A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
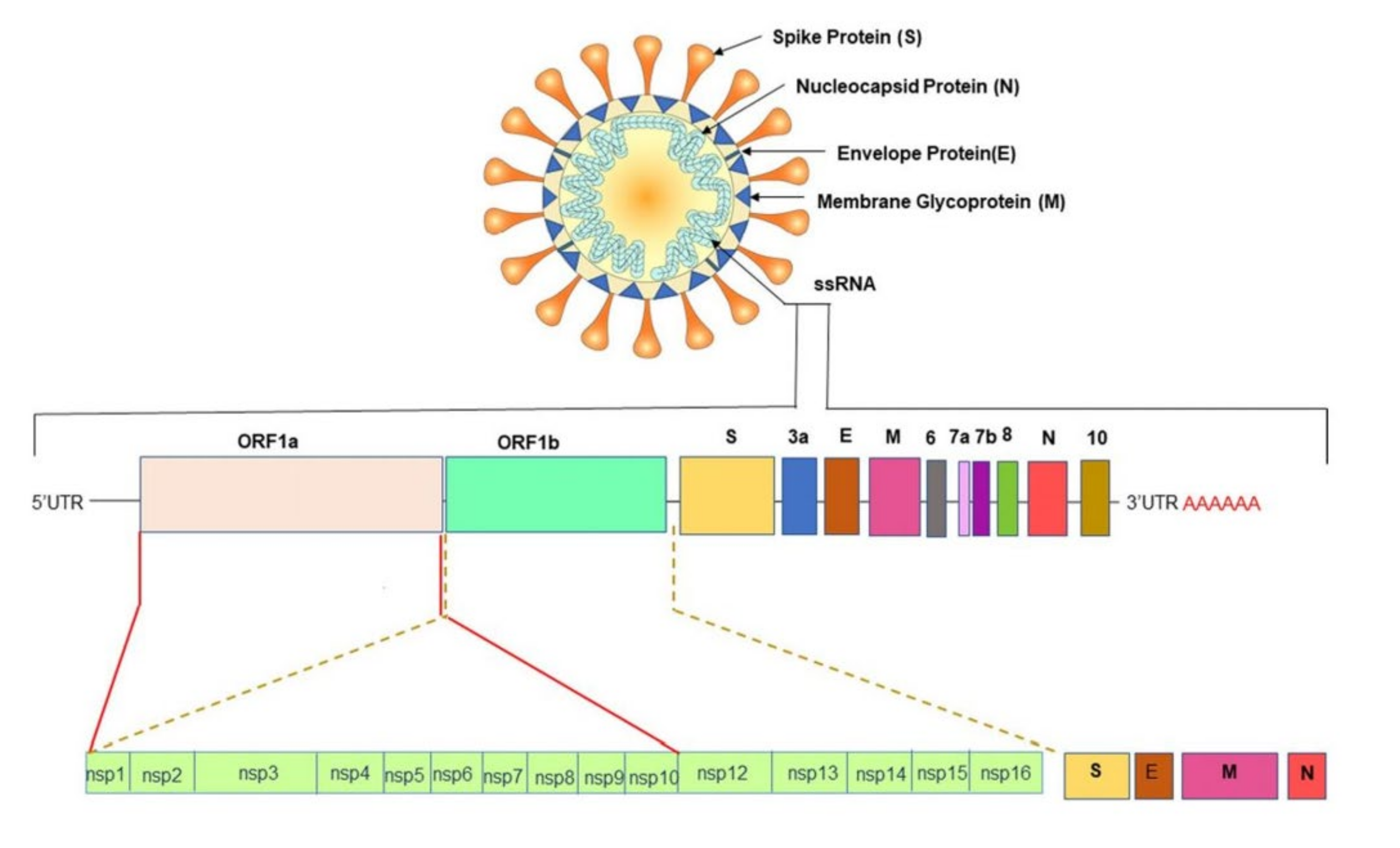
2. SARS-CoV-2, Its Variants and Existing Diagnosis Methods
3. THz Techniques for Virus Sensing
4. THz-Based Sensing and Detections for the Novel SARS-CoV-2
5. Challenges and Future Trends of THz-Based Sensing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Zhong, N.S.; Zheng, B.J.; Li, Y.M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Xie, Z.H.; Chan, K.H.; Li, P.H.; Tan, S.Y.; Chang, Q.; Xie, J.P.; et al. Epidemiology and Cause of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet 2003, 362, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhamlan, F.S.; Majumder, M.S.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hawkins, J.; Al-Abdely, H.M.; Alzahrani, A.; Obaid, D.A.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; BinSaeed, A. Case Characteristics among Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Outbreak and Non-Outbreak Cases in Saudi Arabia from 2012 to 2015. BMJ Open 2017, 7, 11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.F.; Anderson, D.E. Viruses in Bats and Potential Spillover to Animals and Humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus Associated with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeri, N.C.; Shrestha, N.; Siddikur Rahman, M.; Zaki, R.; Tan, Z.; Bibi, S.; Baghbanzadeh, M.; Aghamohammadi, N.; Zhang, W.; Haque, U. The SARS, MERS and Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Epidemics, the Newest and Biggest Global Health Threats: What Lessons Have We Learned? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 49, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; et al. CRISPR–Cas12-Based Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, Q. Viral Load of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Song, Y.; Cai, Z.; Yang, C. Stability Issues of RT-PCR Testing of SARS-CoV-2 for Hospitalized Patients Clinically Diagnosed with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, E.; Ainsworth, M.; Anand, R.; Andersson, M.I.; Auckland, K.; Baillie, J.K.; Barnes, E.; Beer, S.; Bell, J.I.; Berry, T.; et al. Antibody Testing for COVID-19: A Report from the National COVID Scientific Advisory Panel. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Paving the Road for Rapid Detection and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Micromachines 2020, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visseaux, B.; le Hingrat, Q.; Collin, G.; Bouzid, D.; Lebourgeois, S.; le Pluart, D.; Deconinck, L.; Lescure, F.X.; Lucet, J.C.; Bouadma, L.; et al. Evaluation of the Qiastat-Dx Respiratory Sars-Cov-2 Panel, the First Rapid Multiplex PCR Commercial Assay for Sars-Cov-2 Detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00630-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.Q.; Guo, X.; Akbar khan, S.; Lai, C.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Xia, S.; Chen, B.; et al. Detection of COVID-19: A Review of the Current Literature and Future Perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.-P.; Lin, R.T.P.; Renia, L.; Ng, L.F.P. Serological Approaches for COVID-19: Epidemiologic Perspective on Surveillance and Control. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.W.; Schmitz, J.E.; Persing, D.H.; Stratton, C.W. Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19: Current Issues and Challenges. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00512-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eftekhari, A.; Alipour, M.; Chodari, L.; Dizaj, S.M.; Ardalan, M.; Samiei, M.; Sharifi, S.; Vahed, S.Z.; Huseynova, I.; Khalilov, R.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for SARS-CoV-2. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriz, E. Recent Progress in Plasmonic Biosensing Schemes for Virus Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, R.; Navale, G.R.; Dharne, M.S. Biosensors: Frontiers in Rapid Detection of COVID-19. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüce, M.; Filiztekin, E.; Özkaya, K.G. COVID-19 Diagnosis—A Review of Current Methods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochia, R. Developments in Biosensors for CoV Detection and Future Trends. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.; Estevez, M.C.; Cardenosa-Rubio, M.; Astua, A.; Lechuga, L.M. How Nanophotonic Label-Free Biosensors Can Contribute to Rapid and Massive Diagnostics of Respiratory Virus Infections: COVID-19 Case. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2663–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naming the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and the Virus That Causes It. Available online: https://https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/naming-the-coronavirus-disease-(covid-2019)-and-the-virus-that-causes-it (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Corman, V.M.; Muth, D.; Niemeyer, D.; Drosten, C. Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. In Advances in Virus Research; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 100, pp. 163–188. ISBN 9780128152010. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S.R.; Leibowitz, J.L. Coronavirus pathogenesis. In Advances in Virus Research; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 81, pp. 85–164. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, M.; Pandey, N.; Shukla, A.; Singh, S.K. SARS Coronavirus 2: From Genome to Infectome. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus Biology and Replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.; Mehra, M.R.; Scholkmann, F.; SchÃ, R.; Ruschitzka, F.; et al. Electron Microscopy of SARS-CoV-2: A Challenging Task–Authors’ Reply. Lancet 2020, 395, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Science Brief: Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/scientific-brief-emerging-variants.html (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Triple Mutant Corona Virus Found in India, More Impact in Maharashtra and Bengal. Available online: https://www.zoomnews.in/en/news-detail/triple-mutant-corona-virus-found-in-india-more-impact-in-maharashtra-and-bengal-1.html (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Indian Covid-19 Variant (B.1.617) | New Scientist. Available online: https://www.newscientist.com/definition/indian-covid-19-variant-b-1-617/ (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- WHO Classifies Triple-Mutant Covid Variant from India as Global Health Risk. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2021/05/10/who-classifies-triple-mutant-covid-variant-from-india-as-global-health-risk-.html (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Rauseo, A.M.; O’Halloran, J.A. What Are the Clinical Implications of the SARS-CoV-2 Variants: 5 Things Every Cardiologist Should Know. JACC: Basic Transl. Sci. 2021, 6, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Werner, A.P.; Moliva, J.I.; Koch, M.; Choi, A.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Bennett, H.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Shi, W.; Graham, B.S.; et al. MRNA-1273 Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Antibodies against Spike Mutants from Global SARS-CoV-2 Variants. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, I.A.; Hassan, A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Crespilho, F.N. On the Challenges for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Based on a Review of Current Methodologies. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3655–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Luo, Y. Biomedical Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, J. (Ed.) Terahertz Spectroscopy-A Cutting Edge Technology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/54052 (accessed on 19 June 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.J.; Cha, S.H.; Shin, G.A.; Ahn, Y.H. Sensing Viruses Using Terahertz Nano-Gap Metamaterials. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S. Principles of Terahertz Science and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780387095394. [Google Scholar]
- Ajito, K.; Ueno, Y. THz Chemical Imaging for Biological Applications. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Oh, S.J.; Cheon, H. Potential Clinical Applications of Terahertz Radiation. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 190901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Ou, H.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Lin, Y.S. Actively Switchable Terahertz Metamaterial. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fabrizio, M.; Lupi, S.; D’Arco, A. Virus Recognition with Terahertz Radiation: Drawbacks and Potentialities. J. Phys. Photonics 2021, 3, 32001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Park, H.-R. Terahertz Biochemical Molecule-Specific Sensors. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1900662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-K.; Kang, J.-H.; Kwon, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Woo, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Song, C.-S.; Park, Q.-H.; Seo, M. Nano Metamaterials for Ultrasensitive Terahertz Biosensing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acbas, G.; Niessen, K.A.; Snell, E.H.; Markelz, A.G. Optical Measurements of Long-Range Protein Vibrations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.R.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, H.S.; Kyoung, J.S.; Seo, M.A.; Park, D.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Kim, D.S. Terahertz Nanoresonators: Giant Field Enhancement and Ultrabroadband Performance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; He, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Shu, G.; Fang, C.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y. Terahertz Biosensing Metamaterial Absorber for Virus Detection Based on Spoof Surface Plasmon Polaritons. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2018, 28, e21448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Lu, F.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.-S. Terahertz Metamaterial with Multiple Resonances for Biosensing Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, D.; Li, D.; Hui, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Mu, X. Terahertz Biosensing Based on Bi-Layer Metamaterial Absorbers toward Ultra-High Sensitivity and Simple Fabrication. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 143507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Yan, F.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Hou, Y. Ultrasensitive Sensing with Three-Dimensional Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber. J. Opt. 2018, 20, 055101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, G.; Wen, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cumming, D.R.S.; Chen, Q. Metamaterial Absorber Integrated Microfluidic Terahertz Sensors. Laser Photonics Rev. 2016, 10, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, B.; Hoffmann, M.; Helm, H.; Modjesch, G.; Jepsen, P.U. Chemical Recognition in Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy and Imaging. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, W.G.; Gurel, O.; Srinivasan, N.; King, P.D.; Nahar, N.K.; Park, S.; Lehman, N.L.; Sertel, K. Terahertz Imaging and Electromagnetic Model of Axon Demyelination in Alzheimer’s Disease. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadivand, A.; Gerislioglu, B.; Manickam, P.; Kaushik, A.; Bhansali, S.; Nair, M.; Pala, N. Rapid Detection of Infectious Envelope Proteins by Magnetoplasmonic Toroidal Metasensors. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, N.; Legacy, A.; Alam, F.; Pala, N. Hybrid Toroidal Resonance Response in Planar Core-Shell THz Metasurfaces. Plasmonics 2021, 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, N.; Karabiyik, M.; Pala, N. Hybrid Toroidal Modes in Planar Core-Shell Metamaterial Structures. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Photonics Conference (IPC), Reston, VA, USA, 30 September–4 October 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadivand, A.; Gerislioglu, B. Large-Modulation-Depth Polarization-Sensitive Plasmonic Toroidal Terahertz Metamaterial. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 1860–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadivand, A.; Gerislioglu, B.; Tomitaka, A.; Manickam, P.; Kaushik, A.; Bhansali, S.; Nair, M.; Pala, N. Extreme Sensitive Metasensor for Targeted Biomarkers Identification Using Colloidal Nanoparticles-Integrated Plasmonic Unit Cells. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadivand, A.; Gerislioglu, B.; Ahuja, R.; Kumar Mishra, Y. Terahertz Plasmonics: The Rise of Toroidal Metadevices towards Immunobiosensings. Mater. Today 2020, 32, 108–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, A.; Vafapour, Z. Sensing Avian Influenza Viruses Using Terahertz Metamaterial Reflector. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5161–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Siddiqui, O.; Abutarboush, H.; Farhat, M.; Ramzan, R. A THz Graphene Metasurface for Polarization Selective Virus Sensing. Carbon 2021, 176, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.T.; Jun, S.W.; Cha, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Shin, G.A.; Ahn, Y.H. Enhanced Sensitivity in THz Plasmonic Sensors with Silver Nanowires. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, C.; Zuo, J.; Pickwell-MacPherson, E. Label-Free Detection and Characterization of the Binding of Hemagglutinin Protein and Broadly Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Using Terahertz Spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 037006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolai, S.; Tabib-Azar, M. Terahertz Detection of Zika Viruses. Preprints 2020, 2020020232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadivand, A.; Gerislioglu, B.; Ramezani, Z.; Kaushik, A.; Manickam, P.; Ghoreishi, S.A. Functionalized Terahertz Plasmonic Metasensors: Femtomolar-Level Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terahertz Technology for the Identification of the COVID-19. Review of Academic Literature March 2020, TERAGROUP Prepared in Cooperation with: The Israeli Ministry of Defense & Rabatit Engineering & Consulting Ltd. Available online: https://www.iclinics.cl/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/tae-Terahertz-Technology-for-the-Identification-of-the-COVID-19-Academic-Literature.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Qiu, G.; Gai, Z.; Tao, Y.; Schmitt, J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Wang, J. Dual-Functional Plasmonic Photothermal Biosensors for Highly Accurate Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5268–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.-H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.-S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, C.M.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; Kang, L.; Xu, G.; Ho, H.P.; Yong, K.T. Gold Nanorod Assisted Enhanced Plasmonic Detection Scheme of COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Adv. Theory Simul. 2020, 3, 2000185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Kang, S.W.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.; Neethirajan, S. Chiral Zirconium Quantum Dots: A New Class of Nanocrystals for Optical Detection of Coronavirus. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barauna, V.G.; Singh, M.N.; Barbosa, L.L.; Marcarini, W.D.; Vassallo, P.F.; Mill, J.G.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, R.; Campos, L.C.G.; Warnke, P.H.; Martin, F.L. Ultrarapid On-Site Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Using Simple ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and an Analysis Algorithm: High Sensitivity and Specificity. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, C.; Bertazioli, D.; Gualerzi, A.; Picciolini, S.; Banfi, P.I.; Lax, A.; Messina, E.; Navarro, J.; Bianchi, L.; Caronni, A.; et al. COVID-19 Salivary Raman Fingerprint: Innovative Approach for the Detection of Current and Past SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Gai, Z.; Saleh, L.; Tang, J.; Gui, T.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Wang, J. Thermoplasmonic-Assisted Cyclic Cleavage Amplification for Self-Validating Plasmonic Detection of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7536–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Chu, K.Y.; Shen, A.Q. Detection of Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Gold Nanospikes in an Opto-Microfluidic Chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Cui, H.; Song, W.; Ru, X.; Zhou, W.; Yu, X. A Simple Magnetic Nanoparticles-Based Viral RNA Extraction Method for Efficient Detection of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, S.Y.; Shukla, S.; Hong, S.B.; Heo, N.S.; Bajpai, V.K.; Chun, H.S.; Jo, C.H.; Choi, B.G.; Huh, Y.S.; et al. Heteroassembled Gold Nanoparticles with Sandwich-Immunoassay LSPR Chip Format for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen (HBsAg). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Wang, P.; Yu, X. Phase-Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Sensors 2017, 17, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yesilkoy, F.; Terborg, R.A.; Pello, J.; Belushkin, A.A.; Jahani, Y.; Pruneri, V.; Altug, H. Phase-Sensitive Plasmonic Biosensor Using a Portable and Large Field-of-View Interferometric Microarray Imager. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Tan, W.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, P. High-Performance Terahertz Sensing at Exceptional Points in a Bilayer Structure. Adv. Theory Simul. 2018, 1, 1800070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Jevtics, D.; Zhang, F.; Sterzl, S.; Damry, D.A.; Rothmann, M.U.; Guilhabert, B.; Strain, M.J.; Tan, H.H.; Herz, L.M.; et al. Three-Dimensional Cross-Nanowire Networks Recover Full Terahertz State. Science 2020, 368, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Karabiyik, M.; Al-Amin, C.; Vabbina, P.K.; Pala, N. Tunable Room Temperature THz Sources Based on Nonlinear Mixing in a Hybrid Optical and THz Micro-Ring Resonator. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumming, D.R.S.; Liang, L.; Wen, L.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Q. Miniaturized Spectroscopy with Tunable and Sensitive Plasmonic Structures. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4264–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebermeister, L.; Nellen, S.; Kohlhaas, R.B.; Lauck, S.; Deumer, M.; Breuer, S.; Schell, M.; Globisch, B. Optoelectronic Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Terahertz Spectroscopy with 4 THz Bandwidth. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, M.S.; Consolino, L.; Inguscio, M.; Natale, P. de Toward New Frontiers for Terahertz Quantum Cascade Laser Frequency Combs. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valušis, G.; Lisauskas, A.; Yuan, H.; Knap, W.; Roskos, H.G. Roadmap of Terahertz Imaging 2021. Sensors 2021, 21, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.H. Terahertz Bio-Sensing Techniques. In Handbook of Terahertz Technology for Imaging, Sensing and Communications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, M.; Först, M.; Kurz, H. THz Biosensing Devices: Fundamentals and Technology. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Concept of Work | Sensitivity/LOD | Detected Virus | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| THz toroidal metasensor | ~4.2 fmol | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | [70] |
| Dual-functional LSPR biosensor with Au Nanoislands | 0.22 pM | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | [72] |
| Gated graphene-enhanced FET based biosensor | 1.6 × 101 pfu/mL (culture medium) 2.42 × 102 copies/mL (clinical samples) | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | [73] |
| Au nanorod based plasmonics | 111.11 deg/RIU | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | [74] |
| Zr NPs with Zr QDs | 79.15 EID/50 mL | Coronavirus | [75] |
| MIR Spectroscopic technique | 95% | SARS-CoV-2 | [76] |
| Raman Spectroscopic technique | 83.7–97.5% | SARS-CoV-2 | [77] |
| Thermoplasmonic-assisted dual-mode transducing (TP-DMT) | 250 copies/mL | SARS-CoV-2 | [78] |
| LSPR based opto-microfluidic sensing platform with gold nanospikes | 0.08 ng/mL (~0.5 pM) | SARS-CoV-2 | [79] |
| Carboxyl groups (PC)-coated magnetic nanoparticles (pcMNPs) | 10 copy/mL | SARS-CoV-2 RNA | [80] |
| THz Slot antenna with silver nanowire | 32.7 GHz·µm2/particle | PRD1 | [67] |
| THz Toroidal metasensor | 5.81 GHz/log(pg/mL) | Zika virus | [63] |
| THz Toroidal metasensor | 6.47 GHz/log (pg/mL) | Zika virus | [59] |
| THz Au nano-antenna with 2D punctured rectangular slots | 0.35 THz/RIU | H1N1, H9N2, H5N2 | [49] |
| THz Rectangular Au metamaterial | 80 GHz/particle/µm2 | PRD1, MS2 | [42] |
| THz SSPP Jerusalem Cross Aperture | 0.5 THz/RIU | AIV | [53] |
| Hetero-assembled AuNPs sandwich-immunoassay LSPR chip | 100 fg mL−1 | Hepatitis B surface antigen | [81] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akter, N.; Hasan, M.M.; Pala, N. A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2. Biosensors 2021, 11, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100349
Akter N, Hasan MM, Pala N. A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2. Biosensors. 2021; 11(10):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100349
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkter, Naznin, Muhammad Mahmudul Hasan, and Nezih Pala. 2021. "A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2" Biosensors 11, no. 10: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100349
APA StyleAkter, N., Hasan, M. M., & Pala, N. (2021). A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2. Biosensors, 11(10), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100349






