A Rapid and Sensitive Microfluidics-Based Tool for Seroprevalence Immunity Assessment of COVID-19 and Vaccination-Induced Humoral Antibody Response at the Point of Care
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunoreagents and Buffers
2.2. Fabrication of the Microfluidic Cartridge
2.3. Immunoassay, Imaging, and Analysis
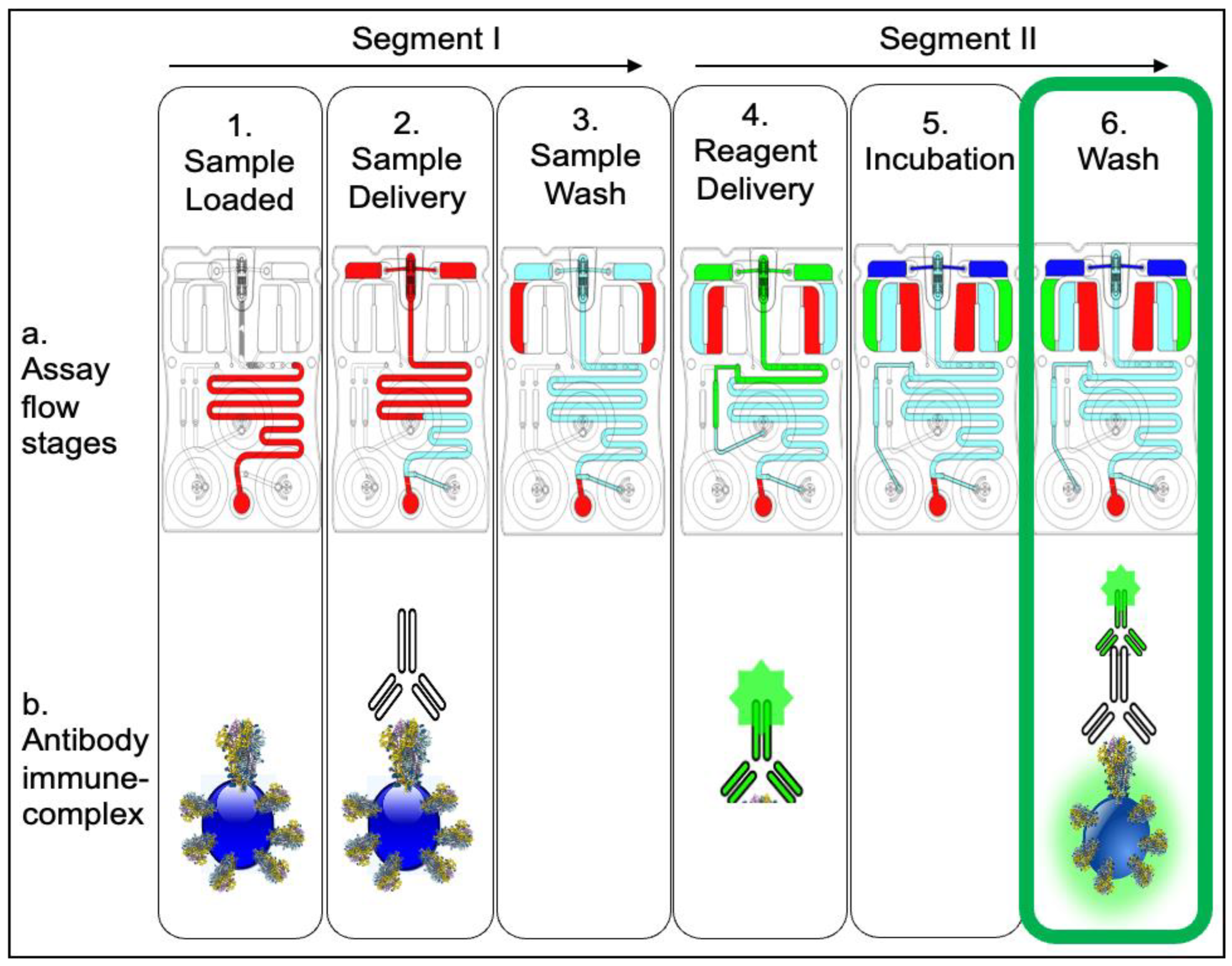
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assay Development
3.2. Assay Optimization and Instrumentation
3.3. Assay Execution and Integration
3.4. Development of Immunity Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Meyer, B.; Andrey, D.O.; Arm-Vernez, I.; Baggio, S.; Didierlaurent, A.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Eckerle, I.; Grasset-Salomon, C.; Huttner, A.; et al. Antibody Persistence in the First 6 Months Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Hospital Workers: A Prospective Longitudinal Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 784.e1–784.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, P.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response up to 10 Months after Infection. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1832–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Shen, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Induces Sustained Humoral Immune Responses in Convalescent Patients Following Symptomatic COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirofski, L. Disease Severity and Durability of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Antibody Response: A View Through the Lens of the Second Year of the Pandemic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1345–e1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD); Division of Viral Diseases Science Brief. SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Induced and Vaccine-Induced Immunity. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/vaccine-induced-immunity.html (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Assessed for up to 8 Months after Infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radbruch, A.; Chang, H.-D. A Long-Term Perspective on Immunity to COVID. Nature 2021, 595, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.; Foulkes, S.; Insalata, F.; Kirwan, P.; Saei, A.; Atti, A.; Wellington, E.; Khawam, J.; Munro, K.; Cole, M.; et al. Protection against SARS-CoV-2 after COVID-19 Vaccination and Previous Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T.A.; McBride, S.K.; Leier, H.C.; Guzman, G.; Lyski, Z.L.; Schoen, D.; Winders, B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, D.X.; Messer, W.B.; et al. Vaccination before or after SARS-CoV-2 Infection Leads to Robust Humoral Response and Antibodies That Effectively Neutralize Variants. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabn8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Sprouse, K.R.; Bowen, J.E.; Joshi, A.; Franko, N.; Navarro, M.J.; Stewart, C.; Cameroni, E.; McCallum, M.; Goecker, E.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infections Elicit Potent, Broad, and Durable Neutralizing Antibody Responses. Cell 2022, 185, 872–880.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.; Blennow, O.; Hansson, L.; Mielke, S.; Nowak, P.; Chen, P.; Söderdahl, G.; Österborg, A.; Smith, C.I.E.; Wullimann, D.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in Five Groups of Immunocompromised Patients and Healthy Controls in a Prospective Open-Label Clinical Trial. eBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Tehrani, Z.R.; Logue, J.; Newman, M.; Frieman, M.B.; Harris, A.D.; Sajadi, M.M. Single Dose Vaccination in Healthcare Workers Previously Infected with SARS-CoV-2. In Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, F.; Srivastava, K.; the PARIS Team; Simon, V. Robust Spike Antibody Responses and Increased Reactogenicity in Seropositive Individuals after a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine. In Allergy and Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Samanovic, M.I.; Cornelius, A.R.; Gray-Gaillard, S.L.; Allen, J.R.; Karmacharya, T.; Wilson, J.P.; Hyman, S.W.; Tuen, M.; Koralov, S.B.; Mulligan, M.J.; et al. Robust Immune Responses after One Dose of BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine Dose in SARS-CoV-2 Experienced Individuals. In Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, T.A.; McBride, S.K.; Winders, B.; Schoen, D.; Trautmann, L.; Curlin, M.E.; Tafesse, F.G. Antibody Response and Variant Cross-Neutralization After SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infection. JAMA 2022, 327, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.G.; et al. Duration of Effectiveness of Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Disease: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC Cases, Data, and Surveillance. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/seroprevalance-surveys-tell-us.html (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Wyllie, D.; Jones, H.E.; Mulchandani, R.; Trickey, A.; Taylor-Phillips, S.; Brooks, T.; Charlett, A.; Ades, A.; EDSAB-HOME investigators; Moore, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Responsive T Cell Numbers and Anti-Spike IgG Levels Are Both Associated with Protection from COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study in Keyworkers. In Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Ren, L.; Su, J.; Zhu, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, B.; et al. Exploring Rapid and Effective Screening Methods for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies in COVID-19 Convalescent Patients and Longitudinal Vaccinated Populations. Pathogens 2022, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing Antibody Levels Are Highly Predictive of Immune Protection from Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Barnes, C.O.; Finkin, S.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Cipolla, M.; Gaebler, C.; Lieberman, J.A.; et al. MRNA Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and Circulating Variants. Nature 2021, 592, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, D.; Juno, J.A.; Khoury, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J.; Davenport, M.P. Prospects for Durable Immune Control of SARS-CoV-2 and Prevention of Reinfection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.; Torre, D.; Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Tan, A.T.; Tabaglio, T.; Mzoughi, S.; Sanchez-Tarjuelo, R.; Le Bert, N.; Lim, J.M.E.; Hatem, S.; et al. Rapid, Scalable Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Cellular Immunity by Whole-Blood PCR. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, P. The T Cell Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, F.; Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Status Report. Immunity 2020, 52, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, L. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: A Key Target for Eliciting Persistent Neutralizing Antibodies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeling, R.W.; Heymann, D.L.; Teo, Y.-Y.; Garcia, P.J. Diagnostics for COVID-19: Moving from Pandemic Response to Control. Lancet 2022, 399, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J.; et al. A Serological Assay to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Sun, X.; Dai, Z.; Gao, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J.; Wen, W. Point-of-Care Testing Detection Methods for COVID-19. Lab. Chip 2021, 21, 1634–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.E.; Lim, B.; Hsu, C.; Xiong, D.; Wu, W.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, M.; et al. RT-LAMP for Rapid Diagnosis of Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguli, A.; Mostafa, A.; Berger, J.; Aydin, M.Y.; Sun, F.; de Ramirez, S.A.S.; Valera, E.; Cunningham, B.T.; King, W.P.; Bashir, R. Rapid Isothermal Amplification and Portable Detection System for SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22727–22735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Herbst, K.; Boerner, K.; Meurer, M.; Kremer, L.P.; Kirrmaier, D.; Freistaedter, A.; Papagiannidis, D.; Galmozzi, C.; Stanifer, M.L.; et al. A Colorimetric RT-LAMP Assay and LAMP-Sequencing for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Clinical Samples. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabc7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seia, M.A.; Pereira, S.V.; Fontán, C.A.; De Vito, I.E.; Messina, G.A.; Raba, J. Laser-Induced Fluorescence Integrated in a Microfluidic Immunosensor for Quantification of Human Serum IgG Antibodies to Helicobacter Pylori. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valera, E.; Berger, J.; Hassan, U.; Ghonge, T.; Liu, J.; Rappleye, M.; Winter, J.; Abboud, D.; Haidry, Z.; Healey, R.; et al. A Microfluidic Biochip Platform for Electrical Quantification of Proteins. Lab. Chip 2018, 18, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.V.; Raba, J.; Messina, G.A. IgG Anti-Gliadin Determination with an Immunological Microfluidic System Applied to the Automated Diagnostic of the Celiac Disease. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, S.T.; Dou, M.; Sun, J.; Li, X. A Paper/Polymer Hybrid Microfluidic Microplate for Rapid Quantitative Detection of Multiple Disease Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Chavez-Pineda, O.G.; Hernandez-Ortiz, J.A.; Amador-Hernandez, J.U.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Patino-Lopez, L.D.; et al. A High-Throughput Multiplexed Microfluidic Device for COVID-19 Serology Assays. Lab. Chip 2021, 21, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Wen, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Microfluidic Immunoassays for Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of IgG/IgM/Antigen of SARS-CoV-2 within 15 Min. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9454–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.B.; Jarlhelt, I.; Pérez-Alós, L.; Hummelshøj Landsy, L.; Loftager, M.; Rosbjerg, A.; Helgstrand, C.; Bjelke, J.R.; Egebjerg, T.; Jardine, J.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses Are Correlated to Disease Severity in COVID-19 Convalescent Individuals. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.P.; Yansouni, C.P.; Basta, N.E.; Desjardins, M.; Kanjilal, S.; Paquette, K.; Caya, C.; Semret, M.; Quach, C.; Libman, M.; et al. Serodiagnostics for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome–Related Coronavirus 2: A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.; Wong, J.; McDevitt, J.T. Programmable Bio-Nanochip Platform: A Point-of-Care Biosensor System with the Capacity to Learn. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.W.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Lu, Z.; Kang, S.K.; Fenyo, D.; Alcorn, T.; Dapkins, I.P.; Sharif, I.; Vurmaz, D.; et al. Clinical Decision Support Tool and Rapid Point-of-Care Platform for Determining Disease Severity in Patients with COVID-19. Lab. Chip 2020, 20, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadfan, B.H.; Simmons, A.R.; Simmons, G.W.; Ho, A.; Wong, J.; Lu, K.H.; Bast, R.C.; McDevitt, J.T. A Multiplexable, Microfluidic Platform for the Rapid Quantitation of a Biomarker Panel for Early Ovarian Cancer Detection at the Point-of-Care. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.W.; Wong, J.; Shadfan, B.; Gopalkrishnan, S.; Christodoulides, N.; McDevitt, J.T. Programmable Bio-Nano-Chip System: A Flexible Point-of-Care Platform for Bioscience and Clinical Measurements. Lab. Chip 2015, 15, 4020–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Measuring Cell Fluorescence Using ImageJ—The Open Lab Book v1.0. Available online: https://theolb.readthedocs.io/en/latest/imaging/measuring-cell-fluorescence-using-imagej.html (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- McRae, M.P.; Bozkurt, B.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Sanchez, X.; Christodoulides, N.; Simmons, G.; Nambi, V.; Misra, A.; Miller, C.S.; Ebersole, J.L.; et al. Cardiac ScoreCard: A Diagnostic Multivariate Index Assay System for Predicting a Spectrum of Cardiovascular Disease. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 54, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulides, N.; De La Garza, R.; Simmons, G.W.; McRae, M.P.; Wong, J.; Newton, T.F.; Smith, R.; Mahoney, J.J., III; Hohenstein, J.; Gomez, S.; et al. Application of Programmable Bio-Nano-Chip System for the Quantitative Detection of Drugs of Abuse in Oral Fluids. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 153, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashidzadeh, H.; Danafar, H.; Rahimi, H.; Mozafari, F.; Salehiabar, M.; Rahmati, M.A.; Rahamooz-Haghighi, S.; Mousazadeh, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Ertas, Y.N.; et al. Nanotechnology against the Novel Coronavirus (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2): Diagnosis, Treatment, Therapy and Future Perspectives. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatatos, L.; Czartoski, J.; Wan, Y.-H.; Homad, L.J.; Rubin, V.; Glantz, H.; Neradilek, M.; Seydoux, E.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; et al. A Single MRNA Immunization Boosts Cross-Variant Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 Infection. In Infectious Diseases (Except HIV/AIDS); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Parihar, A.; Panda, U.; Parihar, D.S. Microfluidics-Based Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) Devices in Dealing with Waves of COVID-19 Pandemic: The Emerging Solution. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2046–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, M.P.; Dapkins, I.P.; Sharif, I.; Anderman, J.; Fenyo, D.; Sinokrot, O.; Kang, S.K.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Vurmaz, D.; Simmons, G.W.; et al. Managing COVID-19 With a Clinical Decision Support Tool in a Community Health Network: Algorithm Development and Validation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e22033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Modak, S.S.; Simmons, G.W.; Trochesset, D.A.; Kerr, A.R.; Thornhill, M.H.; Redding, S.W.; Vigneswaran, N.; Kang, S.K.; Christodoulides, N.J.; et al. Point-of-care Oral Cytology Tool for the Screening and Assessment of Potentially Malignant Oral Lesions. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct Antibody and Memory B Cell Responses in SARS-CoV-2 Naïve and Recovered Individuals after MRNA Vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angyal, A.; Longet, S.; Moore, S.C.; Payne, R.P.; Harding, A.; Tipton, T.; Rongkard, P.; Ali, M.; Hering, L.M.; Meardon, N.; et al. T-Cell and Antibody Responses to First BNT162b2 Vaccine Dose in Previously Infected and SARS-CoV-2-Naive UK Health-Care Workers: A Multicentre Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e21–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Prostko, J.C.; Frias, E.C.; Stewart, J.L.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Braun, J.G.; et al. Antibody Responses to the BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine in Individuals Previously Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Srivastava, K.; Alshammary, H.; Amoako, A.A.; Awawda, M.H.; Beach, K.F.; Bermúdez-González, M.C.; Bielak, D.A.; Carreño, J.M.; Chernet, R.L.; et al. Antibody Responses in Seropositive Persons after a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1372–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Baxter, A.E.; Herati, R.S.; Oldridge, D.A.; Gouma, S.; et al. Rapid Induction of Antigen-Specific CD4 + T Cells Guides Coordinated Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccination. Immunology 2021, 54, 2133–2142.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Reese, H.; Iuliano, A.D.; Patel, N.N.; Garg, S.; Kim, L.; Silk, B.J.; Hall, A.J.; Fry, A.; Reed, C. Estimated Incidence of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Illness and Hospitalization—United States, February–September 2020. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e1010–e1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.E.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Katz, J.; Wanger, A.; Bai, Y.; Sridhar, S.; Patel, B. Screening Donors for COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma. Transfusion 2021, 61, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.B.; Yildirim, I.; Keskinocak, P. Significance of SARS-CoV-2 Specific Antibody Testing during COVID-19 Vaccine Allocation. In Infectious Diseases (Except HIV/AIDS); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kubina, R.; Dziedzic, A. Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Supasa, P.; Liu, C.; Mentzer, A.J.; Ginn, H.M.; Zhao, Y.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; Tuekprakhon, A.; Nutalai, R.; et al. Evidence of Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Variant B.1.351 from Natural and Vaccine-Induced Sera. Cell 2021, 184, 2348–2361.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajsri, K.S.; McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.W.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Matz, H.; Dooley, H.; Koide, A.; Koide, S.; McDevitt, J.T. A Rapid and Sensitive Microfluidics-Based Tool for Seroprevalence Immunity Assessment of COVID-19 and Vaccination-Induced Humoral Antibody Response at the Point of Care. Biosensors 2022, 12, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080621
Rajsri KS, McRae MP, Simmons GW, Christodoulides NJ, Matz H, Dooley H, Koide A, Koide S, McDevitt JT. A Rapid and Sensitive Microfluidics-Based Tool for Seroprevalence Immunity Assessment of COVID-19 and Vaccination-Induced Humoral Antibody Response at the Point of Care. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080621
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajsri, Kritika Srinivasan, Michael P. McRae, Glennon W. Simmons, Nicolaos J. Christodoulides, Hanover Matz, Helen Dooley, Akiko Koide, Shohei Koide, and John T. McDevitt. 2022. "A Rapid and Sensitive Microfluidics-Based Tool for Seroprevalence Immunity Assessment of COVID-19 and Vaccination-Induced Humoral Antibody Response at the Point of Care" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080621
APA StyleRajsri, K. S., McRae, M. P., Simmons, G. W., Christodoulides, N. J., Matz, H., Dooley, H., Koide, A., Koide, S., & McDevitt, J. T. (2022). A Rapid and Sensitive Microfluidics-Based Tool for Seroprevalence Immunity Assessment of COVID-19 and Vaccination-Induced Humoral Antibody Response at the Point of Care. Biosensors, 12(8), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080621






