Rapid and Quantitative Detection of TNF-α in Human Tears Using a Portable Electrochemiluminescence-Based Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Electrodes
2.3. Fabrication of the Device
2.4. Detection of Tear Samples
3. Results and Discussions
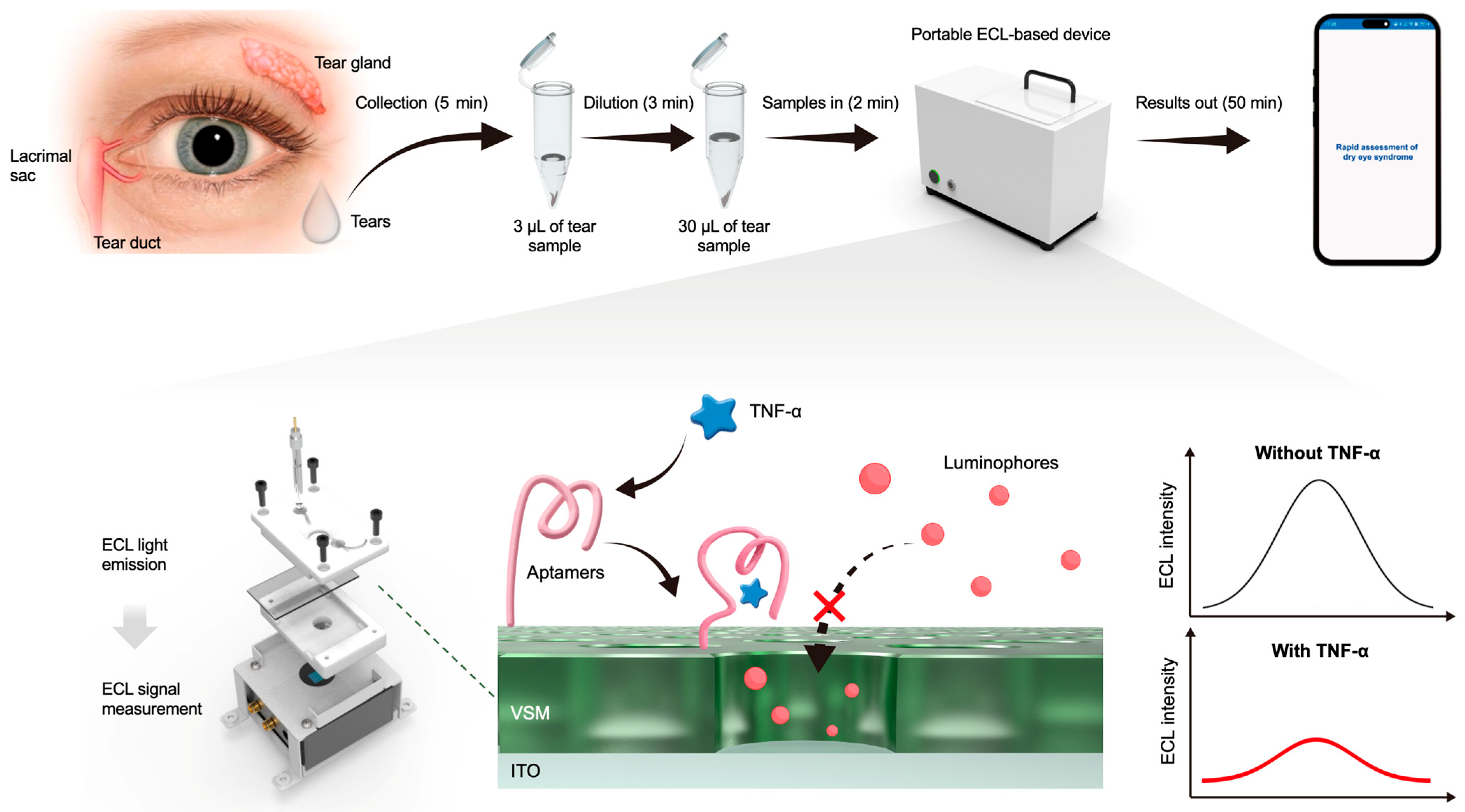
3.1. Design and Fabrication of the Device
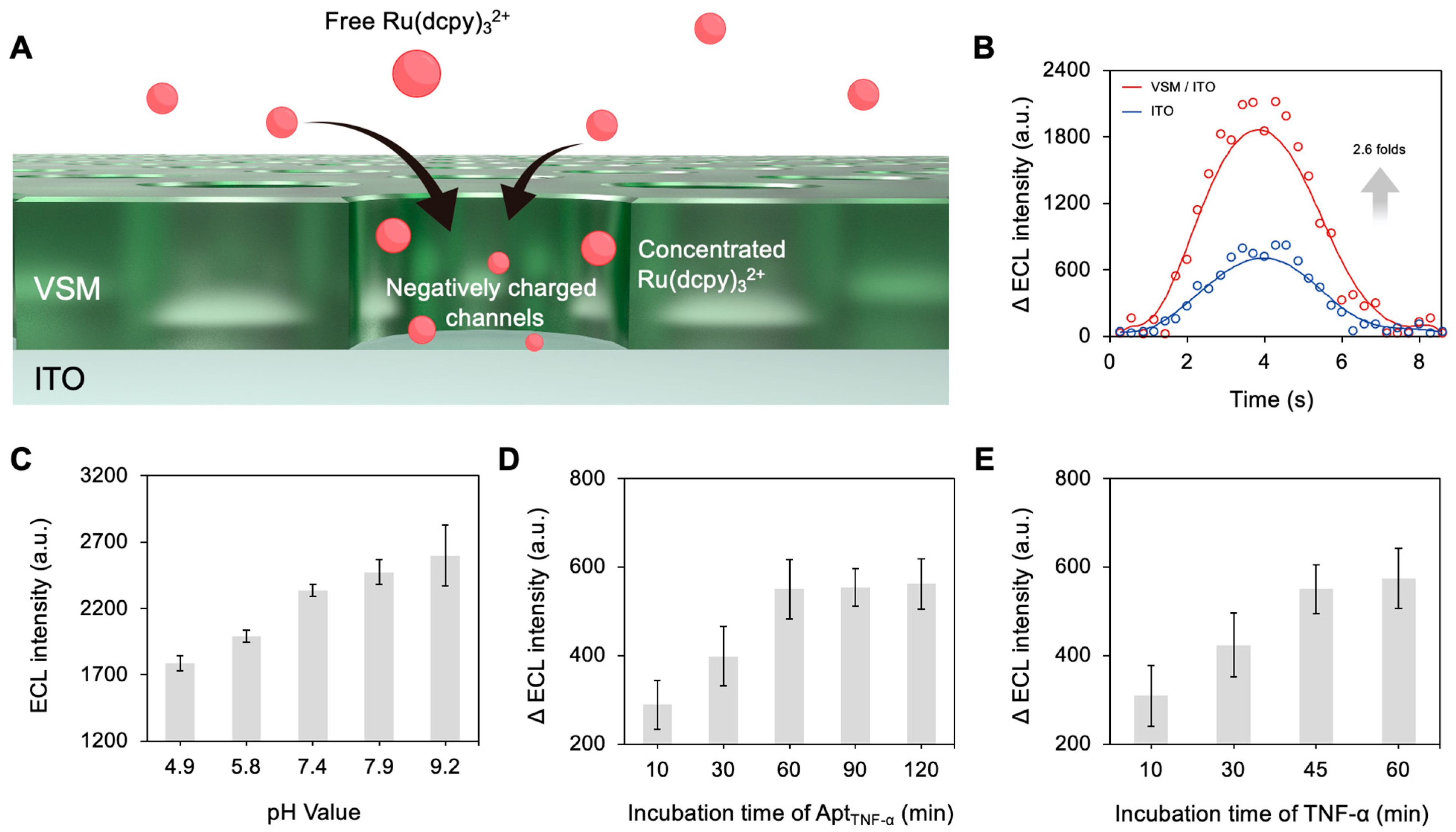
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of the Electrodes
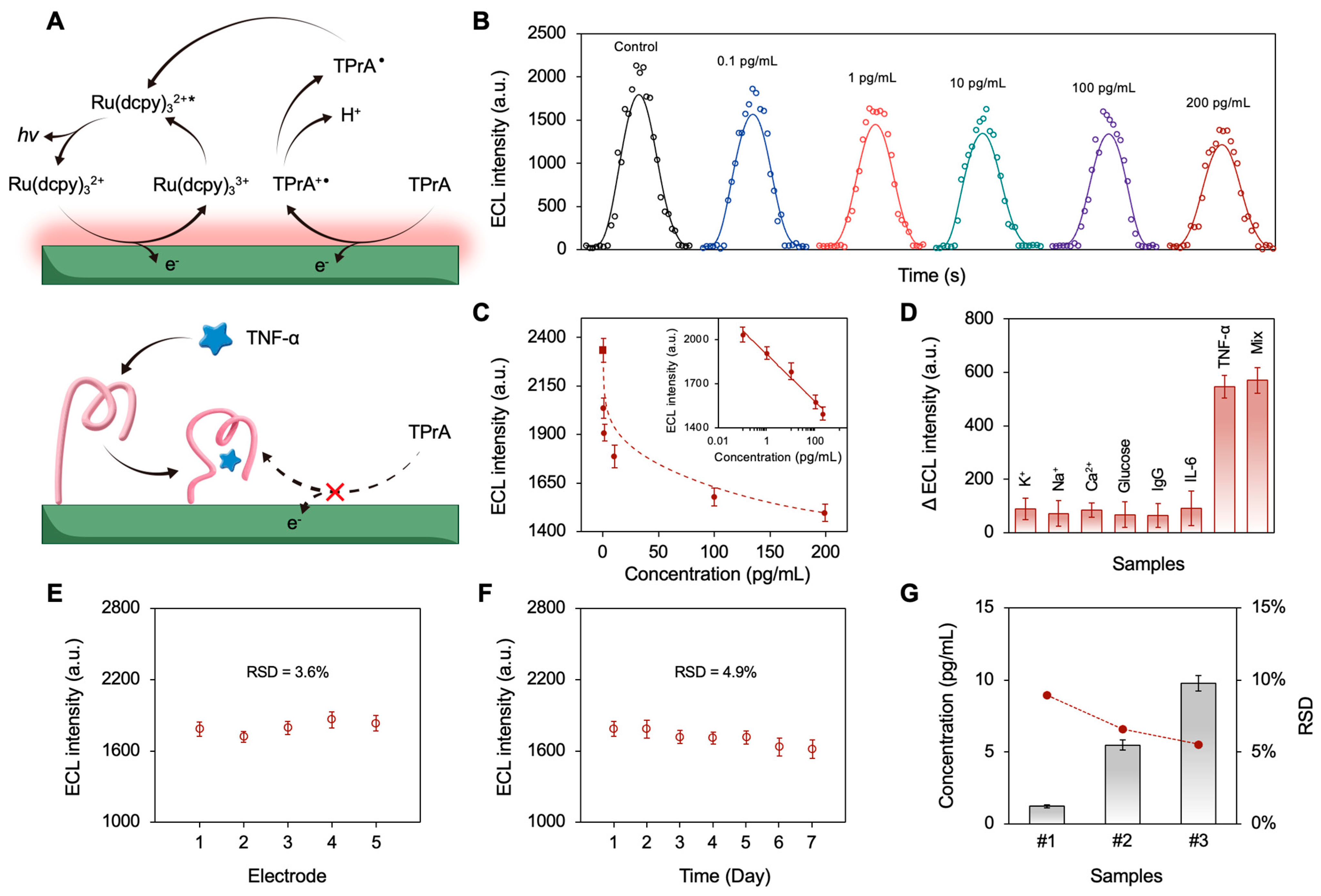
3.3. The Sensing Mechanism and Analytical Performance of the Device
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, T. Microsampling and exosome-enriched optical biochip for non-invasive detection of breast cancer exosomes in clinical human tear fluid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 282, 117507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.-M.; Song, H.; Joo, B.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, E.; Yae, C.-G.; Kim, J.; et al. In-depth correlation analysis between tear glucose and blood glucose using a wireless smart contact lens. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, X.; Song, B.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Shi, H.; Chu, B.; He, Y.; et al. Framework nucleic acids combined with 3D hybridization chain reaction amplifiers for monitoring multiple human tear cytokines. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2400622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, M.; Ogawa, M.; Oshima, M.; Sekine, Y.; Ishida, K.; Yamashita, K.; Ikeda, K.; Shimmura, S.; Kawakita, T.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Functional lacrimal gland regeneration by transplantation of a bioengineered organ germ. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Xue, Z.; Qiao, X.; Li, A.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T. A separation-sensing platform performing accurate diagnosis of jaundice in complex biological tear fluids. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202205628. [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola, C.; Romano, V.; De Tollis, M.; Aceto, F.; dell’Omo, R.; Romano, M.R.; Pedicino, C.; Semeraro, F. TNF-alpha levels in tears: A novel biomarker to assess the degree of diabetic retinopathy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 629529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelagere, Y.; Scholand, K.K.; DeJong, E.N.; Boyd, A.I.; Yu, Z.; Astley, R.A.; Callegan, M.C.; Bowdish, D.M.; Makarenkova, H.P.; de Paiva, C.S. TNF is a critical cytokine in age-related dry eye disease. Ocul. Surf. 2023, 30, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.; Bleiden, L.; De Paiva, C.S.; Farley, W.; Stern, M.E.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Tear cytokine profiles in dysfunctional tear syndrome. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 147, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L. Wearable eye patch biosensor for noninvasive and simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers in human tears. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8659–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Fu, W.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Su, B.; Chen, X. A fully integrated and handheld electrochemiluminescence device for detection of dopamine in bio-samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 366, 131972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor for cancer biomarker detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Qi, M.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Su, B. A Wearable Integrated Microneedle Electrode Patch for Exercise Management in Diabetes. Research 2024, 7, 0508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Su, B. An Overview of Wearable and Implantable Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Electroanalysis 2021, 34, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N. Luminescence during Electrolysis. J. Phys. Chem. 1929, 33, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.M. Electrochemiluminescence (ecl). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3003–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, T.; Epstein, B.; Seo, E.T. Electrochemical generation of solution luminescence. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 2243–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokel, N.E.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. IX. Electrochemistry and emission from systems containing tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) dichloride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 2862–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leland, J.K.; Powell, M.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence: An oxidative-reduction type ECL reaction sequence using tripropyl amine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.L.; Pastore, P.; Wightman, R.M. Free Energy Control of Reaction Pathways in Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11920–11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, M.M.; Novak, B.; Martin, S.A.; Taussig, J.S. Electrochemiluminescence of Ruthenium(II) Tris(bipyridine) Encapsulated in Sol−Gel Glasses. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2914–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeven, E.H.; Barbante, G.J.; Kerr, E.; Hogan, C.F.; Endler, J.A.; Francis, P.S. Red–green–blue electrogenerated chemiluminescence utilizing a digital camera as detector. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alton, L.; Carrara, S.; Barbante, G.J.; Hoxley, D.; Hayne, D.J.; Francis, P.S.; Hogan, C.F. A simple, low-cost instrument for electrochemiluminescence immunoassays based on a Raspberry Pi and screen-printed electrodes. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 146, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J. Direct imaging of single-molecule electrochemical reactions in solution. Nature 2021, 596, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Pan, J.; Dai, D.; Dai, Z.; Yang, M.; Yi, C. Design of portable electrochemiluminescence sensing systems for point-of-care-testing applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dai, D.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zou, G.; Liu, C.; Luo, Z.; Yi, C. A portable smartphone-based electrochemiluminescence device integrated with bipolar electrode detection chip for multi-target respiratory pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 288, 117783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Low, S.S.; Zhu, L.; Cheng, C.; He, Y.; Chen, Q.; Su, B.; et al. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence on smartphone with graphene quantum dots nanocomposites for Escherichia Coli detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Low, S.S.; Su, B.; Liu, Q. Electrochemiluminescence on smartphone with silica nanopores membrane modified electrodes for nitroaromatic explosives detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wei, M.; Liu, S.; Yue, X.; Wang, L.; Luan, F.; Zhuang, X.; Tian, C. Ratiometric electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on Ru(dcbpy)32+ and TiO2 quantum dots for the detection of Urokinase. Talanta 2026, 296, 128491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. A self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on l-Lys-Ru(dcbpy)32+ functionalized porous six arrises column nanorods for detection of CA15-3. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Fan, D.; Kuang, X.; Sun, X.; Wei, Q.; Ju, H. Ru(dcbpy)32+-functionalized γ-cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks as efficient electrochemiluminescence tags for the detection of CYFRA21-1 in human serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 378, 133152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, L.; Luo, L.; You, T. Amplified electrochemiluminescence of Ru(dcbpy)32+ via coreactant active sites on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Talanta 2025, 286, 127554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Yeo, T.; Lim, S.B.; Tan, W.X.; Madden, L.E.; Jin, L.; Long, J.Y.K.; Aloweni, F.A.B.; Liew, Y.J.A.; et al. A flexible multiplexed immunosensor for point-of-care in situ wound monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-Y.; Wang, J.-W.; Huang, B.-T.; Lin, E.P.-Y.; Yang, P.-C. A novel TNF-α-targeting aptamer for TNF-α-mediated acute lung injury and acute liver failure. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Zheng, G.; Dou, Y.; Li, W.; Mou, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Asiri, A.M.; Zhao, D. Highly ordered mesoporous silica films with perpendicular mesochannels by a simple Stöber-solution growth approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2173–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Elzatahry, A.; Li, X.; Zhao, D. Single-micelle-directed synthesis of mesoporous materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcarius, A. Electroinduced surfactant self-assembly driven to vertical growth of oriented mesoporous films. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3563–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Dong, N.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Su, B. Cof-coated microelectrode for space-confined electrochemical sensing of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease model mouse brain. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 23727–23738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, F.; Xi, F. A dual-functional antibiofouling and signal amplification sensing platform enabling accurate analysis in complicated biological samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 439, 137856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, S.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Dong, P.; Zhu, L. Rapid and Quantitative Detection of TNF-α in Human Tears Using a Portable Electrochemiluminescence-Based Device. Biosensors 2025, 15, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100645
Qu S, Zhu B, Liu Z, Chen X, Dong P, Zhu L. Rapid and Quantitative Detection of TNF-α in Human Tears Using a Portable Electrochemiluminescence-Based Device. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100645
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Shaohong, Boyu Zhu, Zihao Liu, Xing Chen, Peifang Dong, and Lihang Zhu. 2025. "Rapid and Quantitative Detection of TNF-α in Human Tears Using a Portable Electrochemiluminescence-Based Device" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100645
APA StyleQu, S., Zhu, B., Liu, Z., Chen, X., Dong, P., & Zhu, L. (2025). Rapid and Quantitative Detection of TNF-α in Human Tears Using a Portable Electrochemiluminescence-Based Device. Biosensors, 15(10), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100645




