A Label-Free and Antibody-Free Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Impedimetric Sensor for NSCLC-Cells-Derived Exosomes Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Exosome Separation and Purification
2.4. Electrode Modification
2.5. Exosome Fixation and Electrochemical Polymerization of EIP Membrane
2.6. The EIP-Based Impedimetric Sensor
3. Results and Discussion
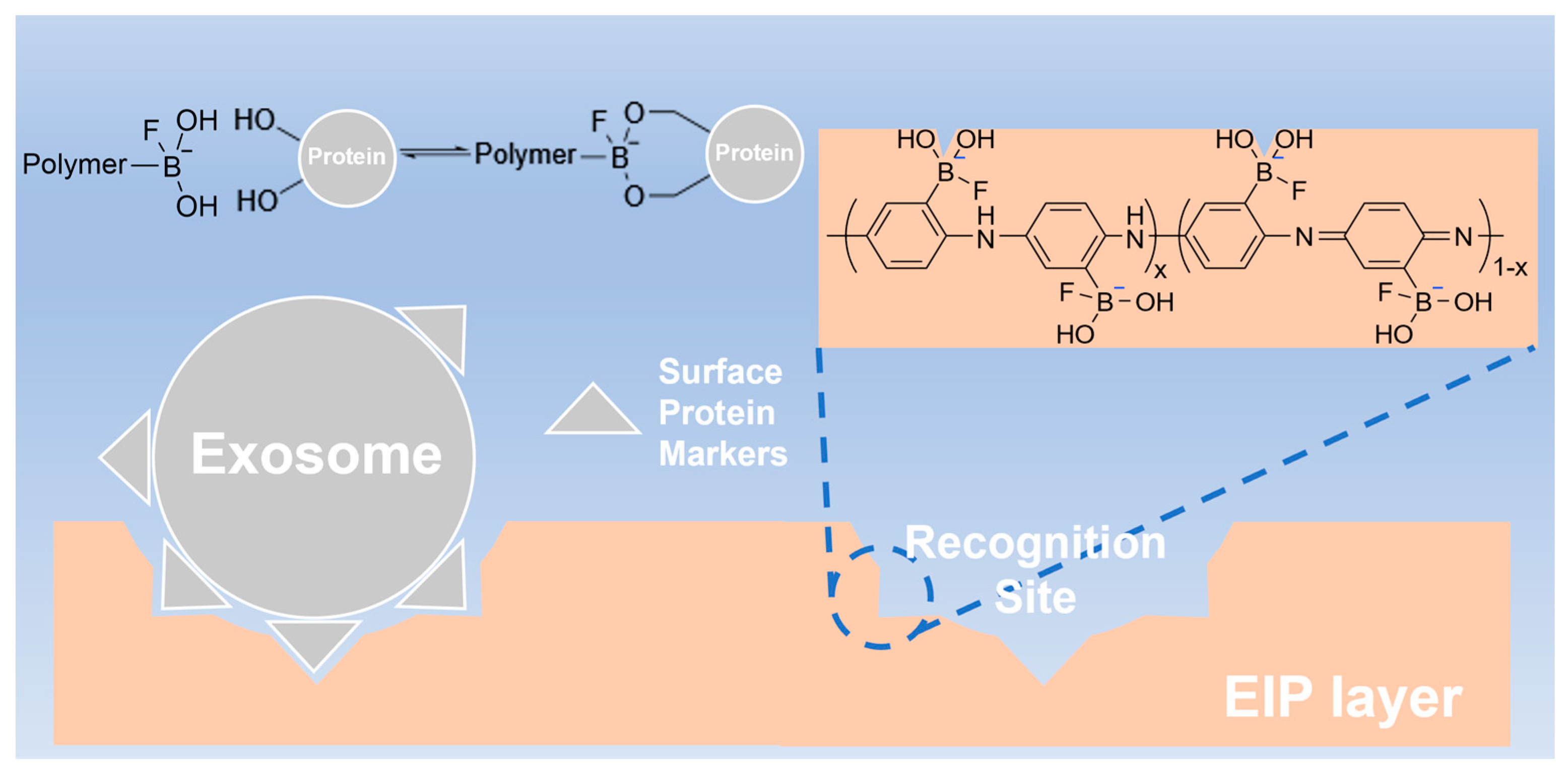
3.1. Design of the EIP-Based Impedimetric Sensor
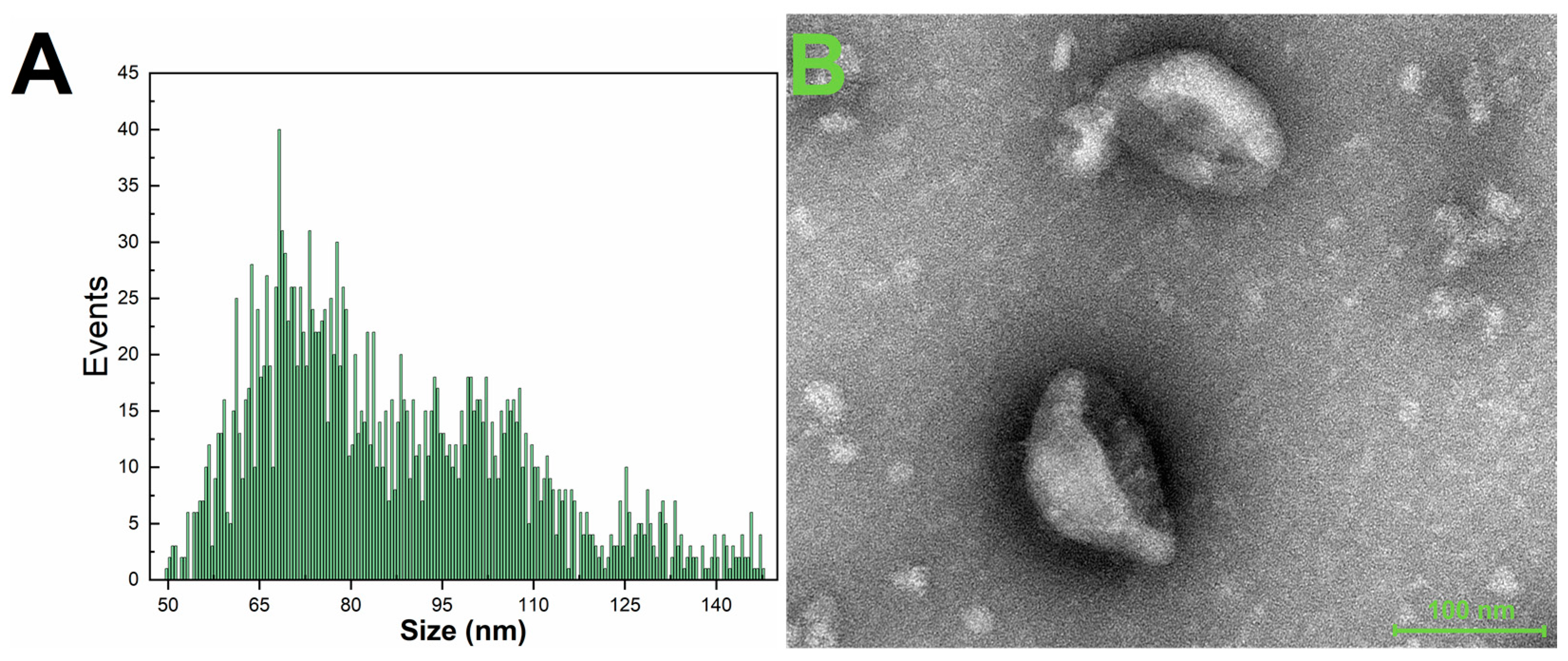
3.2. Characterization of Purified Exosomes
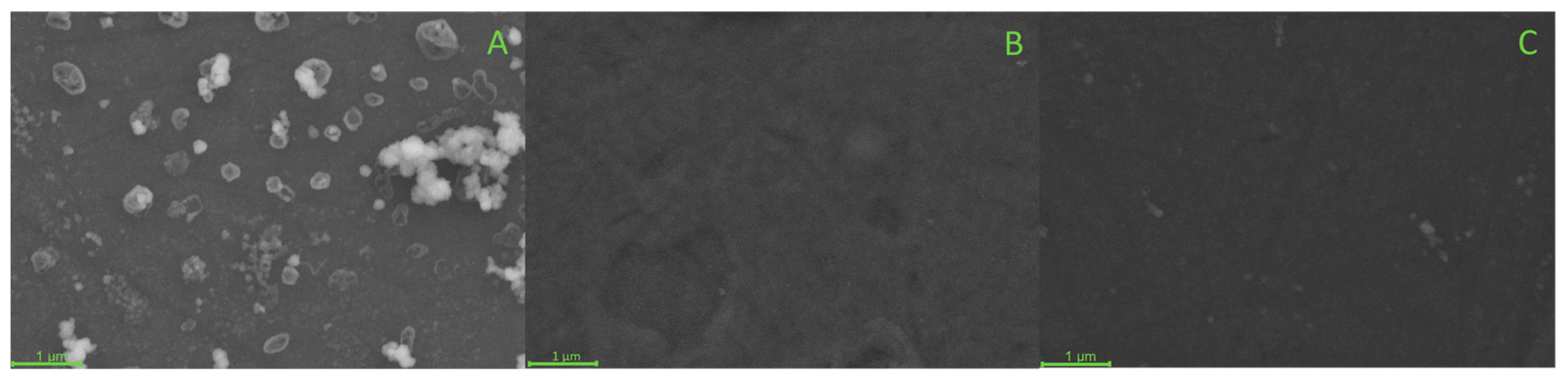
3.3. Morphology of the EIP Membrane
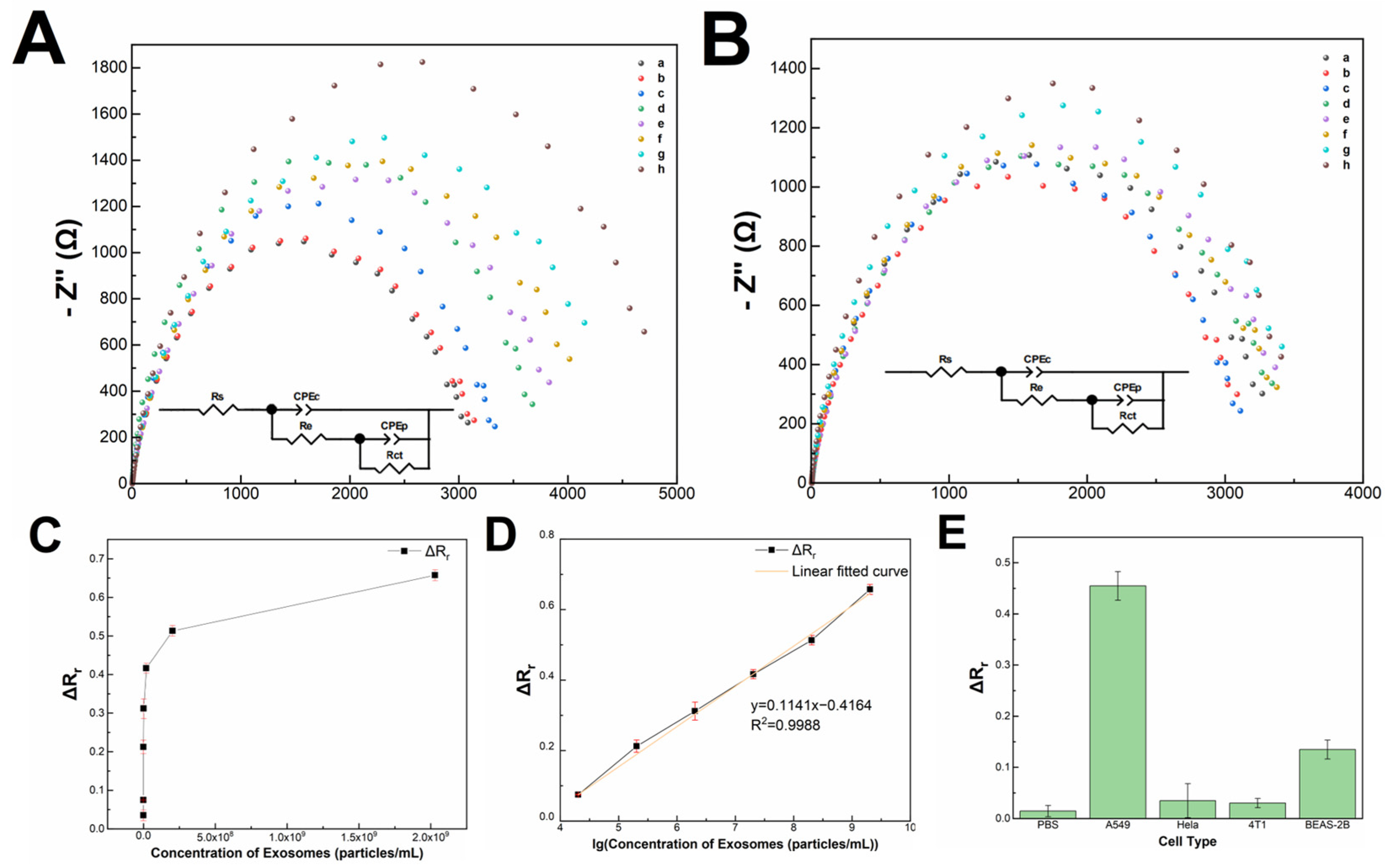
3.4. Methodology Validation of the Impedimetric Sensor
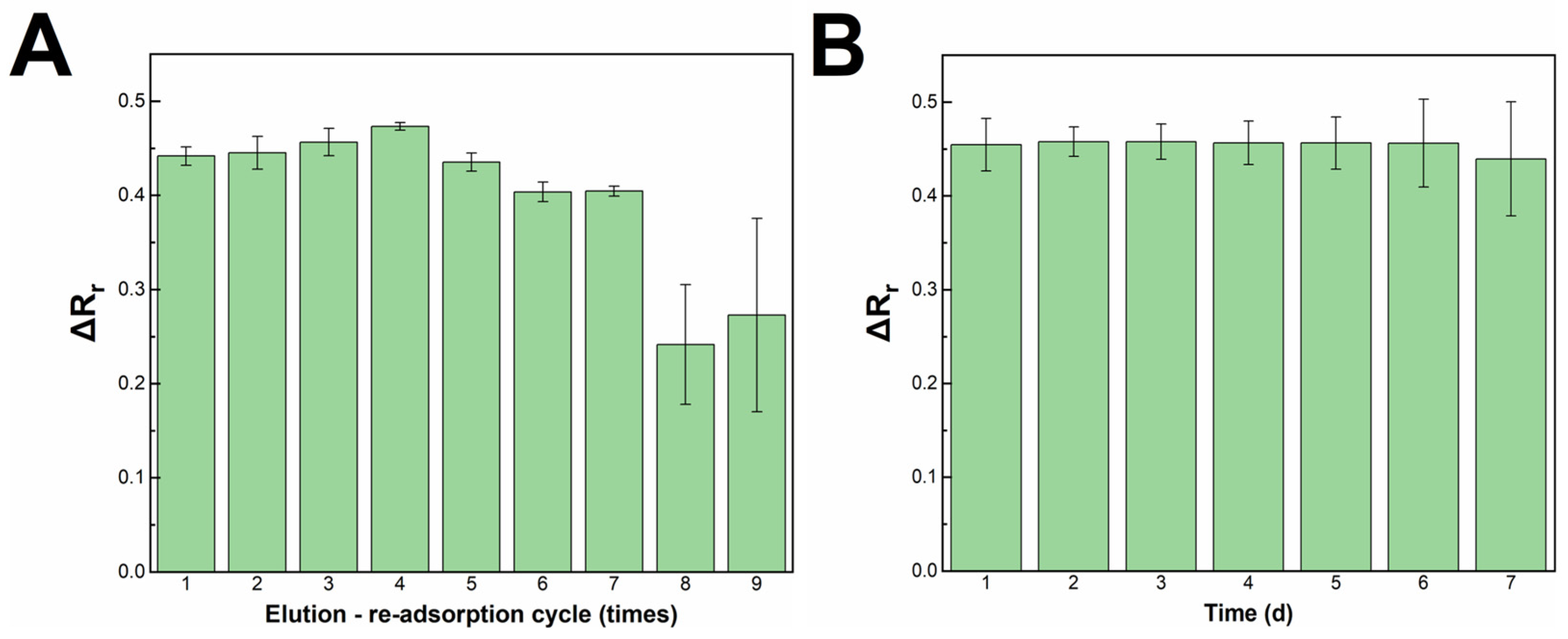
3.5. Recyclability, Stability and Performance of The Impedimetric Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, W.; Liu, J.; He, J. Driving the Improvement of Lung Cancer Prognosis. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosby, D.; Bhatia, S.; Brindle, K.M.; Coussens, L.M.; Dive, C.; Emberton, M.; Esener, S.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Gambhir, S.S.; Kuhn, P.; et al. Early Detection of Cancer. Science 2022, 375, eaay9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Yu, W.; Niu, M.; Tian, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Qian, K.; et al. Ratiometric Electrochemical OR Gate Assay for NSCLC-Derived Exosomes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Ren, M.; Miao, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Ye, K.; Zhang, P.; Ma, X.; Ni, J.; et al. Dual Selective Sensor for Exosomes in Serum Using Magnetic Imprinted Polymer Isolation Sandwiched with Aptamer/Graphene Oxide Based FRET Fluorescent Ignition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 207, 114112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Park, U.; Koo, H.-J.; Park, J.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.; Choi, J. Exosome-Mediated Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer Using Lectin-Conjugated Nanoparticles Bound to Selective Glycans. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Liu, F.; Fan, J.; Sun, D.; Liu, C.; Lyon, C.J.; Bernard, D.W.; Li, Y.; Yokoi, K.; Katz, M.H.; et al. Nanoplasmonic Quantification of Tumour-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma Microsamples for Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, T.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Dai, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, L.P.; Liu, F. Discovering the Secret of Diseases by Incorporated Tear Exosomes Analysis via Rapid-Isolation System: ITEARS. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11720–11732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Zargartalebi, H.; Salahandish, R.; Aburashed, R.; Yong, K.W.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Emerging Technologies and Commercial Products in Exosome-Based Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Di, K.; He, H.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Huang, R.; Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Zheng, S.; He, N.; et al. Progress in Exosome Associated Tumor Markers and Their Detection Methods. Mol. Biomed. 2020, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Loghry, H.J.; Qian, J.; Kimber, M.J.; Dong, L.; Lu, M. Towards Nanovesicle-Based Disease Diagnostics: A Rapid Single-Step Exosome Assay within One Hour through in Situ Immunomagnetic Extraction and Nanophotonic Label-Free Detection. Lab. Chip 2021, 21, 3541–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashkavayi, A.B.; Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Kavoosian, S. Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Sandwich Architecture for Selective Label-Free Detection of Colorectal Cancer (CT26) Cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, T.; Saijou, S.; Takashima, H.; Hara, M.; Hanaoka, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Yasunaga, M. Identification of CD73 as the Antigen of an Antigen-Unknown Monoclonal Antibody Established by Exosome Immunization, and Its Antibody–Drug Conjugate Exerts an Antitumor Effect on Glioblastoma Cell Lines. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Song, H.; Suo, Z.; Li, F.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q. A Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Surface Imprinted Polymerization and Boric Acid Affinity for Selective and Sensitive Detection of P-Glycoproteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1207, 339797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Bacterial Imprinting Methods and Their Applications: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Lv, Y. Selective Recognition of Tumor Cells by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2483–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-C.; Yu, J.-L.; Dai, Q.-Q.; Li, G.; Li, G.-B. Targeting Metalloenzymes by Boron-Containing Metal-Binding Pharmacophores. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 17706–17727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, B.; Freund, M.S. Saccharide Imprinting of Poly(Aniline Boronic Acid) in the Presence of Fluoride. Analyst 2003, 128, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yao, H.; Xia, K.; Liu, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, J. Magnetic Nanoparticles Combining Teamed Boronate Affinity and Surface Imprinting for Efficient Selective Recognition of Glycoproteins under Physiological PH. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Ding, C.; Tan, H.; Li, J. A Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Molecularly Imprinted Poly(Aniline Boronic Acid) Coated onto Carbon Nanotubes for Potentiometric Sensing of Sialic Acid. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, F.; Ma, H.; Guan, M.; Feng, J.; Dong, X. Dumbbell Aptamer Sensor Based on Dual Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 16394–16407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Hai, X.; Bi, S. A Colorimetric and Photothermal Dual-Mode Biosensing Platform Based on Nanozyme-Functionalized Flower-like DNA Structures for Tumor-Derived Exosome Detection. Talanta 2023, 258, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-W.; Haliq, R.; Yiu, P.-M.; Wu, P.-I.; Chu, J.P. Microfluidic Device Using Metallic Nanostructure Arrays for the Isolation, Detection, and Purification of Exosomes. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, A.; Pakseresht, A.; Duran, A.; Castro, Y.; Galusek, D. Electrochemical Characterization of Polymeric Coatings for Corrosion Protection: A Review of Advances and Perspectives. Polymers 2022, 14, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically Synthesized Polymers in Molecular Imprinting for Chemical Sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, K.; Xia, K.; Xiong, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chapman, E.R.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Sorting Sub-150-Nm Liposomes of Distinct Sizes by DNA-Brick-Assisted Centrifugation. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatgheib, Y.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Kardar, P.; Mahdavian, M. A Comparative Study on Fabrication of a Highly Effective Corrosion Protective System Based on Graphene Oxide-Polyaniline Nanofibers/Epoxy Composite. Corros. Sci. 2018, 133, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Exosomes in Cancer Development, Metastasis, and Immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, M.; Han, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Li, G. Functionalization of Covalent Organic Frameworks with DNA via Covalent Modification and the Application to Exosomes Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5055–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, G. An Electrochemical Biosensor Designed by Using Zr-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Detection of Glioblastoma-Derived Exosomes with Practical Application. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3819–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concentration Spiked (Logarithmic Unit) | ΔRr | Concentration Recovered (Logarithmic Unit) | Recovery Ratio (%) | AVG (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.307 | 0.6619 | 9.4507 | 101.54 | 101.17 | 1.07 |
| 0.6417 | 9.2733 | 99.63 | |||
| 0.6688 | 9.5105 | 102.18 | |||
| 6.307 | 0.3339 | 6.5758 | 104.25 | 101.21 | 2.86 |
| 0.2839 | 6.1378 | 97.31 | |||
| 0.3181 | 6.4372 | 102.06 | |||
| 4.307 | 0.0742 | 4.2996 | 99.82 | 99.98 | 0.20 |
| 0.0764 | 4.3192 | 100.27 | |||
| 0.0744 | 4.3015 | 99.86 | |||
| Total | 100.76 | 1.86 |
| Substrate | Recognition Component | Detection Method | LOD (Particles/mL) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptides-modified gold electrodes | Peptide for EGFR/EGFRvIII and Zr-MOF for phospholipid bilayers | SWV * for MB ** | 7.83 × 106 | [28] |
| Aptamers-modified gold electrodes | Aptamers for CD63 and cholesterol group for phospholipid bilayers | SWV for MB | 9.661 × 106 | [29] |
| Microfluidic metallic nanostructure arrays | Biotinylated anti-EpCAM | EIS | 1 × 108 | [22] |
| 96-well plate modified with aptamer | EpCAM aptamer and CD63 aptamer flowers | Colorimetry and photothermal | 1.027 × 106 for colorimetry and 2.170 × 106 for photothermal | [21] |
| Aptamer-modified electrodes assay | EpCAM and CEA *** aptamer | Ratiometric DPV for MB and Fc **** | 1.51 × 104 | [3] |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticles | MIP and CD63 aptamer | Fluorescence “turn-on” | 2.43 × 106 | [4] |
| Cholesterol modified GCE | MIP membrane | EIS | 2.03 × 103 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Gao, X.; Lin, Q.; Suo, Z.; Wu, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q. A Label-Free and Antibody-Free Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Impedimetric Sensor for NSCLC-Cells-Derived Exosomes Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060647
Zhang J, Chen Q, Gao X, Lin Q, Suo Z, Wu D, Wu X, Chen Q. A Label-Free and Antibody-Free Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Impedimetric Sensor for NSCLC-Cells-Derived Exosomes Detection. Biosensors. 2023; 13(6):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060647
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingbo, Quancheng Chen, Xuemin Gao, Qian Lin, Ziqin Suo, Di Wu, Xijie Wu, and Qing Chen. 2023. "A Label-Free and Antibody-Free Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Impedimetric Sensor for NSCLC-Cells-Derived Exosomes Detection" Biosensors 13, no. 6: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060647
APA StyleZhang, J., Chen, Q., Gao, X., Lin, Q., Suo, Z., Wu, D., Wu, X., & Chen, Q. (2023). A Label-Free and Antibody-Free Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Impedimetric Sensor for NSCLC-Cells-Derived Exosomes Detection. Biosensors, 13(6), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060647





