Insulin Regulation of Escherichia coli Abiotic Biofilm Formation: Effect of Nutrients and Growth Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
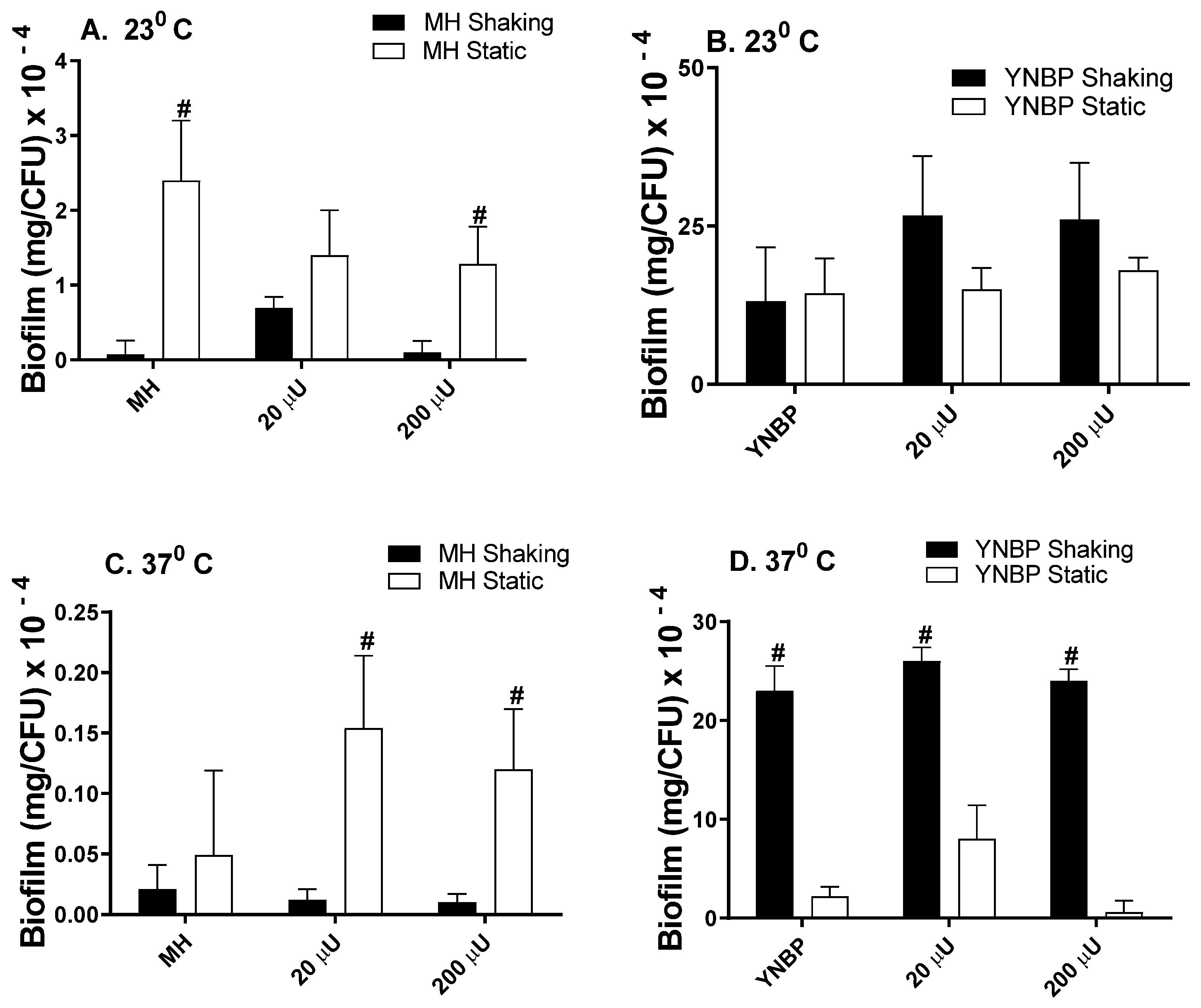
2.1. Insulin Effects on Biofilm Formation
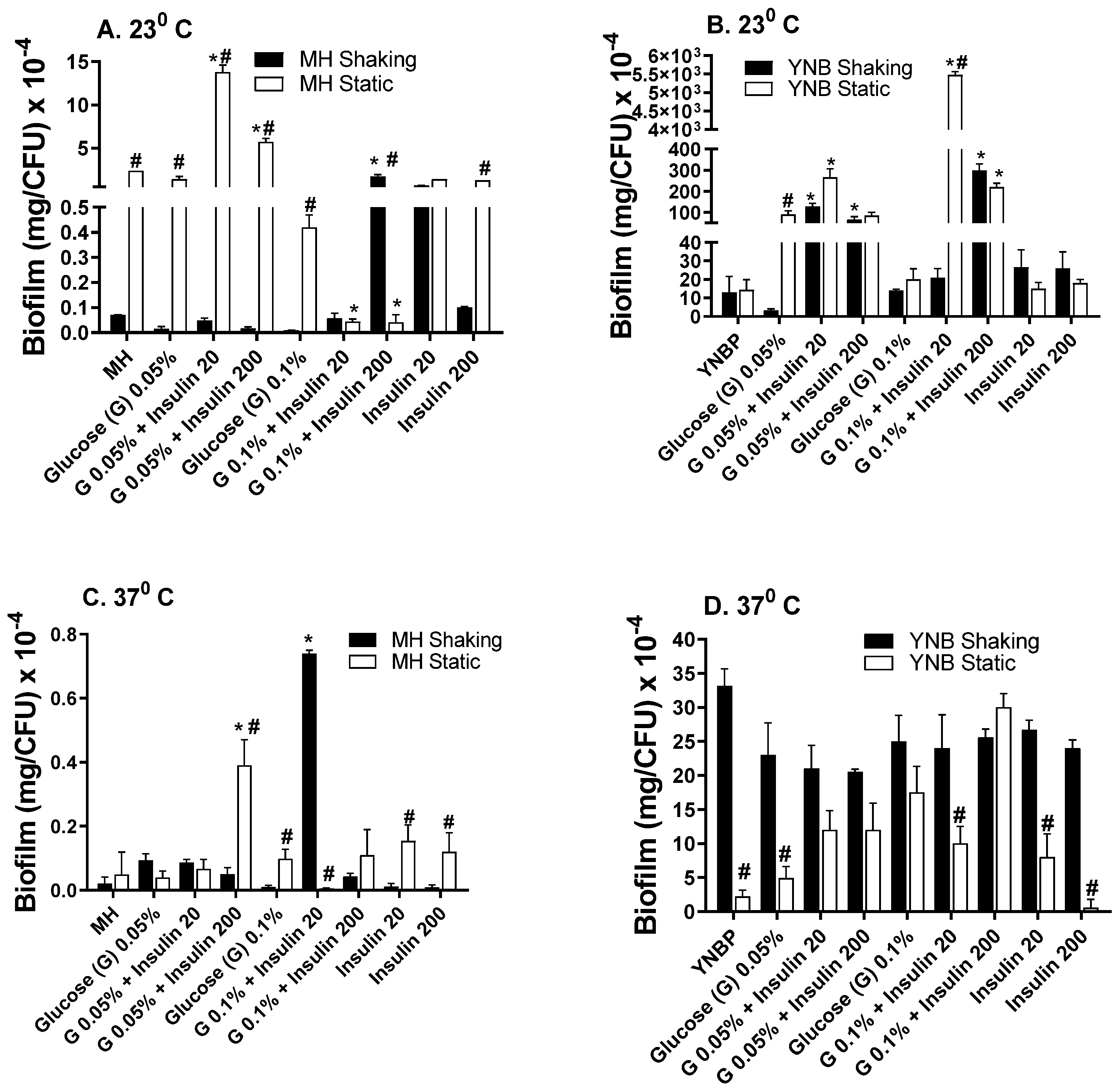
2.2. Insulin Modulation of Glucose Effects on Biofilm Formation
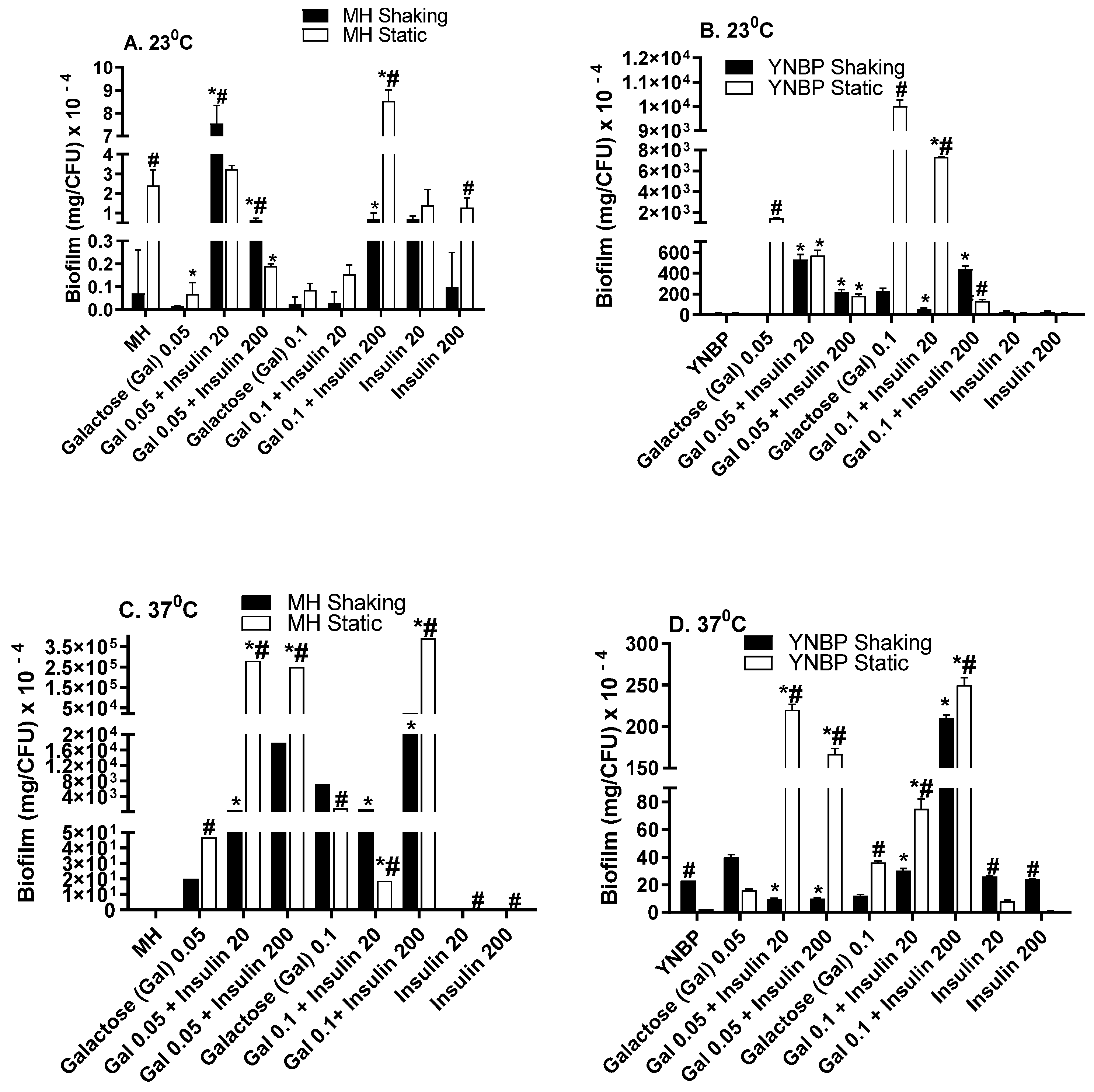
2.3. Galactose Induces Maximal Biofilm Formation
2.4. Lactose Is Inhibitory for Biofilm Formation as Compared to Glucose and Galactose
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramey, B.E.; Koutsoudis, M.; von Bodman, S.B.; Fuqua, C. Biofilm formation in plant–microbe associations. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, P. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 292, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. Antibiotics versus biofilm: An emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, L.; Oliveira, J.A.; Nicolau, A.; Azevedo, N.F.; Vieira, M.J. Biofilm formation with mixed cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa/Escherichia coli on silicone using artificial urine to mimic urinary catheters. Biofouling 2013, 29, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, B.J.; Hatakeyama, T.; Ma, Z. Antimicrobial susceptibility and sub-MIC biofilm formation of Moraxella catarrhalis clinical isolates under anaerobic conditions. Adv. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farzam, F.; Plotkin, B. Effect of sub-MICs of antibiotics on the hydrophobicity and production of acidic polysaccharide by Vibrio vulnificus. Chemotherapy 2001, 47, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surette, M.G.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7046–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-García, L.; Blasco, L.; Trastoy, R.; García-Contreras, R.; Wood, T.K.; Tomás, M. Quorum sensing systems and persistence. In Implication of Quorum Sensing System in Biofilm Formation and Virulence; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Konaklieva, M.; Plotkin, B. Chemical communication--do we have a quorum? Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoith, D.; Shiloach, J.; Heffron, R.; Rubinovitz, C.; Tanenbaum, R.; Roth, J. Insulin-related material in microbes: Similarities and differences from mammalian insulins. Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1985, 63, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoith, D.; Shiloach, J.; Roth, J.; Lesniak, M. Evolutionary origins of vertebrate hormones: Substances similar to mammalian insulins are native to unicellular eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 6184–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LeRoith, D.; Shiloach, J.; Roth, J.; Lesniak, M.A. Insulin or a closely related molecule is native to Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 6533–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.; Quie, H.; Kemp, K.; Rasmussen, L. Insulin produces a biphasic response in Tetrahymena thermophila by stimulating cell survival and activating proliferation in two separate concentration intervals. Cell Biol. Int. 1996, 20, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J. Molecular evolution of insulin in non-mammalian vertebrates. Am. Zool. 2000, 40, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Fawell, S.E.; Lenard, J. A specific insulin receptor and tyrosine kinase activity in the membranes of Neurospora crassa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 155, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, H.K.; Muthukumar, G.; Lenard, J. Purification and properties of a membrane-bound insulin binding protein, a putative receptor, from Neurospora crassa. Biochememistry 1991, 30, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoith, D.; Lesniak, M.; Roth, J. Insulin in insects and annelids. Diabetes 1981, 30, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, D.; Raino, C.; Rabor, S.F., Jr.; Wasson, C.; Plotkin, B. Semi-automated method for multi-tasking measurement of microbial growth, capsule, and biofilm formation. Adv. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klosowska, K.; Plotkin, B. Human insulin modulation of Escherichia coli adherence and chemotaxis. Am. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 2, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, B.; Wu, Z.; Ward, K.; Nadella, S.; Green, J.; Rumnani, B. Effect of human insulin on the formation of catheter-associated E. coli biofilms. Open J. Urol. 2014, 4, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotkin, B.J.; Viselli, S.M. Effect of insulin on microbial growth. Curr. Microbiol. 2000, 41, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursina, F.; Sepehrpour, S.; Mobasherizadeh, S. Biofilm formation in nonmultidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infection in Isfahan, Iran. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2018, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crémet, L.; Corvec, S.; Batard, E.; Auger, M.; Lopez, I.; Pagniez, F.; Dauvergne, S.; Caroff, N. Comparison of three methods to study biofilm formation by clinical strains of Escherichia coli. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, K.; Strzelczyk, A.; Rozalski, A.; Staczek, P. Bacterial biofilm as a cause of urinary tract infection-pathogens, methods of prevention and eradication. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2013, 67, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloete, T.E.; Brözel, V.S.; Von Holy, A. Practical aspects of biofouling control in industrial water systems. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1992, 29, 299–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Bausch, C.; Richmond, C.; Blattner, F.R.; Conway, T. Functional genomics: Expression analysis of Escherichia coli growing on minimal and rich media. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adnan, M.; Morton, G.; Singh, J.; Hadi, S. Contribution of rpoS and bolA genes in biofilm formation in Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 342, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constan, L.; Mako, M.; Juhn, D.; Rubenstein, A.H. The excretion of proinsulin and insulin in urine. Diabetologia 1975, 11, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meguid, M.M.; Aun, F.; Soeldner, J.S. Effect of severe trauma on urine loss of insulin. Surgery 1976, 79, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, A.H. The significance of immunoassayable insulin in urine. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1969, 209, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, A.H.; Lowy, C.; Welborn, T.A.; Fraser, T.R. Urine insulin in normal subjects. Metabolism 1967, 16, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayner, I.M.; Welborn, T.A.; Rubenstein, A.; Fraser, T.R. Serum and urine insulin in late pregnancy and in a few pregnant latent diabetics. J. Endocrinol. 1967, 37, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.A. Insulin resistance in burns and trauma. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynyk, M.; Neufeld, R.J. Insulin and wound healing. Burns 2014, 40, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byappanahalli, M.; Whitman, R.; Shively, D.; Sadowsky, M.; Ishii, S. Population structure, persistence, and seasonality of autochthonous Escherichia coli in temperate, coastal forest soil from a Great Lakes watershed. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silcox, C.A.; Robinson, B.A.; Willoughby, T.C. Concentrations of Escherichia coli in Streams in the Kankakee and Lower Wabash River Watersheds in Indiana, June-September 1999; US Department of the Interior: Denver, CO, USA; US Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2001; Volume 1.
- Conover, M.S.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Palermo, J.J.; Hibbing, M.E.; Dodson, K.W.; Hultgren, S.J. Metabolic requirements of Escherichia coli in intracellular bacterial communities during urinary tract infection pathogenesis. mBio 2016, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Y.; Beauregard, P.B.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Galactose metabolism plays a crucial role in biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis. mBio 2012, 3, e00184-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grover, V.; Ghosh, S.; Sharma, N.; Chakraborti, A.; Majumdar, S.; Ganguly, N.K. Characterization of a galactose specific adhesin of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 390, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutiño-Rodríguez, R.; Hernández-Cruz, P.; Giles-Ríos, H. Lectins in fruits having gastrointestinal activity: Their participation in the hemagglutinating property of Escherichia coli 0157: H7. Arch. Med. Res. 2001, 32, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, H.; Tamm, A. Metabolism of lactose in the human body. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 29, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, S.; Kramer, M.; Stopar, D. Biofilm surface density determines biocide effectiveness. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrakandi, M.M.; Roques, C.; Michel, G. Influence of trophic conditions on exopolysaccharide production: Bacterial biofilm susceptibility to chlorine and monochloramine. Can. J. Microbiol. 1997, 43, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloak, O.M.; Solow, B.T.; Briggs, C.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Fratamico, P.M. Quorum sensing and production of autoinducer-2 in Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli O157:H7, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4666–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotkin, B.; Konaklieva, M. Possible role of sarA in dehydroepiandosterone (DHEA)-mediated increase in Staphylococcus aureus resistance to vancomycin. Chemotherapy 2007, 53, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, B.; Morejon, A.; Laddaga, R.; Viselli, S.; Thijo, J.; Schreckenberger, P. Induction of increased resistance to vancomycin in Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates (MSSA, MRSA) by dehydroepiandosterone (DHEA). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 40, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.K.; Kauffmann, R.M.; Collier, B.R. The place for glycemic control in the surgical patient. Surg. Infect. 2011, 12, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, B.; Clifford, M.; Morgan, L. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and insulin-like immunoreactivity in saliva following sham-fed and swallowed meals. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 177, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolic, D.M. Effects of Candida on insulin secretion of human adult pancreatic islets and possible onset of diabetes. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 71, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Reaven, G.M. Insulin binding in diabetes. Relationships with plasma insulin levels and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 1977, 26, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, B.; Erickson, Q.; Roose, R.; Viselli, S. Effect of androgens and glucocorticoids on microbial growth and antimicrobial susceptibility. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraco, D.; Blaha, M.; Khan, S.; Green, J.M.; Plotkin, B.J. Host environmental signals and effects on biofilm formation. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.; Greenberg, E. Quorum sensing:the explanation of a curious phenomenon reveals a common characteristic of bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 2667–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horswill, A.; Stoodley, P.; Stewart, P.; Parsek, M. The effect of the chemical, biological, and physical environment on quorum sensing in structured microbial communities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuson, H.H.; Weibel, D.B. Bacteria-surface interactions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, S.A.; Koh, K.S.; Queck, S.Y.; Labbate, M.; Lam, K.W.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, B.B.; Haagensen, J.A.; Heydorn, A.; Molin, S. Metabolic commensalism and competition in a two-species microbial consortium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khangholi, M.; Jamalli, A. The effects of sugars on the biofilm formation of Escherichia coli 185p on stainless steel and polyethylene terephthalate surfaces in a laboratory model. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2016, 9, e40137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, D.; Simecka, J.; Romeo, T. Catabolite repression of Escherichia coli biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 3406–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, D.; Suzuki, K.; Oakford, L.; Simecka, J.; Hart, M.; Romeo, T. Biofilm formation and dispersal under the influence of the global regulator CsrA of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kremling, A.; Bettenbrock, K.; Gilles, E.D. Analysis of global control of Escherichia coli carbohydrate uptake. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schembri, M.A.; Kjærgaard, K.; Klemm, P. Global gene expression in Escherichia coli biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M.A.; Haque, A.; Ali, A.; Mohsin, M.; Bashir, S.; Tariq, A.; Afzal, A.; Iftikhar, T.; Sarwar, Y. Relationship of drug resistance to phylogenetic groups of E. coli isolates from wound infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2009, 3, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauglitz, G.G.; Toliver-Kinsky, T.E.; Williams, F.N.; Song, J.; Cui, W.; Herndon, D.N.; Jeschke, M.G. Insulin increases resistance to burn wound infection-associated sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, P.; Brammah, S.; Wills, E. Burns, biofilm and a new appraisal of burn wound sepsis. Burns 2010, 36, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, A.; Cirioni, O.; Schimizzi, A.M.; del Prete, M.S.; Barchiesi, F.; D'Errico, M.M.; Petrelli, E.; Scalise, G. Epidemiology and microbiology of surgical wound infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malone, M.; Bjarnsholt, T.; McBain, A.J.; James, G.A.; Stoodley, P.; Leaper, D.; Tachi, M.; Schultz, G.; Swanson, T.; Wolcott, R.D. The prevalence of biofilms in chronic wounds: A systematic review and meta-analysis of published data. J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sisay, M.; Worku, T.; Edessa, D. Microbial epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance patterns of wound infection in Ethiopia: A meta-analysis of laboratory-based cross-sectional studies. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sierra, M.V.; Gomez, N. Structural characteristics and oxygen consumption of the epipelic biofilm in three lowland streams exposed to different land uses. WaterAirSoil Pollut. 2007, 186, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, D.R.; Ziegler, S.E. Carbon cycling within epilithic biofilm communities across a nutrient gradient of headwater streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byappanahalli, M.; Fowler, M.; Shively, D.; Whitman, R. Ubiquity and Persistence of Escherichia coli in a Midwestern Coastal Stream. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4549–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, N.; Curtis, J.C.; Plotkin, B.J. Insulin Regulation of Escherichia coli Abiotic Biofilm Formation: Effect of Nutrients and Growth Conditions. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111349
Patel N, Curtis JC, Plotkin BJ. Insulin Regulation of Escherichia coli Abiotic Biofilm Formation: Effect of Nutrients and Growth Conditions. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(11):1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111349
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Nina, Jeremy C. Curtis, and Balbina J. Plotkin. 2021. "Insulin Regulation of Escherichia coli Abiotic Biofilm Formation: Effect of Nutrients and Growth Conditions" Antibiotics 10, no. 11: 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111349
APA StylePatel, N., Curtis, J. C., & Plotkin, B. J. (2021). Insulin Regulation of Escherichia coli Abiotic Biofilm Formation: Effect of Nutrients and Growth Conditions. Antibiotics, 10(11), 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111349




