Flexible Textile-Based Sweat Sensors for Wearable Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Preparation Processes of Textile-Based Sweat Sensors
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation Process
2.2.1. Direct Transformation
2.2.2. Textiles Post Treatment
3. Key Components of the Sweat Sensors
3.1. Sweat Transportation Channels and Collectors
3.2. Signal Selection Unit
3.3. Sensing Element
3.4. Integrating Sensing with Communication Technologies
4. Applications in Wearable Sensors
4.1. Sweat-Quantity-Sensing Devices
4.2. Ion-Sensing Devices
4.3. pH-Value-Sensing Devices
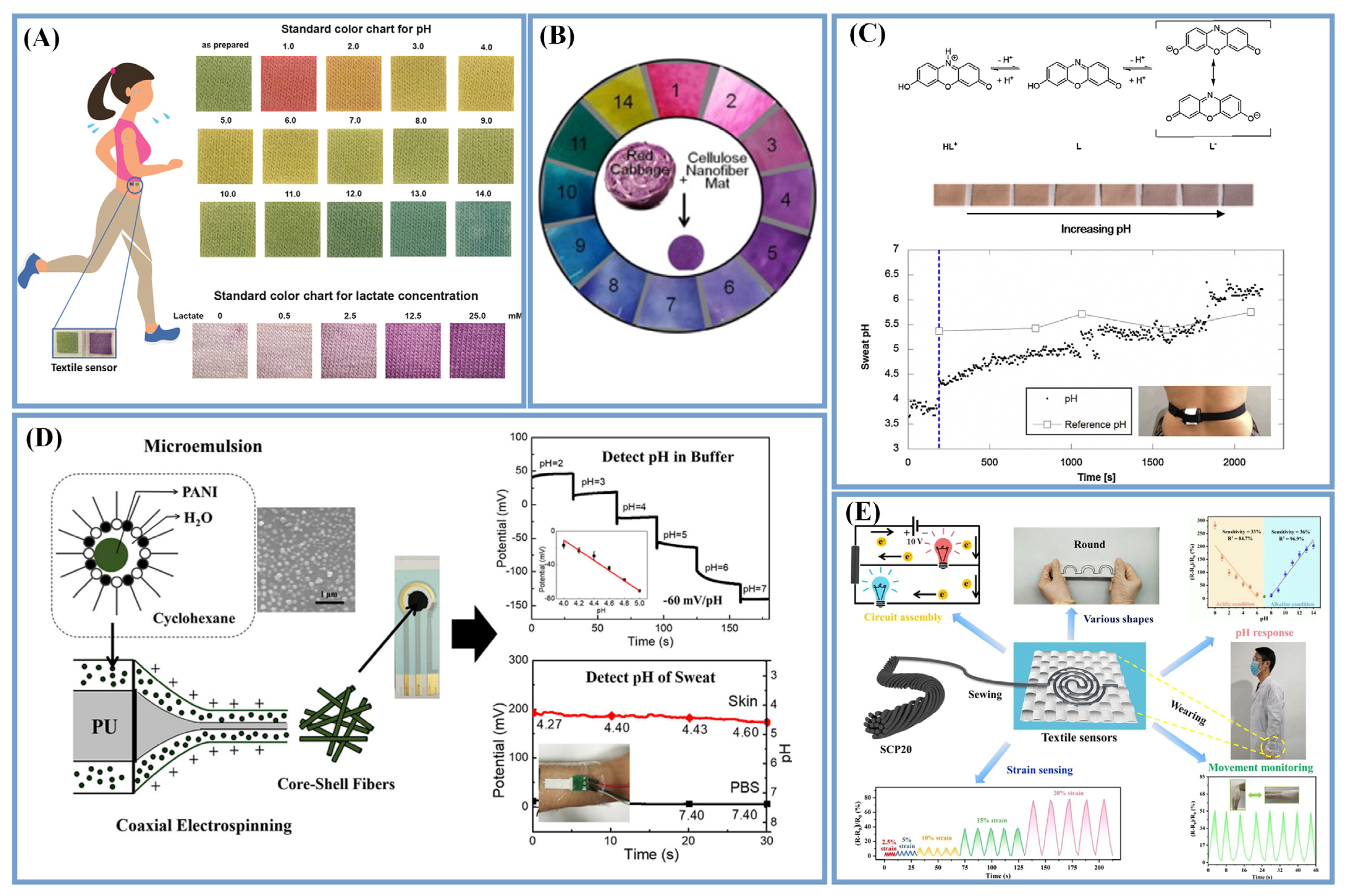
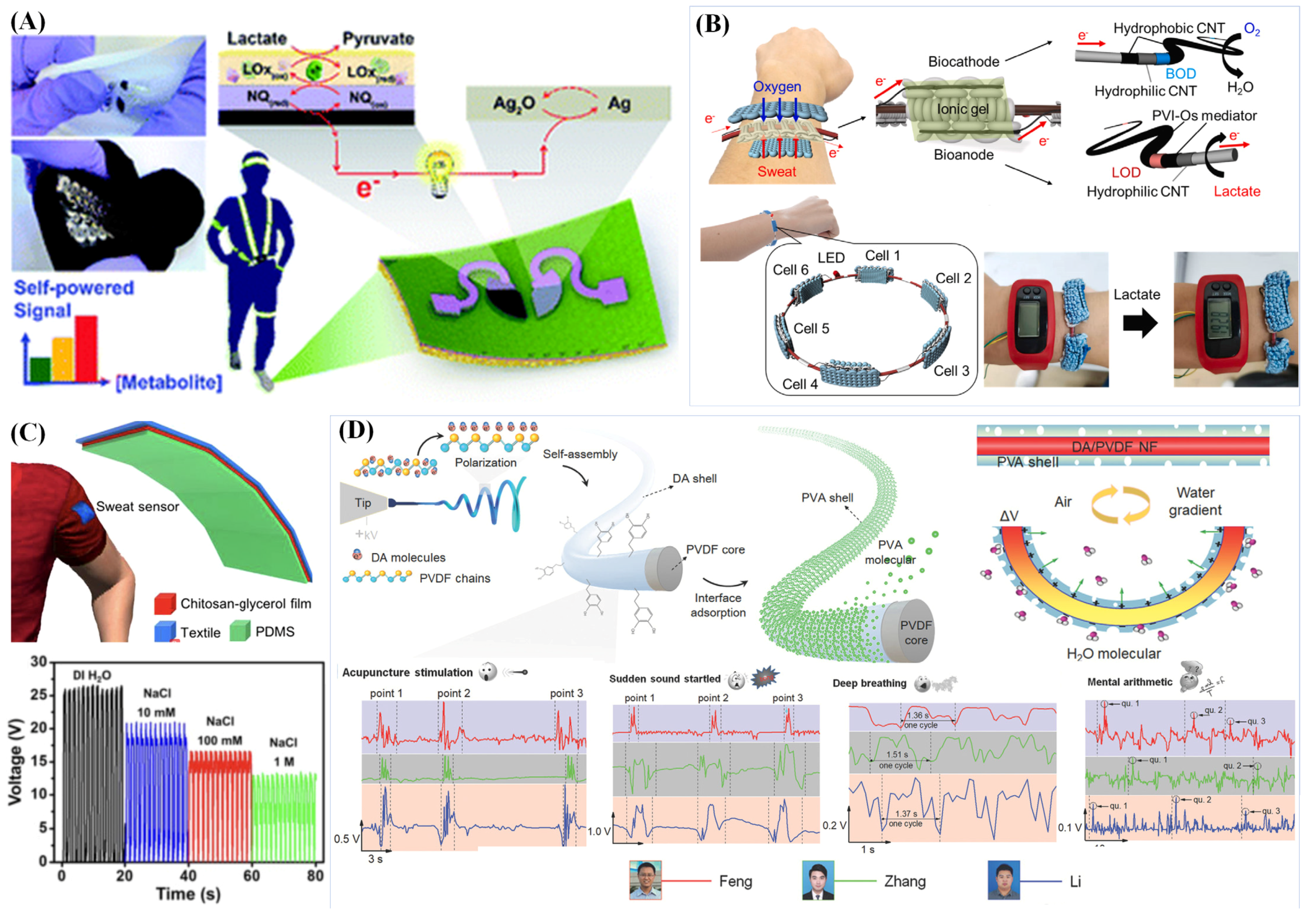
4.4. Glucose- and Lactate-Sensing Devices
4.5. Other Sweat-Biomarker-Sensing Devices
4.6. Sweat Self-Powered Batteries
| Analyte | Sensing Element | Substrate | Preparation Method | Detection Method | Test Range | Sensitivity | Limit of Detection | Flexible | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sweat quantity, saline concentration | - | Cotton textile as sweat collector | Screen-printed Gr-doped carbon paste electrodes | Impedance, capacitive | 0–300 μL, 0–100 mM | - | - | - | [11] |
| Sweat quantity | Conductive threads | Cotton cover | Braiding | Conductive | 0–80 mg | 0.0063–0.2856 V/mg | - | 0–90° bending | [19] |
| Lactate, Na+ | ZnO NWs, LOx electrode, ion-selective electrode | Cotton threads | Weaving | Potentiometric | 0–25 mM (lactate), 0.1–100 mM (Na+) | - | 3.61 mM (lactate, 0.16 mM (Na+) | - | [18] |
| K+ | PAN/PVP/Valinomycin-nylon sheath–core-structured yarns | Polyester yarns | Weaving | Potentiometric | 1 × 10−5–2 × 10−1 M | 34.7 mV/dec | 1 × 10−5 M | - | [45] |
| Cl−, PH | Ag/AgCl (Cl−), PEDOT: BTB (pH) | PEDOT: PSS physical deposition on cotton threads | Electrodeposition | Electrochemically gated | 10–150 mM (Cl−), 4–7 (PH) | (167 ± 3) 10−3 dec−1, (13 ± 1) 10−3 pH unit−1 | - | - | [56] |
| pH, Cl−, glucose | pH indicator, HgSO4/FeSO4(Cl−), GOx(glucose) | Dyed cotton fabric | Embroidering | Colorimetric, RGB value | 4.0–9.0, 10–150 mM (chloride), 10–2000 μM (glucose) | - | 10 mM, 10 μM | - | [62] |
| pH, lactate | BCG and MO (PH), LOx | Knitted cotton fabrics, NaCMC, CTAB, CS | Screen-printing | Colorimetric | 0–14 (PH), 0–25 mM (lactate) | - | - | - | [22] |
| pH | PANI | PU | Coaxial ES | Chronopotentiometry | 2–7 | 60 mV/pH | - | 122% stretching, 250° twisting or bending | [111] |
| pH | IrO2 | Stainless-steel mesh | Electrodeposition | Potentiometric | 4–8 | −47.54 mV/pH | - | Good flexible | [95] |
| pH | Au, 4-MBA | PU nanofiber | ES, sputtering | Surface-enhanced Raman scattering | 5.5–7.0 | ∼0.14–0.33 pH resolution | - | 50% strain | [1] |
| Glucose | Cu2O | Cellulose paper, hand printed graphene paste electrodes | Drop casting | Voltammetric | 0.1 to 1 mM | 182.9 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 52.7 | - | [119] |
| Glucose | Au | Carbon cloth | Electrodeposition | Amperometric | 1–2164 μM | 25.391 μA mM−1 (<114μM), 20.609 μA mM−1 cm−2 (>114 μM) | 0.78 μM | - | [12] |
| Lactate | PPy | MWCNT | Electrodeposition | Chronoamperometric | 51 μM–27.7 mM | 2.9 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 51 µM | - | [122] |
| Lactate | GOx PB/Au/AuNWs-SEBS | Latex rubber core yarn covered with nylon | Electrodeposition | Chronoamperometric | 0–500 μM | 11.7 μA mM−1 cm−2 | 0 | 200% strain | [39] |
| Cortisol | ZnO nanorods | Conductive carbon yarns | Sputtering, growth | Voltammetric | 1 fg/mL–1 μg/mL | 2.12 μA/(g mL−1) | 0.098 fg/mL | - | [36] |
5. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, M.; Skinner, W.H.; Robert, C.; Campbell, C.J.; Rossi, R.M.; Koutsos, V.; Radacsi, N. Fabrication of a Wearable Flexible Sweat pH Sensor Based on SERS-Active Au/TPU Electrospun Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 51504–51518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, R.; Yang, D.S.; Kim, J.; Mansour, A.; Wright, J.A., Jr.; Model, J.B.; Wright, D.E.; Rogers, J.A.; Ray, T.R. State of Sweat: Emerging Wearable Systems for Real-Time, Noninvasive Sweat Sensing and Analytics. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.B. Physiology of sweat gland function: The roles of sweating and sweat composition in human health. Temperature 2019, 6, 211–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, B.; Jiang, K.; Wang, L.; Shen, G. Wearable Sweat Loss Measuring Devices: From the Role of Sweat Loss to Advanced Mechanisms and Designs. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena-Bravo, A.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Sweat: A sample with limited present applications and promising future in metabolomics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 90, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, K.; Martin, A.; Terstegen, L.; Biel, S.S. A short history of sweat gland biology. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2007, 29, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Jeerapan, I.; Krishnan, S.; Wang, J. Wearable Chemical Sensors: Emerging Systems for On-Body Analytical Chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonner, Z.; Wilder, E.; Heikenfeld, J.; Kasting, G.; Beyette, F.; Swaile, D.; Sherman, F.; Joyce, J.; Hagen, J.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; et al. The microfluidics of the eccrine sweat gland, including biomarker partitioning, transport, and biosensing implications. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 031301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D.; et al. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bariya, M.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Javey, A. Wearable sweat sensors. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Shan, S.S.; Liao, Y.T.; Liao, Y.C. Bio-inspired fractal textile device for rapid sweat collection and monitoring. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2524–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Yuwen, T.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zang, G. Glucose determination behaviour of gold microspheres-electrodeposited carbon cloth flexible electrodes in neutral media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1159, 338442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachoin, J.S.; Weisberg, L.S.; McFadden, C.B. Treatment of lactic acidosis: Appropriate confusion. J. Hosp. Med. 2010, 5, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugo, S.M.; Lu, W.; Robertson, S. A Wearable, Textile-Based Polyacrylate Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for Cortisol Detection in Sweat. Biosensors 2022, 12, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnamon, D.; Ghanta, R.; Lin, K.C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Portable biosensor for monitoring cortisol in low-volume perspired human sweat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Promphet, N.; Ummartyotin, S.; Ngeontae, W.; Puthongkham, P.; Rodthongkum, N. Non-invasive wearable chemical sensors in real-life applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1179, 338643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.M.V.; Rajendran, V.; Mishra, R.K.; Jayaraman, M. Recent advances and perspectives in sweat based wearable electrochemical sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X. A thread-based wearable sweat nanobiosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xu, C.; Pan, S.; Xia, S.; Wei, P.; Noh, H.Y.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, X. Conductive Thread-Based Textile Sensor for Continuous Perspiration Level Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, A.; Kang, D.; Xue, Y.; Lee, S.; Pielak, R.M.; Kim, J.; Hwang, T.; Min, S.; Banks, A.; Bastien, P.; et al. A soft, wearable microfluidic device for the capture, storage, and colorimetric sensing of sweat. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 366ra165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Cao, M.; Kim, K.N.; Lin, M.; Moon, J.-M.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Yu, J.; Liu, R.; Wicker, C.; Trifonov, A.; et al. A stretchable epidermal sweat sensing platform with an integrated printed battery and electrochromic display. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanawaleedirojn, P.; Siralertmukul, K.; Soatthiyanon, N.; Potiyaraj, P.; Thanawattano, C.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Rodthongkum, N. Non-invasive textile based colorimetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of sweat pH and lactate. Talanta 2019, 192, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promphet, N.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Rattanawaleedirojn, P.; Soatthiyanon, N.; Siralertmukul, K.; Potiyaraj, P.; Rodthongkum, N. Cotton thread-based wearable sensor for non-invasive simultaneous diagnosis of diabetes and kidney failure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Z.; Meng, Z.; Shi, C.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.Y. Coupling of Silk Fibroin Nanofibrils Enzymatic Membrane with Ultra-Thin PtNPs/Graphene Film to Acquire Long and Stable On-Skin Sweat Glucose and Lactate Sensing. Small Methods 2021, 5, e2000926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Uppal, N.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Stabilization of Enzymes in Silk Films. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gu, K.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Silk-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Glucose in Sweat. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Jian, M.; Wang, Q.; Xia, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y. Hollow core-sheath nanocarbon spheres grown on carbonized silk fabrics for self-supported and nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11856–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Reddy, V.S.; Chinnappan, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Xu, L. Electrospun Micro/Nanofiber with Various Structures and Functions for Wearable Physical Sensors. Polym. Rev. 2022, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharramzadeh, F.; Zarghami, V.; Mazaheri, M.; Simchi, A. Concurrent electrophoretic deposition of enzyme-laden chitosan/graphene oxide composite films for biosensing. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipińska, W.; Siuzdak, K.; Karczewski, J.; Dołęga, A.; Grochowska, K. Electrochemical glucose sensor based on the glucose oxidase entrapped in chitosan immobilized onto laser-processed Au-Ti electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 330, 129409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, F.; Favaretto, L.; Kovtun, A.; Treossi, E.; Corticelli, F.; Gazzano, M.; Palermo, V.; Zanardi, C.; Melucci, M. Electrochemical sensing of glucose by chitosan modified graphene oxide. J. Phys. Mater. 2020, 3, 014011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. Wearable flexible sweat sensors for healthcare monitoring: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Aksay, I.A.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y. Glucose oxidase-graphene-chitosan modified electrode for direct electrochemistry and glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wen, X.; Wang, L.; Ji, D.; Qin, X.; Yu, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Emerging design principles, materials, and applications for moisture-enabled electric generation. eScience 2022, 2, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, S.; Pei, Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Integrated Smart Janus Textile Bands for Self-Pumping Sweat Sampling and Analysis. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Allen, J.A.; Sriramprabha, R.; Pandiaraj, M.; Shekhar, B.; Ponpandian, N.; Viswanathan, C. ZnO Nanorod Integrated Flexible Carbon Fibers for Sweat Cortisol Detection. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhai, Q.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Cheng, W. Stretchable gold fiber-based wearable textile electrochemical biosensor for lactate monitoring in sweat. Talanta 2021, 222, 121484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, B.S.; Matzeu, G.; Presti, M.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Dry Spun, Bulk-Functionalized rGO Fibers for Textile Integrated Potentiometric Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 7, 2101508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Dong, D.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Shi, Q.; Cheng, W. Highly Stretchable and Strain-Insensitive Fiber-Based Wearable Electrochemical Biosensor to Monitor Glucose in the Sweat. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6569–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Byun, J.H.; Oh, Y.; Jung, B.M.; Cha, H.J.; Seong, D.G.; Um, M.K.; Hyun, S.; Chou, T.W. Highly Sensitive Wearable Textile-Based Humidity Sensor Made of High-Strength, Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Filaments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4788–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarayan, K.; Kim, B. Reversible and universal pH sensing cellulose nanofibers for health monitor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ahmed, A.; Xu, L. High-Throughput Free Surface Electrospinning Using Solution Reservoirs with Different Depths and Its Preparation Mechanism Study. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lillehoj, P.B. Embroidered electrochemical sensors for biomolecular detection. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xu, L.; Ahmed, A. Batch Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Porous Polylactic Acid-Based Nanofiber Membranes for Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Ma, X.; Fan, L.; Xin, J.H.; Yu, H. Weavable, large-scaled, rapid response, long-term stable electrochemical fabric sensor integrated into clothing for monitoring potassium ions in sweat. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Testing and evaluation of wearable electronic textiles and assessment thereof. In Performance Testing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 65–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Dhanjai; Stavrakis, A.K.; Stojanovic, G.M. Textile-based electrochemical sensors and their applications. Talanta 2022, 244, 123425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, B.; Peng, H. Weaving Sensing Fibers into Electrochemical Fabric for Real-Time Health Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, G.M.; Radetić, M.M.; Šaponjić, Z.V.; Radoičić, M.B.; Radovanović, M.R.; Popović, Ž.V.; Vukmirović, S.N. A Textile-Based Microfluidic Platform for the Detection of Cytostatic Drug Concentration in Sweat Samples. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; Mao, Q.; Ma, H. Flexible textile ion sensors based on reduced graphene oxide/fullerene and their potential applications of sweat characterization. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3123–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, C.; Wen, N.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Cong, T.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, Z.; Liu, K.; Pan, L. All-fabric-based multifunctional textile sensor for detection and discrimination of humidity, temperature, and strain stimuli. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 13789–13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Canovas, R.; Jeerapan, I.; Andrade, F.J.; Wang, J. A Textile-Based Stretchable Multi-Ion Potentiometric Sensor. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.R.; Zhou, Y.; Dey, A.A.; Arellano, D.L.G.; Okoroanyanwu, U.; Secor, E.B.; Hersam, M.C.; Morse, J.; Rothstein, J.P.; Carter, K.R.; et al. Printed microfluidic sweat sensing platform for cortisol and glucose detection. Lab Chip 2021, 22, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Das, S. Nanomaterials in thin-film form for new-generation energy storage device applications. In Chemical Solution Synthesis for Materials Design and Thin Film Device Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 561–583. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Kampstra, K.L.; Abidian, M.R. High performance conducting polymer nanofiber biosensors for detection of biomolecules. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4954–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Possanzini, L.; Decataldo, F.; Mariani, F.; Gualandi, I.; Tessarolo, M.; Scavetta, E.; Fraboni, B. Textile sensors platform for the selective and simultaneous detection of chloride ion and pH in sweat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Xue, Y.; Xia, W.; Ray, T.R.; Reeder, J.T.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Kang, D.; Xu, S.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Soft, skin-mounted microfluidic systems for measuring secretory fluidic pressures generated at the surface of the skin by eccrine sweat glands. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2572–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Bae, G.Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.; Chung, S.; Cho, K. Cactus-Spine-Inspired Sweat-Collecting Patch for Fast and Continuous Monitoring of Sweat. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2102740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ho, C.; Slappey, N.; Zhou, Z.; Snelgrove, S.E.; Brown, M.; Grabinski, A.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Miller, K.; et al. A wearable conductivity sensor for wireless real-time sweat monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Xia, Q.; Yu, L.; Lu, Z. A wearable, cotton thread/paper-based microfluidic device coupled with smartphone for sweat glucose sensing. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.W.; Toi, P.T.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Lee, H.B.; Hanif, A.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, N.E. Fully Stretchable Capillary Microfluidics-Integrated Nanoporous Gold Electrochemical Sensor for Wearable Continuous Glucose Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14567–14575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. A thread/fabric-based band as a flexible and wearable microfluidic device for sweat sensing and monitoring. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazalé, A.; Sant, W.; Ginot, F.; Launay, J.C.; Savourey, G.; Revol-Cavalier, F.; Lagarde, J.M.; Heinry, D.; Launay, J.; Temple-Boyer, P. Physiological stress monitoring using sodium ion potentiometric microsensors for sweat analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Fan, C.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Biospired Janus Silk E-Textiles with Wet-Thermal Comfort for Highly Efficient Biofluid Monitoring. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8880–8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiao, G.; Chen, X.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Lu, Z. A thermoresponsive microfluidic system integrating a shape memory polymer-modified textile and a paper-based colorimetric sensor for the detection of glucose in human sweat. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23957–23963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisak, G.; Arnebrant, T.; Ruzgas, T.; Bobacka, J. Textile-based sampling for potentiometric determination of ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 877, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Kong, D. Stretchable and Superwettable Colorimetric Sensing Patch for Epidermal Collection and Analysis of Sweat. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, T.; Zhang, T. Highly stretchable potentiometric ion sensor based on surface strain redistributed fiber for sweat monitoring. Talanta 2020, 214, 120869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shin, J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.H.; Liu, H. Engineering Materials for Electrochemical Sweat Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2008130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppedè, N.; Giannetto, M.; Villani, M.; Lucchini, V.; Battista, E.; Careri, M.; Zappettini, A. Ion selective textile organic electrochemical transistor for wearable sweat monitoring. Org. Electron. 2020, 78, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Jian, M.; Lu, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y. Integrated textile sensor patch for real-time and multiplex sweat analysis. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radwan, A.B.; Paramparambath, S.; Cabibihan, J.J.; Al-Ali, A.K.; Kasak, P.; Shakoor, R.A.; Malik, R.A.; Mansour, S.A.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Superior Non-Invasive Glucose Sensor Using Bimetallic CuNi Nanospecies Coated Mesoporous Carbon. Biosensors 2021, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, A.; Muthukumar, S.; Saini, A.; Prasad, S. Simultaneous lancet-free monitoring of alcohol and glucose from low-volumes of perspired human sweat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrilla, M.; Ortiz-Gómez, I.; Cánovas, R.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A. Wearable Potentiometric Ion Patch for On-Body Electrolyte Monitoring in Sweat: Toward a Validation Strategy to Ensure Physiological Relevance. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8644–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, H.; Fu, J.; Si, H.; Ge, C.; Lin, S. Laser-Induced Graphene-Based Wearable Epidermal Ion-Selective Sensors for Noninvasive Multiplexed Sweat Analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Eom, Y.; Koo, J.M.; Cho, H.W.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, K.G.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Yoo, H.J.; et al. Extremely Fast Self-Healable Bio-Based Supramolecular Polymer for Wearable Real-Time Sweat-Monitoring Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46165–46175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.E.; Totti, S.; Velliou, E.; Campagnolo, P.; Hingley-Wilson, S.M.; Ward, N.I.; Varcoe, J.R.; Crean, C. Development of a novel highly conductive and flexible cotton yarn for wearable pH sensor technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ran, J.; Ma, C.; Yang, B. A Universal Approach to Enhance Glucose Biosensor Performance by Building Blocks of Au Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Oh, D.X.; Cho, H.W.; Lee, K.G.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, J.; Choi, B.G. Highly self-healable and flexible cable-type pH sensors for real-time monitoring of human fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Gutruf, P.; Choi, J.; Lee, K.; Sekine, Y.; Reeder, J.T.; Jeang, W.J.; Aranyosi, A.J.; Lee, S.P.; Model, J.B.; et al. Battery-free, skin-interfaced microfluidicelectronic systems for simultaneous electrochemical, colorimetric, and volumetric analysis of sweat. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirza, O.M.; Mujlid, H.; Manoharan, H.; Selvarajan, S.; Srivastava, G.; Khan, M.A. Mathematical Framework for Wearable Devices in the Internet of Things Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, Y.-T.; Yang, P.-K.; Chiu, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-W.; Choi, D.; Lin, Z.-H. A textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with humidity-resistant output characteristic and its applications in self-powered healthcare sensors. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Yi, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Self-Powered and Self-Functional Cotton Sock Using Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Hybrid Mechanism for Healthcare and Sports Monitoring. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeerapan, I.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Pavinatto, A.; You, J.M.; Wang, J. Stretchable Biofuel Cells as Wearable Textile-based Self-Powered Sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2016, 4, 18342–18353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Gu, Y.; Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Bai, J.; Zhou, M. A flexible and wearable epidermal ethanol biofuel cell for on-body and real-time bioenergy harvesting from human sweat. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Yin, L.; Nathan, A.; Wang, J.; Dahiya, R. Energy Autonomous Sweat-Based Wearable Systems. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoorchian, A.; Kamalabadi, M.; Moradi, M.; Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A.; Bagheri, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Khoshsafar, H. Wearable Potentiometric Sensor Based on Na0.44MnO2 for Non-invasive Monitoring of Sodium Ions in Sweat. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, M.; Colleoni, C.; Guido, E.; Re, V.; Rosace, G. Optical monitoring of sweat pH by a textile fabric wearable sensor based on covalently bonded litmus-3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane coating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.A.; Machado-Moreira, C.A. Regional variations in transepidermal water loss, eccrine sweat gland density, sweat secretion rates and electrolyte composition in resting and exercising humans. Extrem. Physiol. Med. 2013, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Qiao, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L. Wearable Sensor for Continuous Sweat Biomarker Monitoring. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Manjakkal, L.; Navaraj, W.T.; Lorenzelli, L.; Vinciguerra, V.; Dahiya, R. Stretchable wireless system for sweat pH monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasiński, A.; Urbanowicz, M.; Guziński, M.; Bocheńska, M. Potentiometric Solid-Contact Multisensor System for Simultaneous Measurement of Several Ions. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinovart, T.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Windmiller, J.R.; Andrade, F.J.; Wang, J. A potentiometric tattoo sensor for monitoring ammonium in sweat. Analyst 2013, 138, 7031–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olart, O.; Chilo, J.e.; Pelegri-Sebastia, J.e.; Barb´e, K.; Moer, W.V. Glucose detection in human sweat using an electronic nose. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1462–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, M.L.; Dominguez, J.M.; Trujillo, R.M.; Goy, C.B.; Sánchez, M.A.; Madrid, R.E. Potentiometric textile-based pH sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legner, C.; Kalwa, U.; Patel, V.; Chesmore, A.; Pandey, S. Sweat sensing in the smart wearables era: Towards integrative, multifunctional and body-compliant perspiration analysis. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 296, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Alberkant, J. Flexible molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for cortisol monitoring in sweat. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xing, S.; Fang, Z.; Li, R.; Koo, H.; Pan, T. Wearable microfluidics: Fabric-based digital droplet flowmetry for perspiration analysis. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, M.; Oudebrouckx, G.; Bormans, S.; Veske, P.; Thoelen, R.; Deferme, W. Monitoring Body Fluids in Textiles: Combining Impedance and Thermal Principles in a Printed, Wearable, and Washable Sensor. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhai, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Umar, M.; Ji, C.; Chen, Z.; Jin, L.; et al. Coolmax/graphene-oxide functionalized textile humidity sensor with ultrafast response for human activities monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, P.; Di Francesco, F.; Costanzo, D.; Ferrari, C.; Trivella, M.G.; De Rossi, D. A Wearable Sensor for Measuring Sweat Rate. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1557–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, M.S.; Kim, S.J.; Park, H.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeong, J.M.; Choi, B.G. Highly Stretchable Sensor Based on Fluid Dynamics-Assisted Graphene Inks for Real-Time Monitoring of Sweat. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 48072–48080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanc, M.; Sophocleous, M.; Atkinson, J.K.; Garcia-Breijo, E. The effect on performance of fabrication parameter variations of thick-film screen printed silver/silver chloride potentiometric reference electrodes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.J.; Galloway, S.D.R.; Nimmo, M.A. Variations in regional sweat composition in normal human males. Exp. Physiol. 2000, 85, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, P. Polyelectrolytes. In Comprehensive Polymer Science and Supplements; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Schueren, L.; De Clerck, K. Coloration and application of pH-sensitive dyes on textile materials. Color. Technol. 2012, 128, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Abu Ali, O.A.; Saleh, D.I.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Khattab, T.A. Preparation of green and sustainable colorimetric cotton assay using natural anthocyanins for sweat sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.S.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Ajarem, J.S.; Maodaa, S.N.; Allam, A.A.; Khattab, T.A. Development of colorimetric cotton swab using molecular switching hydrazone probe in calcium alginate. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1216, 128301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schueren, L.; De Meyer, T.; Steyaert, I.; Ceylan, O.; Hemelsoet, K.; Van Speybroeck, V.; De Clerck, K. Polycaprolactone and polycaprolactone/chitosan nanofibres functionalised with the pH-sensitive dye Nitrazine Yellow. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yapor, J.P.; Alharby, A.; Gentry-Weeks, C.; Reynolds, M.M.; Alam, A.; Li, Y.V. Polydiacetylene Nanofiber Composites as a Colorimetric Sensor Responding To Escherichia coli and pH. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7334–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Coaxial electrospun flexible PANI//PU fibers as highly sensitive pH wearable sensor. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16033–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jihong, M.; You, Y.; Haobin, W.; Yiran, Y.; Haixia, Z.; Wei, G. Wireless battery-free wearable sweat sensor powered by human motion. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9842. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.-Y.; Li, S.; Song, Y.; Tam, K.C. Novel ultrasonic-coating technology to design robust, highly sensitive and wearable textile sensors with conductive nanocelluloses. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, J.; Wilson, D.; Finkelshtein, I.; Wong, B.; Potts, R. Correlation between sweat glucose and blood glucose in subjects with diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, G.; Önder, S.; Göcek, İ.; Trabzon, L.; Kızıl, H.; Kök, F.N.; Kayaoğlu, B.K. Microfluidic device on a nonwoven fabric: A potential biosensor for lactate detection. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1729–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.K.; Huang, T.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yuen, M.M.F.; Gao, Z. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for Wearable Sweat Monitoring: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 14522–14539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hong, Y.J.; Baik, S.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Enzyme-Based Glucose Sensor: From Invasive to Wearable Device. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jena, B.K.; Raj, C.R. Enzyme-free amperometric sensing of glucose by using gold nanoparticles. Chemistry 2006, 12, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, F.F.; Hogg, R.A.; Manjakkal, L. Cu2O-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Non-Invasive and Portable Glucose Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Y.; Qi, Y. Study on the oriented self-assembly of cuprous oxide micro-nano cubes and its application as a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 211, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gui, M.; Asif, M.; Yu, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Xiao, F.; Liu, H. A facile modular approach to the 2D oriented assembly MOF electrode for non-enzymatic sweat biosensors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6629–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Lim, H.; Lee, H.N.; Park, Y.M.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.J. Selective Nonenzymatic Amperometric Detection of Lactic Acid in Human Sweat Utilizing a Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube (MWCNT)-Polypyrrole Core-Shell Nanowire. Biosensors 2020, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Sriramprabha, R.; Sekhar, P.K.; Bhansali, S.; Ponpandian, N.; Pandiaraj, M.; Viswanathan, C. Review-Towards Wearable Sensor Platforms for the Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 067508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Pandiaraj, M.; Bhansali, S.; Ponpandian, N.; Viswanathan, C. Carbon fiber based electrochemical sensor for sweat cortisol measurement. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manickam, P.; Madhu, S.; Fernandez, R.E.; Viswanathan, C.; Bhansali, S. Fabric Based Wearable Biosensor for Continuous Monitoring of Steroids. ECS Trans. 2017, 77, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Wearable biosensor for sensitive detection of uric acid in artificial sweat enabled by a fiber structured sensing interface. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, J.S.; Wojcik, M.H. Transdermal Alcohol Measurement: A Review of the Literature. Can. Soc. Forensic Sci. J. 2006, 39, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamella, M.; Campuzano, S.; Manso, J.; Gonzalez de Rivera, G.; Lopez-Colino, F.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarron, J.M. A novel non-invasive electrochemical biosensing device for in situ determination of the alcohol content in blood by monitoring ethanol in sweat. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 806, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscay, J.; Findlay, E.; Dennany, L. Electrochemical monitoring of alcohol in sweat. Talanta 2021, 224, 121815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirlanci, M.; Rosen, I.G.; Wall, T.L.; Luczak, S.E. Applying a novel population-based model approach to estimating breath alcohol concentration (BrAC) from transdermal alcohol concentration (TAC) biosensor data. Alcohol 2019, 81, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Wearable and flexible electronics for continuous molecular monitoring. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1465–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Liu, X.; Kaji, T.; Nishina, Y.; Miyake, T. Fiber-crafted biofuel cell bracelet for wearable electronics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Yue, W.; Zhou, W.; Shen, G. Perception-to-Cognition Tactile Sensing Based on Artificial-Intelligence-Motivated Human Full-Skin Bionic Electronic Skin. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2202622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingcheng, L.; Reddy, V.S.; Jayathilaka, W.; Chinnappan, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ghosh, R. Intelligent Polymers, Fibers and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Ju, J.; Lu, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, G.; Sun, W.; Li, C.M.; et al. A Weavable and Scalable Cotton-Yarn-Based Battery Activated by Human Sweat for Textile Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Jin, F.; Qu, M.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, T.; Dong, W.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.; Feng, Z.Q. Power Generation from Moisture Fluctuations Using Polyvinyl Alcohol-Wrapped Dopamine/Polyvinylidene Difluoride Nanofibers. Small 2021, 17, e2102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Methods | Mechanism | Advantages | Drawbacks | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical detection | An analytical signal is generated through a recognition element coupled with an electrochemical transducer, providing information about the analyte concentration. | High selectivity, high accuracy and high efficiency. | Ion-selective electrodes, two or three electrodes are required, power is needed calibration is required. | Ion sensing, lactate, glucose, alcohol | [17,18] |
| Conductive detection |
| No need for a reference electrode. | For EIS measurement, the information needs to be transformed according to the impedance spectrum. | Sweat quantity, ion concentration, cortisol | [11,15,19] |
| Colorimetric detection | The content of a substance determined by the color depth of the chromogenic reaction. | Convenient andwithout external power supply | Low accuracy, long reaction time, contrasting colors or graphics captured by users. | pH value, lactate, glucose, alcohol | [20,21,22] |
| Components | Relative Range | Diagnosis Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average sweat rate | 0.72–3.65 mg cm−2 min−1 | Dehydration | [89] |
| Na+ | 10–100 mM | Heat stress, hyponatremia, cystic fibrosis | [17,87,90] |
| K+ | 1–24 mM | Hypokalemia, irregular heartbeat and arrhythmia | [45] |
| Cl− | 10–100 mM | Hyper/hypo chloremia, cystic fibrosis | [62,90,91] |
| Ca2+ | 0.2–0.7 mM | Renal disorder, hypocalcemia | [92] |
| NH4+ | 0.1–1 mM | Metabolic breakdown of proteins | [93] |
| Glucose | 0.02–0.6 mM | Diabetes, blood glucose | [72,94] |
| Lactate | 5–25 mM | Muscle soreness, pain, cramp | [37] |
| PH | 4–7 | Hydration, dermatitis, ichthyosis, fungal infections | [1,95,96] |
| Cortisol | 8–50 ng/mL | Pressure, post-traumatic-stress disorder, bipolar disorder, irritable bowel syndrome | [97] |
| Urea | 2–10 mM | Uraemia indicating renal dysfunction | [91] |
| Ethanol | 2.5–22.5 mM | Hypoglycemia, drinking driver | [73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Li, J.; Reddy, V.S.; Ji, D.; Ramakrishna, S.; Xu, L. Flexible Textile-Based Sweat Sensors for Wearable Applications. Biosensors 2023, 13, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010127
Yin J, Li J, Reddy VS, Ji D, Ramakrishna S, Xu L. Flexible Textile-Based Sweat Sensors for Wearable Applications. Biosensors. 2023; 13(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jing, Jingcheng Li, Vundrala Sumedha Reddy, Dongxiao Ji, Seeram Ramakrishna, and Lan Xu. 2023. "Flexible Textile-Based Sweat Sensors for Wearable Applications" Biosensors 13, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010127
APA StyleYin, J., Li, J., Reddy, V. S., Ji, D., Ramakrishna, S., & Xu, L. (2023). Flexible Textile-Based Sweat Sensors for Wearable Applications. Biosensors, 13(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010127








