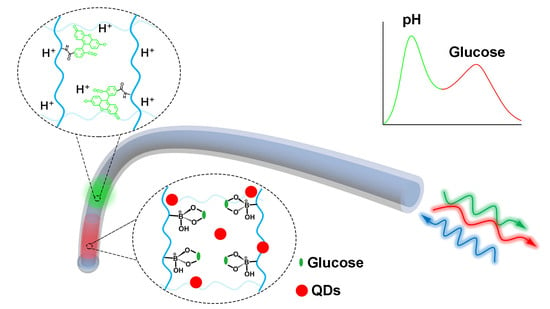
Difunctional Hydrogel Optical Fiber Fluorescence Sensor for Continuous and Simultaneous Monitoring of Glucose and pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of CdTe QDs
2.3. Synthesis of a Fluorescein Derivative
2.4. Fabrication of Difunctional Fluorescent Hydrogel Optical Fiber
2.5. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Fabrication of Fluorophores and Difunctional Fluorescent Hydrogel Optical Fibers and Their Characteristics
3.2. Difunctional Fluorescent Hydrogel Optical Fiber for pH Monitoring
3.3. Difunctional Fluorescent Hydrogel Optical Fibers for Glucose Monitoring
3.4. Difunctional Fluorescent Hydrogel Optical Fibers for Simultaneous Continuous pH and Glucose Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, P.; Salpea, P.; Karuranga, S.; Petersohn, I.; Malanda, B.; Gregg, E.W.; Unwin, N.; Wild, S.H.; Williams, R. Mortality Attributable to Diabetes in 20–79 Years Old Adults, 2019 Estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sehit, E.; Altintas, Z. Significance of Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Glucose Sensors: An Updated Review (2016–2020). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, S.P.; Koh, A.; Storm, W.L.; Shin, J.H.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Biocompatible Materials for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2528–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Jiang, N.; Kazarian, S.G.; Tasoglu, S.; Yetisen, A.K. Optical Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 3, 022004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M.; Beck, R.W.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Dontchev, M.J.; Kollman, C.; Chase, P.; Fox, L.A.; Ruedy, K.J.; Tsalikian, E.; Weinzimer, S.A.; et al. The Accuracy of the FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Children With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, R.L.; Schwartz, S.L.; Brazg, R.L.; Bugler, J.R.; Peyser, T.A.; McGarraugh, G.V. Accuracy of the 5-Day FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durner, J. Clinical Chemistry: Challenges for Analytical Chemistry and the Nanosciences from Medicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 49, 1026–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, A.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Borisov, S.M. Optical Sensing and Imaging of PH Values: Spectroscopies, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12357–12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Jing, N.; Huo, F.; Yin, C. Recent Progress of Organic Small Molecule-Based Fluorescent Probes for Intracellular PH Sensing. Analyst 2021, 146, 7450–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.; Hua Liu, S.; Yin, J. Fluorescent Probes for PH and Alkali Metal Ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrie, S.R.; Coffey, J.W.; Islam, J.; Markey, K.A.; Kendall, M.A.F. Blood, Sweat, and Tears: Developing Clinically Relevant Protein Biosensors for Integrated Body Fluid Analysis. Analyst 2015, 140, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. PH-sensitive Polymers: Classification and Some Fine Potential Applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Dey, T.K.; Nasrin, T.; Khosla, A.; Razeeb, K.M. Review—Nanostructured Materials for Sensing PH: Evolution, Fabrication and Challenges. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 057517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A.M.; Qusti, A.H.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Ultrathin Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets: A Novel Peroxidase Mimetic, Fe Doping-Mediated Catalytic Performance Enhancement and Application to Rapid, Highly Sensitive Optical Detection of Glucose. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical Biosensors: An Exhaustive and Comprehensive Review. Analyst 2020, 145, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Weng, R.; Qiang, T.; Wang, X. Glucose Assay Based on a Fluorescent Multi-Hydroxyl Carbon Dots Reversible Assembly with Phenylboronic Acid Brush Grafted Magnetic Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, W.; Jin, Y.; Wo, F.; Xi, F.; Wu, J. Ratiometric Fluorescent Nanohybrid for Noninvasive and Visual Monitoring of Sweat Glucose. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ji, W.; Chu, S.; Qian, S.; Wang, F.; Masson, J.-F.; Han, X.; Peng, W. Fiber-Optic Surface Plasmon Resonance Glucose Sensor Enhanced with Phenylboronic Acid Modified Au Nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ma, J.; Li, D. A D-Shaped Fiber SPR Sensor with a Composite Nanostructure of MoS2-Graphene for Glucose Detection. Talanta 2020, 219, 121324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lei, M.; Liu, S.-X.; Zhao, Q. Smart Hydrogel-Based Optical Fiber SPR Sensor for PH Measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Glucose Detection through Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1206, 339226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Zhou, Y.; Leblanc, R.M.; Peng, Z. Recent Developments of Carbon Dots in Biosensing: A Review. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2724–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. A Portable Optical Fiber Sensing Platform Based on Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Real-Time PH Detection. Adv. Mater. Inter. 2022, 9, 2101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jang, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, T.S. Fluorescence Sensing of Glucose Using Glucose Oxidase Incorporated into a Fluorophore-Containing PNIPAM Hydrogel. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Du, S.; Liu, B.; Han, M.-Y.; Zhang, Z. A Single Dual-Emissive Nanofluorophore Test Paper for Highly Sensitive Colorimetry-Based Quantification of Blood Glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Li, F. PH-Response Quantum Dots with Orange–Red Emission for Monitoring the Residue, Distribution, and Variation of an Organophosphorus Pesticide in an Agricultural Crop. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ding, H.; Huang, J.; Zhan, C.; Wang, S. Liquid-Core Hydrogel Optical Fiber Fluorescence Probes. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gan, J.; Xia, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.; Qian, G.; Yang, Z. A Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework Integrated Hydrogel Optical Fibre as a Photoluminescence Sensing Platform for Fluorescence Detection. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, G.; Gan, J.; Yang, Z. Hydrogel Optical Fiber Based Ratiometric Fluorescence Sensor for Highly Sensitive pH Detection. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 6653–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, M.; Yang, C.; Kong, L. Quantum Dots-Doped Tapered Hydrogel Waveguide for Ratiometric Sensing of Metal Ions. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12292–12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabahang, S.; Kim, S.; Yun, S. Light-Guiding Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K.; Yuk, H.; Yang, C.; Khademhosseini, A.; Zhao, X.; Yun, S.-H. Highly Stretchable, Strain Sensing Hydrogel Optical Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10244–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, S.; Nizamoglu, S.; Hahn, S.K.; Yun, S.H. Light-Guiding Hydrogels for Cell-Based Sensing and Optogenetic Synthesis in Vivo. Nat. Photon 2013, 7, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Singh, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. 2-D Nanomaterials Assisted LSPR MPM Optical Fiber Sensor Probe for Cardiac Troponin I Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 9504609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2015–2019). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 397–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Singh, R.; Soares, M.S.; Marques, C.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. Convex Fiber-Tapered Seven Core Fiber-Convex Fiber (CTC) Structure-Based Biosensor for Creatinine Detection in Aquaculture. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 13898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Malathi, S.; Marques, C.; Singh, R.; Zhang, B. Plasmon-Based Tapered-in-Tapered Fiber Structure for p-Cresol Detection: From Human Healthcare to Aquaculture Application. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 18493–18500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Singh, R.; Marques, C.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. 2D Material Assisted SMF-MCF-MMF-SMF Based LSPR Sensor for Creatinine Detection. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 38150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Jiang, N.; Fallahi, A.; Montelongo, Y.; Ruiz-Esparza, G.U.; Tamayol, A.; Zhang, Y.S.; Mahmood, I.; Yang, S.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Glucose-Sensitive Hydrogel Optical Fibers Functionalized with Phenylboronic Acid. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, B.; Du, Z.; Yang, C.; Kong, L.; Xu, L. Soft and Plasmonic Hydrogel Optical Probe for Glucose Monitoring. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 3549–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.S.; Christensen, J.B.; Petersen, J.F.; Hoeg-Jensen, T.; Norrild, J.C. Arylboronic Acids: A Diabetic Eye on Glucose Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 45–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Tsuchiya, M.; Itai, S.; Murayama, T.; Kurashina, Y.; Heo, Y.J.; Onoe, H. Janus Hydrogel Microbeads for Glucose Sensing with PH Calibration. Sensors 2021, 21, 4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Jeong, Y.R.; Yun, J.; Park, H.; Jin, S.W.; Lee, G.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.-S.; et al. Skin-Attachable, Stretchable Electrochemical Sweat Sensor for Glucose and PH Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13729–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Huang, Y.; Song, D.; Wu, H.; Cao, F.; Lei, Y. Dual Functional Rhodium Oxide Nanocorals Enabled Sensor for Both Non-Enzymatic Glucose and Solid-State PH Sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Song, D.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chapman, J.H.; Willis, W.S.; Li, B.; Lei, Y. High-Temperature Annealing Enabled Iridium Oxide Nanofibers for Both Non-Enzymatic Glucose and Solid-State PH Sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 281, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Wang, X.; Willis, W.S.; Song, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Lei, Y. Nitrogen-doped Hollow Co3O4 Nanofibers for Both Solid-state PH Sensing and Improved Non-enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, D.A.; Bannwarth, M.B.; Schulenburg, C.; Faccio, G.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Rossi, R.M.; Scherer, L.; Richter, M.; Boesel, L.F. Simultaneous Detection of PH Value and Glucose Concentrations for Wound Monitoring Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, S.; Ying, J.Y. Synthesis and Cell-Imaging Applications of Glutathione-Capped CdTe Quantum Dots. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, H.; Yu, H.; Sun, M.; Huang, D.; Wang, S. Visualizing Gaseous Nitrogen Dioxide by Ratiometric Fluorescence of Carbon Nanodots−Quantum Dots Hybrid. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-Doped Carbon Dots with Strong Blue Luminescence. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13817–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, J.; Yang, C. Ratiometric Fluorescence Sensor for Fe3+ Ions Detection Based on Quantum Dot-Doped Hydrogel Optical Fiber. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldegs, Y.; Elbarghouthi, M.; Elsheikh, A.; Walker, G. Effect of Solution PH, Ionic Strength, and Temperature on Adsorption Behavior of Reactive Dyes on Activated Carbon. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 77, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistela, V.R.; da Costa Cedran, J.; Moisés de Oliveira, H.P.; Scarminio, I.S.; Ueno, L.T.; Eduardo da Hora Machado, A.; Hioka, N. Protolytic Fluorescein Species Evaluated Using Chemometry and DFT Studies. Dye. Pigment. 2010, 86, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, L.I.; Fyles, T.M.; James, T.D. Binary and Ternary Phenylboronic Acid Complexes with Saccharides and Lewis Bases. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11175–11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Losego, M.D.; Braun, P.V. Hydrogel-Based Glucose Sensors: Effects of Phenylboronic Acid Chemical Structure on Response. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3239–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Czarnik, A.W. Fluorescent Chemosensors of Carbohydrates. A Means of Chemically Communicating the Binding of Polyols in Water Based on Chelation-Enhanced Quenching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5874–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Boronic Acid-Containing Hydrogels: Synthesis and Their Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartain, F.K.; Yang, X.; Lowe, C.R. Holographic Lactate Sensor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5664–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Akanuma, H.; Yamanouchi, T. Increased Fructose Concentrations in Blood and Urine in Patients With Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Ding, L.; Lin, H.; Wu, W.; Huang, J. A Novel Optical Fiber Glucose Biosensor Based on Carbon Quantum Dots-Glucose Oxidase/Cellulose Acetate Complex Sensitive Film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Li, M.; Ding, L.; Huang, J. A Fiber Optic Biosensor Based on Hydrogel-Immobilized Enzyme Complex for Continuous Determination of Cholesterol and Glucose. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Ding, L. Complex of Hydrogel with Magnetic Immobilized GOD for Temperature Controlling Fiber Optic Glucose Sensor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 114, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Laursen, B.W.; Frankær, C.G.; Sørensen, T.J. A Fluorescence Intensity Ratiometric Fiber Optics–Based Chemical Sensor for Monitoring PH. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankær, C.G.; Hussain, K.J.; Dörge, T.C.; Sørensen, T.J. Optical Chemical Sensor Using Intensity Ratiometric Fluorescence Signals for Fast and Reliable PH Determination. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Luo, S.; Gui, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, Z.; Yu, H. Difunctional Hydrogel Optical Fiber Fluorescence Sensor for Continuous and Simultaneous Monitoring of Glucose and pH. Biosensors 2023, 13, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020287
Li Y, Luo S, Gui Y, Wang X, Tian Z, Yu H. Difunctional Hydrogel Optical Fiber Fluorescence Sensor for Continuous and Simultaneous Monitoring of Glucose and pH. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020287
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yangjie, Site Luo, Yongqiang Gui, Xin Wang, Ziyuan Tian, and Haihu Yu. 2023. "Difunctional Hydrogel Optical Fiber Fluorescence Sensor for Continuous and Simultaneous Monitoring of Glucose and pH" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020287
APA StyleLi, Y., Luo, S., Gui, Y., Wang, X., Tian, Z., & Yu, H. (2023). Difunctional Hydrogel Optical Fiber Fluorescence Sensor for Continuous and Simultaneous Monitoring of Glucose and pH. Biosensors, 13(2), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020287