Supramolecular Hydrogel Dexamethasone–Diclofenac for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Experimental Animals
2.3. Fabrication of Supramolecular Hydrogel
2.4. TEM Analysis
2.5. Rheological Analysis
2.6. FTIR Analysis
2.7. XRD Analysis
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release
2.9. Hemolytic Assay
2.10. Cytotoxicity Study
2.11. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities
2.12. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.13. Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Model and Monitoring
2.14. Assessment of Arthritis Progression upon CFA Administration
2.15. Radiography and Histological Analysis
2.16. Biochemical Analysis
2.17. Index of Spleen and Thymus Assay
2.18. Western Blotting
2.19. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
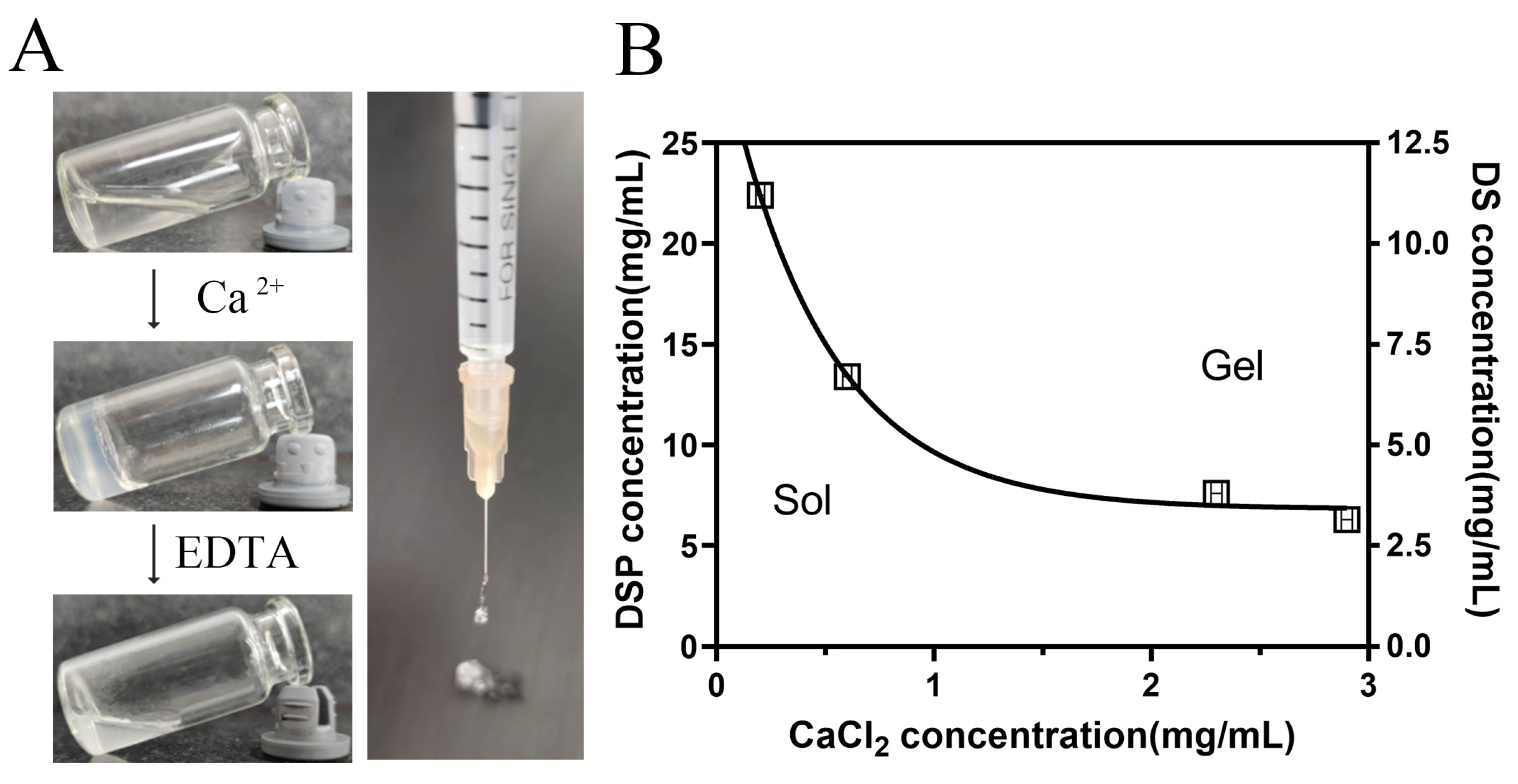
3.1. Formation of DSP–DS Supramolecular Hydrogel
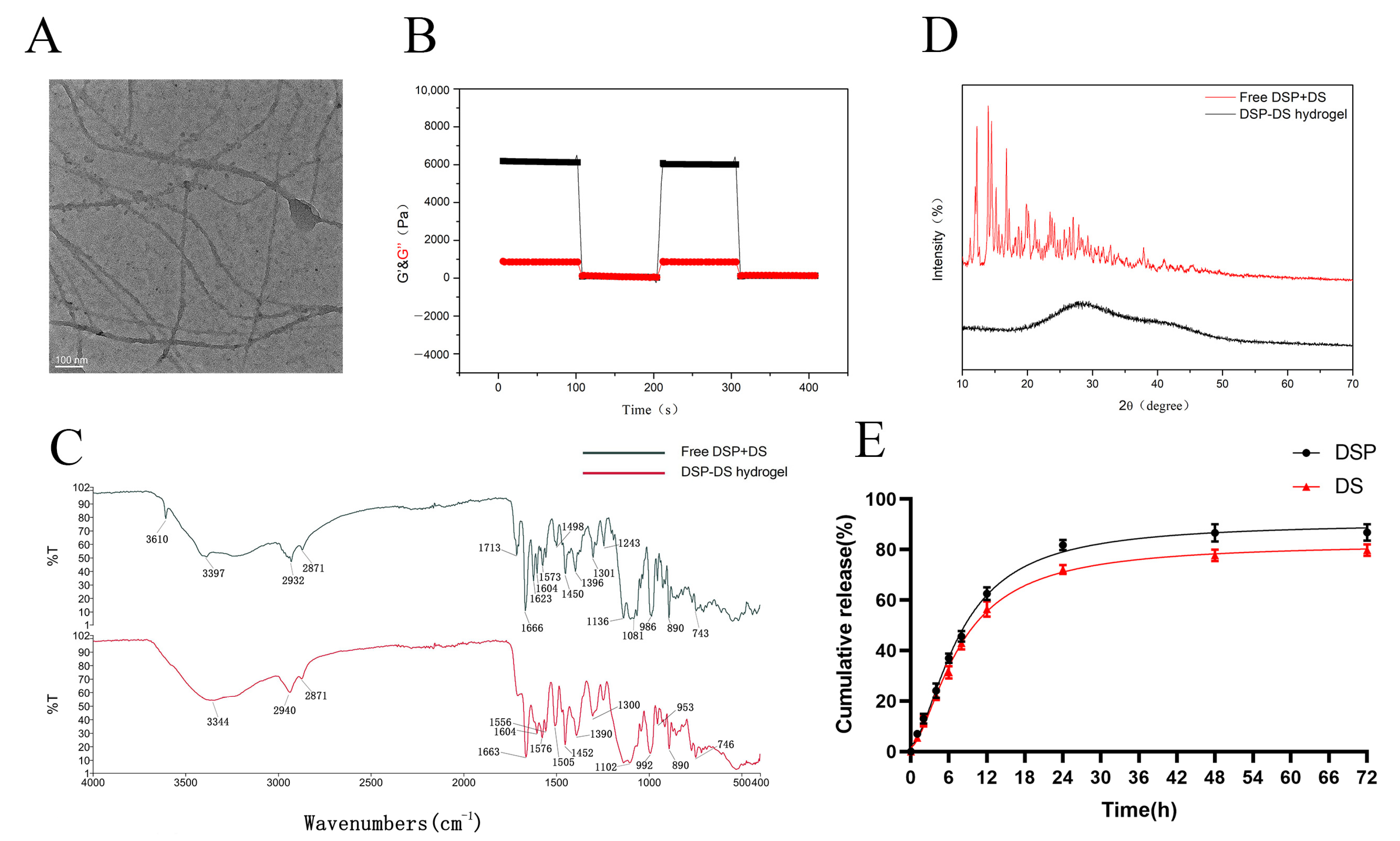
3.2. Characterization of DSP–DS Hydrogel
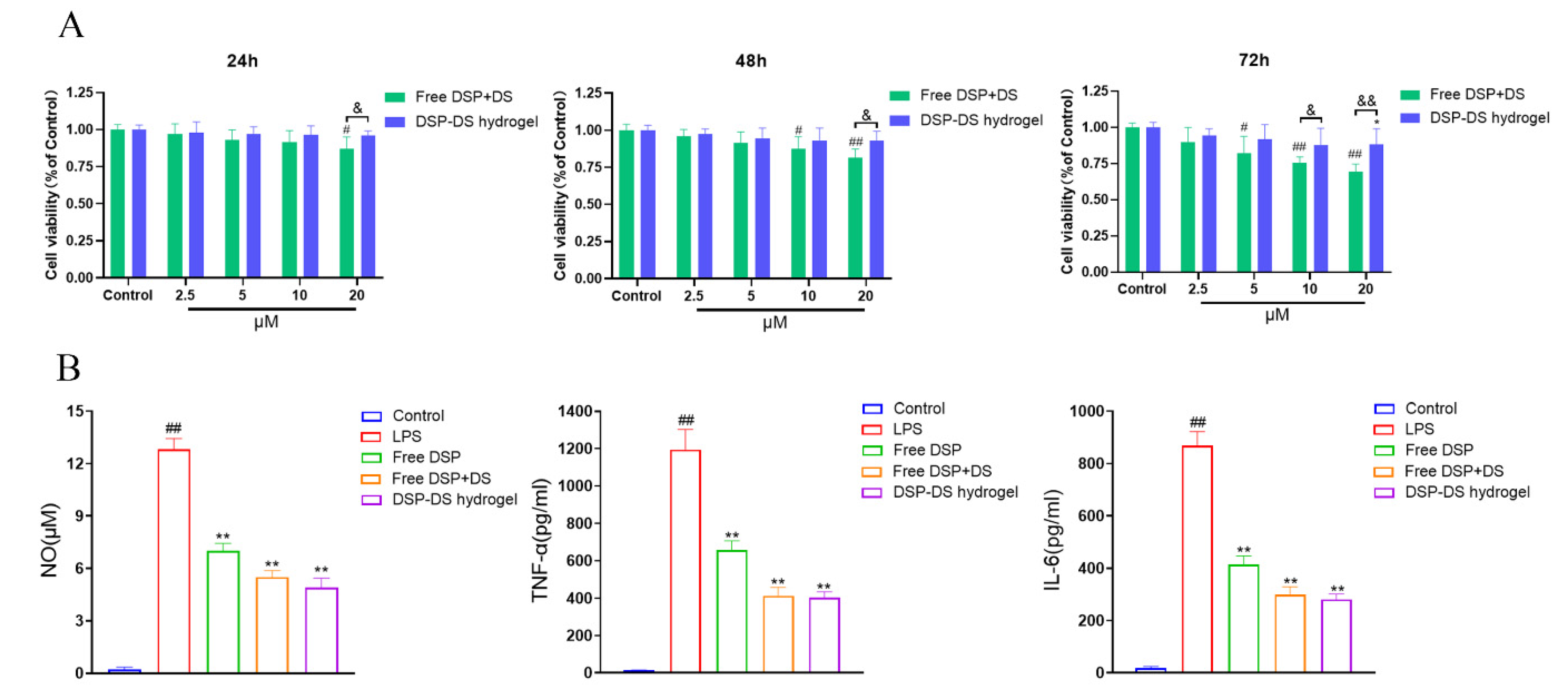
3.3. Effect of DSP–DS Hydrogel on the Cytotoxicity and Level of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 in RAW264.7
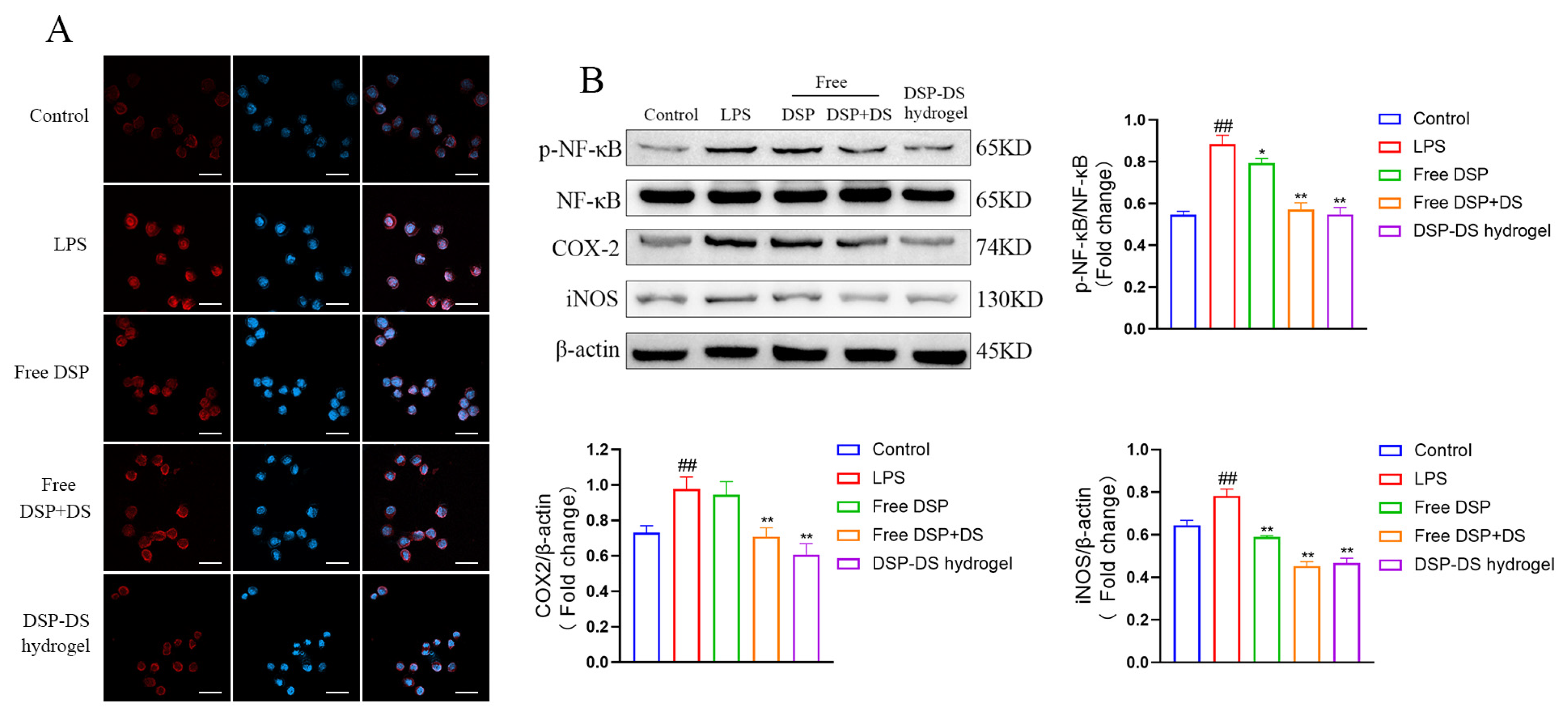
3.4. Effect of DSP–DS Hydrogel on the NF-κB/COX-2/iNOS Pathway Suppression in LPS-Activated RAW264.7
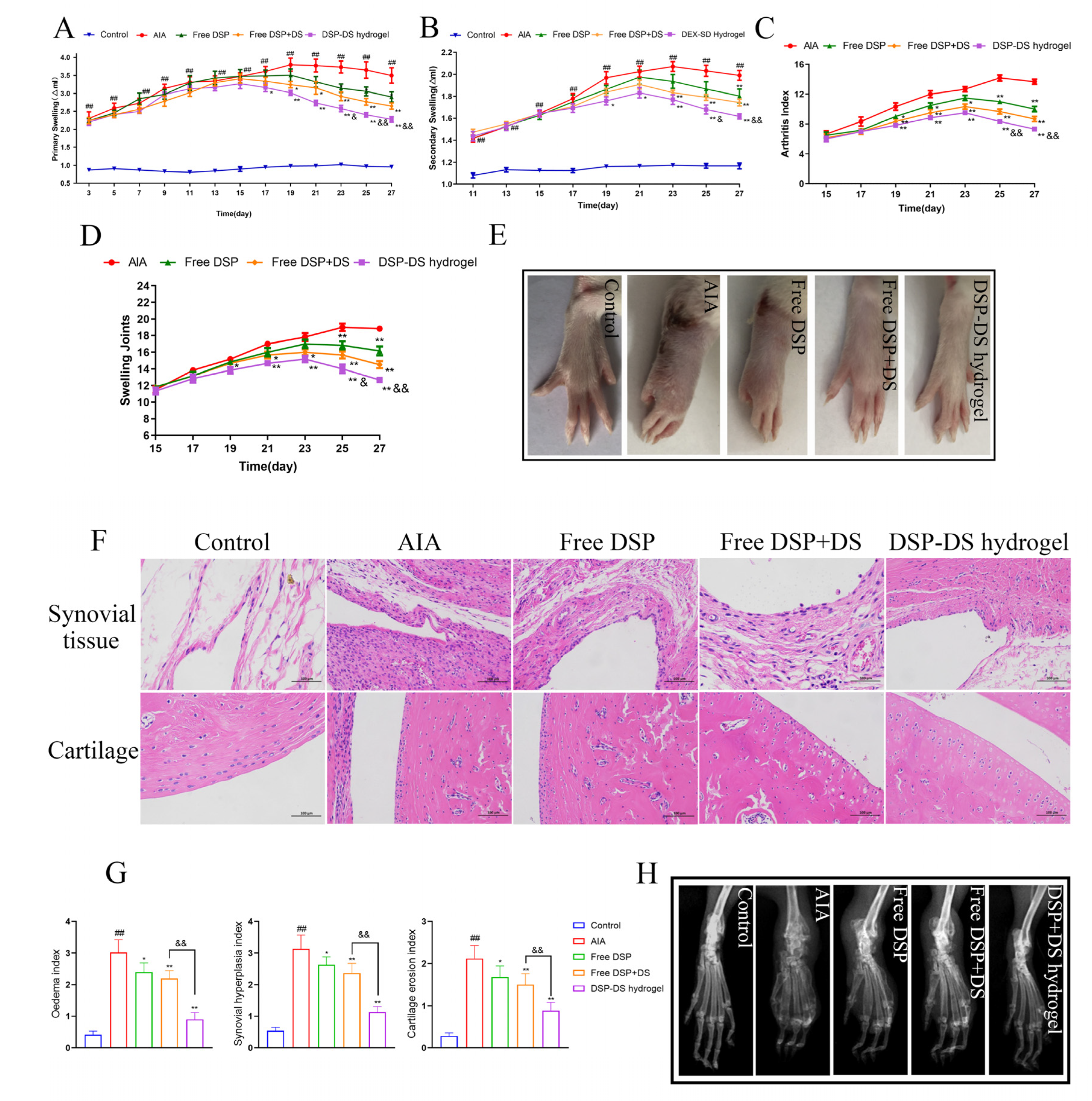
3.5. Effect of DSP–DS Hydrogel on the Therapeutic Efficacy in AIA Rats
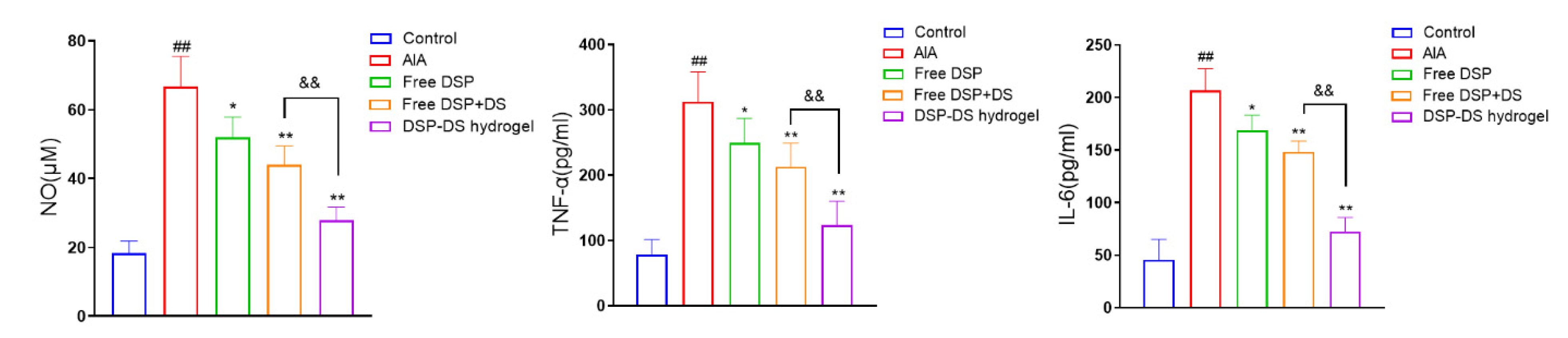
3.6. Effect of DSP–DS Hydrogel on the Level of NO, TNF-α and IL-6 in Serum of AIA Rats
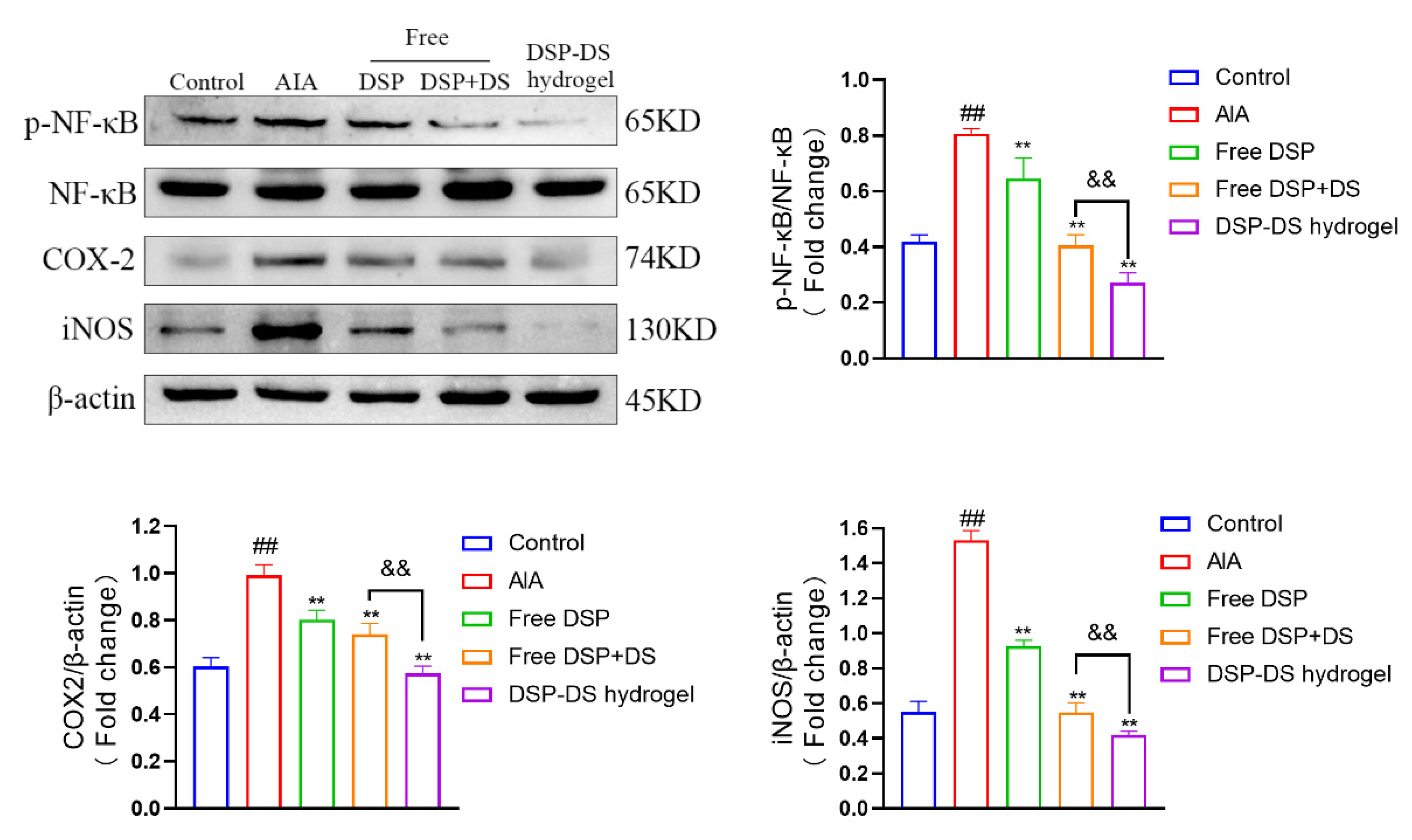
3.7. Effect of DSP–DS Hydrogel on the NF-κB/COX-2/iNOS Pathway Suppression in AIA Rats
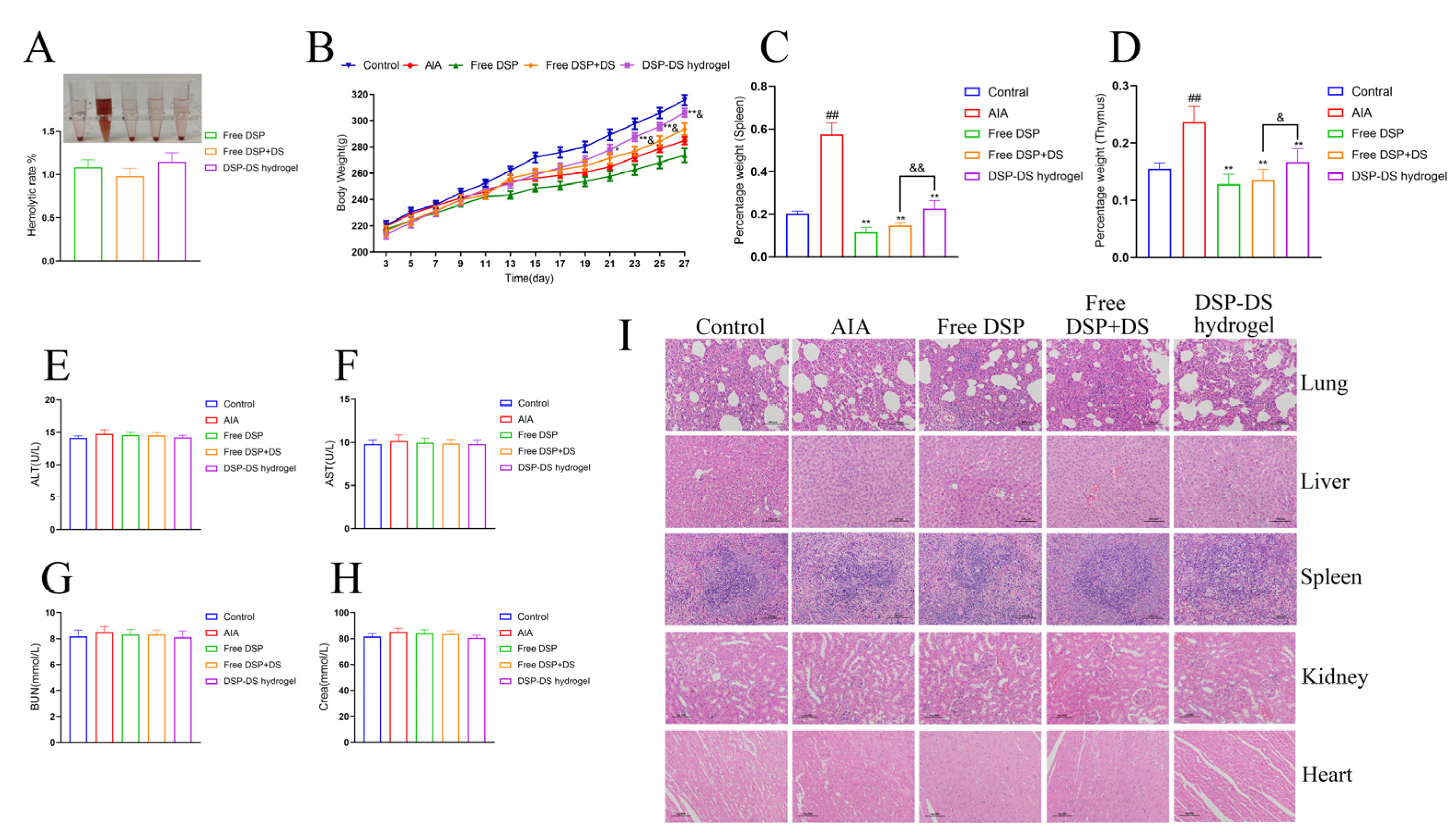
3.8. Evaluation of Biocompatibility and Adverse Effects on DSP–DS Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Gu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qi, W.; Lin, Z.; Zhai, W.; Zhan, J.; Li, Q.; Cai, Y.; Lu, Y. Robust drug bioavailability and safety for rheumatoid arthritis therapy using D-amino acids-based supramolecular hydrogels. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 15, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, G.; Huang, G. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Chemical Drugs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Top. Curr. Chem. 2019, 377, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anita, C.; Munira, M.; Mural, Q.; Shaily, L. Topical nanocarriers for management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Ren, R.; Wei, X.; Jia, Z.; Chen, N.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lele, S.M.; Zhong, H.A.; Goldring, M.B.; et al. Thermoresponsive polymeric dexamethasone prodrug for arthritis pain. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, S.; Peng, X.; Zhao, T.; He, Q.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. An intra-articular injectable phospholipids-based gel for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Qin, X.; Yang, R.; Qin, J.; Li, W.; Luan, K.; Wu, Z.; Song, L. Intra-articular Administration of Chitosan Thermosensitive In Situ Hydrogels Combined With Diclofenac Sodium-Loaded Alginate Microspheres. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, S.; Tibbitt, M.W. Supramolecular engineering of hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Biomedical applications of supramolecular hydrogels with enhanced mechanical properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 321, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Kim, S.W.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, W.C.; Kang, Y.J.; Khang, D. Suppression of human arthritis synovial fibroblasts inflammation using dexamethasone-carbon nanotubes via increasing caveolin-dependent endocytosis and recovering mitochondrial membrane potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5761–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Fu, F. Combined treatment with low dose prednisone and escin improves the anti-arthritic effect in experimental arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 31, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buritova, J.; Honoré, P.; Chapman, V.; Besson, J.M. Enhanced effects of co-administered dexamethasone and diclofenac on inflammatory pain processing and associated spinal c-Fos expression in the rat. Pain 1996, 64, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zeng, R.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Tasneem, S.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, Y.X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Cai, X.; et al. Kadsura heteroclita stem suppresses the onset and progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Ismail, M.; Shan, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Ling, L. ROS-mediated liposomal dexamethasone: A new FA-targeted nanoformulation to combat rheumatoid arthritis via inhibiting iRhom2/TNF-α/BAFF pathways. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 20170–20185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Tan, Y.; Dong, Z.; Lu, J.; Han, X.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, W.; Shen, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Injectable Anti-inflammatory Nanofiber Hydrogel to Achieve Systemic Immunotherapy Post Local Administration. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6763–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maver, T.; Gradišnik, L.; Smrke, D.M.; Stana Kleinschek, K.; Maver, U. Systematic Evaluation of a Diclofenac-Loaded Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Wound Dressing and Its Release Performance with Changing pH and Temperature. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa’adon, S.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Yusof, A.H.M.; Faudzi, A.A.M.; Sagadevan, S.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Anand, J.S.; Amin, K.A.M. Electrospun Nanofiber and Cryogel of Polyvinyl Alcohol Transdermal Patch Containing Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Release Studies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Naeem, M.; Noh, J.K.; Lee, E.H.; Yoo, J.W. Dexamethasone phosphate-loaded folate-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles for selective delivery to activated macrophages and suppression of inflammatory responses. Macromol. Res. 2015, 23, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, T.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, R.; Chen, H.; Li, X. Calcium ion coordinated dexamethasone supramolecular hydrogel as therapeutic alternative for control of non-infectious uveitis. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ran, Y.; Ge, Y.; Raza, F.; Li, S.; Zafar, H.; Wu, Y.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Yu, C.; Sun, M.; et al. pH-Sensitive Peptide Hydrogels as a Combination Drug Delivery System for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Sheng, R.; Li, P.; Liu, P.; Luo, J.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, S. Integration of transdermal chemistry and network pharmacology to decipher the mechanism of ShexiangZhuifeng analgesic plaster to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Phytomedicine 2023, 108, 154507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Alivernini, S. Synovial tissue macrophages in joint homeostasis, rheumatoid arthritis and disease remission. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Körner, H.; Liu, X. Susceptibility to Intracellular Infections: Contributions of TNF to Immune Defense. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.J. Nitric oxide scavengers based on o-phenylenediamine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Peng, J.; Yang, K.L.; Wang, C.H.; Guo, Y.F.; Guo, Z.S.; Du, S.Y. Therapeutic effects of Chinese medicine Di-Long (Pheretima vulgaris) on rheumatoid arthritis through inhibiting NF-κB activation and regulating Th1/Th2 balance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, G.; Shyni, G.L.; Mohan, S.; Abraham, B.; Nisha, P.; Ranjith, S.; Rajankutty, K.; Raghu, K.G. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effect of Tinospora cordifolia via modulation of JAK/STAT pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crunkhorn, S. Hydrogel fights infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Cheng, L.; Song, J.; Wang, M.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Wu, Z. Therapeutic effects of Caesalpinia minax Hance on complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis and the anti-inflammatory activity of cassane diterpenes as main active components. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 226, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-κB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Lee, W.S.; Shin, J.S.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, K.T. Xanthotoxin suppresses LPS-induced expression of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6 via AP-1, NF-κB, and JAK-STAT inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athari, S.S. Targeting cell signaling in allergic asthma. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2019, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Rosa, I.A.; Perez-Sanchez, C.; Ruiz-Limon, P.; Patiño-Trives, A.; Torres-Granados, C.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Del Carmen Abalos-Aguilera, M.; Cecchi, I.; Ortega, R.; Caracuel, M.A.; et al. Impaired microRNA processing in neutrophils from rheumatoid arthritis patients confers their pathogenic profile. Modulation by biological therapies. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, J.; Luypaert, A.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Yang, P.; Guo, W.; Lu, P.; Huang, C.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yang, G.; Du, Y.; Zhao, F. Supramolecular Hydrogel Dexamethasone–Diclofenac for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070645
Song Y, Yang P, Guo W, Lu P, Huang C, Cai Z, Jiang X, Yang G, Du Y, Zhao F. Supramolecular Hydrogel Dexamethasone–Diclofenac for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(7):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070645
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yanqin, Pufan Yang, Wen Guo, Panpan Lu, Congying Huang, Zhiruo Cai, Xin Jiang, Gangqiang Yang, Yuan Du, and Feng Zhao. 2024. "Supramolecular Hydrogel Dexamethasone–Diclofenac for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis" Nanomaterials 14, no. 7: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070645
APA StyleSong, Y., Yang, P., Guo, W., Lu, P., Huang, C., Cai, Z., Jiang, X., Yang, G., Du, Y., & Zhao, F. (2024). Supramolecular Hydrogel Dexamethasone–Diclofenac for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nanomaterials, 14(7), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070645




