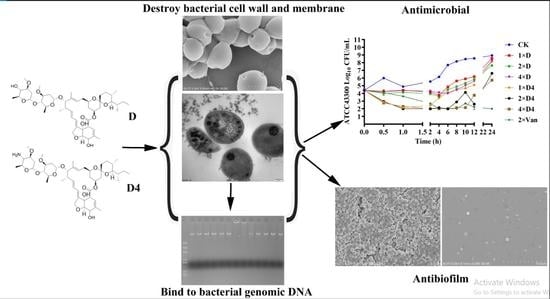
A Novel Ivermectin-Derived Compound D4 and Its Antimicrobial/Biofilm Properties against MRSA
Abstract
Share and Cite
Tan, X.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Dou, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, N. A Novel Ivermectin-Derived Compound D4 and Its Antimicrobial/Biofilm Properties against MRSA. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020208
Tan X, Xie H, Zhang B, Zhou J, Dou Z, Wang X, Wang N. A Novel Ivermectin-Derived Compound D4 and Its Antimicrobial/Biofilm Properties against MRSA. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020208
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Xinyi, Haoji Xie, Bin Zhang, Jiale Zhou, Zhende Dou, Xiao Wang, and Ning Wang. 2021. "A Novel Ivermectin-Derived Compound D4 and Its Antimicrobial/Biofilm Properties against MRSA" Antibiotics 10, no. 2: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020208
APA StyleTan, X., Xie, H., Zhang, B., Zhou, J., Dou, Z., Wang, X., & Wang, N. (2021). A Novel Ivermectin-Derived Compound D4 and Its Antimicrobial/Biofilm Properties against MRSA. Antibiotics, 10(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020208