Co-Assembled Nanosystems Exhibiting Intrinsic Fluorescence by Complexation of Amino Terpolymer and Its Quaternized Analog with Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Quaternization of P(DEGMA-co-DMAEMA-co-OEGMA)
2.3. Co-Assembly of Dye-Loaded Polymeric Nanocarriers
2.4. Effect of FBS and Ionic Strength
2.5. Characterization Methods
2.5.1. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-NMR)
2.5.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.5.3. Electrophoretic Light Scattering (ELS)
2.5.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy (FS)
2.5.5. Absorption Spectroscopy (UV-Vis)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. P(DEGMA-co-DMAEMA-co-OEGMA)–Dye Interactions
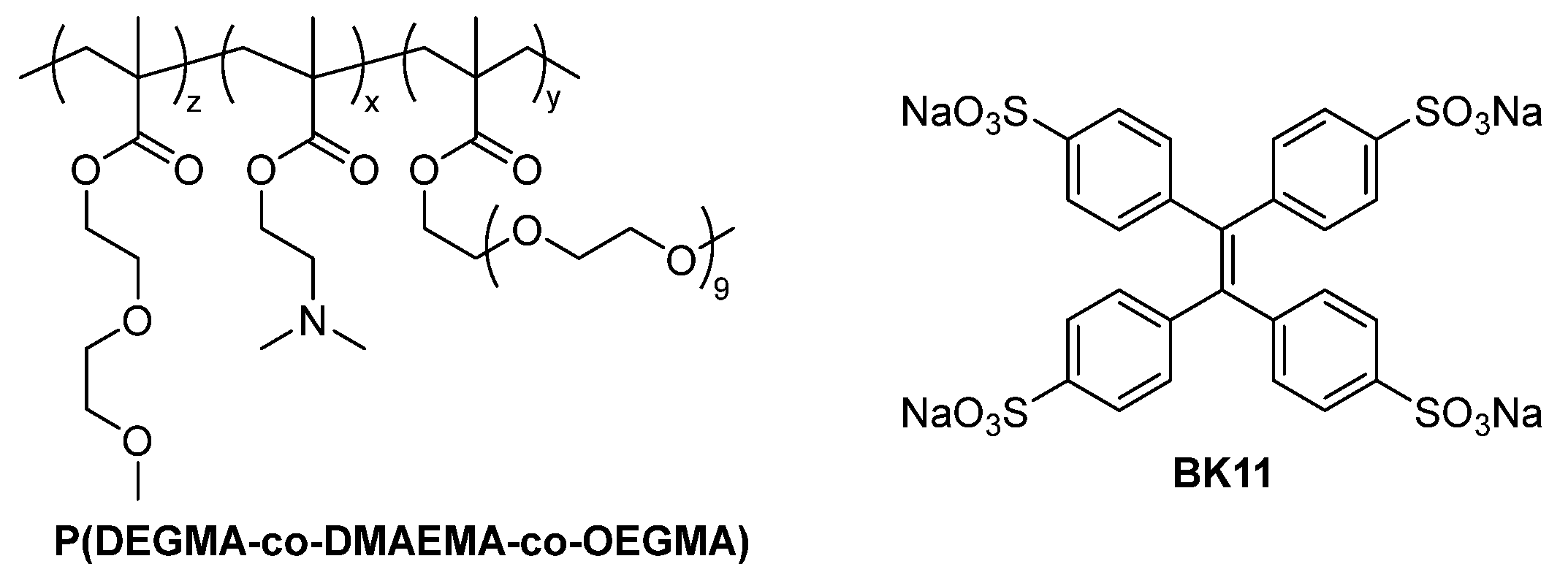
3.1.1. P(DEGMA-co-DMAEMA-co-OEGMA) Synthesis
3.1.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Sodium Tetraphenylethylene 4,4′,4″,4‴-Tetrasulfonate Dye (BK11)
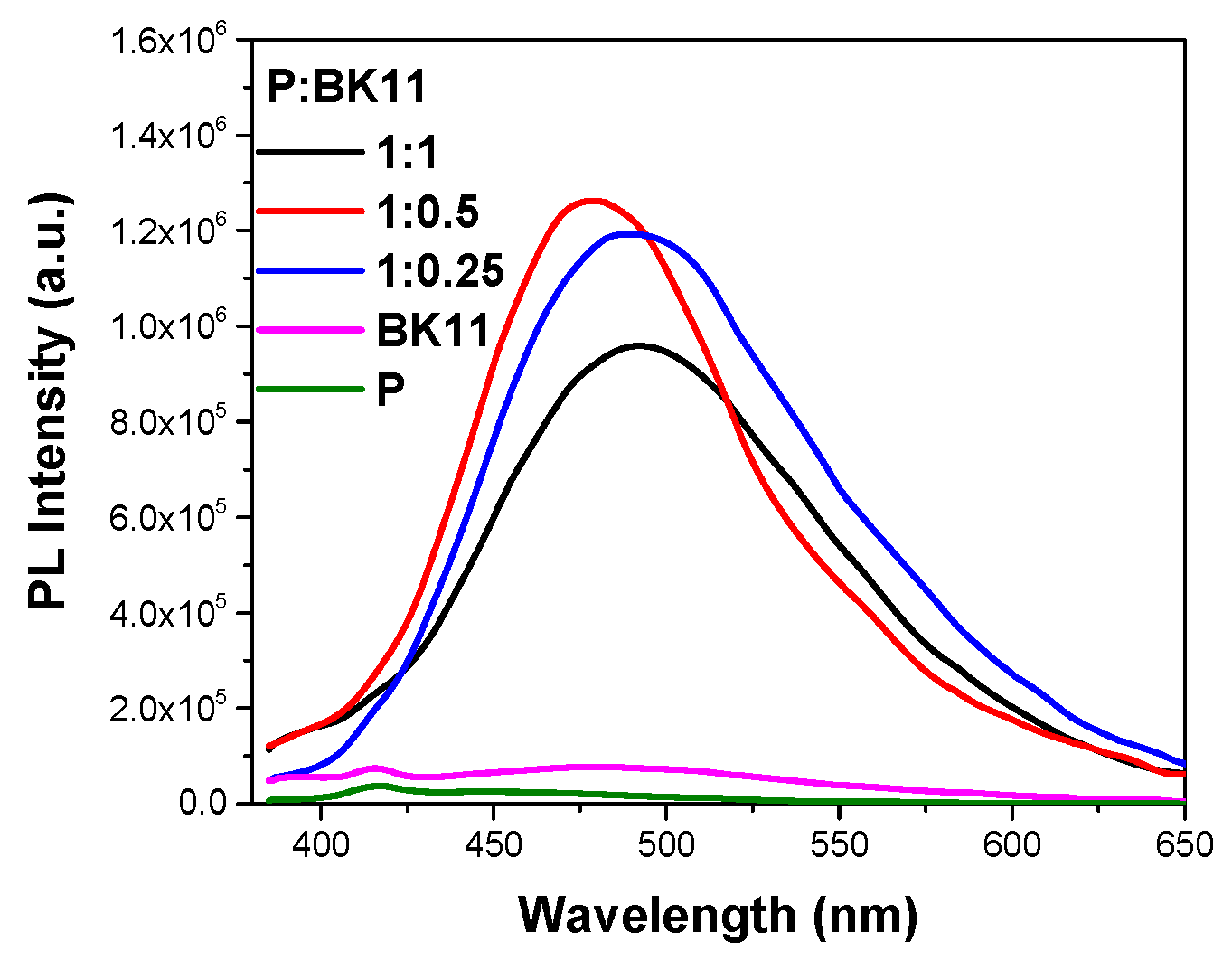
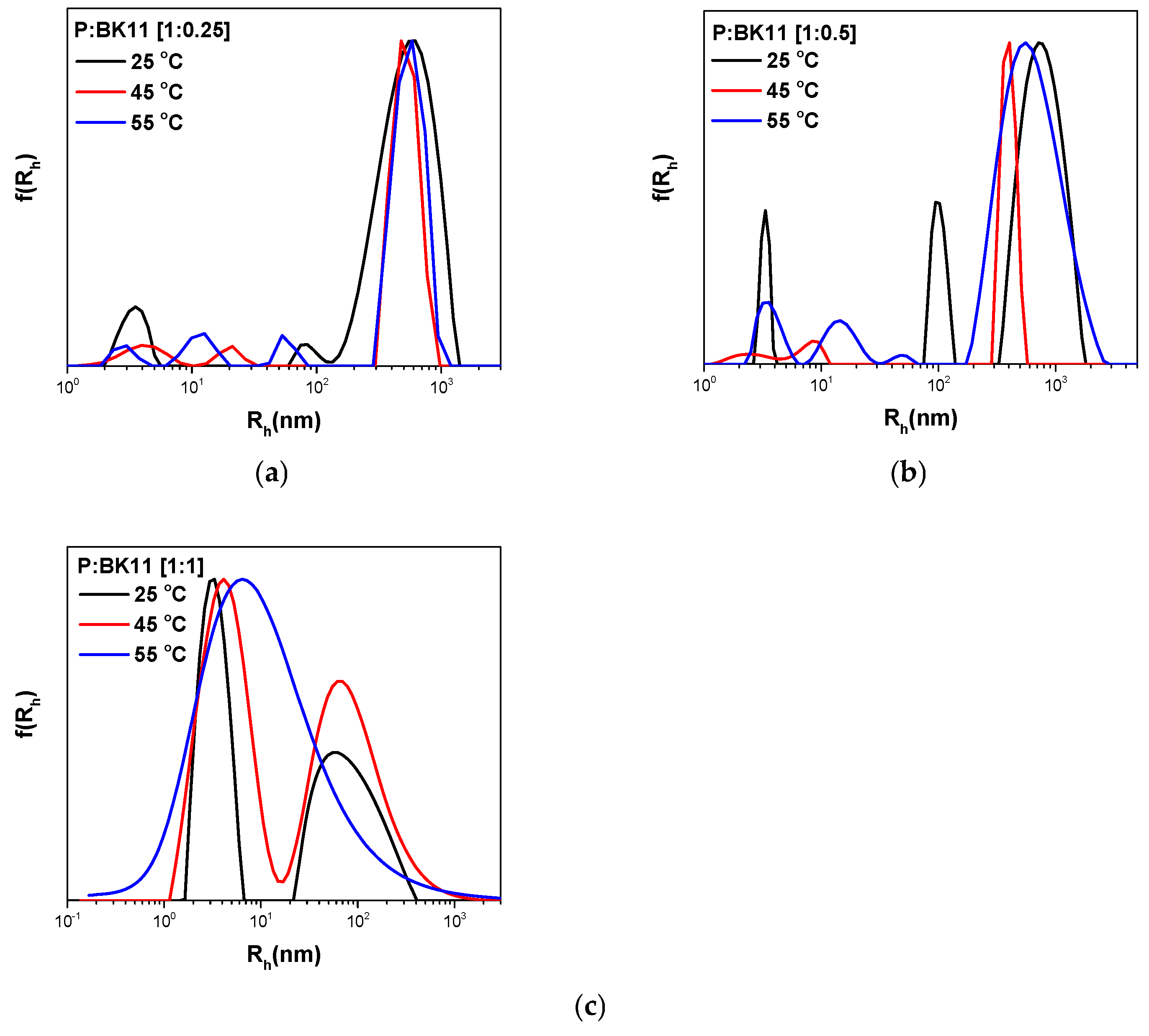
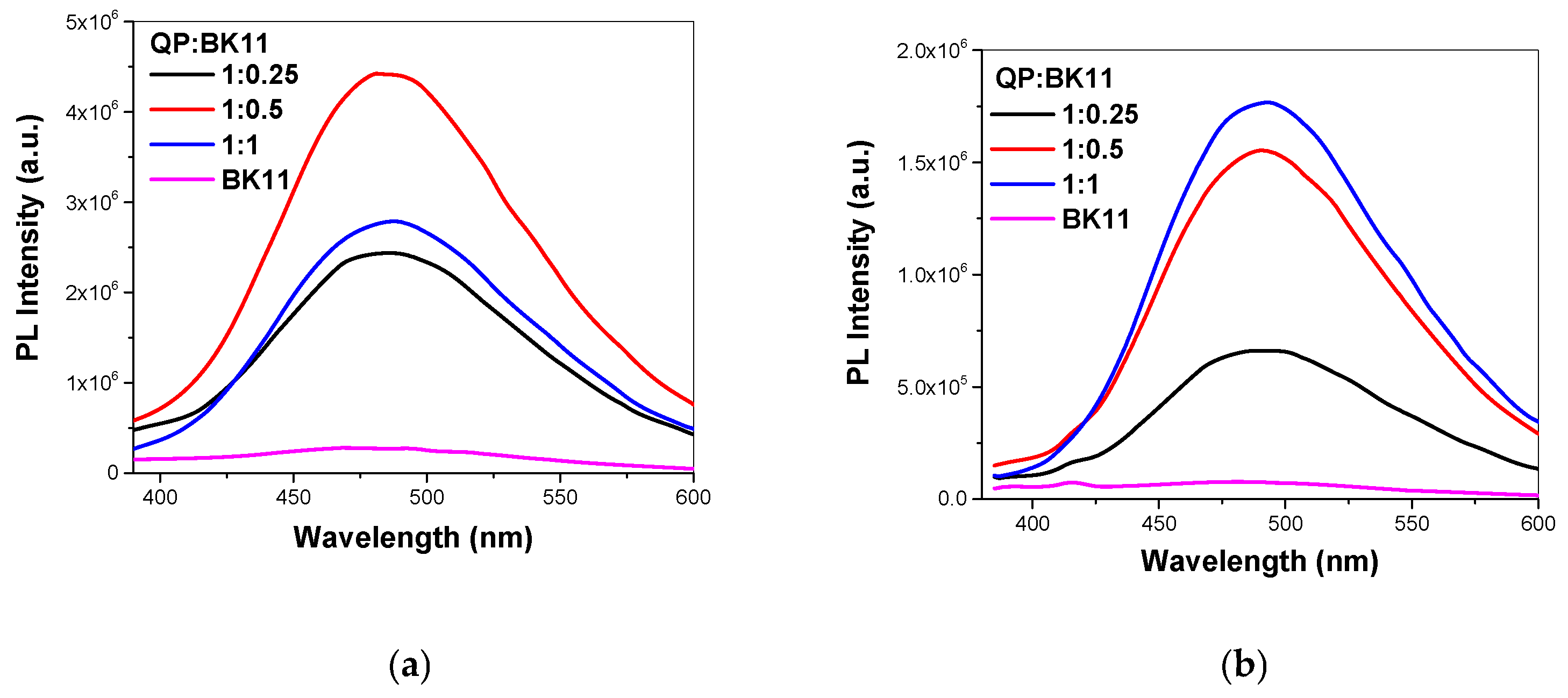
3.1.3. Co-Assembly of P(DEGMA-co-DMAEMA-co-OEGMA) and BK11 Dye
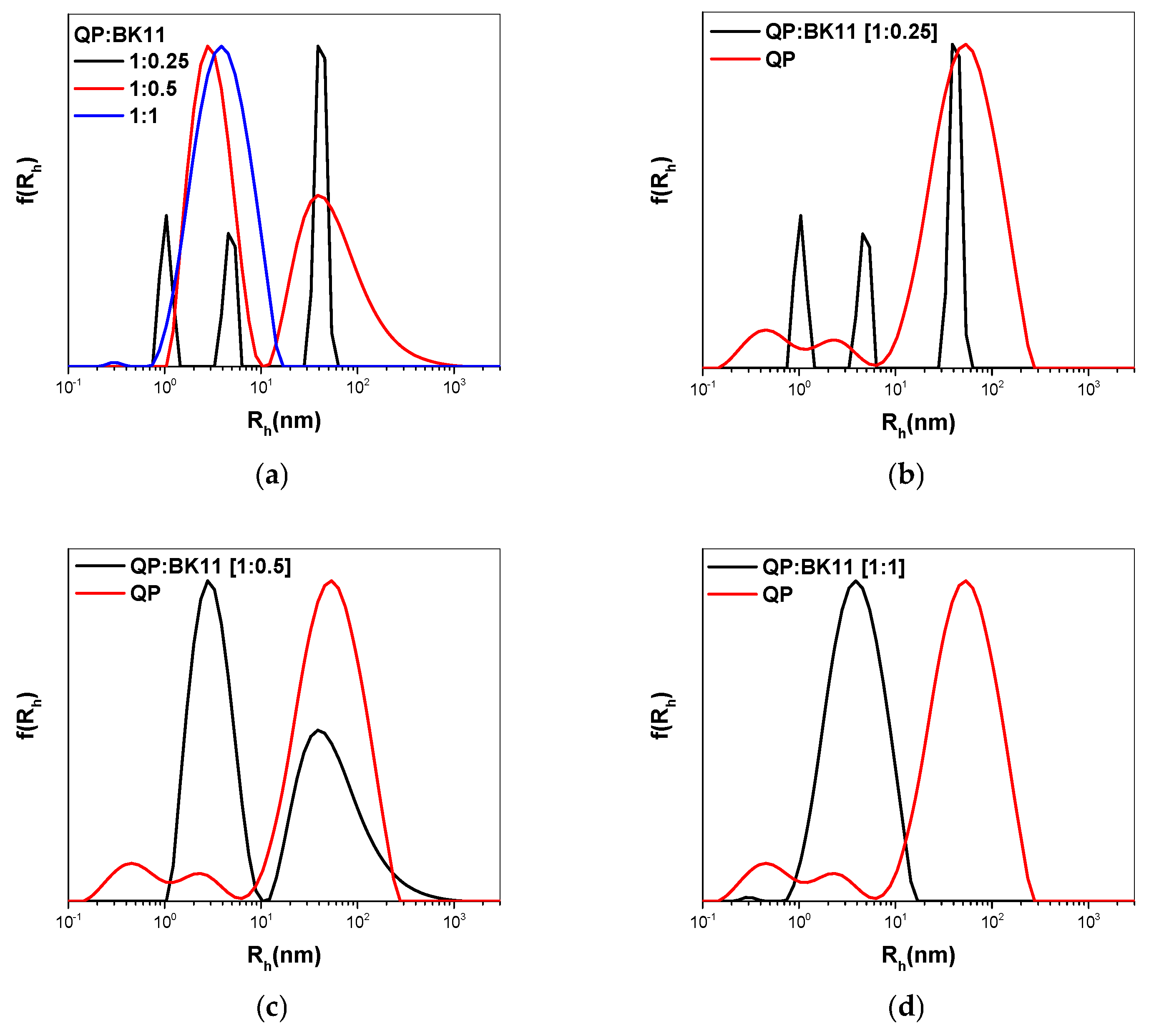
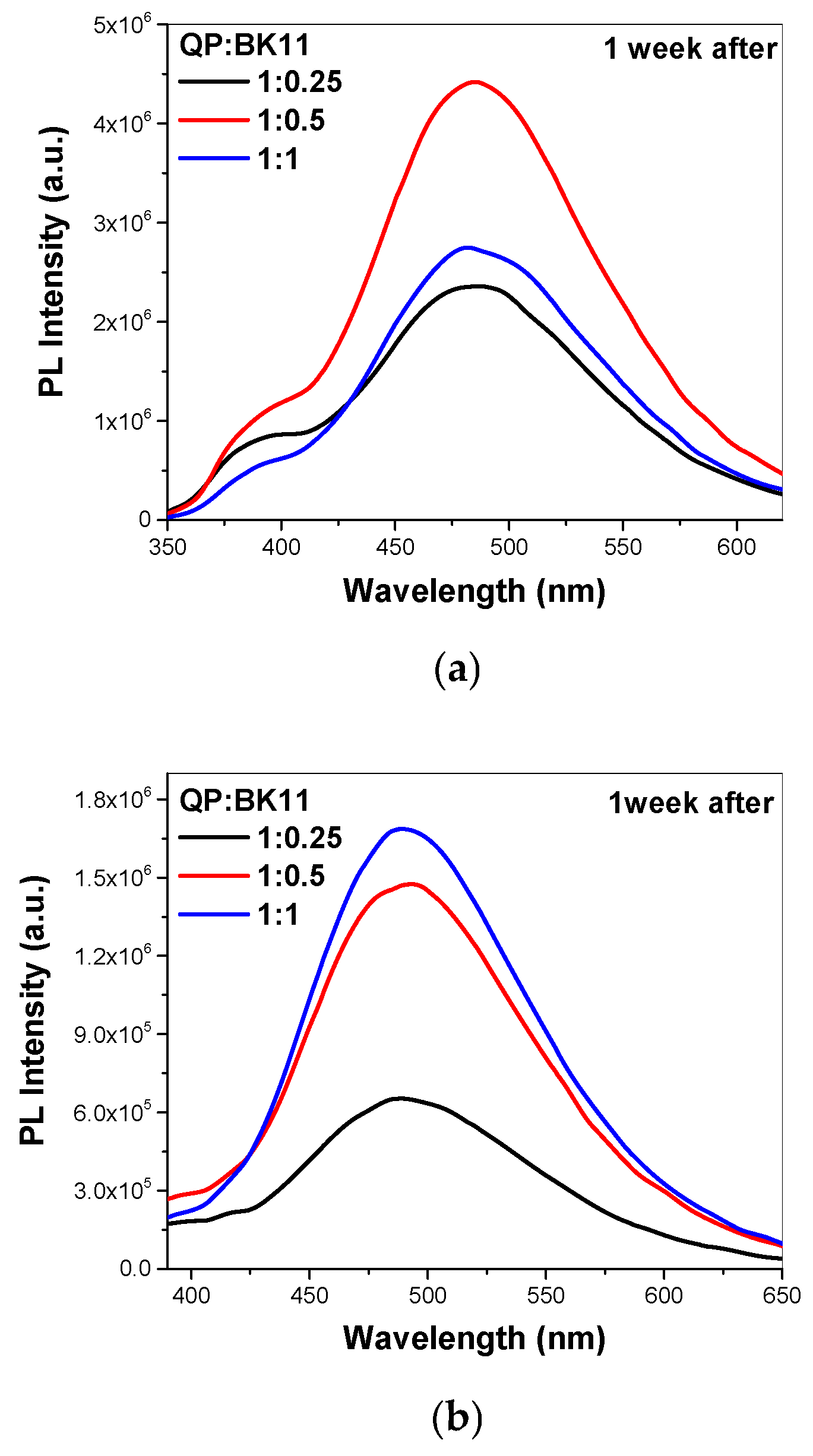
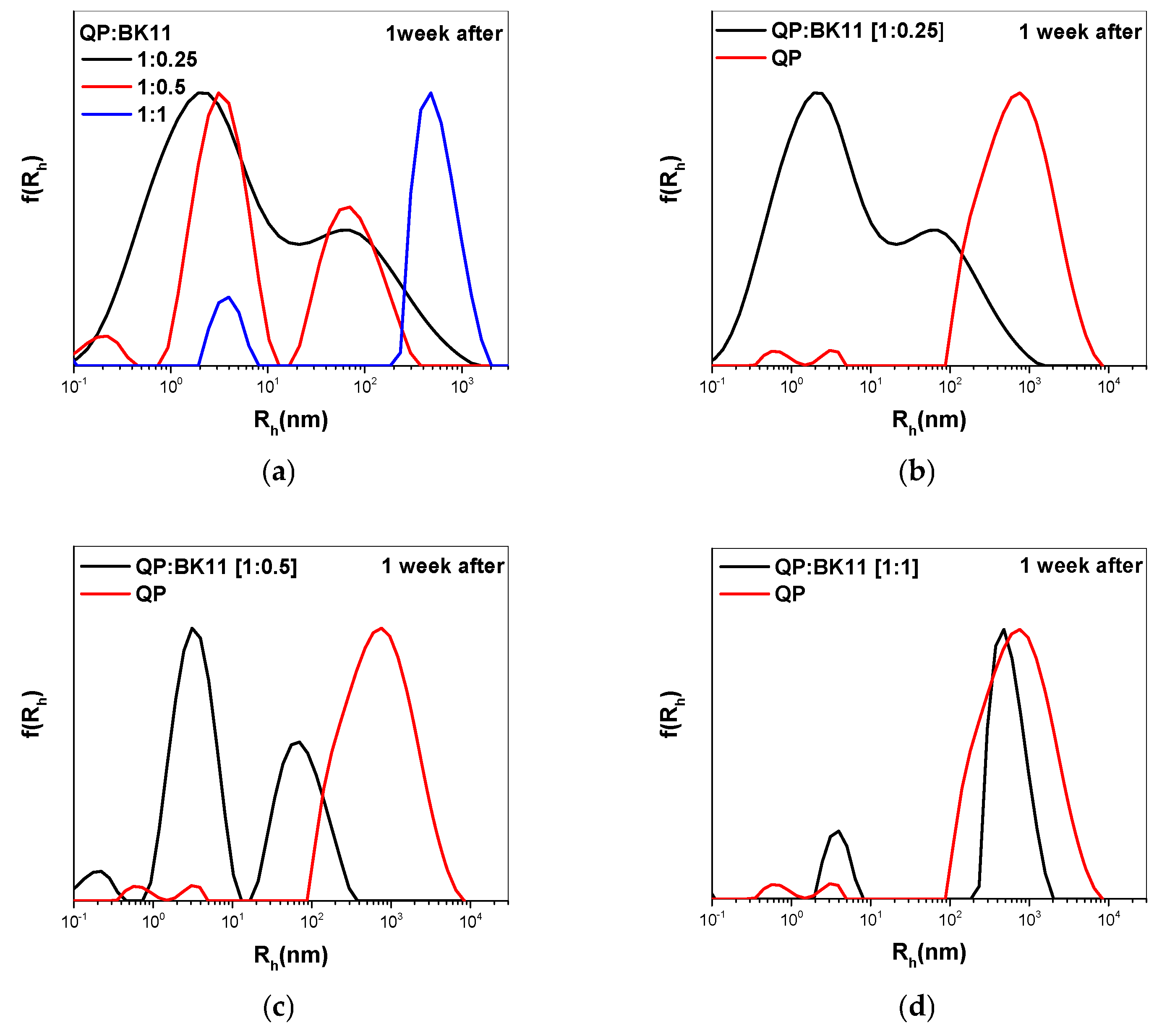
3.2. Co-Assembly of QP(DEGMA-co-DMAEMA-co-OEGMA) and BK11 Dye
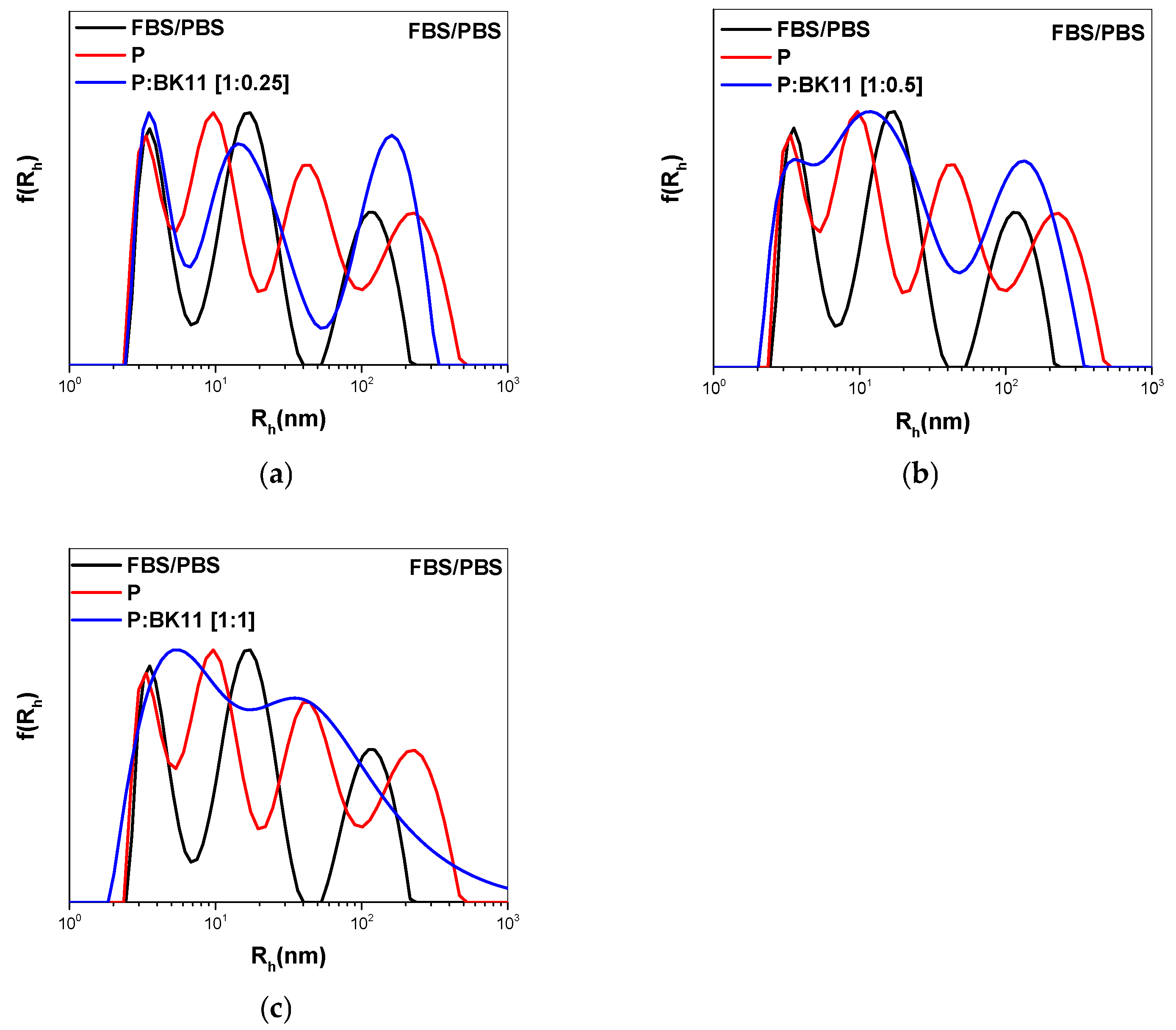
3.3. FBS Interactions with Polymer–Dye Co-Assembled Nanoparticles
3.4. NaCl Effects on Polymer–Dye Co-Assembled Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Würthner, F. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE): A Historical Perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14192–14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Tang, B.Z.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Emission of 1-Methyl-1,2,3,4,5-Pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Fundamental Understanding and Future Developments. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, G.R.; Pandey, M.; Chakravarthy, A.S.J. Review on New Horizons of Aggregation Induced Emission: From Design to Development. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 1541–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Law, C.C.W.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Dong, Y.; Lo, S.M.F.; Williams, I.D.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B.Z. Synthesis, Light Emission, Nanoaggregation, and Restricted Intramolecular Rotation of 1,1-Substituted 2,3,4,5-Tetraphenylsiloles. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Yan, D.; Wu, Q.; Song, N.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D. Aggregation-Induced Emission: A Rising Star in Chemistry and Materials Science. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugaperumal, R.; Shellaiah, M.; Srinivasadesikan, V.; Awasthi, K.; Sun, K.W.; Lin, M.-C.; Ohta, N.; Chung, W.-S. Diversiform Nanostructures Constructed from Tetraphenylethene and Pyrene-Based Acid/Base Controllable Molecular Switching Amphiphilic [2]Rotaxanes with Tunable Aggregation-Induced Static Excimers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45222–45234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Liu, B. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Recent Advances in Materials and Biomedical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9868–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, R.; Shen, W. Aggregation-Induced Emission Active Luminescent Polymeric Nanofibers: From Design, Synthesis, Fluorescent Mechanism to Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 146, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.-S.; Lu, G.-H. Natural Protoberberine Alkaloid–Montmorillonite Nanocomposite Powders with AIE Features for Visualizing High-Resolution Latent Fingerprints. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 300, 122908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuri, A.; Banerjee, M.; Chatterjee, A. Sulfonate-Functionalized AIEgens: Strategic Approaches Beyond Water Solubility for Sensing and Imaging Applications. ChemPhotoChem 2022, 6, e202100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, D.S.; Roy, A.; Pandit, S.; Alghamdi, S.; Almehmadi, M.; Alsaiari, A.A.; Abdulaziz, O.; Alsharif, A.; Khandaker, M.U.; Faruque, M.R.I. Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. e-Polymers 2023, 23, 20230049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Bhattacharyya, C.; Sahu, R.; Dua, T.K.; Kandimalla, R.; Dewanjee, S. Polymeric Nanotherapeutics: An Emerging Therapeutic Approach for the Management of Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 91, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, G.; Meher, M.; Dash, S.; Rout, R.N.; Pradhan, S.; Sahoo, D. Strategies for Targeted Delivery via Structurally Variant Polymeric Nanocarriers. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202301626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, G.; Qin, W.; Ouyan, Q.; Law, W.-C.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Yoon, H.S.; Wang, X.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dye Loaded Polymer Nanoparticles for Gene Silencing in Pancreatic Cancer and Their in Vitro and in Vivo Biocompatibility Evaluation. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Binder, W.H.; Zhu, J. Hydrogen-Bonded Polymer Nanomedicine with AIE Characteristic for Intelligent Cancer Therapy. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeldell, S.B.; Ruble, B.K.; Dmochowski, I.J. Oligonucleotide Modifications Enhance Probe Stability for Single Cell Transcriptome In vivo Analysis (TIVA). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 10001–10009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, N.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Yan, P.; Sun, S. Fabrication of AIE-Featured Probe-Incorporated Multifunctional Polymeric Micelles for Cellular Imaging and Intelligent Delivery of Paclitaxel. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liang, N.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Gong, X.; Yan, P.; Sun, S. AIE-Active Polymeric Micelles Based on Modified Chitosan for Bioimaging-Guided Targeted Delivery and Controlled Release of Paclitaxel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Ke, J.; Liu, Y.; Pei, B.; Hu, Q.; Tang, B.Z.; Wang, Z. Cationic Quaternized Chitosan Bioconjugates with Aggregation-Induced Emission Features for Cell Imaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalva, N.; Uthaman, S.; Jang, E.H.; Augustine, R.; Jeon, S.H.; Huh, K.M.; Park, I.-K.; Kim, I. Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Hyperbranched Polymer-Based Nanoparticles and Their Biological Imaging Applications. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 186, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, M. Aggregation-Induced Emission Shining in the Biomedical Field: From Bench to Bedside. Eng. Regen. 2021, 2, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Alam, P.; Bai, H.; Bhalla, V.; Bryce, M.R.; Cao, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE), Life and Health. ACS Nano. 2023, 17, 14347–14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Tang, B.Z. AIE-Based Cancer Theranostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 402, 213076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiefari, J.; Chong, Y.K.; Ercole, F.; Krstina, J.; Jeffery, J.; Le, T.P.T.; Mayadunne, R.T.A.; Meijs, G.F.; Moad, C.L.; Moad, G.; et al. Living Free-Radical Polymerization by Reversible Addition−Fragmentation Chain Transfer: The RAFT Process. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 5559–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Ding, J.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, F.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, Y. Recent Advances in RAFT Polymerization: Novel Initiation Mechanisms and Optoelectronic Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keddie, D.J. A Guide to the Synthesis of Block Copolymers Using Reversible-Addition Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) Polymerization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moad, C.L.; Moad, G. Fundamentals of Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT). Chem. Teach. Int. 2021, 3, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagenas, D.; Pispas, S. Four-Component Statistical Copolymers by RAFT Polymerization. Polymers 2024, 16, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagenas, D.; Pispas, S. Triple Hydrophilic Statistical Terpolymers via RAFT Polymerization: Synthesis and Properties in Aqueous Solutions. Polymers 2023, 15, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooyama, Y.; Sugino, M.; Enoki, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsunoji, N.; Ohshita, J. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Characteristic of Water-Soluble Tetraphenylethene (TPE) Bearing Four Sulfonate Salts. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4747–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimimarand, M.; La, D.D.; Kobaisi, M.A.; Bhosale, S.V. Flower-like Superstructures of AIE-Active Tetraphenylethylene through Solvophobic Controlled Self-Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.G.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Du, W.-T.; Kuo, S.-W. Meso/Microporous Carbons from Conjugated Hyper-Crosslinked Polymers Based on Tetraphenylethene for High-Performance CO2 Capture and Supercapacitor. Molecules 2021, 26, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-K.; Gao, Z.-Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Z.-T. Self-Assembly of Supramolecular Polymers in Water from Tetracationic and Tetraanionic Monomers in Water through Cooperative Electrostatic Attraction and Aromatic Stacking. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Int 90 (Kcps) | PDI | Rh, Cont (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | 23 | 0.57 | 2.3 | −0.4 |
| 103 | ||||
| 1:0.25 | 108 | 0.57 | 3.3 | −10.7 |
| 283 | ||||
| 1:0.5 | 106 | 0.55 | 3.5 | −1.8 |
| 258 | ||||
| 1:1 | 87 | 0.6 | 3.6 | −10.3 |
| 245 |
| Sample | Int 90 (Kcps) | PDI | Rh, Cont (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:0.25 | 235 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 498 | |||
| 1:0.5 | 230 | 0.52 | 3 101 |
| 758 | |||
| 1:1 | 37 | 0.48 | 3 |
| 78 |
| Sample | Int 90 (Kcps) | PDI | Rh, Cont (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QP | 27 | 0.58 | 32 | +60 |
| 1:0.25 | 21 | 0.56 | 1 5 | +42 |
| 42 | ||||
| 1:0.5 | 32 | 0.53 | 3 | +29 |
| 54 | ||||
| 1:1 | 29 | 0.39 | 4 | −6.5 |
| Sample | Int 90 (Kcps) | PDI | Rh, Cont (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| QP | 130 | 0.52 | 1.3 685 |
| 1:0.25 | 15 | 0.56 | 2 |
| 70 | |||
| 1:0.5 | 31 | 0.53 | 3 73 |
| 1:1 | 183 | 0.56 | 4 |
| 550 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantelaiou, M.A.; Vagenas, D.; Karvelis, E.S.; Rotas, G.; Pispas, S. Co-Assembled Nanosystems Exhibiting Intrinsic Fluorescence by Complexation of Amino Terpolymer and Its Quaternized Analog with Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dye. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201631
Pantelaiou MA, Vagenas D, Karvelis ES, Rotas G, Pispas S. Co-Assembled Nanosystems Exhibiting Intrinsic Fluorescence by Complexation of Amino Terpolymer and Its Quaternized Analog with Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dye. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(20):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201631
Chicago/Turabian StylePantelaiou, Michaila Akathi, Dimitrios Vagenas, Evangelos S. Karvelis, Georgios Rotas, and Stergios Pispas. 2024. "Co-Assembled Nanosystems Exhibiting Intrinsic Fluorescence by Complexation of Amino Terpolymer and Its Quaternized Analog with Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dye" Nanomaterials 14, no. 20: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201631
APA StylePantelaiou, M. A., Vagenas, D., Karvelis, E. S., Rotas, G., & Pispas, S. (2024). Co-Assembled Nanosystems Exhibiting Intrinsic Fluorescence by Complexation of Amino Terpolymer and Its Quaternized Analog with Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dye. Nanomaterials, 14(20), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201631







