Biological Effects of C60 Fullerene Revealed with Bacterial Biosensor—Toxic or Rather Antioxidant?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Fullerene C60 Aqueous Solutions
2.2. Measurement of the Fullerene Nanoparticles Size by Dynamic Light Scattering
2.3. Bacterial Strain Used
2.4. Bioluminescent Experiments
2.5. Calculation of the Protective Effect
3. Results
3.1. Stability of the Aqueous Solution. Determination of C60 Concentration
3.2. Size of C60 Fullerene Nanoparticles in Solution
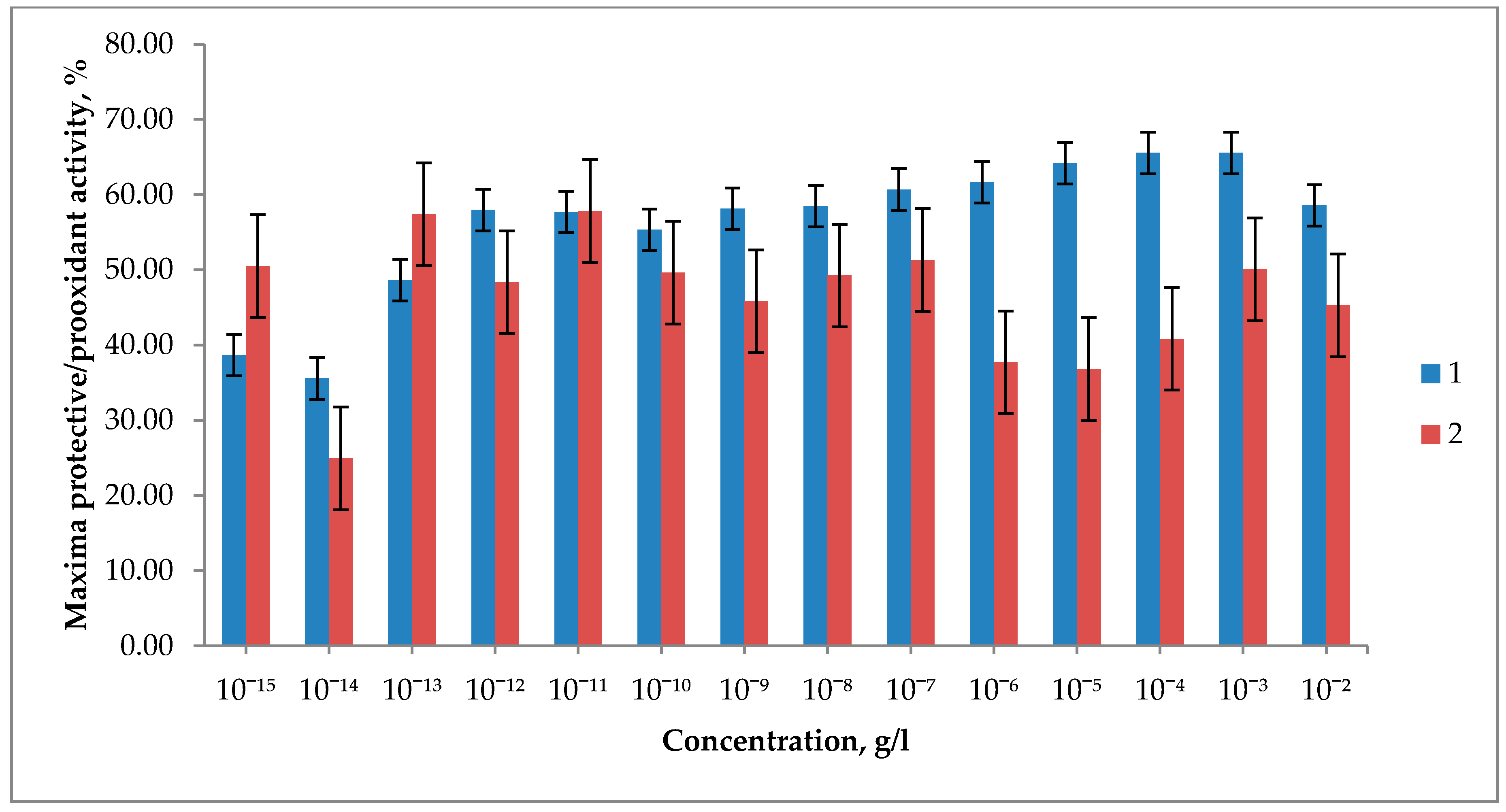
3.3. Biological Effects of Fullerene C60
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crowley, C.; Taylor, R.; Kroto, H.W.; Walton, D.R.M.; Cheng, P.-C.; Scott, L.T. Pyrolytic production of fullerenes. Synth. Met. 1996, 77, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroto, H.W.; Heath, J.R.; O’Brien, S.C.; Curl, R.F.; Smalley, R.E. C60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature 1985, 318, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, E. Manufactured nanomaterials (fullerenes, C60) induce oxidative stress in the brain of juvenile largemouth bass. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortner, J.D.; Lyon, D.Y.; Sayes, C.M.; Boyd, A.M.; Falkner, J.C.; Hotze, E.M.; Alemany, L.B.; Tao, Y.J.; Guo, W.; Ausman, K.D.; et al. C60 in Water: Nanocrystal Formation and Microbial Response. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4307–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayes, C.M.; Fortner, J.D.; Guo, W.; Lyon, D.; Boyd, A.M.; Ausman, K.D.; Tao, Y.J.; Sitharaman, B.; Wilson, L.J.; Hughes, J.B.; et al. The Differential Cytotoxicity of Water-Soluble Fullerenes. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ros, T.; Prato, M. Medicinal chemistry with fullerenes and fullerene derivatives. Chem. Commun. 1999, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.W.; Wilson, S.R.; Schuster, D.I. Biological applications of fullerenes. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, E.; Zhu, S.; Blickley, T.M.; McClellan-Green, P.; Haasch, M.L. Ecotoxicology of carbon-based engineered nanoparticles: Effects of fullerene (C60) on aquatic organisms. Carbon 2006, 44, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B.; Grieger, K.; Kusk, K.O. Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: A brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrovsky, L.B.; Eropkin, M.Y.; Eropkina, E.M.; Dumpis, M.A.; Kiselev, O.I. Mechanisms of biologic action of fullerenes—Dependence on aggregate state. Psychopharmacol. Biol. Narcol. 2007, 7, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Oguri, I.; Yamakoshi, Y.N.; Miyata, N. Novel harmful effects of [60] fullerene on mouse embryos in vitro and in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1996, 393, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, V.A.; Smirnova, Y.O.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Soldatov, A.V. Possible mechanisms of fullerene C60 antioxidant action. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, Z.; Trajkovic, V. Biomedical potential of the reactive oxygen species generation and quenching by fullerenes (C60). Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakoshi, Y.; Umezawa, N.; Ryu, A.; Arakane, K.; Miyata, N.; Goda, Y.; Masumizu, T.; Nagano, T. Active Oxygen Species Generated from Photoexcited Fullerene (C60) as Potential Medicines: O2-• versus 1O2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 12803–12809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova, M.A.; Trofimova, T.P.; Orlov, A.P.; Shatalov, O.A. Perspectives of fullerene derivatives in PDT and radiotherapy of cancers. Br. J. Med. Med. Res. 2013, 3, 1731–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, Y.P.; Alperovich, I.; Zolotukhin, P.; Prazdnova, E.; Mazanko, M.; Belanova, A.; Chistyakov, V. Fullerenes as Anti-Aging Antioxidants. Curr. Aging Sci. 2017, 10, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korshunov, S.S.; Skulachev, V.P.; Starkov, A.A. High protonic potential actuates a mechanism of production of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1997, 416, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroik, D.; Yuen, S.; Kleinboehl, E.; Janicek, K.; Schaaf, T.; Cornea, R.; Thomas, D. Live-Cell FRET Biosensors for High-Throughput Screening Targeting the SERCA2a/Plb Complex. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 128a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, C.; Xia, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X. Highly sensitive microbial biosensor based on recombinant Escherichia coli overexpressing catechol 2,3-dioxygenase for reliable detection of catechol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Bhalla, N.; Chu, K.-Y.; Söderström, B.; Shen, A.Q. Nanoplasmonics for Real-Time and Label-Free Monitoring of Microbial Biofilm Formation. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W. Dynamic Light Scattering: The Method and Some Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MS, USA, 1993; Volume 49, ISBN 0198539428. [Google Scholar]
- Kotova, V.Y.; Manukhov, I.V.; Zavilgelskii, G.B. Lux-biosensors for detection of SOS-response, heat shock, and oxidative stress. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2010, 46, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igonina, E.V.; Marsova, M.V.; Abilev, S.K. Lux Biosensors: Screening Biologically Active Compounds for Genotoxicity. Russ. J. Genet. Appl. Res. 2018, 8, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, T.; Fritsch, E.F.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 545. [Google Scholar]
- Prazdnova, E.V.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Churilov, M.N.; Mazanko, M.S.; Bren, A.B.; Volski, A.; Chikindas, M.L. DNA-protection and antioxidant properties of fermentates from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1895 and Bacillus subtilis KATMIRA1933. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsova, M.; Abilev, S.; Poluektova, E.; Danilenko, V. A bioluminescent test system reveals valuable antioxidant properties of lactobacillus strains from human microbiota. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, D.Y.; Adams, L.K.; Falkner, J.C.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antibacterial Activity of Fullerene Water Suspensions: Effects of Preparation Method and Particle Size. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4360–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, M.; Nairz, O.; Vos-Andreae, J.; Keller, C.; van der Zouw, G.; Zeilinger, A. Wave–particle duality of C60 molecules. Nature 1999, 401, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulachev, M.V.; Antonenko, Y.N.; Anisimov, V.N.; Chernyak, B.V.; Cherepanov, D.A.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Egorov, M.V.; Kolosova, N.G.; Korshunova, G.A.; Lyamzaev, K.G.; et al. Mitochondrial-Targeted Plastoquinone Derivatives. Effect on Senescence and Acute Age-Related Pathologies. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 800–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, V.A.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Soldatov, A.V.; Smirnova, Y.O.; Alperovich, I. Can C60 fullerene demonstrate properties of mitochondria-targeted antioxidant from the computational point of view. Int. J. Biol. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 8, 59–62. [Google Scholar]





| Day | 10 min Stirring, Followed by Ultrasound 15 W | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance (arb. Units) | CM, mol/L | C, g/L | ||
| 1 | 1.86 | 9.82 × 10−5 | 7.07 × 10−2 | |
| 2 | 1.62 | 8.56 × 10−5 | 6.16 × 10−2 | |
| 3 | 1.60 | 8.46 × 10−5 | 6.09 × 10−2 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emelyantsev, S.; Prazdnova, E.; Chistyakov, V.; Alperovich, I. Biological Effects of C60 Fullerene Revealed with Bacterial Biosensor—Toxic or Rather Antioxidant? Biosensors 2019, 9, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9020081
Emelyantsev S, Prazdnova E, Chistyakov V, Alperovich I. Biological Effects of C60 Fullerene Revealed with Bacterial Biosensor—Toxic or Rather Antioxidant? Biosensors. 2019; 9(2):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9020081
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmelyantsev, Sergey, Evgeniya Prazdnova, Vladimir Chistyakov, and Igor Alperovich. 2019. "Biological Effects of C60 Fullerene Revealed with Bacterial Biosensor—Toxic or Rather Antioxidant?" Biosensors 9, no. 2: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9020081
APA StyleEmelyantsev, S., Prazdnova, E., Chistyakov, V., & Alperovich, I. (2019). Biological Effects of C60 Fullerene Revealed with Bacterial Biosensor—Toxic or Rather Antioxidant? Biosensors, 9(2), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9020081





