Modeling of Self-Aligned Selector Based on Ultra-Thin Metal Oxide for Resistive Random-Access Memory (RRAM) Crossbar Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
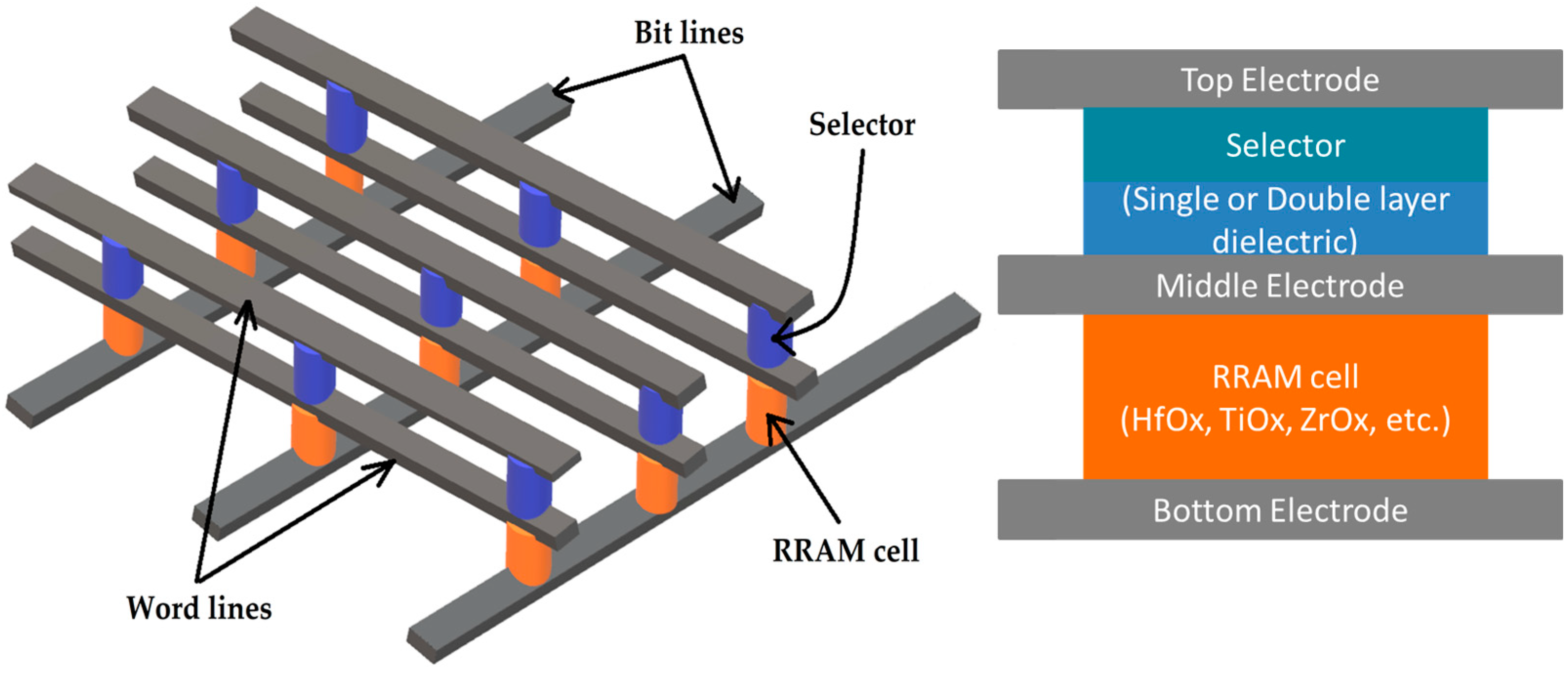
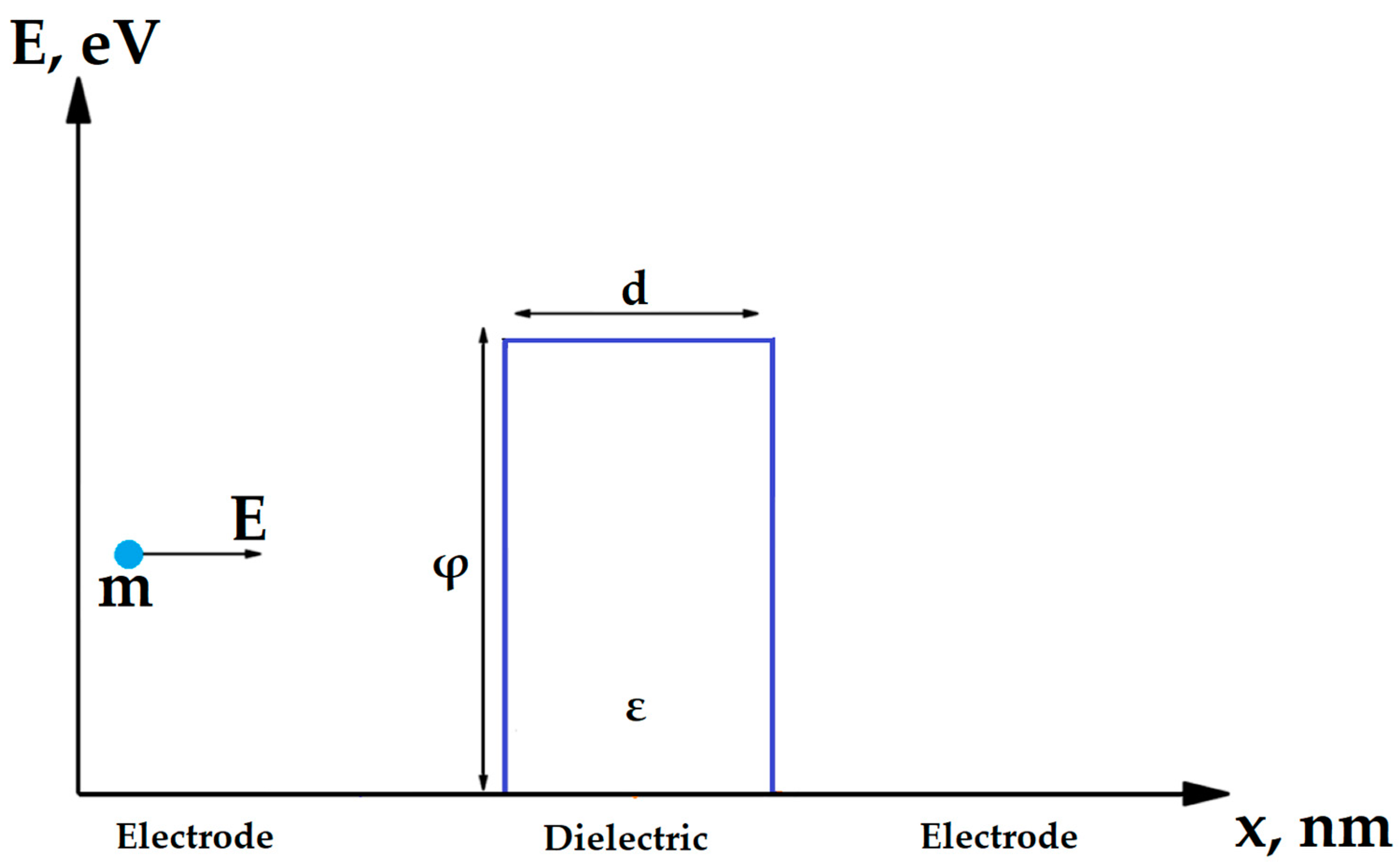
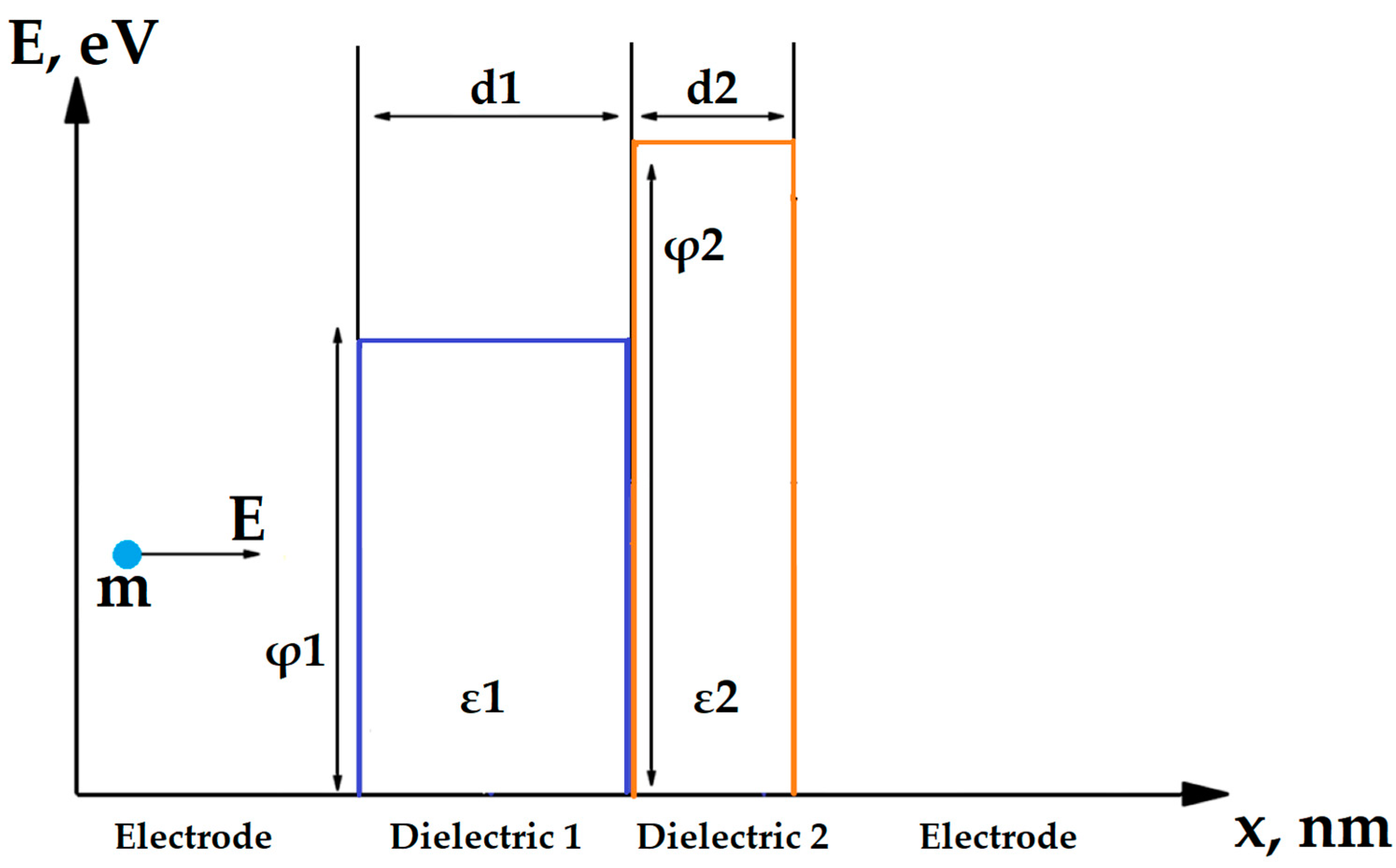
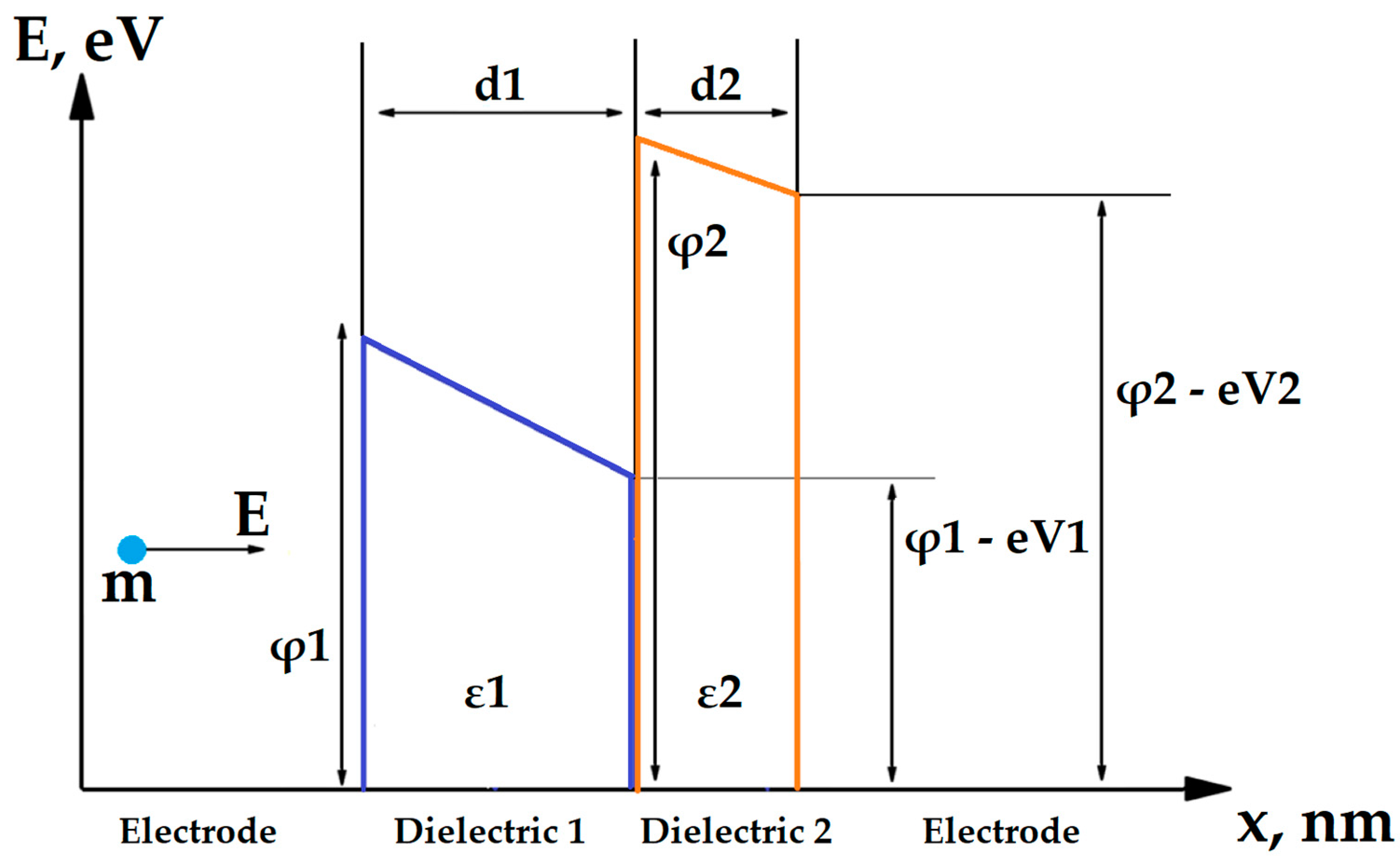
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
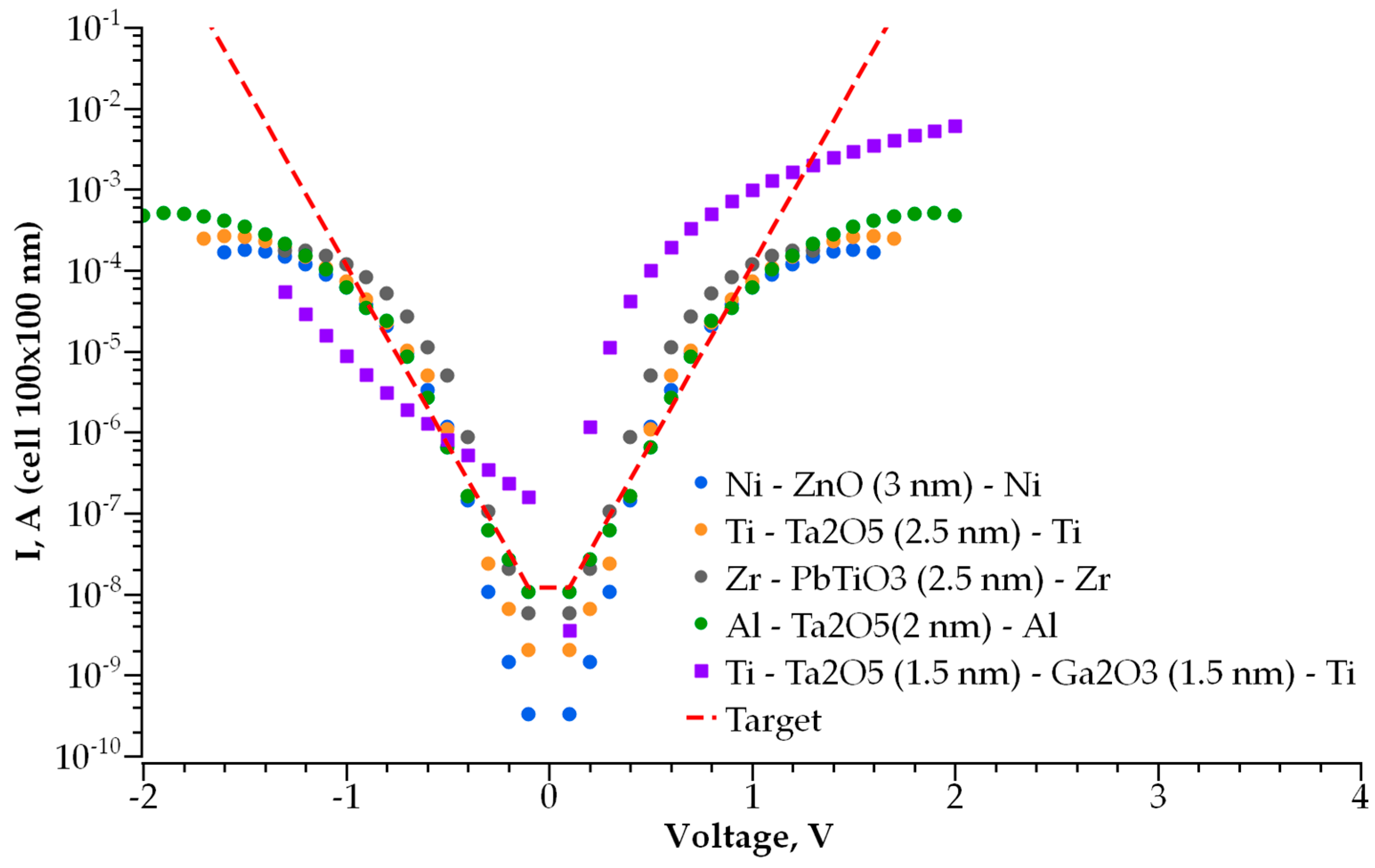
- The current–voltage characteristics are diode-like [22], without hysteresis during forward and reverse voltage sweep; i.e., the selector material should be free of shallow and deep traps, which are able to capture and hold negative charge.
- (2)
- Selector resistance at a programming voltage (typically of 0.5 V to 1 V) should be in a range of 102 to 104 Ω, depending on the memory cell resistance in its low-resistance state (LRS) [23].
- (3)
- Selector resistance at a reading voltage (typically 0.1 V) should be in a range of 104 to 106 Ω, depending on the memory cell resistance in its high-resistance state (HRS) [24].
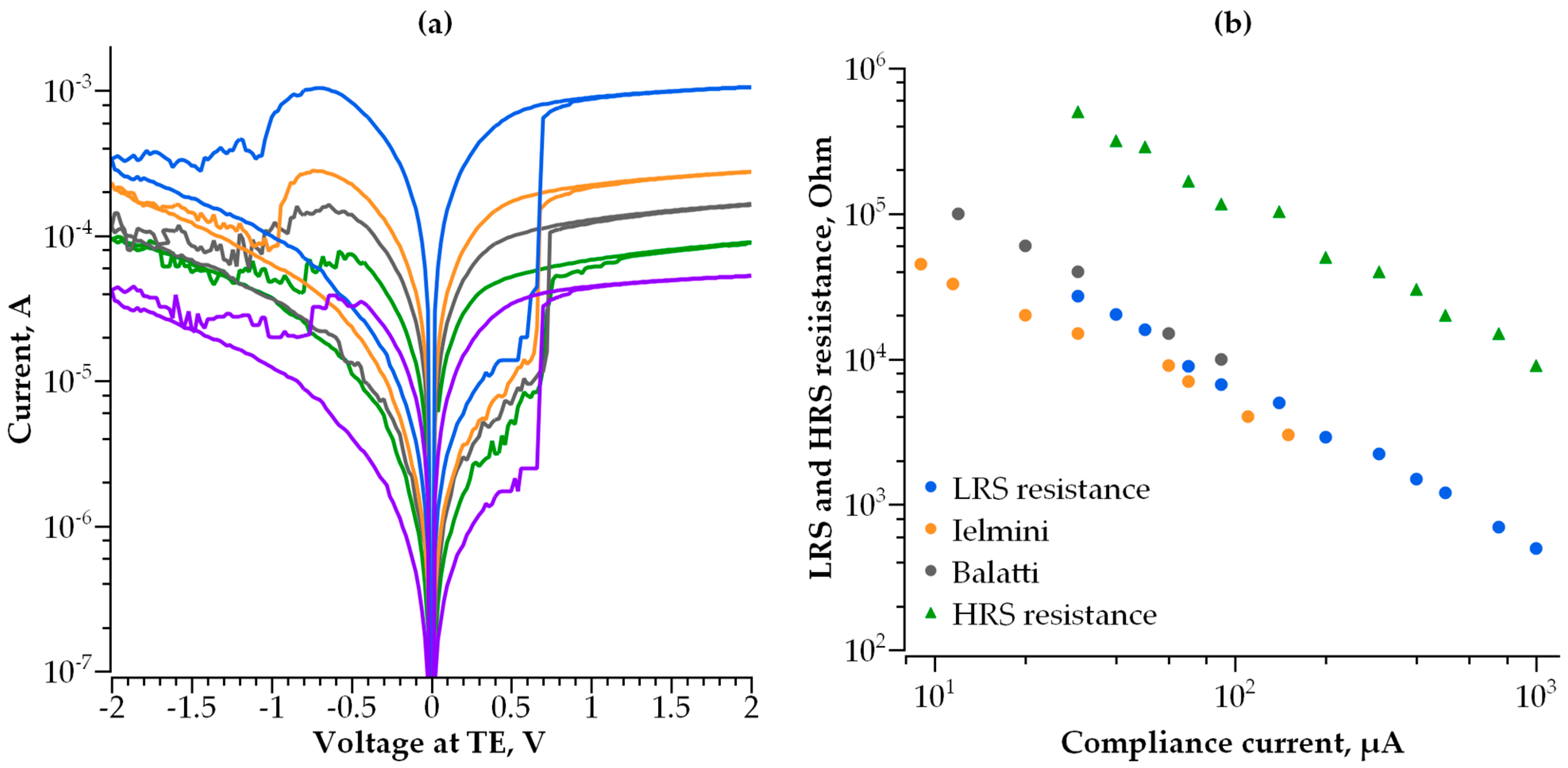
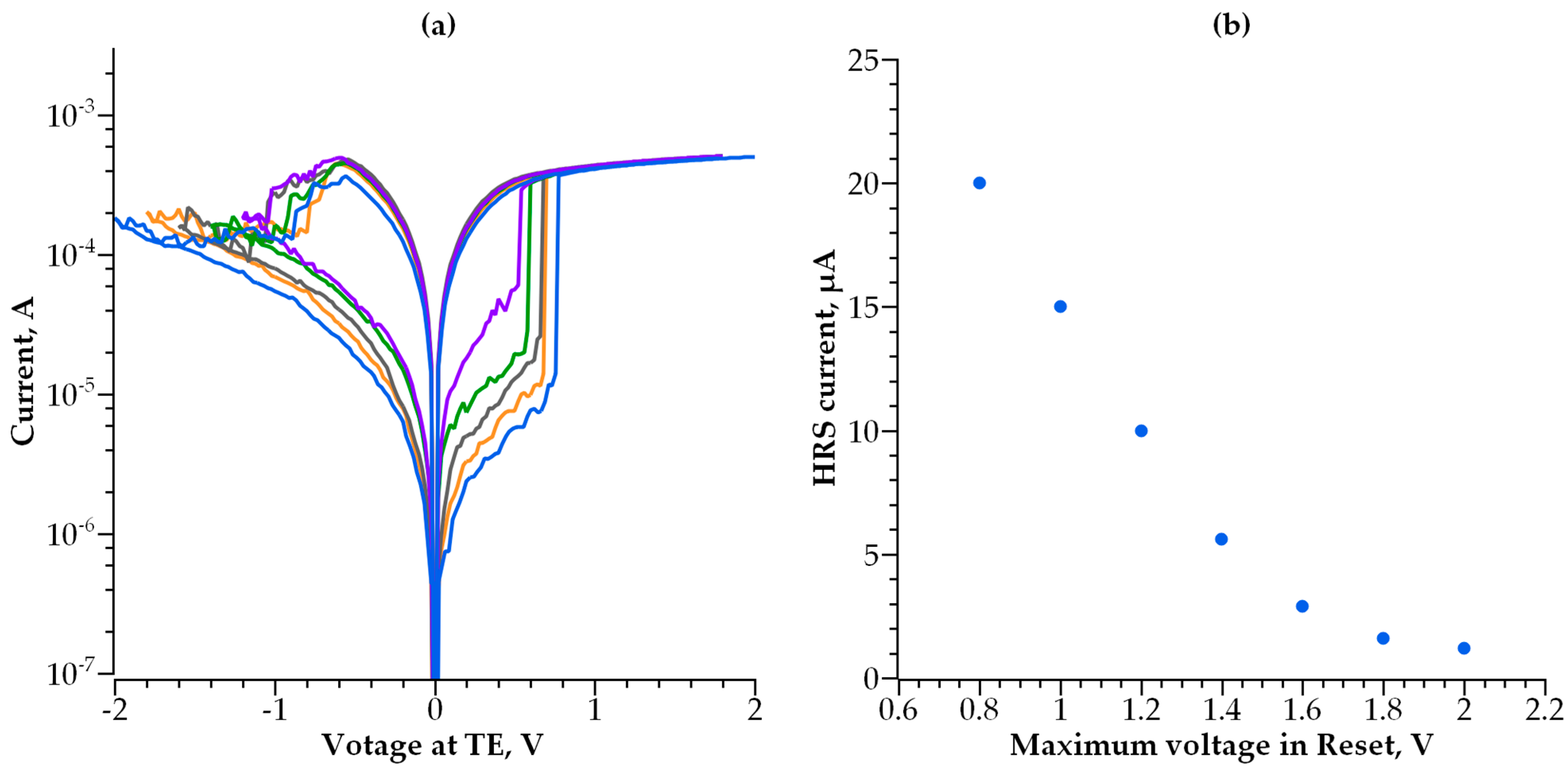
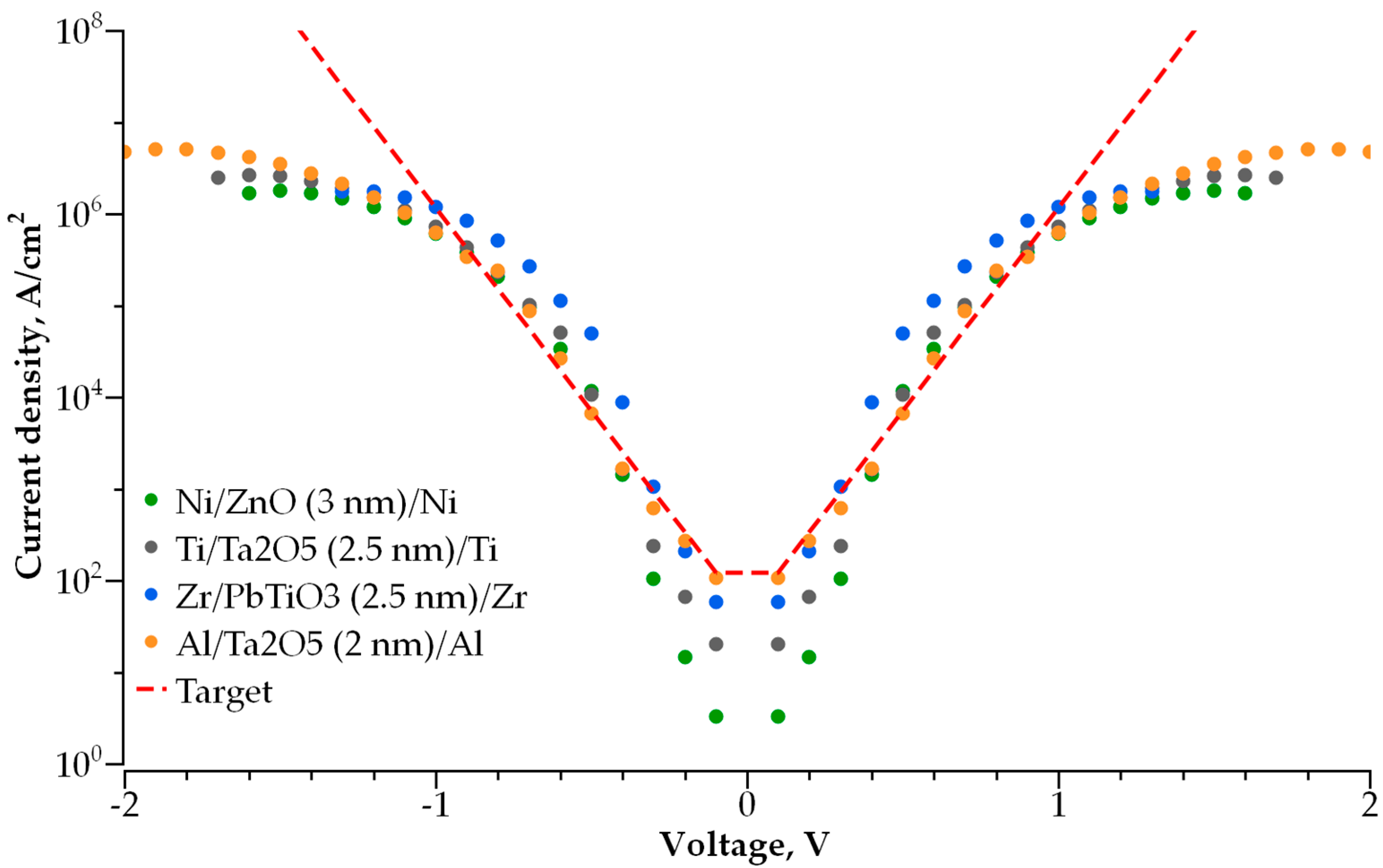
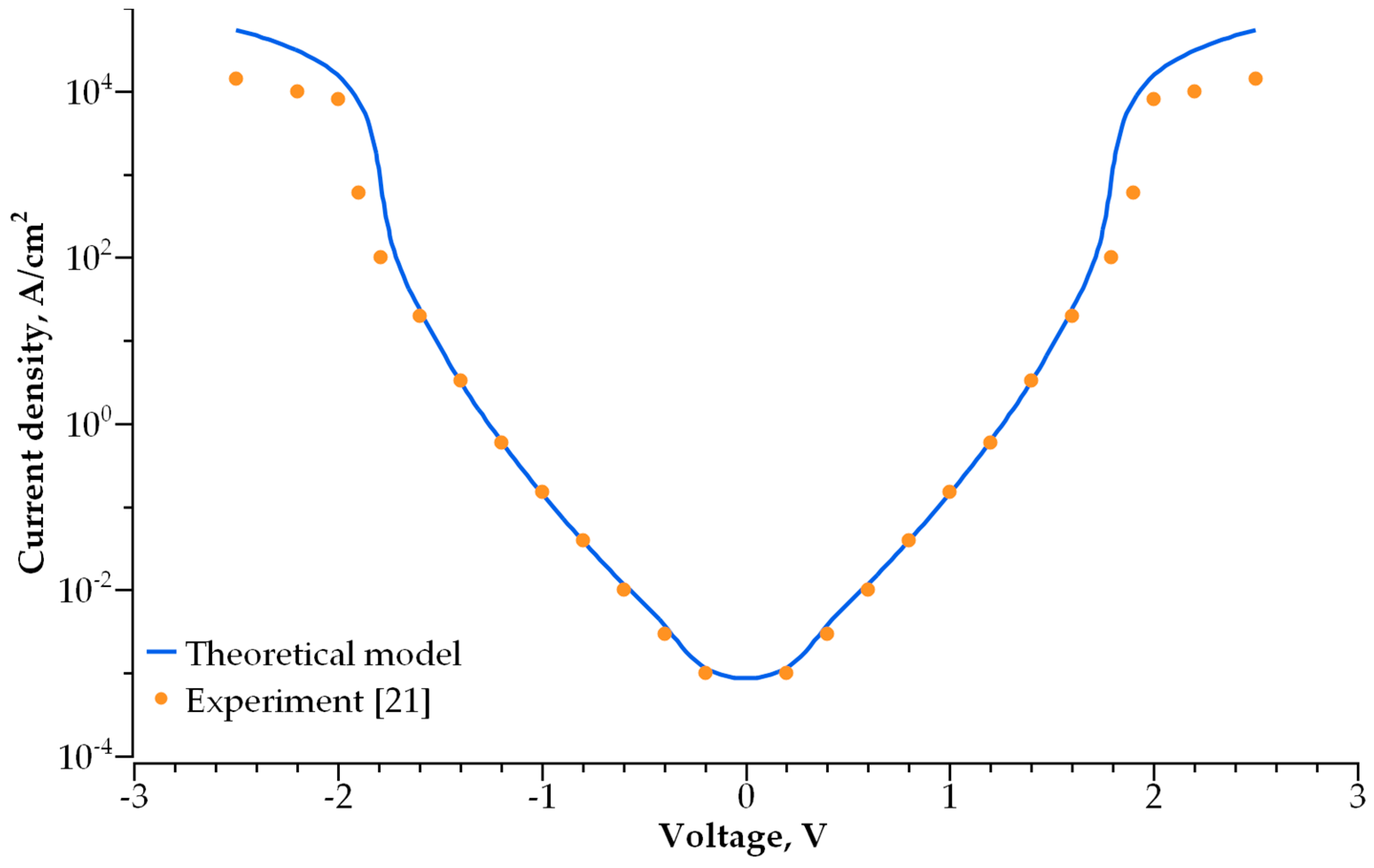
3. Results
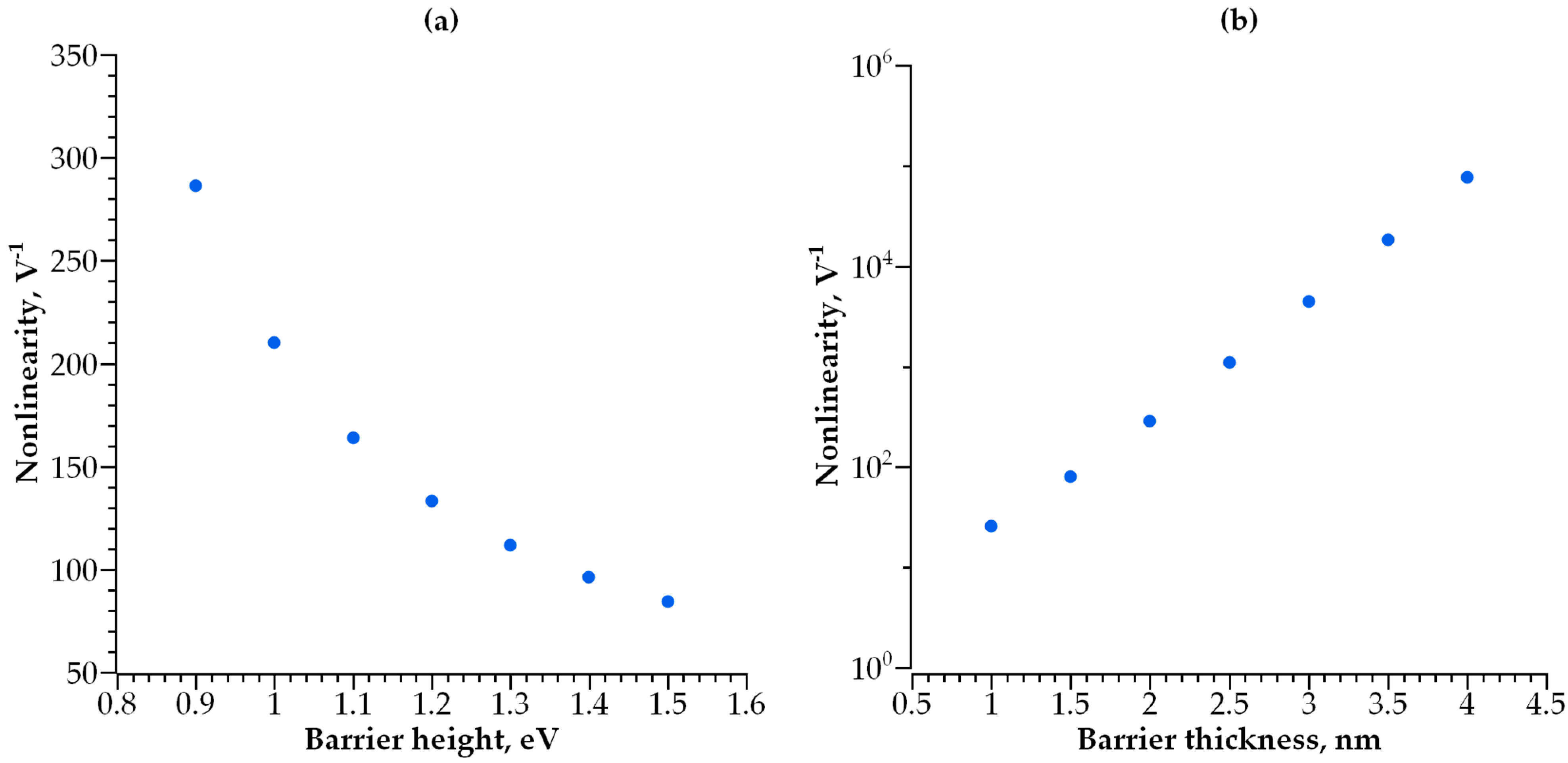
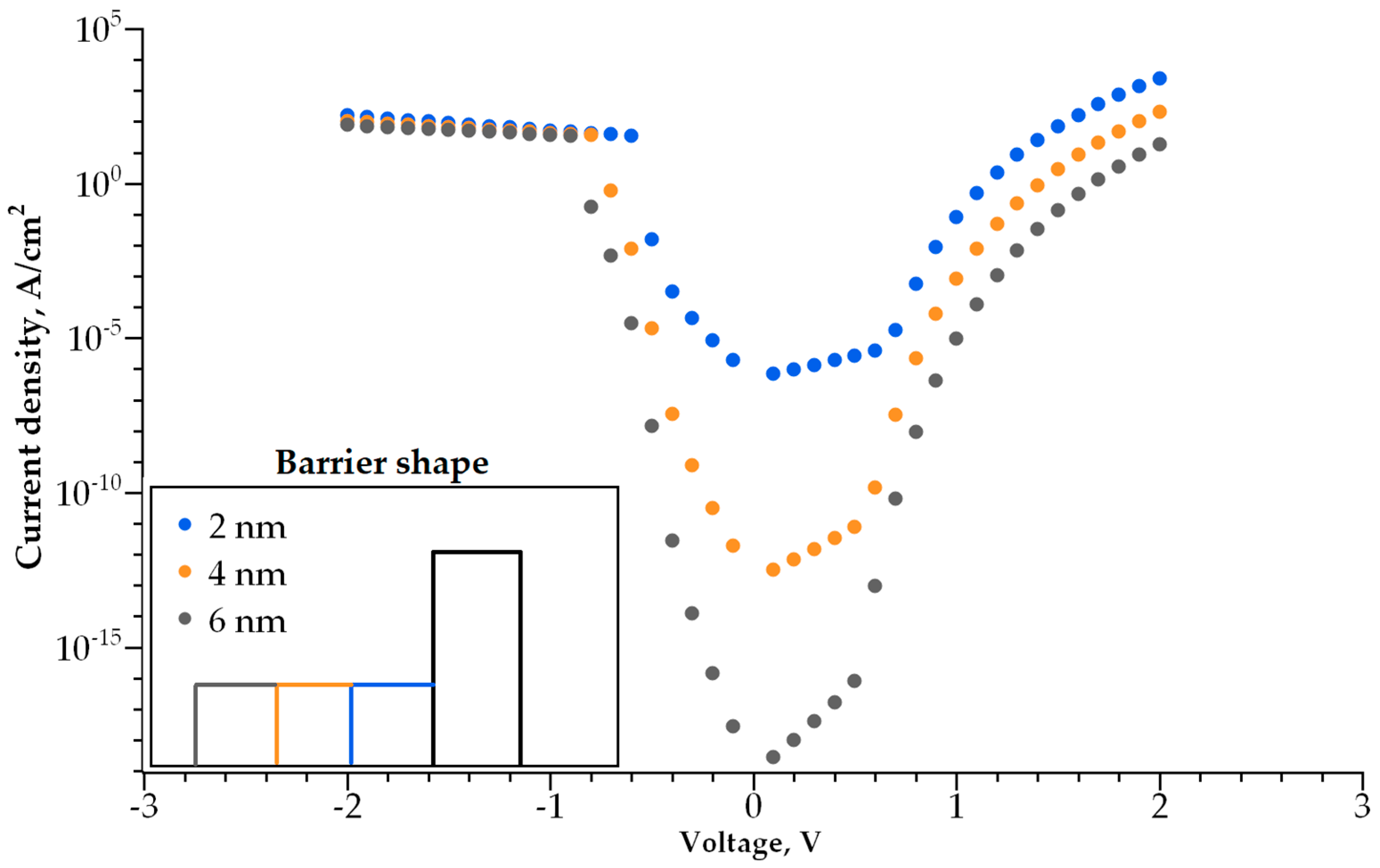
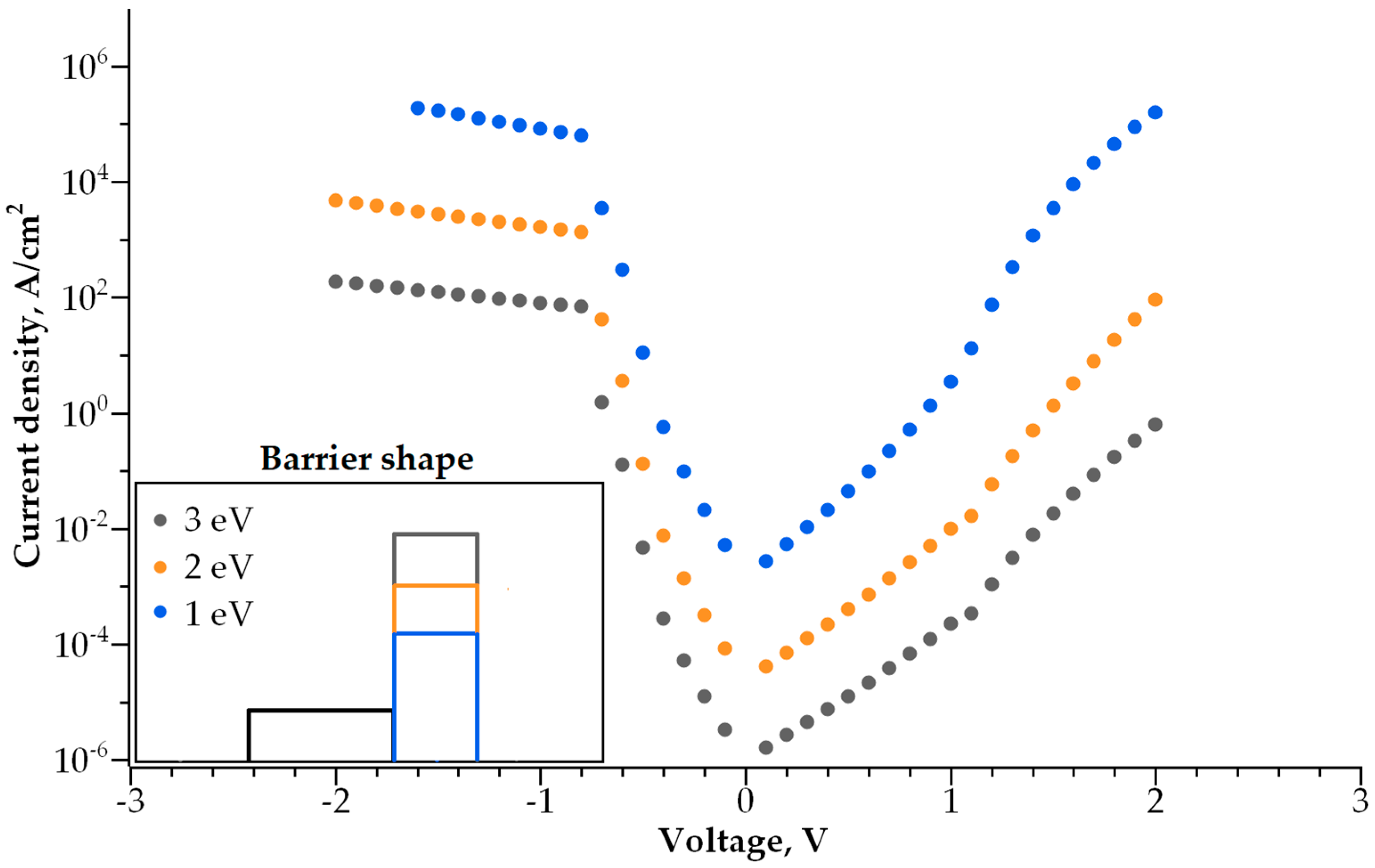
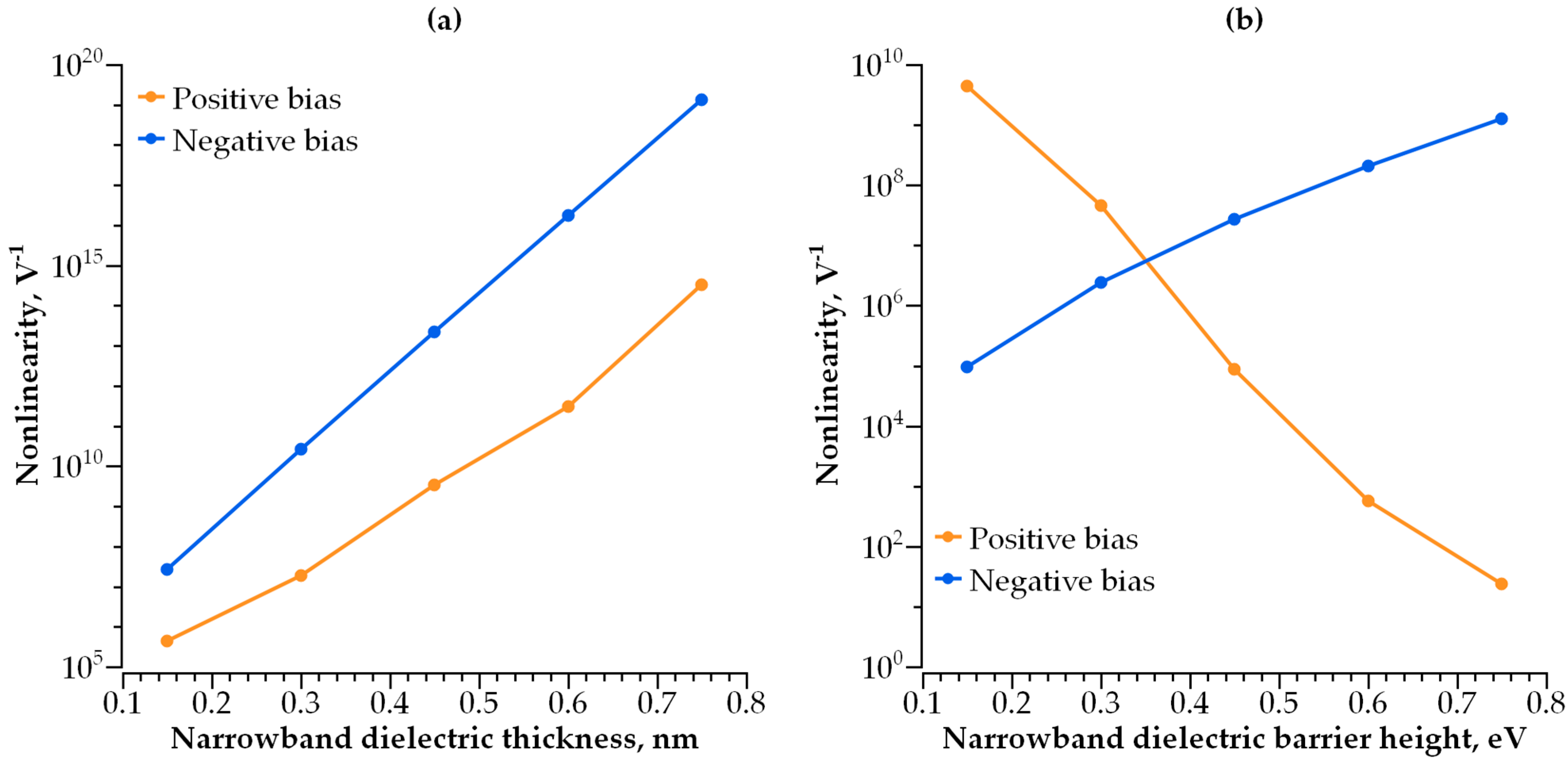
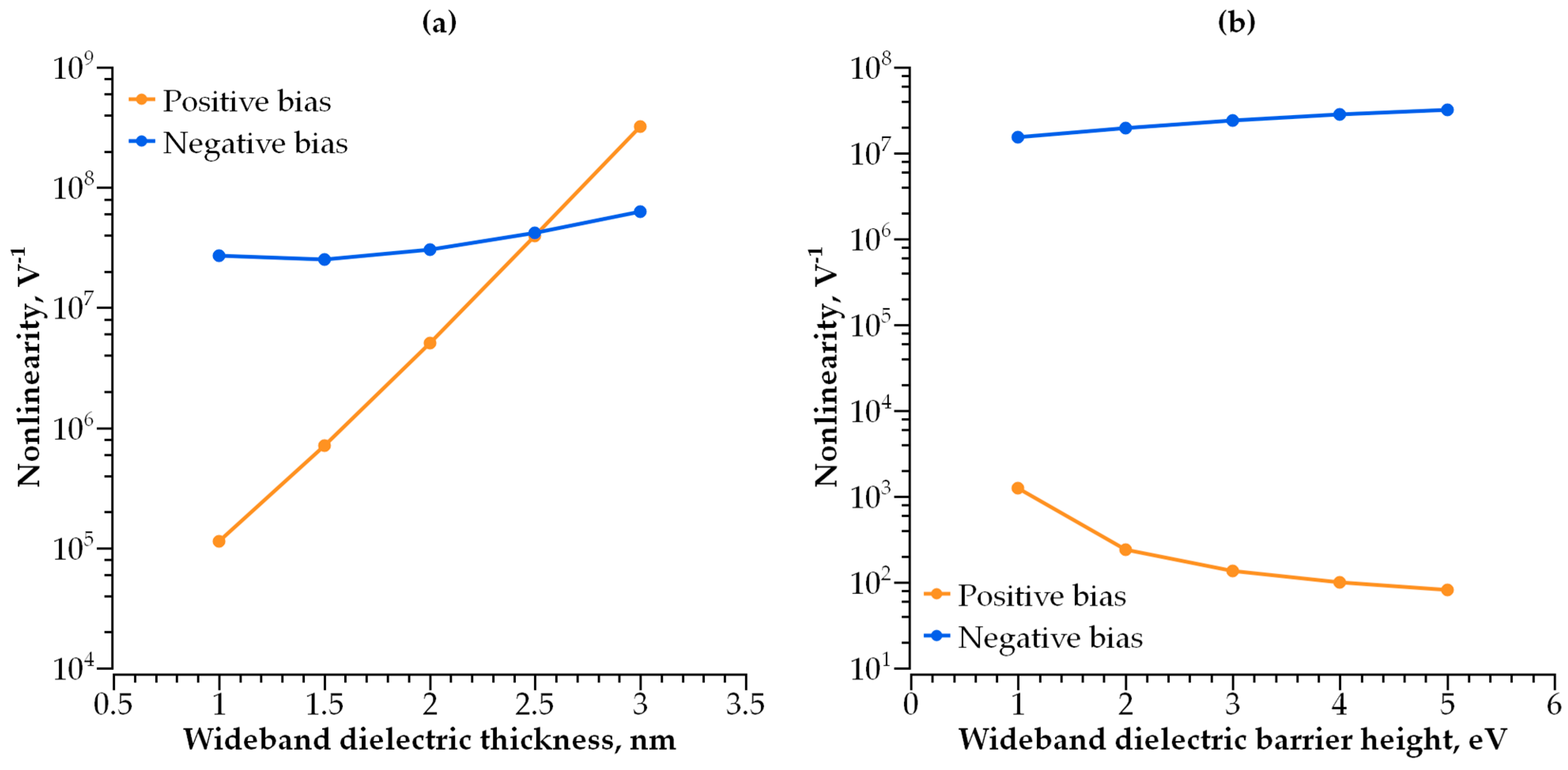
3.1. Single-Layer Selector
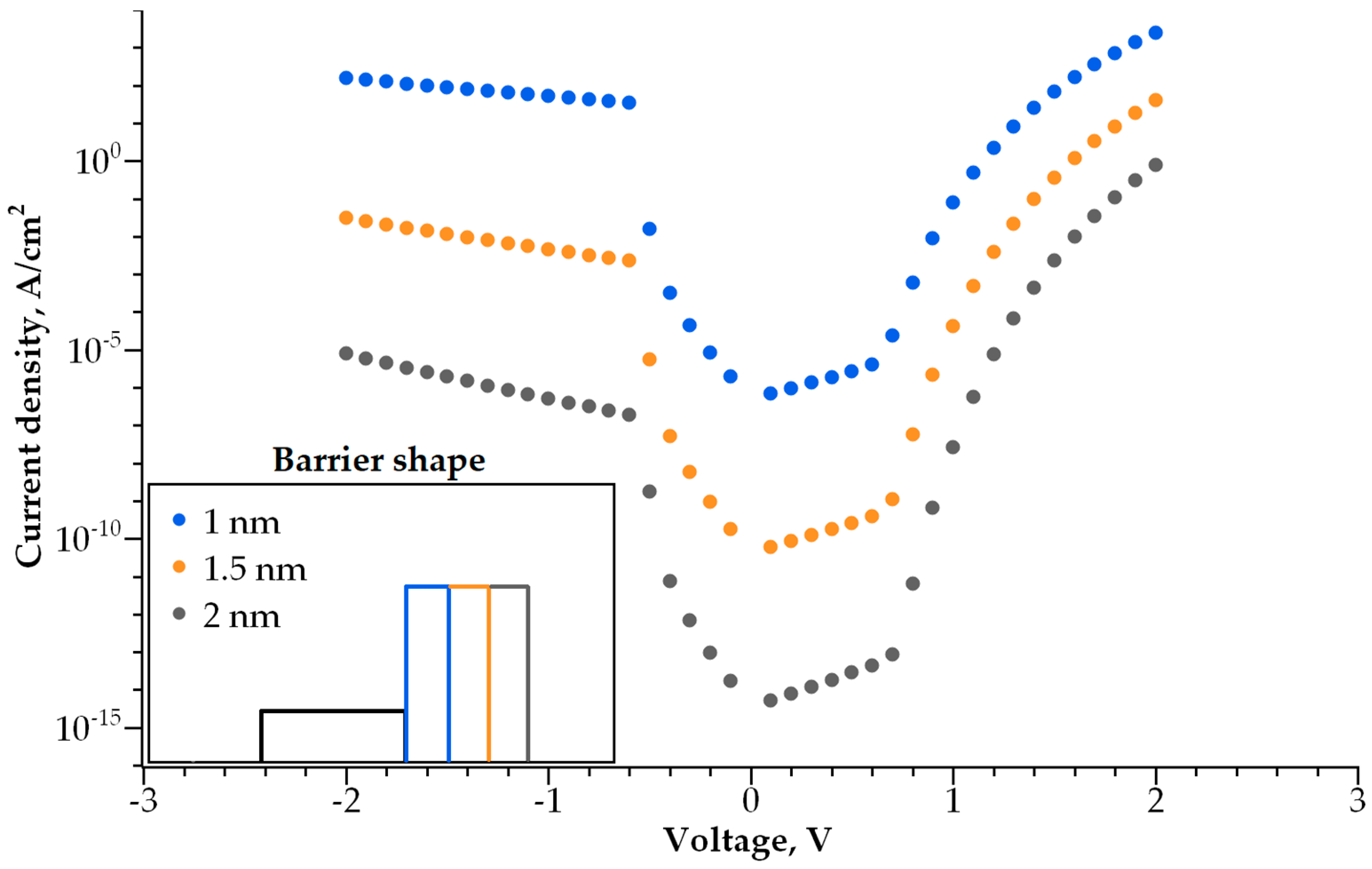
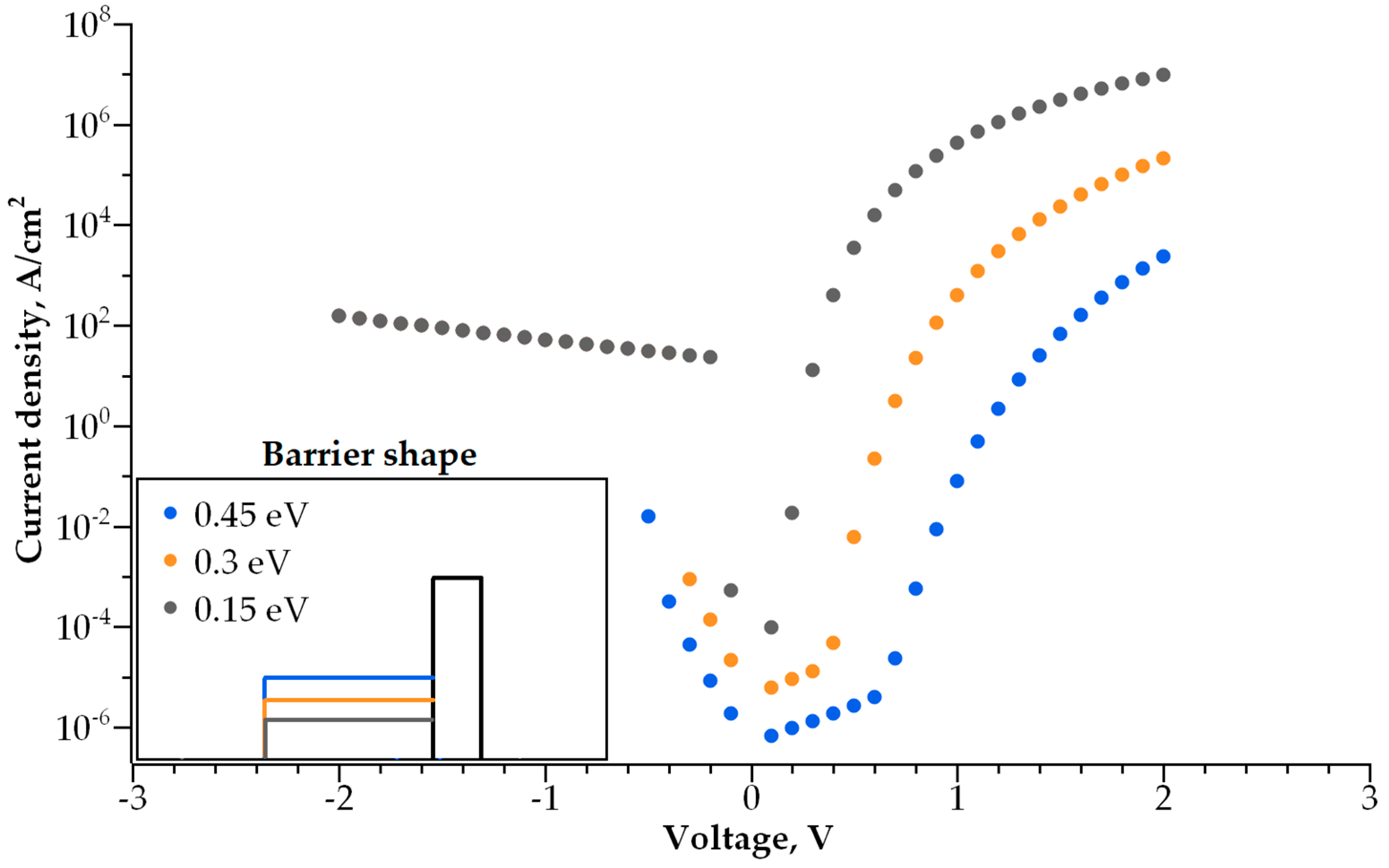
3.2. Double-Layer Selector
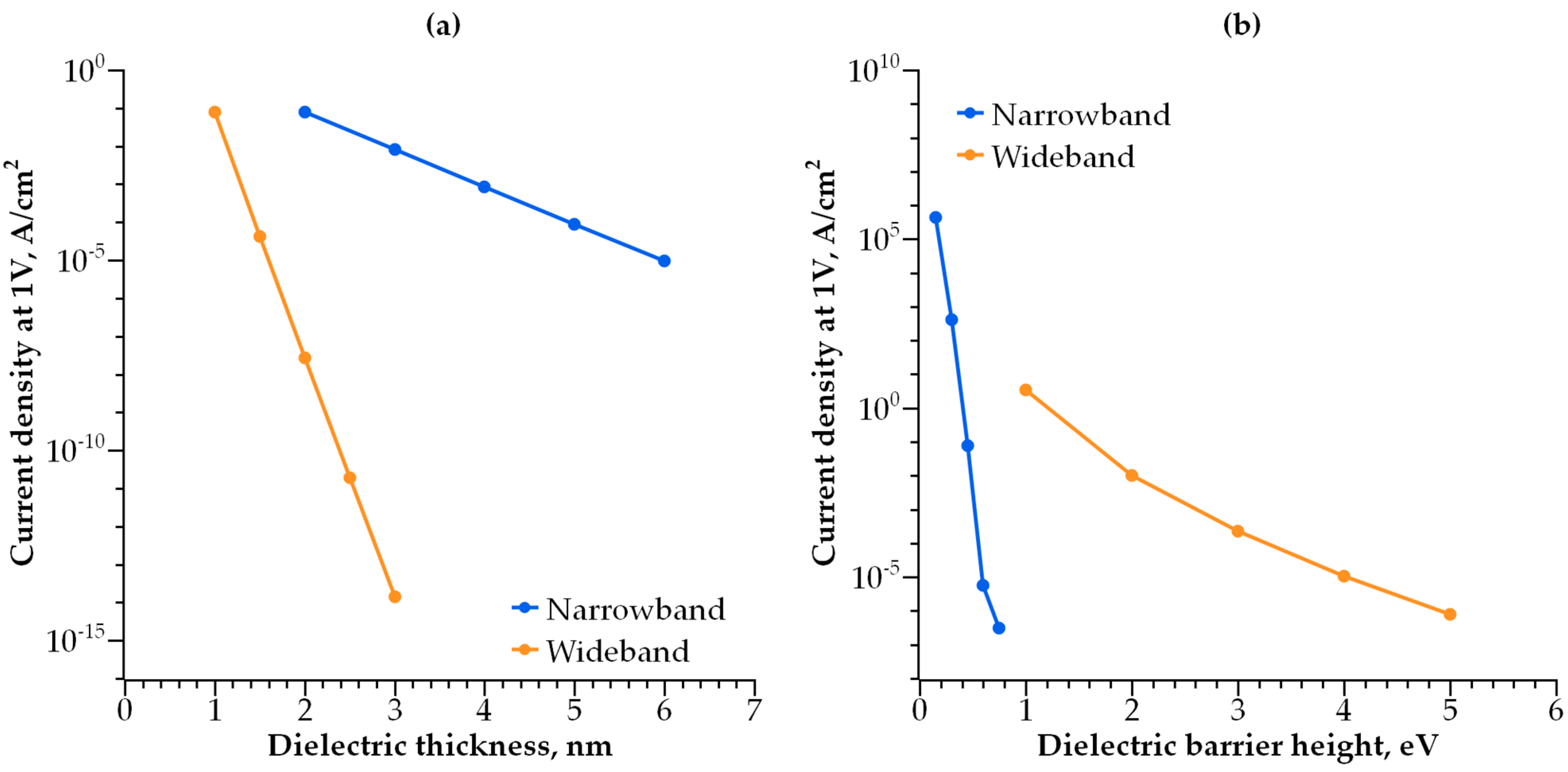
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waser, R.; Aono, M. Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Strukov, D.B.; Stewart, D.R. Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Feng, Y.H.; Jinfeng, K. Low-Power Resistive Switching Characteristic in HfO2/TiOx Bi-Layer Resistive Random-Access Memory. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, F.; Zulkifli, T.Z.A.; Khanday, F. Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM): An Overview of Materials, Switching Mechanism, Performance, Multilevel Cell (mlc) Storage, Modeling, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezioso, M.; Merrikh-Bayat, F.; Hoskins, B.; Adam, G.C.; Likharev, K.K.; Strukov, D.B. Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors. Nature 2015, 521, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Kubendran, R.; Schaefer, C.; Eryilmaz, S.B.; Zhang, W.; Wu, D.; Deiss, S.; Raina, P.; Qian, H.; Gao, B.; et al. A compute-in-memory chip based on resistive random-access memory. Nature 2022, 608, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogio, S.; Balatti, S.; Cubeta, A.; Calderoni, A.; Ramaswamy, N.; Ielmini, D. Statistical Fluctuations in HfOx Resistive-Switching Memory: Part I—Set/Reset Variability. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 2014, 61, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Hsu, C.-L.; Chen, C.-C.; Liu, J.-T.; Wu, C.-S.; Huang, C.-C.; Hu, C.; Yang, F.-L. 9 nm Half-Pitch Functional Resistive Memory Cell with <1 μA Programming Current Using Thermally Oxidized Sub-Stoichiometric WOx Film. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–8 December 2010; pp. 19.1.1–19.1.4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, I.-W. Scalability of Voltage-Controlled Filamentary and Na-nometallic Resistance Memories. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12690–12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balatti, S.; Ambrogio, S.; Ielmini, D.; Gilmer, D.C. Variability and failure of set process in HfO2 RRAM. In 2013 5th IEEE International Memory Workshop; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bousoulas, P.; Stathopoulos, S.; Tsialoukis, D.; Tsoukalas, D. Low-power and highly uniform 3-b multilevel switching in forming free TiO2-x-based RRAM with embedded Pt nanocrystals. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2016, 37, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Chang, S.P.; Chang, S.J.; Hsieh, W.K.; Lin, C.H. Highly stable ultrathin TiO2-based resistive random access memory with low operation voltage. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, Q3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikap, J. Dutta Self-compliance RRAM characteristics using a novel W/TaOx/TiN structure. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.L.; Cheng, W.H.; Jeng, J.S.; Chen, W.C.; Jhan, S.A.; Chen, J.S. Joint contributions of Ag ions and oxygen vacancies to conducting filament evolution of Ag/TaOx/Pt memory device. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 164502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Long, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q.; Shao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, M.; et al. Resistive switching properties of Au/ZrO2/Ag structure for low-voltage nonvolatile memory applications. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2009, 31, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Tseng, T.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Effects of Ti top electrode thickness on the resistive switching behaviors of rf-sputtered ZrO2 memory films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 112904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.G.; Lee, M.S.; Seo, S.; Lee, M.J.; Seo, D.H.; Suh, D.S.; Park, J.C.; Park, S.O.; Kim, H.S.; Yoo, I.K.; et al. Highly scalable non-volatile resistive memory using simple binary oxide driven by asymmetric unipolar voltage pulses. In Technical Digest—International Electron Devices Meeting; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Ielmini, D. Brain-inspired computing with resistive switching memory (RRAM): Devices, synapses and neural networks. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 190, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Gu, P.; Li, B.; Tang, T.; Yin, X.; Huangfu, W.; Tu, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Technological Exploration of RRAM Crossbar Array for Matrix-Vector Multiplication. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flocke, A.; Noll, T.G. Fundamental analysis of resistive nanocrossbars for the use in hybrid nano/CMOS-memory. In Proceedings of the 33rd ESSCIRC, Munich, Germany, 11–13 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Govoreanu, B.; Adelmann, C.; Redolfi, A.; Zhang, L.; Clima, S.; Jurczak, M. High-Performance Metal-Insulator-Metal Tunnel Diode Selectors. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2014, 35, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, G.; Jia, X. Resistance requirements of threshold switching selectors in 1S1R crossbar array. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering, Zhuhai, China, 22–24 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Zhou, J.; Lu, W.D. Crossbar RRAM Arrays: Selector Device Requirements During Write Operation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Lu, W. Crossbar RRAM Arrays: Selector Device Requirements During Read Operation. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2014, 61, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, C.B.; Yin, H.; Ahn, S.E.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.C.; Kim, C.J.; Song, I.; et al. Low-temperature-grown transition metal oxide based storage materials and oxide transistors for high-density non-volatile memory. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 19, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-J.; Tseng, Y.-M.; Hsu, C.W.; Hou, T.H. Bipolar nonlinear Ni/TiO2/Ni selector for 1S1R crossbar array applications. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2011, 32, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, I.; Biju, K.; Jo, M.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; et al. TiO2-based metal-insulator-metal selection device for bipolar resistive random access memory cross-point application. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Park, J.; Shin, J.; Woo, J.; Kim, S.; Choi, G.; Jung, S.; Park, S.; Lee, D.; Cha, E.; et al. Varistor-type bidirectional switch (JMAX > 107A/cm2, selectivity 104) for 3D bipolar resistive memory arrays. In Proceedings of the 2012 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSIT), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–14 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, K.; Shenoy, R.S.; Rettner, C.T.; Virwani, K.; Bethune, D.S.; Shelby, R.M.; Burr, G.W.; Kellock, A.; King, R.S.; Nguyen, K.; et al. Highly-scalable novel access device based on mixed ionic conduction (MIEC) materials for high density phase change memory (PCM) array. In Proceedings of the 2010 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSIT), Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–17 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, V.S.S.; Chopra, S.; Karkare, P.; Bafna, P.; Lashkare, S.; Kumbhare, P.; Kim, Y.; Srinivasan, S.; Kuppurao, S.; Lodha, S.; et al. Punchthrough-Diode-Based Bipolar RRAM Selector by Si Epitaxy. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 33, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Jeon, J.; Hutin, L.; Liu, T.-J.K. Electromechanical Diode Cell for Cross-Point Nonvolatile Memory Arrays. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2011, 33, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Tao, C.; Jiang, X.; Sun, P. Feasibility study of using a Zener diode as the selection device for bipolar RRAM and WORM memory arrays. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 47, 25103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Leon, J.J.; Norris, K.J.; Yang, J.J.; Sevic, J.F.; Kobayashi, N. A niobium oxide-tantalum oxide selector-memristor self-aligned nanostack. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Fang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Gao, B.; Kang, J.F.; Kwong, D.L. Highly compact 1T-1R architecture (4F2 footprint) involving fully CMOS compatible vertical GAA nano-pillar transistors and oxide-based RRAM cells exhibiting excellent NVM properties and ultra-low power operation. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012; pp. 20.6.1–20.6.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, M.I.; Korotitsky, V.I.; Koveshnikov, S.V. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Intrinsic Variability in Hafnium Oxide Based RRAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE 22nd International Conference of Young Professionals in Electron Devices and Materials (EDM), Souzga, Russia, 30 June–4 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri, S.; Belete, M.; Litta, E.D.; Smith, A.D.; Lupina, G.; Lemme, M.C.; Östling, M. Bilayer insulator tunnel barriers for graphene-based vertical hot-electron transistors. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13096–13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.; Ziegler, M.; Kolberg, L.; Soni, R.; Dirkmann, S.; Mussenbrock, T.; Kohlstedt, H. A double barrier memristive device. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, J.G. Generalized Formula for the Electric Tunnel Effect between Similar Electrodes Separated by a Thin Insulating Film. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagath, A.L.; Kumar, T.N.; Almurib, H.A.; Jinesh, K.B.P. Analytical modelling of tantalum/titanium oxide-based multi-layer selector to eliminate sneak path current in RRAM arrays. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2020, 14, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, D.; Shimizu, M.; Yugami, H. High-current density and high-asymmetry MIIM diode based on oxygen-non-stoichiometry controlled homointerface structure for optical rectenna. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valov, I.; Waser, R.; Jameson, J.R.; Kozicki, M.N. Electrochemical metallization memories—Fundamentals, applications, prospects. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 254003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. Dual Buffer Layers for Developing Electrochemical Metallization Memory with Low Current and High Endurance. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2020, 42, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fedotov, M.; Korotitsky, V.; Koveshnikov, S. Modeling of Self-Aligned Selector Based on Ultra-Thin Metal Oxide for Resistive Random-Access Memory (RRAM) Crossbar Arrays. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080668
Fedotov M, Korotitsky V, Koveshnikov S. Modeling of Self-Aligned Selector Based on Ultra-Thin Metal Oxide for Resistive Random-Access Memory (RRAM) Crossbar Arrays. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(8):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080668
Chicago/Turabian StyleFedotov, Mikhail, Viktor Korotitsky, and Sergei Koveshnikov. 2024. "Modeling of Self-Aligned Selector Based on Ultra-Thin Metal Oxide for Resistive Random-Access Memory (RRAM) Crossbar Arrays" Nanomaterials 14, no. 8: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080668
APA StyleFedotov, M., Korotitsky, V., & Koveshnikov, S. (2024). Modeling of Self-Aligned Selector Based on Ultra-Thin Metal Oxide for Resistive Random-Access Memory (RRAM) Crossbar Arrays. Nanomaterials, 14(8), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080668





