Quantitative Analysis of Bioluminescence Optical Signal
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Why Do We Have to Quantify the Optical Signal?
2. What Is an Absolute Optical Signal? How Is an Absolute Optical Signal Quantified?
3. Determination of Quantum Yield on Luminescence Reaction
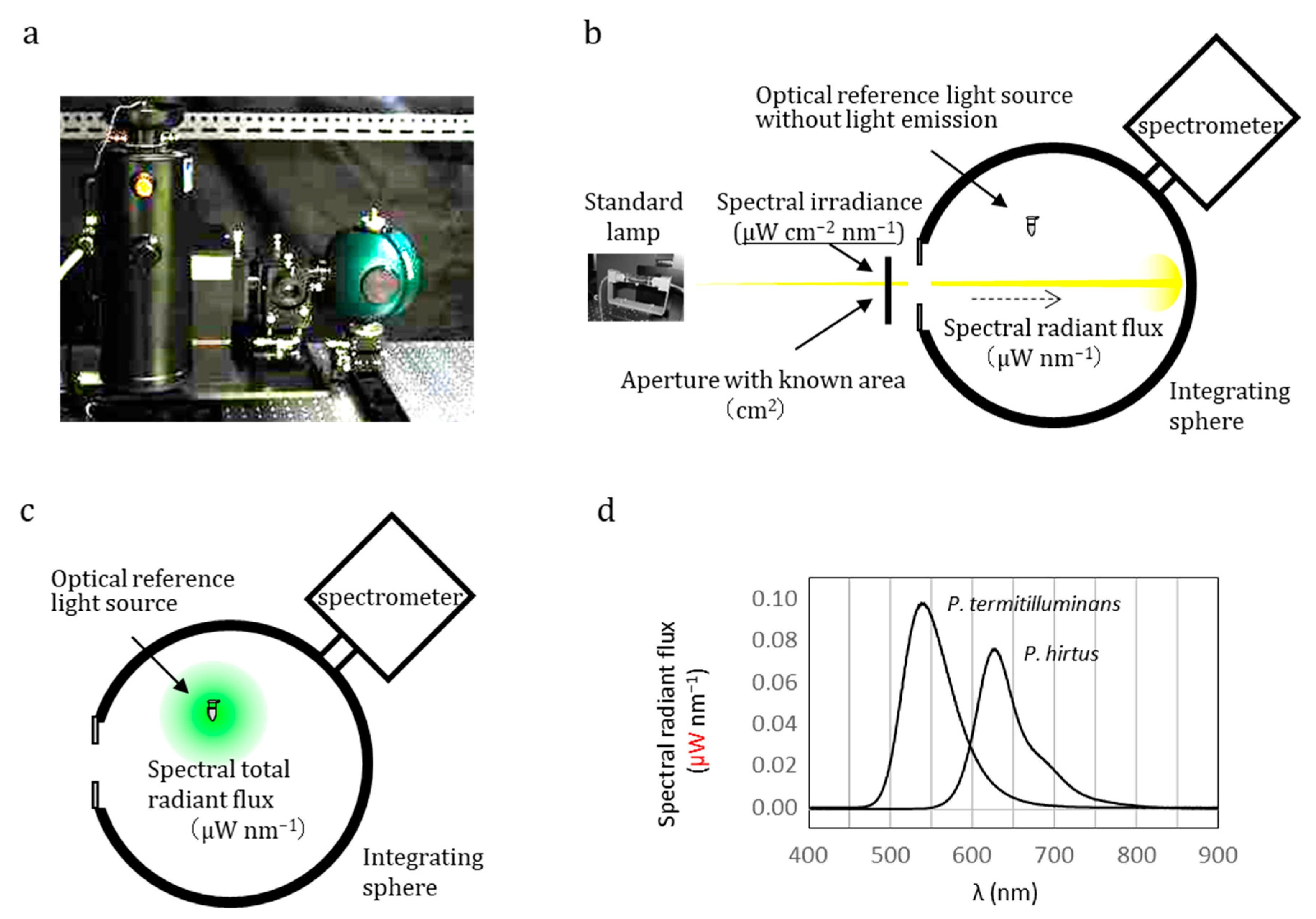
4. Establishing an Ultra-Weak Light Source as an Optical Reference
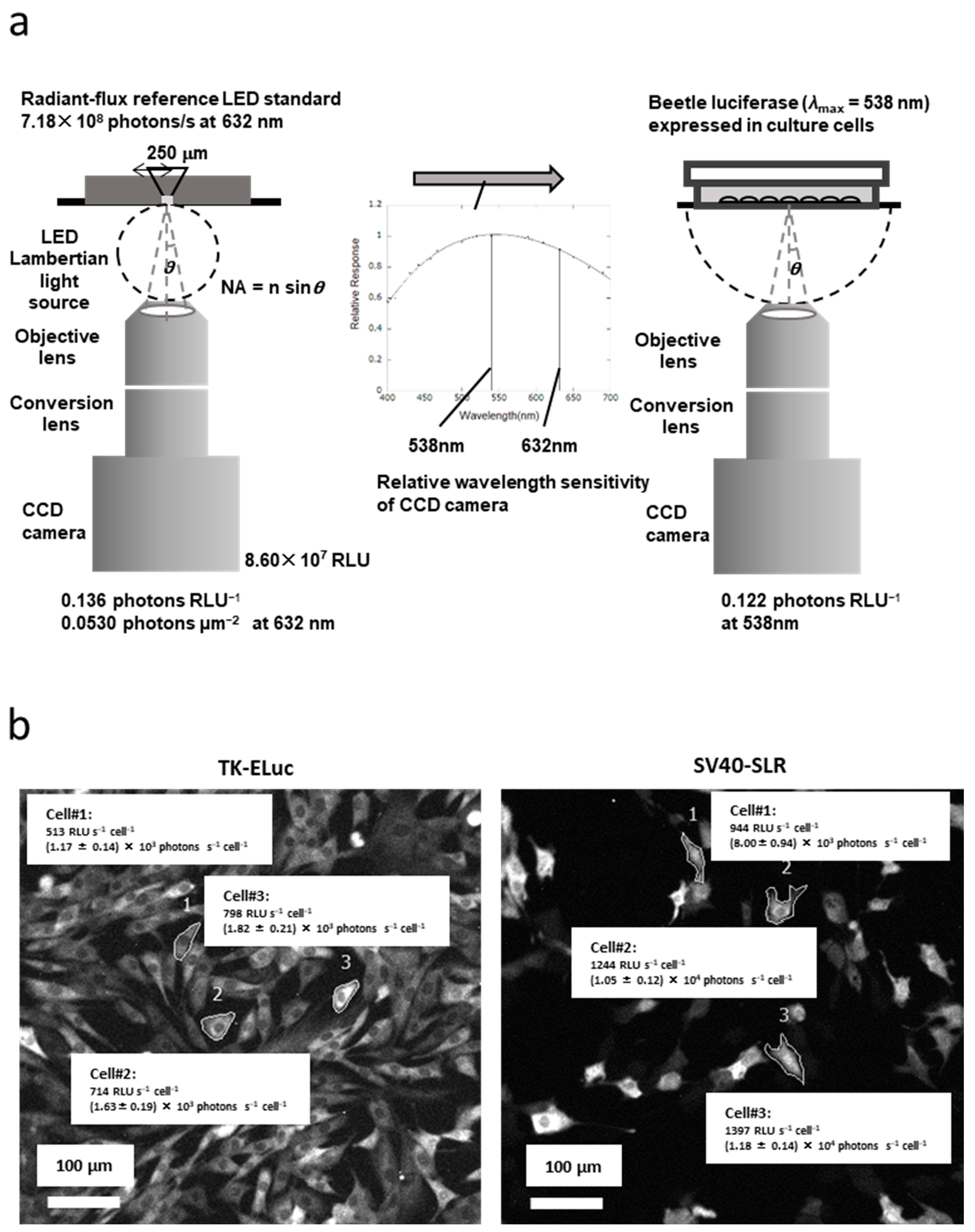
5. Quantification of Bioluminescence Optical Signal from the Living Cells
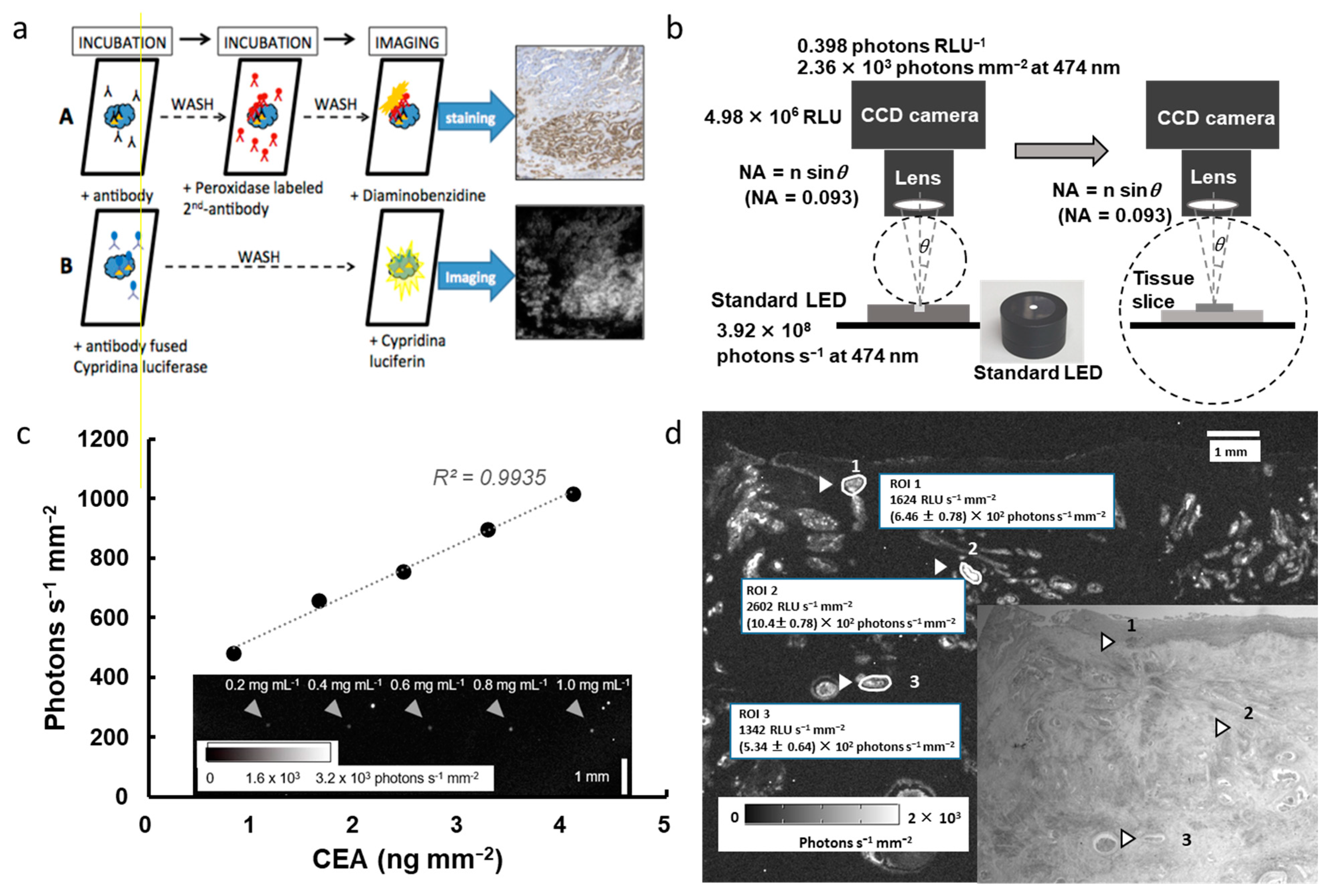
6. Application of Bioluminescent Immunohistochemistry
7. Closing Remark: Open to Quantitative Biology by Quantifying the Optical Light Signal
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimomura, O. Bioluminescence Chemical Principles and Methods; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.; Hastings, J.W. Bioluminescence: Living Lights, Lights for Living; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, A.J.; Anderson, J.C. Applications of bioluminescence in biotechnology and beyond. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5668–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Spying on cancer: Molecular imaging in vivo with genetically encoded reporters. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y.; Ohmiya, Y. Bioluminescence assays: Multicolor luciferase assay, secreted luciferase assay and imaging luciferase assay. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Guardigli, M. Analytical chemiluminescence and bioluminescence: Latest achievements and new horizons. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Class, B.; Thorne, N.; Aguisanda, F.; Southall, N.; McKew, J.C.; Zheng, W. High-throughput viability assay using an autonomously bioluminescent cell line with a bacterial Lux reporter. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmiya, Y. Simultaneous multicolor luciferase reporter assays for monitoring of multiple genes expressions. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2015, 18, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlobay, A.A.; Kaskova, Z.M.; Yampolsky, I.V. Palette of luciferases: Natural biotools for new applications in biomedicine. Acta Nat. 2020, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabei, Y.; Murotomi, K.; Umeno, A.; Horie, M.; Tsujino, Y.; Masutani, B.; Yoshida, Y.; Nakajima, Y. Antioxidant properties of 5-hydroxy-4-phenyl-butenolide via activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, P.; Kawano, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Van Griensven, L.J.L.D.; Miyazaki, K. Novel and stable dual-color IL-6 and IL-10 reporters derived from RAW 264.7 for anti-inflammation screening of natural products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Fujimura, C.; Aiba, S. The modified IL-8 Luc assay, an in vitro skin sensitisation test, can significantly improve the false-negative judgment of lipophilic sensitizers with logKow values > 3.5. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakuri, S.; Yamakage, K.; Kazuki, Y.; Kazuki, K.; Oshimura, M.; Aburatani, S.; Yasunaga, M.; Nakajima, Y. Correlation between luminescence intensity and cytotoxicity in cell-based cytotoxicity assay using luciferase. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 522, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watthaisong, P.; Kamutira, P.; Kesornpun, C.; Pongsupasa, V.; Phonbuppha, J.; Tinikul, R.; Maenpuen, S.; Wongnate, T.; Nishihara, R.; Ohmiya, Y.; et al. Luciferin synthesis and pesticide detection by luminescence Enzymatic cascades. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202116908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehemtulla, A.; Stegman, L.D.; Cardozo, S.J.; Gupta, S.; Hall, D.E.; Contag, C.H.; Ross, B.D. Rapid and quantitative assessment of cancer treatment response using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, H.; Kwon, H.J.; Ozaki, M.; Yasuda, K.; Honma, K.; Ohmiya, Y. In vivo bioluminescence imaging of bone marrow-derived cells in brain inflammation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, N.; Haga, S.; Ohmiya, Y.; Ozaki, M. Long-term ex vivo and in vivo monitoring of tumor progression by using dual luciferases. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 497, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Sato, M.; Ohmiya, Y. In vivo simultaneous analysis of gene expression by dual-color luciferases in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trube, G.; Lopez, J.R.; Taylor, S.R. Calcium transients in asymmetrically activated skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys. J. 1981, 36, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikantha, T.; Klapach, A.; Lorenz, W.W.; Tsai, L.K.; Laughlin, L.A.; Gorman, J.A.; Soll, D.R. The sea pansy Renilla reniformis luciferase serves as a sensitive bioluminescent reporter for differential gene expression in Candida albicans. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Ohmiya, Y. Single-cell imaging with fluorescent protein excited by luciferin-luciferase reaction. Nat. Methods 2007, 8, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurdinger, T.; Badr, C.; Pike, L.; de Kleine, R.; Weissleder, R.; Breakefield, X.O.; Tannous, B.A. A secreted luciferase for ex-vivo monitoring of in vivo processes. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neefjes, M.; Housmans, B.A.C.; van den Akker, G.G.H.; van Rhijn, L.W.; Welting, T.J.M.; van der Kraan, P.M. Reporter gene comparison demonstrates interference of complex body fluids with secreted luciferase activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, E.M.; Nagata, S.; Tsuji, F.I. Vargula hilgendorfii luciferase: A secreted reporter enzyme for monitoring gene expression in mammalian cells. Gene 1990, 96, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.; Ohmiya, Y.; Toya, Y.; Tsuji, F.I. Imaging of luciferase secretion from transformed Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9584–9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamagishi, K.; Enomoto, T.; Ohmiya, Y. cDNA cloning and characterization of a secreted luciferase from the luminous Japanese ostracod, Cypridina noctiluca. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjou, N.; Nagao, A.; Ohmiya, Y.; Ohgiya, S. Yeast mutant with efficient secretion identified by a novel secretory reporter, Cluc. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Mino, K.; Akimoto, H.; Kawabata, M.; Nakamura, K.; Ozaki, M.; Ohmiya, Y. In vivo far-red luminescence imaging of a biomarker based on BRET from Cypridina bioluminescence to an organic dye. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15599–15603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Enomoto, T.; Takahashi, M.; Honma, S.; Honma, K.; Ohmiya, Y. Multichannel perfusion culture bioluminescence reporter system for long-term detection in living cells. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 402, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroz, M.A.; Zurita, J.; Moroz, A.; Nikolov, E.; Likar, Y.; Dobrenkov, K.; Lee, J.; Shenker, L.; Blasberg, R.; Serganova, I.; et al. Introducing a new reporter gene, membrane-anchored Cypridina luciferase, for multiplex bioluminescence imaging. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 21, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Kawasaki, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Ohgiya, S.; Ohmiya, Y. Preparation of biotinylated Cypridina luciferase and its use in bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Irie, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Ohmiya, Y. A bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay for prostaglandin E(2) using Cypridina luciferase. Luminescence 2009, 24, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, K.; Ichino, Y.; Ohmiya, Y. Quantum yield measurements of firefly bioluminescence reactions using a commercial luminometer. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, H.H.; McElroy, W.D. Quantum yield in the oxidation of firefly luciferin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1959, 1, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, F.H.; Shimomura, O.; Saiga, Y.; Gershman, L.C.; Reynolds, G.T.; Waters, J.R. Quantum efficiency of Cypridina luminescence, with a note on that of Aequorea. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 1962, 60, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Seliger, H.H. Absolute spectral sensitivity of phototubes and the application to the measurement of the absolute quantum yields of chemiluminescence and bioluminescence. Photochem. Photobiol. 1965, 4, 1015–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, D.J.; Ahmad, M.; Matheson, I.B.C.; Lee, J. Absolute calibration of luminometers with low-level light standards. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 305, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O.; Johnson, F.H. Properties of the bioluminescent protein aequorin. Biochemistry 1969, 8, 3991–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O.; Johnson, F.H. Calcium binding, quantum yield, and emitting molecule in aequorin bioluminescence. Nature 1970, 227, 1356–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, O. Isolation and properties of various molecular forms of aequorin. Biochem. J. 1986, 234, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loening, A.M.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Gambhir, S.S. A red-shifted Renilla luciferase for transient reporter-gene expression. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.H.; McCapra, F.; Field, G.F.; McElroy, W.D. The Structure and Synthesis of Firefly Luciferin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 2402–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.H.; McCapra, F.; Field, G.F. The structure and synthesis of firefly luciferin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviani, V.R. The origin, diversity, and structure function relationships of insect luciferases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1833–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Niwa, K.; Yamada, N.; Enomoto, T.; Irie, T.; Kubota, H.; Ohmiya, Y.; Akiyama, H. Firefly bioluminescence quantum yield and colour change by pH-sensitive green emission. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Niwa, K.; Yamada, N.; Irie, T.; Enomoto, T.; Kubota, H.; Ohmiya, Y.; Akiyama, H. Development of a quantitative bio/chemiluminescence spectrometer determining quantum yields: Re-examination of the aqueous luminol chemiluminescence standard. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, R.; Osawa, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Noguchi, Y.; Kitada, N.; Saito-Moriya, R.; Hirano, T.; Maki, S.A.; Shibata, K.; Akiyama, H.; et al. Quantum yield of near-infrared bioluminescence with firefly luciferin analog: AkaLumine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2023, 434, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, K.; Ichino, Y.; Kumata, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Hiraishi, Y.; Kato, D.; Viviani, V.R.; Ohmiya, Y. Quantum yields and kinetics of the firefly bioluminescence reaction of beetle luciferases. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, R.; Kihara, Y.; Niwa, K.; Mimura, M.; Tomita, S.; Kurita, R. Quantum yield enhancement of firefly bioluminescence with biomolecular condensates. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 13317–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Nishihara, R.; Hiruta, Y.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K.; Niwa, K. Quantitative evaluation of luminescence intensity from enzymatic luminescence reaction of coelenterazine and analogues. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2020, 394, 112459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/FDIS 24421; Biotechnology: Minimum Requirements for Optical Signal Measurements in Photometric Methods for Biological Samples. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Sasaki, A.; Ohmiya, Y. Standardization of luminescence, fluorescence measurements, and light microscopy: Current situation and perspectives. Biophys. Phys. 2022, 19, e190037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshita, M.; Kubota, H.; Shimogawara, M.; Mori, K.; Ohmiya, Y.; Akiyama, H. Light-emitting-diode Lambertian light sources as low-radiant-flux standards applicable to quantitative luminescence-intensity imaging. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 093704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATTO Homepage. Available online: https://www.attoeng.site/ledlightsources (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Wilsbacher, L.D.; Yamazaki, S.; Herzog, E.D.; Song, E.J.; Radcliffe, L.A.; Abe, M.; Block, G.; Spitznagel, E.; Menaker, M.; Takahashi, J.S. Photic and circadian expression of luciferase in mPeriod1-luc transgenic mice in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.K.; Yoo, S.H.; Liu, A.C.; Takahashi, J.S.; Kay, S.A. Bioluminescence imaging of individual fibroblasts reveals persistent, independently phased circadian rhythms of clock gene expression. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 2289–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Ikeda, M.; Ohmiya, Y.; Nakajima, Y. A dual-color luciferase assay system reveals circadian resetting of cultured fibroblasts by co-cultured adrenal glands. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Enomoto, T.; Shimogawara, M.; Yasuda, K.; Nakajima, Y.; Ohmiya, Y. Bioluminescence imaging of dual gene expression at the single-cell level. BioTechniques 2010, 48, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunaga, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Ohmiya, Y. Dual-color bioluminescence imaging assay using green- and red-emitting beetle luciferases at subcellular resolution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5735–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochigi, Y.; Sato, N.; Sahara, T.; Wu, C.; Saito, S.; Irie, T.; Fujibuchi, W.; Goda, T.; Yamaji, R.; Ogawa, M.; et al. Sensitive and Convenient Yeast Reporter Assay for High-Throughput Analysis by Using a Secretory luciferase from Cypridina noctiluca. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5768–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Chang, Y.F.; Horikawa, K.; Hatsugai, N.; Higuchi, Y.; Hashida, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Arai, Y.; Nagai, T. Luminescent proteins for high-speed single-cell and whole-body imaging. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, C.; Pape, J.K.; Gwosch, K.C.; Gilat, T.; Sahl, S.J.; Hell, S.W. Autonomous bioluminescence imaging of single mammalian cells with the bacterial bioluminescence system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26491–26496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, T.; Kubota, H.; Mori, K.; Shimogawara, M.; Yoshita, M.; Ohmiya, Y.; Akiyama, H. Absolute bioluminescence imaging at the single-cell level with a light signal at the Attowatt level. BioTechniques 2018, 64, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coons, A.H.; Creech, H.J.; Jones, R.N. Immunological properties of an antibody containing a fluorescent group. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1941, 47, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrameas, S. Enzyme markers: Their linkage with proteins and use in immuno-histochemistry. Histochem. J. 1972, 4, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A. Technical aspects of immunohistochemistry. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, A.S.Y.; Leong, T.Y.M. Newer developments in immunohistology. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Krusenstjerna-Hafstrøm, R.; Lohse, J.; Petersen, K.H.; Derand, H. A novel quantitative immunohistochemistry method for precise protein measurements directly in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens: Analytical performance measuring HER2. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, K.Y.; Guo, X.; Sato, M.; Ozaki, M.; Shimajiri, S.; Ohmiya, Y.; Sasaguri, Y. Rapid methods of detecting the target molecule in immunohistology using a bioluminescence probe. Luminescence 2013, 28, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, J.; Ono, M.; Honda, K.; Negishi, A.; Ueno, H.; Okusaka, T.; Furuse, J.; Furuta, K.; Sugiyama, E.; Saito, Y.; et al. Survival prediction for pancreatic cancer patients receiving gemcitabine treatment. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.Y.; Wu, C.; Shimajiri, S.; Enomoto, T.; Kubota, H.; Akiyama, H.; Ohmiya, Y. Quantitative immunohistochemistry using an antibody-fused bioluminescent protein. BioTechniques 2020, 69, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Luciferase | λMax † (nm) | QY | ±σ ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrearinus termitilluminans, wild type | 539 | 0.61 | 0.019 |
| Phrixothrix hirtus, wild type | 625 | 0.15 | 0.017 |
| Pyrocoelia miyako, wild type | 554 | 0.45 | 0.055 |
| Pyrocoelia miyako, mutant N230S | 606 | 0.21 | 0.0072 |
| Pyrocoelia miyako, mutant S199T | 559 | 0.48 | 0.056 |
| Pyrocoelia miyako, mutant S200A | 556 | 0.46 | 0.036 |
| Photinus pyralis, native § | 566 | 0.48 | 0.039 |
| Photinus pyralis, recombinant wild type | 560 | 0.45 | 0.055 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niwa, K.; Kubota, H.; Enomoto, T.; Ichino, Y.; Ohmiya, Y. Quantitative Analysis of Bioluminescence Optical Signal. Biosensors 2023, 13, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020223
Niwa K, Kubota H, Enomoto T, Ichino Y, Ohmiya Y. Quantitative Analysis of Bioluminescence Optical Signal. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020223
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiwa, Kazuki, Hidehiro Kubota, Toshiteru Enomoto, Yoshiro Ichino, and Yoshihiro Ohmiya. 2023. "Quantitative Analysis of Bioluminescence Optical Signal" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020223
APA StyleNiwa, K., Kubota, H., Enomoto, T., Ichino, Y., & Ohmiya, Y. (2023). Quantitative Analysis of Bioluminescence Optical Signal. Biosensors, 13(2), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020223






