Label-Free, Portable, and Color-Indicating Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Test Kit for Acute Myocardial Infarction by Spectral Analysis and Naked-Eye Observation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
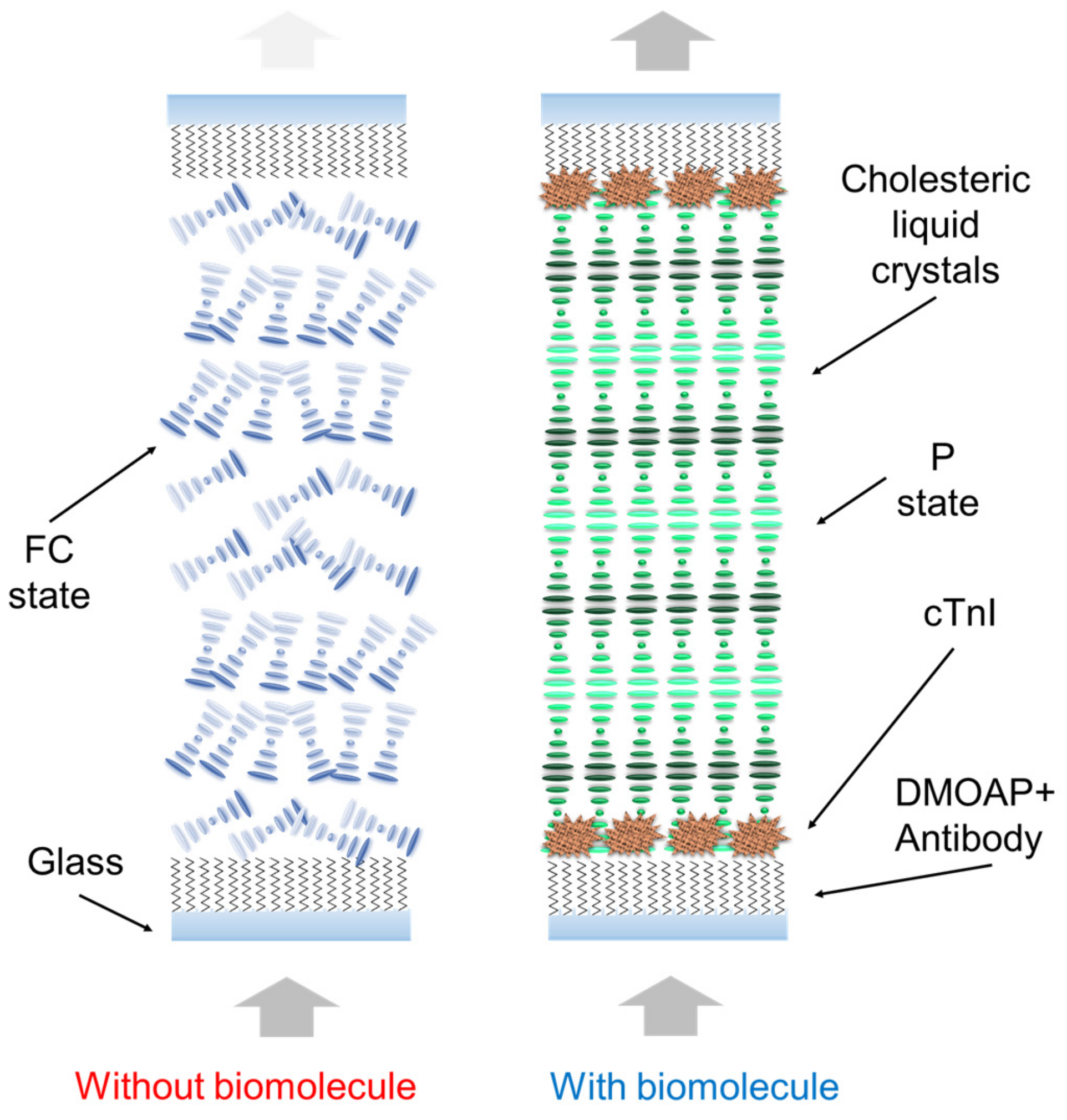
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westfall, M.; Rust, E.; Metzger, J.; Westfall, M.V.; Rust, E.M.; Metzger, J.M. Slow skeletal troponin I gene transfer, expression, and myofilament incorporation enhances adult cardiac myocyte contractile function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5444–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramirez-Correa, G.A.; Murphy, A.M. Is phospholamban or troponin I the “prima donna” in beta-adrenergic induced lusitropy? Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 326–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eggers, K.; Lind, L.; Ahlström, H.; Bjerner, T.; Barbier, C.E.; Larsson, A.; Venge, P.; Lindahl, B. Prevalence and pathophysiological mechanisms of elevated cardiac troponin I levels in a population-based sample of elderly subjects. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeddinghaus, J.; Twerenbold, R.; Nestelberger, T.; Badertscher, P.; Wildi, K.; Puelacher, C.; de Lavallaz, J.F.; Keser, E.; Giménez, M.R.; Wussler, D. Clinical validation of a novel high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I assay for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippi, G.; Favaloro, E.; Kavsak, P. Measurement of High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin in Pulmonary Embolism: Useful Test or a Clinical Distraction, Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 784–792. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, L.; Martinez, E.; Faraday, N.; Dorman, T.; Fleisher, L.; Perler, B.; Williams, G.; Chan, D.; Pronovost, P. Cardiac troponin I predicts short-term mortality in vascular surgery patients. Circulation 2002, 106, 2366–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavsak, P.; MacRae, A.; Yerna, M.; Jaffe, A. Analytic and clinical utility of a next-generation, highly sensitive cardiac troponin I assay for early detection of myocardial injury. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melanson, S.; Morrow, D.; Jarolim, P. Earlier detection of myocardial injury in a preliminary evaluation using a new troponin I assay with improved sensitivity. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 128, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labugger, R.; Organ, L.; Collier, C.; Atar, D.; Van Eyk, J. Extensive troponin I and T modification detected in serum from patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2000, 102, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, T.; Zeller, T.; Ojeda, F.; Tzikas, S.; Lillpopp, L.; Sinning, C.; Wild, P.; Genth-Zotz, S.; Warnholtz, A.; Giannitsis, E.; et al. Serial changes in highly sensitive troponin I assay and early diagnosis of myocardial infarction. JAMA 2011, 306, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zethelius, B.; Johnston, N.; Venge, P. Troponin I as a predictor of coronary heart disease and mortality in 70-year-old men: A community-based cohort study. Circulation 2006, 113, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Lowenthal, M.; Cole, K.; Bunk, D.; Wang, L. An immunoprecipitation coupled with fluorescent Western blot analysis for the characterization of a model secondary serum cardiac troponin I reference material. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, F.; Collinson, P. Analytical characteristics of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burklund, A.; Tadimety, A.; Nie, Y.; Hao, N.; Zhang, J.X. Advances in diagnostic microfluidics. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 95, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apple, F.; Pearce, L.; Smith, S.; Kaczmarek, J.; Murakami, M. Role of monitoring changes in sensitive cardiac troponin I assay results for early diagnosis of myocardial infarction and prediction of risk of adverse events. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Wen, X. Rapid identification of falsely elevated serum cardiac troponin I values in a stat laboratory. Lab. Med. 2014, 45, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Takahashi, R.; Hiura, Y.; Hirokawa, G.; Fukushima, Y.; Iwai, N. Plasma miR-208 as a biomarker of myocardial injury. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Tian, S.; Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. A sensitive and quantitative prognosis of C-reactive protein at picogram level using mesoporous silica encapsulated core-shell up-conversion nanoparticle based lateral flow strip assay. Talanta 2021, 230, 122335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Tian, S.; Liu, K.; Ni, J.; Zhao, M.; Kang, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. 5G-enabled ultra-sensitive fluorescence sensor for proactive prognosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Paek, E.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Paek, S. Chemiluminometric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA)-on-a-chip biosensor based on cross-flow chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imazio, M.; Demichelis, B.; Cecchi, E.; Belli, R.; Ghisio, A.; Bobbio, M.; Trinchero, R. Cardiac troponin I in acute pericarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Y.; Bian, Z.-P.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.-J. PDMS gold nanoparticle composite film-based silver enhanced colorimetric detection of cardiac troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cropek, D.; West, A.; Banta, S. Development of a troponin I biosensor using a peptide obtained through phage display. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8235–8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; He, M.; Ma, J.; Tang, W.; Gao, G.; He, R.; Su, H.; Cui, D. Phase and size controllable synthesis of NaYbF4 nanocrystals in oleic acid/ionic liquid two-phase system for targeted fluorescent imaging of gastric cancer. Theranostics 2013, 3, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, E.-Y.; Huang, W.-H.; Hyo, T.-L.; Wang, P.-C.; Hsiao, Y.-C. IR-inspired visual display/response device fabricated using photothermal liquid crystals for medical and display applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 429, 132213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-Y.; Lu, W.-F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liao, M.-Y.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Y.-J.; Chuang, E.-Y.; Yu, J. Keratin-Based Nanoparticles with Tumor-Targeting and Cascade Catalytic Capabilities for the Combinational Oxidation Phototherapy of Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 38074–38089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Martin, S. Enantioselective cholesteric liquid crystalline membranes characterized using nonchiral HPLC with circular dichroism detection. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dischinger, S.; Rosenblum, J.; Noble, R.; Gin, D.; Linden, K. Application of a lyotropic liquid crystal nanofiltration membrane for hydraulic fracturing flowback water: Selectivity and implications for treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Guo, Y.; Qi, L.; Hu, Q.; Yu, L. Highly sensitive and label-free detection of catalase by a H2O2-responsive liquid crystal sensing platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.; Jang, C.-H. Detection of arginase through the optical behaviour of liquid crystals due to the pH-dependent adsorption of stearic acid at the aqueous/liquid crystal interface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, J.; Pan, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, A.; Jiang, Z. A novel small molecular liquid crystal catalytic amplification-nanogold SPR aptamer absorption assay for trace oxytetracycline. Talanta 2021, 233, 122528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Huo, W.; Yang, D.; Luan, C.; Xu, J. Label-free liquid crystal immunosensor for detection of HBD-2. Talanta 2019, 203, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnouf, T.; Chen, C.-H.; Tan, S.-J.; Tseng, C.-L.; Lu, K.-Y.; Chang, L.-H.; Nyambat, B.; Huang, S.-C.; Jheng, P.-R.; Aditya, R. A bioinspired hyperthermic macrophage-based polypyrrole-polyethylenimine (Ppy-PEI) nanocomplex carrier to prevent and disrupt thrombotic fibrin clots. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, F.; Liou, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Hong, Z.; Lin, J.; Hsiao, Y. Label-Free Multi-Microfluidic Immunoassays with Liquid Crystals on Polydimethylsiloxane Biosensing Chips. Polymers 2020, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Luh, H.; Hsiao, Y. Label-Free, Color-Indicating, Polarizer-Free Dye-Doped Liquid Crystal Microfluidic Polydimethylsiloxane Biosensing Chips for Detecting Albumin. Polymers 2021, 13, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.; Tang, C.; Lee, W. Fast-switching bistable cholesteric intensity modulator. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9744–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, C.; Zyryanov, V.; Lee, W. Electro-optical device based on photonic structure with a dual-frequency cholesteric liquid crystal. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 2632–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.; Hou, C.; Zyryanov, V.; Lee, W. Multichannel photonic devices based on tristable polymer-stabilized cholesteric textures. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 23952–23957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-C.; Zou, Y.-H.; Timofeev, I.; Zyryanov, V.; Lee, W. Spectral modulation of a bistable liquid-crystal photonic structure by the polarization effect. Opt. Mater. Express 2013, 3, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.; Sung, Y.; Lee, M.; Lee, W. Highly sensitive color-indicating and quantitative biosensor based on cholesteric liquid crystal. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 5033–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luh, H.-T.; Chung, Y.-W.; Cho, P.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-C. Label-Free Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Biosensing Chips for Heme Oxygenase-1 Detection within Cerebrospinal Fluid as an Effective Outcome Indicator for Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Biosensors 2022, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, F.-L.; Shang, L.-D.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, B.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-C. Label-Free, Portable, and Color-Indicating Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Test Kit for Acute Myocardial Infarction by Spectral Analysis and Naked-Eye Observation. Biosensors 2023, 13, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010060
Chen F-L, Shang L-D, Lin Y-C, Chang B-Y, Hsiao Y-C. Label-Free, Portable, and Color-Indicating Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Test Kit for Acute Myocardial Infarction by Spectral Analysis and Naked-Eye Observation. Biosensors. 2023; 13(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Fu-Lun, Li-Dan Shang, Yen-Chung Lin, Bo-Yen Chang, and Yu-Cheng Hsiao. 2023. "Label-Free, Portable, and Color-Indicating Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Test Kit for Acute Myocardial Infarction by Spectral Analysis and Naked-Eye Observation" Biosensors 13, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010060
APA StyleChen, F.-L., Shang, L.-D., Lin, Y.-C., Chang, B.-Y., & Hsiao, Y.-C. (2023). Label-Free, Portable, and Color-Indicating Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Test Kit for Acute Myocardial Infarction by Spectral Analysis and Naked-Eye Observation. Biosensors, 13(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010060




