Disposable Stainless-Steel Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor for In Vivo Continuous Monitoring of Hydrogen Peroxide in Vein of Tomato Leaf
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Material Preparation
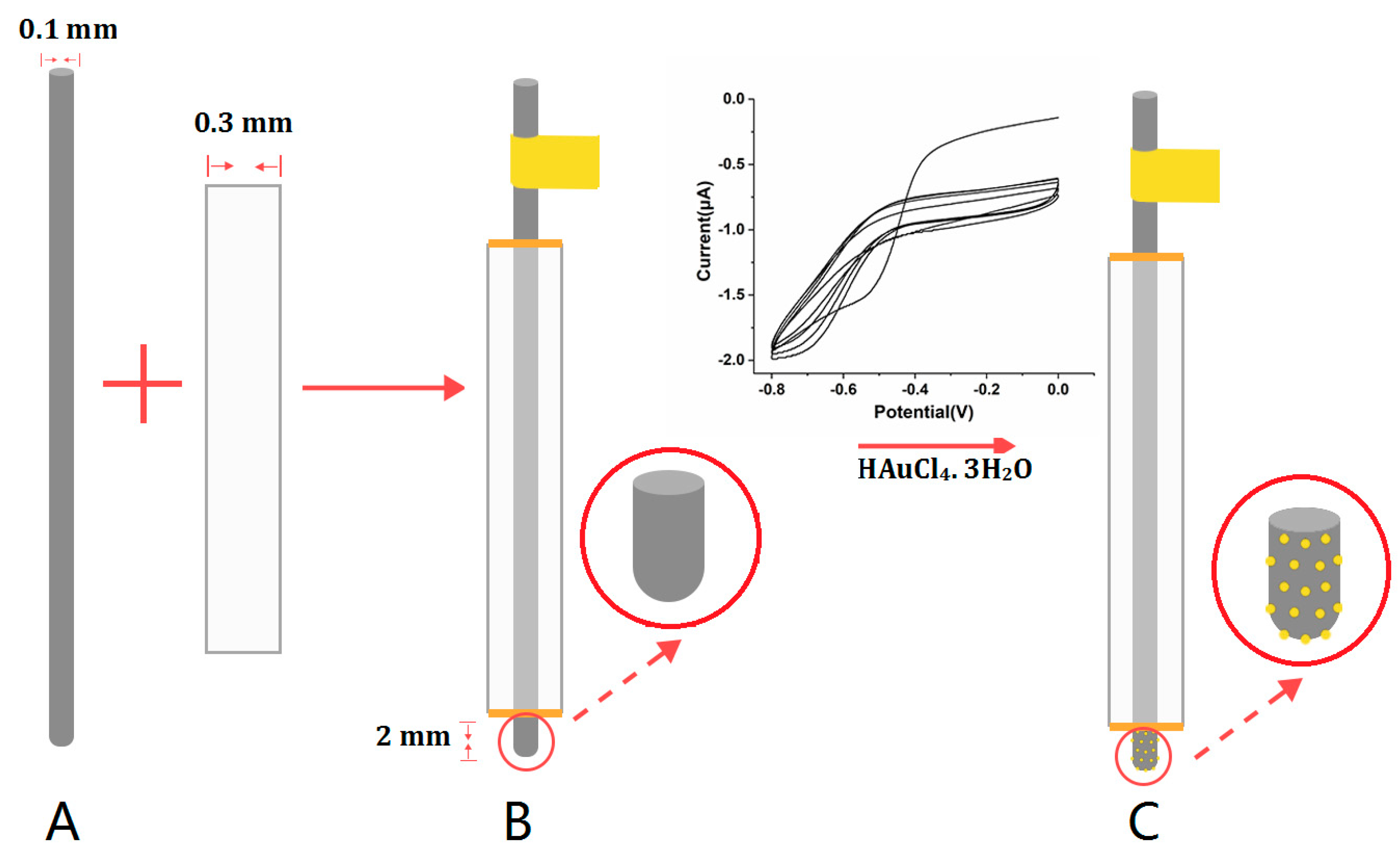
2.3. The Preparation of SS Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
2.5. qRT-PCR Analysis of Gene Expression
3. Results and Discussion
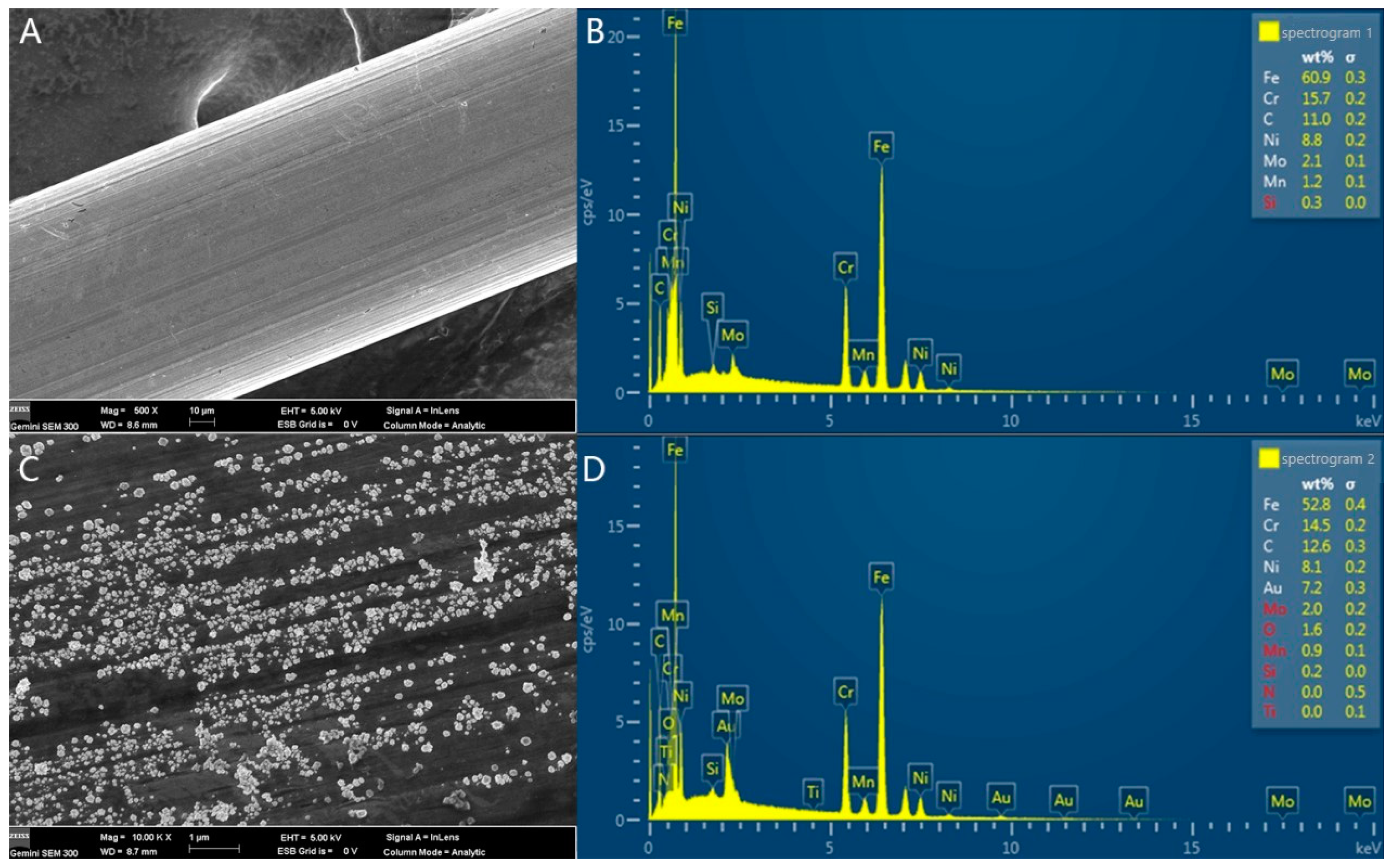
3.1. Characterization of theModified Electrodes
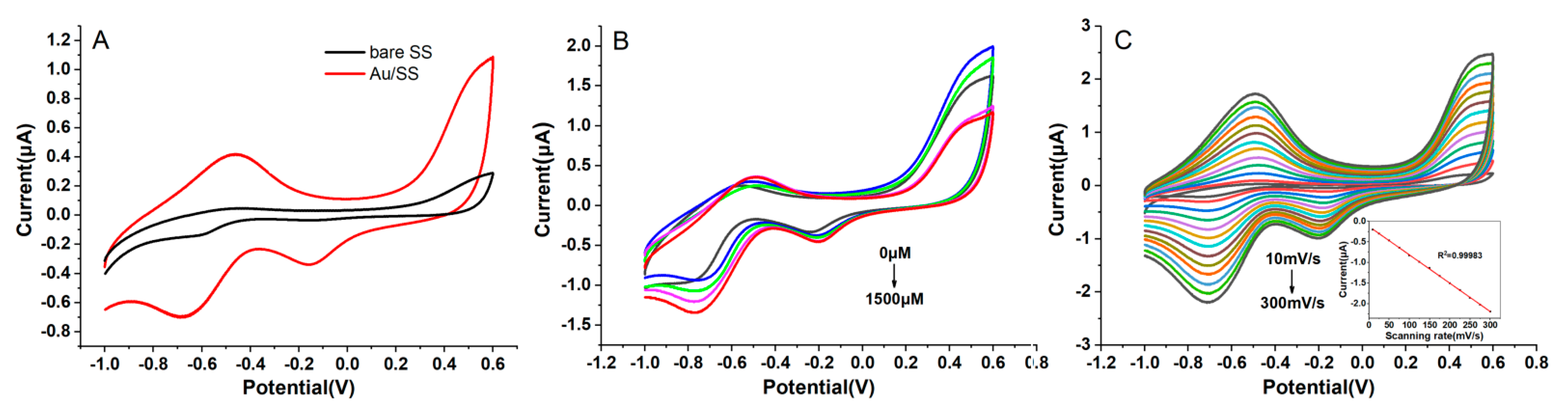
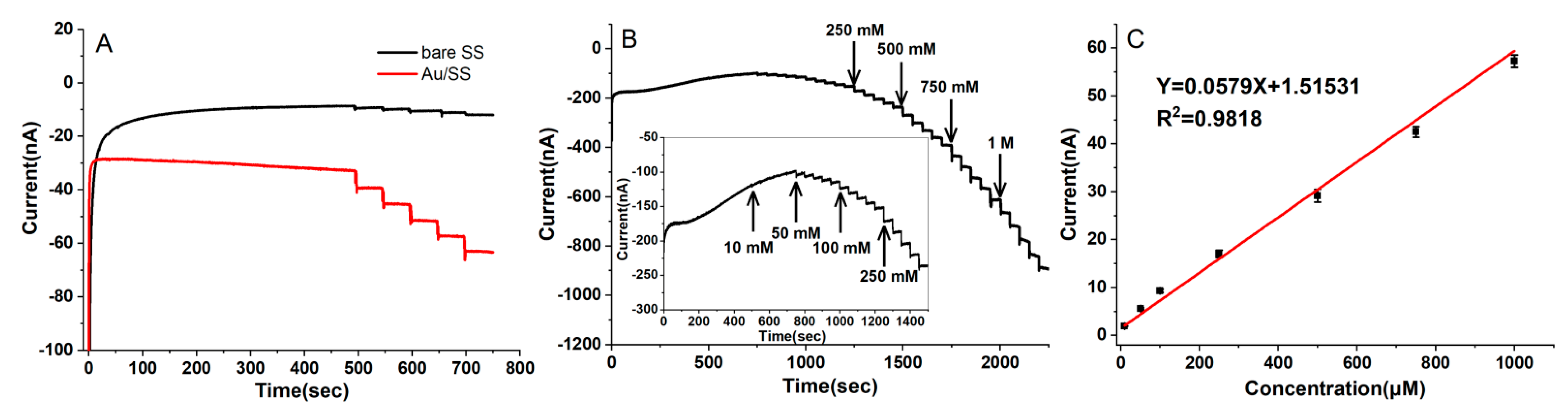
3.2. The Electrochemical Performance of the Au/SSWire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor
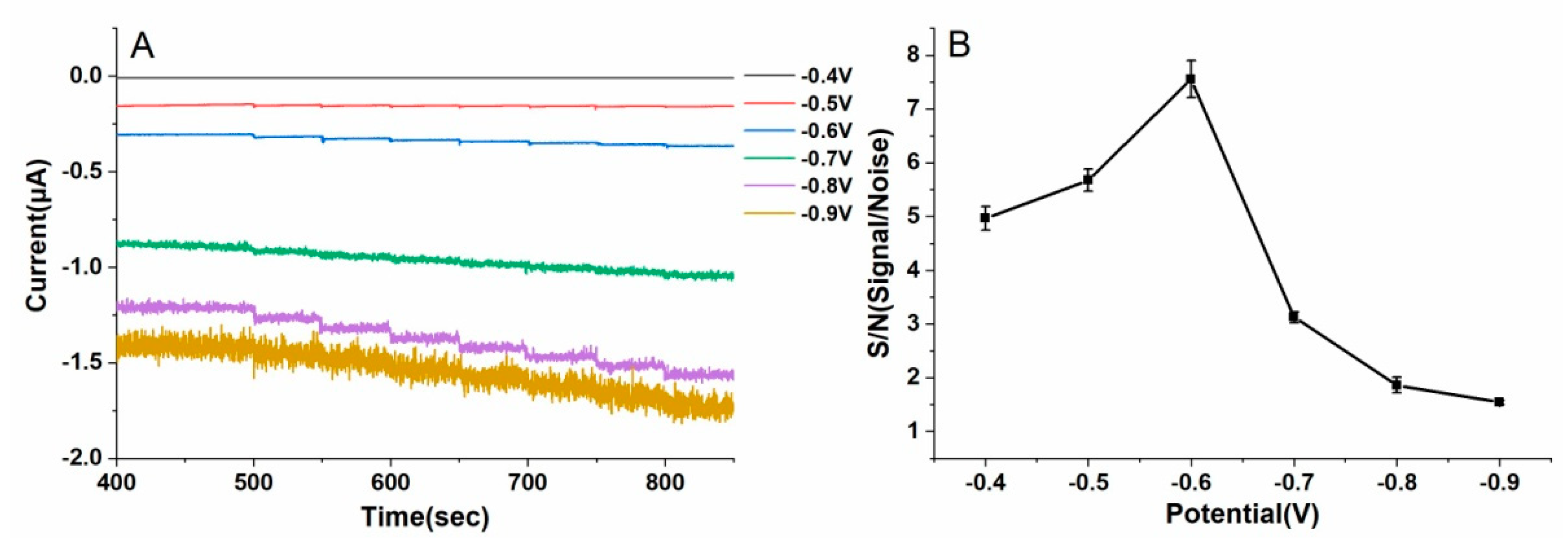
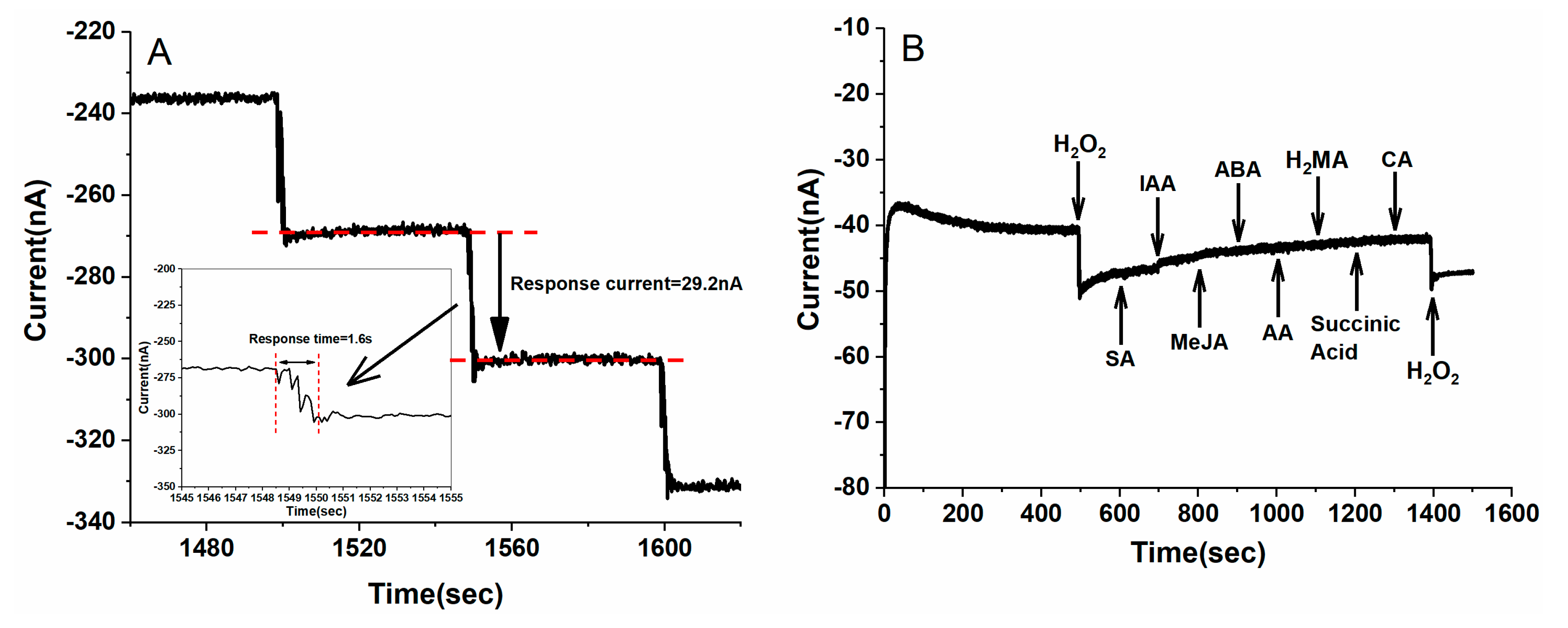
3.3. Amperometric Detection of H2O2 with the Au/SS Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor
3.4. In Vivo and Continuous Electrochemical Monitoring of H2O2 in Vein of Tomato Leaf
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Černý, M.; Habánová, H.; Berka, M.; Luklová, M.; Brzobohatý, B. Hydrogen peroxide: Its role in plant biology and crosstalk with signalling networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietz, K.J.; Turkan, I.; Krieger-Liszkay, A. Redox- and reactive oxygen species-dependent signaling into and out of the photosynthesizing chloroplast. Plant Physiol 2016, 171, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Van-Aken, O.; Schwarzländer, M.; Belt, K.; Millar, A.H. The roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cellular signaling and stress response in plants. Plant Physiol 2016, 171, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khorobrykh, S.A.; Karonen, M.; Tyystjärvi, E. Experimental evidence suggesting that H2O2 is produced within the thylakoid membrane in a reaction between plastoquinol and singlet oxygen. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wrzaczek, M.; Brosché, M.; Kangasjärvi, J. Ros signalling loops -production, perception, regulation. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2013, 16, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, J.M. Hydrogen peroxide concentrations in leaves under natural conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaparzadeh, N.; D’Amico, M.L.; Khavari-Nejad, R.A.; Izzo, R.; Navari-Izzo, F. Antioxidative responses of calendula officinalis under salinity conditions. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2004, 42, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Silva, H.; Klessig, D. Active oxygen species in the induction of plant systemic acquired resistance induced by salicylic acid. Science 1993, 262, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, R.K.; Singh, P.K.; Watanabe, M. The spatial patterns of oxidative stress indicators co-locate with early signs of natural senescence in maize leaves. Acta. Physiol Plant 2013, 35, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress ktolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010, 48, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, I.; Srikanth, S.; Chen, Z. Cross talk between H2O2 and interacting signal molecules under plant stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, Z.M.; Murata, Y.; Benning, G.; Thomine, S.; Klüsener, B.; Allen, G.J.; Grill, E.; Schroeder, J.I. Calcium channels activated by hydrogen peroxide mediate abscisic acid signalling in guard cells. Nature 2000, 406, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Klessig, D.F. Identification of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein that may function in signal transduction in the plant disease-resistance response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8179–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levine, A.; Tenhaken, R.; Dixon, R. H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersenesitive disease resistance response. Cell 1994, 79, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnemma, E.M. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen peroxide by a hydroquinone-aniline system catalyzed by molybdate. Bull. Korean. Chem. Soc. 2004, 25, 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, N.V.; Marchington, D.; McGowan, H.C.E. H2O2 determination by the I3- method and by KMnO4 titration. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, E.; Keisari, Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J. Immunol. Methods 1980, 38, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, T.; Kamidate, T.; Watanabe, H. Determination of hydrogen peroxide with fluorescein chemiluminescence catalyzed by horseradish peroxidase. Anal. Sci. 1990, 6, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Kumazawa, S.; Nakayama, T. Deter- mination of hydrogen peroxide by high-performance liquid chromatography with a cation-exchange resin gel column and electrochemical detector. Anal. Sci. 1999, 15, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.; Qin, J.; Feng, Y.; Wei, J. Synthesis of mesoporous cuo hollow sphere nanozyme for paper-based hydrogen peroxide sensor. Biosensors 2021, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, E.; Hatamie, A.; Berahman, M.; Simchi, M.; Angizi, S.; Rahmati, R.; Kennedy, J.; Simchi, A. Synthesis, first-principle simulation, and application of three-dimensional ceria nanoparticles/graphene nanocomposite for non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, H3167–H3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Kruse, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. Solid state sensors for hydrogen peroxide detection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Deswal, R.; Narwal, V. Quantitative analysis of hydrogen peroxide with special emphasis on biosensors. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Xie, Y.; Yan, Y.F.; Yang, H.; Gu, H.Y.; Bao, N. Paper-based analytical devices for direct electrochemical detection of free IAA and SA in plant samples with the weight of several milligrams. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Feng, Q.M.; Yan, Y.; Pan, Z.Q.; Li, X.H.; Song, F.M.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.J.; Bao, N.; Gu, H.Y. Paper-based electroanalytical devices for in situ determination of salicylic acid in living tomato leaves. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacci, C.; Abedi, T.; Lee, J.W.; Gabrielsson, E.O.; Berggren, M.; Simon, D.; Niittylä, T.; Stavrinidou, E. Diurnal in vivo xylem sap glucose and sucrose monitoring using implantable organic electrochemical transistor sensors. Iscience 2020, 24, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Wei, F.; Dong, X.Y.; Cheng, J.K.; Huang, W.H. Real-time monitoring of oxidative burst from single plant protoplasts using microelectrochemical sensors modified by platinum nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8453–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.S.; Prieto, K.R.; Santos, C.S.; Valerio, H.P.; Garcia-Ochoa, E.Y.; Huerta-Robles, A.; Beltran-Garcia, M.J.; Di Mascio, P.; Bertotti, M. In-vivo electrochemical monitoring of H2O2 production induced by root-inoculated endophytic bacteria in Agave tequilana leaves. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.Q.; Yuan, X.J.; Huang, X.R.; Wen, W.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chen, W. In vivo monitoring of oxidative burst on aloe under salinity stress using hemoglobin and single-walled carbon nanotubes modified carbon fiber ultra microelectrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Pan, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, D.Y.; Hui, M.Q.; Zhu, S.Q.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, D.Y.; Song, F.M.; Zhang, C.K. Paper-Based Analytical Devices for the Rapid and Direct Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide in Tomato Leaves Inoculated with Botrytis cinerea. Sensors 2020, 20, 5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Havakeshian, E.; Ensafi, A.A. Decoration of nanoporous stainless steel with nanostructured gold via galvanicreplacement reaction and its application for electrochemical determination of dopamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 213, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, L.; Havakeshian, E.; Ensafi, A.A. An electrochemical biosensor based on nanoporous stainless steelmodified by gold and palladium nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of levodopa and uric acid. Talanta 2016, 158, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitte, S.A.; Li, S.; Nsabimana, A.; Gao, W.Y.; Lai, J.P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xu, G.B. Stainless steel electrode for simultaneous stripping analysis of Cd(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Hg(II). Talanta 2019, 191, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.H.; Shek, C.H.; Lai, J. Recent developments in stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 65, 39–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, T.; McKnight, M.; Dickey, M.D.; Bozkurt, A. In vitroelectrochemical assessment of electrodes for neurostimulation in roach biobots. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Gao, F. A mediator-free amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on HRP immobilized on a nano-Au/poly 2,6-pyridinediamine-coated electrode. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 30, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Mercado, E.; Martinez-Diaz, Y.; Roman-Tehandon, N.; Garcia-Pineda, E. Analysis of reactive oxygen species production and antioxidative responses in unripe avocado (Persea americana Mill var Hass) fruits in response to wounding. Protoplasma 2009, 235, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Di, J.; Tu, Y. Electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles on indium/tin oxide electrode for fabrication of a disposable hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Talanta 2009, 77, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Miller, G.; Morales, J.; Shulaev, V.; Torres, M.A.; Mittler, R. Respiratory burst oxidases: The engines of ROS signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, A.; Mittler, R.; Suzuki, N. ROS as key players in plant stress signaling. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devireddy, A.R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Mittler, R. Integration of reactive oxygen species and hormone signaling during abiotic stress. Plant J. 2021, 105, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Tian, L.M.; Huang, L.; Liu, S.X.; Li, D.Y.; Song, F.M. Tomato SlRbohB, a member of the NADPH oxidase family, is required for disease resistance against Botrytis cinerea and tolerance to drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, D.; Li, D.; Xu, S.; Tang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, D.; Song, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Sun, L. Disposable Stainless-Steel Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor for In Vivo Continuous Monitoring of Hydrogen Peroxide in Vein of Tomato Leaf. Biosensors 2022, 12, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010035
Huo D, Li D, Xu S, Tang Y, Xie X, Li D, Song F, Zhang Y, Li A, Sun L. Disposable Stainless-Steel Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor for In Vivo Continuous Monitoring of Hydrogen Peroxide in Vein of Tomato Leaf. Biosensors. 2022; 12(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Doudou, Daodong Li, Songzhi Xu, Yujie Tang, Xueqian Xie, Dayong Li, Fengming Song, Yali Zhang, Aixue Li, and Lijun Sun. 2022. "Disposable Stainless-Steel Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor for In Vivo Continuous Monitoring of Hydrogen Peroxide in Vein of Tomato Leaf" Biosensors 12, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010035
APA StyleHuo, D., Li, D., Xu, S., Tang, Y., Xie, X., Li, D., Song, F., Zhang, Y., Li, A., & Sun, L. (2022). Disposable Stainless-Steel Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor for In Vivo Continuous Monitoring of Hydrogen Peroxide in Vein of Tomato Leaf. Biosensors, 12(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010035





