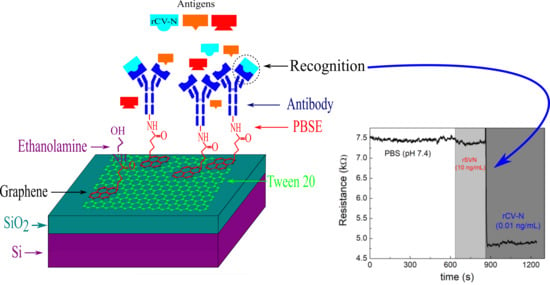
Development of a Graphene-Based Biosensor for Detecting Recombinant Cyanovirin-N
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
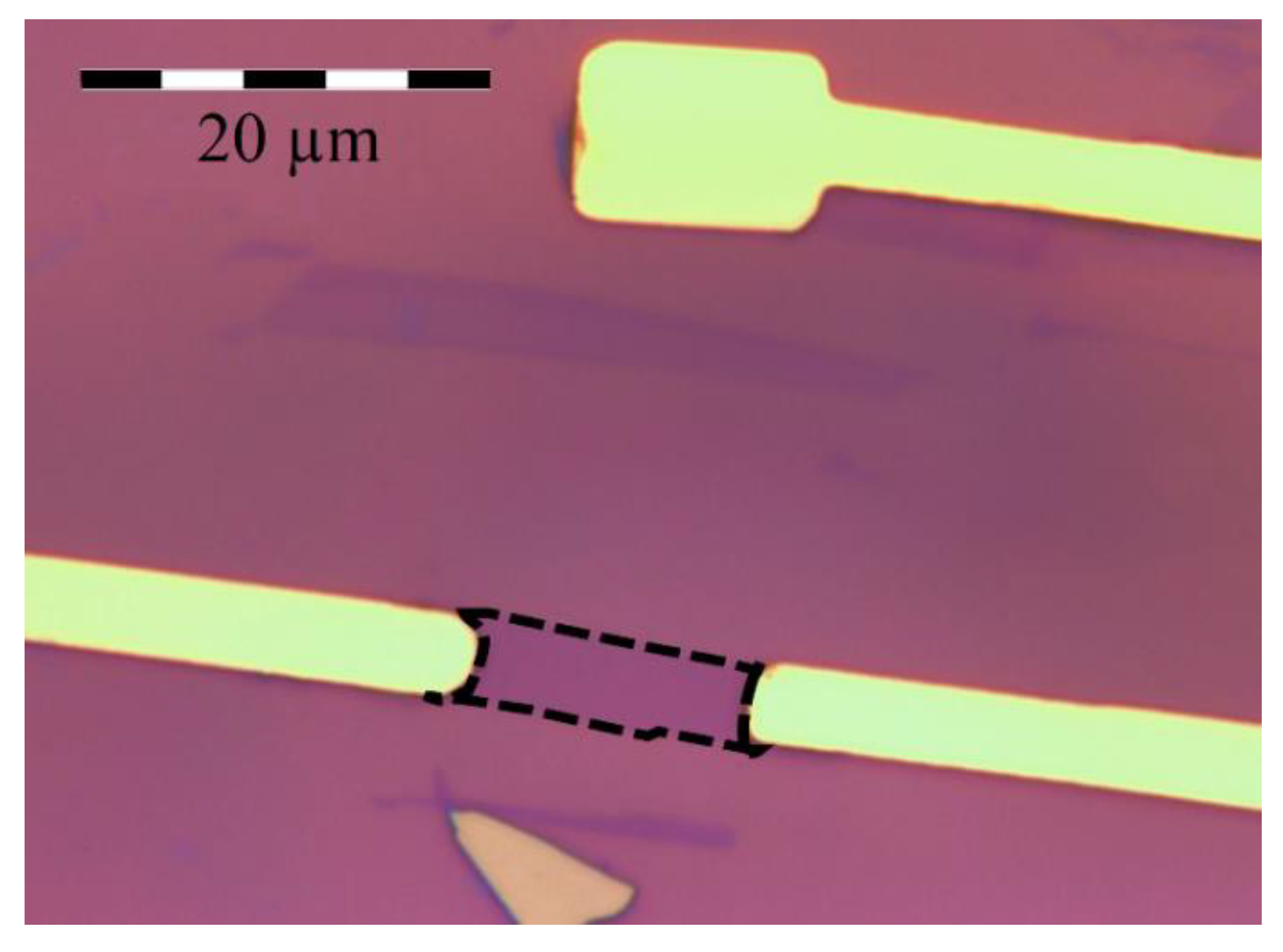
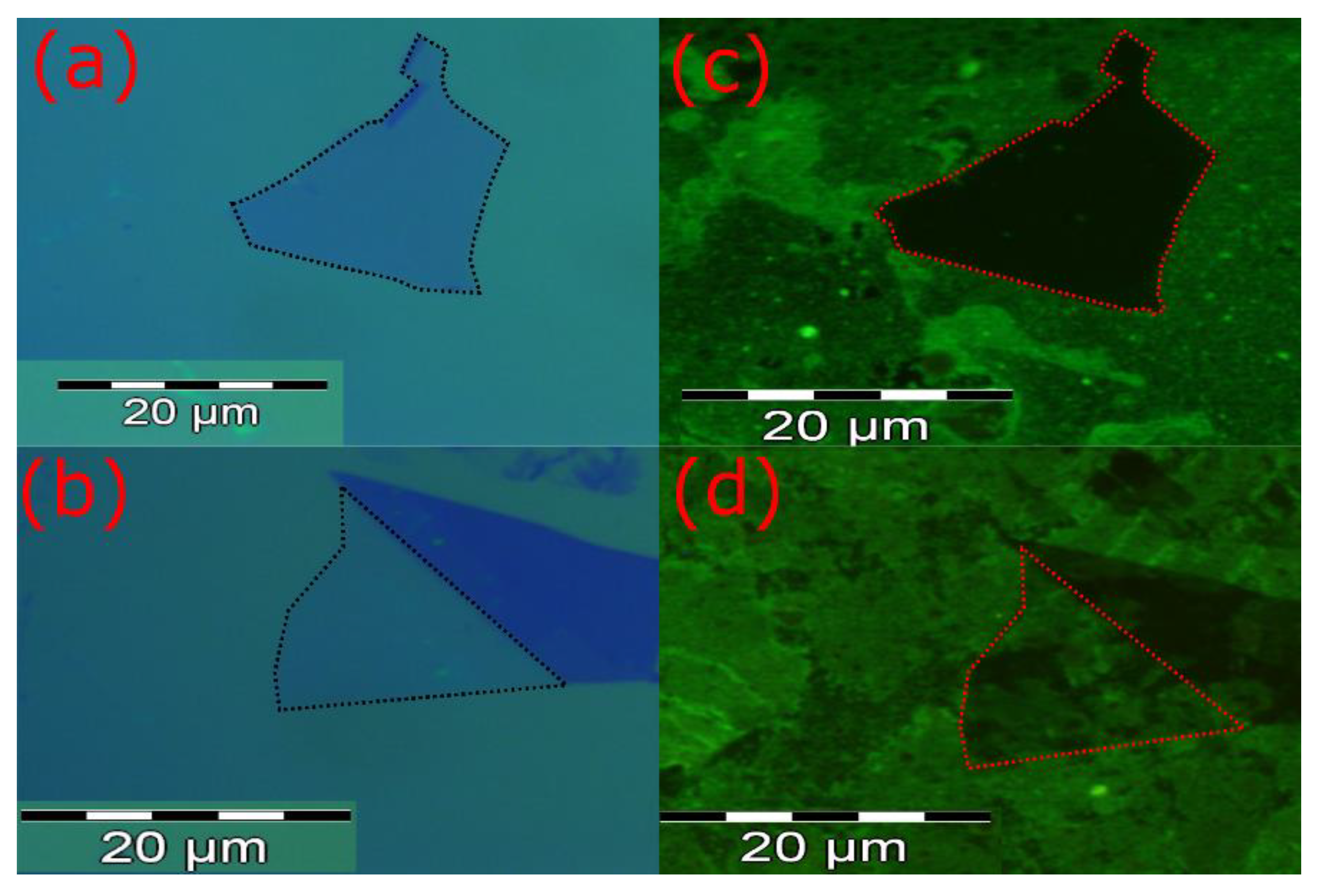
2.1. Device Fabrication
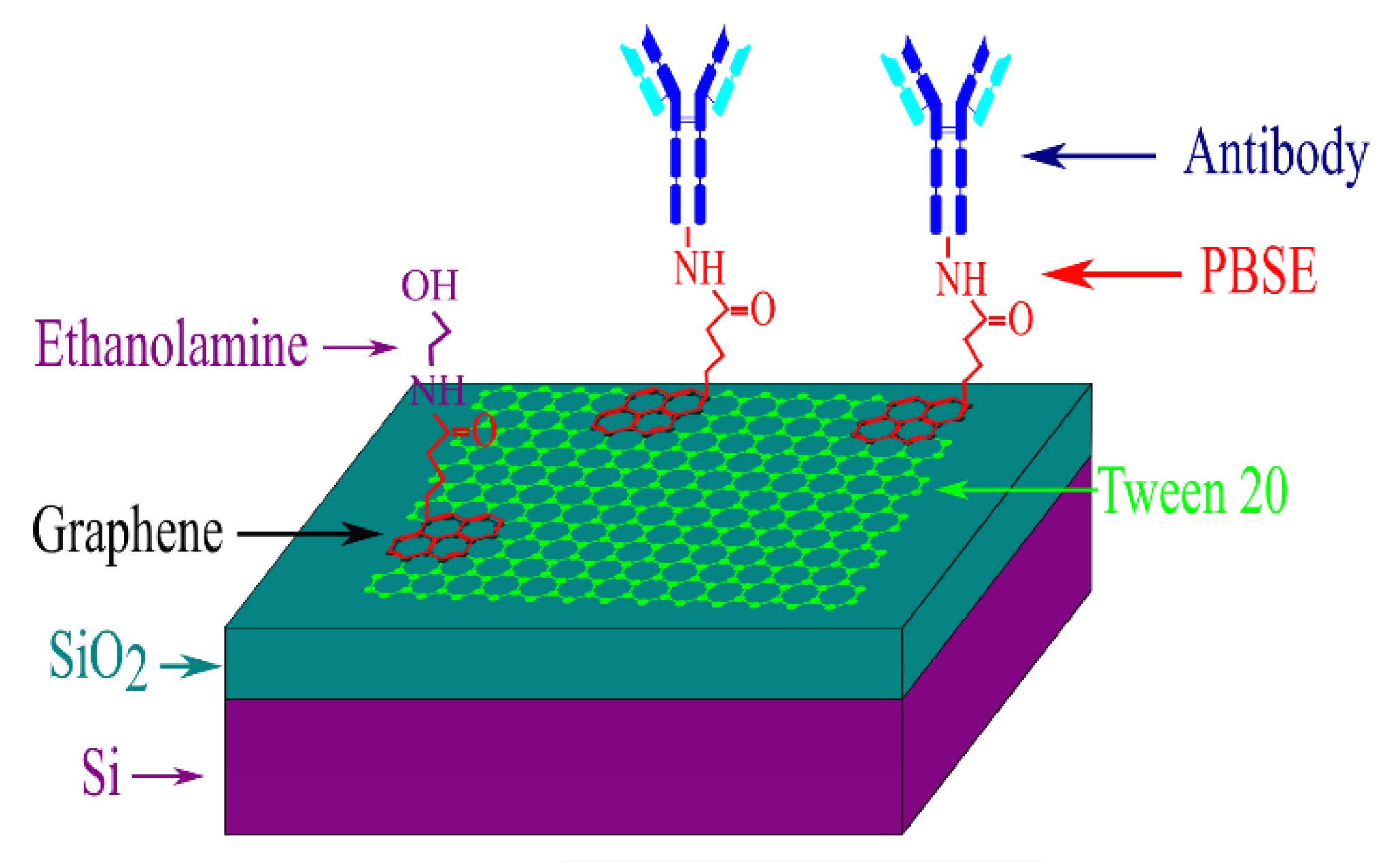
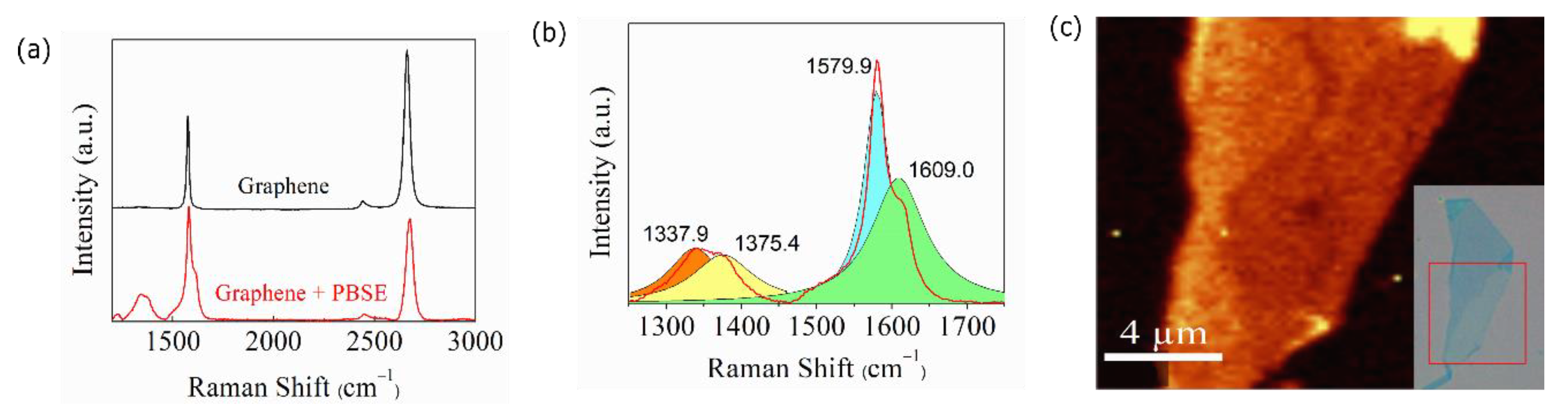
2.2. Functionalization
2.3. Proteins Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
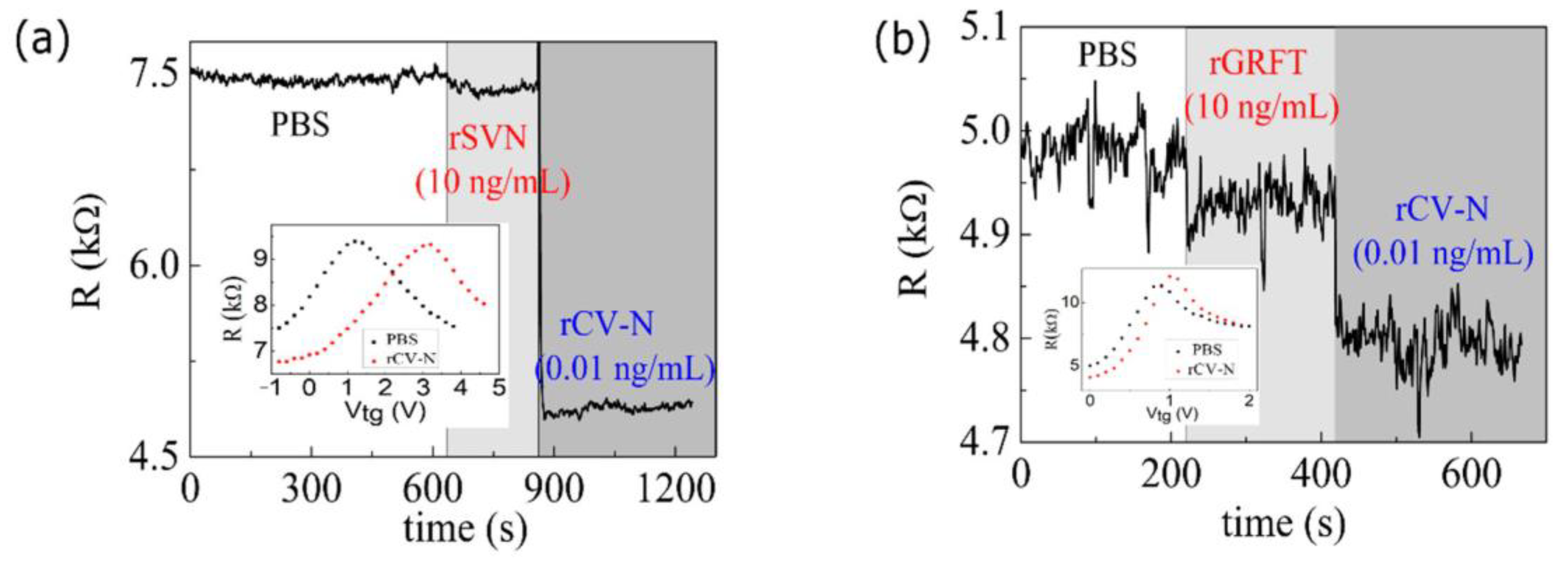
3.1. Protein Detection
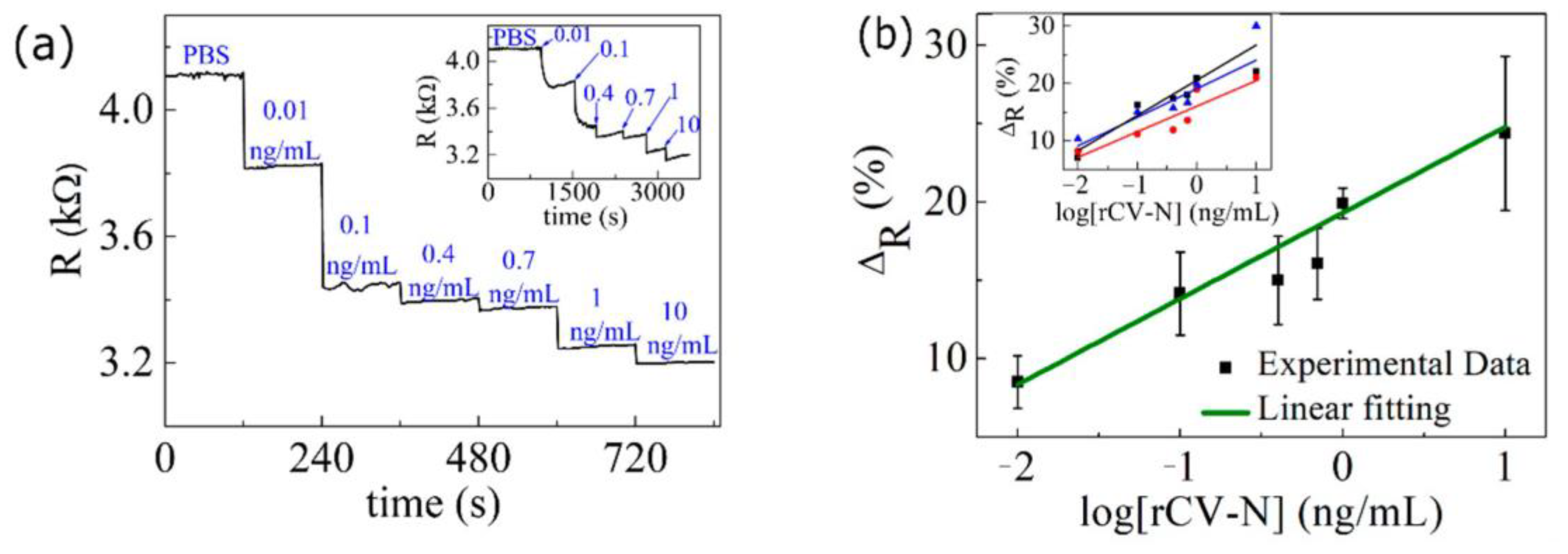
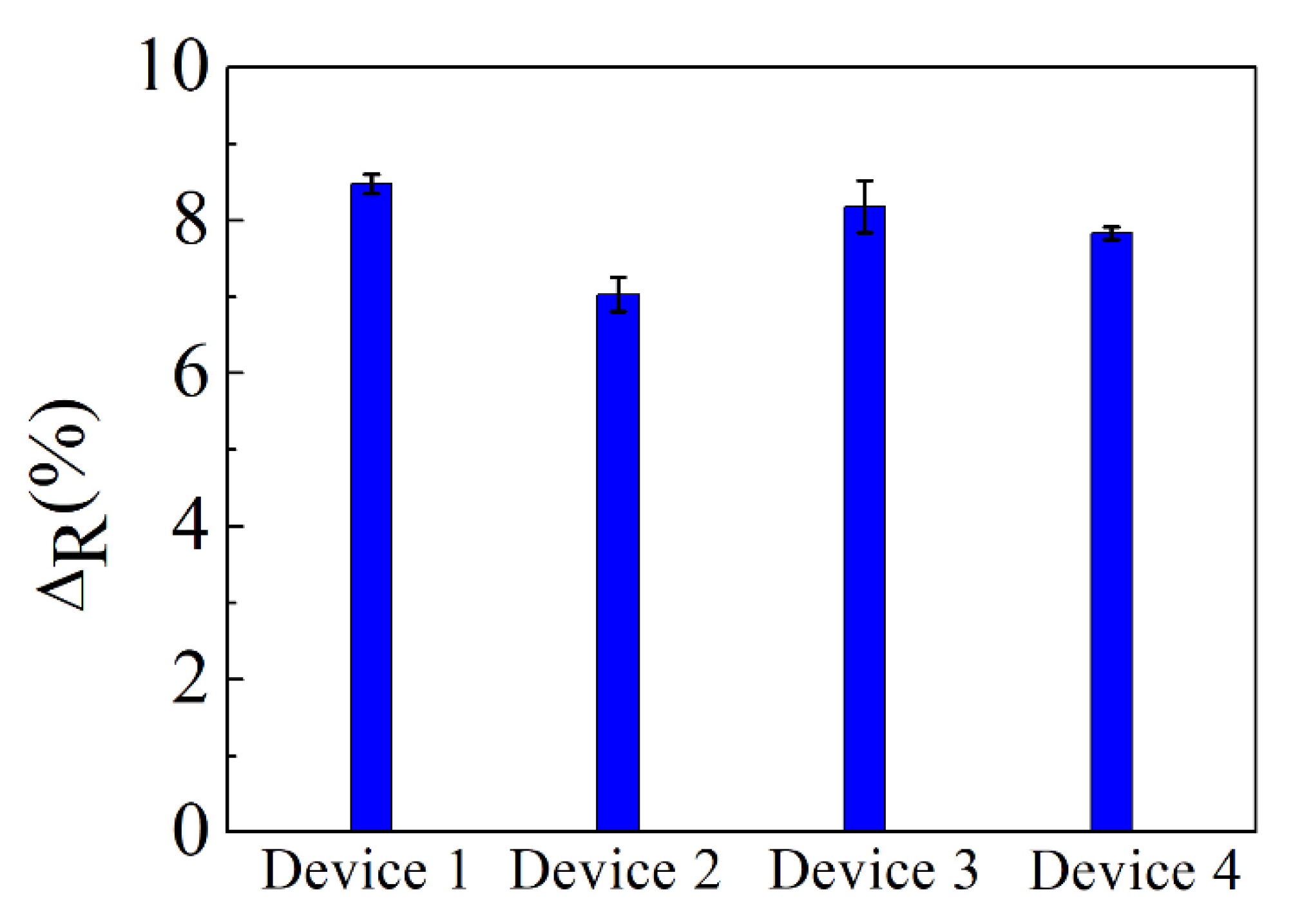
3.2. Sensitivity of the Graphene Biosensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, M.R.; Gustafson, K.R.; McMahon, J.B.; Shoemaker, R.H. Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus-inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: Potential applicatn. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokesch, H.R.; O’Keefe, B.R.; McKee, T.C.; Pannell, L.K.; Patterson, G.M.L.; Gardella, R.S.; Sowder, R.C.; Turpin, J.; Watson, K.; Buckheit, R.W.; et al. A Potent Novel Anti-HIV Protein from the Cultured CyanobacteriumScytonema varium. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Sowder, R.C.; Bringans, S.; Gardella, R.; Berg, S.; Cochran, P.; Turpin, J.A.; Buckheit, R.W.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Griffithsin, a Novel HIV-inactivating Protein, from the Red Alga Griffithsia sp. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9345–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grooms, T.N.; Vuong, H.R.; Tyo, K.M.; Malik, D.A.; Sims, L.B.; Whittington, C.P.; Palmer, K.E.; Matoba, N.; Steinbach, J.M. Griffithsin-Modified Electrospun Fibers as a Delivery Scaffold to Prevent HIV Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6518–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Emau, P.; Jiang, Y.; Agy, M.B.; Shattock, R.J.; Schmidt, A.; Morton, W.R.; Gustafson, K.R.; Boyd, M.R. Cyanovirin-N Inhibits AIDS Virus Infections in Vaginal Transmission Models. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2004, 20, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, B.R.; Murad, A.M.; Vianna, G.R.; Ramessar, K.; Saucedo, C.J.; Wilson, J.; Buckheit, K.W.; Da Cunha, N.B.; Araujo, A.C.G.; Lacorte, C.C.; et al. Engineering soya bean seeds as a scalable platform to produce cyanovirin-N, a non-ARV microbicide against HIV. Plant. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colleluori, D.M.; Tien, D.; Kang, F.; Pagliei, T.; Kuss, R.; McCormick, T.; Watson, K.; McFadden, K.; Chaiken, I.; Buckheit, R.W.; et al. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant cyanovirin-N for vaginal anti-HIV microbicide development. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 39, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, P. Biosensors and their applications—A review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2016, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Săndulescu, R.; Tertiş, M.; Cristea, C.; Bodoki, E. New Materials for the Construction of Electrochemical Biosensors. Biosens. Micro Nanoscale Appl. 2015, 2015, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Memelink, J.; Swords, K.M.M.; Staehelin, L.A.; Hoge, J.H.C. Southern, Northern and Western blot analysis. Plant. Mol. Biol. Man. 1994, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, K.N.A. The Rise of Graphene. Nat. Mater 2007, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, E.W.; Vijayaragahvan, A.; Novoselov, K. Graphene Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Xiong, C.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yan, F. Detection of Bisphenol A Using DNA-Functionalized Graphene Field Effect Transistors Integrated in Microfluidic Systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23522–23528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Borme, J.; Guerreiro, J.R.; Machado, G.; Cerqueira, M.F.G.; Petrovykh, D.Y.; Alpuim, P. Attomolar Label-Free Detection of DNA Hybridization with Electrolyte-Gated Graphene Field-Effect Transistors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xia, H.; Zauberman, J.; Tomaiuolo, M.; Ping, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ducos, P.; Ye, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; et al. Detection of Sub-fM DNA with Target Recycling and Self-Assembly Amplification on Graphene Field-Effect Biosensors. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3509–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.; Tang, L.; Wu, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Jia, C.; Jin, Q.; et al. Label-free graphene biosensor targeting cancer molecules based on non-covalent modification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afsahi, S.; Lerner, M.B.; Goldstein, J.M.; Lee, J.; Tang, X.; Bagarozzi, D.A.; Pan, D.; Locascio, L.; Walker, A.; Barron, F.E.; et al. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.-J.; Chen, P. Graphene-based biosensors for detection of bacteria and their metabolic activities. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 12358–12362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Maehashi, K.; Matsumoto, K. Label-Free Biosensors Based on Aptamer-Modified Graphene Field-Effect Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18012–18013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, D.K.H.; Lieberthal, T.J.; Watts, C.; Dunlop, I.E.; Ramadan, S.; Hernández, A.D.R.; Klein, N. Chemically Functionalised Graphene FET Biosensor for the Label-free Sensing of Exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Dai, Z.; Tang, X.; Lin, Z.; Lo, P.K.; Meyyappan, M.; Lai, K.W.C. Graphene Field-Effect Transistors for the Sensitive and Selective Detection of Escherichia coli Using Pyrene-Tagged DNA Aptamer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, T.; Bunting, A.; Cheung, R. Optical lithography technique for the fabrication of devices from mechanically exfoliated two-dimensional materials. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 154, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Otyepka, M.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Chandra, V.; Kim, N.; Kemp, K.C.; Hobza, P.; Zboril, R.; Kim, K.S. Functionalization of Graphene: Covalent and Non-Covalent Approaches, Derivatives and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6156–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.; Cabral, P.D.; Campos, R.; Machado, G.; Cerqueira, M.F.; Sousa, C.; Freitas, P.P.; Borme, J.; Petrovykh, D.Y.; Alpuim, P. Functionalization of single-layer graphene for immunoassays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 480, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, L.M.; Nilsson, J.; Elias, D.C.; Brant, J.C.; Plentz, F.; Alves, E.S.; Neto, A.H.C.; Pimenta, M.A. Probing the electronic structure of bilayer graphene by Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodali, V.K.; Scrimgeour, J.; Kim, S.; Hankinson, J.H.; Carroll, K.M.; De Heer, W.A.; Berger, C.; Curtis, J.E. Nonperturbative Chemical Modification of Graphene for Protein Micropatterning. Langmuir 2011, 27, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Meyyappan, M.; Lai, K.W.C. Graphene field-effect transistors-based biosensors for Escherichia coli detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Sendai, Japan, 22–25 August 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, L.; Nerngchamnong, N.; Nai, C.T.; Sangeeth, C.S.S.; Feng, Y.P.; et al. Giant enhancement in vertical conductivity of stacked CVD graphene sheets by self-assembled molecular layers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 399–401. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Liu, G.; Hou, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C. Electrochemical immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a reduced graphene oxide functionalized with a high molecular-weight silk peptide. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2061–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Hotani, K.; Hideshima, S.; Kuroiwa, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Mori, Y.; Osaka, T. Field Effect Transistor Biosensor Using Antigen Binding Fragment for Detecting Tumor Marker in Human Serum. Materials 2014, 7, 2490–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Gao, T.; Yang, X.; Dai, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, A.; Lieber, C.M. Specific detection of biomolecules in physiological solutions using graphene transistor biosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14633–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Almeida, P.R., III; Murad, A.M.; Silva, L.P.; Rech, E.L.; Alves, E.S. Development of a Graphene-Based Biosensor for Detecting Recombinant Cyanovirin-N. Biosensors 2020, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120206
de Almeida PR III, Murad AM, Silva LP, Rech EL, Alves ES. Development of a Graphene-Based Biosensor for Detecting Recombinant Cyanovirin-N. Biosensors. 2020; 10(12):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120206
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Almeida, Pedro Rodrigues, III, André Melro Murad, Luciano Paulino Silva, Elibio Leopoldo Rech, and Elmo Salomão Alves. 2020. "Development of a Graphene-Based Biosensor for Detecting Recombinant Cyanovirin-N" Biosensors 10, no. 12: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120206
APA Stylede Almeida, P. R., III, Murad, A. M., Silva, L. P., Rech, E. L., & Alves, E. S. (2020). Development of a Graphene-Based Biosensor for Detecting Recombinant Cyanovirin-N. Biosensors, 10(12), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120206