Antimicrobial Treatment on a Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI) Case Due to Transition of a Multi-Drug-Resistant Ralstonia mannitolilytica from Commensal to Pathogen during Hospitalization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antimicrobial Agent Treatment
2.1.1. Phase I: From Admission to Day 3
2.1.2. Phase II: From Day 4 to 18
2.1.3. Phase III: From Day 19 to 27
2.1.4. Phase IV: After Day 27 to Discharging
2.2. Bacterial Identification
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
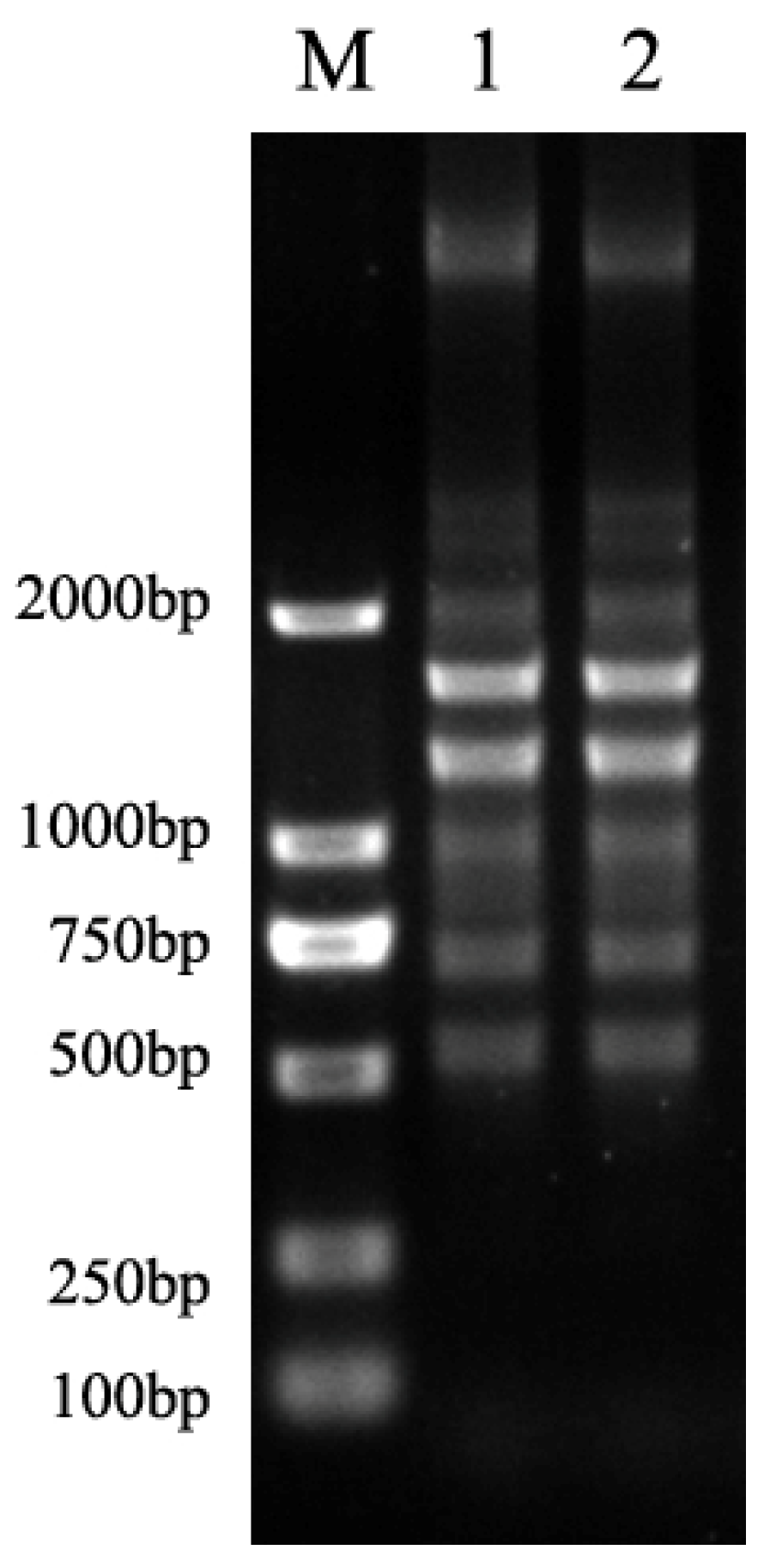
2.4. Clonal Relatedness of R. mannitolilytica Strains
2.5. Extensive Surveillance on R. mannitolilytica Strains
2.6. Transition from Commensal to Pathogen
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Clinical Samples and Bacterial Strains
3.2. Clinical Case
3.3. Species Identification
3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.5. Analysis on Clonal Relatedness of R. mannitolilytica Strains
3.6. Extensive Surveillance on R. mannitolilytica Strains
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adeloye, D.; Song, P.; Zhu, Y.; Campbell, H.; Sheikh, A.; Rudan, I. Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: A systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Gao, P.; Bao, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Cong, S.; Juan, J.; Fan, J.; Lu, K.; et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China: A nationwide prevalence study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Kang, J.; Ran, P.; Shen, H.; Wen, F.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): A national cross-sectional study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Stampfli, M.R.; Zhou, H.; Shu, W.; Brightling, C.E.; et al. A refined view of airway microbiome in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at species and strain-levels. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 30(11), 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, R.M.; Elhag, K.M.; Shaw, E.J. Pseudomonas Thomasii in a hospital distilled-water supply. J. Med. Microbiol. 1976, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.J.; Teng, L.-J.; Tzeng, M.S.; Chang, S.-C.; Ho, S.W.; Luh, K.T.; Hsieh, W.C. Identification and typing of Pseudomonas pickettii during an episode of nosocomial outbreak. Zhonghua Minguo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 1992, 25, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jhung, M.A.; Sunenshine, R.H.; Noble-Wang, J.; Coffin, S.E.; John, K.S.; Lewis, F.M.; Jensen, B.; Peterson, A.; LiPuma, J.; Arduino, M.J.; et al. A National Outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica Associated With Use of a Contaminated Oxygen-Delivery Device Among Pediatric Patients. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boattini, M.; Bianco, G.; Biancone, L.; Cavallo, R.; Costa, C. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteraemia: A case report and literature review. Infez. Med. 2018, 26, 374–378. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, M.; Venditti, C.; Raponi, G.; Navazio, A.S.; Alessandri, F.; Giombini, E.; Nisii, C.; Di Caro, A.; Venditti, M. A case of persistent bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica and Ralstonia pickettii in an intensive care unit. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, D.C.; Palmeiro, J.K.; Maestri, A.C.; Cogo, L.L.; Rauen, C.H.; Graaf, M.E.; Grein, F.L.; Nogueira, K.D.S. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit. Rev. da Soc. Bras. de Med. Trop. 2018, 51, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaneechoutte, M.; De Baere, T.; Wauters, G.; Steyaert, S.; Claeys, G.; Vogelaers, D.; Verschraegen, G. One Case Each of Recurrent Meningitis and Hemoperitoneum Infection with Ralstonia mannitolilytica. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4588–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, M.; Acheampong, G.; Annan, A.; Marfo, K.S.; Osei, I.; Amuasi, J.; Sarpong, N.; Im, J.; Mogeni, D.; Chiang, H.-Y.; et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica sepsis: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 13, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotis, J.; Printza, N.; Orfanou, A.; Papathanasiou, E.; Papachristou, F. Peritonitis due to Ralstonia mannitolilytica in a pediatric peritoneal dialysis patient. New Microbiol. 2012, 35, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.P.; Adley, C.C. Ralstonia spp.: Emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 33, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; LiPuma, J.J. Infection by Ralstonia Species in Cystic Fibrosis Patients: Identification of R. pickettii and R. mannitolilytica by Polymerase Chain Reaction. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.Y.; Peng, C.H. Ralstonia mannitolilytica and COPD: A case report. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 1482–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coman, I.; Bilodeau, L.; Lavoie, A.; Carricart, M.; Tremblay, F.; Zlosnik, J.; Berthiaume, Y. Ralstonia mannitolilytica in cystic fibrosis: A new predictor of worse outcomes. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 20, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, C.; Bhargava, A.; Ayyagari, A. Ralstonia mannitolilytica infection in renal transplant recipient: First report. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 21, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, M.; Rampure, S.; Siddini, V.; Ballal, H. Outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica in hemodialysis unit: A case series. Indian J. Nephrol. 2018, 28, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröbner, S.; Heeg, P.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Schulte, B. Monoclonal outbreak of catheter-related bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica on two haemato-oncology wards. J. Infect. 2007, 55, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; Dangor, Y.; Van Hougenhouck-Tulleken, W.; Mbelle, N.; Strydom, K.-A.; Ismail, F. First outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteraemia in patients undergoing haemodialysis at a tertiary hospital in Pretoria, South Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 73, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiman, L. Providing a Safety Net for Children: Investigating a Multistate Outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica Related to a Contaminated Reusable Device. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 1207–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayot, M.L.; Bragg, B.N. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vaneechoutte, M.; Kampfer, P.; De Baere, T.; Falsen, E.; Verschraegen, G. Wautersia gen. nov., a novel genus accommodating the phylogenetic lineage including Ralstonia eutropha and related species, and proposal of Ralstonia [Pseudomonas] syzygii (Roberts et al. 1990) comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54 Pt 2, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroy, M.L.G.; Lopez, J.S.; Torres, B.C.L.; Loy, M.J.; Tuaño, P.M.C.; Matias, R.R. Identification of unknown ocular pathogens in clinically suspected eye infections using ribosomal RNA gene sequence analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, P.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Manaia, C.M. Association between gentamicin resistance and stress tolerance in water isolates of Ralstonia pickettii and R. mannitolilytica. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.T.S.; Lee, S.E. A rare case of Ralstonia mannitolilytica infection in an end stage renal patient on maintenance dialysis during municipal water contamination. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackebrant, E.; Goodfellow, M.; Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Tech-Niques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrant, E., Goodfellow., M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Daxboeck, F.; Stadler, M.; Assadian, O.; Marko, E.; Hirschl, A.M.; Koller, W. Characterization of clinically isolated Ralstonia mannitolilytica strains using random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) typing and antimicrobial sensitivity, and comparison of the classification efficacy of phenotypic and genotypic assays. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenye, T.; Spilker, T.; Reik, R.; Vandamme, P.; LiPuma, J.J. Use of PCR Analyses To Define the Distribution of Ralstonia Species Recovered from Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3463–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Nishio, H.; Asagoe, K.; Kida, K.; Suzuki, S.; Matsui, M.; Shibayama, K. Genome Sequence of a Carbapenem-Resistant Strain of Ralstonia mannitolilytica. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00405-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Detection | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission Time | Temperature (°C) | WBC (×109 L) | Neutrophils (%) | Blood Gas: pH/HCO3 * (mmol/L) /SpO2 * /PaCO2 * (mm Hg) /PaO2 * (mm Hg) | PCT * (ng/mL) | HCCT * | |
| Phase I | D1 | 38.3 | 16.6 | 77.4 | 7.42/24.5 /98%/51.2/90.6 | 0.45 | RLLLA * |
| D2 | 38.8–40 | 20.6 | 90.1 | ||||
| D3 | 37.5 | 19.8 | 94.1 | ||||
| Phase II | D4 | 18.3 | 84.7 | 7.435/29.1/96.3%/42.8/85.6 | |||
| D5 | 15.7 | 82.9 | |||||
| D6 | 15.6 | 82.3 | 7.504/26.5/98.8%/33.9/159 | 4.08 | RLLLA | ||
| D7 | 37.6–38.0 | 14.6 | 81.9 | ||||
| D8 | 38.8 | ||||||
| D9 | 38.4 | ||||||
| D10 | 36.7–38.3 | ||||||
| D11 | 38.0 | ||||||
| D12 | 38.0 | 14.3 | 81.2 | ||||
| D13 | 37.7 | ||||||
| D14 | 38.0 | ||||||
| D15 | 38.3 | ||||||
| D16 | 37.9 | ||||||
| D17 | 38.0 | ||||||
| D18 | 36.9 | 16.0 | 90.7 | ||||
| Phase III | D19 | 37.0–38.5 | 7.346/24.7/98.1%/47.1/152 | ||||
| D20 | 39.4 | ||||||
| D21 | 37.9 | 13.7 | 75.5 | ||||
| D22 | 37.0–37.9 | 14.1 | 88.9 | ||||
| D23 | 38.3 | ||||||
| D24 | 37.2–38.3 | ||||||
| D25 | 38.0 | ||||||
| D26 | 37.1 | 11.7 | 89.0 | 7.365/25.3/98.5%/47.2/119 | 0.80 | Not done | |
| D27 | 37.2 | 9.6 | 82.7 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Peters, B.M.; Yang, L.; Yu, H.; Feng, D.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z. Antimicrobial Treatment on a Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI) Case Due to Transition of a Multi-Drug-Resistant Ralstonia mannitolilytica from Commensal to Pathogen during Hospitalization. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101376
Liu J, Peters BM, Yang L, Yu H, Feng D, Chen D, Xu Z. Antimicrobial Treatment on a Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI) Case Due to Transition of a Multi-Drug-Resistant Ralstonia mannitolilytica from Commensal to Pathogen during Hospitalization. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101376
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Junyan, Brian M. Peters, Ling Yang, Hui Yu, Donghua Feng, Dingqiang Chen, and Zhenbo Xu. 2022. "Antimicrobial Treatment on a Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI) Case Due to Transition of a Multi-Drug-Resistant Ralstonia mannitolilytica from Commensal to Pathogen during Hospitalization" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101376
APA StyleLiu, J., Peters, B. M., Yang, L., Yu, H., Feng, D., Chen, D., & Xu, Z. (2022). Antimicrobial Treatment on a Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI) Case Due to Transition of a Multi-Drug-Resistant Ralstonia mannitolilytica from Commensal to Pathogen during Hospitalization. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101376










