Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
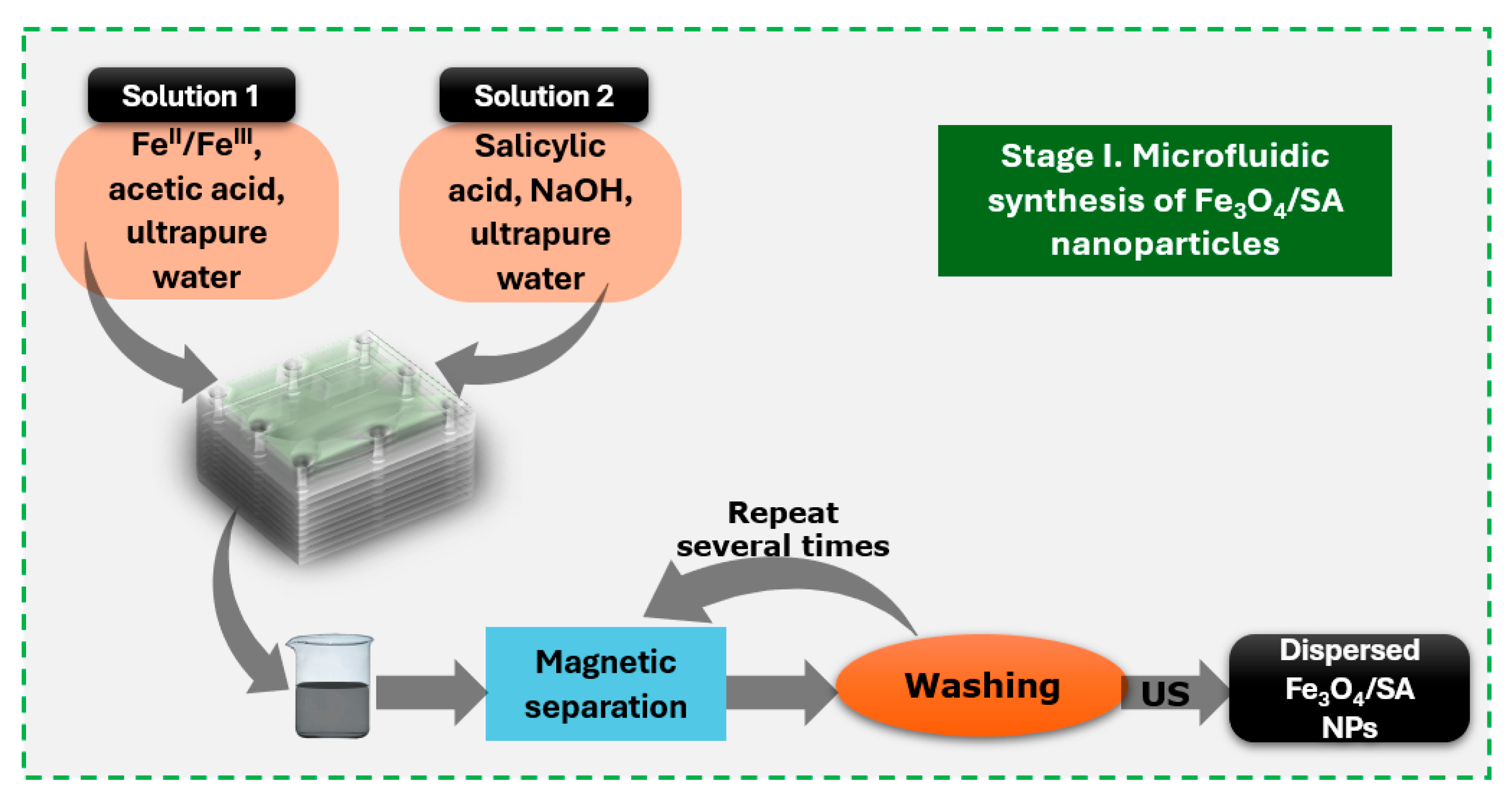
2.2. Salicylic Acid-Surface Modified Nanoparticles Synthesis
2.3. Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
2.4. Silica-Based Aerogel Thin Coatings
2.5. Nanoparticle Characterization
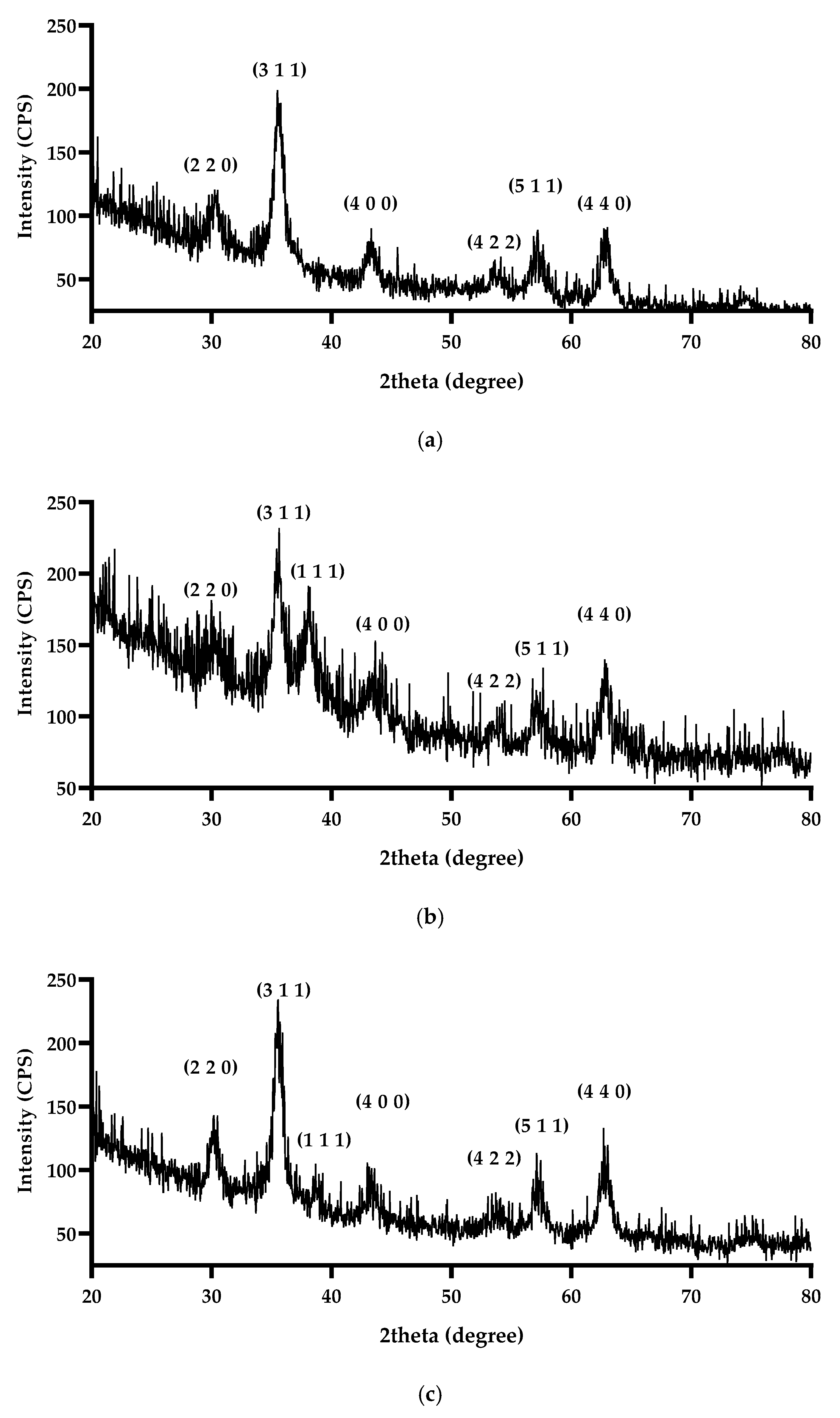
2.5.1. X-Ray Diffraction
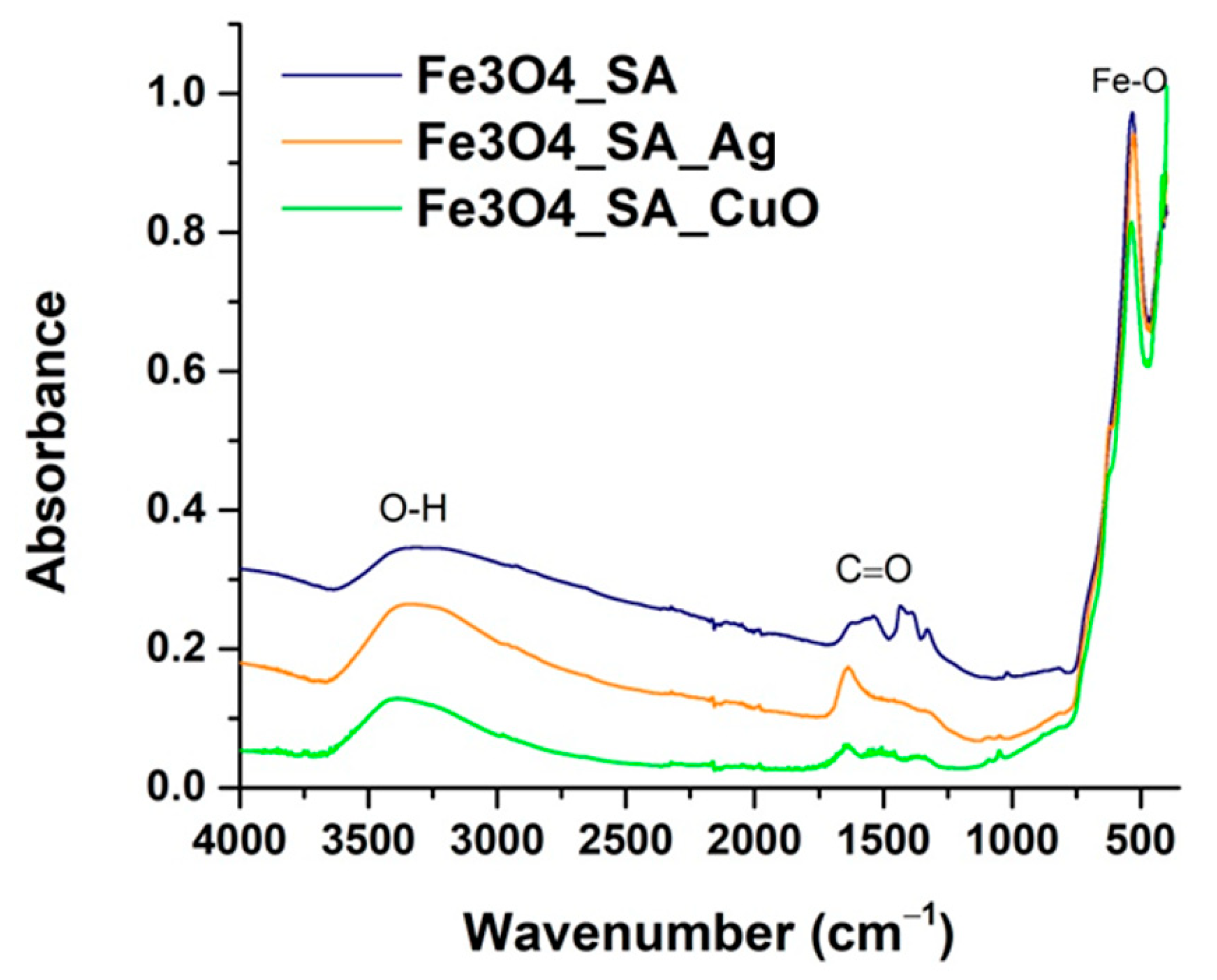
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
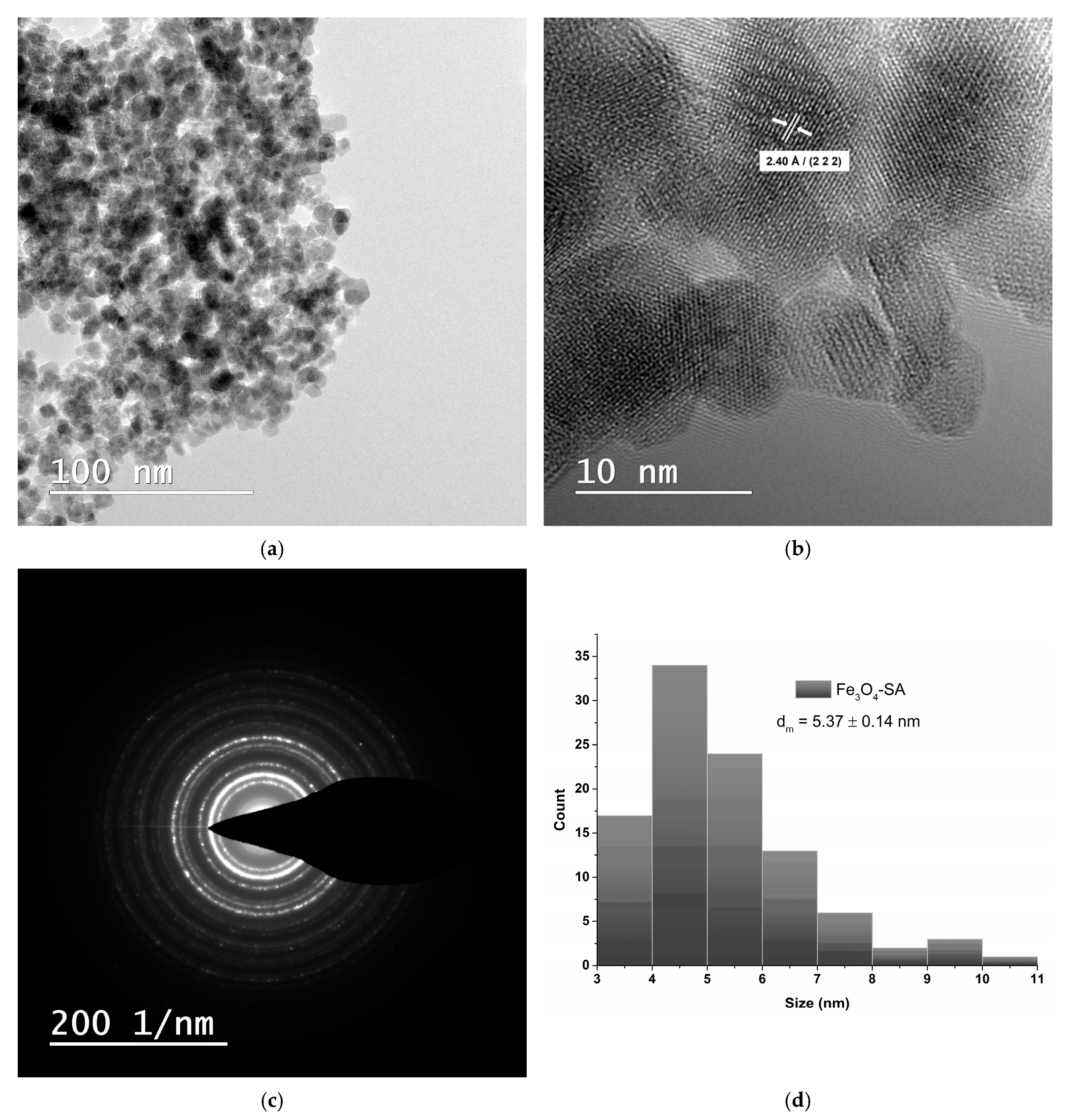
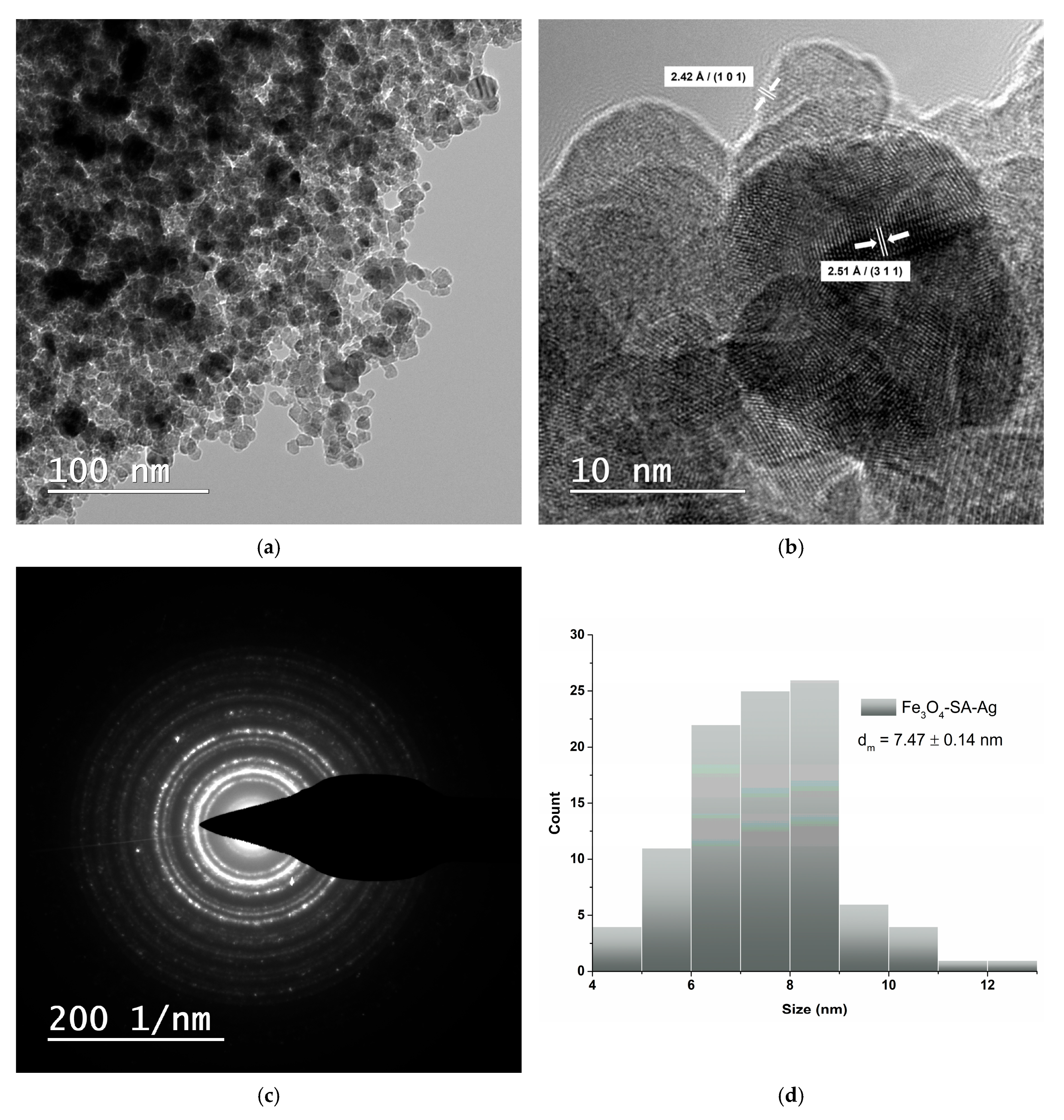
2.5.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Selected Area Electron Diffraction
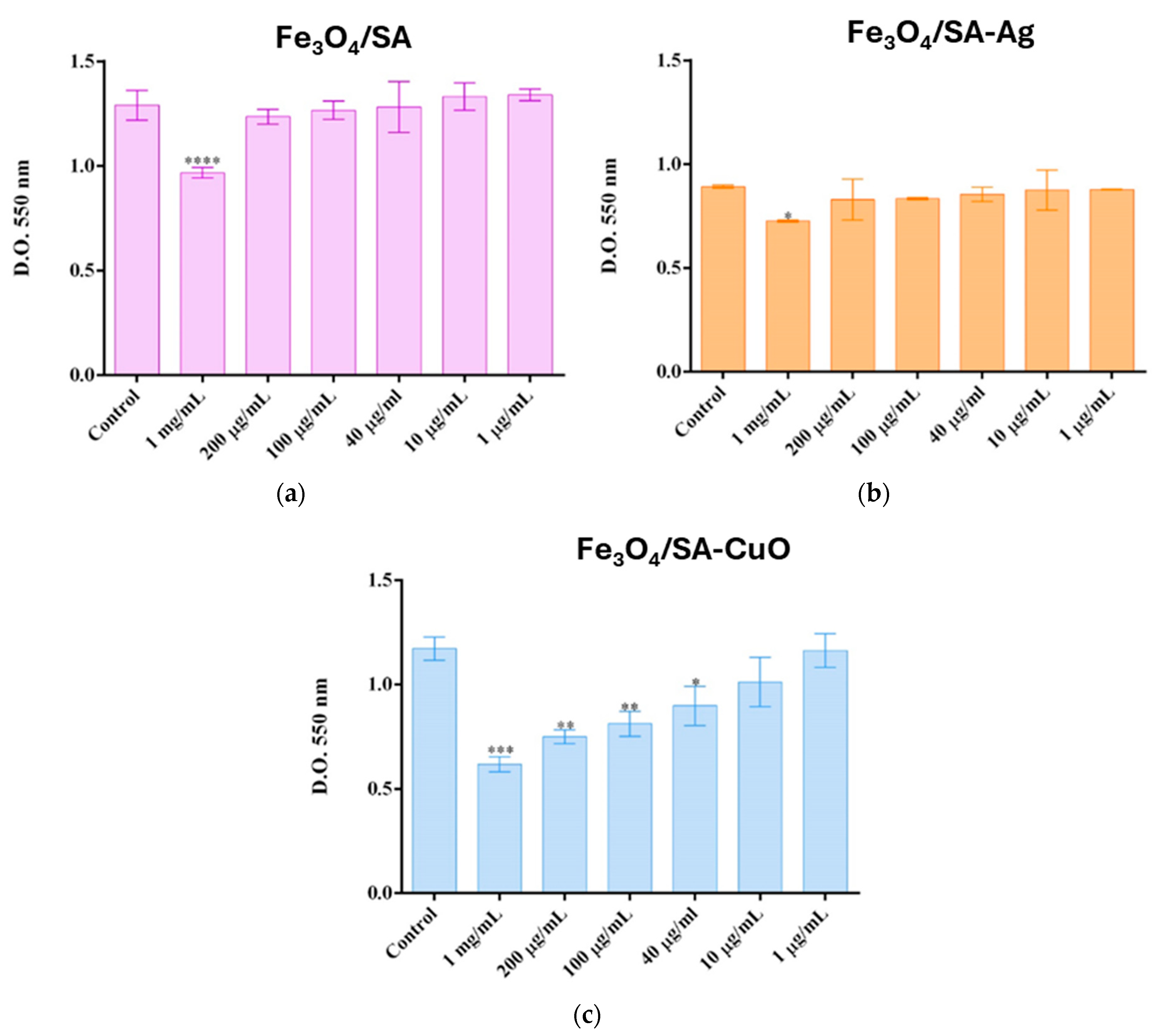
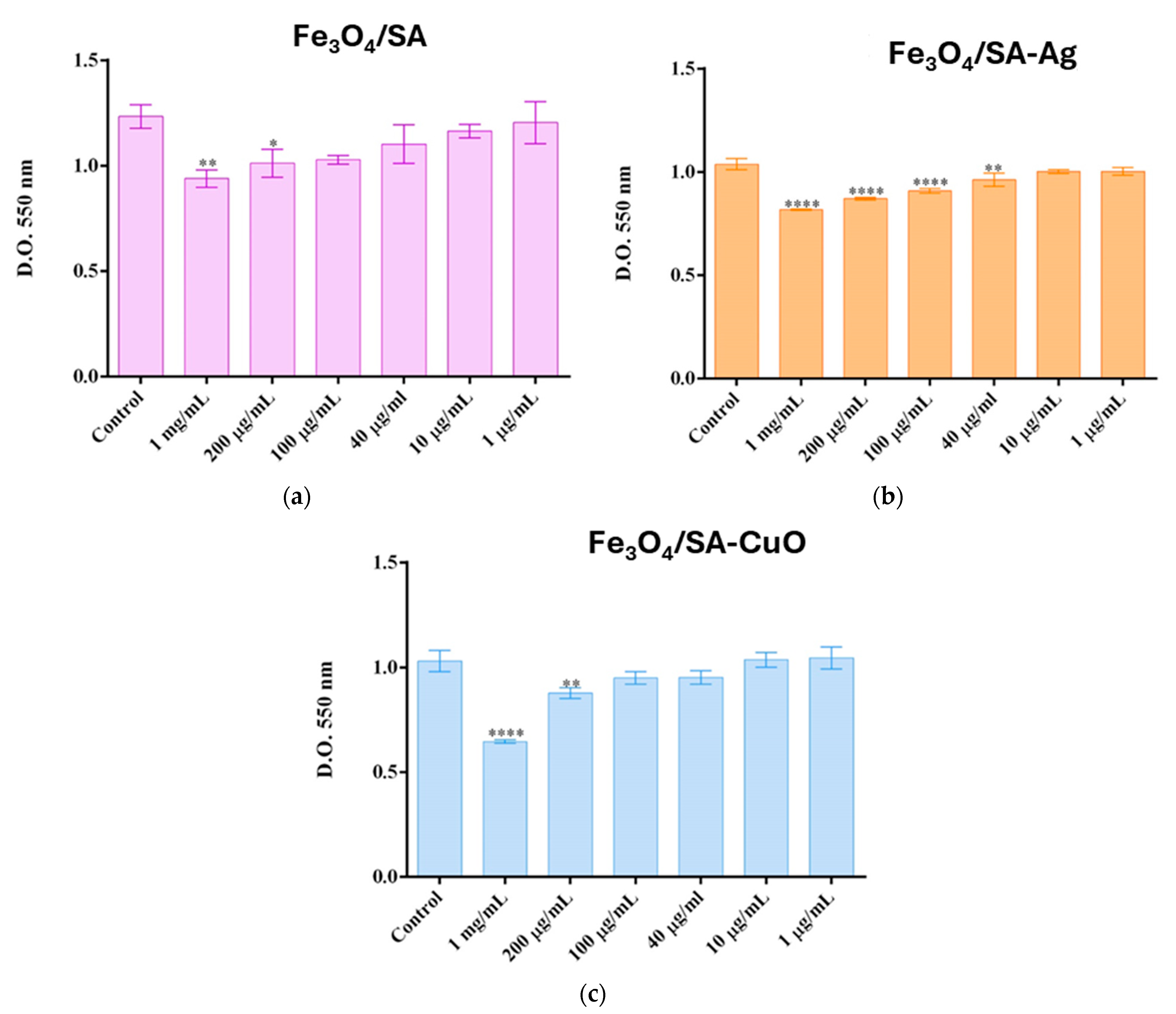
2.5.4. Cell Viability and Proliferation of Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
2.5.5. Antimicrobial Assay
2.6. Coatings Characterization
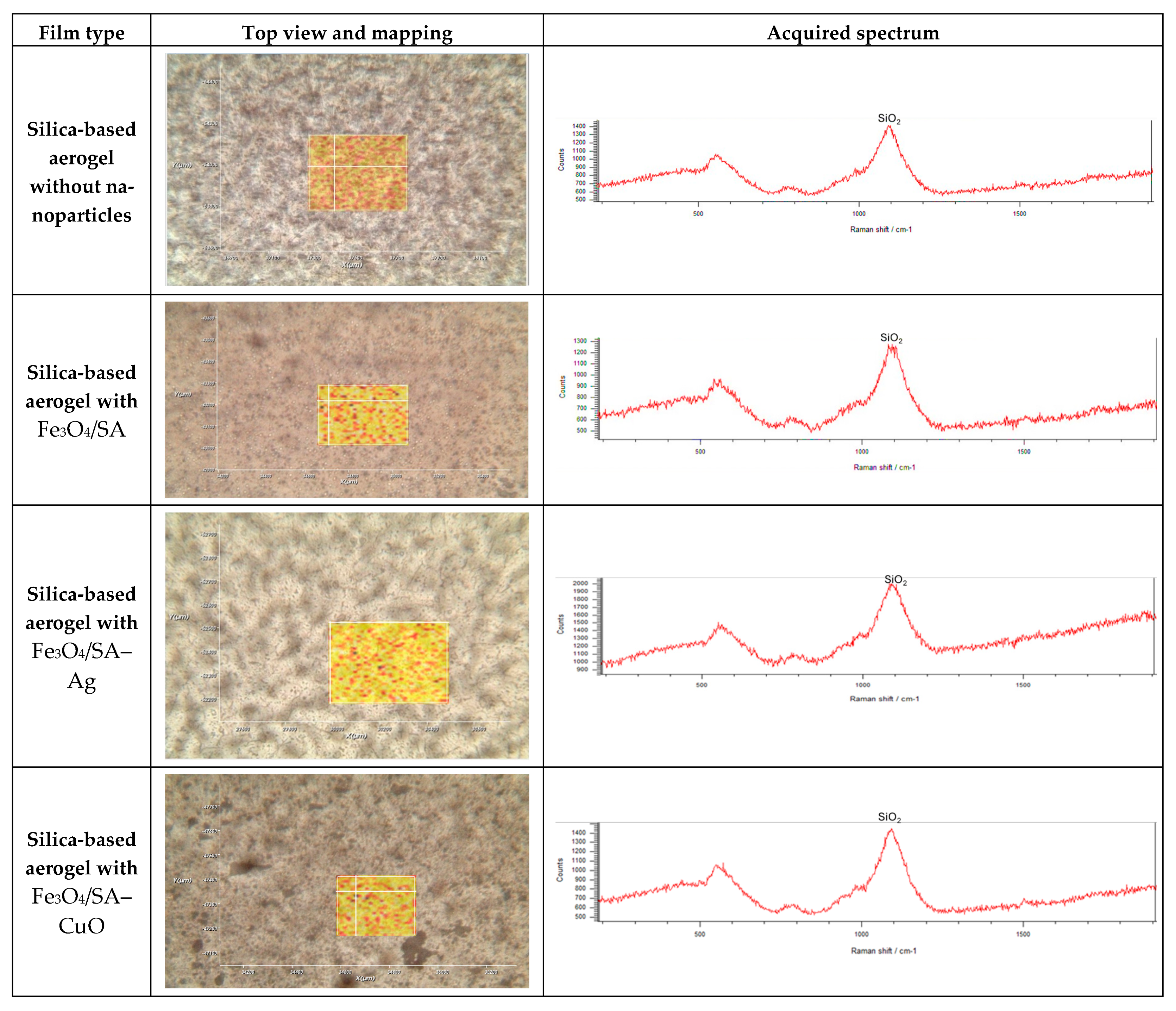
2.6.1. Raman Microscopy and Spectroscopy
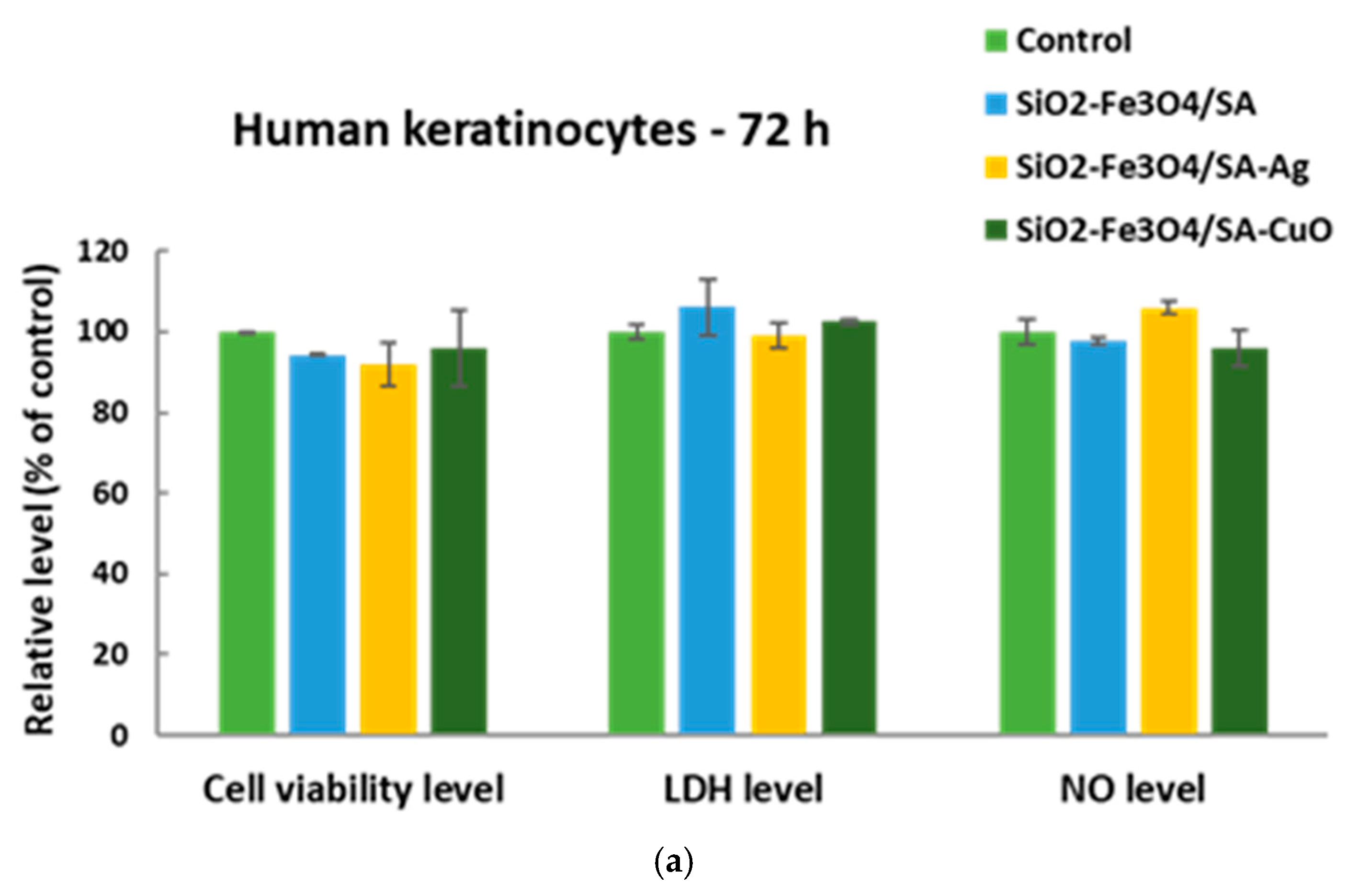
2.6.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Screening Protocol of Hybrid Iron Oxide Coatings
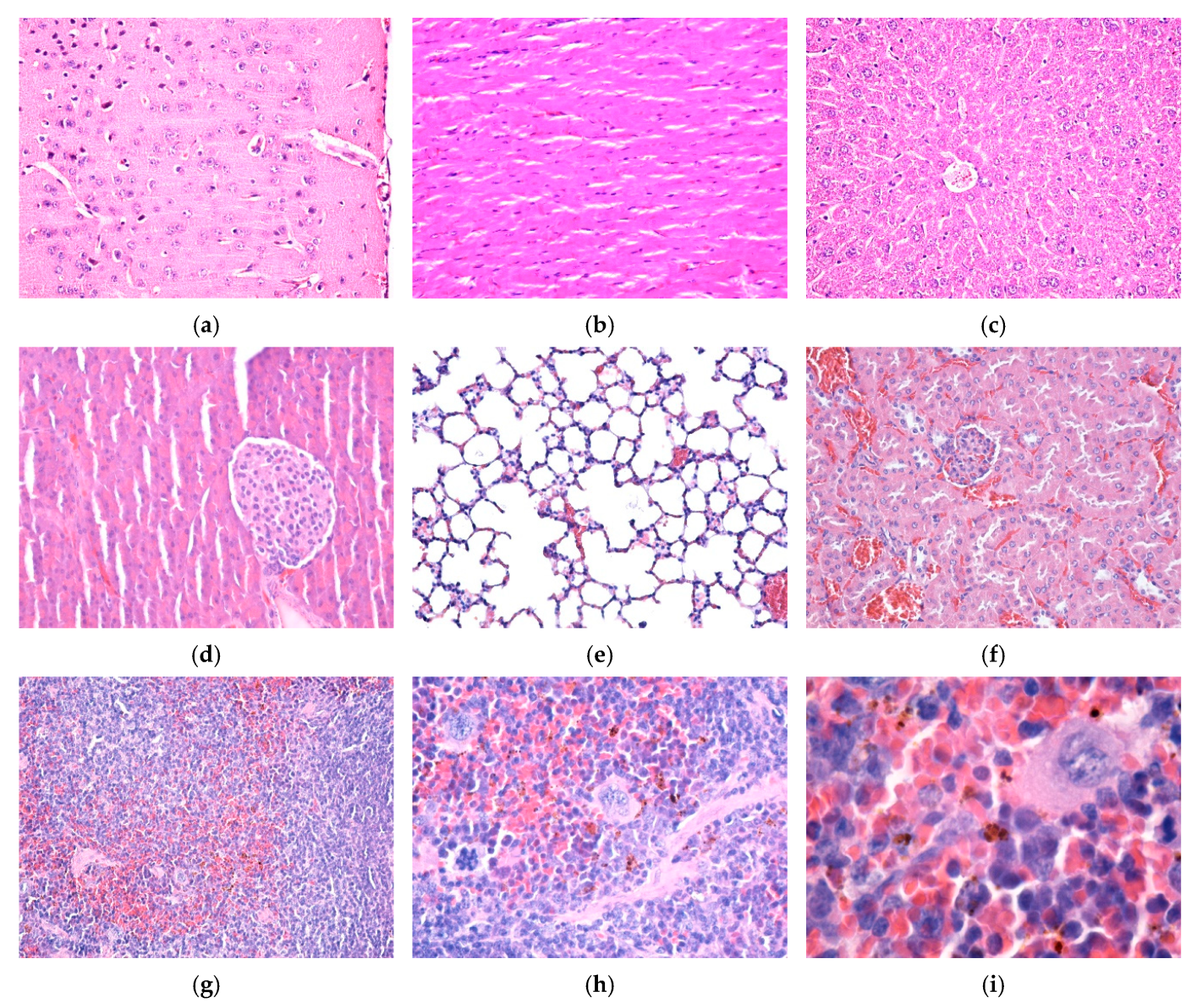
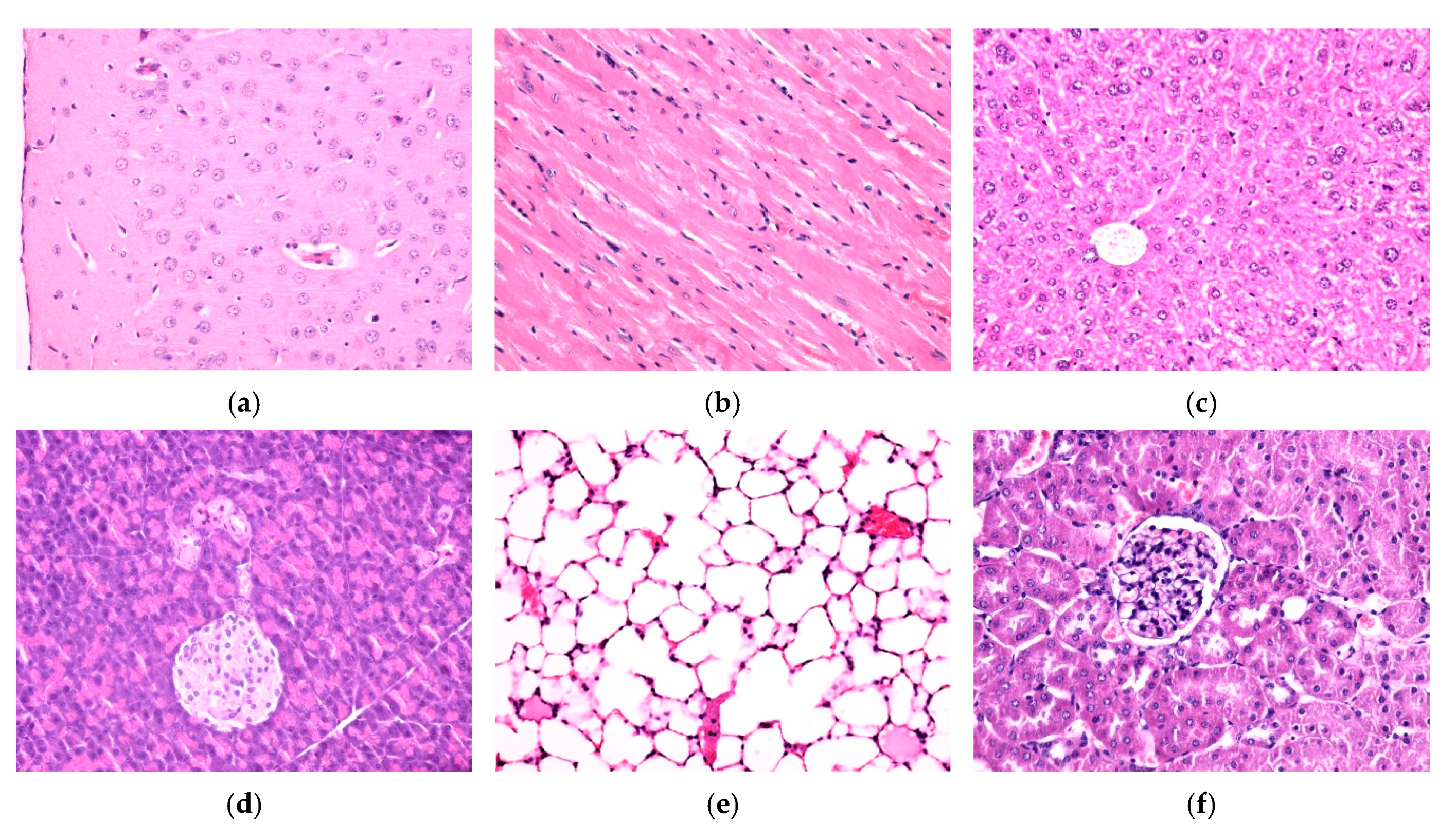
2.7. In Vivo Experimental Model
3. Results
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Selected Area Electron Diffraction
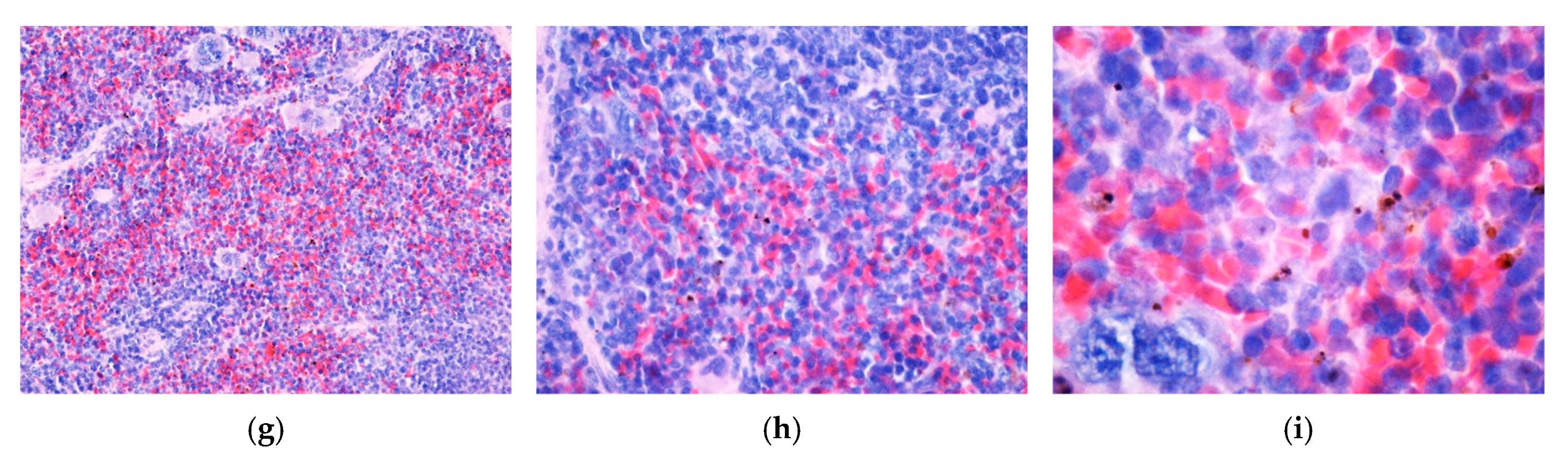
3.4. In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
3.5. Antibacterial Characterization
3.6. Silica-Aerogel-Based Coatings Characterization
3.7. In Vitro Behaviour of Human Keratinocytes on Thin Coatings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.K.; Gawad, F.A.E.; Ali, E.A.E.; Karunanithi, S.; Yugiani, P.; Srivastav, P.P. Nanotechnology: Current applications and future scope in food packaging systems. Meas. Food 2024, 13, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology in Healthcare and Medicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardet, T.; Venturini, P.; Martinez, H.; Dupin, J.-C.; Cleymand, F.; Fleutot, S. Spinel Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Properties, Synthesis and Washing Methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.M.; Hassan, A.I. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanomaterials for Application in Cost-Effective Electrochemical Devices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, C.; Jin, B.; Sun, T.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Fan, Z. Advances in smart nanotechnology-supported photodynamic therapy for cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimondi, S.; Ferreira, H.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Microfluidic Devices: A Tool for Nanoparticle Synthesis and Performance Evaluation. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 14205–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Zhu, P.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Zou, M.; Qi, X.; Liang, P.; Chen, Q. Synthesis of nanoparticles via microfluidic devices and integrated applications. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezelya, A.; Küçüktürkmen, B.; Bozkır, A. Microfluidic Devices for Precision Nanoparticle Production. Micro 2023, 3, 822–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Kumar, R.; Acooli, A.; Roy, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Chattaraj, S.; Nayak, J.; Jeon, B.-H.; Basu, A.; Banerjee, S.; et al. Transforming Nanomaterial Synthesis through Advanced Microfluidic Approaches: A Review on Accessing Unrestricted Possibilities. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. Synthesis of energetic materials by microfluidics. Def. Technol. 2025, 44, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.L.; Preda, M.D.; Neacșu, I.A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Ginghină, O. Traditional vs. Microfluidic Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Sun, R.; Han, S.; Yang, Z.; Teng, L. Microfluidics for nano-drug delivery systems: From fundamentals to industrialization. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 3277–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Bao, G. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 20, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiufiuc, G.F.; Stiufiuc, R.I. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Use in Biomedical Field. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel Schneider, M.G.; Martín, M.J.; Otarola, J.; Vakarelska, E.; Simeonov, V.; Lassalle, V.; Nedyalkova, M. Biomedical Applications of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Current Insights Progress and Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, J.-P.; Natekar, N.A.; Ciannella, S.; González-Fernández, C.; Gomez-Pastora, J.; Bao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, S.; Wu, X.; et al. Roadmap on magnetic nanoparticles in nanomedicine. Nanotechnology 2024, 36, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Munteanu, O.M.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Moroșan, A.; Purcăreanu, B.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Istrati, D.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Hadibarata, T.; Grumezescu, A.M. New 3D Vortex Microfluidic System Tested for Magnetic Core-Shell Fe3O4-SA Nanoparticle Synthesis. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Jary, J.; Machnicka, B. Comprehensive Analysis of the Potential Toxicity of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Medical Applications: Cellular Mechanisms and Systemic Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.; Ahmad, R.; Tanweer, M.S.; Azam, I. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Tool for the Advancement of Biomedical and Environmental Application: A Review. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2024, 2, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedylakova, M.; Medinger, J.; Mirabello, G.; Lattuada, M. Iron oxide magnetic aggregates: Aspects of synthesis, computational approaches and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 323, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Magnetite nanoparticles: Synthesis methods—A comparative review. Methods 2022, 199, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, J.; Singh, A. Lignin Derived Biofabrication of Magnetic Iron Nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2024, 13, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Ezealigo, U.S.; Ezealigo, B.N.; Aisida, S.O.; Ezema, F.I. Iron oxide nanoparticles in biological systems: Antibacterial and toxicology perspective. JCIS Open 2021, 4, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, R.; Makwana, N.; Kumar, R.; Joshi, M.; Patel, A.; Bhatia, D.; Sahoo, D.K. Nanomedicines as a cutting-edge solution to combat antimicrobial resistance. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33568–33586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, A.G.; Lopez-Barbera, J.F.; Lafuente, A.; Özel, F.; Fantechi, E.; Muro-Cruces, J.; Hémadi, M.; Sepulveda, B.; Nogues, J. Iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3 and FeO) as photothermal heat mediators in the first, second and third biological windows. Phys. Rep. 2023, 1043, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Moroșan, A.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Oprea, O.C.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Purcăreanu, B.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Rădulescu, M.; Grumezescu, A.M. Microwave-Assisted Silanization of Magnetite Nanoparticles Pre-Synthesized by a 3D Microfluidic Platform. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdussalam-Mohammed, W.; Abraheem, M.S.; Mezoughi, A.B.; Mohamed, L.; Alwahsh, M.A.A. Comparative Analysis of Novel Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Different Approaches with Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activities. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Fadeev, M.; Kozlovskiy, A.; Korolkov, I.; Egizbek, K.; Nazarova, A.; Chudoba, D.; Rusakov, V.; Zdorovets, M. Iron oxide @ gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties and potential use as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 603, 125178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Tiama, T.M.; Farghaly, A.; Elhaes, H.; Ibrahim, M.A. Assessment of the functionalization of chitosan/iron oxide nanoparticles. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem 2023, 13, 582. [Google Scholar]
- Albukhaty, S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Mohammed, H.A.; Hassan, A.S.; Alshammari, A.A.A.; Ahmad, A.M.; Madhi, R.; Almalki, F.A.; Khashan, K.S.; et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles: The versatility of the magnetic and functionalized nanomaterials in targeting drugs, and gene deliveries with effectual magnetofection. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 99, 105838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmalingam, N.; Arumugasamy, V.; Mariappan, R. Amoxicillin Encapsulated Magnetite Nanomaterial for Antibiotic Drug Delivery and Deoxyribonucleic Acid Interaction. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2024, 13, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Salehirozveh, M.; Dehghani, P.; Mijakovic, I. Synthesis, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs). J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.M.; Fu, H.E.; Moon, J.H.; Oh, E.; Kim, Y.; Ko, M.J.; Kim, Y.K. Porous Iron Oxide Core–Gold Satellite Nanocomposite: A Cost-Effective and Recyclable Solution for Photocatalytic Wastewater Treatment. Small Sci. 2024, 4, 2300266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. Recent advances in synthesis and surface modification of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with silica. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQurashi, D.M.; AlQurashi, T.F.; Alam, R.I.; Shaikh, S.; Tarkistani, M.A.M. Advanced Nanoparticles in Combating Antibiotic Resistance: Current Innovations and Future Directions. J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaz, S.V.; Nobar, H.M.; Sarıgül, H.; Soylukan, C.; Akyüz, L.; Yüce, M. Nanomaterial surface modification toolkit: Principles, components, recipes, and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 322, 103035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandorkar, Y.; Valeske, M.; Kolrosova, B.; Elbs-Glatz, Y.; Zuber, F.; Schoeller, J.; Kummer, N.; Ren, Q.; Rottmar, M.; Maniura-Weber, K. Bioactive Salicylic Acid Containing Coating for Dental Implants to Combat Infection and Inflammation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2300750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, E.M.E.; White, D.; McLaughlin, S.; Kumar, A. Salicylic acids and pathogenic bacteria: New perspectives on an old compound. Can. J. Microbiol. 2023, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewonkem, M.B.; Deussom, P.M.; Mbock, M.A.; Tiakouang, E.N.; Toze, A.F.A.; Wansi, D.J. Antibacterial, antifungal activities and toxicity of new synthetic fatty acid salicylate esters. Med. Chem. Res. 2023, 32, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, V.; Cozzolino, A.; Rizzo, P.; Rodriquez, M.; Vestuto, V.; Bertamino, A.; Daniel, C.; Guerra, G. Salicylic Acid Release from Syndiotactic Polystyrene Staple Fibers. Molecules 2023, 28, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Hu, D.; Cheng, E.W.C.; Vargas-Reus, M.A.; Reip, P.; Allaker, R.P. Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, N.; Joo, S.W.; Mandal, T.K. Nanomaterial-Based Strategies to Combat Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and Applications. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, T.K. Nanomaterial-Enhanced Hybrid Disinfection: A Solution to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furno, F.; Morley, K.S.; Wong, B.; Sharp, B.L.; Arnold, P.L.; Howdle, S.M.; Bayston, R.; Brown, P.D.; Winship, P.D.; Reid, H.J. Silver nanoparticles and polymeric medical devices: A new approach to prevention of infection? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ejaz, U.; Vithanage, M.; Bolan, N.; Siddique, K.H.M. Synthesis, characterization, and advanced sustainable applications of copper oxide nanoparticles: A review. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2024, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meti, P.; Wang, Q.; Mahadik, D.B.; Lee, K.-Y.; Gong, Y.-D.; Park, H.-H. Evolutionary Progress of Silica Aerogels and Their Classification Based on Composition: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshutina, N.; Tsygankov, P.; Ivanov, S. Synthesis and Properties of Silica and Alginate Hybrid Aerogel Particles with Embedded Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) for Selective Sorption. Materials 2018, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareda, J.P.; Maximiano, P.; Cunha, L.P.; Ferreira, A.F.; Simões, P.N.; Durães, L. Effect of different types of surfactants on the microstructure of methyltrimethoxysilane-derived silica aerogels: A combined experimental and computational approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Qian, K.; Lv, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, J.; Ai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Encapsulation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles into N, S co-Doped Graphene Sheets with Greatly Enhanced Electrochemical Performance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanje, A.S.; Sharma, S.J.; Pode, R.B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: A safer alternative to conventional antimicrobial and antibacterial agents. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 478–483. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, B.; Qin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Wu, H.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Qu, X. The formation of CuO porous mesocrystal ellipsoids via tuning the oriented attachment mechanism. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samberg, M.E.; Oldenburg, S.J.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Evaluation of silver nanoparticle toxicity in skin in vivo and keratinocytes in vitro. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihodceva, S.; Šutka, A.; Iesalnieks, M.; Orlova, L.; Pludonis, A.; Otsus, M.; Sihtmäe, M.; Vija, H.; Nefedova, A.; Ivask, A.; et al. Emerging investigator series: CeO2/CuO nanostructured composite with enhanced antimicrobial properties and low cytotoxicity to human keratinocytes in vitro. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.; Bauer, C.; Vasioukhin, V.; Fuchs, E. Actin cable dynamics and Rho/Rock orchestrate a polarized cytoskeletal architecture in the early steps of assembling a stratified epithelium. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Hui, Y.; Ranaweera, S.; Zhao, C.-X. Microfluidic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Small 2022, 18, 2106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, S.J.; Issadore, D.; Mitchell, M.J. Microfluidic formulation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2021, 274, 120826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Chircov, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Nanomaterials Synthesis through Microfluidic Methods: An Updated Overview. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan Kumar, M.A.; Suresh, D.; Sneharani, A.H. Eco-friendly Ag-CuO nanoparticles for antidiabetic, antimicrobial, anti-cancer, platelet aggregation inducing, antioxidant and photocatalytic applications. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yahia, L.; Sacher, E. Antimicrobial Properties of the Ag, Cu Nanoparticle System. Biology 2021, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschini, E.; Colombo, G.; Chirico, G.; Capitani, G.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Mantecca, P. Biological mechanism of cell oxidative stress and death during short-term exposure to nano CuO. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semisch, A.; Ohle, J.; Witt, B.; Hartwig, A. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of nano-and microparticulate copper oxide: Role of solubility and intracellular bioavailability. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and Cytotoxic Properties of Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.E.; Choi, J.; Chung, K.H.; Park, K.; Yi, J.; Ryu, D.Y. Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, H.L.; Cronholm, P.; Gustafsson, J.; Möller, L. Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Are Highly Toxic: A Comparison between Metal Oxide Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, A.M.; Limbach, L.K.; Van Duc, L.; Krumeich, F.; Athanassiou, E.K.; Gerber, L.C.; Moch, H.; Stark, W.J. Nanoparticle cytotoxicity depends on intracellular solubility: Comparison of stabilized copper metal and degradable copper oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 197, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunsona, E.O.; Muthuraj, R.; Ojogbo, E.; Valerio, O.; Mekonnen, T.H. Engineered nanomaterials for antimicrobial applications: A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Sahraian, M.A.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Laurent, S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Promises for diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrinet, P.; Bengele, H.H.; Bonnemain, B.; Dencausse, A.; Idee, J.M.; Jacobs, P.M.; Lewis, J.M. Preclinical safety and pharmacokinetic profile of ferumoxtran-10, an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide magnetic resonance contrast agent. Investig. Radiol. 2006, 41, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Hussain, S.M.; Krestin, G.P. Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: Physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Cao, J.; Qi, X.; Shen, S. Ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles cause significant toxicity by specifically inducing acute oxidative stress to multiple organs. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahajuddin; Arora, S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A. Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xing, F.; Yu, P.; Zhe, M.; Shakya, S.; Liu, M.; Xiang, Z.; Duan, X.; Ritz, U. Multifunctional aerogel: A unique and advanced biomaterial for tissue regeneration and repair. Mater. Des. 2024, 243, 113091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Firoozi, A.A.; El-Abbasy, A.A.; Aati, K. Enhanced perspectives on silica aerogels: Novel synthesis methods and emerging engineering applications. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.C.; Pajonk, G.M. Chemistry of Aerogels and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4243–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamikamkar, S.; Yalcintas, E.P.; Haghniaz, R.; de Barros, N.R.; Mecwan, M.; Nasiri, R.; Davoodi, E.; Nasrollahi, F.; Erdem, A.; Kang, H.; et al. Aerogel-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications: From Fabrication Methods to Disease-Targeting Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Yoo, S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Han, S.I.; Lee, H. Nature-inspired surface modification strategies for implantable devices. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Schüth, F.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M. Engineering mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Where are we after two decades? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5365–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.A.; Sosnik, A.; Kalmár, J.; De Marco, I.; Erkey, C.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Aerogels in drug delivery: From design to application. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guihua, Z.; Liangliang, L.; Tingting, W.; Samuel, B.; Sandra, G.; Jianting, B.; Malfait, W.J.; Shanyu, Z.; Ostrikov, K. Silica aerogels: From materials research to industrial applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 2023, 68, 862–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercan, D.-A.; Tudorache, D.-I.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Mogoantă, L.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Hudiță, A.; Voinea, I.C.; Stan, M.S.; et al. Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090637
Mercan D-A, Tudorache D-I, Niculescu A-G, Mogoantă L, Mogoşanu GD, Bîrcă AC, Vasile BȘ, Hudiță A, Voinea IC, Stan MS, et al. Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(9):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090637
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercan, Doina-Antonia, Dana-Ionela Tudorache (Trifa), Adelina-Gabriela Niculescu, Laurenţiu Mogoantă, George Dan Mogoşanu, Alexandra Cătălina Bîrcă, Bogdan Ștefan Vasile, Ariana Hudiță, Ionela Cristina Voinea, Miruna S. Stan, and et al. 2025. "Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 15, no. 9: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090637
APA StyleMercan, D.-A., Tudorache, D.-I., Niculescu, A.-G., Mogoantă, L., Mogoşanu, G. D., Bîrcă, A. C., Vasile, B. Ș., Hudiță, A., Voinea, I. C., Stan, M. S., Hadibarata, T., Mihaiescu, D. E., Grumezescu, A. M., & Alberts, A. (2025). Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Hybrid Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 15(9), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090637













