Enhanced Adsorptivity of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions Using CTS@nZVI Modified Wheat Straw-Derived Porous Carbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials
2.2. Adsorption Experiment
2.2.1. Choice of Adsorbent
2.2.2. Effects of Adsorbent Dose and Solution pH
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherm Experiment
2.2.4. Adsorption Kinetics Experiment
2.2.5. The Reusability of CTS@nZVI-WSPC
3. Results and Discussion
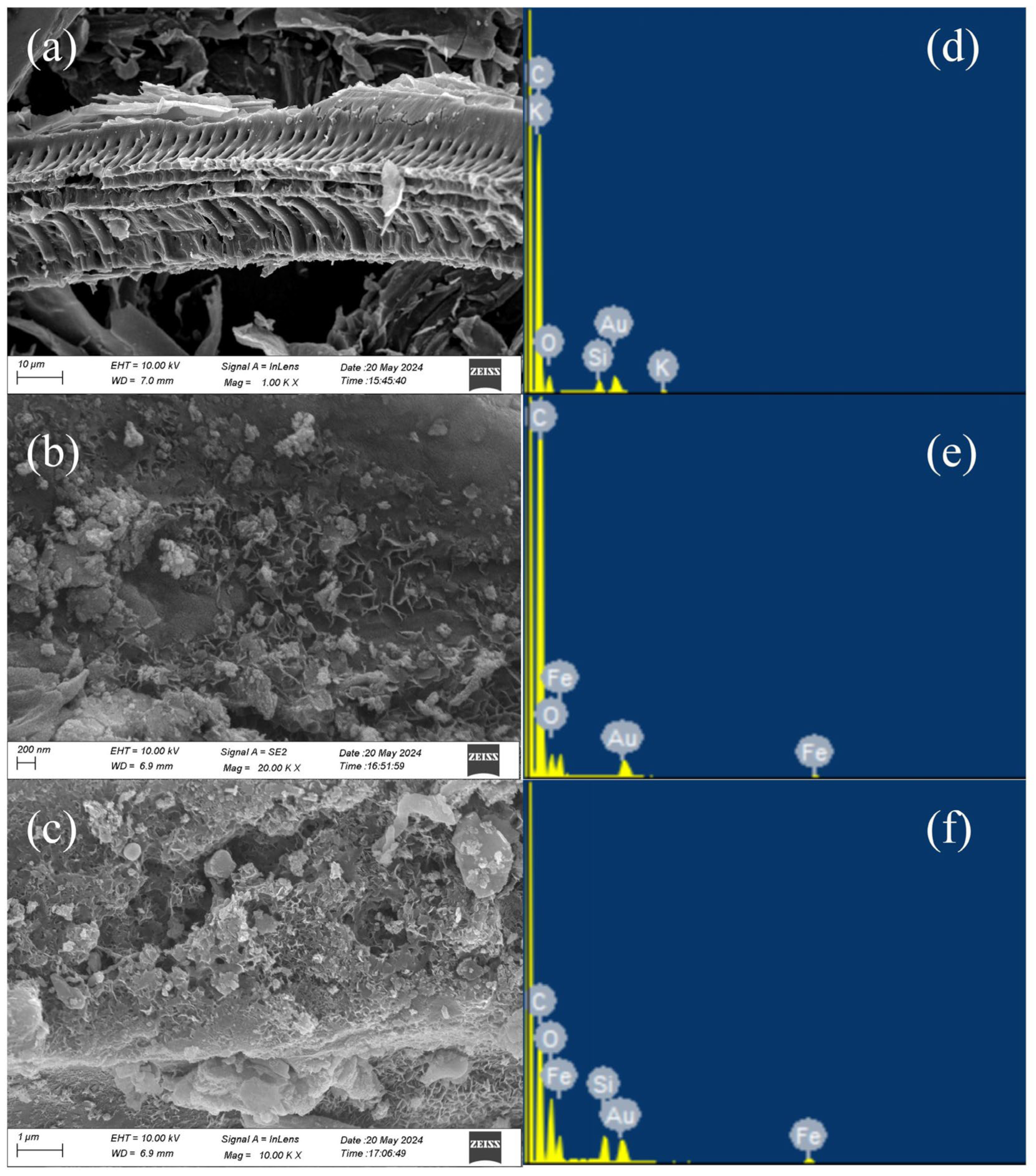
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Batch Experiments
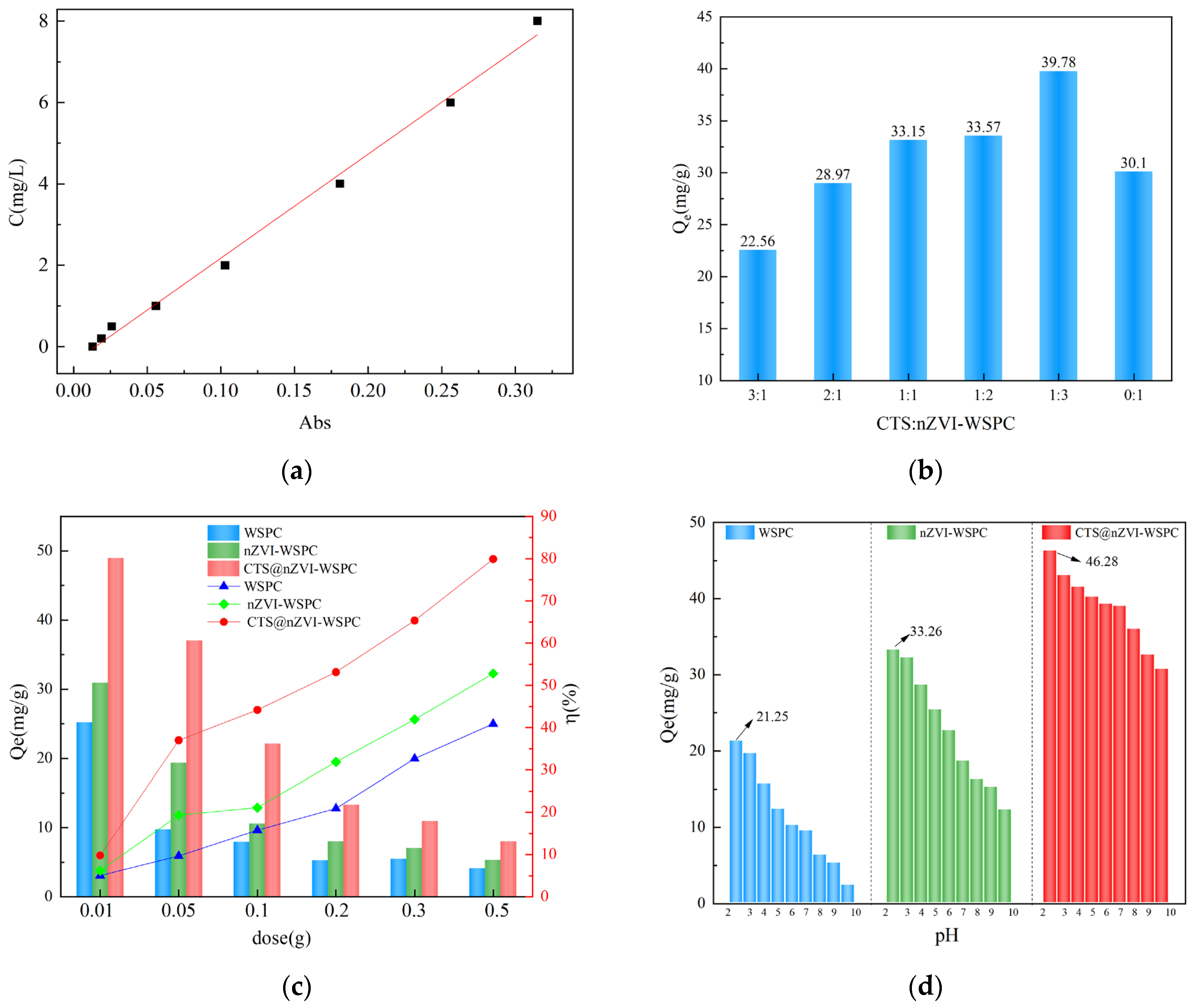
3.2.1. Effect of Ratio
3.2.2. Effect of the Dose of Adsorbent
3.2.3. Effect of Initial pH
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
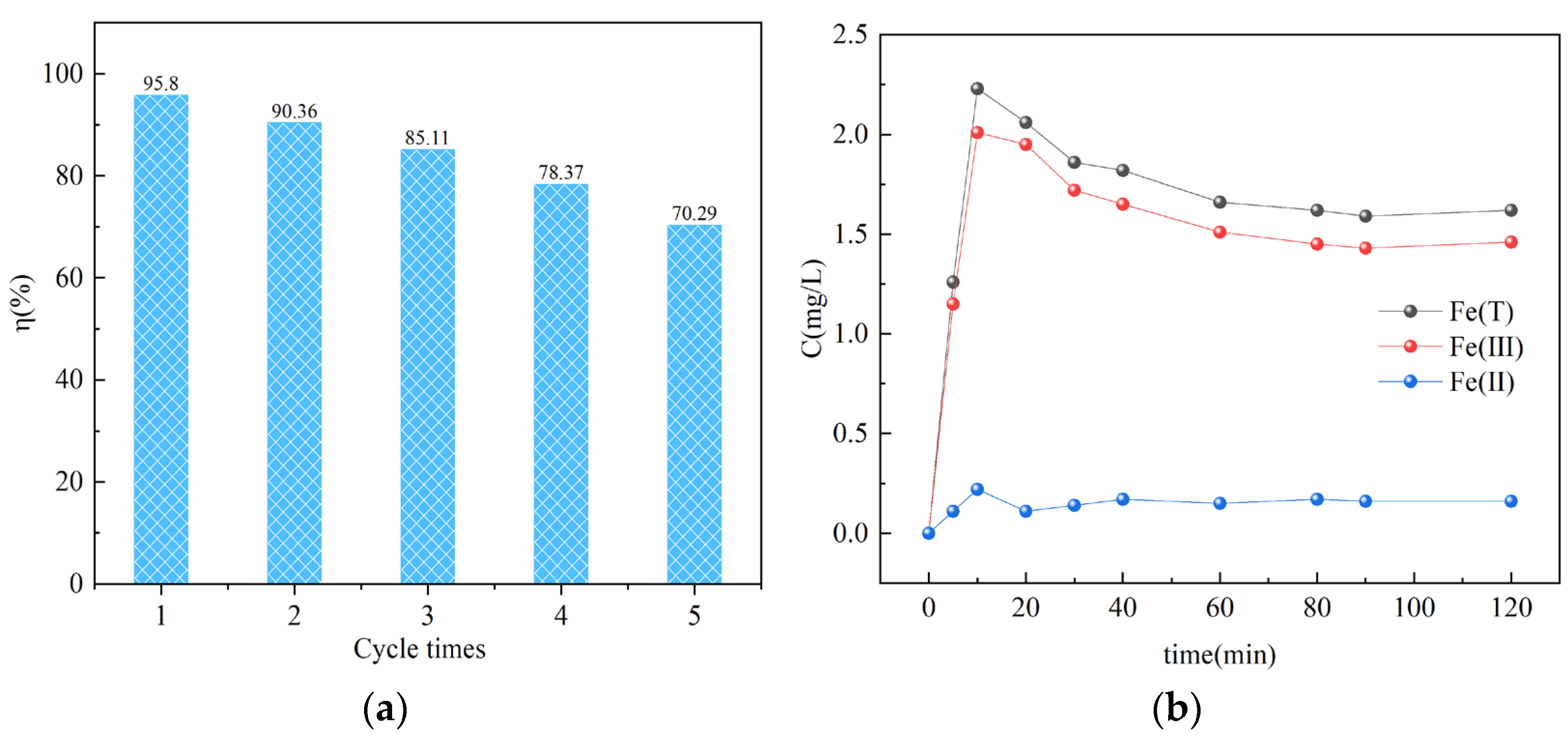
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
3.5. Reusability of CTS@nZVI-WSPC
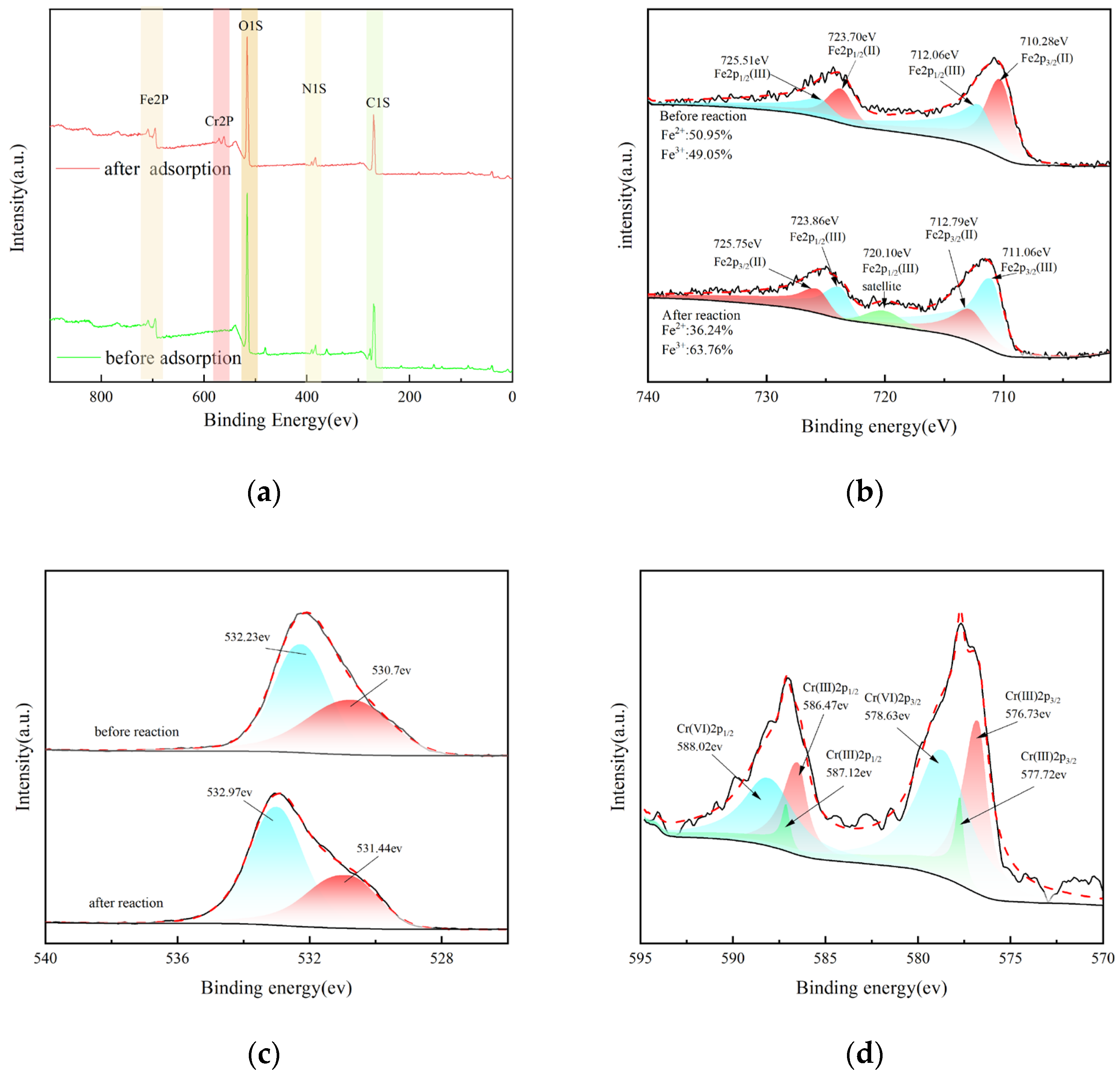
3.6. XPS Analysis
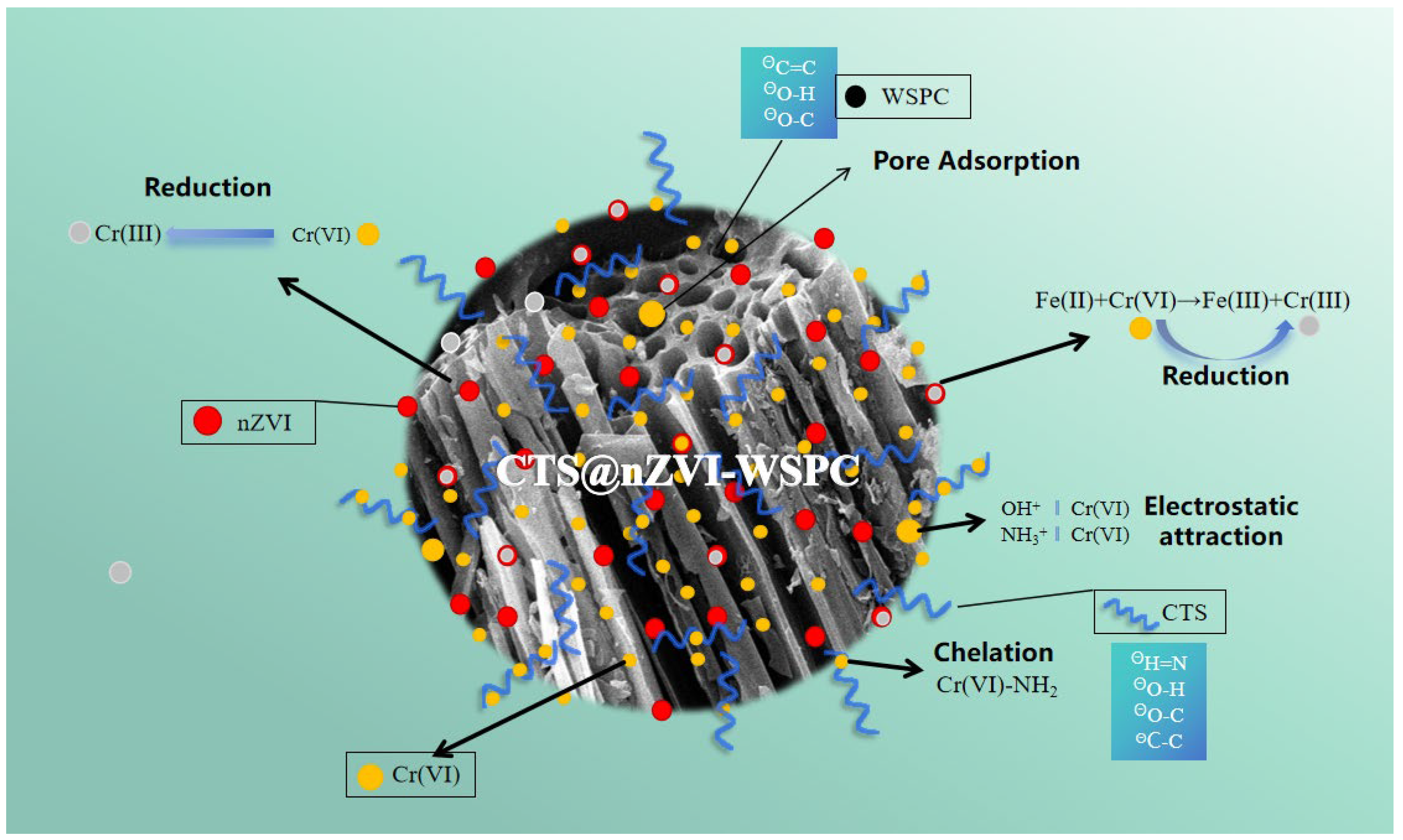
3.7. Discussion of Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samuel, M.S.; Selvarajan, E.; Chidambaram, R.; Patel, H.; Brindhadevi, K. Clean approach for chromium removal in aqueous environments and role of nanomaterials in bioremediation: Present research and future perspective. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cui, T.; Chen, D.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J.; Sun, R.; Zi, W.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hexavalent chromium elimination from wastewater by integrated micro-electrolysis composites synthesized from red mud and rice straw via a facile one-pot method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Qiu, Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium by biochar supported nZVI composite: Batch and fixed-bed column evaluations, mechanisms, and secondary contamination prevention. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Tiemann, K.; Armendariz, V.; Bess-Oberto, L.; Chianelli, R.; Rios, J.; Parsons, J.; Gamez, G. Characterization of Cr(VI) binding and reduction to Cr(III) by the agricultural byproducts of Avena monida (Oat) biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 80, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witek-Krowiak, A. Application of beech sawdust for removal of heavy metals from water: Biosorption and desorption studies. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2013, 71, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, S.M. Rice Husk Silica Adsorbent for Removal of Hexavalent Chromium Pollution from Aquatic Solutions. Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2014, 5, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Z. Immobilization of Cd(II) in acid soil amended with different biochars with a long term of incubation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12597–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Hasan, S.; Talat, M.; Singh, V.; Gangwar, S. Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using wheat bran. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osasona, I.; Onyemari, J.; Johnson, J.A.; Siyanbola, T.O. Phosphoric Acid and Cashew Bark Extract Activated Carbons derived from Coconut (Cocos nucifera) Shells for Cr (VI) Adsorption. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced aqueous Cr(VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Haron, J.; Rahman, M.Z.A. Adsorption of Cr(III) from aqueous solutions by polyacrylamide-grafted rubberwood fibre: Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. BioResources 2011, 6, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Tanweer, M.S.; Alam, M. Recent advances in adsorptive removal of wastewater pollutants by chemically modified metal oxides: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 46, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika, S.; Kumar, M.; Pisharody, L.; Malhotra, M.; Kumar, G.; Sreedharan, V.; Singh, L.; Nidheesh, P.; Bhatnagar, A. Modified biochar as a green adsorbent for removal of hexavalent chromium from various environmental matrices: Mechanisms, methods, and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zheng, W.; Mašek, O.; Chen, X.; Gu, B.; Sharma, B.K.; Cao, X. Roles of Phosphoric Acid in Biochar Formation: Synchronously Improving Carbon Retention and Sorption Capacity. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.F.; Heng, Z.W.; Teoh, H.C.; Chong, W.C.; Pang, Y.L. Recent development of magnetic biochar crosslinked chitosan on heavy metal removal from wastewater—Modification, application and mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, U.K.; Ji, W.; Liang, Y.; Ma, H.; Pu, S. Mechanism enhanced active biochar support magnetic nano zero-valent iron for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from simulated polluted water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-F.; Yan, C.-C.; Wang, Q.; Pan, L.; Chen, L.-F. Carbothermal synthesis of activated carbon-supported nano zero valent iron: Effects of temperature, characterization, and reactivity. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 9520–9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, X.-Q.; Li, G.; Yin, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Meng, N.; Dong, L.; Lyu, X.-J.; Li, L.; et al. Preparation of Novel ALRCs/nZVI Composite and Its Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 14, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Liu, N.; Lv, J.; Yang, Y. Enhanced removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a green synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on oak wood biochar. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; El-Naggar, A.; Niazi, N.K.; Sun, C.; Shaheen, S.M.; Hou, D.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. Enhanced sorption of trivalent antimony by chitosan-loaded biochar in aqueous solutions: Characterization, performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, F.; Anbia, M.; Sepehrian, M. Recent advances in removal of inorganic anions from water by chitosan-based composites: A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, H.M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Liyanage, S.; Ekanayake, A.; Selvasembian, R.; Daverey, A.; Vithanage, M. Enhanced adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium in aqueous media using chitosan-modified biochar: Synthesis, sorption mechanism, and reusability. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 115982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M. Fate and mechanistic insights into nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) activation of sludge derived biochar reacted with Cr(VI). J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L.; Wang, B.; Qiu, M. Spectroscopic investigation of Cr(VI) sorption on nZVI/biochar composites. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 120262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Shaaban, M.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, B.; Peng, Q.-A. Efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from an aquatic system using nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by ramie biochar. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.; Samy, M.; Shokry, H.; El-Subruiti, G.; El-Sharkawy, A.; Hamad, H.; Elkady, M. The superior performance of silica gel supported nano zero-valent iron for simultaneous removal of Cr (VI). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Ling, D.; Feng, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Enhanced elimination of Cr(VI) from aqueous media by polyethyleneimine modified corn straw biochar supported sulfide nanoscale zero valent iron: Performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huangpu, J.; Shen, J.; Gu, M.; Yang, J. Removal of p-nitrophenols by BC@nZVI activated persulfate: A study of key factors and mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by biochars produced at different temperatures: Synthesis mechanism and effect on Cr(VI) removal. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, M.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Tang, C.; Hu, X. A novel preparation of S-nZVI and its high efficient removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Cheng, S.; Yue, L.; You, Z.; Cai, J. N-doped biochar from chitosan gel-like solution: Effect of hydrothermal temperature and superior aqueous Cr (VI) removal performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 641, 128426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, J.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Meenakshi, S. Performance of chitosan engraved iron and lanthanum mixed oxyhydroxide for the detoxification of hexavalent chromium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Iqbal, J.; Yang, Z.; Du, Y. Preparation of magnetic chitosan corn straw biochar and its application in adsorption of amaranth dye in aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Ma, J.; Ning, P. Formation and mechanism of nanoscale zerovalent iron supported by phosphoric acid modified biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Shen, C.; Bi, X.; Li, T. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by fabricating novel heteroaggregates of montmorillonite microparticles with nanoscale zero-valent iron. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Long, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Liang, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, M. Unveiling the role of biochar in simultaneous removal of hexavalent chromium and trichloroethylene by biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 889, 164243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Koyama, S. Optimization of adsorption isotherm types for desiccant air-conditioning applications. Renew. Energy 2018, 121, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, G.A.; Herath, A.; Crisler, G.B.; Bridges, D.; Patel, S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T. Cadmium and Copper Removal From Aqueous Solutions Using Chitosan-Coated Gasifier Biochar. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 541203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.; Islam, S.; Arifin, M.T.; Firoz, S.H. Synthesis, Characterization and Sorption Properties of Biochar, Chitosan and ZnO-Based Binary Composites towards a Cationic Dye. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakatos, J.; Brown, S.D.; Snape, C.E. Coals as sorbents for the removal and reduction of hexavalent chromium from aqueous waste streams. Fuel 2002, 81, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution: Reactivity, characterization and mechanism. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, G.; Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, X. The remediation of hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil by nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on sludge-based biochar. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Qian, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Xue, G. Synergizing redox of zerovalent iron and singlet oxygen to remove aniline, chromium and antimony in printing and dyeing wastewater synchronously: Multifunctional effect of sludge derived biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-L.; Li, F.; Xie, X.J.; Li, Z.; Chen, L. Nanoscale zero-valent iron and chitosan functionalized Eichhornia crassipes biochar for efficient hexavalent chromium removal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Cr(VI) immobilization in soil using lignin hydrogel supported nZVI: Immobilization mechanisms and long-term simulation. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, S.; Dong, W.; Xiao, Y.; Riaz, M.S.; Dong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, F. Highly Hydroxylated Porous Nanozirconia for Complete Trace Cr(VI) Removal. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, P.P.; Cho, P.P.; Chanadana, L.; Kumar, K.A.; Dobhal, S.; Shashidhar, T.; Madras, G.; Subrahmanyam, C. Bio-waste assisted phase transformation of Fe3O4/carbon to nZVI/graphene composites and its application in reductive elimination of Cr(VI) removal from aquifer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Sirajudheen, P.; Nikitha, M.; Ramkumar, K.; Meenakshi, S. Facile synthesis of sulfur-doped chitosan/biochar derived from tapioca peel for the removal of organic dyes: Isotherm, kinetics and mechanisms. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Guo, X.; Shao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Qiu, L. Adsorption performance and mechanism of Fe-loaded biochar derived from waste zanthoxylum branch for removing Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Biomass-Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 14, 10201–10215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, B.; Liu, G.; Abbas, Q.; Wang, R.; Ullah, H.; Mian, M.; Amina, A.; Rashid, A. Enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous media using a highly stable and magnetically separable rosin-biochar-coated TiO2@C nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25983–25996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, Z.; Xian, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Pu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) by a novel nanoscale FeS/chitosan/biochar composite from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.S.; Sahu, M.K.; Sahu, E.; Patel, R.K. Fluoride removal from aqueous solutions using cerium loaded mesoporous zirconium phosphate. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 7300–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasbaji, M.; Mennani, M.; Oubenali, M.; Benhamou, A.A.; Boussetta, A.; Ablouh, E.-H.; Mbarki, M.; Grimi, N.; El Achaby, M.; Moubarik, A. Bio-based functionalized adsorptive polymers for sustainable water decontamination: A systematic review of challenges and real-world implementation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Lee, W. Influence of Riboflavin on Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Reactivity during the Degradation of Carbon Tetrachloride. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Bi, D.; Zhang, W. Fast and highly efficient removal of chromium (VI) using humus-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Influencing factors, kinetics and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G. Removal of hexavalent chromium by bentonite supported organosolv lignin -stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, V.N.; Quici, N.; Halac, E.B.; Leyva, A.G.; Custo, G.; Bengio, S.; Zampieri, G.; Litter, M.I. Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water with nanoparticulated zerovalent iron: Understanding the Fe(III)–Cr(III) passive outer layer structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-J.; Li, M.-F.; Ma, J.-F.; Bian, J.; Peng, F. Chitosan crosslinked composite based on corncob lignin biochar to adsorb methylene blue: Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, B.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; He, F.; Han, X. Wheat straw biochar amendments on the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Noerpel, M.R.; Scheckel, K.G.; Ippolito, J.A. Wheat straw biochar reduces environmental cadmium bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.L.; Guo, S.; Qiu, Y.F.; Di Liu, Y.; Duan, X.L.; Yu, Y.J. Wheat straw biochar-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron for removal of trichloroethylene from groundwater. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L. Study on the performance of sewage sludge biochar modified by nZVI to remove Cu(II) and Cr(VI) in water. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm mg/g | KL L/mg | R2 | KF | n | R2 | A | B | R2 | ||
| 25 °C | 111.23 | 0.0037 | 0.9920 | 12.116 | 2.1683 | 0.9769 | 1.3573 | 17.1767 | 0.9074 | |
| 35 °C | CTS@nZVI-WSPC | 125.00 | 0.0405 | 0.9956 | 12.965 | 2.2762 | 0.9795 | 1.3671 | 19.9112 | 0.9242 |
| 45 °C | 147.93 | 0.0686 | 0.9821 | 14.532 | 1.8126 | 0.9580 | 1.3788 | 25.1972 | 0.9572 | |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Intra-Particle | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe mg/g | K1 L/mg | R2 | Qe mg/g | K2 | R2 | Kp1 | Kp2 | ||
| 25 °C | 42.826 | 0.1410 | 0.9611 | 41.271 | 0.0047 | 0.9999 | 1.95 | 0.002 | |
| 35 °C | CTS@nZVI-WSPC | 44.511 | 0.1468 | 0.9309 | 44.762 | 0.0054 | 0.9999 | 2.23 | 0.015 |
| 45 °C | 47.816 | 0.2088 | 0.9649 | 47.984 | 0.0089 | 0.9999 | 1.91 | 0.049 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, T.; Li, H.; Ding, S.; Chen, F.; Fu, J.; Zhao, J. Enhanced Adsorptivity of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions Using CTS@nZVI Modified Wheat Straw-Derived Porous Carbon. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14110973
Deng T, Li H, Ding S, Chen F, Fu J, Zhao J. Enhanced Adsorptivity of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions Using CTS@nZVI Modified Wheat Straw-Derived Porous Carbon. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(11):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14110973
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Tiantian, Hansheng Li, Su Ding, Feng Chen, Jingbao Fu, and Junwei Zhao. 2024. "Enhanced Adsorptivity of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions Using CTS@nZVI Modified Wheat Straw-Derived Porous Carbon" Nanomaterials 14, no. 11: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14110973
APA StyleDeng, T., Li, H., Ding, S., Chen, F., Fu, J., & Zhao, J. (2024). Enhanced Adsorptivity of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions Using CTS@nZVI Modified Wheat Straw-Derived Porous Carbon. Nanomaterials, 14(11), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14110973





