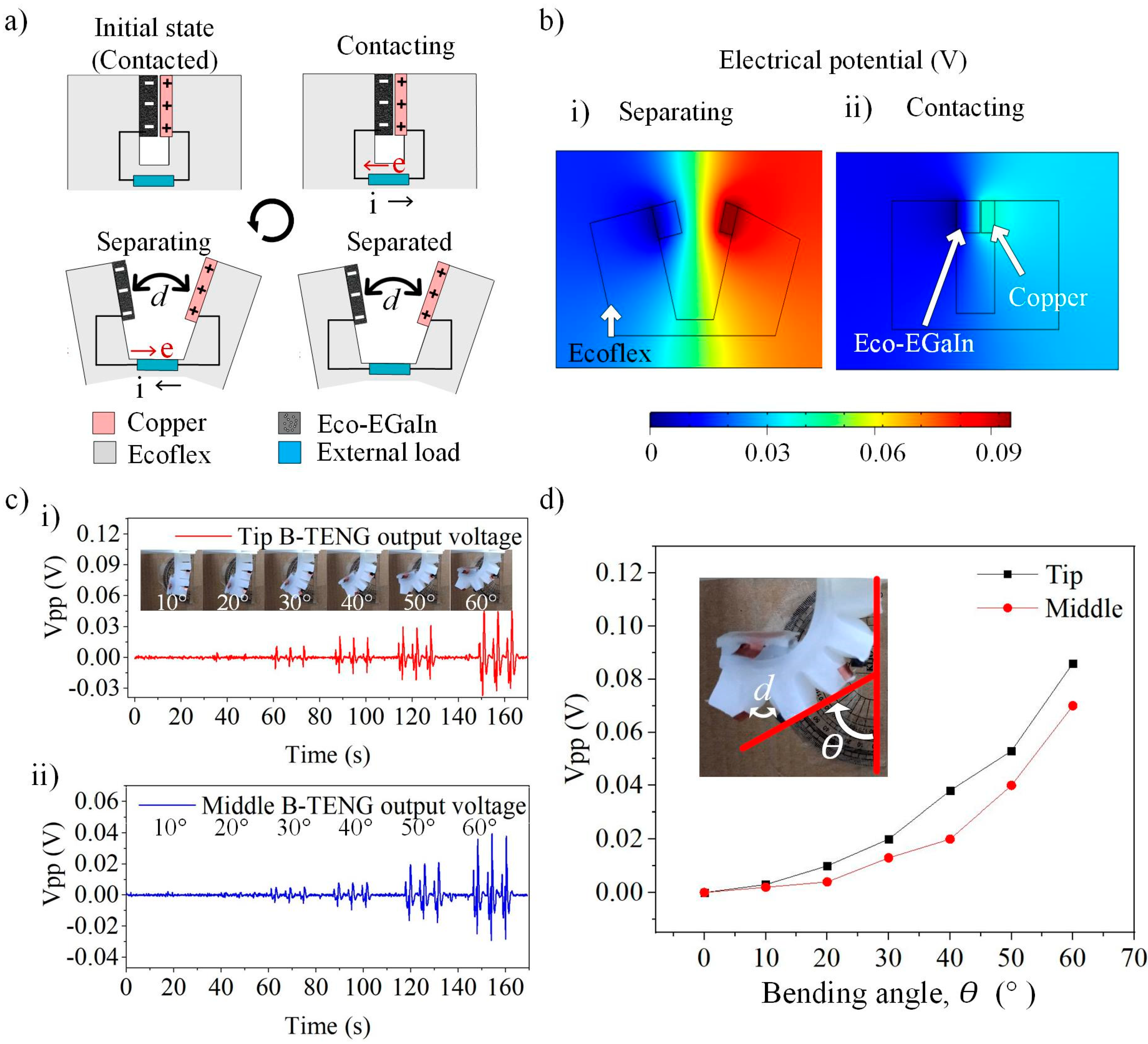
3.2. Double-Electrodes Mode P-TENG Sensor
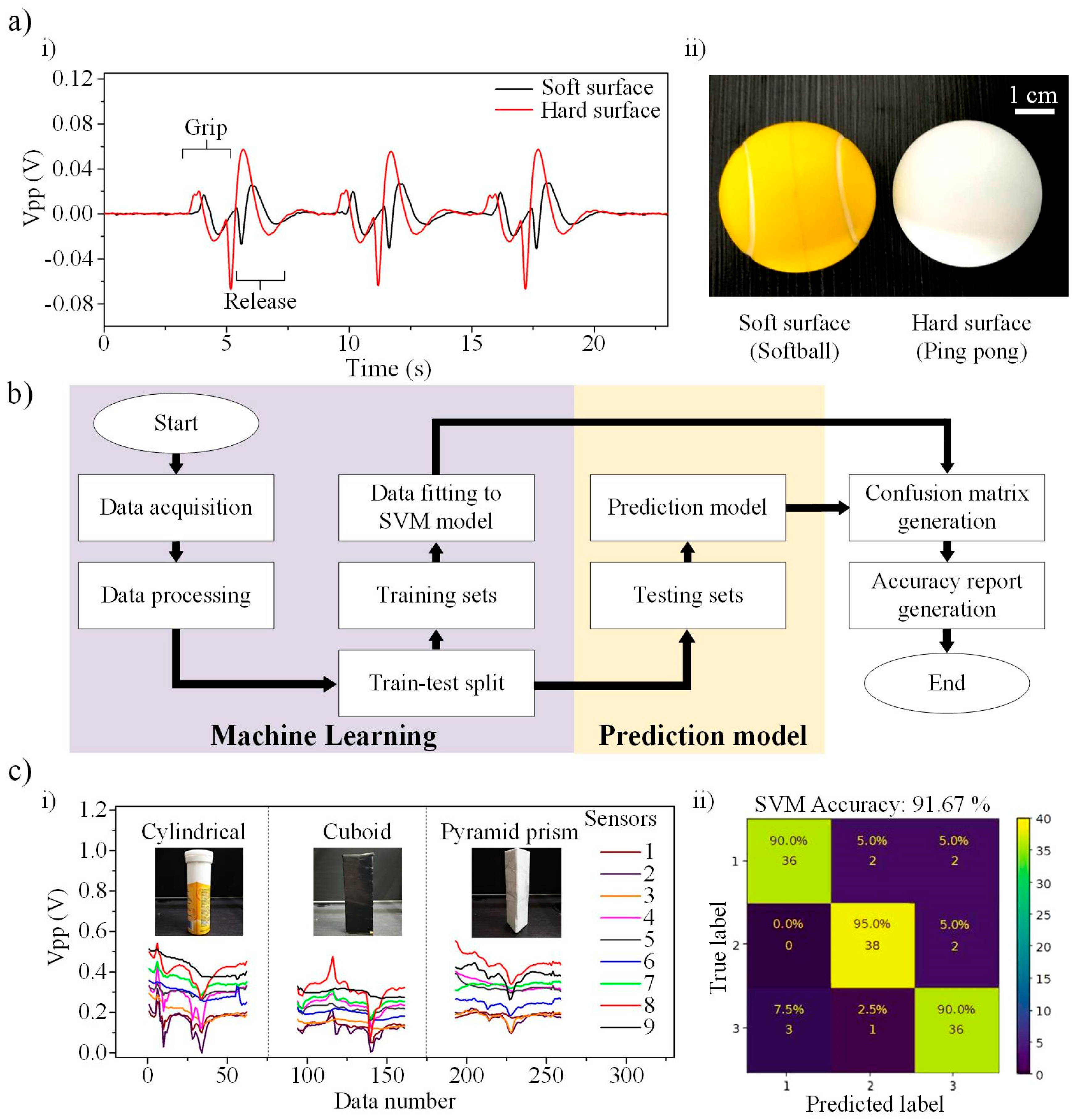
3.3. Characterisation of B-TENG Sensor
3.4. TENG Sensing and Object Recognition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dollar, A.M.; Howe, R.D. The Highly Adaptive SDM Hand: Design and Performance Evaluation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Rodenberg, N.; Amend, J.; Mozeika, A.; Steltz, E.; Zakin, M.R.; Lipson, H.; Jaeger, H.M. Universal Robotic Gripper Based on the Jamming of Granular Material. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18809–18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deimel, R.; Brock, O. A Compliant Hand Based on a Novel Pneumatic Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A.A.; Shepherd, R.F.; Morin, S.A.; Ilievski, F.; Whitesides, G.M. A Hybrid Combining Hard and Soft Robots. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Pre-Charged Pneumatic Soft Gripper with Closed-Loop Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Gong, Z.; Xie, Z.; Guan, S.; Yang, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, T.; Wen, L. Universal Soft Pneumatic Robotic Gripper with Variable Effective Length. In Proceedings of the 2016 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Chengdu, China, 27–29 July 2016; Volume 2016-August, pp. 6109–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, P.S.; Minjal, M.N.; Leow, P.L.; Ali, M.S.M. Wireless Powered Thermo-Pneumatic Micropump Using Frequency-Controlled Heater. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chee, P.S.; Nafea, M.; Leow, P.L.; Ali, M.S.M. Thermal Analysis of Wirelessly Powered Thermo-Pneumatic Micropump Based on Planar LC Circuit. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, M.; Hassan, T.; Passetti, G.; D’Elia, N.; Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M. A Bioinspired Soft Robotic Gripper for Adaptable and Effective Grasping. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slesarenko, V.; Engelkemier, S.; Galich, P.I.; Vladimirsky, D.; Klein, G.; Rudykh, S. Strategies to Control Performance of 3D-Printed, Cable-Driven Soft Polymer Actuators: From Simple Architectures to Gripper Prototype. Polymers 2018, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, J.E.; Quan, Y.J.; Wang, W.; Rodrigue, H.; Song, S.H.; Ahn, S.H. A Smart Soft Actuator Using a Single Shape Memory Alloy for Twisting Actuation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Wang, W.; Han, M.W.; Kim, T.J.Y.; Ahn, S.H. An Overview of Shape Memory Alloy-Coupled Actuators and Robots. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Wang, W.; Kim, D.R.; Ahn, S.H. Curved Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Actuators and Application to Soft Gripper. Compos. Struct. 2017, 176, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kumar, K.; Jawed, M.K.; Mohammadi Nasab, A.; Ye, Z.; Shan, W.; Majidi, C. Highly Dynamic Shape Memory Alloy Actuator for Fast Moving Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.R.; Teo, C.Y.; Leow, P.L.; Lai, K.C.; Chee, P.S. Wireless-Powered Electroactive Soft Microgripper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 055014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, M.; Truby, R.L.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Lewis, J.A.; Wood, R.J. An Integrated Design and Fabrication Strategy for Entirely Soft, Autonomous Robots. Nature 2016, 536, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidi, C. Soft Robotics: A Perspective—Current Trends and Prospects for the Future. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, M.; Bouazza-Marouf, K.; Kerr, D.; Vloeberghs, M. Robust Contact Force Controller for Slip Prevention in a Robotic Gripper. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2010, 224, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, C.; Lian, B.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Sun, T. Visual–Tactile Object Recognition of a Soft Gripper Based on Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network and Machining Learning Algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H. Clinical Usefulness of Augmented Reality Using Infrared Camera Based Real-Time Feedback on Gait Function in Cerebral Palsy: A Case Study. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faccio, M.; Ferrari, E.; Galizia, F.G.; Gamberi, M.; Pilati, F. Real-Time Assistance to Manual Assembly through Depth Camera and Visual Feedback. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hai, Y. Easy Calibration of a Blind-Spot-Free Fisheye Camera System Using a Scene of a Parking Space. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 12, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Régnier, S. Three-Dimensional Automated Micromanipulation Using a Nanotip Gripper with Multi-Feedback. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 075009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Chee, P.S.; Lim, E.H.; Low, J.H.; Nguyen, N.T. A Stretchable Kirigami-Inspired Self-Powered Electroactive Sensor for Tensile Strain and Torsion Sensing. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 2100961, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Chee, P.S.; Lim, E.H.; Tan, C.H. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Throat Sensor Using Ionic Polymer-Metal Composite (IPMC) Material. Polymers 2021, 13, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Yuan, C.; Liang, X.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bowen, C. Triboelectric and Piezoelectric Nanogenerators for Future Soft Robots and Machines. iScience 2020, 23, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Bo, L.; Li, Z. Recent Progress in Human Body Energy Harvesting for Smart Bioelectronic System. Fundam. Res. 2021, 1, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, M.A.; Arafa, M.H.; Bowen, C.R. Experimental and Analytical Investigation of the Response of a Triboelectric Generator Under Different Operating Conditions. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 2000576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Q.L.; Chee, P.S.; Lim, E.H.; Liew, G.G. Self-Powered Pressure Sensor Based on Microfluidic Triboelectric Principle for Human-Machine Interface Applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 75012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Jiang, D.; Qu, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, Z. A Stretchable, Self-Healable Triboelectric Nanogenerator as Electronic Skin for Energy Harvesting and Tactile Sensing. Materials 2021, 14, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Pang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Tan, X.; Cao, C. Smart Soft Actuators and Grippers Enabled by Self-Powered Tribo-Skins. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1901075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zheng, Q.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.; Yan, L.; Shi, B.; Li, Z. A Size-Unlimited Surface Microstructure Modification Method for Achieving High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2016, 28, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Q.L.; Chee, P.S.; Lim, E.H. A Parametric Study of a Sponge-Based Triboelectric Energy Harvester. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Langkawi Island, Malaysia, 1–3 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Chun, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.N.; Kang, N.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Shin, K.S.; Gupta, M.K.; Baik, J.M.; et al. Hydrophobic Sponge Structure-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5037–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.F. Topology Optimized Design, Fabrication, and Characterization of a Soft Cable-Driven Gripper. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2463–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemfica, J.R.; Melchiorri, C.; Moriello, L.; Palli, G.; Scarcia, U. A Three-Fingered Cable-Driven Gripper for Underwater Applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Peng, C.; Grimstad, L.; From, P.J.; Isler, V. Development and Field Evaluation of a Strawberry Harvesting Robot with a Cable-Driven Gripper. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.D.I.G.; Silva, S.R.P. Towards Optimized Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors Based on Micropatterned Plastic Films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Guo, H.; He, X.; Liu, G.; Xi, Y.; Shi, H.; Hu, C. Enhancing Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Filling High Dielectric Nanoparticles into Sponge PDMS Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the Triboelectric Series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, K. A Novel Fault Diagnosis System on Polymer Insulation of Power Transformers Based on 3-Stage GA-SA-SVM OFC Selection and ABC-SVM Classifier. Polymers 2018, 10, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baghdadi, A.; Megahed, F.M.; Esfahani, E.T.; Cavuoto, L.A. A Machine Learning Approach to Detect Changes in Gait Parameters Following a Fatiguing Occupational Task. Ergonomics 2018, 61, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeian, M.; Bhardwaj, N.; Esquivel, B.; Mozumdar, M. Real Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using a Logistic-Regression-Based Machine Learning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Green Energy and Systems Conference (IGSEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 6–7 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler-Schwartz, A.; Yilmaz, R.; Mirchi, N.; Bissonnette, V.; Ledwos, N.; Siyar, S.; Azarnoush, H.; Karlik, B.; Del Maestro, R. Machine Learning Identification of Surgical and Operative Factors Associated with Surgical Expertise in Virtual Reality Simulation. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e198363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goh, Q.-L.; Chee, P.-S.; Lim, E.-H.; Ng, D.W.-K. An AI-Assisted and Self-Powered Smart Robotic Gripper Based on Eco-EGaIn Nanocomposite for Pick-and-Place Operation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081317
Goh Q-L, Chee P-S, Lim E-H, Ng DW-K. An AI-Assisted and Self-Powered Smart Robotic Gripper Based on Eco-EGaIn Nanocomposite for Pick-and-Place Operation. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(8):1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081317
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoh, Qi-Lun, Pei-Song Chee, Eng-Hock Lim, and Danny Wee-Kiat Ng. 2022. "An AI-Assisted and Self-Powered Smart Robotic Gripper Based on Eco-EGaIn Nanocomposite for Pick-and-Place Operation" Nanomaterials 12, no. 8: 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081317
APA StyleGoh, Q.-L., Chee, P.-S., Lim, E.-H., & Ng, D. W.-K. (2022). An AI-Assisted and Self-Powered Smart Robotic Gripper Based on Eco-EGaIn Nanocomposite for Pick-and-Place Operation. Nanomaterials, 12(8), 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081317






