Abstract
An immunosensor is a kind of affinity biosensor based on interactions between an antigen and specific antigen immobilized on a transducer surface. Immunosensors possess high selectivity and sensitivity due to the specific binding between antibody and corresponding antigen, making them a suitable platform for several applications especially in the medical and bioanalysis fields. Electrochemical immunosensors rely on the measurements of an electrical signal recorded by an electrochemical transducer and can be classed as amperometric, potentiometric, conductometric, or impedimetric depending on the signal type. Among the immunosensors, electrochemical immunosensors have been more perfected due to their simplicity and, especially their ability to be portable, and for in situ or automated detection. This review addresses the potential of immunosensors destined for application in clinical analysis, especially cancer biomarker diagnosis. The emphasis is on the approaches used to fabricate electrochemical immunosensors. A general overview of recent applications of the developed electrochemical immunosensors in the clinical approach is described.
1. Introduction
1.1. What Is Immunosensor?
An immunosensor is a type of affinity solid-state based biosensor in which a specific target analyte, antigen (Ag), is detected by formation of a stable immunocomplex between antigen and antibody as a capture agent (Ab) resulting in generating a measurable signal given by a transducer [1,2]. There is a delicate distinction between immunosensors and immunoassays; an immunoassay system is based on the interaction between the antibody and the antigen in that the recognition process of the antigen takes place elsewhere [3,4]. However, in immunosensors, the formation of the immunocomplex and diagnosis take place on the same platform [5,6,7]. An example of the immunoassay system is the commercial Enzyme-Linked-Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) used in the clinical assay and biochemical field [8]. In the conventional ELISA kits, a specific Ag is immobilized on a solid substrate and bonded to a specific Ab (primary Ab). In the last step, the Ab linked to an enzyme (as a type of label) is added and the antigen is sandwiched between the primary Ab and secondary Ab with an enzyme label. From this reaction, a detectable signal by changing color is readable by an optical transducer [9]. Since, ELISA is an optical immunoassay approach, it faces some drawbacks depending to the type of measurements such as direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, competitive ELISA, and sandwich ELISA. These limitations can be associated with the potential false signals arising from colored samples, a relatively long analysis time, a requirement of power-intensive light sources, monochromators and detectors, as well as sample size and usage problem outside the classical diagnostic laboratory [10]. In this regard, the use of immunosensors is a promising alternative to optical immunoassay approach for diagnosis of clinically important analytes due to high sensitivity and selectivity [5,11,12]. Furthermore, they provide the possibility of progression of immunoreactions at detector surfaces in real time. Immunosensors can be classified based on their transduction mode into three main class including optical (luminescence, fluorescence, refractive index), electrochemical (amperometric, potentiometric, impedance, and conductometric), and piezoelectric devices [9,13]. Among them, the use of electrochemical immunosensors simplifies the analysis with rapid and reliable signals. Electrochemical immunosensors are usually fabricated via the immobilization of a recognition element (i.e., antibody or antigen) on the electrode surface, which relies on measuring of currents and/or voltage resulting from binding between antibody and antigen [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Antibodies (Abs) are glycoproteins from the category of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE) made by specialized B lymphocyte cells of the host animal in response of the immune system to a foreign species called an antigen [20]. Among immunoglobulins, IgG, the most widely used in the developed immunosensors has “Y”-shaped molecules in which two identical light chains (molecular weights about 25,000 Da) and two heavy chains (MW about 50,000 Da) are linked together by disulfide bonds as well as noncovalent interactions (hydrogen bonds). Abs have physiological sites of action and variable regions for both chains, VL and VH, depending on the amino acid sequences to bind the specific antigen. They are complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) providing hypervariable loops that indicate the binding site to the antigen. The high diversity of CDRs allows the production of a high specific antibody towards many kinds of Ag. Abs are bivalent and can bind with two specific Ags according to size, shape, and chemical compatibility. The Ag-binding site is called the “paratope”, and the complementary region on the Ag is called the “epitope”. The antibodies are classified into two types such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and polyclonal antibodies (pAbs). Monoclonal antibodies are generated by identical immune B cells (clones of a single parent cell) and are used as a primary Ab in fabrication of immunosensors to recognize a single epitope of an antigen. On the other hand, the mAbs have monovalent affinity, resulting in high specificity towards an Ag. Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are usually produced by different immune B cell clones in the live animal body by injecting an immunogen. They are a heterogeneous mixture of immunoglobulins against a particular Ag which each of them can recognize and bind to different epitopes of a specific antigen. In contrast, mAbs are produced ex vivo by tissue-culture techniques [21].
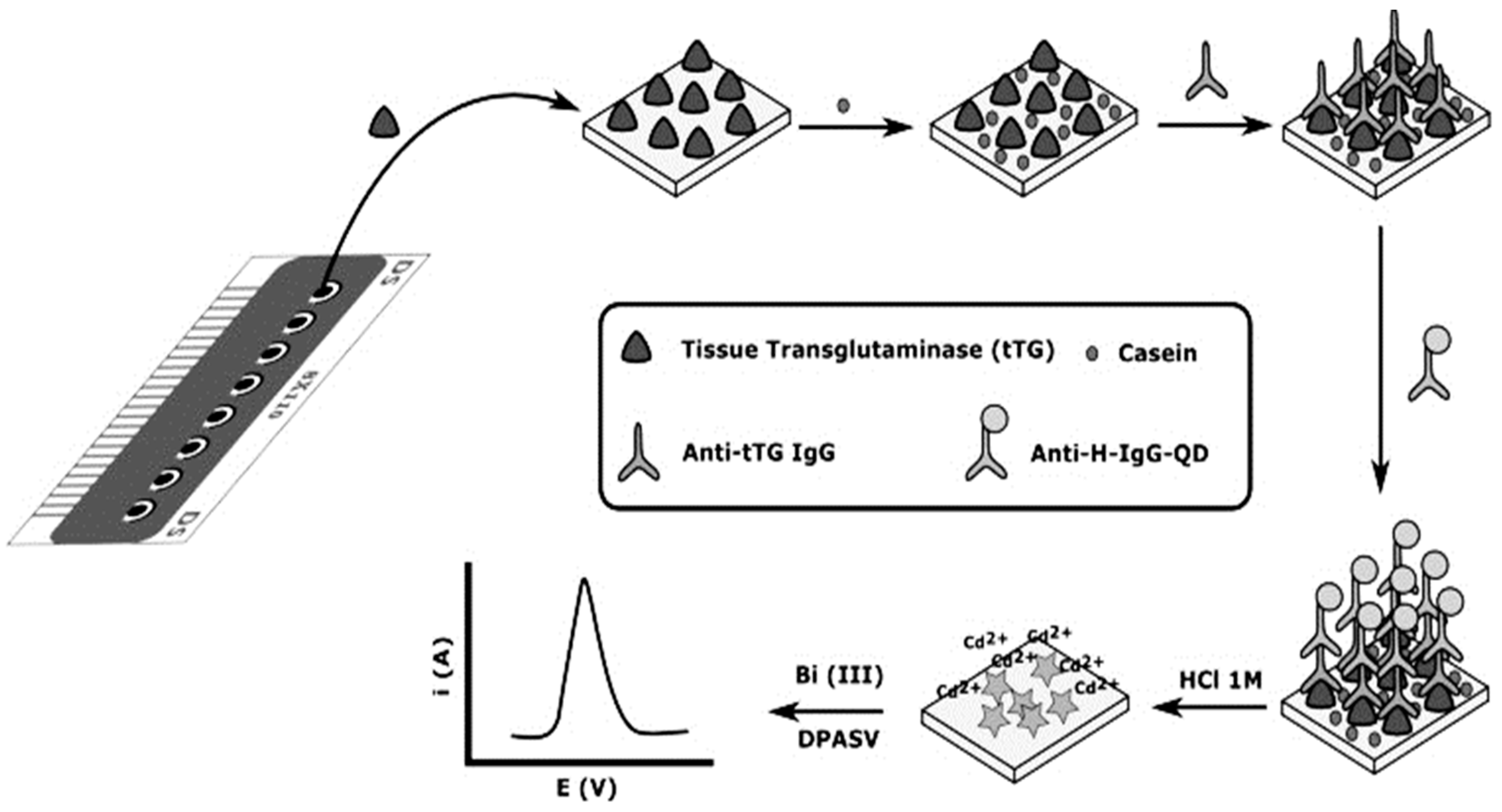
The aimed target in an immunosensor could be either an antibody (Ab) or an antigen (Ag). Although the most popular immunosensors are based on detecting antigen using antibodies, some researchers have reported an immunosensor for Ab detection. For example, in 2014 and 2015, Martín-Yerga et al. [22,23] described an electrochemical immunosensor for anti-tissue transglutaminase (anti-tTG) and anti-transglutaminase antibodies sensing, based on 8-channel screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCE) modified with tissue-transglutaminase by adsorption. Transduction was performed by the immunoreaction with anti-human IgG labeled with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots (QDs) for the detection of Cd2+ released from QDs. The concentration of Cd2+ was measured in situ after acid attack of the QDs by voltammetric stripping without a transfer step (Figure 1). The electrochemical response was correlated with the anti-transglutaminase IgG concentration and the LOD of anti-tTG IgG antibodies was 2.2 U mL−1. Also in 2019, Gogola et al. [24] reported a label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on a gold electrode modified with Hantavirus (strain Araucaria) antigen/protein for detection of anti-Hantavirus antibody. The functionalization of the surface electrode was done by self-assembled monolayer (SAM) with 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) diluted in acidified ethanol (99.6%) and then for the activation of the surface, N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-Hydroxysuccinimide (EDC/NHS) were used. Therefore, the Hantavirus Araucaria nucleoprotein (HNp) could bind covalently onto the modified gold surface by immersing the electrode in the HNp solution. Finally, the Au-MPA-HNp electrode was immersed in the solution containing the antibody to couple the antigen with antibody. Transduction was made by using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements. The detection range was from 0.400 to 300 μg mL−1.
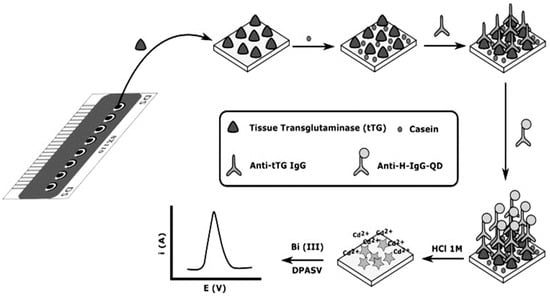
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the electrochemical biosensor array. The bioassay is carried out using the working electrodes of the array as transducers and in situ electrochemical detection of QDs. Reprinted with Permission [22].
Detection approaches are divided into label-free and labeled assays. Label-free assays are performed by measuring the presence of an analyte directly via biochemical reactions on a transducer surface, while in the labeled assays, the analyte is sandwiched between the capture agent and labeled agent with a special label such as an enzyme, quantum dot, fluorophore, or radioisotope, for obtaining signal.
1.1.1. Direct Immunosensors
Direct immunosensors, in other words label free immunosensors, are capable of detecting the physical or chemical changes arising directly from the immune antigen-antibody complex formation without needing to label. In this type of immunosensor, there is no need to use the label and it can be applied for fast, real-time analysis. Hence, the application of label free immunosensors in a clinical approach has become increasingly favoritized in the last decades. However, the label free immunosensors suffer from a significant effect of non-specific adsorption on their response [11,25,26,27]. Generally, no signal should be observed in the absence of an antigen–antibody (Ag–Ab) interaction, but a small signal is always obtained due to the non-specific binding of the antigen or others proteins on the surface of the substrate. Non-specific adsorption can occur when the other proteins existing in the sample, which can adsorb to antibodies or support surface, lead to an increase in the background signal. This phenomenon results in decreasing sensitivity. Hence, the use of a proper blocking agent is necessary. Several compounds are used as blocking agents such as surfactants (Tween 20, polyethylene glycol), casein, bovine serum albumin (BSA), and thionic compounds for gold surfaces [28,29,30,31].
1.1.2. Indirect Immunosensors
Indirect immunosensors, generally labeled immunosensors, are based on the signal generating from one or several labels allowing highly sensitive and versatile detection. In indirect measurements such as enzymes, e.g., horseradish peroxidase [32], catalase and glucose oxidase [33], alkaline phosphatase [34], and electroactive compounds as a mediator such as ferrocene, Prussian blue is usually used in the electrochemical immunosensor, especially when antigens and antibodies are not intrinsically electroactive. Moreover, several nanomaterials such as gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) or different quantum dots (QDs) can be used to amplify the signal. In the labeled immunosensors, labels can be attached to an antibody or antigen to achieve an electron-transfer and assuming that the number of labels detected during measurement correspond to the number of target analytes. In contrast to label free, labeled immunosensors have some advantages such as higher sensitivity and a lower effect of non-specific adsorption on the signal, but face some drawbacks like; the effect on antigen antibody binding efficiency on labelling a biomolecule due to the variability of the biomolecule label coupling reaction [19,28,30,35].
Labeled immunosensors can be divided into two other types of possible formats: competitive format and non-competitive format.
Competitive Immunosensors
Competitive immunosensors are useful for small antigens with one epitope in which the sample analyte and labeled analyte compete with each other to access the limited number of antibody-binding sites. Due to the use of the limited amount of antibody, this format is known as “limited reagent assay”. In general, antibody is firstly immobilized on the substrate surface and then incubated with a mixed solution of a known amount of labeled antigen and an unknown sample. The signal obtained from the labeled analyte is inversely proportional to the sample analyte amount. Thus, a larger signal is obtained for a fixed number of antibody sites when the quantity ratio of sample to labeled analyte is low [19,28,30,35].
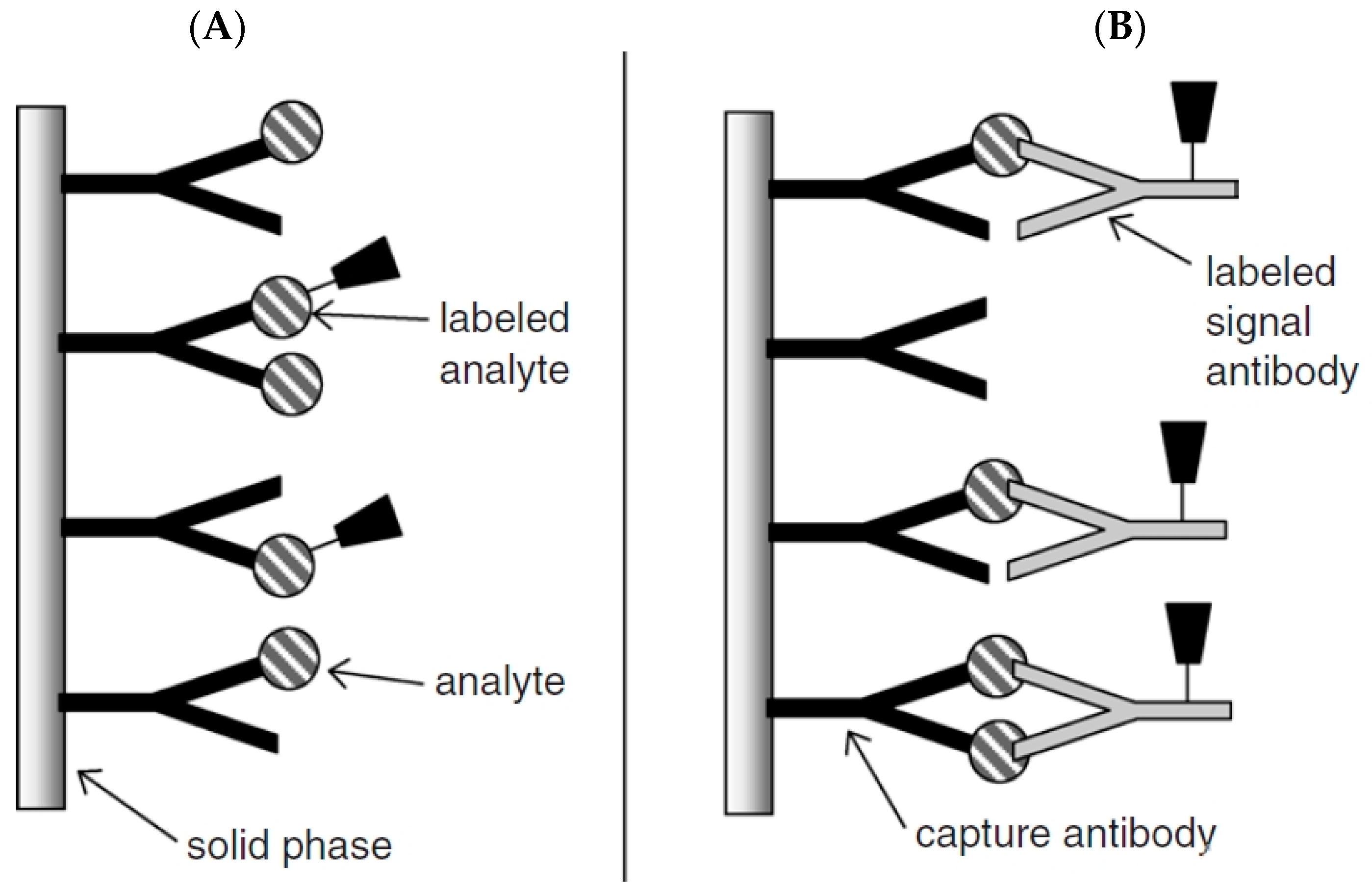
Competitive immunoassays can be carried out in two different ways e.g., homogenous or heterogeneous approach. In the homogenous assay, the amount of labeled unbound antigen is measured with no need for separation steps, but in the heterogeneous assay, the labeled bound antigen is measured after removing the labeled unbound antigen by using a washing step. Although the homogenous assay is faster than the heterogeneous, the sensitivity is lower than that due to non-specific adsorption. The scheme principle of competitive immunosensors is given in Figure 2A [35] There are several papers based on competitive immunosensors [36,37].
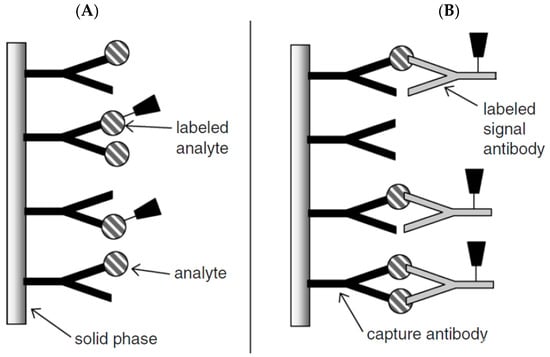
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of (A) competitive and (B) non-competitive immunoassay formats. Reprinted with Permission [35].
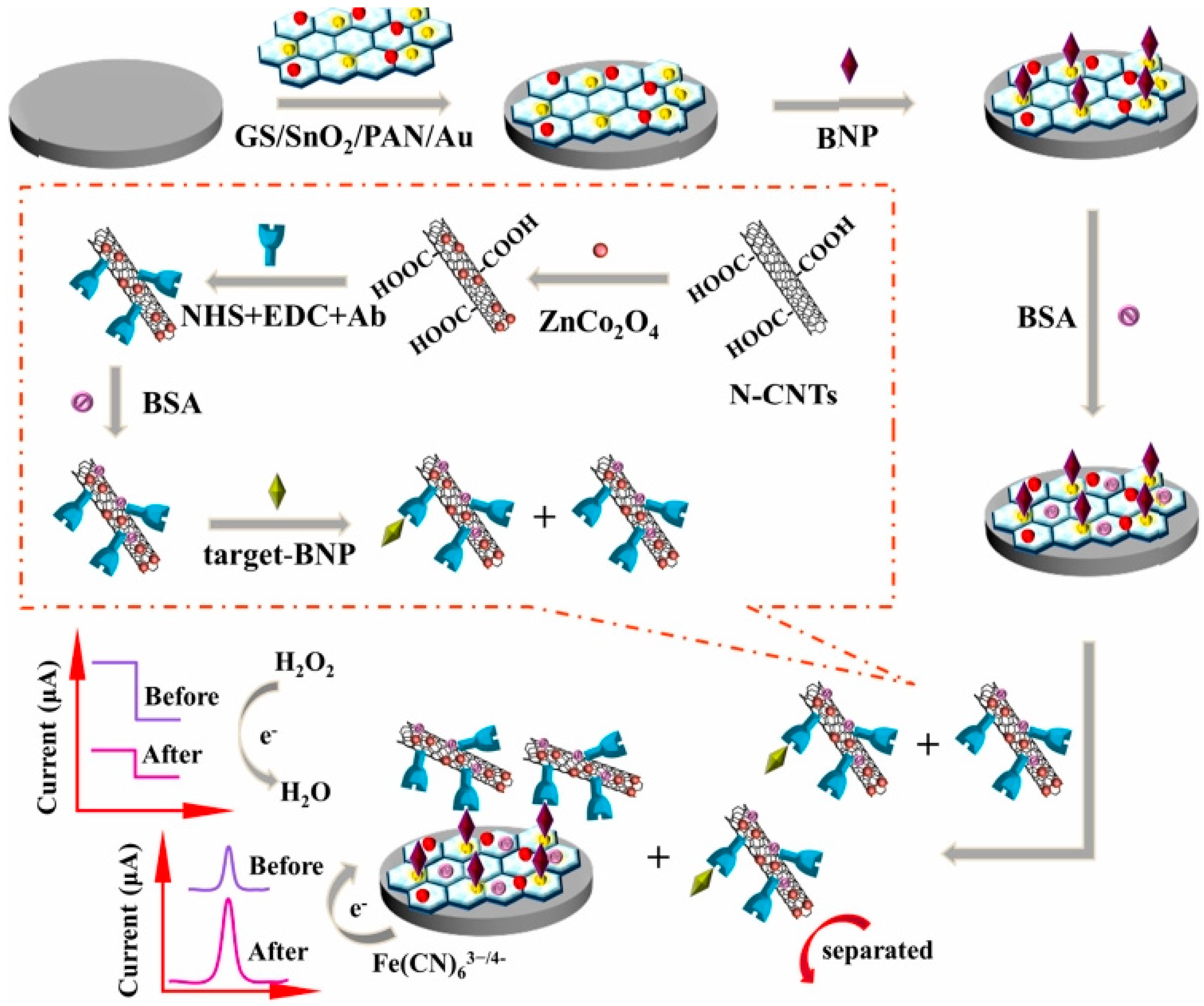
In 2019, Li et al. described a dual competitive electrochemical immunosensor based on differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and amperometric i-t curve response modes for the detection of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) [38]. In this work, glassy carbon electrode was modified with GS/SnO2/PAN-Au which acted as the platform for the DPV signal and ZnCo2O4/N-CNTs complex acted as the label for providing an amperometric signal for the reduction of H2O2 (Figure 3). Under the optimum conditions, the immunosensor displayed a remarkable analytical performance with a linear range from 0.01 pg/mL to 1 ng/mL and a detection limit of 3.4 fg/mL for the determination of BNP (S/N = 3). This method has been suggested to become a universal approach for other biological detection.
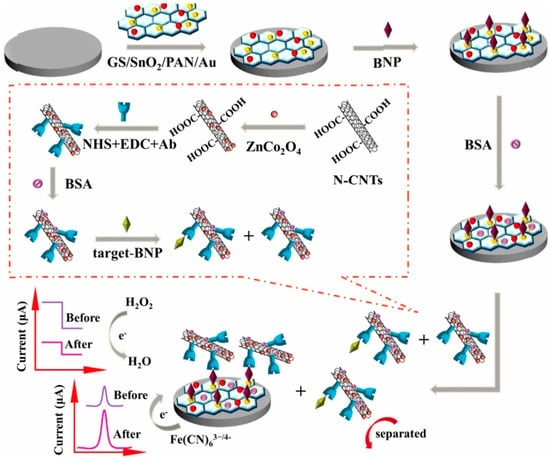
Figure 3.
The schematic illustration of the dual mode competitive electrochemical immunosensor. Reprinted with Permission [38].
A competitive immunosensor was also developed by Zhang et al. in 2019, for ultrasensitive detection of microcystin-LR (MC-LR) using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) material [39]. Anti-MC-LR was immobilized on the glassy carbon electrode surface modified by electrodeposition of graphene oxide (GO). Au NPs@MIL-101 was used as a label to detect MC-LR using the competitive method and had a catalytic effect on the oxidation of ascorbic acid (AA) to achieve MC-LR detection. With optimizing of the conditions, the sensitivity and selectivity of the MC-LR immunosensors are significantly improved with a wide linear range from 0.05 ng/mL to 75 μg/mL and a low detection limit of 0.02 ng/mL (S/N = 3). For detection of cortisol in human saliva, Kämäräinen et al. described an electrochemical immunosensor based on a direct competitive enzyme linked immunoassay using a disposable graphite screen-printed electrode. The electroanalytical response was generated by using an alkaline phosphatase (AP)-conjugated cortisol and 1-naphtyl phosphate as enzyme substrate. Square wave voltammetry (SWV) was used to monitor the enzyme activity. A low LOD of 0.6 ng/mL was obtained [40].
Non-Competitive Immunosensors
Non-competitive immunosensors, known as two-site “sandwich” immunoassays, are applied for large antigens with epitopes of more than one. In this assay, excess amounts of secondary and primary antibodies are used and the antigen is sandwiched between two antibodies. An antibody which is immobilized on the solid substrate surface is called a capture antibody (primary) that captures the antigen from the sample and another antibody is labeled antibody (secondary) which binds to the antigen–antibody complex, leading to production of a detected signal (Figure 2B). The signals usually arise from catalytic reaction of the enzyme labeled as a probe with the detection antibody. A washing step is necessary after each incubation step to remove unbound reagents [19,28,30,35].
A “one-site” assay is based on the immunoreaction between an immobilized antigen and a labeled antibody. The unbound labeled antibody is removed by washing to prevent precipitation in the binding event, so that the signal obtained by the bound antibody can be measured. Although the non-competitive sandwich format, as a common format of immunosensors, has higher sensitivity, specificity, and a wider dynamic range in compression to the competitive assays, it is not usable for the assay of small molecules (monovalent with molecular weight < 1000 Da) [19,28,30,35].
1.2. Electrochemical Immunosensing
The electrochemical immunosensors can be also classified according to the applied technique in potentiometric, conductometric, impedance, and amperometric mode [3,12,19,28,30,35,41,42,43].
1.2.1. Amperometric Immunosensors
Most electrochemical immunosensors are based on amperometric measurement by applying a constant potential at the working electrode related to the reference electrode in which a current is obtained from the electrochemical oxidation or electroreduction of an electroactive species. Only a small number of label free immunosensors have been reported as amperometric immunosensors [44] because most antibodies and antigens are not electroactive and cannot give amperometric response. Hence, in the majority of amperometric immunosensors, the use of electroactive labels or mediators is required to achieve a response for the detection of biomarkers. The major disadvantage of the amperometric immunosensor is limitation to the indirect detection system, however, it is compensated for by excellent sensitivity due to a linear relationship between the immunosensor response and the concentration of analyte (antigen), compared to a logarithmic relationship for potentiometric systems [9,30].
1.2.2. Potentiometric Immunosensors
Potentiometric immunosensors are based on measuring the change of potential due to the formation of immunocomplex between antibody and antigen. The sensitivity of this type is lower than others because the difference of potential is small during the immunoaffinity reaction as well as the effect of interferences being serious. Some of the label-free immunosensors belong to this group [45]. The main advantage of potentiometric immunosensors is the simplicity of operation, allowing use in automation and miniaturization of solid-state sensors [30,35].
1.2.3. Impedimetric Immunosensors
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is an important and useful technique widely used for surface characterization in chemical sensors and biosensors especially for label-free detection. In addition, it can be used for the investigation of the electrode/electrolyte interface and for study of the kinetics of the electrode surface and the binding kinetics between molecules such as receptors, DNAs, proteins, antibodies, antigens, ions etc. The fundamental effect of EIS is based on applying a constant AC potential with a small perturbation, usually 5 or 10 mV, over a wide range of frequencies. The results are then plotted in a Nyquist plot where the imaginary part of impedance (−Z’’) is plotted versus the real part of impedance (Z’) and/or in a Bode plot, where the total impedance (|Z|) is plotted versus the frequency [46].
Most of the impedimetric model circuits (Randless cell circuit) designed are based on elements of electrolyte solution resistance (Rs), Warburg impedance (W), charge transfer resistance (Rct), and a pure capacitor (C). EIS is widely used for the development of label-free immunosensors. This type of immunosensor is very suitable for the detection of various target biomarkers, resulting in monitoring the formation of antibody-antigen directly without the need of a further label. The response is based on the change of interfacial properties (charge–transfer resistance) related to the immune-recognition event [40,41,42,43]. The advantages of this type of immunosensor are simple and fast detection, low cost, insensitivity to environmental condition changes, no sample pretreatment, and the application for the detection of a wide range of analytes. For label-free detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) by using the impedimetric method, Ganganboina and Doong reported an immunosensor based on a Pt electrode modified by casting of N, S-graphene quantum dots@Au-polyaniline (N, S-GQDs@Au-PANI) nanowires on the electrode surface [47]. Using Fe(CN)63−/4− as redox probe in solution and EIS as electrochemical technique, the immunosensor was sensitive to the concentration of the CEA on the immobilized Ab, showing an LOD of 0.01 ng mL−1 and a linear detection range between 0.5 and 1000 ng mL−1. The N, S-GQDs@Au-PANI nanowires as excellent conducting materials can accelerate the electron transfer, but after the formation of CEA antibody-antigen bio conjugates by adding CEA, the charge transfer resistance is significantly increased, and subsequently a highly stable and label-free immunosensor platform is fabricated for the impedimetric detection of CEA.
1.2.4. Conductometric Immunosensors
Conductometric immunosensors rely on a relationship between conductance and a bio-recognition event. When the reaction occurs between a bio-recognition element and an antigen, the conductivity of the solution or current flow is changed due to the change in ionic species concentration. On the other hand, the conductivity of the supporting electrolyte is changed when antibodies labeled with enzyme are conjugated with antigens in the sample solution, the enzyme’s performance stops by the inhibitory effect of the antigen–antibody complex blocking the surface of the electrode. This signal can be measured by an ohmmeter or multimeter. Conductometric immunosensors have a number of advantages, including low driving voltage, large-scale production, and suitability for miniaturization without a reference electrode [48].
1.3. Immobilization Methods
Since the immobilization procedure of antibody on the electrode surface plays a critical role in the signal obtained by the specific immunoreactions between an immobilized antibody and antigen, the choice of an appropriate immobilization approach is a major step for achieving a high performance immunosensor. In addition, the proper immobilization method for the antibody can guarantee the stability and applicability of the affinity biosensor. For this purpose, a more appropriate method is that, first, it can maintain the biological activity of the bioelement (antibody or aptamer) and second, it provides a good orientation in terms of binding sites exposed towards the aimed analyte as well as a proper density [30]. A high density of the bioelement can hinder the binding of antigen. Hence, the bioelement layer needs to be immobilized on the surface of the sensor by various methods [36,49,50].
1.3.1. Physical Adsorption
Physical adsorption is the simplest method for binding an antibody to the electrode surface based on non-covalent interactions between the bioelement and the surface of the sensing device, including electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals, and hydrophobic interaction. The immobilization of antibodies on the ELISA micro-titer plate or on the self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of gold nanoparticles with thiol groups, via electrostatic adsorption attractions, are common examples for the adsorption method. If the concentration of antibody is sufficient, a layer of proteins is formed on the electrode surface [49]. The application of a physical adsorption strategy faces some limitations due to the problems arising when the concentration of the immobilized antibody is very low forming dense packing. Many factors may affect the quality of immunosensors based on physical adsorption such as (i) surface contamination at a low concentration of antibody; (ii) blocking the idiotypic sites of IgG when the adsorption takes place near to the substrate surface, leading to loss of binding capacity; (iii) partial denaturation of IgG [49]. Direct physical adsorption of bioelements on solid substrata has a random orientation of bioelements and a probability of desorption due to weak bonds resulting in low sensitivity and reproducibility [18], conformational changes, as well as decreased bioactivities with time [49,51,52,53,54]. Despite these drawbacks of antibody adsorption, these methods are used in many applications such as antibody arrays, ELISA, and immunosensors, due to their simple and easy procedure, and high antibody-binding capacity [55].
1.3.2. Trapping Methods
This procedure is based on the encapsulation of bioelements in polymer matrices such as molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) and sol-gel. The trapping method possesses more stability in comparison to the physical adsorption procedure. The sol-gel-based immobilization method has a number of advantages such as simplicity, low-temperature encapsulation of bioelements, optical transparency, high thermal stability, tunable porosity, mechanical rigidity, and low chemical reactivity [49,52,53,54,56].
1.3.3. Covalent Binding
The covalent binding strategy as the most common method is used in the immobilization of bioelements based on covalent interactions between the surface of the modified electrode and the functional groups of antibodies or aptamers [18]. Functional groups of antibodies for covalent binding can include amine, carboxyl, carbohydrate, and thiol moieties. The covalent attachment depends on the various chemistries such as substrate functionality, functional groups on the antibody, and some physical conditions like pH, temperature, and degree of conjugation [57]. Generally, electrode surfaces have no sites for covalent bonding, so it is necessary to first coat a thin film of the functional groups in order to covalently bond with the amino groups of the antibodies for example. For this purpose, some reagents such as glutaraldehyde, carbodiimide succinimide ester, N-hydroxysuccinimide, periodate, or maleinimide can be used. Glutaraldehyde is suitable for smaller sized molecules and N, N′-carbonyldiimidazole is recommended for higher sized molecules (>20 nm). Glutaraldehyde has two aldehyde groups and can react as a bi-functional cross-linking agent with amine groups to form peptide bonds [58,59]. Another approach to obtain functionalized films on the surface electrode for the immobilization of bioelements (e.g., antibodies, antigens and aptamers) is the self-assembled monolayer (SAM) technique [60,61]. Based on this strategy, semi-covalent binding is formed between a sulfide group (disulfides, sulfides and thiols) and the noble metal surfaces (e.g., Au, Ag or Pt) to form highly organized SAMs. Thiol functionalized antibodies can be easily immobilized on Au surfaces [62]. The formation of thin layers is perfected because it reduces the diffusion time of the analytes and improves the speed of the sensor response. In addition, because most of the reactants used in these systems are organic molecules, a thinner layer will have a lower insulating effect. The use of oligo-ethylene glycol thiol owning to its regular structure, high biocompatibility, minimal desorption as well as the functionalized alkyl silanes with amine, aldehyde, thiol, or carboxylic groups is another common strategy for cross-linking [58]. The covalent attachment method of proteins has been reported in much detail in some reviews [57,63]. This procedure is more stable and has better oriented immobilization [64,65].
1.3.4. Affinity Immobilization Techniques
Affinity immobilization techniques are favorable strategies for obtaining high capture efficiency and oriented immobilization of the biorecognition elements to achieve a high performance immunosensor. Bio-affinity immobilization techniques are based on material binding peptides, Protein A or G, biotin–streptavidin interaction, Fc-binding peptides and aptamers, lectin-sugar, His- Tag systems, nucleotide binding site, and DNA-directed immobilization [54,66,67,68].
Protein A or G are small bacterial proteins which specifically bind to the Fc regions of antibodies, allowing oriented immobilization to be obtained on the solid support. Protein A was originally isolated from Staphylococcus aureus and shows five Fc binding domains placed near the terminal-NH2 [69].
(Strept)avidin-biotin is widely used for oriented immobilization of various biomolecules such as polysaccharides, nucleic acids, and protein like antibodies in which biotinylated capture antibodies are bound to avidin or streptavidin surfaces. Biotin–(strept)avidin has a strong non-covalent interaction which is resistant at high temperatures, pH variations as well as exposure to chemicals (e.g., protein denaturants) [70,71,72,73,74].
2. Recent Applications of Electrochemical Immunosensors in Clinical Analyses
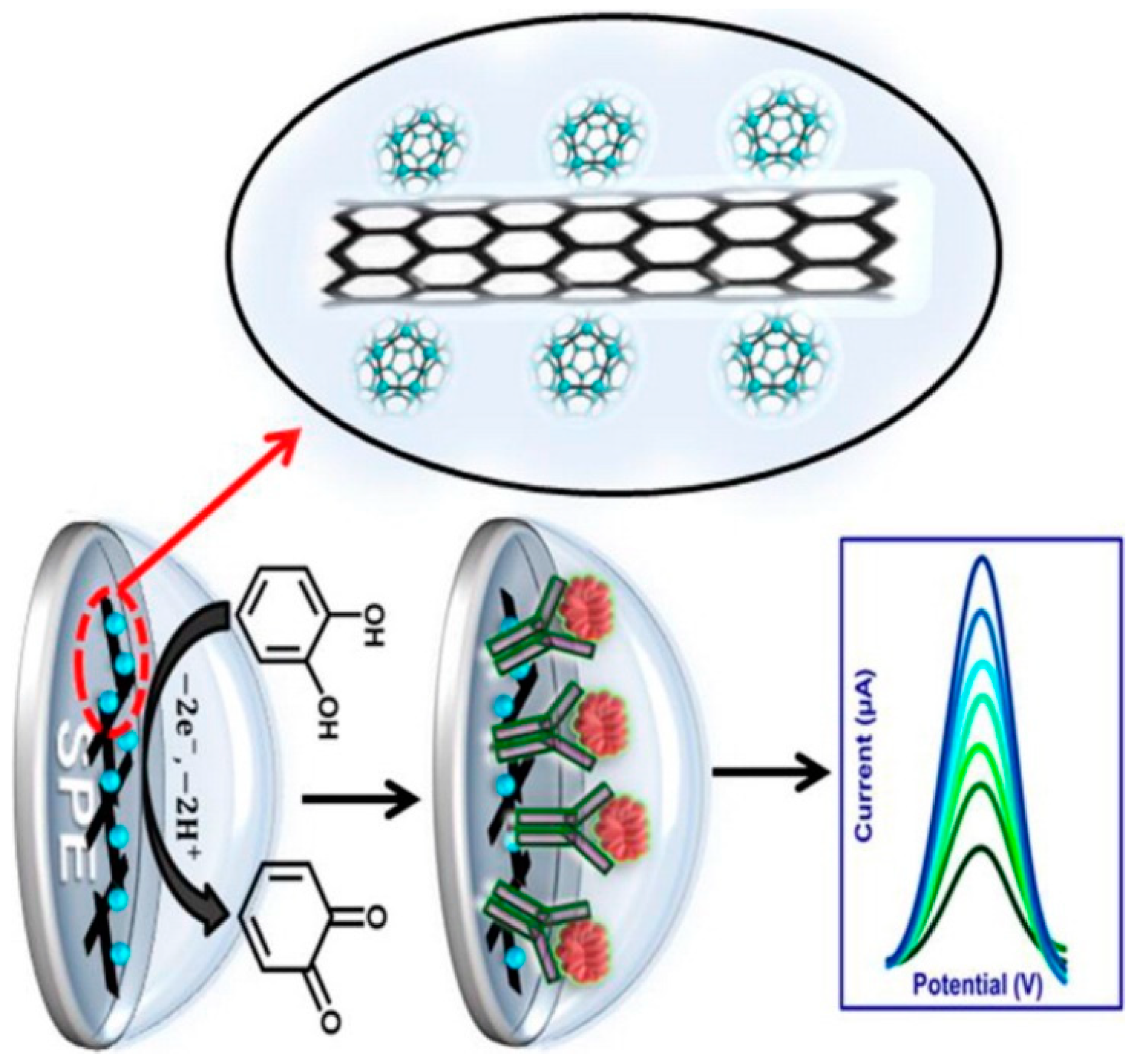
Immunosensors can be designed for cancer biomarkers, autoimmune diseases, cardiac diseases, etc. In their study, Mazloum-Ardakani et al., developed a Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor for Detection of Tumor Necrosis Factor α Based on Fullerene-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes/Ionic Liquid (C60–CNTs–IL) (Figure 4). The biosensor has a linear range between 5.0 pg·mL−1 and 75 pg·mL−1 with a low detection limit of 2.0 pg·mL−1 for TNF-α. Moreover, the designed label-free electrochemical immunosensor was successfully applied to serum samples [75].
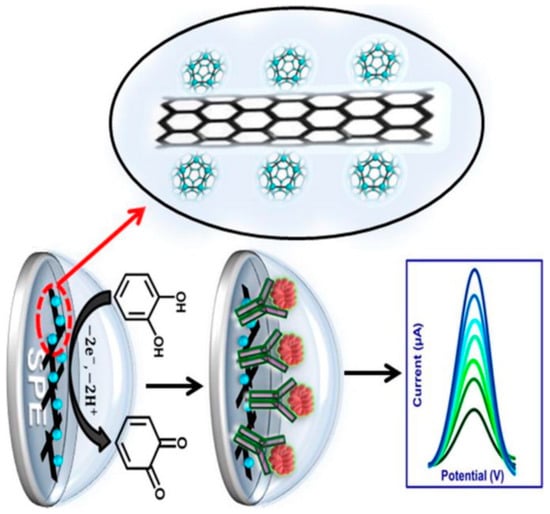
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of Fullerene-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes/Ionic Liquid based label-free electrochemical immunosensor. Reprinted with Permission [75].
AFP, which is a liver, ovarian, testicular cancer biomarker, was detected using one-step electrochemical immunoassay by Chen and co-workers. Horseradish peroxidase–anti-AFP (HRP–anti-AFP) was immobilized on a nanogold-functionalized graphene interface and antigen–antibody complex formation was followed by HRP for the catalytic reduction of H2O2 in the solution. AFP was detected in the linear range of 0.1–200 ng·mL−1 with a detection limit (LOD) of 0.05 ng·mL−1 AFP [76].
Carcino-embryonic antigen (CEA) was detected using a novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on PtPd bimetallic nanoparticles graphene quantum dots and gold nanoparticles (PtPd/N-GQDs@Au). Due to the large surface area, high conductivity, and high biocompatibility, the biosensor showeda linear range between 5 fg/mL and 50 ng/mL with a very low detection limit of 2 fg/mL which is of the order 10−15 [77]. In another work, simultaneous detection of CEA and AFP was suggested using gold nanoparticles decorated multiwall carbon nanotubes. A novel sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor was developed with a linear range of 0.01 to 60 ng mL−1 for CEA and AFP and with detection limits of 3.0 pg mL−1 for CEA and 4.5 pg mL−1 for AFP [78]. In their work, Stoeva et al., developed a biosensor for multiple detection of protein cancer biomarkers; CEA, CA 125, CA 153, CA 199. A screen printed array was used for this purpose, and linear ranges of 0.16–9.2 ng/mL for CEA, 0.084–16 U/mL for CA 153, 0.11–13 U/mL CA 125, 0.16–15 U/mL for CA 199 were obtained with LOD values of 0.04 ng/mL CEA, 0.06 U/mL CA 153, 0.03 U/mL CA 125, 0.1 U/mL CA 199 [79].
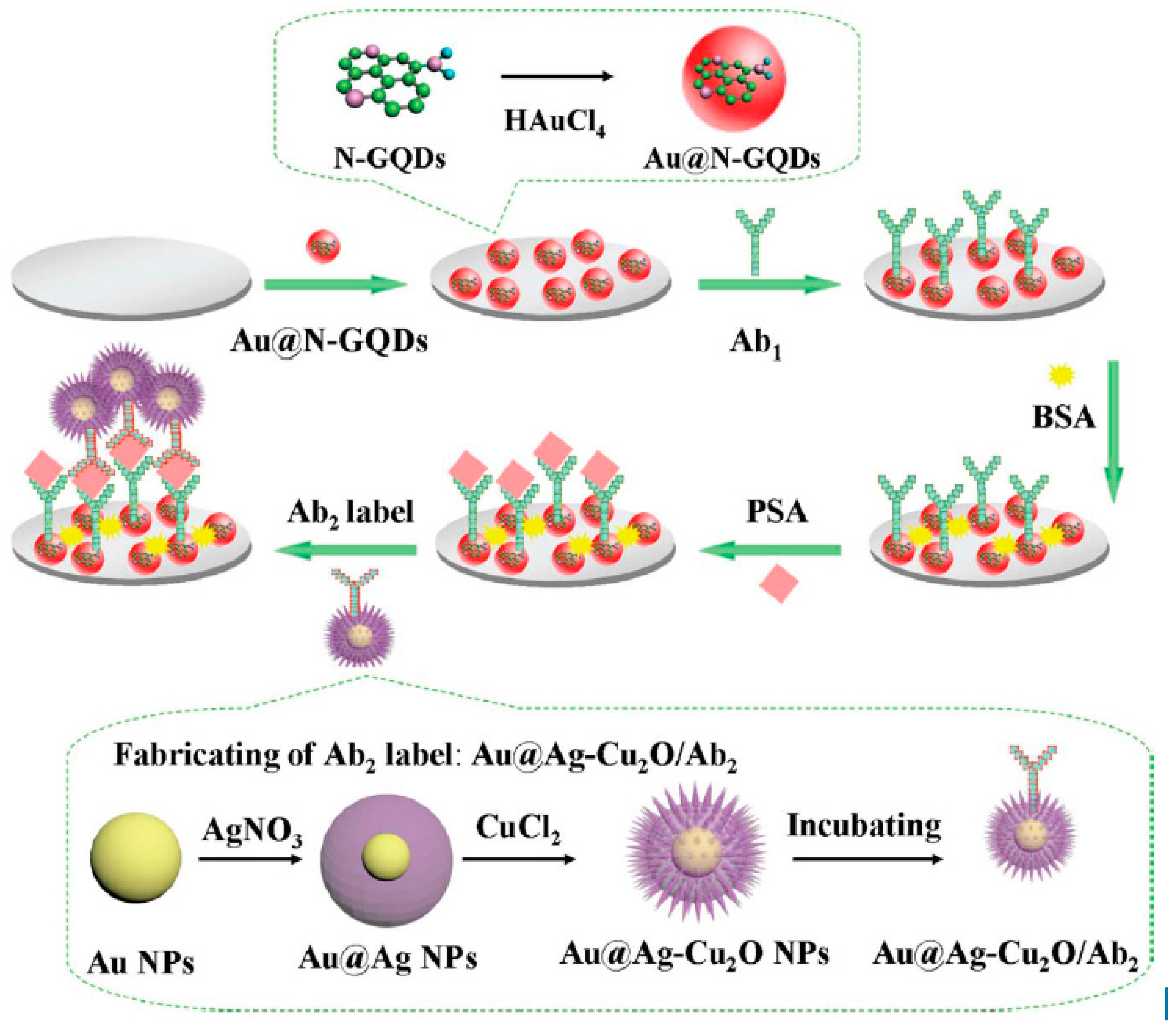
IL-6, which is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus biomarker, was detected using Poly-HRP labeled anti-IL-6 antibodies, Gold compact disc, and an 8-electrode array system. IL-6 detection was obtained within a linear range of 10–1300 fg/mL with an LOD value of 10 fg/mL [80]. In another work, a 16-electrode SPCE array was used for ultrasensitive multiplexing electrochemical immunosensing of PSA with IL-8. LOD values of 5 pg/mL and 8 pg/mL, for PSA and IL-8, respectively [81]. An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor was developed by Yang et al., using gold nanoparticles functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (Au@N-GQDs) for Prostate specific antigen (PSA). Highly specific interaction between antigen and antibody was obtained with a dynamic range from 0.01 pg.m−1 to 100 ng·mL−1 with a low detection limit of 0.003 pg·mL−1 followed by the reduction of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with amperometric response at −0.4 V [82]. (Figure 5).
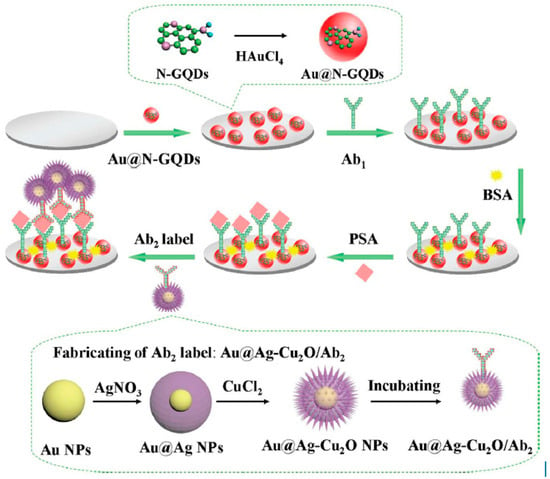
Figure 5.
The schematic illustration of the sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor and the preparation procedure of Au@N-GQDs NPs and Au@Ag-Cu2O/Ab2 Reprinted with Permission [82].
Herein, we report the research progress of electrochemical immunosensors applied in clinical analysis that were published in the last years (Table 1).

Table 1.
Some selected studies on electrochemical immunosensors in clinical analyses.
3. Conclusions
Every protein is a biomarker of one or more diseases. CA 15-3, CA 27-29, HER2/NEU are biomarkers for Breast cancer, CA 125 Ovarian CEA Colon is a biomarker of cancer, PSA is a biomarker of the Prostate, NMP22, Fibrin/FDP, BTA, high molecular weight CEA are biomarkers for Bladder cancer, α-fetoprotein and Human gonadotropin-β are biomarkers for Testicular cancer, CA 19-9 is a biomarker of Pancreatic cancer. The level of determination of these biomarkers is important to see if they exist or not in the sample with rapid and reliable detection. Cut-off values of these biomarkers gives information about whether the patient is ill or not, and gives the analytical chemist the opportunity to develop methods that can detect these or even lower values accurately and precisely. All the biomarkers have unique and different cut off values such as, TNF-α has cut-off value of 11.63 pg·mL−1 whereas CRP has a cut-off value of 60 mg·L−1. The analytical chemist should discuss these cut-off values and find suitable analytical methods for immunosensing. Electrochemical methods especially impedance based ones give a ground for choice by researchers and companies as they give a rapid response and a specific electrochemical response towards analyte. Electrochemical immunosensors in clinical analyses have frequently found a place due to their rapid response in terms of “exist or not exist”. We believe that as the technology is developing very quickly, there will be picomolar level sensors as early grade detection of illness, save lives.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; PB: protein biomarker; anti-CCP: anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide; IL: interleukin; ACAB: anti-chromatin (anti-nucleosome) autoantibodies; CRP: C-reactive protein; TA-Ab: transglutaminase autoantibody; IL-17RA: interleukin-17 receptor A; MBP: myelin basic protein; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; PS: psoriasis; ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome; MS: multiple sclerosis; n.s.: not stated. CA: cancer/carbohydrate antigen; CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen; HER2/NEU: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; PSA: prostate specific antigen; NMP22: nuclear matrix protein 22; FDP: fibrin degradation product; BTA: bladder tumor associated antigen. PA: Polyaniline; PAA: polyacrylic acid; CHT: Chitosan; GA: glutaraldehyde; NA: nafion; GRNS: graphene nanosheets; Pt–PdBiMNP: platinum–palladium bimetallic nanoparticles; AuNPs: gold nanoparticles; CE: Carbon electrode; GONS: Graphene oxide nanosheets PGDE: pyrolytic graphite disk electrode C60: fullerene.
References
- Ghindilis, A.L.; Atanasov, P.; Wilkins, M.; Wilkins, E. Immunosensors: Electrochemical sensing and other engineering approaches. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.L.; Newman, D.J.; Price, C.P. Immunosensors: Technology and opportunities in laboratory medicine. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warsinke, A.; Benkert, A.; Scheller, F.W. Electrochemical immunoassays. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 366, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voller, A.; Bidwell, D.E.; Bartlett, A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Bull. World Health Organ. 1976, 53, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Electrochemical sensors for clinic analysis. Sensors 2008, 8, 2043–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosu, O.; Selvolini, G.; Marrazza, G. Recent advances of immunosensors for detecting food allergens. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skládal, P. Advances in Electrochemical Immunosensors. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, K.K.; Layek, K.; Mahapatra, A.; RoyChaudhuri, C.; Saha, H. A review on amperometric-type immunosensors based on screen-printed electrodes. Analyst 2014, 139, 2289–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Moscone, D.; Ricci, F.; Piermarini, S.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F.; Micheli, L. Electrochemical biosensors based on nanomodified screen-printed electrodes: Recent applications in clinical analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Daniels, J.S.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-free impedance biosensors: Opportunities and challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconu, I.; Cristea, C.; Hârceagǎ, V.; Marrazza, G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Sǎndulescu, R. Electrochemical immunosensors in breast and ovarian cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 425, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzetti, A.P.; Fiorile, M.C.; Primavera, A.; Lo Bello, M. Glutathione transferases and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 82, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghindilis, A.L.; Atanasov, P.; Wilkins, E. Enzyme-Catalyzed Direct Electron Transfer: Fundamentals and Analytical Applications. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Bhirde, A.A.; Morgan, N.Y.; Eden, H.S.; Chen, X. Electrochemical immunosensors for detection of cancer protein biomarkers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6546–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.S. Electrochemical immunosensors for the simultaneous detection of two tumor markers. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Y. Nanomaterial labels in electrochemical immunosensors and immunoassays. Talanta 2007, 74, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, G.; Fan, C. Development of electrochemical immunosensors towards point of care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, O.A.; Van Emon, J.M. Applications of electrochemical immunosensors to environmental monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1996, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrameas, S.; Ternynck, T.; Guesdon, J.-L. Coupling of Enzymes to Antibodies and Antigens. Scand. J. Immunol. 1978, 8, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, N.S.; Jackson, L.R.; Trudel, L.J.; Weis-Garcia, F. Monoclonal Versus Polyclonal Antibodies: Distinguishing Characteristics, Applications, and Information Resources. ILAR J. 2013, 46, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; González-García, M.B.; Costa-García, A. Electrochemical immunosensor for anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies based on the in situ detection of quantum dots. Talanta 2014, 130, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; Costa-García, A. Towards a blocking-free electrochemical immunosensing strategy for anti-transglutaminase antibodies using screen-printed electrodes. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 105, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogola, J.L.; Martins, G.; Caetano, F.R.; Ricciardi-Jorge, T.; Duarte dos Santos, C.N.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for quick detection of anti-hantavirus antibody. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 842, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, Q. Label-free electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for detection of prostate specific antigen based on mesoporous graphite-like carbon nitride. Talanta 2018, 188, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Kerman, K.; Tamiya, E.; Vestergaard, M.; Kerman, K.; Tamiya, E. An Overview of Label-free Electrochemical Protein Sensors. Sensors 2007, 7, 3442–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xueji, Z.; Huangxian, J.; Joseph, W. Electrochemical Sensors, Biosensors and Their Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 0123737389. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Xu, X.; Ying, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, J. Immunosensors for detection of pesticide residues. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, B.E.; Gruhl, F.J.; Länge, K. Biosensors with label-free detection designed for diagnostic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppa, P.B.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W. Immunosensors-Principles and Applications to Clinical Chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 314, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, M.; Morioka, A.; Matsuoka, H.; Suzuki, S.; Nagamura, Y.; Shinohara, R.; Ishiguro, I. An enzyme immunosensor for IgG. J. Solid-Phase Biochem. 1976, 1, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Mao, K.; Li, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Q. Electrochemical immunosensor for α-fetoprotein detection using ferroferric oxide and horseradish peroxidase as signal amplification labels. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 465, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, D.; Li, Q.; Su, B.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G. Sensitive electrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen with signal dual-amplification using glucose oxidase and an artificial catalase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 697, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, J.J. Electrochemical immunosensor of tumor necrosis factor α based on alkaline phosphatase functionalized nanospheres. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1890–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.M.; Wong, D.K.Y.; Brian Halsall, H.; Heineman, W.R. Recent developments in electrochemical immunoassays and immunosensors. In Electrochemical Sensors, Biosensors and Their Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 115–143. ISBN 9780123737380. [Google Scholar]
- Giannetto, M.; Bianchi, M.V.; Mattarozzi, M.; Careri, M. Competitive amperometric immunosensor for determination of p53 protein in urine with carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles screen-printed electrodes: A potential rapid and noninvasive screening tool for early diagnosis of urinary tract carcinoma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 991, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Gong, L.; Zang, L.; Dai, H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Y. Dual-responsive competitive immunosensor for sensitive detection of tumor marker on g-CN/rGO conjugation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Dong, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; Fang, J.; Cui, M.; Wei, Q.; Cao, W. Dual mode competitive electrochemical immunoassay for B-type natriuretic peptide based on GS/SnO2/polyaniline-Au and ZnCo2O4/N-CNTs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Dai, K.; Bai, R.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Hu, R.; Yang, Y. A competitive microcystin-LR immunosensor based on Au NPs@metal-organic framework (MIL-101). Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämäräinen, S.; Mäki, M.; Tolonen, T.; Palleschi, G.; Virtanen, V.; Micheli, L.; Sesay, A.M. Disposable electrochemical immunosensor for cortisol determination in human saliva. Talanta 2018, 188, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Adornetto, G.; Palleschi, G. A review of experimental aspects of electrochemical immunosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-A.A.; Chiu, J.-K.; Hong, J.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Hwang, K.-C.; Hwu, J.-R.R. Gold-Nanostructured Immunosensor for the Electrochemical Sensing of Biotin Based on Liposomal Competitive Assay. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 2324–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Chen, M.; Zhao, C.; Liu, A.; Lin, L.; Liu, Q.; Lin, J.; Lin, X. Label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on K3[Fe(CN)6] as signal for facile and sensitive determination of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chao, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Pang, X.; Fan, D.; Wei, Q. A label-free amperometric immunosensor for detection of zearalenone based on trimetallic Au-core/AgPt-shell nanorattles and mesoporous carbon. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 847, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollarasouli, F.; Serafín, V.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Asadpour-Zeynali, K. Ultrasensitive determination of receptor tyrosine kinase with a label-free electrochemical immunosensor using graphene quantum dots-modified screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1011, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ErtuğruL, H.D.; Uygun, Z. State of the Art in Biosensors—General Aspects; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 9535110047. [Google Scholar]
- Ganganboina, A.B.; Doong, R.A. Graphene Quantum Dots Decorated Gold-Polyaniline Nanowire for Impedimetric Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.G. Conductometric immunosensors for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B based bio-electrocalytic reaction on micro-comb electrodes. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 31, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, W.; Paek, S.H.; Voss, G. Strategies for the Immobilization of Antibodies. Immunomethods 1993, 3, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Kavosi, B.; Fathi, F.; Hallaj, R. Highly sensitive immunosensing of prostate-specific antigen based on ionic liquid-carbon nanotubes modified electrode: Application as cancer biomarker for prostate biopsies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, Z.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Gupta, V.; Malhotra, B.D. Fundamentals and Application of Ordered Molecular Assemblies to Affinity Biosensing. ChemInform 2012, 41, 1363–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Spain, J.C.; Naik, R.R.; Stone, M.O. Enzyme immobilization in a biomimetic silica support. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.V.; Anderson, K.W.; Bachas, L.G. Oriented immobilization of proteins. Mikrochim. Acta 2005, 128, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brena, B.; González-Pombo, P.; Batista-Viera, F. Immobilization of enzymes: A literature survey. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1051, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Chung, B.H. Recent advances in immobilization methods of antibodies on solid supports. Analyst 2008, 133, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Yang, G.; Shao, H.; Qin, A. A label-free impedimetric immunosensor for detection of 1-aminohydantoin residue in food samples based on sol-gel embedding antibody. Food Control 2014, 39, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, N.G.; Scoble, J.A.; Muir, B.W.; Pigram, P.J. Orientation and characterization of immobilized antibodies for improved immunoassays (Review). Biointerphases 2017, 12, 02D301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, A.S. Electrochemical Affinity Sensors for Biomedical, Food and Environmental Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, Villeurbanne, France, November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncagil, S.; Kayahan, S.K.S.K.; Bayramoglu, G.; Arica, M.Y.Y.; Toppare, L. l-Dopa synthesis using tyrosinase immobilized on magnetic beads. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2009, 58, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulman, A. Formation and Structure of Self-Assembled Monolayers. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 1533–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Biebuyck, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterning Self-Assembled Monolayers: Applications in Materials Science. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1498–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, R.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.S. Nanoparticles: Functionalization and Multifunctional Applications in Biomedical Sciences. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4559–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, J. Oriented immobilization of proteins on solid supports for use in biosensors and biochips: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, D.; Tang, D.; Niessner, R. Review: Bioanalytical applications of biomolecule-functionalized nanometer-sized doped silica particles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 647, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.J.; Mustafaoglu, N.; Bilgicer, B. Conjugation of a Reactive Thiol at the Nucleotide Binding Site for Site-Specific Antibody Functionalization. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisan, J.M. (Ed.) Immobilization of Enzymes and Cells; Methods in BiotechnologyTM; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 22, ISBN 978-1-58829-290-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Carbon-nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreescu, S.; Bucur, B.; Marty, J.-L. Affinity Immobilization of Tagged Enzymes. In Immobilization of Enzymes and Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, I.; Gupta, M.N. Bioaffinity Immobilization. In Immobilization of Enzymes and Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.L.; Kurzban, G.P. Noncooperativity of Biotin Binding to Tetrameric Streptavidin. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 11750–11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; Milea, J.S.; Nguyen, G.H. Immobilization of Nucleic Acids Using Biotin-Strept(avidin) Systems. In Immobilisation of DNA on Chips II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 63–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lesch, H.P.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Pikkarainen, J.T.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. Avidin-biotin technology in targeted therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilchek, M.; Bayer, E.A.; Livnah, O. Essentials of biorecognition: The (strept)avidin–biotin system as a model for protein–protein and protein–ligand interaction. Immunol. Lett. 2006, 103, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teulon, J.-M.; Delcuze, Y.; Odorico, M.; Chen, S.W.; Parot, P.; Pellequer, J.-L. Single and multiple bonds in (strept)avidin-biotin interactions. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Khoshroo, A. Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for detection of tumor necrosis factor α based on fullerene-functionalized carbon nanotubes/ionic liquid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 757, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. One-step electrochemical immunoassay of biomarker based on nanogold-functionalized graphene sensing platform. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y. A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple biomarkers using gold nanoparticles decorated multiwall carbon nanotubes as signal enhancers. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 482, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Y.; Yan, F.; Ju, H. Electric field-driven strategy for multiplexed detection of protein biomarkers using a disposable reagentless electrochemical immunosensor array. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6072–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.K.; Vaze, A.; Rusling, J.F. Fabrication of immunosensor microwell arrays from gold compact discs for detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Deng, W.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X.; Peng, C.; Hu, H.; Peng, H.; Song, S.; Fan, C. Carbon nanotube-based ultrasensitive multiplexing electrochemical immunosensor for cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification strategy of echinoidea-shaped Au@Ag-Cu2O nanoparticles for prostate specific antigen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. Graphene and Nanogold-Functionalized Immunosensing Interface with Enhanced Sensitivity for One-Step Electrochemical Immunoassay of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Human Serum. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2720–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Zou, Z.; Shin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Engelhard, M.H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, L.A.; Lin, Y. Sensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker based on dual signal amplification strategy of graphene sheets and multienzyme functionalized carbon nanospheres. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Akter, R.; Han, O.H.; Rhee, C.K.; Rahman, M.A. Increased electrocatalyzed performance through dendrimer-encapsulated gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotube-assisted multiple bienzymatic labels: Highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for protein detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1784–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Chu, Q.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification strategy of mesoporous core–shell Pd@Pt nanoparticles/amino group functionalized graphene nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Feng, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, P. A novel sandwich-type immunosensor for detection of carcino-embryonic antigen using silver hybrid multiwalled carbon nanotubes/manganese dioxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 786, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Dai, H.; Pan, X.; Liu, S. Simultaneous detection of dual proteins using quantum dots coated silica nanoparticles as labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, M.; Yan, F.; Ju, H. Triple signal amplification of graphene film, polybead carried gold nanoparticles as tracing tag and silver deposition for ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensing. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, N.; Ma, Z. Platinum porous nanoparticles hybrid with metal ions as probes for simultaneous detection of multiplex cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinos, C.; Angelopoulou, M.; Economou, A.; Prodromidis, M.; Florou, A.; Haasnoot, W.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Lab-on-a-membrane foldable devices for duplex drop-volume electrochemical biosensing using quantum dot tags. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, R.C.B.; Costa-Rama, E.; Viswanathan, S.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Costa-García, A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; González-García, M.B. Voltammetric immunosensor for the simultaneous analysis of the breast cancer biomarkers CA 15-3 and HER2-ECD. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, G.C.; Krause, C.E.; Sotzing, G.A.; Rusling, J.F. Inkjet-printed gold nanoparticle electrochemical arrays on plastic. Application to immunodetection of a cancer biomarker protein. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4888–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, R.; Patel, V.; Vaqué, J.P.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for oral cancer biomarker IL-6 using carbon nanotube forest electrodes and multilabel amplification. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, D.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for prostate-specific antigen based on silver hybridized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 434, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, G.C.; Yu, X.; Gong, J.D.; Munge, B.; Bhirde, A.; Kim, S.N.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; Rusling, J.F. Characterization of Multienzyme-Antibody-Carbon Nanotube Bioconjugates for Immunosensors. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavosi, B.; Salimi, A.; Hallaj, R.; Moradi, F. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for PSA biomarker detection in prostate cancer cells using gold nanoparticles/PAMAM dendrimer loaded with enzyme linked aptamer as integrated triple signal amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker proteins using gold nanoparticle film electrodes and multienzyme-particle amplification. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Mani, V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4477–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyerhoff, M.E.; Duan, C.; Meusel, M. Novel nonseparation sandwich-type electrochemical enzyme immunoassay system for detecting marker proteins in undiluted blood. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raeisi, H.; Ganjali, M.R.; Safarnejad, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Haji-Hashemi, H.; Habibi, M.M.; Larijani, B. Sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for citrus bacterial canker disease detection using fast Fourier transformation square-wave voltammetry method. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 820, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Eletxigerra, U.; Martinez-Perdiguero, J.; Merino, S. Disposable microfluidic immuno-biochip for rapid electrochemical detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, R.; Özkütük, E.B.; Ünlüer, Ö.B.; Uğurağ, D.; Ersöz, A. Nano anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha based potentiometric sensor for tumor necrosis factor-alpha detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).