Cadmium Ions’ Trace-Level Detection Using a Portable Fiber Optic—Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
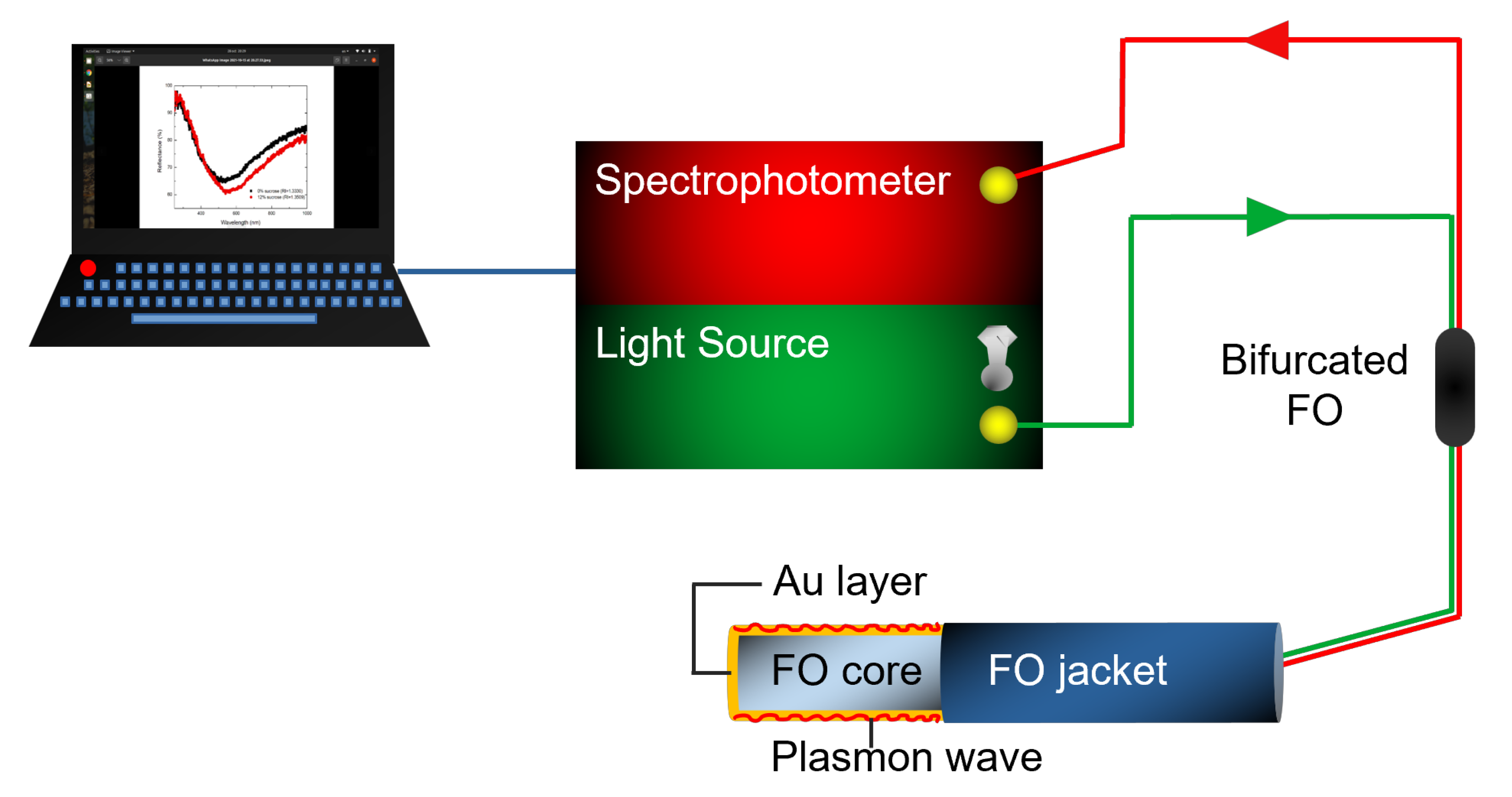
2.2. FO-SPR Portable System
2.3. Sensor Functionalization Strategies for Cd Detection
2.4. Characterization of the FO-SPR Surfaces
3. Results and Discussion
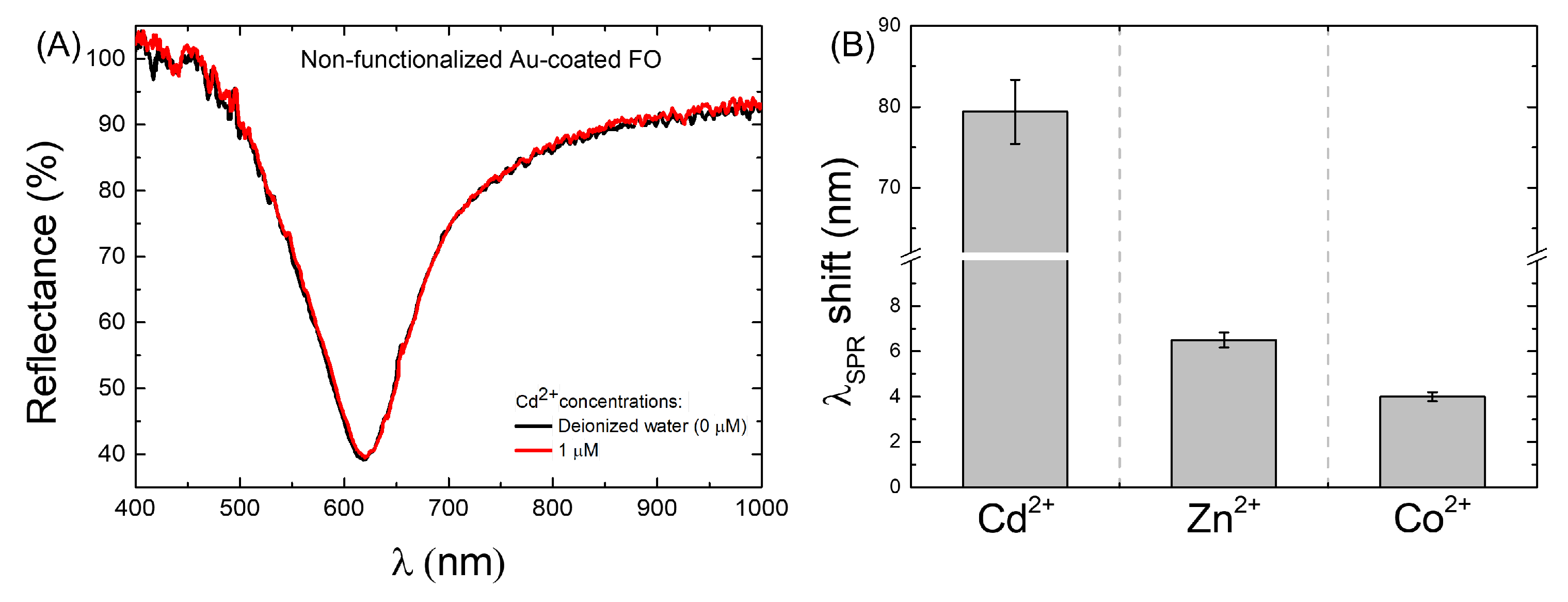
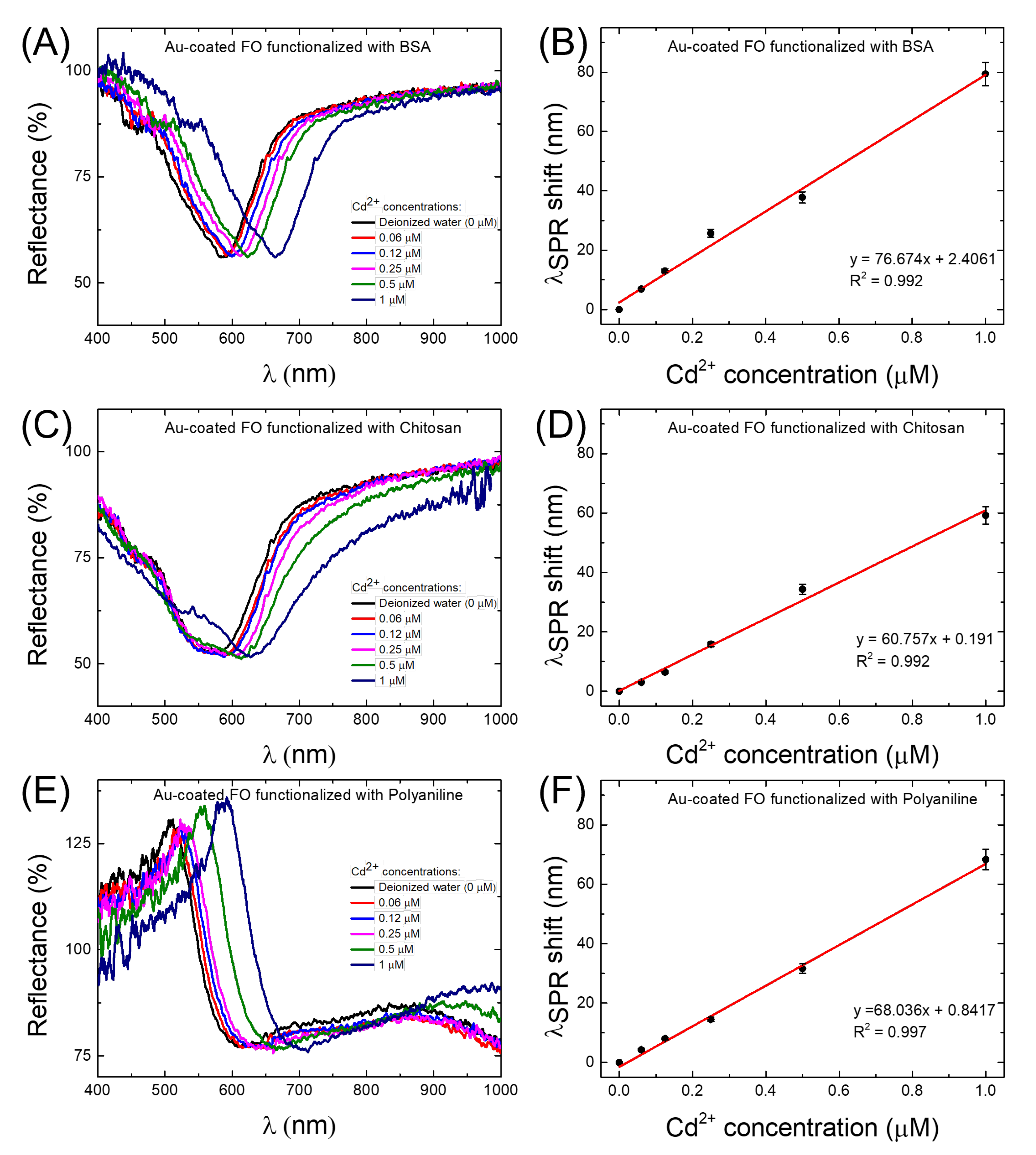
3.1. Cd Detection Strategies: Sensitivity and Limit of Detection Evaluation
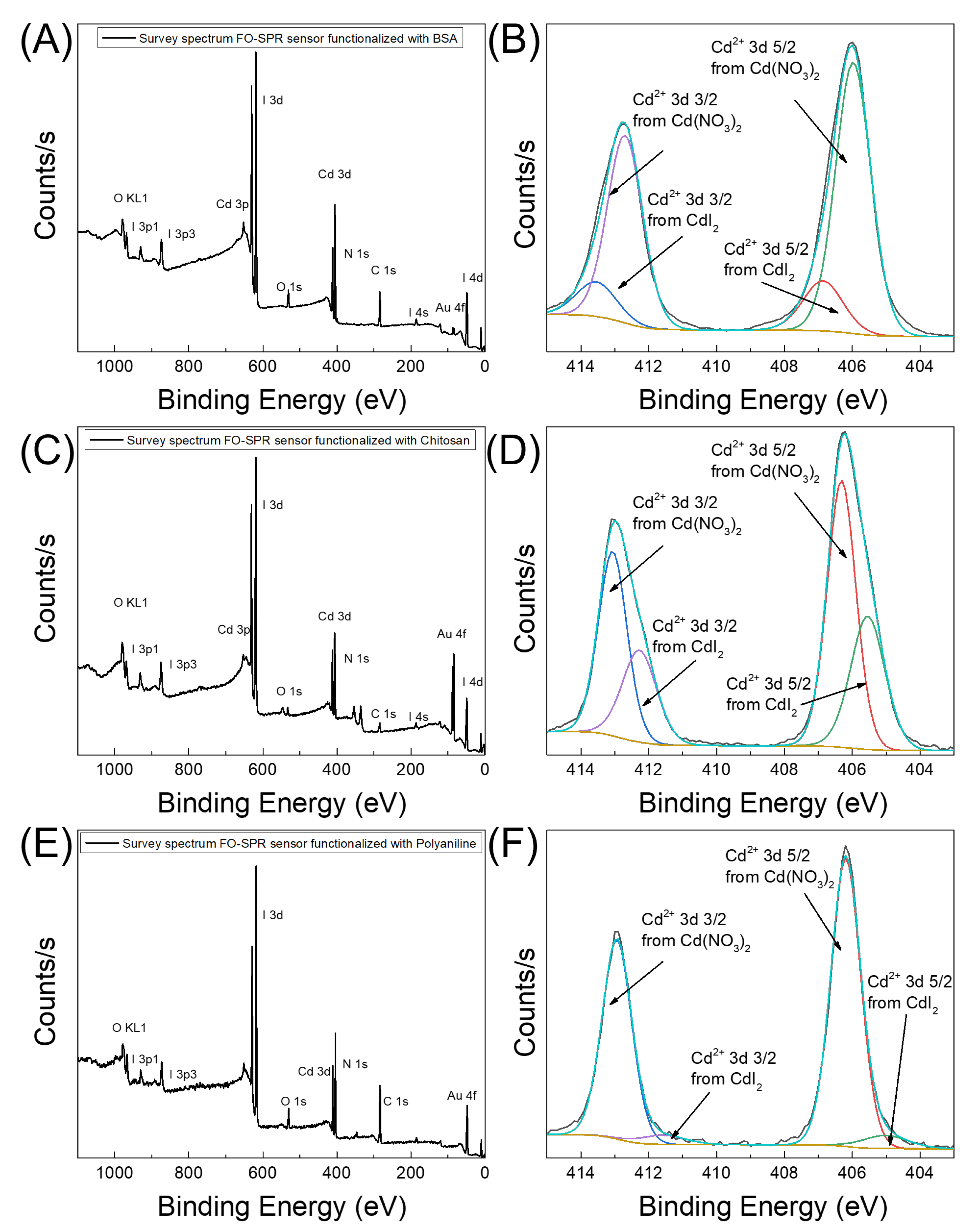
3.2. Characterization of the FO-SPR Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| INFLPR | National Institute for Laser, Plasma and Radiation Physics |
| R&D | Research & Development |
| MDEO | R&D Center for Materials and Electronic & Optoelectronic Devices |
| IMCN | Institute of Condensed Matter and Nanosciences |
| UCLouvain | Université catholique de Louvain |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SPs | Surface Plasmons |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| FO-SPR | Fiber Optic–Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| RI | Refractive Index |
| ITO | Indium Tin Oxide |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| PVA | Polyvinyl Alcohol |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| UV–VIS | Ultraviolet–Visible |
| QCM | Quartz Crystal Microbalance |
| RSF | Relative Sensitivity Factor |
| DIW | Deionized Water |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| XPS | X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| AOSR | Academy of Romanian Scientists |
| UEFISCDI | Executive Unit for Financing Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation |
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, L.P.; Shoora, S.K.; Sethi, B. Cadmium (II) ion sensing through p-tert-butyl calix[6]arene based potentiometric sensor. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 195, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinuthia, G.K.; Ngure, V.; Beti, D.; Lugalia, R.; Wangila, A.; Kamau, L. Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: Community health implication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, A.; Torre, A.D.; Benedetto, A.D.; Rinaldi, R. Bio-Recognition in Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors for *Heavy Metals-Water and Waterborne Contamination Analysis. Biosensors 2019, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satarug, S.; Baker, J.R.; Urbenjapol, S.; Haswell-Elkins, M.; Reilly, P.E.B.; Williams, D.J.; Moore, M.R. A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed population. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 137, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Xu, L.; Song, S.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L. Effects of long-term low-dose cadmium exposure on genomic DNA methylation in human embryo lung fibroblast cells. Toxicology 2008, 244, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.R.; de Jesus Rodrigues, S.W.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Tanaka, A.A.; Tanaka, S.M.C.N.; Kubota, L.T. Alternating Layers of Iron(III) Tetra(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)-porphyrin and Copper Tetrasulfonated Phthalocyanine for Amperometric Detection of 4-Nitrophenol in Nanomolar Levels. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneyo, I.A.; Doherty, F.V.; Adebesin, O.A.; Hammed, M.O. Biodegradation of Pollutants in Waste Water from Pharmaceutical, Textile and Local Dye Effluent in Lagos, Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2016, 6, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, A.K.; Kaur, V.; Verma, N. A review on solid phase microextraction-High performance liquid chromatography as a novel tool for the analysis of toxic metal ions. Talanta 2006, 68, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Pan, H.; González-Vila, A.; Guo, T.; Gillan, D.C.; Wattiez, R.; Caucheteur, C. Selective detection of cadmium ions using plasmonic optical fiber gratings functionalized with bacteria. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 19740–19749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wu, J.; Ju, H. Electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions with inorganic, organic and bio-materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumpu, M.B.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. A review on detection of heavy metal ions in water—An electrochemical approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 213, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J.; Hayat, K.; Yang, X.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, P. Label-Free and Sensitive Determination of Cadmium Ions Using a Ti-Modified Co3O4-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor. Biosensors 2020, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Liu, H.X.; Ying, Y.L.; Xiu, G.; Long, Y.T. A thumb-size electrochemical system for portable sensors. Analyst 2018, 143, 2760–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Faye, D.; Lefèvre, J.P.; Delaire, J.A.; Leray, I. Selective fluorimetric detection of cadmium in a microfluidic device. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Ren, W.X.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3210–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Park, Y.; Kang, T.; Lee, L.P. Selective and sensitive detection of metal ions by plasmonic resonance energy transfer-based nanospectroscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antohe (Arghir), I.; Schouteden, K.; Goos, P.; Delport, F.; Spasic, D.; Lammertyn, J. Thermal annealing of gold coated fiber optic surfaces for improved plasmonic biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antohe, I.; Spasic, D.; Delport, F.; Li, J.; Lammertyn, J. Nanoscale patterning of gold-coated optical fibers for improved plasmonic sensing. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 215301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arghir, I.; Spasic, D.; Verlinden, B.E.; Delport, F.; Lammertyn, J. Improved surface plasmon resonance biosensing using silanized optical fibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schasfoort, R.B.M. (Ed.) Handbook of Surface Plasmon Resonance; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 1–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Dillen, A.; Saeys, W.; Lammertyn, J.; Spasic, D. Advancements in SPR biosensing technology: An overview of recent trends in smart layers design, multiplexing concepts, continuous monitoring and in vivo sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghir, I.; Delport, F.; Spasic, D.; Lammertyn, J. Smart design of fiber optic surfaces for improved plasmonic biosensing. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokribousjein, Z.; Galan, D.R.; Losada-Pérez, P.; Wagner, P.; Lammertyn, J.; Arghir, I.; Golreihan, A.; Verachtert, H.; Aydın, A.A.; Maeyer, M.D.; et al. Mechanism of Nonpolar Model Substances to Inhibit Primary Gushing Induced by Hydrophobin HFBI. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4673–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antohe, I.; Iordache, I.; Antohe, V.A.; Socol, G. A polyaniline/platinum coated fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor for picomolar detection of 4-nitrophenol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antohe, I.; Jinga, L.I.; Antohe, V.A.; Socol, G. Sensitive pH Monitoring Using a Polyaniline-Functionalized Fiber Optic-Surface Plasmon Resonance Detector. Sensors 2021, 21, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.S.; Vidal, M.; Santos, N.F.; Costa, F.M.; Marques, C.; Pereira, S.O.; Ao, C.L. Immunosensing Based on Optical Fiber Technology: Recent Advances. Biosensors 2021, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, B.S.; Biswas, R. An optical fiber based surface plasmon resonance technique for sensing of lead ions: A toxic water pollutant. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 46, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, K.; Hurston, E.; Prabhu, R.; Joseph, G.P. Fibre optic sensor to detect heavy metal pollutants in water environments. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2017—Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadani, K.; Nag, P.; Mukherji, S. LSPR based optical fiber sensor with chitosan capped gold nanoparticles on BSA for trace detection of Hg (II) in water, soil and food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 134, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Gupta, B.D. Detection of heavy metal ions in contaminated water by surface plasmon resonance based optical fibre sensor using conducting polymer and chitosan. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Rao, F.; Yu, C.; Zhou, G.; Huang, X.G. Differential Fresnel-reflection-based fiber biochemical sensor with temperature self-compensation for high-resolution measurement of Cd2+ concentration in solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Feng, W. Fiber-Optic Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor for Trace Cadmium-Ion Detection Based on Ag-PVA/TiO2 Sensing Membrane. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18650–18655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono, E.; Thalib, I.; Aflanie, I.; Noor, Z.; Idroes, R. Study of Interaction between Cadmium and Bovine Serum Albumin with UV-Vis Spectrocopy Approach. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 350, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M.; Malik, S.; Badshah, S.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Engineering Functionalized Chitosan-Based Sorbent Material: Characterization and Sorption of Toxic Elements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attout, A.; Yunus, S.; Bertrand, P. Electroless deposition of polyaniline: Synthesis and characterization. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, E.N.; Motahari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Nanoadsorbents based on conducting polymer nanocomposites with main focus on polyaniline and its derivatives for removal of heavy metal ions/dyes: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boruah, B.S.; Biswas, R. Localized surface plasmon resonance based U-shaped optical fiber probe for the detection of Pb2+ in aqueous medium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.; Stickle, W.; Sobol, P.; Bomben, K. A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data. In Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Chastain, J., Ed.; Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Physical Electronics Division: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Babcock, J.J.; Brancaleon, L. Bovine serum albumin oligomers in the E- and B-forms at low protein concentration and ionic strength. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 53, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, D.; Mao, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Kissel, T. Effect of chitosan structure properties and molecular weight on the intranasal absorption of tetramethylpyrazine phosphate in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y. Molecular weight of chemically polymerized polyaniline. Die Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 1988, 9, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, T. Study of Plasmon Resonance. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 381, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadatkar, N.S.; Waghuley, S. Characterizing the electro-optical properties of polyaniline/poly(vinylacetate) composite films as-synthesized through chemical route. Results Surf. Interfaces 2021, 4, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shard, A.G.; Counsell, J.D.P.; Cant, D.J.H.; Smith, E.F.; Navabpour, P.; Zhang, X.; Blomfield, C.J. Intensity calibration and sensitivity factors for XPS instruments with monochromatic Ag Lα and Al Kα sources. Surf. Interface Anal. 2019, 51, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Feng, W. Cadmium-ion detection: A comparative study for a SnO2, MoS2, SnO2/MoS2, SnO2-MoS2 sensing membrane combination with a fiber-optic Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Gupta, B.D. Fiber Optic Surface Plasmon Resonance based Cadmium Sensor using SnO2 Nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–28 September 2018; p. ThE9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FO-SPR Sensor Type | Sensitivity | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Atomic Percentage of |
|---|---|---|---|
| [nm/M] | [nM] | Absorbed Cd [%] | |
| BSA/Au | 76.67 | 7.1 | 21 |
| PANI/Au | 68.03 | 8.8 | 16 |
| Chitosan/Au | 60.75 | 9.4 | 14.7 |
| FO-SPR Sensor Configuration | Cd Sensitive Layers | Sensitivity | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| [nM/M] | Range [M] | ||
| Reflection [this work] | BSA/Au | 76.67 | 0–1 |
| Reflection [33] | Ag-PVA/TiO | 48.2 | 0–1 |
| 315.2 | 0–0.04 | ||
| Transmission [46] | SnO-MoS | 0.03 | 0–100 |
| Transmission [47] | SnO/Ag | 23.71 | 0–10 |
| Transmission [31] | Pyrrole/chitosan/ITO/Ag | 146.8 | 0–1.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Şolomonea, B.-G.; Jinga, L.-I.; Antohe, V.-A.; Socol, G.; Antohe, I. Cadmium Ions’ Trace-Level Detection Using a Portable Fiber Optic—Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor. Biosensors 2022, 12, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080573
Şolomonea B-G, Jinga L-I, Antohe V-A, Socol G, Antohe I. Cadmium Ions’ Trace-Level Detection Using a Portable Fiber Optic—Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080573
Chicago/Turabian StyleŞolomonea, Bianca-Georgiana, Luiza-Izabela Jinga, Vlad-Andrei Antohe, Gabriel Socol, and Iulia Antohe. 2022. "Cadmium Ions’ Trace-Level Detection Using a Portable Fiber Optic—Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080573
APA StyleŞolomonea, B.-G., Jinga, L.-I., Antohe, V.-A., Socol, G., & Antohe, I. (2022). Cadmium Ions’ Trace-Level Detection Using a Portable Fiber Optic—Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor. Biosensors, 12(8), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080573









