Multifunctional Smart ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescent Aptasensor for the Detection of Ochratoxin A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis of ZnSe Nanostructures
2.1.1. Fabrication of ZnSe Nanorods
2.1.2. Fabrication of ZnSe µ-Spheres
2.1.3. Fabrication of ZnSe Nanoclusters
2.2. ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescence Quenching
2.3. ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescent Aptasensor for OTA Detection
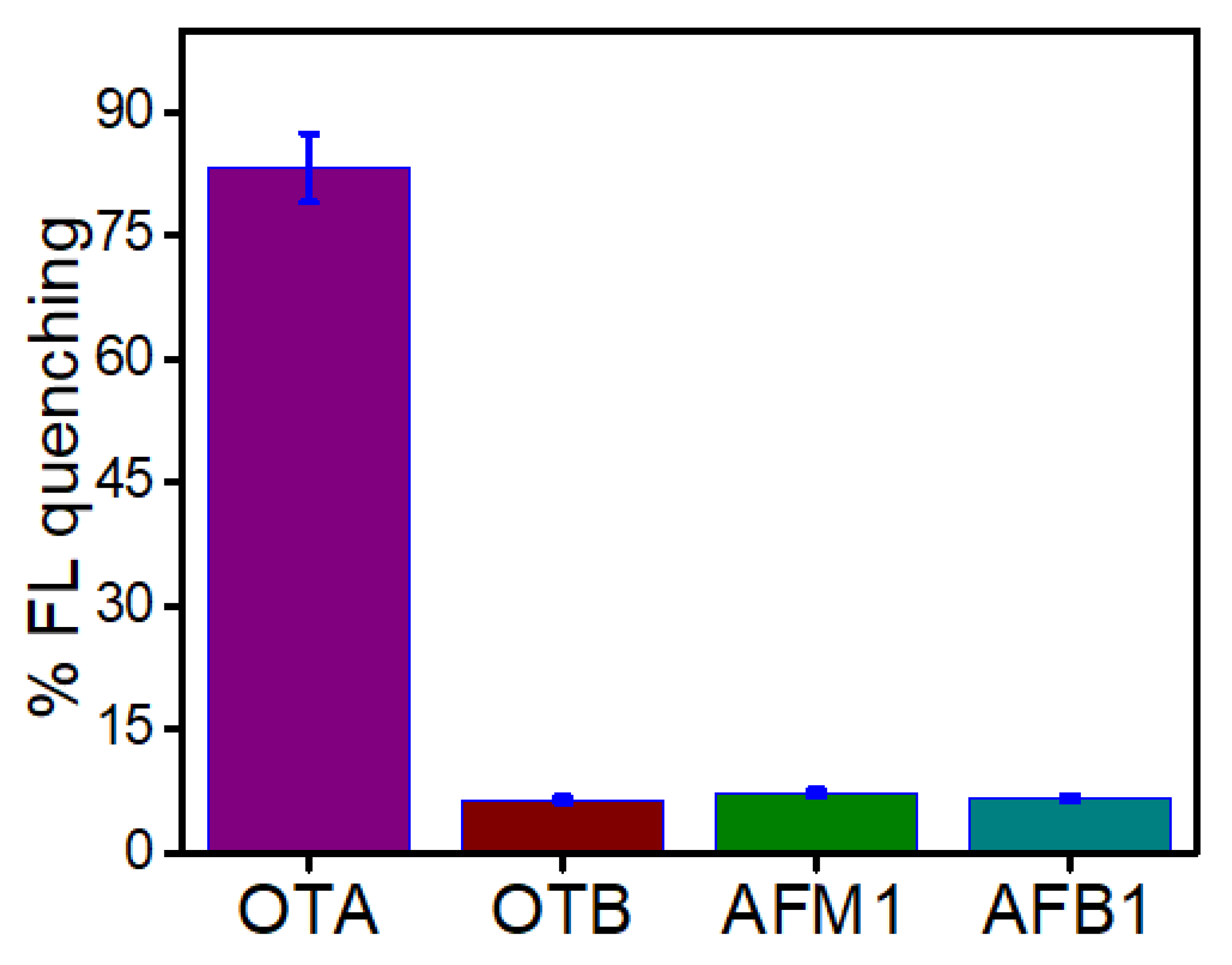
2.4. Interference and Real Sample Studies
3. Results and Discussion
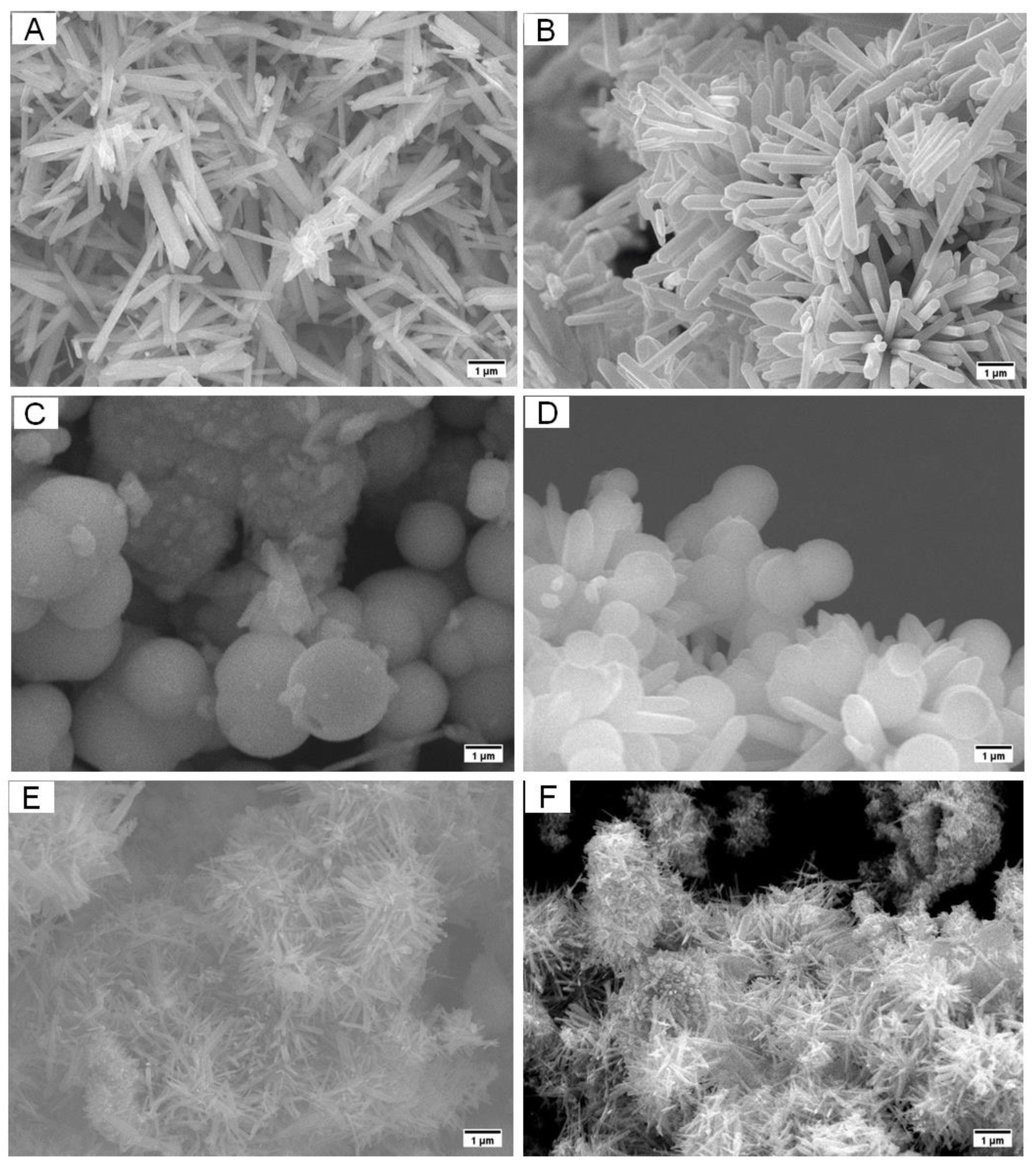
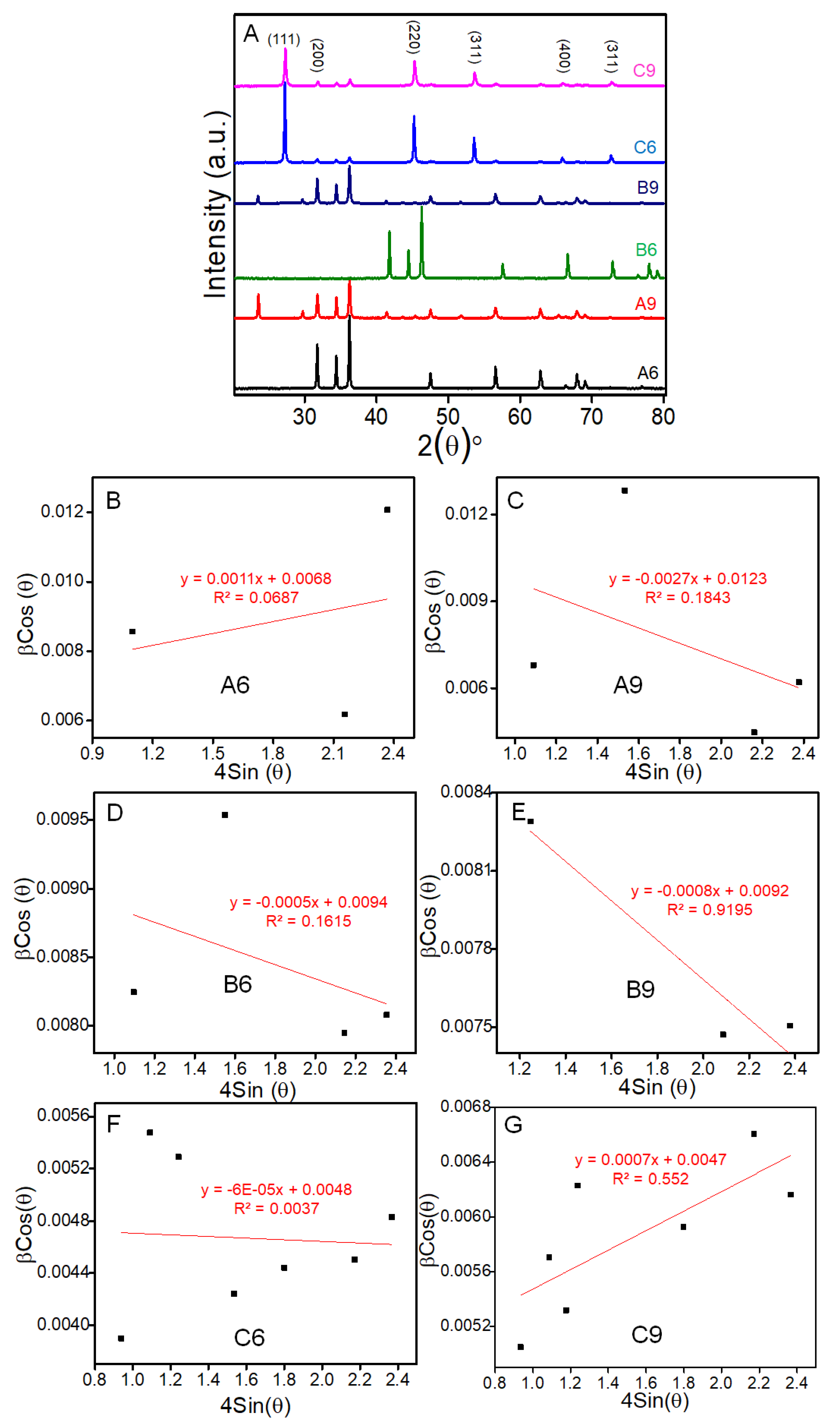
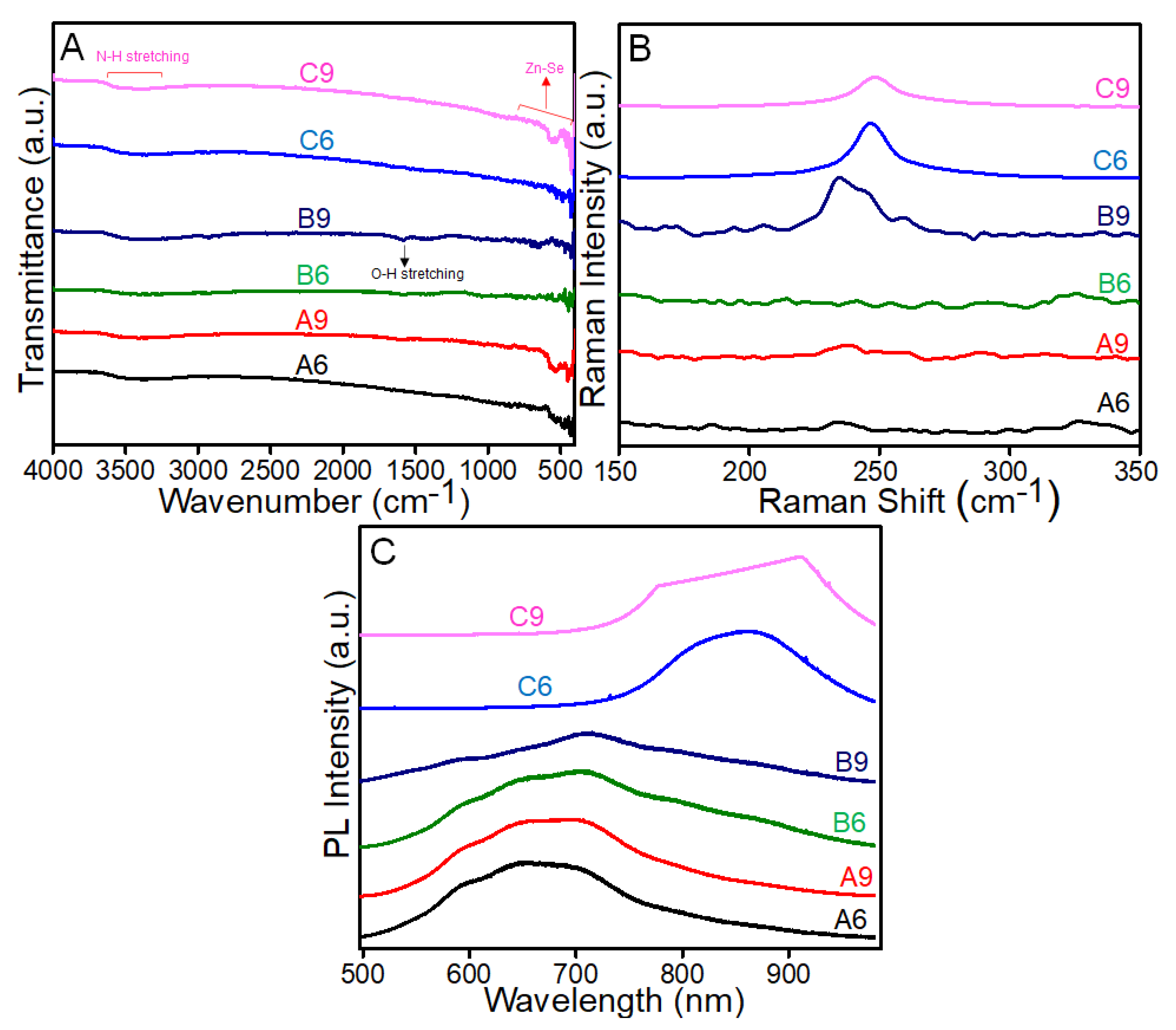
3.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization of ZnSe Nanostructures
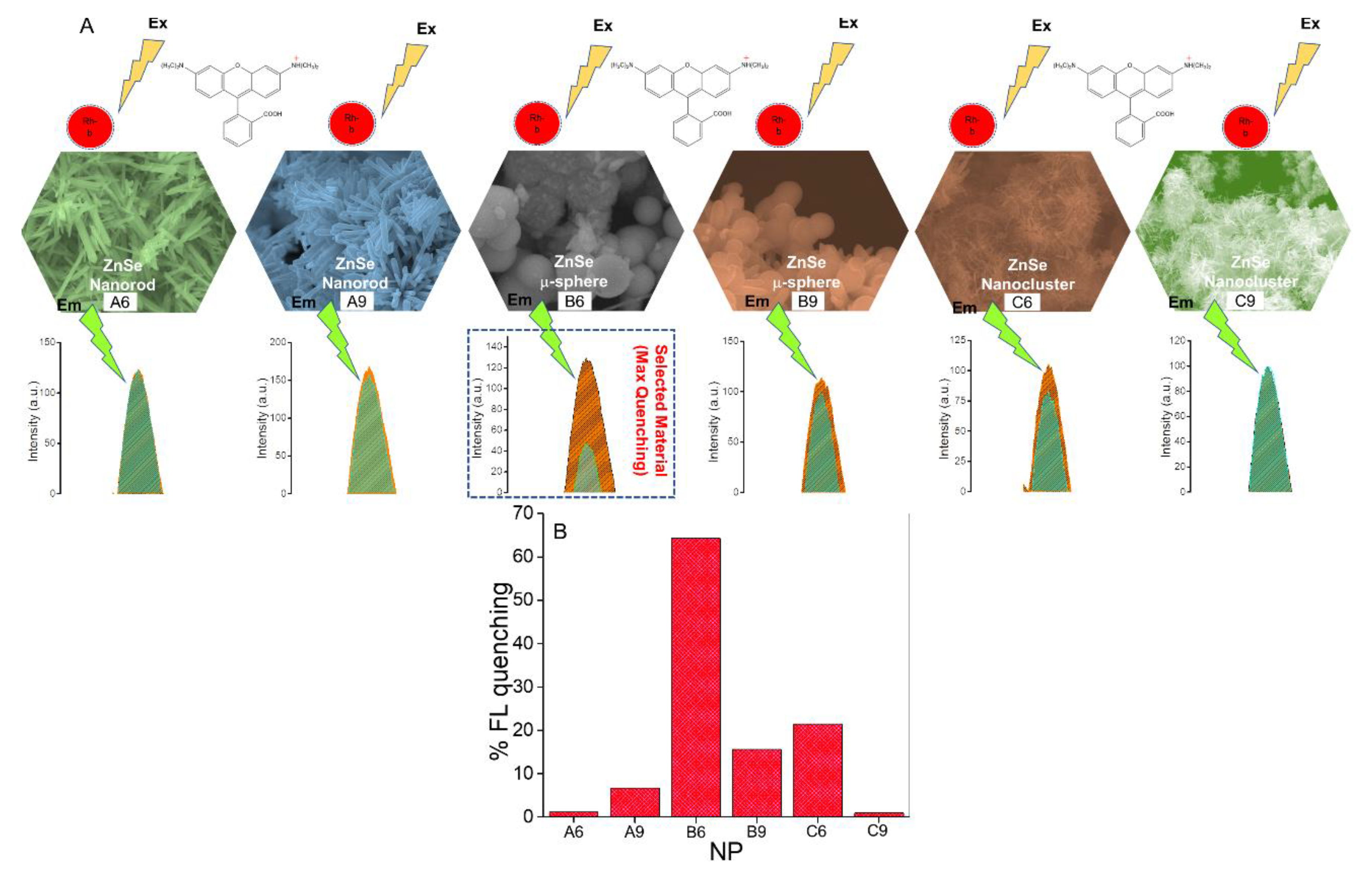
3.2. Morphological-Based Fluorescence Quenching of the ZnSe Nanostructures
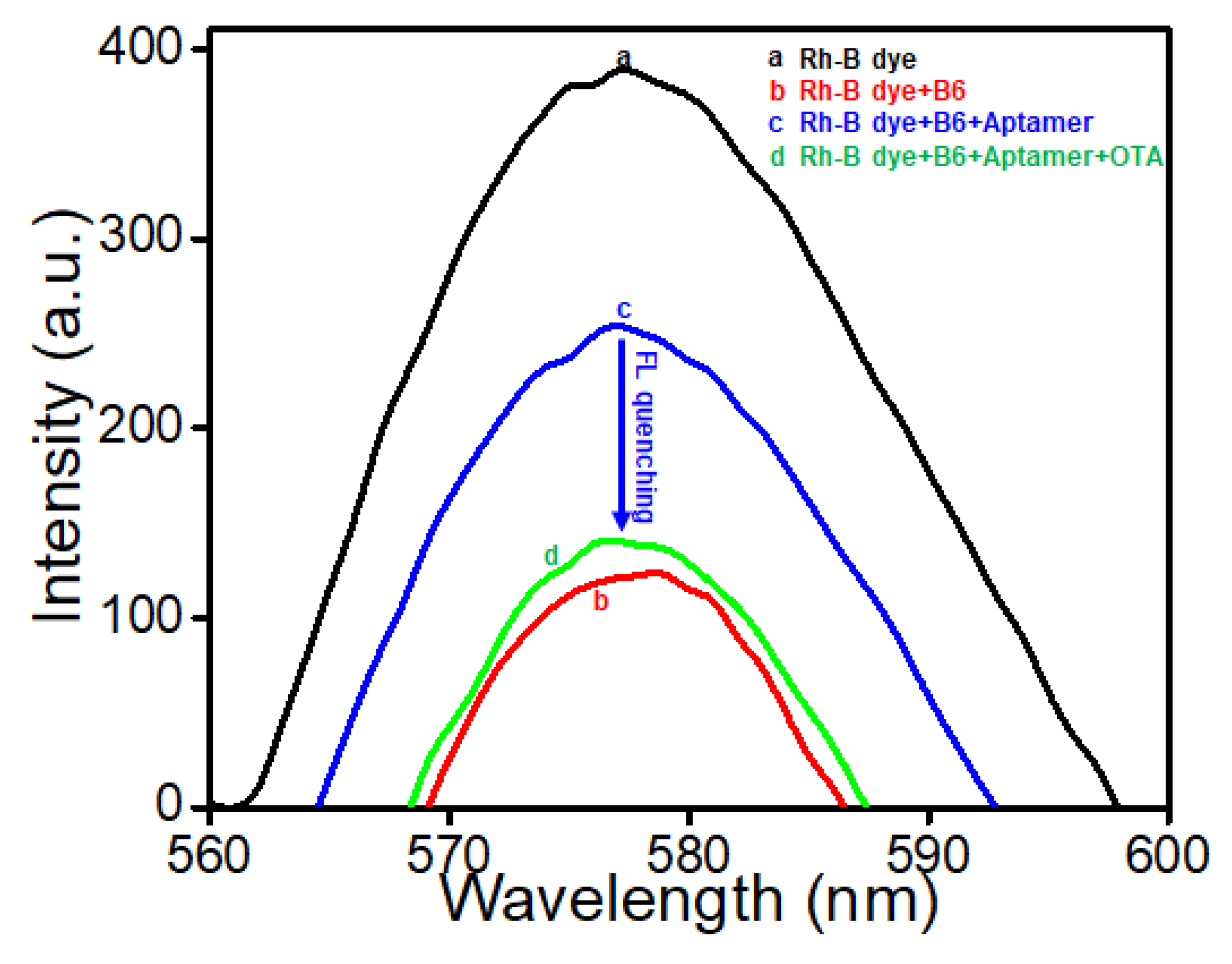
3.3. Fabrication of the ZnSe-Based Aptasensor
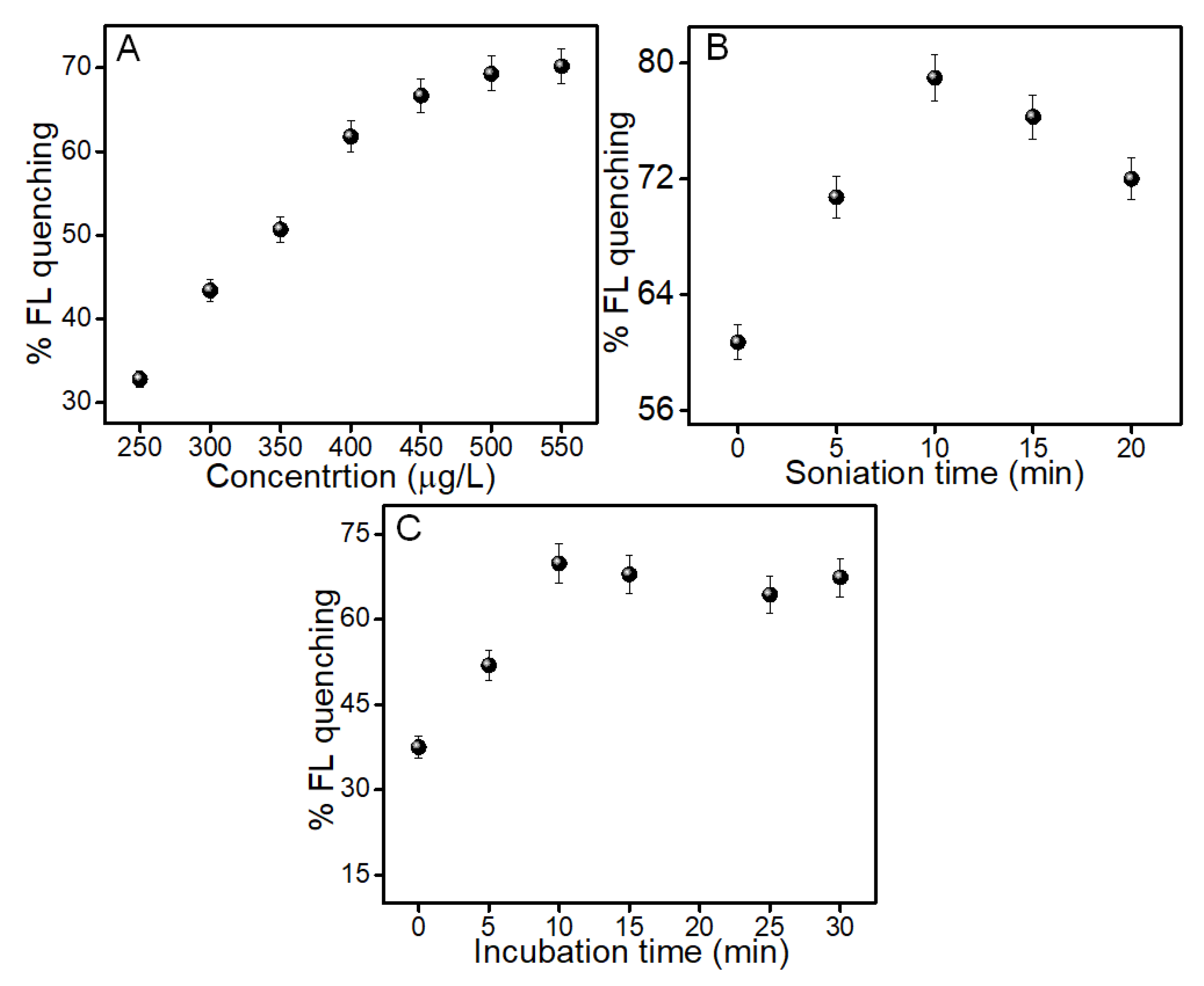
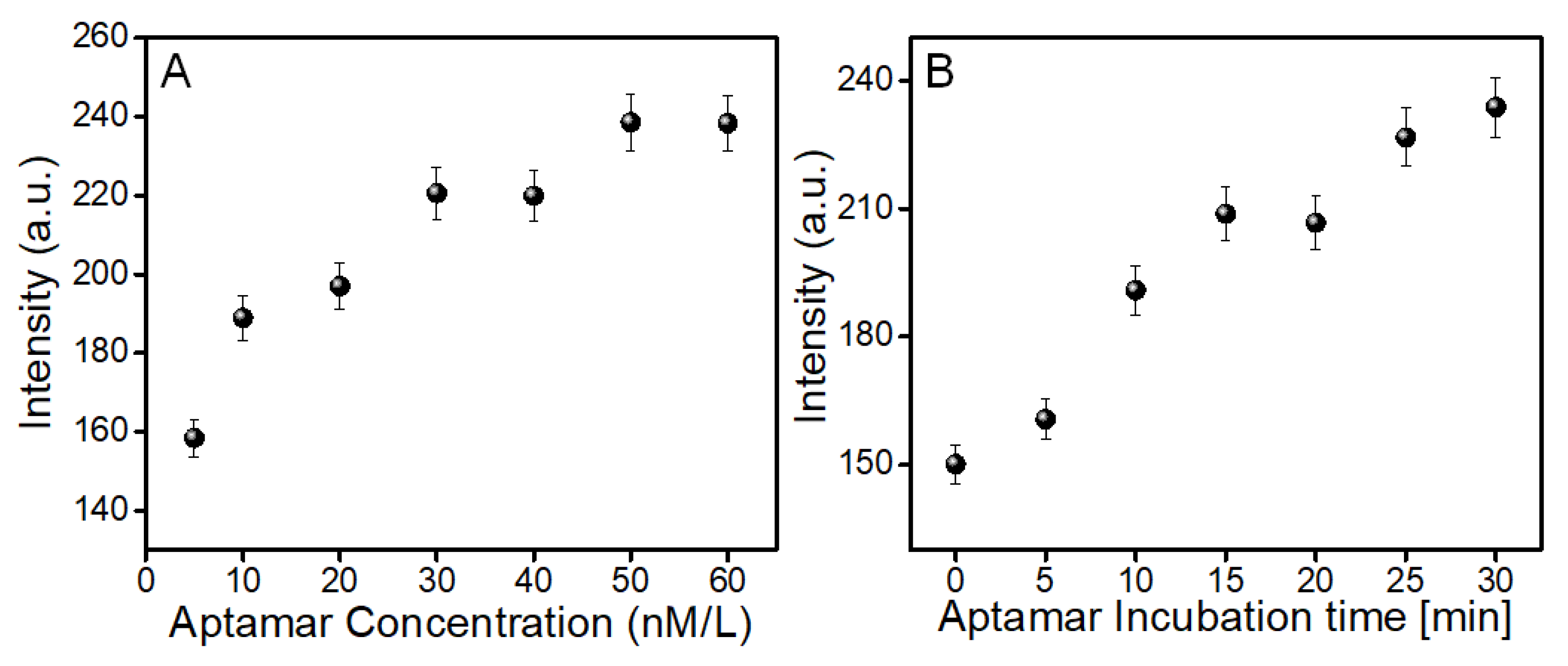
3.4. Optimization
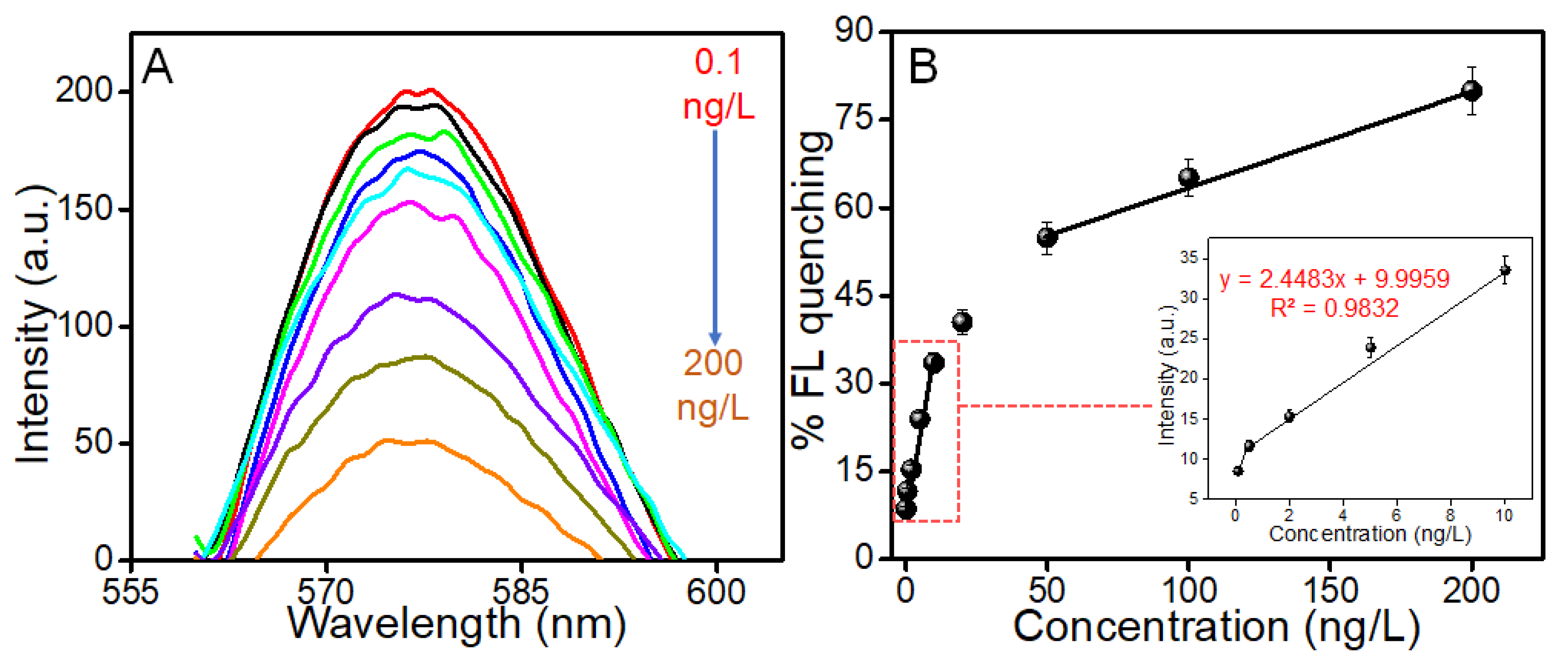
3.5. Analytical Performance of the Developed Aptasensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bankole, O.E.; Verma, D.K.; González, M.L.C.; Ceferino, J.G.; Sandoval-Cortés, J.; Aguilar, C.N. Recent trends and technical advancements in biosensors and their emerging applications in food and bioscience. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, J.H.; Male, K.B.; Glennon, J.D. Biosensor technology: Technology push versus market pull. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J. Semiconducting polymer dots as fluorescent probes for in vitro biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6248–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W. Bright, Compact and Biocompatible Quantum Dot/Rod-Bioconjugates for Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Based Ratiometric Biosensing and Cellular Imaging. University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, W. Recent advances in design of fluorescence-based assays for high-throughput screening. Anal. Chem. 2018, 91, 482–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Han, D. Characterization and photocatalytic activity of ZnSe nanoparticles synthesized by a facile solvothermal method, and the effects of different solvents on these properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudiksen, M.S.; Wang, J.; Lieber, C.M. Synthetic Control of the Diameter and Length of Single Crystal Semiconductor Nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 4062–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Yuan, X. Preparation and photoluminescent properties of doped nanoparticles of ZnS by solid-state reaction. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.S.; Kim, M.-S.; Byun, E.K.; Lee, Y.L. Facile synthesis and characterization of zinc selenide nanoparticles in aqueous solution at room temperature. J. Cryst. Growth 2020, 535, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yin, W.; Fernandes, C.; Ruda, H.E. Fabrication of one-dimension ZnSe and ZnO nanostructures via anodic alumina template assisted vapor–liquid–solid growth process. Thin Solid Films 2013, 548, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Yi, G.C. ZnSe–Si Bi-coaxial Nanowire Heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhai, T.; Bando, Y.; Liao, M.; Gautam, U.K.; Koide, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Y.; Golberg, D. High-performance blue/ultraviolet-light-sensitive ZnSe-nanobelt photodetectors. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 5016–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lai, J.; Fu, X.; Sun, J.; Ying, Z.; Wu, J.; Lu, H.; Xu, N. Growth of ZnSe nano-needles by pulsed laser deposition and their application in polymer/inorganic hybrid solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2013, 529, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, Y. Temperature dependent photoluminescence of surfactant assisted electrochemically synthesized ZnSe nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Park, J.; Gou, X.; Cheng, X. Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of ZnSe nanoplates. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 3645–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Han, H. One-step synthesis of water-soluble ZnSe quantum dots via microwave irradiation. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1099–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zou, G.; Yu, W.; Qian, Y. Synthesis and characterization of ZnSe hollow nanospheres via a hydrothermal route. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, H.; Jie, W.; Yang, L. The growth and characterization of ZnSe nanoneedles by a simple chemical vapor deposition method. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 289, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.-H.; Fu, Y.-S.; Shih, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-C.; Guo, T.-F.; Lin, W.-T. Effects of hydrazine on the solvothermal synthesis of Cu2ZnSnSe4 and Cu2CdSnSe4 nanocrystals for particle-based deposition of films. Thin Solid Films 2013, 544, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Jamwal, D.; Rana, D.; Katoch, A. Microwave synthesized nanocomposites for enhancing oral bioavailability of drugs. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 619–632. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Kachhap, S.; Singh, P.; Singh, S. Lanthanide-based hybrid nanostructures: Classification, synthesis, optical properties, and multifunctional applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 472, 214795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Pham, D.K.; Tran, N.Q.; Dang, L.H.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen, T.H.; Luong, T.B. Comparative Studies of Blue-Emitting Zinc Selenide Nanocrystals Doped with Ag, Cu, and Mg towards Medical Applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Ryskevic, N.; Oztekin, Y.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Jursenas, S.; Baniukevic, J.; Kirlyte, J.; Bubniene, U.; Ramanaviciene, A. Immunosensor based on fluorescence quenching matrix of the conducting polymer polypyrrole. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 3105–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Kurilcik, N.; Jursenas, S.; Finkelsteinas, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Conducting polymer based fluorescence quenching as a new approach to increase the selectivity of immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Iyer, P.K.; Giri, P.K. Role of molecular interactions and structural defects in the efficient fluorescence quenching by carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2012, 50, 4495–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kataoka, M.; Shimamoto, D.; Muramatsu, H.; Jung, Y.C.; Tojo, T.; Hayashi, T.; Kim, Y.A.; Endo, M.; Terrones, M. Defect-Enhanced Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in DNA Solutions. ChemPhysChem 2009, 10, 2414–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, R.; Toh, H.T.; Liu, X.; Lin, G.; Yin, F.; Yoon, H.S.; Yong, K.-T. Assembling Mn: ZnSe quantum dots-siRNA nanoplexes for gene silencing in tumor cells. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Khan, A.; Ali, N.; Malik, S.; Khan, H.; Ali, N.; Iqbal, H.M.; Bilal, M. Designing, characterization, and evaluation of chitosan-zinc selenide nanoparticles for visible-light-induced degradation of tartrazine and sunset yellow dyes. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaor, D.; Michelazzi, M.; Leonelli, C.; Sorrell, C.C. The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei, S.Z.; Somaghian, S.A.; Lashgarian, H.E.; Karkhane, M.; Cheraghipour, K.; Marzban, A. Phyco-fabrication of bimetallic nanoparticles (zinc–selenium) using aqueous extract of Gracilaria corticata and its biological activity potentials. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 5580–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. Fluorescent Sensors for Biosensing Applications: Immunosensors for Mycotoxins and Aptasensors for Interferon-Gamma. 2019. Available online: https://www.researchonline.mq.edu.au/vital/access/manager/Repository/mq:71337 (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Yang, C.; Abbas, F.; Rhouati, A.; Sun, Y.; Chu, X.; Cui, S.; Sun, B.; Xue, C. Design of a Quencher-Free Fluorescent Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Detection in Red Wine Based on the Guanine-Quenching Ability. Biosensors 2022, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, S.; Zhu, T. Application of activated carbon derived from scrap tires for adsorption of Rhodamine B. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhu, J.; Cui, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q. Removal of Rhodamine B, a cationic dye from aqueous solution using poly (cyclotriphosphazene-co-4, 4′-sulfonyldiphenol) nanotubes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2015, 52, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Nawaz, M.A.H.; Akhtar, N.; Raza, R.; Yu, C.; Andreescu, S.; Hayat, A. Morphology controlled NiO nanostructures as fluorescent quenchers for highly sensitive aptamer-based FRET detection of ochratoxin A. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 566, 150647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, E.; Carvajal, N.; Morel, M.; Marín, C. Fabrication of ZnSe nanoparticles: Structural, optical and Raman Studies. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; You, J.; Zhan, F.; Kong, M.; Fang, C. Controllable morphology evolution and photoluminescence of ZnSe hollow microspheres. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11301–11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, L. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of hollow ZnSe microspheres via Ostwald ripening. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 473, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, S.; Chen, G.; Lu, J. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor between nanoceria and graphene quantum dots for the determination of ochratoxin A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Jin, Y.; Kang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, C.; Guo, Z. PVP-coated gold nanoparticles for the selective determination of ochratoxin A via quenching fluorescence of the free aptamer. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Hayat, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Catanante, G.; Bhand, S.; Marty, J.L. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2) quenching based aptasensing platform: Application to ochratoxin A detection. Toxins 2015, 7, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, X.; Hu, W. A fluorescence aptasensor based on semiconductor quantum dots and MoS2 nanosheets for ochratoxin A detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghdisi, S.M.; Danesh, N.M.; Beheshti, H.R.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K. A novel fluorescent aptasensor based on gold and silica nanoparticles for the ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3439–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Xiong, Y.; Pei, K.; Nie, L.; Xiong, Y. Silver nanoparticle-based fluorescence-quenching lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of ochratoxin A in grape juice and wine. Toxins 2017, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Du, L.; Wang, S. Aptamer-based fluorescent detection of ochratoxin A by quenching of gold nanoparticles. Rsc. Adv. 2017, 7, 16290–16294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, E.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Wei, W.; Liu, S. A simple and sensitive electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for determination of ochratoxin A based on a nicking endonuclease-powered DNA walking machine. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sr. No. | Zeta (mV) ZnSe NP | Zeta (mV) ZnSe NP+ Rhd-B |
|---|---|---|
| B6 | −437 | −229 |
| B9 | −95.2 | −319 |
| C6 | −320 | −284 |
| C9 | −409 | −333 |
| A6 | −332 | −366 |
| A9 | −379 | −297 |
| Sr. No. | OTA Added (ng/L) | OTA Found (ng/L) | R.S.D % | R.E % | R % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 5 | 5.04 | 0.5634 | 0.8 | 100.8 |
| 2. | 50 | 50.16 | 0.2259 | 0.32 | 100.32 |
| 3. | 100 | 100.31 | 0.2188 | 0.31 | 100.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, M.A.H.; Fazal, M.W.; Akhtar, N.; Nawaz, M.H.; Hayat, A.; Yu, C. Multifunctional Smart ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescent Aptasensor for the Detection of Ochratoxin A. Biosensors 2022, 12, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100844
Nawaz MAH, Fazal MW, Akhtar N, Nawaz MH, Hayat A, Yu C. Multifunctional Smart ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescent Aptasensor for the Detection of Ochratoxin A. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100844
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Muhammad Azhar Hayat, Muhammad Waseem Fazal, Naeem Akhtar, Mian Hasnain Nawaz, Akhtar Hayat, and Cong Yu. 2022. "Multifunctional Smart ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescent Aptasensor for the Detection of Ochratoxin A" Biosensors 12, no. 10: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100844
APA StyleNawaz, M. A. H., Fazal, M. W., Akhtar, N., Nawaz, M. H., Hayat, A., & Yu, C. (2022). Multifunctional Smart ZnSe-Nanostructure-Based Fluorescent Aptasensor for the Detection of Ochratoxin A. Biosensors, 12(10), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100844






