Microfluidics-Based Biosensing Platforms: Emerging Frontiers in Point-of-Care Testing SARS-CoV-2 and Seroprevalence
Abstract
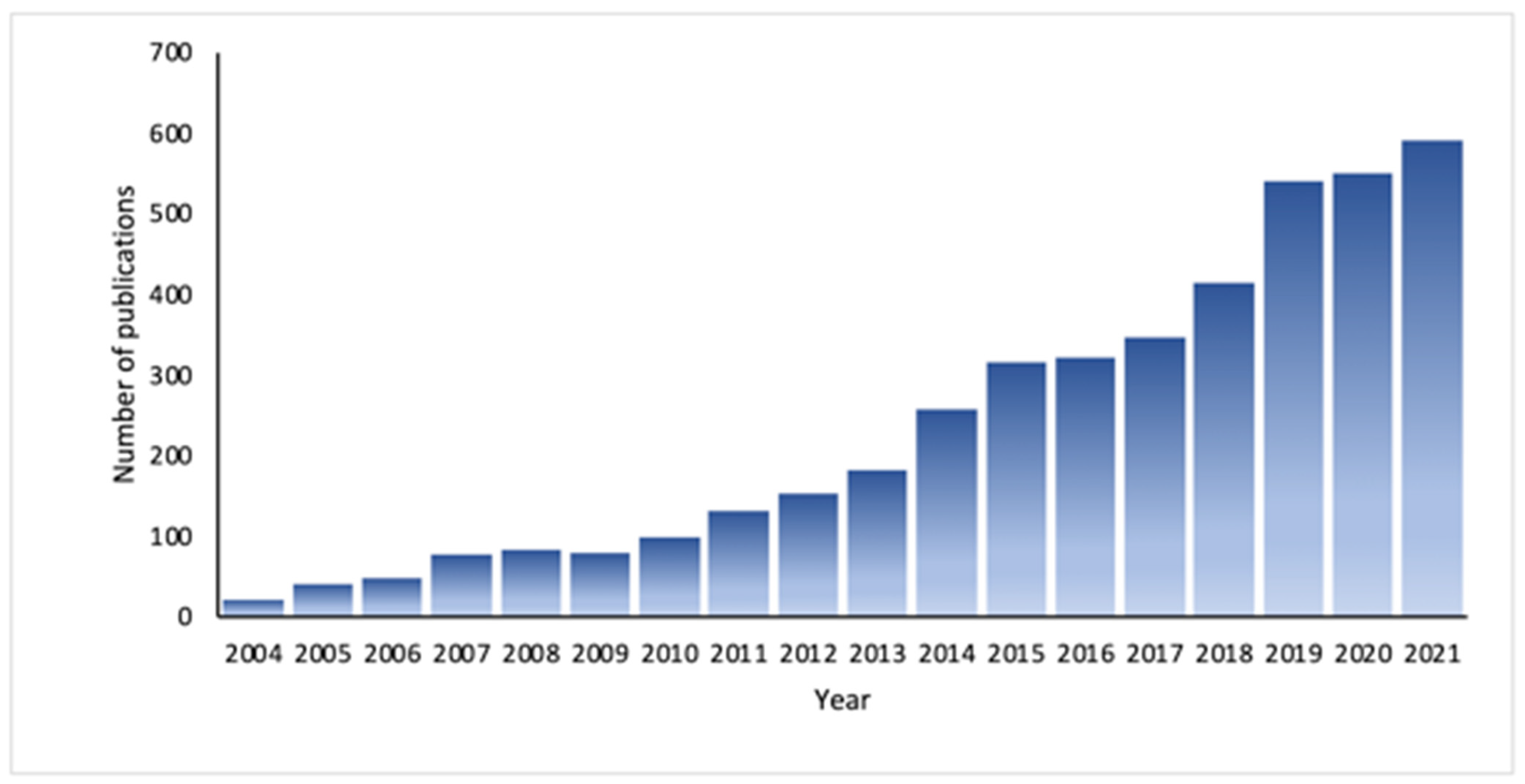
:1. Introduction
2. Microfluidics Applied to COVID-19
3. Nucleic Acid Detection
3.1. Based on PCR
3.2. Based on Isothermal Amplification
3.3. Based on CRISPR
3.4. Other Microfluidic Developments
4. Antigen Detection
| Type Immunoassay | Specimen | LOD | Target Protein | Detection Method | Processing Time (Minutes) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandwich Immunoassay | Serum | 33.28 pg/mL | N | Fluorescence | <120 | [61] |
| Direct Immunoassay | Saliva | NR | VP | Fluorescence | <30 | [56] |
| Sandwich Immunoassay | Serum, Saliva, Nasopharyngeal and urine | 8 µg/mL | N | Colorimetric | >30 | [64] |
| Direct and sandwich Immunoassay | Saliva | NR | N | Absorbance | 15 | [62] |
| Direct Immunoassay | Blood | 1 fg/mL | S | Voltage | 0.05 | [57] |
| Direct Immunoassay | Saliva | 4000 viral particles/mL | S | Electrochemical | 5 | [58] |
| Direct Immunoassay | Food | 2.29 × 10−6 ng/mL | S | Voltage | 0.33 | [59] |
| Direct immunoassay | Saliva | 90 fM | S | Electrochemical | 0.5 | [65] |
| Sandwich immunoassay | Serum | 230 pg/mL | N | Electrochemical | <60 | [60] |
| Sandwich immunoassay | Nasopharyngeal and serum | NR | VP | Fluorescence | 15 | [67] |
| Sandwich immunoassay | Nasopharyngeal | <100 copies/mL | N | Colorimetric | >30 | [53] |
| Sandwich immunoassay | Nasopharyngeal | 30 ng/mL | N | Fluorescence | <120 | [68] |
| Direct immunoassay | Nasopharyngeal | 2.42 × 102 copies/mL | S | Voltage | >1 | [66] |
| Direct immunoassay | Serum | 1 pg/mL | S | Voltage | 15 | [70] |
| Direct immunoassay | Nasopharyngeal | 15 fM | N | Electrochemical | >30 | [63] |
5. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection
| Type Immunoassay | Specimen | LOD | Target Antibodies | Detection Method | Processing Time (Minutes) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect immunoassay | Serum | NR | Anti-S | Colorimetric | <150 | [80] |
| Sandwich immunoassay | Blood | NR | Anti-S | Colorimetric | <5 | [81] |
| Indirect immunoassay | Serum | 0.06–1 ng/mL | Anti-N and S | Chemiluminescent | 15 | [88] |
| Indirect immunoassay | Serum, nasopharyngeal | NR | Anti-RBD | Fluorescence | 30 | [86] |
| Indirect immunoassay | Serum | 1.6 ng/mL | Anti-N, S and RBD | Fluorescence | <90 | [87] |
| Sandwich immunoassay | Blood | 0.12 ng/mL | Anti-N, S and RBD | Fluorescence | 60 | [82] |
| Direct immunoassay | Serum | 10 ng/mL | Anti-RBD | Electrochemical | 30 | [84] |
| Direct and indirect immunoassay | Blood | 2–3 nM | Anti-N and S | Absorbance | 30 | [89] |
| Indirect immunoassay | Blood | 0.08 ng/mL | Anti-S | Absorbance | 30 | [79] |
| Indirect immunoassay | Serum | 0.82–0.45 ng/mL | Anti-S | Absorbance | 7 | [90] |
| Indirect immunoassay | Serum | NR | Anti-S and RBD | Absorbance | NR | [83] |
6. Commercially Available Microfluidic Tests for SARS-CoV-2
7. Limitations and Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard|WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ho, N.R.Y.; Sundah, N.R.; Natalia, A.; Liu, Y.; Miow, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Tambyah, P.A.; et al. Accessible detection of SARS-CoV-2 through molecular nanostructures and automated microfluidics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113629–113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mondal, S.; Pal, S.; Roy, S.; Vidyadharan, A.; Dadwal, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mishra, D.K.; Chandy, M. COVID diagnostics by molecular methods: A systematic review of nucleic acid based testing systems. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 39, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugama, B.; Kadhiresan, P.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Malekjahani, A.; Osborne, M.; Li, V.Y.C.; Chen, H.; Mubareka, S.; Gubbay, J.B.; Chan, W.C.W. Diagnosing COVID-19: The disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esbin, M.N.; Whitney, O.N.; Chong, S.; Maurer, A.; Darzacq, X.; Tjian, R. Overcoming the bottleneck to widespread testing: A rapid review of nucleic acid testing approaches for COVID-19 detection. RNA 2020, 26, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, L.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Miao, G.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Xia, N.; Yu, D.; Qiu, X. Rapid PCR powered by microfluidics: A quick review under the background of COVID-19 pandemic. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2021, 143, 116377–116386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, M.D.; Pamme, N. Microfluidics. Ref. Modul. Chem. Mol. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X. Sensing of inorganic ions in microfluidic devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129171–129188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Reis, N.M. Modern microfluidic approaches for determination of ions. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106845–106857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yin, Y.; Starostin, S.A.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, K.; He, C.; Hessel, V. Microfluidic fabrication of fluorescent nanomaterials: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131511–131525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.; Jänis, J.; Sánchez, S. Microfluidic fuel cells for energy generation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2754–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.M.; Tai, Q.; Tsai, D.P.; Chan, H.L.W. Optofluidic planar reactors for photocatalytic water treatment using solar energy. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 043004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigl, B.; Domingo, G.; LaBarre, P.; Gerlach, J. Towards non- and minimally instrumented, microfluidics-based diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saez, J.; Catalan-Carrio, R.; Owens, R.M.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Microfluidics and materials for smart water monitoring: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1186, 338392–338405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Salazar, J.R.; Cruz, K.R.; Vásques, E.M.M.; de Oliveira, O.N. Microfluidic point-of-care devices: New trends and future prospects for eHealth diagnostics. Sensors 2020, 20, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachdeva, S.; Davis, R.W.; Saha, A.K. Microfluidic point-of-care testing: Commercial landscape and future directions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Lien, K.Y.; Lee, G.B.; Lei, H.Y. An integrated microfluidic system using magnetic beads for virus detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 60, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.; Batule, B.S.; Kim, M.G. Lab-on-paper for all-in-one molecular diagnostics (LAMDA) of zika, dengue, and chikungunya virus from human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112400–1124228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, L.A.; Kinghorn, A.B.; Dirkzwager, R.M.; Liang, S.; Cheung, Y.W.; Lim, B.; Shiu, S.C.C.; Tang, M.S.L.; Andrew, D.; Manitta, J.; et al. A portable microfluidic Aptamer-Tethered Enzyme Capture (APTEC) biosensor for malaria diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.A.; de Oliveira, E.G.; Franco-Luiz, A.P.M.; Almeida, L.T.; Gonçalves, A.B.; Borges, I.A.; de Rocha, F.; Rocha, R.P.; Bezerra, M.F.; Miranda, P.; et al. Optimization and clinical validation of colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification, a fast, highly sensitive and specific COVID-19 molecular diagnostic tool that is robust to detect SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, K.; Ozer, E.; Shagan, M.; Lakkakula, S.; Plotkin, N.; Bhandarkar, N.S.; Kushmaro, A. Direct RT-qPCR assay for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (Alpha, B.1.1.7 and Beta, B.1.351) detection and quantification in wastewater. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111653–1116661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Salit, M. Testing at scale during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kidd, M.; Nordquist, A.R.; Smith, S.D.; Hurth, C.; Modlin, I.M.; Zenhausern, F. A Sensitive, portable microfluidic device for SARS-CoV-2 detection from self-collected saliva. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 13, 1061–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassy, J.; Lacoux, C.; Leroy, S.; Noussair, L.; Hubac, S.; Degoutte, A.; Vassaux, G.; Leclercq, V.; Rouquié, D.; Marquette, C.H.; et al. Versatile and flexible microfluidic qPCR test for high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 and cellular response detection in nasopharyngeal swab samples. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Gjorgjieva, T.; Attieh, Z.; Dieng, M.M.; Arnoux, M.; Khair, M.; Moussa, Y.; Al Jallaf, F.; Rahiman, N.; Jackson, C.A.; et al. Microfluidic nano-scale qPCR enables ultra-sensitive and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2. Process 2020, 8, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, R.; Yaseen, I.; Unrau, P.J.; Lowe, C.F.; Ritchie, G.; Romney, M.G.; Sin, D.D.; Gill, S.; Slyadnev, M. Microchip RT-PCR detection of nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Xia, Y.; Loo, J.F.C.; Li, L.; Ho, H.P.; He, J.; Gu, D. Automated multiplex nucleic acid tests for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2, influenza A and B infection with direct reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (dirRT-qPCR) assay in a centrifugal microfluidic platform. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 34088–34098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.H.; Lee, Y.; Yu, E.S.; Na, H.; Kang, M.; Huh, H.J.; Jeong, K.H. Ultrafast and real-time nanoplasmonic on-chip polymerase chain reaction for rapid and quantitative molecular diagnostics. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 10194–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chung, H.K.; Pireku, P.K.; Beitzel, B.F.; Sanborn, M.A.; Tang, C.Y.; Hammer, R.D.; Ritter, D.; Wan, X.F.; Berry, I.M.; et al. Rapid high-throughput whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 by using one-step reverse transcription-PCR amplification with an integrated microfluidic system and next-generation sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02784-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millier, M.J.; Stamp, L.K.; Hessian, P.A. Digital-PCR for gene expression: Impact from inherent tissue RNA degradation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, W.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Ao, T.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.; Kong, W.; Pan, T.; Ding, Y.; et al. A low-cost, programmable, and multi-functional droplet printing system for low copy number SARS-CoV-2 digital PCR determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130678–130689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Z.; Shi, N.; Qi, Y.; Jian, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Mao, H. Ultrafast multiplexed detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using a rapid droplet digital PCR system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113282–113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qi, T.; Jin, Q.; Jia, C.; Zhao, J.; Feng, S.; Liang, L. Wet-etched microchamber array digital PCR chip for SARS-CoV-2 virus and ultra-early stage lung cancer quantitative detection. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, K.G.; Estrela, P.F.N.; Mendes, G.D.M.; Dos Santos, C.A.; Silveira-Lacerda, E.D.P.; Duarte, G.R.M. Rapid molecular diagnostics of COVID-19 by RT-LAMP in a centrifugal polystyrene-toner based microdevice with end-point visual detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J. A fully automated centrifugal microfluidic system for sample-to-answer viral nucleic acid testing. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreejith, K.R.; Umer, M.; Dirr, L.; Bailly, B.; Guillon, P.; von Itzstein, M.; Soda, N.; Kasetsirikul, S.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Nguyen, N.T. A portable device for LAMP based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, A.; Mostafa, A.; Berger, J.; Aydin, M.Y.; Sun, F.; Stewart de Ramirez, S.A.; Valera, E.; Cunningham, B.T.; King, W.P.; Bashir, R. Rapid isothermal amplification and portable detection system for SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22727–22735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.B.; Veigas, B.; Baptista, P.V. Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids: The race for the next “Gold Standard”. Front. Sens. 2021, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.L.; Wang, J.; Maruthamuthu, M.K.; Dextre, A.; Pascual-Garrigos, A.; Mohan, S.; Putikam, S.V.S.; Osman, F.O.I.; McChesney, D.; Seville, J.; et al. A paper-based colorimetric molecular test for SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2021, 9, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Jayawardena, A.; Chan, J.; Tan, S.M.; Alan, T.; Kwan, P. An ultra-portable, self-contained point-of-care nucleic acid amplification test for diagnosis of active COVID-19 infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Abbas, N.; Shin, S. A rapid diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 using DNA hydrogel formation on microfluidic pores. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 113005–113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhu, M.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. A microfluidic-integrated lateral flow recombinase polymerase amplification (MI-IF-RPA) assay for rapid COVID-19 detection. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Shan, X.; Cao, R.; Jin, X.; Lin, X.; He, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, R.; Du, W.; Lv, W.; et al. Microfluidic chip with two-stage isothermal amplification method for highly sensitive parallel detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Measles Virus. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, A.; Huyke, D.A.; Sharma, E.; Sahoo, M.K.; Huang, C.; Banaei, N.; Pinsky, B.A.; Santiago, J.G. Electric field-driven microfluidics for rapid CRISPR-based diagnostics and its application to detection of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29518–29525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Yin, K.; Avery, L.; Ballesteros, E.; Liu, C. Instrument-free, CRISPR-based diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 using self-contained microfluidic system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113865–113872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Y.; Knott, G.J.; Smock, D.C.J.; Desmarais, J.J.; Son, S.; Bhuiya, A.; Jakhanwal, S.; Prywes, N.; Agrawal, S.; Díaz de León Derby, M.; et al. Accelerated RNA detection using tandem CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Park, N.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.D.; Park, S.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, J.H. Ultra-fast and recyclable DNA biosensor for point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 185, 113177–113182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, M. High-sensitivity high-throughput detection of nucleic acid targets on metasurface fluorescence biosensors. Biosensors 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.Q.; Guo, X.; Akbar Khan, S.; Lai, C.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Xia, S.; Chen, B.; et al. Detection of COVID-19: A review of the current literature and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112455–112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, P.S. Coronavirus genomic RNA packaging. Virology 2019, 537, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Han, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, G.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y. Accuracy of a nucleocapsid protein antigen rapid test in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 289.e1–289.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Suo, W.; Goulev, Y.; Sun, L.; Kerr, L.; Paulsson, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lao, T. Handheld microfluidic filtration platform enables rapid, low-cost, and robust self-testing of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Small 2021, 17, 2104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Fu, Q.; Lin, M.; He, J.; He, S.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhou, J. Reciprocating-flowing on-a-chip enables ultra-fast immunobinding for multiplexed rapid ELISA detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112920–112927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyosei, Y.; Yamura, S.; Namba, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Watabe, S.; Ito, E. Antigen tests for COVID-19. Biophys. Physicobiol. 2021, 18, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Akarapipad, P.; Nguyen, B.T.; Breshears, L.E.; Sosnowski, K.; Baker, J.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Yoon, J.-Y. Direct capture and smartphone quantification of airborne SARS-CoV-2 on a paper microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 200, 956–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.K.; Kim, E.S.; Mishra, S.; Ganbold, E.; Seong, R.S.; Kaushik, A.K.; Kim, N.Y. Ultrasensitive and reusable graphene oxide-modified double-interdigitated capacitive (DIDC) sensing chip for detecting SARS-CoV-2. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 3468–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, H.; Mahmud, A.; Chang, D.; Das, J.; Gomis, S.; Chen, J.B.; Wang, H.; Been, T.; Yip, L.; Coomes, E.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 viral particles using direct, reagent-free electrochemical sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Mao, Y.; Qi, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; You, F.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L. Real-time, selective, and low-cost detection of trace level SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein for cold-chain food quarantine. NPJ Sci. Food 2021, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lillehoj, P.B. Microfluidic magneto immunosensor for rapid, high sensitivity measurements of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in serum. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, K.; Wang, D.; Zha, L.; Hu, X.; Li, R. Aptamer/antibody sandwich method for digital detection of SARS-CoV2 nucleocapsid protein. Talanta 2022, 236, 122847–122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, D.; Bhatia, H.; Sai, V.V.R.; Satija, J. P-FAB: A fiber-optic biosensor device for rapid detection of COVID-19. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziq, A.; Kidakova, A.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Development of a portable MIP-based electrochemical sensor for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113029–113035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Han, M.; Xu, S.; Yan, K.; Nigal, G.; Zhang, T.; Song, B. Paper-based microfluidic chip for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahari, S.; Roberts, A.; Shahdeo, D.; Gandhi, S. Ecovsens-ultrasensitive novel in-house built printed circuit board based electrochemical device for rapid detection of nCovid-19 antigen, a spike protein domain 1 of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Wen, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Microfluidic immunoassays for sensitive and simultaneous detection of IgG/IgM/Antigen of SARS-CoV-2 within 15 min. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9454–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambaugh, A.; Parks, J.W.; Stott, M.A.; Meena, G.G.; Hawkins, A.R.; Schmidt, H. Optofluidic multiplex detection of single SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A antigens using a novel bright fluorescent probe assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wen, J.; Zhou, M.; Ni, S.; Le, W.; Chen, G.; Wei, L.; Zeng, Y.; Qi, D.; Pan, M.; et al. On-site detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen by deep learning-based surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy and its biochemical foundations. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9174–9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.-R.; Qiao, Y.-C.; Gao, J.-W.; Wang, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L.; Wang, J.-W.; Zhang, C.-H.; et al. Ultrasensitive detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein using laser induced graphene field-effect transistor. Molecules 2021, 26, 6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Tan, M.; He, H.; Tan, H.; Mai, J.; Long, Y.; Jiang, X.; He, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies and associated factors at different hospitalization time points in 192 COVID-19 cases. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2021, 6, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.M.; Emmenegger, M.; Xu, C.K.; Condado Morales, I.; Meisl, G.; Turelli, P.; Zografou, C.; Zimmermann, M.R.; Frey, B.M.; Fiedler, S.; et al. Microfluidic characterisation reveals broad range of SARS-CoV-2 antibody affinity in human plasma. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L. Profile of IgG and IgM antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Infect. Dis. An Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2020, 71, 2255–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffaf, T.; Ghafar-Zadeh, E. COVID-19 diagnostic strategies. Part i: Nucleic acid-based technologies. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Khosh, E.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. The outlook for diagnostic purposes of the 2019-novel coronavirus disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9211–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Mei, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, F.; Geng, S.; Pan, A. Low-dose corticosteroid therapy does not delay viral clearance in patients with COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 147–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Narváez, E.; Dincer, C. The impact of biosensing in a pandemic outbreak: COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112274–112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A.; Jablonski, M.; Molinnus, D.; Wege, C.; Schöning, M.J. Field-effect sensors for virus detection: From Ebola to SARS-CoV-2 and plant viral enhancers. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Chu, K.Y.; Shen, A.Q. Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein by gold nanospikes in an opto-microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112578–112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, E.; Garcia-Ramirez, R.; Díaz-Armas, G.G.; Esparza, M.; Aguilar-Avelar, C.; Flores-Contreras, E.A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Delgado-Balderas, J.R.; Soto-García, B.; Aráiz-Hernández, D.; et al. Automated ELISA on-chip for the detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Sensors 2021, 21, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Agrawal, A. Blood plasma microfluidic device: Aiming for the detection of COVID-19 antibodies using an on-chip ELISA platform. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggestad, J.T.; Kinnamon, D.S.; Olson, L.B.; Liu, J.; Kelly, G.; Wall, S.A.; Oshabaheebwa, S.; Quinn, Z.; Fontes, C.M.; Joh, D.Y.; et al. Multiplexed, quantitative serological profiling of COVID-19 from blood by a point-of-care test. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognetti, J.S.; Steiner, D.J.; Abedin, M.; Bryan, M.R.; Shanahan, C.; Tokranova, N.; Young, E.; Klose, A.M.; Zavriyev, A.; Judy, N.; et al. Disposable photonics for cost-effective clinical bioassays: Application to COVID-19 antibody testing. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qin, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, T.; Peng, R.; Li, Z.; Rini, J.M.; Liu, X. Enhancing the performance of paper-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy nanobiosensors: An experimental approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112672–112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo, A.M.M.; Tomé-Amat, J.; Ramírez, Y.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; Valle, L.G.; Hernández-Ramírez, G.; Tramarin, L.; Herreros, P.; Santamaría, B.; Díaz-Perales, A.; et al. Developing an optical interferometric detection method based biosensor for detecting specific SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulins in Serum and Saliva, and their corresponding ELISA correlation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130394–130403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Kim, H.; Bae, P.K.; Lee, S.; Yang, S.; Kim, J. A single snapshot multiplex immunoassay platform utilizing dense test lines based on engineered beads. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113388–113398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Chavez-Pineda, O.G.; Hernandez-Ortiz, J.A.; Amador-Hernandez, J.U.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Patino-Lopez, L.D.; et al. A high-throughput multiplexed microfluidic device for COVID-19 serology assays. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Krel, M.; Dolgov, E.; Park, S.; Li, X.; Wu, W.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Khaing Oo, M.K.; Perlin, D.S.; et al. Rapid and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG for convalescent serum evaluation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112572–112580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaileb, A.; Jodaylami, M.H.; Coutu, J.; Ricard, P.; Lamarre, M.; Rochet, L.; Cellier-Goetghebeur, S.; Macaulay, D.; Charron, B.; Lavallée, É.; et al. Cross-validation of ELISA and a portable surface plasmon resonance instrument for IgG antibody serology with SARS-CoV-2 positive individuals. Cite Anal. 2021, 146, 4905–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Song, D.; Li, C.; Zhu, A.; Long, F. Rapid, label-free, and sensitive point-of-care testing of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG using all-fiber Fresnel reflection microfluidic biosensor. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 161–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Jiang, X.; Mou, L.; Jiang, X. Materials for microfluidic immunoassays: A Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601403–1601412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Detection of Variant SARS-CoV-2 Strains on the ePlex® Respiratory Panel 2. Available online: https://www.genmarkdx.com/detection-of-variant-sars-cov-2-strains-on-eplex-rp2-panel/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- BioFire COVID-19 Testing Solutions|BioFire Diagnostics. Available online: https://www.biofiredx.com/covid-19/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- QIAstat-Dx SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/ca/products/diagnostics-and-clinical-research/infectious-disease/qiastat-dx-syndromic-testing/qiastat-dx-ca/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Lucira COVID-19 All-In-One Test Kit + PDF Report (Good For Travel)—Plus PDF Results (Good for Travel). Available online: https://www.meenta.io/product/lucira-covid-19-all-in-one-test/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Respiratory Virus Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (Isothermal Amplification Chip Meth—FIND. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/product/respiratory-virus-nucleic-acid-detection-kit-isothermal-amplification-chip-meth/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Cepheid|Cepheid|Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2—FDA Emergency Use Authorization. Available online: https://www.cepheid.com/en/coronavirus (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Microchip RT-PCR COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Detection Test System by rt PCR. Available online: https://www.lumexinstruments.com/applications/covid-19_detection_system.php (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Qorvo Biotechnologies Omnia SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test Detects Delta and Other Circulating Variants in Two Studies—Qorvo. Available online: https://www.qorvo.com/newsroom/news/2021/qorvo-biotechnologies-omnia-sars-cov-2-antigen-test-detects-delta-and-other-circulating-variants (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- The LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test Is a Rapid Microfluidic Immunoassay Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Antigen. Available online: https://www.lumiradx.com/uk-en/test-menu/antigen-test (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- SAMPINUTETM. Available online: https://www.celltrion.com/en-us/kit/sampinute (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Niculescu, A.G.; Chircov, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Fabrication and Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Sun, H.; Tian, J.; Song, Q.; Zhang, W. Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 773304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Type of Technique | LOD | Target Gene | Detection Method | Processing Time (Minutes) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPCR | 9 copies/rxn | N | Fluorescence | NR | [23] |
| qPCR | 7 copies/rxn | N, E, ORF1ab, S and NSP6 | Fluorescence | <120 | [24] |
| qPCR | 7 copies/μL | N | Fluorescence | <120 | [25] |
| qPCR | 1 copy/rxn | N | Fluorescence | 30 | [26] |
| qPCR | 20 copies/rxn | N | Fluorescence | 90 | [27] |
| qPCR | 259 copies/μL | E | Nanoplasmonic | 5 | [28] |
| dPCR | 4.68 copies/μL | N and ORF1ab | Fluorescence | 45 | [31] |
| dPCR | 5 copies/rxn | N and ORF1ab | Fluorescence | 5 | [32] |
| dPCR | 10 copies/μL | ORF1ab | Fluorescence | <60 | [33] |
| LAMP | 2 copies/rxn | N, E and ORF1ab | Fluorescence | 70 | [35] |
| LAMP | 100 copies/rxn | ORF1ab | Fluorescence | 20 | [36] |
| LAMP | 50 copies/μL | N, ORF1ab and ORF8 | Fluorescence | 30 | [37] |
| LAMP | <1 copy/μL | N | Fluorescence | 10 | [38] |
| LAMP | 200 copies/μL | N and ORF1ab | Colorimetric | 60 | [39] |
| LAMP | 300 copies/rxn | N and E | Colorimetric | 35 | [40] |
| RCA | 30 aM/rxn | ORF1ab | Gelation | 5 | [41] |
| RPA-LFA | 1 copy/μL | N | Colorimetric | 30 | [42] |
| RPA-LAMP | 10 copies/rxn | S | Fluorescence | 60 | [43] |
| CRISPR | 10 copies/μL | N and E | Fluorescence | 40 | [44] |
| CRISPR-LFA | 100 copies/rxn | N | Colorimetric | NR | [45] |
| CRISPR | 31 copies/μL | N, S and ORF1ab | Fluorescence | 20 | [46] |
| Product | Manufacturer Name | Type of Platform | Target | Detection Method | Processing Time (Minutes) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ePlex SARS-CoV-2 Test | GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. | RT-qPCR | Nucleic Acid | Voltage | ~120 | [92] |
| BioFire COVID-19 test | BioFire Defense, LLC | Multiplex RT-qPCR | Nucleic Acid | Fluorescence | 50 | [93] |
| QIAstat-Dx Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 panel | QIAGEN GmbH | Multiplex RT-qPCR | Nucleic Acid | Fluorescence | ~60 | [94] |
| Lucira COVID-19 All-In-One Test Kit | Lucira Health, Inc. | RT-LAMP | Nucleic Acid | Colorimetric | 30 | [95] |
| Respiratory Virus Nucleic Acid Detection kit | CapitalBio Technology | Isothermal amplification | Nucleic Acid | Fluorescence | 90 | [96] |
| Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test | Cepheid | RT-qPCR | Nucleic Acid | Fluorescence | 45 | [97] |
| Microchip RT-PCR COVID-19 detection system | Lumex Instruments Canada | RT-qPCR | Nucleic Acid | Fluorescence | 50 | [98] |
| Omnia SARS-CoV-2 | Qorvo Biotechnologies | Antigen immunoassay | Proteins | Resonance frequency | ~20 | [99] |
| LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 Ag test | LumiraDx | Antigen immunoassay | Proteins | Fluorescence | 12 | [100] |
| Sampinute COVID-19 | Celltrion | Antigen immunoassay | Proteins | Electrochemical | 30–45 | [101] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Contreras, E.A.; González-González, R.B.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Yee-de León, J.F.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; González-González, E. Microfluidics-Based Biosensing Platforms: Emerging Frontiers in Point-of-Care Testing SARS-CoV-2 and Seroprevalence. Biosensors 2022, 12, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030179
Flores-Contreras EA, González-González RB, Rodríguez-Sánchez IP, Yee-de León JF, Iqbal HMN, González-González E. Microfluidics-Based Biosensing Platforms: Emerging Frontiers in Point-of-Care Testing SARS-CoV-2 and Seroprevalence. Biosensors. 2022; 12(3):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030179
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Contreras, Elda A., Reyna Berenice González-González, Iram P. Rodríguez-Sánchez, Juan F. Yee-de León, Hafiz M. N. Iqbal, and Everardo González-González. 2022. "Microfluidics-Based Biosensing Platforms: Emerging Frontiers in Point-of-Care Testing SARS-CoV-2 and Seroprevalence" Biosensors 12, no. 3: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030179
APA StyleFlores-Contreras, E. A., González-González, R. B., Rodríguez-Sánchez, I. P., Yee-de León, J. F., Iqbal, H. M. N., & González-González, E. (2022). Microfluidics-Based Biosensing Platforms: Emerging Frontiers in Point-of-Care Testing SARS-CoV-2 and Seroprevalence. Biosensors, 12(3), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030179






