Lateral Flow Immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen with SERS-Based Registration: Development and Comparison with Traditional Immunoassays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Chemicals, and Apparatuses
2.2. Biotinylation of Antibody RBDF5
2.3. Sandwich ELISA of RBD
2.4. Preparation of AuNP
2.5. Preparation of Antibody RBDF5 Conjugate with AuNP
2.6. Preparation of SERS Nanotag
2.7. Manufacturing of Tests Strips for LFIA
2.8. LFIA and Data Processing
2.9. SERS-Based LFIA and Data Processing
2.10. Spike RBD Protein Detection in the Lysate of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Vero Cell
3. Results
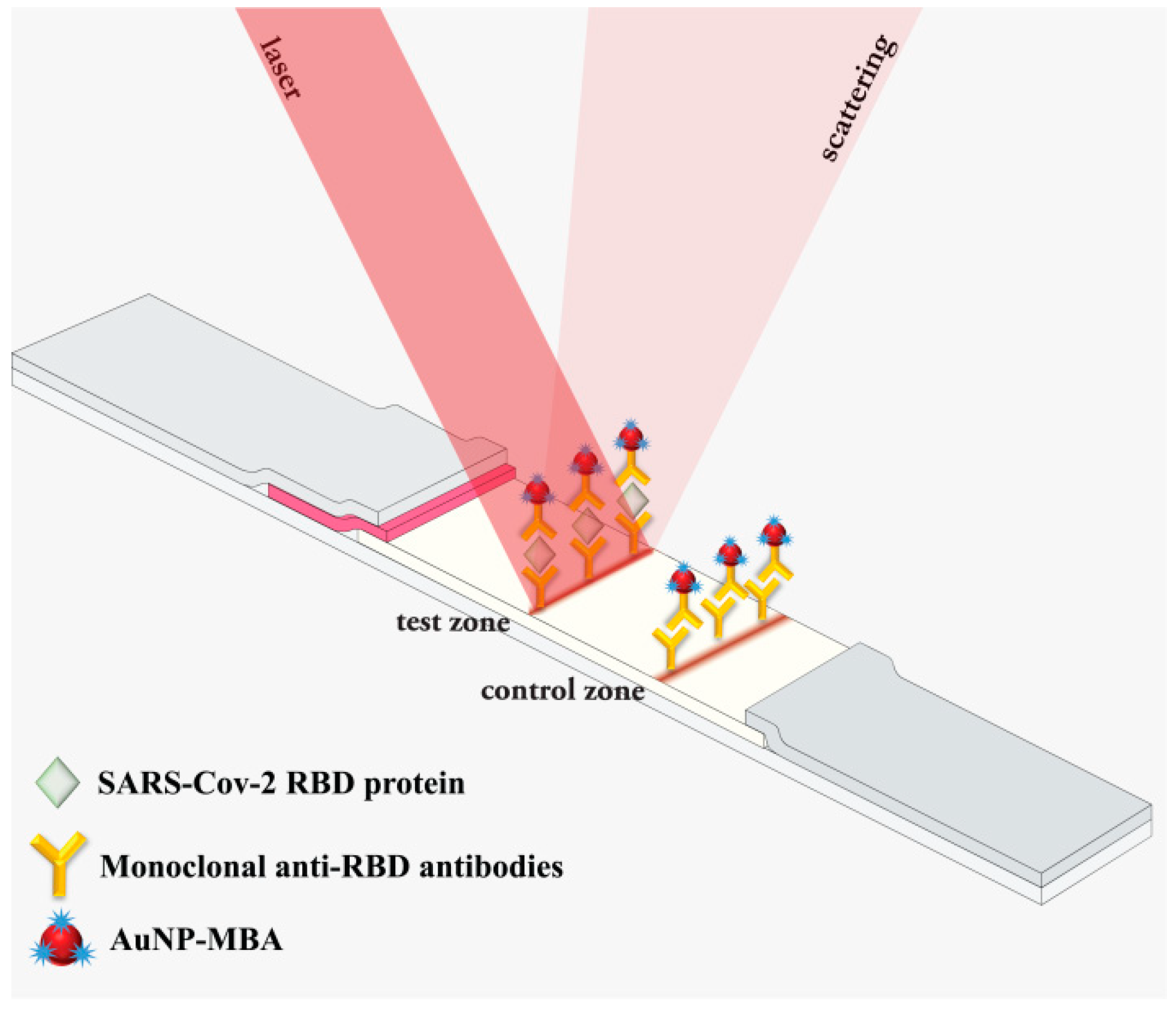
3.1. Principle of SERS-Based LFIA for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RBD
3.2. Characterization of AuNP and MBA-Modified AuNP
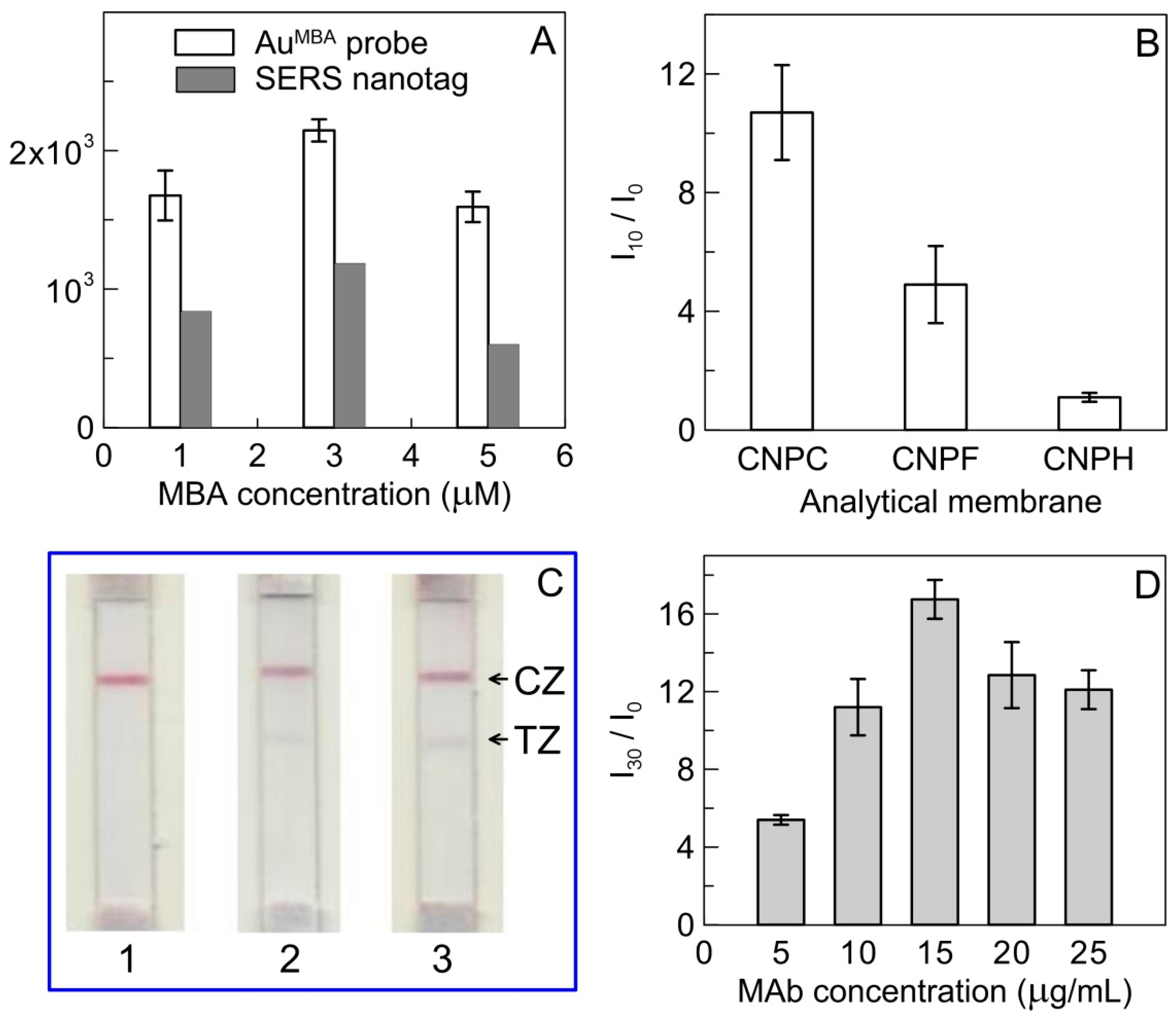
3.3. The Optimization of Experimental Conditions of SERS-Based LFIA
3.4. SERS-Based LFIA for RBD Detection
3.5. Comparison of SERS-Based LFIA with ELISA and Standard AuNP-Based LFIA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Synowiec, A.; Szczepański, A.; Barreto-Duran, E.; Lie, L.K.; Pyrc, K. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A systemic infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00133-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariano, G.; Farthing, R.J.; Lale-Farjat, S.L.M.; Bergeron, J.R.C. Structural characterization of SARS-CoV-2: Where we are, and where we need to be. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 605236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Feng, P.; Liu, K.; Wu, M.; Lin, H. Computational identification of small interfering RNA targets in SARS-CoV-2. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wassie, G.T.; Azene, A.G.; Bantie, G.M.; Dessie, G.; Aragaw, A.M. Incubation period of severe acute respiratory syndrome novel coronavirus 2 that causes coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2020, 93, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, N.; Mohamed, E.A. The estimations of the COVID-19 incubation period: A scoping reviews of the literature. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsatsakis, A.; Calina, D.; Falzone, L.; Petrakis, D.; Mitrut, R.; Siokas, V.; Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Libra, M.; Doukas, S.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 pathophysiology and its clinical implications: An integrative overview of the pharmacotherapeutic management of COVID-19. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaira, L.A.; Salzano, G.; Deiana, G.; De Riu, G. Anosmia and ageusia: Common findings in COVID-19 patients. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouadma, L.; Wiedemann, A.; Patrier, J.; Surénaud, M.; Wicky, P.-H.; Foucat, E.; Diehl, J.-L.; Hejblum, B.P.; Sinnah, F.; de Montmollin, E.; et al. Immune alterations in a patient with SARS-CoV-2-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Situation Report, 60th ed.; Coronavirus Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kanji, J.N.; Zelyas, N.; MacDonald, C.; Pabbaraju, K.; Khan, M.N.; Prasad, A.; Hu, J.; Diggle, M.; Berenger, B.M.; Tipples, G. False negative rate of COVID-19 PCR testing: A discordant testing analysis. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lascarrou, J.-B.; Colin, G.; Le Thuaut, A.; Serck, N.; Ohana, M.; Sauneuf, B.; Geri, G.; Mesland, J.-B.; Ribeyre, G.; Hussenet, C.; et al. Predictors of negative first SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR despite final diagnosis of COVID-19 and association with outcome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, C.F.; Gherasim, C.; O’Shea, K.; Manthei, D.M.; Chen, J.; Giacherio, D.; Troost, J.P.; Baldwin, J.L.; Baker, J.R. Accurate point-of-care serology tests for COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, S.; Batra, R.; Snell, L.B.; Merrick, B.; Nebbia, G.; Douthwaite, S.; Patel, A.; Ik, M.T.K.; Patel, B.; Charalampous, T.; et al. Comparative performance of SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow antigen tests and association with detection of infectious virus in clinical specimens: A single-centre laboratory evaluation study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e461–e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral-flow immunoassay. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-Y.; You, E.-M.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Moskovits, M. Electromagnetic theories of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4042–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, B.N.; Bratashov, D.N.; Byzova, N.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Khlebtsov, N.G. SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay of troponin I by using gap-enhanced Raman tags. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Meng, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Ali, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, M.; Yi, M.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; et al. SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive and simultaneous detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibodies by using gap-enhanced Raman nanotags. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Tang, S.; Luo, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Duplex surface enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow immunosensor for the low-level detection of antibiotic residues in milk. Molecules 2020, 25, 5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanain, W.A.; Spoors, J.; Johnson, C.L.; Faulds, K.; Keegan, N.; Graham, D. Rapid ultra-sensitive diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection using a SERS-based lateral flow assay. Analyst 2021, 146, 4495–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Gu, C.; Wei, G.; Jiang, T. Improved lateral flow strip based on hydrophilic−hydrophobic SERS substrate for ultra−sensitive and quantitative immunoassay. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, B.; Ma, X. Simultaneous detection of inflammatory biomarkers by SERS nanotag-based lateral flow assay with portable cloud Raman spectrometer. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Xiao, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, S. Fe3O4@Au SERS tags-based lateral flow assay for simultaneous detection of serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein in unprocessed blood sample. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Yu, Q. The development of lateral flow immunoassay strip tests based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with gold nanoparticles for the rapid detection of soybean allergen β-conglycinin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 241, 118640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Li, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Hu, Y.; Sun, H. A novel lateral flow assay for rapid and sensitive nucleic acid detection of Avibacterium paragallinarum. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 738558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Xu, L.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Gu, B. Rapid, quantitative, high-sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by gold-shell silica-core nanospheres-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering lateral flow immunoassay. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 596005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dai, E.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Z.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K.; Tu, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Development of a SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in clinical samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, E.A.; Wilchek, M. Protein biotinylation. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 184, 138–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuithschick, M.; Birnbaum, A.; Witte, S.; Sztucki, M.; Vainio, U.; Pinna, N.; Rademann, K.; Emmerling, F.; Kraehnert, R.; Polte, J.R. Turkevich in new robes: Key questions answered for the most common gold nanoparticle synthesis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7052–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panferov, V.G.; Byzova, N.A.; Biketov, S.F.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Comparative study of in situ techniques to enlarge gold nanoparticles for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2. Biosensors 2021, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.G.; Fang, Y.; Hao, G.L.; Wang, W.G. Adsorption behaviors of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid on silver and gold films. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 23, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.J.; de Almeida, P.M.; Nunes, D.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Pereira, E.; Byrne, H.J.; Águas, H.; Franco, R. Design and simple assembly of gold nanostar bioconjugates for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy immunoassays. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Israelsen, N.D.; Wooley, D.; Hanson, C.; Vargis, E. Rational design of Raman-labeled nanoparticles for a dual-modality, light scattering immunoassay on a polystyrene substrate. J. Biol. Eng. 2016, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleinman, S.; Frontiera, R.; Henry, A.-I.; Dieringer, J.; van Duyne, R. Creating, characterizing, and controlling chemistry with SERS hot spots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Oton, J.; Qu, K.; Cortese, M.; Zila, V.; McKeane, L.; Nakane, T.; Zivanov, J.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; et al. Structures and distributions of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on intact virions. Nature 2020, 588, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, R.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Gleizer, S.; Bernsthein, B.; Flamholz, A.; Phillips, R.; Milo, R. The total number and mass of SARS-CoV-2 virions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024815118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Lu, L.; Rong, Z.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Portable and multiplexed lateral flow immunoassay reader based on SERS for highly sensitive point-of-care testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Anfossi, L. Ten years of lateral flow immunoassay technique applications: Trends, challenges and future perspectives. Sensors 2021, 21, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Starovoitova, T.A.; Dzantiev, B.B. A triple immunochromatographic test for simultaneous determination of cardiac troponin I, fatty acid binding protein, and C-reactive protein biomarkers. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebrennikova, K.V.; Samsonova, J.V.; Osipov, A.P. A semi-quantitative rapid multi-range gradient lateral flow immunoassay for procalcitonin. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qin, W.; Hou, Y.; Xiao, K.; Yan, W. The application of lateral flow immunoassay in point of care testing: A review. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2016, 8, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernasconi, L.; Oberle, M.; Gisler, V.; Ottiger, C.; Fankhauser, H.; Schuetz, P.; Fux, C.A.; Hammerer-Lercher, A. Diagnostic performance of a SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM lateral flow immunochromatography assay in symptomatic patients presenting to the emergency department. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, e159–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basgalupp, S.; dos Santos, G.; Bessel, M.; Garcia, L.; de Moura, A.C.; Rocha, A.C.; Brito, E.; de Miranda, G.; Dornelles, T.; Dartora, W.; et al. Diagnostic properties of three SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamani, B.S.; Uppal, T.; Verma, S.C.; Misra, M. Functionalized TiO2 nanotube-based electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sensors 2020, 20, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyüksünetçi, Y.T.; Çitil, B.E.; Tapan, U.; Anık, U. Development and application of a SARS-CoV-2 colorimetric biosensor based on the peroxidase-mimic activity of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoudi, K.; Ramachandran, K.; Alawadhi, H.; Boukherroub, R.; Dogheche, E.; Khakani, M.; Gaidi, M. Ultra-sensitive and fast optical detection of the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 using AgNPs/SiNWs nanohybrid based sensors. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, A.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, P.; Jia, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. Development of a colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip for rapid detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike protein. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ju, C.; Han, C.; Shi, R.; Chen, X.; Duan, D.; Yan, J.; Yan, X. Nanozyme chemiluminescence paper test for rapid and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 173, 112817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristov, D.; Rijal, H.; Gomez-Marquez, J.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Developing a paper-based antigen assay to differentiate between coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 spike variants. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7825–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Tian, S.; Liu, K.; Ni, J.; Zhao, M.; Kang, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. 5G-enabled ultra-sensitive fluorescence sensor for proactive prognosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sensor | Limit of Detection | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip | 62.5 ng/mL | Standard solution | [48] |
| Chemiluminescence paper assay using Co–Fe@hemin-peroxidase nanozyme | 0.1 ng/mL | Standard solution | [49] |
| LFIA using gold-enhanced AuNP | 1 pg/mL | Saliva | [30] |
| Paper-based antigen test | 0.07 nM | Standard solution | [50] |
| LFIA using mesoporous Si encapsulated up-conversion nanoparticles | 1.6 ng/mL | Standard solution | [51] |
| SERS-based LFIA | 0.1 ng/mL | Standard solution | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serebrennikova, K.V.; Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Khlebtsov, N.G.; Khlebtsov, B.N.; Biketov, S.F.; Dzantiev, B.B. Lateral Flow Immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen with SERS-Based Registration: Development and Comparison with Traditional Immunoassays. Biosensors 2021, 11, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120510
Serebrennikova KV, Byzova NA, Zherdev AV, Khlebtsov NG, Khlebtsov BN, Biketov SF, Dzantiev BB. Lateral Flow Immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen with SERS-Based Registration: Development and Comparison with Traditional Immunoassays. Biosensors. 2021; 11(12):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120510
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerebrennikova, Kseniya V., Nadezhda A. Byzova, Anatoly V. Zherdev, Nikolai G. Khlebtsov, Boris N. Khlebtsov, Sergey F. Biketov, and Boris B. Dzantiev. 2021. "Lateral Flow Immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen with SERS-Based Registration: Development and Comparison with Traditional Immunoassays" Biosensors 11, no. 12: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120510
APA StyleSerebrennikova, K. V., Byzova, N. A., Zherdev, A. V., Khlebtsov, N. G., Khlebtsov, B. N., Biketov, S. F., & Dzantiev, B. B. (2021). Lateral Flow Immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen with SERS-Based Registration: Development and Comparison with Traditional Immunoassays. Biosensors, 11(12), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120510