Role of Wearable Sensing Technology to Manage Long COVID
Abstract
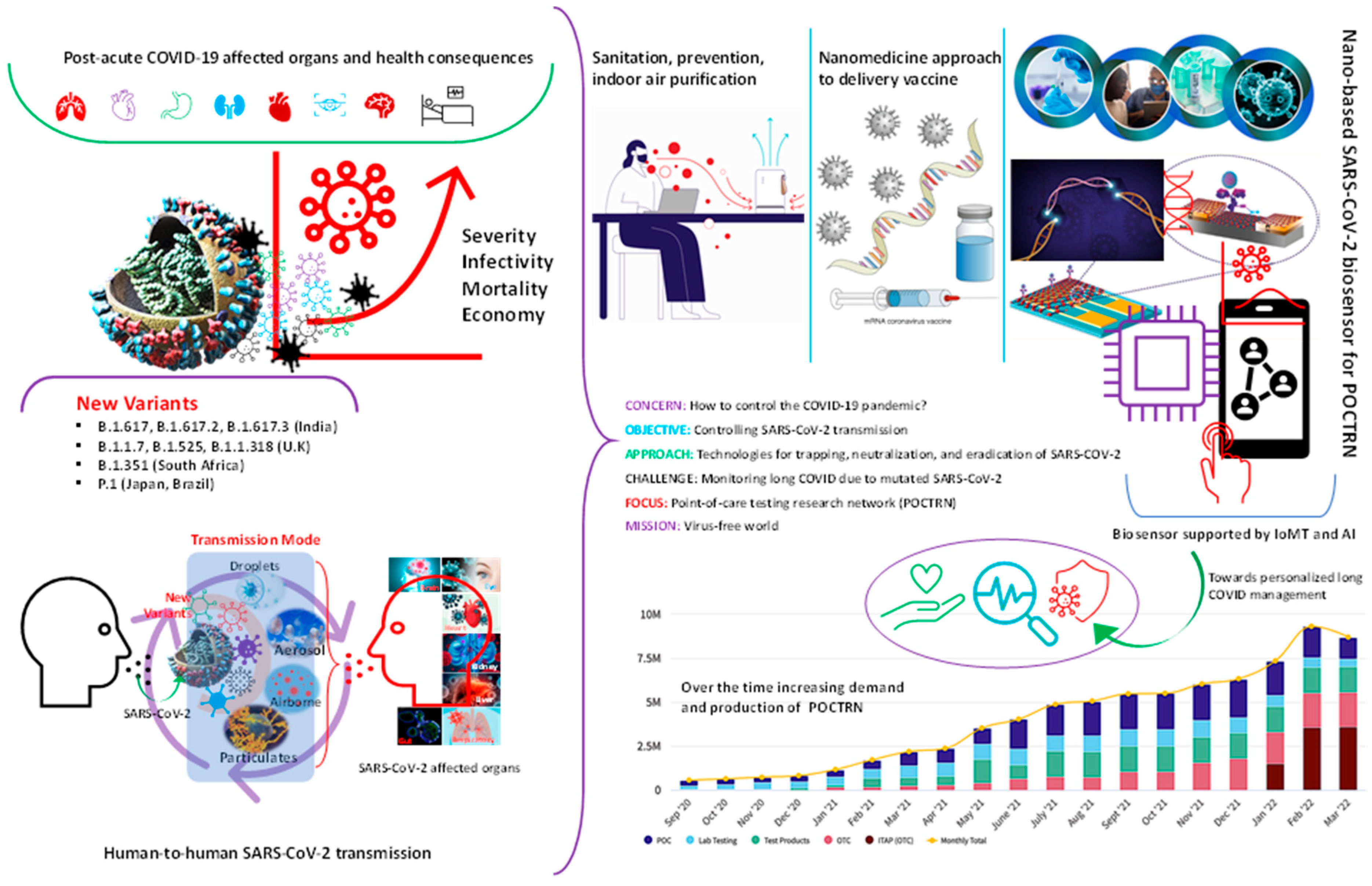
:1. Introduction
2. What Are Post-COVID Ailments?
3. Clinical Challenges Associated with Long COVID
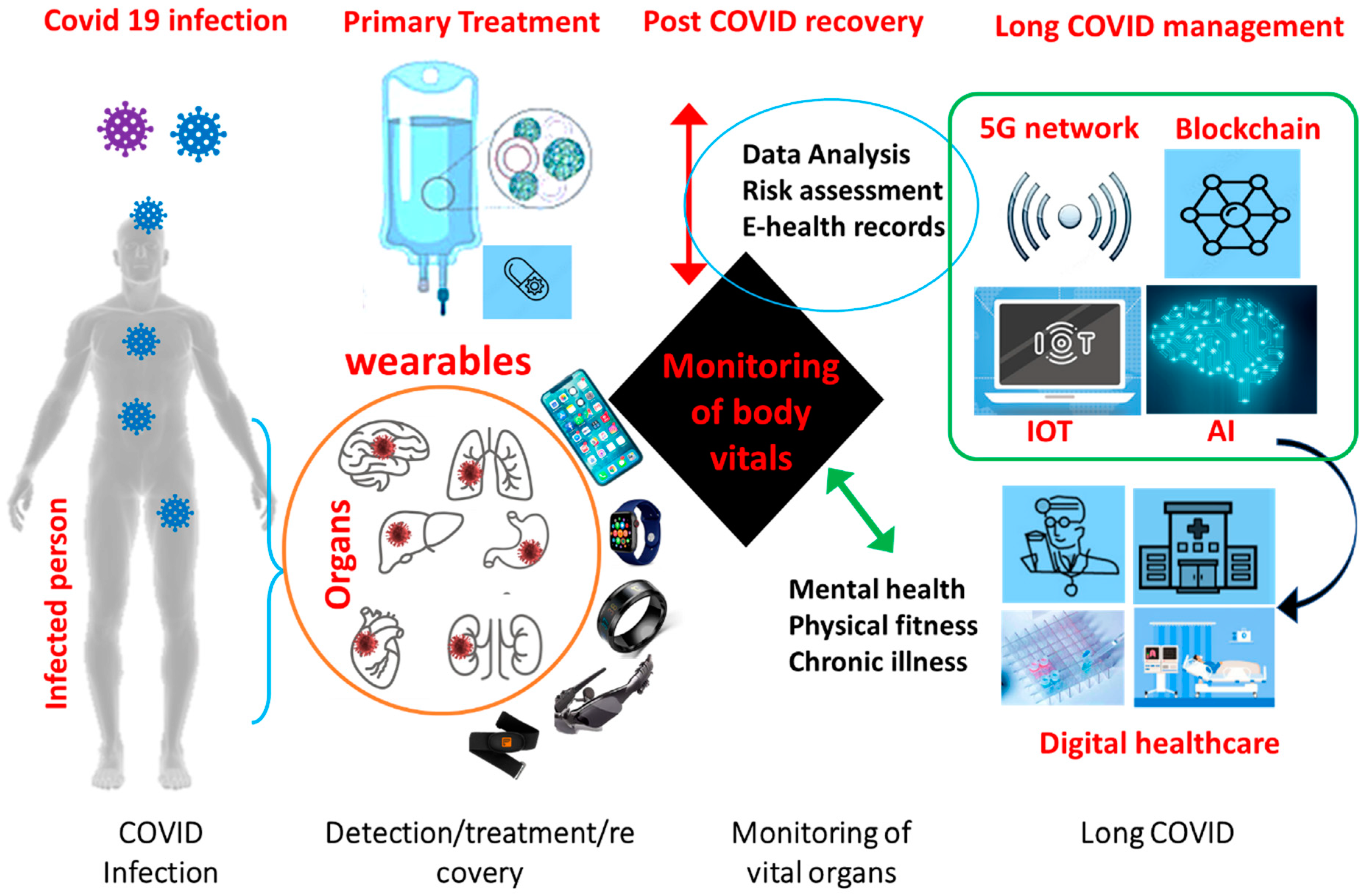
4. Digital Biomarker and Wearable Sensors
5. How Wearable Sensor Can Manage Long COVID?
Commercial Wearable Sensors
6. Discussion
7. Challenge of Connecting Wearable Sensors for Long COVID Management
8. Conclusions and Viewpoint
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sudre, C.H.; Murray, B.; Varsavsky, T.; Graham, M.S.; Penfold, R.S.; Bowyer, R.C.; Pujol, J.C.; Klaser, K.; Antonelli, M.; Canas, L.S. Attributes and predictors of long COVID. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soga, M.; Evans, M.J.; Cox, D.T.; Gaston, K.J. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on human–nature interactions: Pathways, evidence and implications. People Nat. 2021, 3, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya, J.-M.; Rojas, M.; Salinas, M.L.; Rodríguez, Y.; Roa, G.; Lozano, M.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, M.; Montoya, N.; Zapata, E.; Monsalve, D.M. Post-COVID syndrome. A case series and comprehensive review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, E.; Dubey, A.K.; Teodori, L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kaushik, A. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: A next phase of the COVID-19 pandemic and a call to arms for system sciences and precision medicine. MedComm 2022, 3, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Juneja, S.; Ghosal, A.; Bandara, N.; Khan, R.; Wallen, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kaushik, A. Antibacterial and antiviral high-performance nano-systems to mitigate new SARS-CoV-2 variants of concerns. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 21, 100363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawska, M.; Mostafavi, E.; Kaushik, A. SARS-CoV-2 getting into the brain; neurological phenotype of COVID-19, and management by nano-biotechnology. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, A.; Jayadevan, R.; Sashidharan, S. Long COVID: An overview. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, H.; Raza, S.; Nowell, J.; Young, M.; Edison, P. Long covid—Mechanisms, risk factors, and management. BMJ 2021, 374, n1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherusseri, J.; Savio, C.M.; Khalid, M.; Chaudhary, V.; Numan, A.; Varma, S.J.; Menon, A.; Kaushik, A. SARS-CoV-2-on-Chip for Long COVID Management. Biosensors 2022, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Dubey, A.K.; Ganguly, A.; Bhattacharya, B.; Mishra, Y.K.; Mostafavi, E.; Kaushik, A. State-of-art high-performance Nano-systems for mutated coronavirus infection management: From Lab to Clinic. OpenNano 2022, 8, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, M.; Lai, C.-L. Long COVID-19 syndrome: A comprehensive review of its effect on various organ systems and recommendation on rehabilitation plans. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehandru, S.; Merad, M. Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Khanna, V.; Awan, H.T.A.; Singh, K.; Khalid, M.; Mishra, Y.; Bhansali, S.; Li, C.-Z.; Kaushik, A. Towards hospital-on-chip supported by 2D MXenes-based 5th generation intelligent biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 220, 114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, V.; Kaushik, A.K.; Furukawa, H.; Khosla, A. Towards 5th generation ai and iot driven sustainable intelligent sensors based on 2d mxenes and borophene. ECS Sens. Plus 2022, 1, 013601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, M.; Dirksen, A.; Taraborrelli, P.; Torocastro, M.; Panagopoulos, D.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B. Autonomic dysfunction in ‘long COVID’: Rationale, physiology and management strategies. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.M.; Zake, L.G.; El Kady, N.K. Role of Chest Computed Tomography versus Real Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction for Diagnosis of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2021, 2021, 8798575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saiegh, F.; Ghosh, R.; Leibold, A.; Avery, M.B.; Schmidt, R.F.; Theofanis, T.; Mouchtouris, N.; Philipp, L.; Peiper, S.C.; Wang, Z.-X. Status of SARS-CoV-2 in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with COVID-19 and stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, Y.M.; Abdelmajid, Y.; Al Madani, A.A.R. Cerebrospinal fluid confirmed COVID-19-associated encephalitis treated successfully. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2020, 13, e237378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral flow assays for viruses diagnosis: Up-to-date technology and future prospects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, T.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Chang, H.-F.; Tsai, C.-H.; Wu, H.-T.; Lin, C.-S. Development and efficacy of lateral flow point-of-Care testing devices for rapid and mass COVID-19 diagnosis by the detections of SARS-CoV-2 antigen and anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighe, K.; Moitra, P.; Alafeef, M.; Gunaseelan, N.; Pan, D. A rapid RNA extraction-free lateral flow assay for molecular point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2 augmented by chemical probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 200, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbani, A.V.; Pulakuntla, S.; Pannuru, P.; Aramgam, S.; Badri, K.R.; Reddy, V.D. COVID-19: Comprehensive review on mutations and current vaccines. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, P.; Sanfilippo, T.; Guggino, R.; Scalisi, L.; Monastero, R.; Baschi, R.; Mandalà, V.; San Biagio, L.; Rizzo, M.; Giacomazza, D. Neurological Consequences, Mental Health, Physical Care, and Appropriate Nutrition in Long-COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrott, B.; Head, R.; Pringle, K.G.; Lumbers, E.R.; Martin, J.H. “LONG COVID”—A hypothesis for understanding the biological basis and pharmacological treatment strategy. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2022, 10, e00911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Mostafavi, E. To manage long COVID by selective SARS-CoV-2 infection biosensing. Innovation 2022, 3, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, A.; Bogu, G.K.; Wang, M.; Rangan, E.S.; Brooks, A.W.; Wang, Q.; Higgs, E.; Celli, A.; Mishra, T.; Metwally, A.A. Real-time alerting system for COVID-19 using wearable data. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, M.; Radin, J.M.; Baca-Motes, K.; Ramos, E.; Kheterpal, V.; Topol, E.J.; Steinhubl, S.R.; Quer, G. Passive detection of COVID-19 with wearable sensors and explainable machine learning algorithms. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routen, A.; O’Mahoney, L.; Ayoubkhani, D.; Banerjee, A.; Brightling, C.; Calvert, M.; Chaturvedi, N.; Diamond, I.; Eggo, R.; Elliott, P. Understanding and tracking the impact of long COVID in the United Kingdom. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Koh, G.C.H.; Car, J. Covid-19: A remote assessment in primary care. BMJ 2020, 368, m1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, K.K.; Dey, S.; Wuethrich, A.; Wang, J.; Behren, A.; Antaw, F.; Wang, Y.; Sina, A.A.I.; Trau, M. In Situ single cell proteomics reveals circulating tumor cell heterogeneity during treatment. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11231–11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khondakar, K.R.; Dey, S.; Wuethrich, A.; Sina, A.A.I.; Trau, M. Toward Personalized Cancer Treatment: From Diagnostics to Therapy Monitoring in Miniaturized Electrohydrodynamic Systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, K.K.; Ali, M.A.; Singh, M.K.; Agrawal, V.V.; Biradar, A. Amperometric enzymatic determination of bisphenol A using an ITO electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide and Mn3O4 nanoparticles in a chitosan matrix. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil Reza, K.; Wang, J.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Dey, S.; Wang, Y.; Trau, M. Electrohydrodynamic-induced SERS immunoassay for extensive multiplexed biomarker sensing. Small 2017, 13, 1602902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, K.K.; Ali, M.A.; Srivastava, S.; Agrawal, V.V.; Biradar, A. Tyrosinase conjugated reduced graphene oxide based biointerface for bisphenol A sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, K.K.; Singh, N.; Yadav, S.K.; Singh, M.K.; Biradar, A. Pearl shaped highly sensitive Mn3O4 nanocomposite interface for biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, D.R.; Davies, E.V.; Harlow, E.R.; Hsu, J.J.; Knighton, S.C.; Walker, T.A.; Voos, J.E.; Drummond, C.K. Wearable Sensors for COVID-19: A Call to Action to Harness Our Digital Infrastructure for Remote Patient Monitoring and Virtual Assessments. Front. Digit. Health 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassantabar, S.; Stefano, N.; Ghanakota, V.; Ferrari, A.; Nicola, G.N.; Bruno, R.; Marino, I.R.; Jha, N.K. CovidDeep: SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Test Based on Wearable Medical Sensors and Efficient Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Wang, J. Non-invasive wearable electrochemical sensors: A review. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Wang, J. Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Su, R.; Teng, L.; Tian, Q.; Han, F.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, R.; Li, G.; Liu, X. Recent advances in flexible and wearable sensors for monitoring chemical molecules. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1653–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Dao, D.V.; Mitsubayashi, K. Biosensors and Chemical Sensors for Healthcare Monitoring: A Review. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 17, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jeerapan, I.; Wang, J. Wearable chemical sensors: Present challenges and future prospects. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Wang, M.; Gao, W. The era of digital health: A review of portable and wearable affinity biosensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, P.P.; Forkan, A.R.M.; Morshed, A.; Haghighi, P.D.; Kang, Y.B. Healthcare 4.0: A review of frontiers in digital health. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 10, e1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quer, G.; Radin, J.M.; Gadaleta, M.; Baca-Motes, K.; Ariniello, L.; Ramos, E.; Kheterpal, V.; Topol, E.J.; Steinhubl, S.R. Wearable sensor data and self-reported symptoms for COVID-19 detection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Rogers, J.A.; Xu, S. Continuous on-body sensing for the COVID-19 pandemic: Gaps and opportunities. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, J.A.; Liu, C.; Kotzen, K.; Tsutsui, K.; Corino, V.D.; Singh, J.; Pimentel, M.A.; Warrick, P.; Zaunseder, S.; Andreotti, F. Remote health diagnosis and monitoring in the time of COVID-19. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 10TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, R.R.; Rock, M.A.; Vasilevsky, N.; Carmody, L.; Rando, H.; Anzalone, A.J.; Basson, M.D.; Bennett, T.D.; Bergquist, T.; Boudreau, E.A. Characterizing long COVID: Deep phenotype of a complex condition. EBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, J.; Löfström, E.; Malmborg, J.S.; Nygren, J.; Undén, J.; Larsson, I. Patients’ Health Experiences of Post COVID-19 Condition—A Qualitative Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; Kirchner, E.; Calabrese, L.H. Long COVID and rheumatology: Clinical, diagnostic, and therapeutic implications. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Xi, D.; Chen, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhu, L. The mechanism underlying extrapulmonary complications of the coronavirus disease 2019 and its therapeutic implication. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Bose, D.; Nouri-Vaskeh, M.; Tajiknia, V.; Zand, R.; Ghasemi, M. Long-term side effects and lingering symptoms post COVID-19 recovery. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, V.C.; Mohan, A.; Chennabasappa, L.K. Status of mental health and its associated factors among the general populace of India during COVID-19 pandemic. Asia-Pac. Psychiatry 2022, 14, e12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Kuczyńska, K. Psychiatric and neurological complications of long COVID. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 156, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzin-Frankel, J. Long Covid clues emerge from patients’ blood. Science 2022, 377, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Torres-Macho, J.; Velasco-Arribas, M.; Arias-Navalón, J.A.; Guijarro, C.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Canto-Diez, M. Similar prevalence of long-term post-COVID symptoms in patients with asthma: A case-control study. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 237–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunjaya, A.P.; Allida, S.M.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Jenkins, C. Asthma and risk of infection, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality from COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Morales, A.; Tiwari, R.; Sah, R.; Dhama, K. COVID-19, an emerging coronavirus infection: Current scenario and recent developments-an overview. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Deng, Y.; Li, W. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): What we know? J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cossarizza, A.; De Biasi, S.; Guaraldi, G.; Girardis, M.; Mussini, C.; Group, M.C.W. SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19: Cytometry and the new challenge for global health. Cytometry 2020, 97, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.K.; Kim, E.-S.; Mishra, S.; Ganbold, E.; Seong, R.-S.; Kaushik, A.K.; Kim, N.-Y. Ultrasensitive and reusable graphene oxide-modified double-interdigitated capacitive (DIDC) sensing chip for detecting SARS-CoV-2. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3468–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A. Manipulative magnetic nanomedicine: The future of COVID-19 pandemic/endemic therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.K.; Dhau, J.S.; Gohel, H.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kateb, B.; Kim, N.-Y.; Goswami, D.Y. Electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 sensing at point-of-care and artificial intelligence for intelligent COVID-19 management. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7306–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coravos, A.; Khozin, S.; Mandl, K.D. Developing and adopting safe and effective digital biomarkers to improve patient outcomes. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadivand, A.; Gerislioglu, B.; Ramezani, Z.; Kaushik, A.; Manickam, P.; Ghoreishi, S.A. Functionalized terahertz plasmonic metasensors: Femtomolar-level detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujawar, M.A.; Gohel, H.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Srinivasan, S.; Hickman, N.; Kaushik, A. Nano-enabled biosensing systems for intelligent healthcare: Towards COVID-19 management. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Kaushik, A. Exploring nanoselenium to tackle mutated SARS-CoV-2 for efficient COVID-19 management. Front. Nanotechnol. 2022, 4, 1004729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtis, L.C.; Regele, O.B.; Wright, J.M.; Jones, G.B. Digital biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: The mobile/wearable devices opportunity. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.M.; Regele, O.B.; Kourtis, L.C.; Pszenny, S.M.; Sirkar, R.; Kovalchick, C.; Jones, G.B. Evolution of the digital biomarker ecosystem. Digit. Med. 2017, 3, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, B.; Silva, I.; Mehraei, G.; Damiano, R.; Gross, B.; Salvati, E.; Feng, T.; Schneider, J.; Olson, N.; Rizzo, A.G. Real-time infection prediction with wearable physiological monitoring and AI to aid military workforce readiness during COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Nehra, M.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N.; Hu, T.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, A.; Li, C.-Z. Internet of medical things (IoMT)-integrated biosensors for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turakhia, M.P.; Desai, M.; Hedlin, H.; Rajmane, A.; Talati, N.; Ferris, T.; Desai, S.; Nag, D.; Patel, M.; Kowey, P.; et al. Rationale and design of a large-scale, app-based study to identify cardiac arrhythmias using a smartwatch: The Apple Heart Study. Am. Heart J. 2019, 207, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, D.; Olcese, U.; Frumento, P.; Bazzani, A.; Bruno, S.; d’Ascanio, P.; Maestri, M.; Bonanni, E.; Faraguna, U. Heart rate detection by Fitbit ChargeHR™: A validation study versus portable polysomnography. J. Sleep Res. 2021, 30, e13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Marozas, V. Wearable photoplethysmography devices. In Photoplethysmography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 401–439. [Google Scholar]
- Baca, A.; Dabnichki, P.; Hu, C.-W.; Kornfeind, P.; Exel, J. Ubiquitous Computing in Sports and Physical Activity—Recent Trends and Developments. Sensors 2022, 22, 8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kim, J.; Walter, J.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Rogers, J.A. Translational gaps and opportunities for medical wearables in digital health. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirten, R.P.; Danieletto, M.; Tomalin, L.; Choi, K.H.; Zweig, M.; Golden, E.; Kaur, S.; Helmus, D.; Biello, A.; Pyzik, R. Use of physiological data from a wearable device to identify SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms and predict COVID-19 diagnosis: Observational study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e26107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, S.; Daim, T.U. Technology Roadmap: Smartwatches. In Roadmapping Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Imani, S.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Mohan, A.V.; Kumar, R.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Mercier, P.P. A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quaid, M.A.K.; Jalal, A. Wearable sensors based human behavioral pattern recognition using statistical features and reweighted genetic algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 6061–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qi, J.; Fan, S.; Qiao, Z.; Yeo, J.C.; Lim, C.T. Flexible wearable sensors for cardiovascular health monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, T.; Wang, M.; Metwally, A.A.; Bogu, G.K.; Brooks, A.W.; Bahmani, A.; Alavi, A.; Celli, A.; Higgs, E.; Dagan-Rosenfeld, O. Pre-symptomatic detection of COVID-19 from smartwatch data. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerry, R.G.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Kumari, S.; Maurya, G.K.; Patra, S.; Panigrahi, B.; Majhi, S.; Rout, J.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Das, G. A comprehensive review on the applications of nano-biosensor-based approaches for non-communicable and communicable disease detection. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 3576–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bag, S.; Mandal, D. Overview of Biosensors and Its Application in Health Care. In Next Generation Smart Nano-Bio-Devices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bustos-López, M.; Cruz-Ramírez, N.; Guerra-Hernández, A.; Sánchez-Morales, L.N.; Cruz-Ramos, N.A.; Alor-Hernández, G. Wearables for Engagement Detection in Learning Environments: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaklauskas, A.; Abraham, A.; Milevicius, V. Diurnal emotions, valence and the coronavirus lockdown analysis in public spaces. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 98, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parab, J.; Lanjewar, M.; Pinto, C.; Sequeira, M.; Naik, G. COVID-19 Patient Remote Health Monitoring System Using IoT. In Convergence of Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ucak, S.; Dissanayake, H.U.; Sutherland, K.; de Chazal, P.; Cistulli, P.A. Heart rate variability and obstructive sleep apnea: Current perspectives and novel technologies. J. Sleep Res. 2021, 30, e13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, G.; Postolache, O.; Martín, F.F. A Practical Approach to Health Status Monitoring Based on Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Messina, Italy, 22–24 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, D.; Zulkernine, F.; Masroor, R.; Rasool, R.; Jaffar, N. Measuring heart rate and heart rate variability with smartphone camera. In Proceedings of the 2021 22nd IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–18 June 2021; pp. 248–249. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, A.; Su, H.-W.; Heneghan, C. Assessment of physiological signs associated with COVID-19 measured using wearable devices. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, A.H.; Alam, F.; Roychoudhury, S.; Umasankar, Y.; Pala, N.; Bhansali, S. Prospects and Challenges of Volatile Organic Compound Sensors in Human Healthcare. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1246–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Bai, O. A fast, efficient domain adaptation technique for cross-domain electroencephalography (EEG)-based emotion recognition. Sensors 2017, 17, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, B.; Broza, Y.Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gui, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Multiplexed nanomaterial-based sensor array for detection of COVID-19 in exhaled breath. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12125–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ali, S.; Bermak, A. Recent developments in printing flexible and wearable sensing electronics for healthcare applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.J.; Roach, G.D.; Lastella, M.; Scanlan, A.T.; Bellenger, C.R.; Halson, S.L.; Sargent, C. A validation study of a commercial wearable device to automatically detect and estimate sleep. Biosensors 2021, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, S.; Rades, T.; Rantanen, J.; Scherließ, R. Additive Manufacturing in respiratory sciences-current applications and future prospects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, P.; Mariappan, S.A.; Murugesan, S.M.; Hansda, S.; Kaushik, A.; Shinde, R.; Thipperudraswamy, S.P. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare. Biosensors 2022, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, J.; Hao, Y.; Mao, S.; Hwang, K. A 5G cognitive system for healthcare. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2017, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, M.; Cheema, M.A.; Cheema, O.; Li, H.; Lu, H. Impact of COVID-19 on IoT adoption in healthcare, smart homes, smart buildings, smart cities, transportation and industrial IoT. Sensors 2021, 21, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Wearable | Type | O2 Level | Heart Rate | Respiratory Rate | Temperature | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple watch | Wrist | yes | Yes | yes | no | ECG |
| Fitbit | Wrist | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Sleep |
| Oura | Ring | no | Yes | yes | yes | Sleep |
| Hexoskin | Shirt | yes | Yes | yes | no | Sleep |
| Whoop | Arm/wrist | no | Yes | yes | yes | Sleep |
| BioIntelliSense | Patch | no | Yes | yes | yes | Sleep, coughing |
| Garmin | Wrist | yes | Yes | yes | no | sleep |
| Biobeat | Wrist/patch | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Blood pressure, ECG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khondakar, K.R.; Kaushik, A. Role of Wearable Sensing Technology to Manage Long COVID. Biosensors 2023, 13, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010062
Khondakar KR, Kaushik A. Role of Wearable Sensing Technology to Manage Long COVID. Biosensors. 2023; 13(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhondakar, Kamil Reza, and Ajeet Kaushik. 2023. "Role of Wearable Sensing Technology to Manage Long COVID" Biosensors 13, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010062
APA StyleKhondakar, K. R., & Kaushik, A. (2023). Role of Wearable Sensing Technology to Manage Long COVID. Biosensors, 13(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010062






