MXene-Carbon Nanotube Composites: Properties and Applications
Abstract
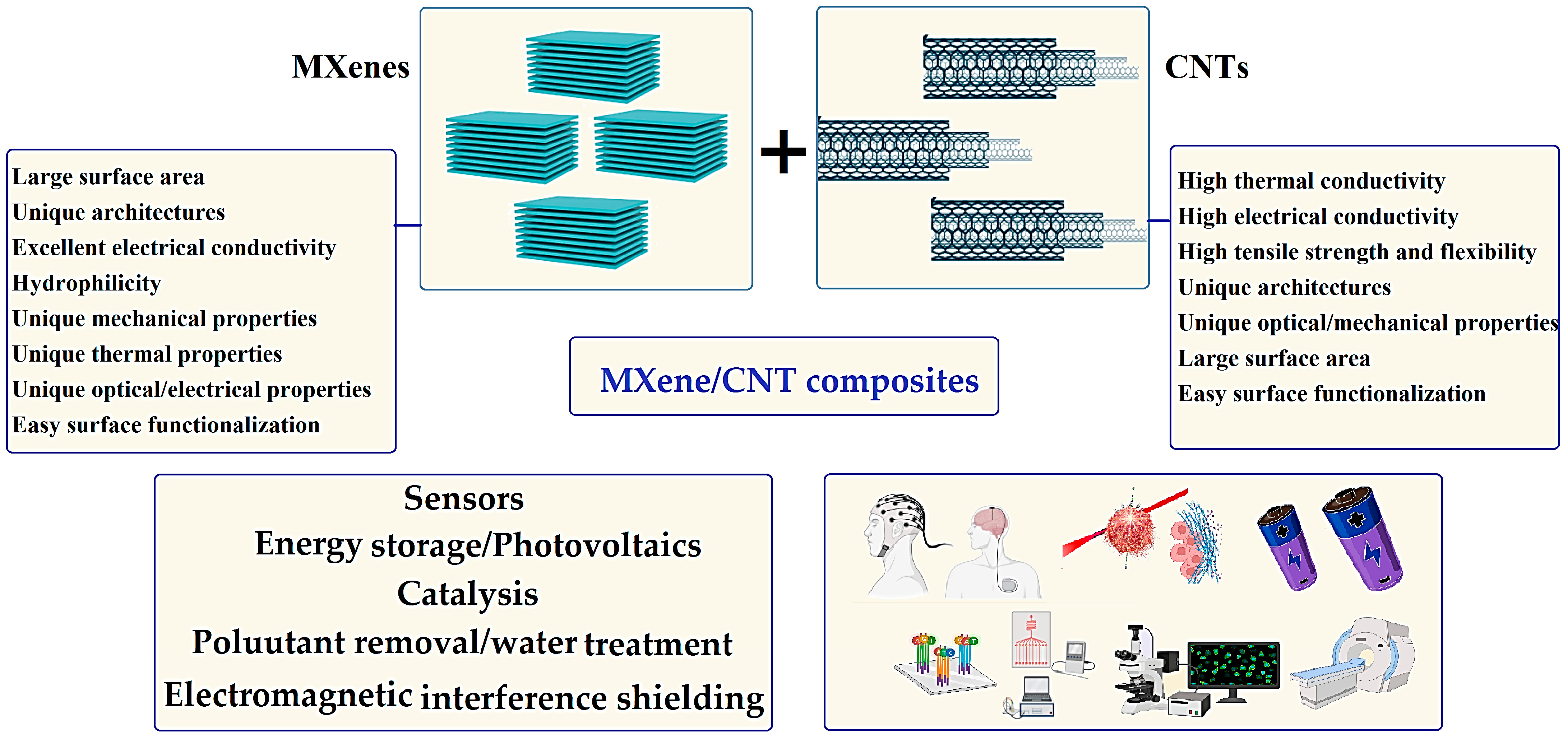
1. Introduction
2. MXene-CNT Composites
2.1. Sensing
2.2. Wastewater Treatment/Remediation and Pollutants Removal
2.3. EMI Shielding Performance
2.4. Catalysis
2.5. Supercapacitors and Batteries
3. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, X.; Si, C.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z. MXene and MXene-based composites: Synthesis, properties and environment-related applications. Nanoscale Horiz 2020, 5, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Luo, C.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Z.-Z.; Ma, J.; Nishihara, H.; He, Y.-B.; Kang, F.; Lv, W.; Yang, Q.-H. Lamellar MXene Composite Aerogels with Sandwiched Carbon Nanotubes Enable Stable Lithium–Sulfur Batteries with a High Sulfur Loading. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Wan, P. MXene hydrogel for wearable electronics. Matter 2021, 4, 2655–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; El-Demellawi, J.K.; Jiang, Q.; Ge, G.; Liang, H.; Lee, K.; Dong, X.; Alshareef, H.N. MXene hydrogels: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7229–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lin, L.; He, Q.; Hu, H.; Luo, R.; Xian, D.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, F.; et al. Titanium carbide MXene-based hybrid hydrogel for chemo-photothermal combinational treatment of localized bacterial infection. Acta Biomaterialia 2022, 142, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Two-dimensional MXene-based and MXene-derived photocatalysts: Recent developments and perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Kwon, J.; Kim, M.-K.; Koo, C.M. MXenes for electromagnetic interference shielding: Experimental and theoretical perspectives. Mater. Adv. 2021, 9, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan Saeed, M.; Kim, T.H.; Ahn, H.; Park, N.W.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.; Shahzad, A.; Shim, J.W. 2D MXene Additive-Induced Treatment Enabling High-Efficiency Indoor Organic Photovoltaics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 11, 2202135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan Saeed, M.; Shahzad, A.; Rasool, K.; Mateen, F.; Oh, J.-M.; Shim, J.W. 2D MXene: A Potential Candidate for Photovoltaic Cells? A Critical Review. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbankowski, P.; Anasori, B.; Makaryan, T.; Er, D.; Kota, S.; Walsh, P.L.; Zhao, M.; Shenoy, V.B.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Synthesis of two-dimensional titanium nitride Ti4N3 (MXene). Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shao, B.; Guo, A.; Gao, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cui, F.; Yang, X. Improved electrochemical performance of CoOx-NiO/Ti3C2Tx MXene nanocomposites by atomic layer deposition towards high capacitance supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 862, 158546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shah, S.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Z.; Gao, H.; Habib, T.; Radovic, M.; Green, M. Electrochemical etching of Ti2AlC to Ti2CTx (MXene) in low-concentration hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 21663–21668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ting, L.R.L.; Molinari, V.; Giordano, C.; Yeo, B.S. Efficient hydrogen evolution reaction catalyzed by molybdenum carbide and molybdenum nitride nanocatalysts synthesized via the urea glass route. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8361–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bai, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, G. Facile microwave-assisted synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for ratiometric fluorescence detection of hypochlorite. Microchim. Acta 2021, 15, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Kang, N.; Ma, X.-L.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Large-area high-quality 2D ultrathin Mo2C superconducting crystals. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yao, L.; Liu, Q.; Gu, J.; Luo, R.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, B. Fluorine—Free Synthesis of High—Purity Ti3C2Tx (T=OH, O) via Alkali Treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6115–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaki, M.; Maleki, A.; Varma, R.S. MXenes and ultrasonication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10843–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Luo, X.; Yang, R.Z.; Dai, F.; Zhu, D.D.; Bai, J.N.; Zhang, L.; Lei, H. Highly Thermoelectric ZnO@MXene (Ti3C2Tx) Composite Films Grown by Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 34562–34570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Fan, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, Z. The Advances of Carbon Nanotubes in Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 3418932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, E.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S.; Khatami, M.; Rahbarizadeh, F. Eco-friendly synthesis of carbon nanotubes and their cancer theranostic applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 4765–4782. [Google Scholar]
- Utreja, P.; Jain, S.; Tiwary, A.K. Novel drug delivery systems for sustained and targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Torti, S.V. Carbon nanotubes in hyperthermia therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 2045–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S. MXenes and MXene-based (nano)structures: A perspective on greener synthesis and biomedical prospects. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 24144–24156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXenes and MXene-based materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Recent advances. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2906–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXenes for Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis: Recent Advances and Current Challenges. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXenes in photomedicine: Advances and prospects Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7336–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Bioinspired and biomimetic MXene-based structures with fascinating properties: Recent advances. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 4783–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXenes in Cancer Nanotheranostics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, P.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXene-Chitosan Composites and Their Biomedical Potentials. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Iravani, P.; Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, S. MXenes for antimicrobial and antiviral applications: Recent advances. Mater. Technol. Adv. Perform. Mater. 2022, 37, 1890–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Iravani, S. MXenes and MXene-based Materials for the Removal of Water Pollutants: Challenges and Opportunities. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2021, 41, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shah, T.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Three dimensional porous MXene/CNTs microspheres: Preparation, characterization and microwave absorbing properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 145, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.P.; Zhou, X.H.; Lu, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.J. MXene/Carbon Nanotube Hybrids: Synthesis, Structures, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2021, 14, 5079–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Zhitomirsky, I. MXene–carbon nanotube composite electrodes for high active mass asymmetric supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10335–10344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Min, B.K.; Yi, Y.; Cho, C.-G. Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotubes/waterborne polyurethane based composite ink for electromagnetic interference shielding and sheet heater applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Fan, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Fu, Z.; Wang, R.; Hong, T.; Cheng, J. MXene (Ti3C2Tx) and Carbon Nanotube Hybrid-Supported Platinum Catalysts for the High-Performance Oxygen Reduction Reaction in PEMFC. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19539–19546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.-H.; Mao, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.-Q.; Huang, P.; Fu, S.-Y. MXene-carbon nanotubes-Cellulose-LiFePO4 based self-supporting cathode with ultrahigh-area-capacity for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 420, 140464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Wu, H.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y.; Miao, M.; Cao, S.; Shi, L.; Feng, X. Yarn-ball-shaped CNF/MWCNT microspheres intercalating Ti3C2Tx MXene for electromagnetic interference shielding films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhong, J.; Ou, J. Superdurable fiber-reinforced composite enabled by synergistic bridging effects of MXene and carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2022, 190, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.-D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Jing, Y.-X.; Cao, X.-L.; Zhang, F.; Sun, S.-P. Enhancing interfacial adhesion of MXene nanofiltration membranes via pillaring carbon nanotubes for pressure and solvent stable molecular sieving. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Zhu, J.; Wua, W. The facile synthesis of layered Ti2C MXene/carbon nanotube composite paper with enhanced electrochemical properties. Dalton Trans 2017, 46, 14880–14887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajer, F.; Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Badiei, A.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Advanced MXene-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXene-based composites as nanozymes in biomedicine: A perspective. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Han, G.; Huang, P. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5109–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Panatdasirisuk, W.; Mathis, T.S.; Anasori, B.; Lu, C.; Zhang, X.; Liao, Z.; Gogotsi, Y.; Yang, S. Layer-by-layer assembly of MXene and carbon nanotubes on electrospun polymer films for flexible energy storage. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6005–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Du, X.; Mathis, T.S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Shui, J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Xu, M. Maximizing ion accessibility in MXene-knotted carbon nanotube composite electrodes for high-rate electrochemical energy storage. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, A.; Glushenkov, A.M.; Anasori, B.; Urbankowski, P.; Li, J.; Byles, B.W.; Blake, B.; Van Aken, K.L.; Kota, S.; Pomerantseva, E.; et al. Lithium-ion capacitors with 2D Nb2CTx (MXene)—carbon nanotube electrodes. J. Power Sources 2016, 326, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhao, M.-Q.; Anasori, B.; Maleski, K.; Ren, C.E.; Li, J.; Byles, B.W.; Pomerantseva, E.; Wang, G.; Gogotsi, Y. Porous heterostructured MXene/carbon nanotube composite paper with high volumetric capacity for sodium-based energy storage devices. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yan, X. Realizing high-performance lithium ion hybrid capacitor with a 3D MXene-carbon nanotube composite anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Ye, H.; Han, K. Impeding polysulfide shuttling with a three-dimensional conductive carbon nanotubes/MXene framework modified separator for highly efficient lithium-sulfur batteries. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 573, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Lu, M.; Chen, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B. Three-dimensional architectures based on carbon nanotube bridged Ti2C MXene nanosheets for Li–S batteries. Particuology 2021, 57, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jin, S.; Miao, L.; Cai, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, K.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J. A 3D Hydroxylated MXene/Carbon Nanotubes Composite as a Scaffold for Dendrite-Free Sodium-Metal Electrodes. Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 16705–16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. Sandwich-like N-doped carbon nanotube@Nb2C MXene composite for high performance alkali ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 20610–20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Cao, G.; Yi, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Sun, X.; Wang, K.; Ma, Y. Binder-free 2D titanium carbide (MXene)/carbon nanotube composites for high-performance lithium-ion capacitors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5906–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Li, G.; Song, F.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Tang, K.; Xie, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, N. Surfactant-free self-assembled MXene/carbon nanotubes hybrids for high-rate sodium- and potassium-ion storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Luo, S.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Asif, M.; Chan, V.; Liao, K.; Sun, Y. MXene-carbon nanotubes layer-by-layer assembly based on-chip micro-supercapacitor with improved capacitive performance. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 386, 138420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Cui, C.; Shi, C.; Wu, Z.-S.; Yang, J.; Cheng, R.; Guang, T.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, X. High-Energy-Density Hydrogen-Ion-Rocking-Chair Hybrid Supercapacitors Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene and Carbon Nanotubes Mediated by Redox Active Molecule. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6899–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Bian, S.-W. Vacuum-filtration assisted layer-by-layer strategy to design MXene/carbon nanotube@MnO2 all-in-one supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 21347–21356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, P.; Soomro, R.A.; Xu, B. Alkali-Induced Porous MXene/Carbon Nanotube-Based Film Electrodes for Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater 2022, 5, 4180–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Chao, Y.; Liu, W. High-performance MnO2@MXene/carbon nanotube fiber electrodes with internal and external construction for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 3613–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhitomirsky, I. Composite Fe3O4-MXene-Carbon Nanotube Electrodes for Supercapacitors Prepared Using the New Colloidal Method. Materials 2021, 14, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aakyiir, M.; Oh, J.-A.; Araby, S.; Zheng, Q.; Naeem, M.; Ma, J.; Adu, P.; Zhang, L.; Mai, Y.-W. Combining hydrophilic MXene nanosheets and hydrophobic carbon nanotubes for mechanically resilient and electrically conductive elastomer nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 214, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Lang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kong, W.; Peng, O.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J.; He, T.; Amini, A.; et al. Polyoxometalate-Derived Hexagonal Molybdenum Nitrides (MXenes) Supported by Boron, Nitrogen Codoped Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution from Seawater. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, H.; Chen, B.; Jin, T.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. 3D MXene anchored carbon nanotube as bifunctional and durable oxygen catalysts for Zn–air batteries. Carbon 2021, 185, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agnese, Y.; Rozier, P.; Taberna, P.-L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Simon, P. Capacitance of two-dimensional titanium carbide (MXene) and MXene/carbon nanotube composites in organic electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2016, 306, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Ye, F.; Chen, R.; Luo, X.; Chang, G.; Li, R. A wide sensing range and high sensitivity flexible strain sensor based on carbon nanotubes and MXene. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 10220–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Tian, G.; Zhang, D. Co@N-CNT/MXenes in situ grown on carbon nanotube film for multifunctional sensors and flexible supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 14460–14468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Chen, X.; Lu, C.; Ye, C.; Li, W.; Chu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B. Electrochemical determination of capsaicinoids content in soy sauce and pot-roast meat products by glassy carbon electrode modified with MXene/PDDA-carbon nanotubes/β-cyclodextrin. Food Control 2022, 138, 109022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Liao, X.; Xiong, W.; Du, J.; Hong, Y. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified two dimensional MXene with high antifouling property for sensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 455501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. Growing CoNi nanoalloy@N-doped carbon nanotubes on MXene sheets for excellent microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Ma, C.; Tan, S.; Ma, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, F. Ultrathin and Flexible CNTs/MXene/Cellulose Nanofibrils Composite Paper for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Jia, Z.; Dong, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, G. Layered 3D structure derived from MXene/magnetic carbon nanotubes for ultra-broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Yao, Z.; Liu, D. In-situ growth of bamboo-shaped carbon nanotubes and helical carbon nanofibers on Ti3C2Tx MXene at ultra-low temperature for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 6338–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, C.; Yang, B.; Wang, L.; You, W.; Che, R. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotubes Hollow Microsphere with Confined Magnetic Nanospheres for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Small 2022, 18, 2104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Han, M.; Song, C.; Xu, H.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Ti3C2 MXenes modified with in situ grown carbon nanotubes for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4068–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Chen, S.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q.; Qu, M.; Zou, Q.; Li, J.; Tan, H.; Liu, L.; Fan, D.; et al. Two-Dimensional MXene (Ti3C2)-Integrated Cellulose Hydrogels: Toward Smart Three-Dimensional Network Nanoplatforms Exhibiting Light-Induced Swelling and Bimodal Photothermal/Chemotherapy Anticancer Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27631–27643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bao, W.; Jaumaux, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, G. MXene—Based composites: Synthesis and applications in rechargeable batteries and supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1802004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; He, D. MXenes for Solar Cells. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bilal, M.; Adeel, M.; Barceló, D.; Iqbal, H.M.N. MXene-based designer nanomaterials and their exploitation to mitigate hazardous pollutants from environmental matrices. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Yi, Y. Innovative strategy based on novel Ti3C2Tx MXenes nanoribbons/carbon nanotubes hybrids for anodic stripping voltammetry sensing of mercury ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tu, X.; Gao, F.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X.; Fernandez, C.; Qu, F.; Liu, G.; Lu, L.; Yu, Y. Hierarchical porous MXene/amino carbon nanotubes-based molecular imprinting sensor for highly sensitive and selective sensing of fisetin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, N.; Medetalibeyoglu, H.; Akyıldırım, O.; Atar, N.; Yola, M.L. Electrochemical detection of amyloid-β protein by delaminated titanium carbide MXene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite with molecularly imprinted polymer. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, P.; Xie, Y.; Fei, J. A high-sensitive dopamine electrochemical sensor based on multilayer Ti3C2 MXene, graphitized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ZnO nanospheres. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Molecularly imprinted ratiometric electrochemical sensor based on carbon nanotubes/cuprous oxide nanoparticles/titanium carbide MXene composite for diethylstilbestrol detection. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Ren, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Tang, Z.; Lu, G.; et al. High-Performance Foam-Shaped Strain Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Ti3C2Tx MXene for the Monitoring of Human Activities. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9690–9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; He, P.; Wang, S.; Ling, K.; Liu, L.; Lei, P.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Cao, J.; et al. Wearable CNT/Ti3C2Tx MXene/PDMS composite strain sensor with enhanced stability for real-time human healthcare monitoring. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Huang, W.; Shao, J.; Yang, J.; Dong, X. Stretchable Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotube Composite Based Strain Sensor with Ultrahigh Sensitivity and Tunable Sensing Range. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, C.; Ma, K.; Wang, X. Lifetime health monitoring of fiber reinforced composites using highly flexible and sensitive MXene/CNT film sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Nie, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.-n.; Yin, K.; Sun, L. Multifunctional, Light-Weight Wearable Sensor Based on 3D Porous Polyurethane Sponge Coated with MXene and Carbon Nanotubes Composites. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Lai, X.; Zeng, X. Superhydrophobic MXene@carboxylated carbon nanotubes/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogel for piezoresistive pressure sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hu, X.; Li, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; An, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Self-assembly of dendritic-lamellar MXene/Carbon nanotube conductive films for wearable tactile sensors and artificial skin. Carbon 2020, 164, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.-F.; Yang, Z.; Song, X.; Lee, J.H.; Tang, C.Y.; Park, H.-D. Interlayered Forward Osmosis Membranes with Ti3C2Tx MXene and Carbon Nanotubes for Enhanced Municipal Wastewater Concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13219–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, R.; Hou, P.-X.; Ma, Y.; Majeed, A.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. MXene-Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Membrane for Robust Recovery of Au from Trace-Level Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43032–43041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Fan, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Simple and robust MXene/carbon nanotubes/cotton fabrics for textile wastewater purification via solar-driven interfacial water evaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Kong, Q.; Lin, T.; Tao, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Xie, Z. Construction of a hierarchical carbon nanotube/MXene membrane with distinct fusiform channels for efficient molecular separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 22666–22673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; Cui, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Xing, W.; Jing, W. Assembly of multidimensional MXene-carbon nanotube ultrathin membranes with an enhanced anti-swelling property for water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumal, V.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Ravi, G.; Keerthana, S.P.; Velauthapillai, D. Facile single-step synthesis of MXene@CNTs hybrid nanocomposite by CVD method to remove hazardous pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ruan, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Shao, W.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Gu, C.; Qiao, W. MXene-like carbon sheet/carbon nanotubes derived from metal-organic frameworks for efficient removal of tetracycline by non-radical dominated advanced oxidation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Tang, P.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.-B.; Yu, Z.-Z. Superelastic, Ultralight, and Conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene/Acidified Carbon Nanotube Anisotropic Aerogels for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 20539–20547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.-M.; Li, J.; Alhabeb, M.; Karpovich, C.; Wang, H.; Lipton, J.; Maleski, K.; Kong, J.; Shaulsky, E.; Elimelech, M.; et al. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Cross-Functional Semi-transparent MXene-Carbon Nanotubes Composite Films for Next-Generation Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Nie, W.; Wang, P.; Li, C. Roll-to-roll layer-by-layer assembly bark-shaped carbon nanotube/Ti3C2Tx MXene textiles for wearable electronics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raagulan, K.; Braveenth, R.; Lee, L.R.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.M.; Moon, J.J.; Lee, S.B.; Chai, K.Y. Fabrication of Flexible, Lightweight, Magnetic Mushroom Gills and Coral-Like MXene–Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites for EMI Shielding Application. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambyal, P.; Iqbal, A.; Hong, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.-K.; Hong, S.M.; Han, M.; Gogotsi, Y.; Koo, C.M. Ultralight and Mechanically Robust Ti3C2Tx Hybrid Aerogel Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38046–38054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Feng, Y. Fire/heat-resistant, anti-corrosion and folding Ti2C3Tx MXene/single-walled carbon nanotube films for extreme-environmental EMI shielding and solar-thermal conversion applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 10425–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, B.; Yao, Q.; Dong, G.; Zuo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. A MXene-based multiple catalyst for highly efficient photocatalytic removal of nitrate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58149–58160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, P.; Low, J.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.; Fan, J. MXene-based photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 18–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Dall’Agnese, Y.; Dall’Agnese, C.; Duan, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.-F. 2D MXenes as co-catalysts in photocatalysis: Synthetic methods. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zou, D.; Fang, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Z. MXene Ti3C2 derived Z–scheme photocatalyst of graphene layers anchored TiO2/g–C3N4 for visible light photocatalytic degradation of refractory organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Shi, C.; Fan, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Ultrastable MXene@Pt/SWCNTs’ Nanocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, P.; Hu, F.; Li, L.; Chou, S.; et al. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotubes for Low Overpotential and Long-Life Li-CO2 Batteries. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8407–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, X.; Lyu, F.; Zhong, Q.; Hu, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Q. Integrating MXene nanosheets with cobalt-tipped carbon nanotubes for an efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H.; He, Q.; Wu, C.; Duan, T.; Song, L. In Situ Growth of Cobalt Nanoparticles Encapsulated Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes among Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Matrix for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jia, Q.; Duan, F.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; He, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z. Multiwall carbon nanotubes loaded with MoS2 quantum dots and MXene quantum dots: Non–Pt bifunctional catalyst for the methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions in alkaline solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Arianpouya, N. NiCoFe-layered double hydroxides/MXene/N-doped carbon nanotube composite as a high performance bifunctional catalyst for oxygen electrocatalytic reactions in metal-air batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 901, 115797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Qiao, N.; Xu, B. Carbon nanotubes enhance flexible MXene films for high-rate supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Luo, M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhou, X. Ti3C2Tx/carbon nanotube/porous carbon film for flexible supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 132002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-Z.; Fang, Y.-S.; Cao, W.-Q.; He, P.; Cao, M.-S. MXene-CNT/PANI ternary material with excellent supercapacitive performance driven by synergy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 868, 159159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-D.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, L.-Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, W.-Y.; Ma, M.-G. Preparation of Flexible N-Doped Carbon Nanotube/MXene/PAN Nanocomposite Films with Improved Electrochemical Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 15352–15363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Gong, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.; An, J.; Lv, F.; Guo, S.; Sun, G. A Solid-State Fibriform Supercapacitor Boosted by Host–Guest Hybridization between the Carbon Nanotube Scaffold and MXene Nanosheets. Small 2018, 14, 1801203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.; Tian, W.B.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, Z.M. MXene/CNTs films prepared by electrophoretic deposition for supercapacitor electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 830–831, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.-P.; Guo, C.-F.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y. Strong Surface-Bound Sulfur in Carbon Nanotube Bridged Hierarchical Mo2C-Based MXene Nanosheets for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. Small 2019, 15, 1804338. [Google Scholar]








| Applications | MXene/CNT Composites | Advantages and Properties | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible energy storage; electroanalytical chemistry; brain electrodes; electrocatalysis | MXene (Ti3C2Tx) nanoflakes/multi-walled CNT on electrospun polycaprolactone fiber networks | Areal capacitance (30–50 mF cm−2). Highly enhanced rate function (14–16% capacitance retention at a scan rate of 100 V s−1). Suitable flexibility and tolerance against repeated mechanical deformation | [45] |
| Composite electrodes for high-rate electrochemical energy storage | MXene (Ti3C2)/CNTs composite | Significant capacitance (up to 130 F g−1) in organic electrolytes. Significant capacitance retention over a wide scan rate range of 10 mV s−1 to 10 V s−1. Supercapacitors at low temperatures | [46] |
| Li-ion capacitors | Nb2CTx (MXene)-CNT electrodes | High volumetric energy density (50–70 Wh L−1). The lithiated graphite/Nb2CTx-CNT exhibited the highest gravimetric activity | [47] |
| Sodium-based energy storage devices | Porous MXene (Ti3C2)/CNT composite films | Excellent volumetric capacity of 421 mA h cm−3 at 20 mA g−1. Good rate performance. High cycling stability | [48] |
| Li-based batteries and hybrid capacitors | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CNT composite | High energy and power density | [49] |
| Li-S batteries with a high sulfur loading | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/CNT sandwiches | Significant capacity of 712 mAh g−1; a sulfur loading of 7 mg cm−2. Superb cycling stability; 0.025% capacity decay per cycle over 800 cycles at 0.5 C | [2] |
| Li-S batteries | 3D conductive CNT/MXene framework modified separator | The separator provided initial capacity of 1415 mA h g−1 at 0.1 C, with the capacity retention of 614 mA h g−1 even after 600 cycles at 1 C | [50] |
| Li-S batteries | CNT/MXene (Ti2C) nanocomposites | High density electrochemical energy storage systems | [51] |
| Dendrite-free sodium-metal electrodes | Fibrous hydroxylated MXene (Ti3C2)/CNT composite | Significant average Coulombic efficiency of 99.2%. No dendrite after 1000 cycles. Long lifespan over 4000 h at 1.0 mA cm−2 with a capacity of 1.0 mAh cm−2 | [52] |
| High performance alkali ion batteries | Sandwich-like N-doped CNT@MXene (Nb2C) composite | Excellent electrochemical performance | [53] |
| High-performance Li-ion capacitors | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/CNT composite films | Remarkable energy density of 67 Wh kg−1 with good capacity retention of 81.3% even after 5000 cycles | [54] |
| High-rate sodium- and potassium-ion storage | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CNT composite | High electrochemical features for sodium- and potassium-ion storage. The electrode with superb rate capability | [55] |
| Flexible microelectronic devices; supercapacitors | MXene (Ti3C2TX)-CNT composite | Good areal capacitance of 61.38 mF cm−2 at a current density of 0.5 mA cm−2 | [56] |
| Hybrid supercapacitors | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/CNTs | Hydrogen ion aqueous-based hybrid supercapacitors. Significant energy density of 62 Wh kg−1. Excellent cycling stability | [57] |
| Supercapacitors | MXene/CNT@MnO2 composite film electrode | Significant specific capacity of 221 F g−1. High flexibility and good cycling stability | [58] |
| Supercapacitors | Porous MXene/CNT films | Superb cycling stability with a capacitance retention of 99.0% (20,000 cycles) at 100 A g−1 | [59] |
| Supercapacitors | MnO2@MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/CNT fiber electrodes | Outstanding cycling stability of 86.3% after 10,000 cycles and excellent capacitance of 371.1 F cm−3 | [60] |
| Supercapacitors | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/multi-walled CNT electrodes | Areal capacitance of 1.93 F cm−2 was obtained, which was higher than pure Ti3C2Tx and its composites | [34] |
| Supercapacitors | Fe3O4-MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CNT electrodes | Good capacitive performance | [61] |
| Mechanically resilient and electrically conductive elastomer nanocomposites | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CNT composite | Enhanced electrical conductivity. Improved mechanical properties | [62] |
| Electrochemical hydrogen evolution from seawater | Polyoxometalate-derived hexagonal molybdenum nitrides (MXenes) supported by boron, N co-doped CNTs | Remarkable electrochemical stability in environments with different pH values. Small over-potential of 78 mV at 10 mA cm−2 and Tafel slope of 46 mV per decade | [63] |
| Oxygen evolution and reduction reactions | Fe/Co-CNT@MXene composite | Excellent electro-activities. Significant specific capacity of 759 mA h g −1 at a current density of 10 mA cm−2. High durability cycling | [64] |
| Electrochemical performance; organic electrolytes | MXene (Ti3C2)/CNT composite | At 2 mV s−1, the capacitance values of 85 F g−1 and 245 F cm−3 could be achieved. Excellent rate capability and suitable cyclability. Enhanced capacitance | [65] |
| Sensing | Polydimethylsiloxane/MXene/CNT foam strain sensor | Enough conductive reliability and stability with great compressibility (~75%) and outstanding durability (>1000 cycles) | [66] |
| Multifunctional sensors | Cobalt (Co)@nitrogen (N)-CNT/MXene composite | High stability and tensile range. Flexible supercapacitors (great cycling stability of ~85,000 cycles with coulombic efficiency of ~99.7%) | [67] |
| Electrochemical sensor for the determination of capsaicinoid content | MXene/poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)-CNTs/β- cyclodextrin composite | The wide linear range was 0.1–50 μmol L−1, the low limit of detection (LOD) was ~0.06 μmol L−1, the recovery rate was ~84.00–125.60% | [68] |
| Electrochemical sensor for detection of ochratoxin A | MXene (Ti3C2)-multi-walled CNT composite | The concentration range was 0.09–10 μmol L−1 with LOD of 0.028 μmol L−1 | [69] |
| Microwave absorption | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CoNi@N-doped CNT composite | High surface areas (55.6–103.7 m2 g−1), moderate magnetism (19.8–24.6 emu g−1). Improved thermal oxidation stability (≥307 °C) | [70] |
| EMI shielding | CNT/MXene (Ti3C2)/ cellulose composite | The improved electrical conductivity was 2506.6 S m−1. EMI shielding effectiveness was 38.4 dB | [71] |
| Ultra-broadband electromagnetic wave absorption | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/ magnetic CNT composite | Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption The minimum reflection loss of −51.98 dB (at thicknesses of 1.9 mm) and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth of 7.76 GHz (at thicknesses of 2.1 mm) could be achieved. | [72] |
| Improved electromagnetic wave absorption features | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CNT composite | A minimal reflection loss of −52.56 dB (99.9994% electromagnetic wave absorption) in the X-band. High performance. | [73] |
| Broadband microwave absorption | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/CNT hollow microspheres | Remarkable microwave absorption properties. The maximum reflection loss was −40.1 dB The effective bandwidth was 5.8 GHz | [74] |
| Electromagnetic wave absorption | MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-CNT nanocomposite | The minimum reflection coefficient reached −52.9 dB, ~99.999% absorption | [75] |
| EMI shielding films | Cellulose nanofibrils/multi-walled CNT microspheres intercalating MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | Excellent mechanical robustness and durability | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohajer, F.; Ziarani, G.M.; Badiei, A.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXene-Carbon Nanotube Composites: Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13020345
Mohajer F, Ziarani GM, Badiei A, Iravani S, Varma RS. MXene-Carbon Nanotube Composites: Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(2):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13020345
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohajer, Fatemeh, Ghodsi Mohammadi Ziarani, Alireza Badiei, Siavash Iravani, and Rajender S. Varma. 2023. "MXene-Carbon Nanotube Composites: Properties and Applications" Nanomaterials 13, no. 2: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13020345
APA StyleMohajer, F., Ziarani, G. M., Badiei, A., Iravani, S., & Varma, R. S. (2023). MXene-Carbon Nanotube Composites: Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials, 13(2), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13020345











