Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) of the Island of Maio, Cape Verde
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterisation of Isolates’ Antimicrobial Resistance Profile
2.2. Characterisation of Isolates’ Virulence Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
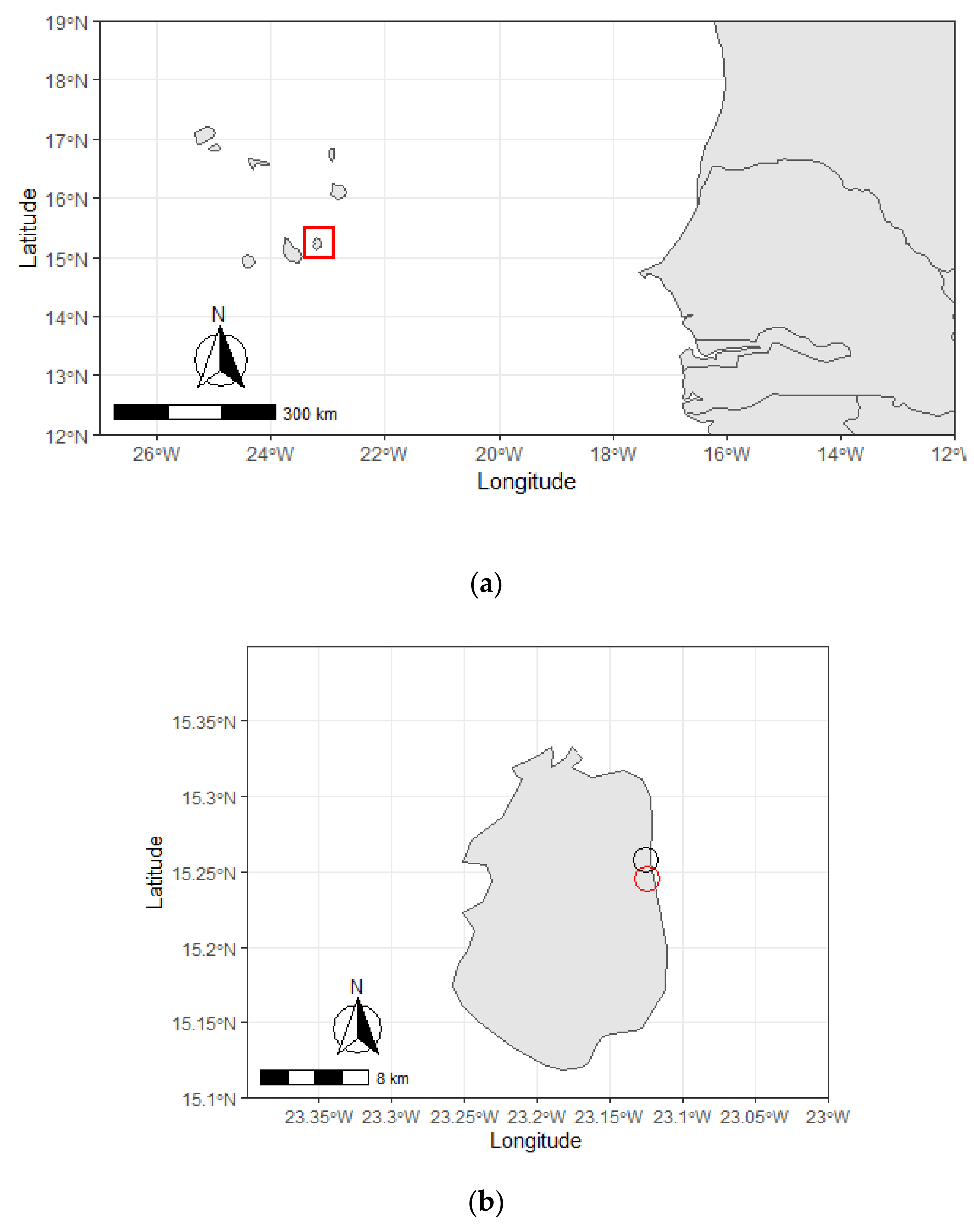
4.1. Area of Study
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. Isolation and Identification of Gram-Negative Bacteria
4.4. Evaluation of Isolates’ Antimicrobial Resistance Profile
4.5. Evaluation of Isolates’ Virulence Profile
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Antimicrobial Resistance: Fact Sheets. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Foti, M.; Giacopello, C.; Bottari, T.; Fisichella, V.; Rinaldo, D.; Mammina, C. Antibiotic Resistance of Gram Negatives Isolates from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, A.; Dipineto, L.; Fioretti, A.; Hochscheid, S. Loggerhead Sea Turtles as Sentinels in the Western Mediterranean: Antibiotic Resistance and Environment-Related Modi Fi Cations of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Serrano, I.; Santos, J.P.; Bilocq, F.; Pereira, N.; de Santos Loureiro, N.; Tavares, L.; Pirnay, J.P.; De Vos, D. Pseudomonads from Wild Free-Living Sea Turtles in Príncipe Island, Gulf of Guinea. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkour, N.; Jones, K.; Kophamel, S.; Hipolito, T.; Ahasan, S.; Walker, G.; Jakob-Hoff, R.; Whittaker, M.; Hamann, M.; Bell, I.; et al. Disease Risk Analysis in Sea Turtles: A Baseline Study to Inform Conservation Efforts. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazebrook, J.S.; Campbell, R.S.F. A Survey of the Diseases of Marine Turtles in Northern Australia. I. Farmed Turtles. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1990, 9, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Ianniello, D.; Borrelli, L.; Cringoli, G.; Fioretti, A.; Hochscheid, S.; Dipineto, L. Gastrointestinal Investigation of Parasites and Enterobacteriaceae in Loggerhead Sea Turtles from Italian Coasts. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orós, J.; Torrent, A.; Calabuig, P.; Déniz, S. Diseases and Causes of Mortality among Sea Turtles Stranded in the Canary Islands, Spain (1998-2001). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casale, P.; Marco, A. Caretta caretta (North East Atlantic Subpopulation). In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; 2015: e.T83776383A83776554; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 8235. [Google Scholar]
- Casale, P.; Tucker, A.D. Caretta caretta (Amended Version of 2015 Assessment) Supplementary Material. In IUCN Red List Threatened Species; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2017; p. 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino-martinez, J.; Passos, L.D.O.S.; Afonso, I.; Teixidor, A.; Maio Biodiversity Foundation, Cidade Porto-Inglês, 6110 Ilha do Maio, Cabo Verde. Globally Important Loggerhead Sea Turtle Conservation Refuge: Maio Island, Cabo Verde. Unpublished work. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, S.; Soares, F.; Ribeiro, E.; Abella, E.; Koenen, F.; Marco, A. Importance of the Island of Maio (Cape Verde) for Current and Future Loggerhead Conservation in the Eastern Atlantic. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual Symposium on Sea Turtle Biology and Conservation: 2013 International Sea Turtle Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–8 February 2013; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Laloë, J.O.; Cozens, J.; Renom, B.; Taxonera, A.; Hays, G.C. Conservation Importance of Previously Undescribed Abundance Trends: Increase in Loggerhead Turtle Numbers Nesting on an Atlantic Island. Oryx 2020, 54, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahasan, M.S.; Picard, J.; Elliott, L.; Kinobe, R.; Owens, L.; Ariel, E. Evidence of Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacteriales Isolated from Green Sea Turtles, Chelonia Mydas on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanci, A.K.J.; Roden, S.E.; Bowman, A.; Lacasella, E.L.; Frey, A.; Dutton, P.H. Evaluating Buccal and Cloacal Swabs for Ease of Collection and Use in Genetic Analyses of Marine Turtles. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2012, 11, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Monteiro, J.L.; Rana, S.; Vilela, C.L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Positive Bacteria from Timorese River Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Skin Microbiota. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, M.F.; Migliore, L.; Mattei, D.; Rotini, A.; Thaller, M.C.; Alduina, R. Antibiotic Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria from Wild Captured Loggerhead Sea Turtles. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Bahry, S.; Mahmoud, I.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Harthy, A.; Al-Ghafri, S.; Al-Amri, I.; Alkindi, A. Bacterial Flora and Antibiotic Resistance from Eggs of Green Turtles Chelonia Mydas: An Indication of Polluted Effluents. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, M.L.; Toline, C.A.; Rice, C.D. Humoral Immune Responses to Select Marine Bacteria in Loggerhead Sea Turtles Caretta caretta and Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Lepidochelys Kempii from the Southeastern United States. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2018, 30, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyneken, J.; Burke, T.J.; Salmon, M.; Pedersen, D.K. Egg Failure in Natural and Relocated Sea Turtle Nests. J. Herpetol. 1988, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, K.S.; Awong-Taylor, J.; Griffiths, L.; Bass, C.; Muscarella, M. Identification of Bacterial Isolates from Unhatched Loggerhead (Caretta caretta) Sea Turtle Eggs in Georgia, USA. Mar. Turt. Newsl. 2007, 115, 11, ISBN 2-525-04764-8. [Google Scholar]
- Awong-Taylor, J.; Craven, K.S.; Griffiths, L.; Bass, C.; Muscarella, M. Comparison of Biochemical and Molecular Methods for the Identification of Bacterial Isolates Associated with Failed Loggerhead Sea Turtle Eggs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bahry, S.N.; Mahmoud, I.Y.; Al-Zadjali, M.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Harthy, A.; Al-Alawi, W. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria as Bio-Indicator of Polluted Effluent in the Green Turtles, Chelonia Mydas in Oman. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raza, A.; Ngieng, S.C.; Sime, F.B.; Cabot, P.J.; Roberts, J.A.; Popat, A.; Kumeria, T.; Falconer, J.R. Oral Meropenem for Superbugs: Challenges and Opportunities. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 26, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.E.; Williams, N.J.; Bennett, M. “Disperse Abroad in the Land”: The Role of Wildlife in the Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.Q.A.; Cabello, F.C.; L’Abée-Lund, T.M.; Tomova, A.; Godfrey, H.P.; Buschmann, A.H.; Sørum, H. Antimicrobial Resistance and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Marine Bacteria from Salmon Aquaculture and Non-Aquaculture Sites. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quesne, W.J.F.; Baker-Austin, C.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Balkhy, H.H.; Lyons, B.P. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Gulf Cooperation Council Region: A Proposed Framework to Assess Threats, Impacts and Mitigation Measures Associated with AMR in the Marine and Aquatic Environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Indexing of Escherichia Coli to Identify High-Risk Sources of Faecal Contamination of Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 1983, 22, 10969–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, R.; Pissarra, H.; Santos, J.; Bernardino, R.; Fernandes, T.; Correia, J.; Vilela, C.L.; Oliveira, M. Severe Fibrinonecrotic Enteritis Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Captive Monitor Lizard (Varanus niloticus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2014, 45, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, T.F.; Pitts, B.; Pellock, B.; Walker, G.C.; Stewart, P.S.; O’Toole, G.A. A Genetic Basis for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Antibiotic Resistance. Nature 2003, 426, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial Biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Ekka, R.; Mishra, M.; Mohapatra, H. Association Study of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence: A Strategy to Assess the Extent of Risk Posed by Bacterial Population in Aquatic Environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, H.M.; Gahrn-Hansen, B.; Bruun, B. Shewanella algae and Shewanella putrefaciens: Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Other vibrio infections. In Red Book: 2009 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases; Pickering, L., Baker, C., Kimberlin, D., Long, S., Eds.; American Academy of Pediatrics: Elk Grove Village, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 729–730. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Pathogenicity, and Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.Y.; Wang, S.M.; Chiu, N.C.; Chung, H.Y.; Wang, H.K. Neonatal Morganella morganii Sepsis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pediatrics Int. 2011, 53, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Pembroke, J.T. Brevundimonas spp: Emerging Global Opportunistic Pathogens. Virulence 2018, 9, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- South, A. Rnaturalearth: World Map Data from Natural Earth; R Package Version 0.1.0; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. Policy Statement on Research Involving Species at Risk of Extinction. In Proceedings of the 27th Meeting of IUCN Council, Gland, Switzerland, 14 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS). Sea Turtle Research Techniques Manual; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-579; NMFS: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008; p. 92.
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals, 5th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, I.; Oliveira, M.; Santos, J.P.; Bilocq, F.; Leitão, A.; Tavares, L.; Pirnay, J.P.; De Vos, D. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Rep-PCR Fingerprints of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains from Animals on the Background of the Global Population Structure. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elder, B.L.; Trujillo, I.; Blazevic, D.J. Rapid Deoxyribonuclease Test with Methyl Green. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1977, 6, 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrisope, G.L.; Fox, C.W.; Marshall, R.T. Lecithin Agar for Detection of Microbial. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, D.J.; Falkiner, F.R.; Keane, C.T. New Method for Detecting Slime Production by Coagulase Negative Staphylococci. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 42, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rewatkar, A.R.; Wadher, B.J. Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa- Biofilm Formation Methods. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, P.A.; Ohman, D.E.; Iglewski, B.H. A More Sensitive Plate Assay for Detection of Protease Production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1979, 9, 538–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobial Compound (Dose) | Number of Isolates Tested | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible | Intermediate | Resistant | ||
| Amikacin (30 µg) | 19 | 0 | 0 | |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin (120 µg) | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Tobramycin (10 µg) | 19 | 0 | 0 | |
| Carbapenems | Meropenem (10 µg) | 18 | 1 | 0 |
| Imipenem (10 µg) | 13 | 6 | 0 | |
| Cephalosporins | Cefoperazone (75 µg) | 17 | 1 | 1 |
| Ceftazidime (30 µg) | 18 | 1 | 0 | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin (5 µg) | 18 | 1 | 0 |
| Enrofloxacin (5 µg) | 16 | 2 | 1 | |
| Ofloxacin (5 µg) | 19 | 0 | 0 | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline (30 µg) | 17 | 0 | 2 |
| Ureidopenicillins | Piperacillin (100 µg) | 18 | 0 | 1 |
| Isolate Number | Animal ID (Flipper Tag) | Sample Type | Isolate Identification | Resistance Profile | MAR Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate | Resistant | |||||
| 1 | 276/030 | C | A. hydrophila/caviae | IMP; ENR | CFP | 0.33 |
| 2 | 786/785 | C | B. vesicularis | IMP | - | 0.08 |
| 3 | 329/328 | E | B. cepacia | ENR; CFP | - | 0.17 |
| 4 | 276/030 | C | S. putrefaciens | - | - | 0.00 |
| 5 | 049/050 | C | S. putrefaciens | - | T | 0.08 |
| 6 | 045/046 | E | S. putrefaciens | - | - | 0.00 |
| 7 | 045/046 | C | S. putrefaciens | IMP | - | 0.08 |
| 8 | 072/073 | C | S. putrefaciens | IMP | - | 0.08 |
| 9 | 276/030 | E | V. alginolyticus | - | - | 0.00 |
| 10 | 276/030 | E | V. alginolyticus | - | - | 0.00 |
| 11 | 060/061 | C | V. alginolyticus | - | - | 0.00 |
| 12 | 503/504 | O | V. alginolyticus | - | T | 0.08 |
| 13 | 330/331 | C | E. cloacae | - | - | 0.00 |
| 14 | 049/050 | C | E. cloacae | CIP | ENR; PIP | 0.25 |
| 15 | 045(046 | C | M. morganii | MEM | - | 0.08 |
| 16 | 045/046 | E | M. morganii | - | - | 0.00 |
| 17 | 276/030 | O | M. morganii | IMP | - | 0.08 |
| 18 | 503/504 | C | M. morganii | IMP | - | 0.08 |
| 19 | 228/229 | C | Citrobacter spp. | CAZ | - | 0.08 |
| Isolate Number | Isolate Identification | Virulence Profile | V. Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEM | DNase | LIP | LEC | PT | GEL | BF | |||
| 1 | A. hydrophila/caviae | β | + | + | + | + | − | 24 | 0.86 |
| 2 | B. vesicularis | α | + | + | − | + | + | 24 | 0.86 |
| 3 | B. cepacia | α | + | + | − | + | + | − | 0.43 |
| 4 | S. putrefaciens | α | + | + | + | + | − | 24 | 0.86 |
| 5 | S. putrefaciens | α | + | + | + | − | + | - | 0.43 |
| 6 | S. putrefaciens | β | + | + | + | + | − | 24 | 1.00 |
| 7 | S. putrefaciens | α | + | + | Inc | + | − | 24 | 0.86 |
| 8 | S. putrefaciens | α | + | + | Inc | + | − | 24 | 0.86 |
| 9 | V. alginolyticus | α | + | − | Inc | + | − | 48 | 0.57 |
| 10 | V. alginolyticus | α | + | − | − | + | − | 24 | 0.57 |
| 11 | V. alginolyticus | α | + | − | − | − | − | 24 | 0.43 |
| 12 | V. alginolyticus | α | + | − | − | − | − | 24 | 0.43 |
| 13 | E. cloacae | α | + | + | − | − | − | 48 | 0.57 |
| 14 | E. cloacae | α | + | + | − | + | − | 48 | 0.71 |
| 15 | M. morganii | β | + | + | − | − | − | − | 0.43 |
| 16 | M. morganii | α | + | + | − | − | − | − | 0.43 |
| 17 | M. morganii | α | + | + | − | − | − | − | 0.43 |
| 18 | M. morganii | α | − | + | − | − | − | 24 | 0.57 |
| 19 | Citrobacter spp. | α | − | + | − | − | − | 72 | 0.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, M.; Grilo, M.L.; Carneiro, C.; Cunha, E.; Tavares, L.; Patino-Martinez, J.; Oliveira, M. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) of the Island of Maio, Cape Verde. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070771
Fernandes M, Grilo ML, Carneiro C, Cunha E, Tavares L, Patino-Martinez J, Oliveira M. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) of the Island of Maio, Cape Verde. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(7):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070771
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Matilde, Miguel L. Grilo, Carla Carneiro, Eva Cunha, Luís Tavares, Juan Patino-Martinez, and Manuela Oliveira. 2021. "Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) of the Island of Maio, Cape Verde" Antibiotics 10, no. 7: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070771
APA StyleFernandes, M., Grilo, M. L., Carneiro, C., Cunha, E., Tavares, L., Patino-Martinez, J., & Oliveira, M. (2021). Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) of the Island of Maio, Cape Verde. Antibiotics, 10(7), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070771







