Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella pertussis: Current Situation and Future Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pertussis Diagnostics
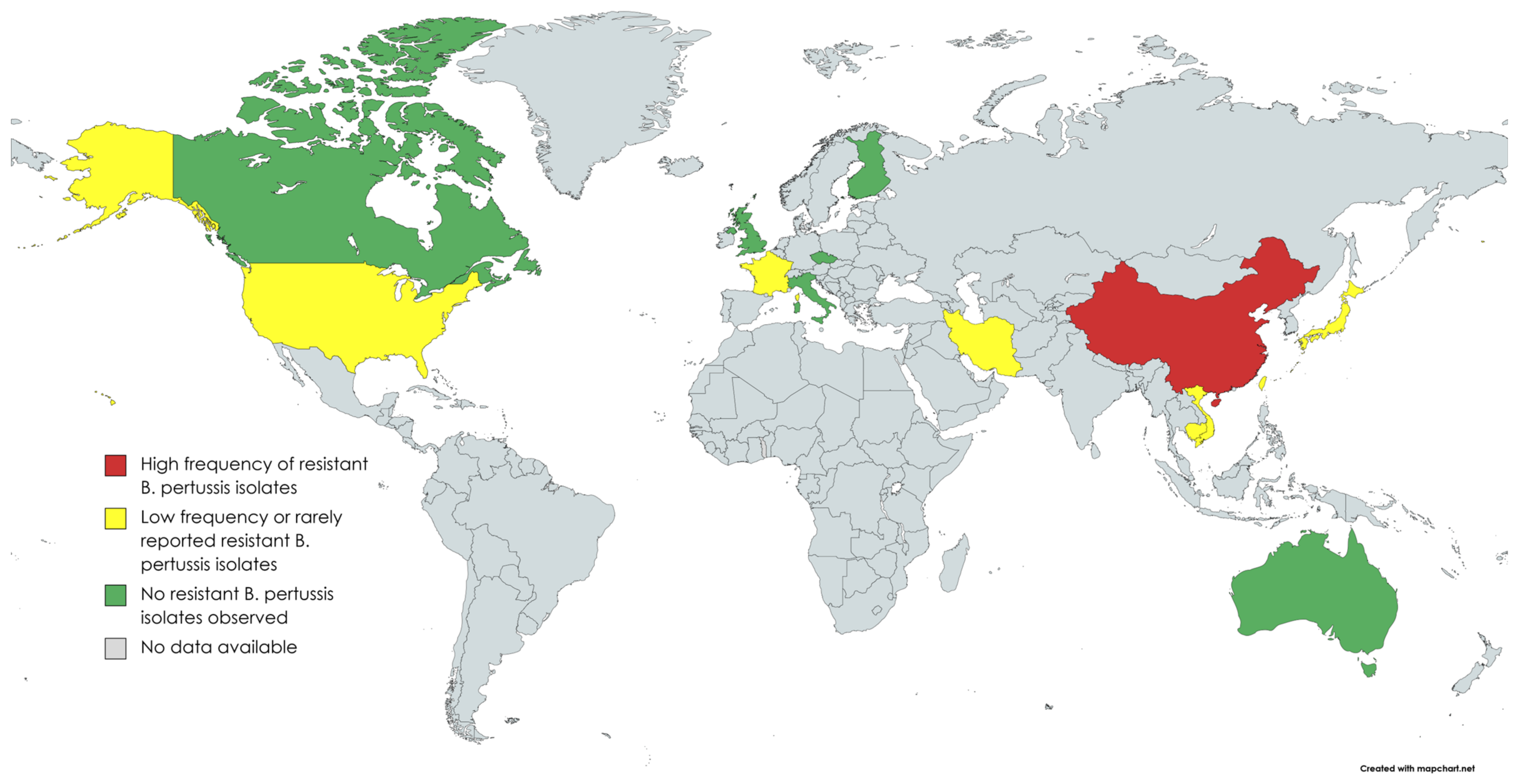
3. Epidemiology
| Country | Region/City | Year | Resistant Isolates Identified (Frequency %) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | New South Wales, Perth | 1971–2010 | 0/120 (0.0) | [24,25] |
| Cambodia | Whole country | 2017–2020 | 1/71 (1.4) | [19] |
| Canada | Ontario | 2011–2013 | 0/275 (0.0) | [26] |
| China | Xi’an | 2012–2020 | 274/299 (91.6) | [27,28,29,30,31] |
| Shandong | 2011 | 2/2 (100.0) | [21] | |
| Northern | 1970–2014 ** | 91/124 ** (91.9) | [22] | |
| Shanghai | 2016–2017 | 81/141 (57.5) | [32] | |
| Zhejiang | 2016–2020 | 271/381 (71.1) | [33,34,35] | |
| Beijing, Jinan, Nanjing, Shenzhen | 2014–2016 | 292/335 (87.2) | [36] | |
| Midwest | 2012–2015 | 163/167 (97.6) | [37] | |
| Whole country | 1950–2018 | 316/388 (81.4) | [23] | |
| Hunan | 2017–2018 | 27/55 (49.1) | [38] | |
| Shenzhen | 2015–2017 | 51/105 (48.6) | [39] | |
| Whole country | 2017–2019 | 265/311 (85.2) | [40] | |
| Czech republic | Whole country | 1967–2015 | 0/135 (0.0) | [41] |
| Finland | Whole country | 2006–2017 | 0/148 (0.0) | [42] |
| France | Bordeaux & Lyon | 2003 and 2012 | 1/41 (2.4) | [10,11] |
| Iran | Whole country | 2009–2010 | 2/11 (18.2) | [16,43] |
| Italy | Rome | 2012–2015 | 0/18 (0.0) | [44] |
| Japan | Whole country | 2017–2019 | 1/33 (3.0) | [17,19] |
| Taiwan | Whole country | 2003–2007 | 2/76 (2.6) | [19,23] |
| United Kingdom | Whole country | 2001–2009 | 0/582 (0.0) | [45] |
| United States | Colorado, Maryland, Oklahoma, Wisconsin | 1986 | 0/75 (0.0) | [46] |
| Arizona—Yuma County | 1994 | 1/1 (100.0) | [47] | |
| Utah | 1985–1997 | 1/47 (2.1) | [12] | |
| Northern California | 1998–1999 | 0/36 (0.0) | [48] | |
| Phoenix, Oakland *, San Diego | N/A *** | 1/48 (2.1) | [49] | |
| California, New York, Minnesota, Massachusetts, Illinois, Arizona, Georgia | 1994–2000 | 5/1030 **** (0.5) | [13] | |
| Minnesota | 1997–1999 | 1/8 (12.5) | [50] | |
| Vietnam | Hanoi, Ha Nam, Thai Binh | 2016–2020 | 24/184 (13.0) | [18,19] |
4. Mechanisms behind Macrolide Resistance in B. pertussis
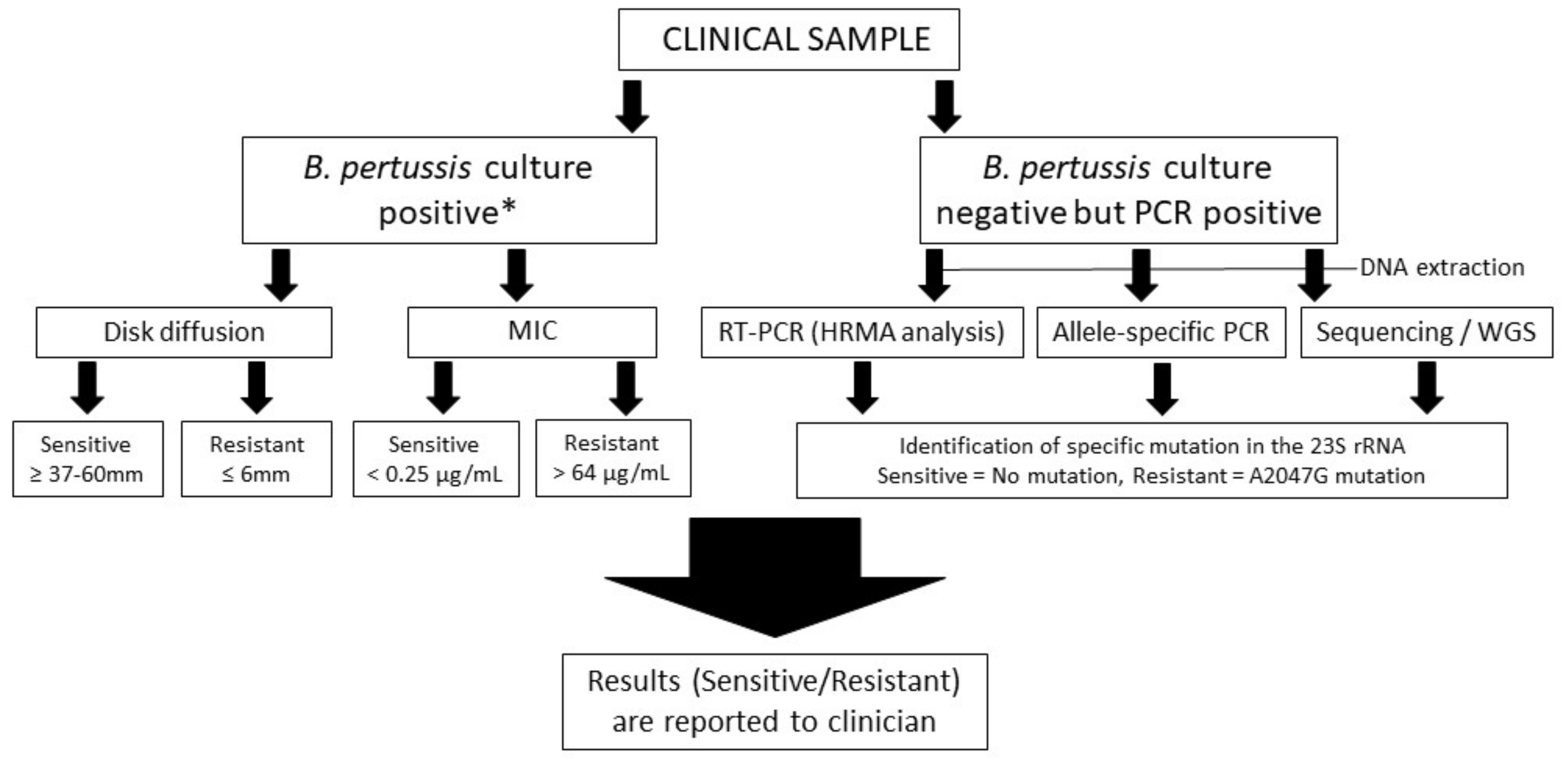
5. Methods to Detect Macrolide Resistant B. pertussis
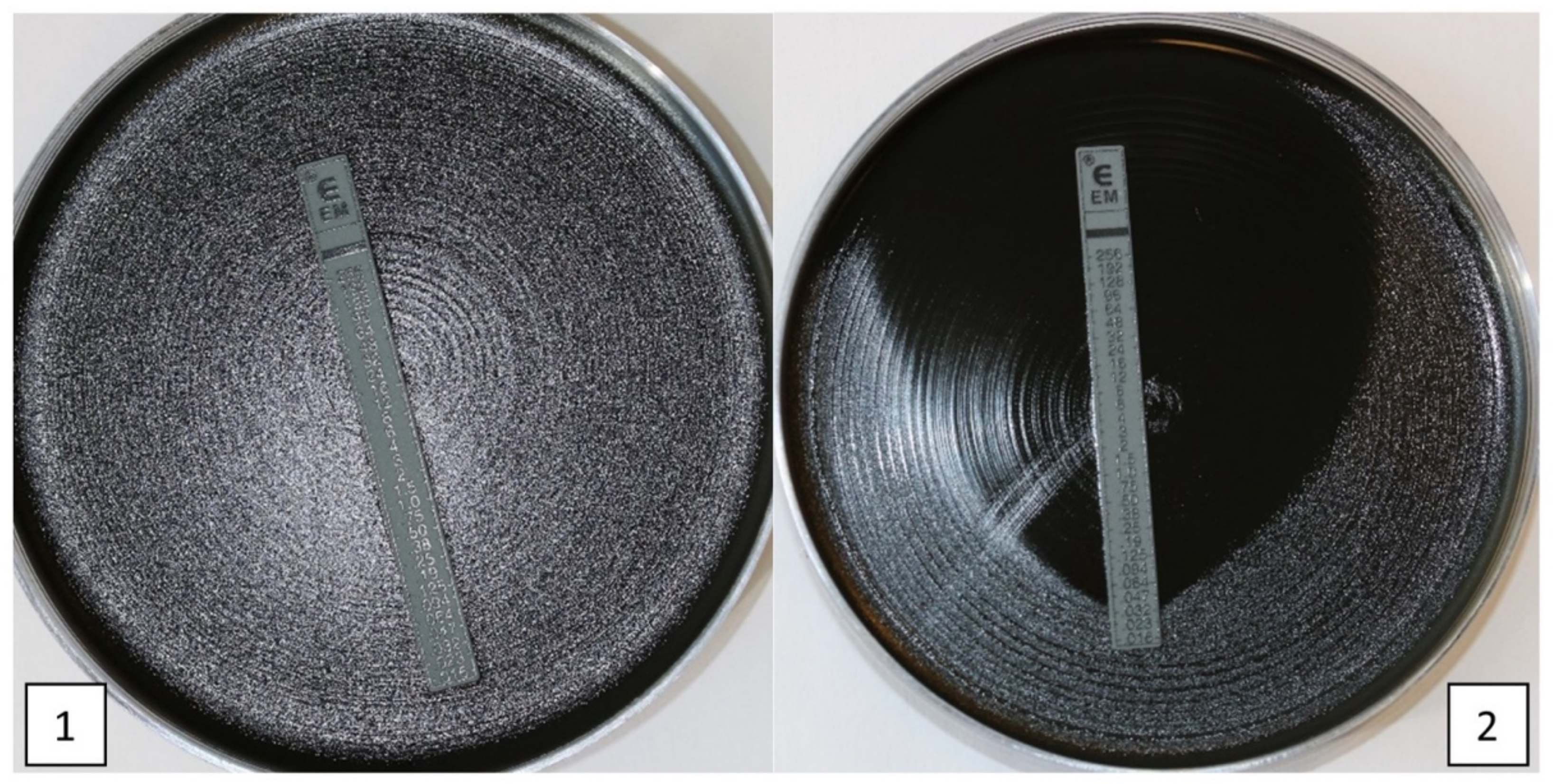
5.1. Disk Diffusion and Minimum Inhibition Concentration Methods
5.2. DNA-Based Identification of A2047G Mutation in the 23S rRNA
6. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeung, K.H.T.; Duclos, P.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Hutubessy, R.C.W. An Update of the Global Burden of Pertussis in Children Younger than 5 Years: A Modelling Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Barnett, E.D.; Lynfield, R.; Sawyer, M.H. (Eds.) Pertussis (Whooping Cough). In Red Book: 2021 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): Itasca, IL, USA, 2021; pp. 578–589. ISBN 978-1-61002-521-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, J.W.; Crast, F.W.; Kotheimer, J.B.; Mitchell, I.A. Susceptibility of Bordetella Pertussis to Nine Antimicrobial Agents. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1969, 117, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, D.J.; Hensey, D.M.; Beyer, J.M.; Vojtko, C.; McDonald, E.J.; Fernandes, P.B. Comparative in Vitro Activities of New 14-, 15-, and 16-Membered Macrolides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, T.; Murphy, T.V.; Moran, J. Recommended Antimicrobial Agents for the Treatment and Postexposure Prophylaxis of Pertussis: 2005 CDC Guidelines. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2005, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carbonetti, N.H. Bordetella Pertussis: New Concepts in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, K.; Saubolle, M.A.; Tenover, F.C.; Rudinsky, M.F.; Barbour, S.D.; Cherry, J.D. Pertussis Caused by an Erythromycin-Resistant Strain of Bordetella Pertussis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1995, 14, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirsing Von König, C.H. Pertussis Diagnostics: Overview and Impact of Immunization. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 13, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintgraff, J.; Irazu, L.; Lara, C.S.; Rodriguez, M.; Santos, M. The Classical Bordetella Species and MALDI-TOF Technology: A Brief Experience. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Laboratory Manual for the Diagnosis of Whooping Cough Caused by Bordetella Pertussis/Bordetella Parapertussis. Update 2014; World Health Organisation (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guiso, N.; Liese, J.; Plotkin, S. The Global Pertussis Initiative: Meeting Report from the Fourth Regional Roundtable Meeting, France, April 14–15, 2010. Hum. Vaccin. 2011, 7, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korgenski, E.K.; Daly, J.A. Surveillance and Detection of Erythromycin Resistance in Bordetella Pertussis Isolates Recovered from a Pediatric Population in the Intermountain West Region of the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2989–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.E.; Cassiday, P.K.; Popovic, T.; Sanden, G.N. Bordetella Pertussis Isolates with a Heterogeneous Phenotype for Erythromycin Resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2942–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourgeois, N.; Ghnassia, J.C.; Doucet-Populaire, F. In Vitro Activity of Fluoroquinolones against Erythromycin-Susceptible and -Resistant Bordetella Pertussis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guillot, S.; Descours, G.; Gillet, Y.; Etienne, J.; Floret, D.; Guiso, N. Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Infection in Newborn Girl, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahcheraghi, F.; Lotfi, M.N.; Nikbin, V.S.; Shooraj, F.; Azizian, R.; Parzadeh, M.; Torkaman, M.R.A.; Zahraei, S.M. The First Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Strains Isolated From Iranian Patients. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, 10880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Katsukawa, C.; Kawahara, R.; Kawatsu, K. The First Report of Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Isolation in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamachi, K.; Duong, H.T.; Dang, A.D.; Do, H.T.; Koide, K.; Otsuka, N.; Shibayama, K.; Hoang, H.T.T. Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis, Vietnam, 2016−2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2511–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, K.; Yao, S.; Chiang, C.; Thuy, P.T.B.; Nga, D.T.T.; Huong, D.T.; Dien, T.M.; Vichit, O.; Vutthikol, Y.; Sovannara, S.; et al. Genotyping and Macrolide-Resistant Mutation of Bordetella Pertussis in East and South-East Asia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 31, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katsukawa, C.; Otsuka, N.; Kenri, T.; Kamachi, K. Complete Genome Sequence of a Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Isolated in Japan. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e00718-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Xin, T.; He, Q. High-Resolution Melting Analysis for the Detection of Two Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Strains Carried by Healthy Schoolchildren in China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, E260–E262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yao, K.; Ma, X.; Shi, W.; Yuan, L.; Yang, Y. Variation in Bordetella Pertussis Susceptibility to Erythromycin and Virulence-Related Genotype Changes in China (1970–2014). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Dai, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, K.; Ye, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; et al. The Epidemic of Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis with Limited Genome Variation Associated with Pertussis Resurgence in China. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintchenko, V.; Brown, M.; Gilbert, G.L. Is Bordetella Pertussis Susceptibility to Erythromycin Changing? MIC Trends among Australian Isolates 1971–2006. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 1178–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, D.; Graham, R.M.; Richmond, P.; Keil, A.; Mukkur, T.K. Biofilm Forming Potential and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Newly Emerged Western Australian Bordetella Pertussis Clinical Isolates. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand-Austin, A.; Memari, N.; Patel, S.N.; Tang, P.; Deeks, S.L.; Jamieson, F.B.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Farrell, D.J. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Contemporary Clinical Isolates of Bordetella Pertussis in Ontario, Canada. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hou, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, T.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; He, Q. Appearance of Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Strains in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5193–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Hou, T.; Liu, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; He, Q. High Prevalence of Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis in Xi’an, China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O825–O830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Du, Q.; Shu, C.; Peng, X.; Wei, H.; Hou, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. The Global Prevalence PtxP3 Lineage of Bordetella Pertussis Was Rare in Young Children with the Co-Purified APV Vaccination: A 5 Years Retrospective Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Luan, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; He, Q. Pertussis Outbreak in a Primary School in China: Infection and Transmission of the Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, E145–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Li, H. Macrolide Susceptibility and Molecular Characteristics of Bordetella Pertussis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 03000605221078782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Wang, C.; Tian, H.; Kang, Z.; Zeng, M. Bordetella Pertussis Infection in Infants and Young Children in Shanghai, China, 2016-2017: Clinical Features, Genotype Variations of Antigenic Genes and Macrolides Resistance. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.Z.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, X.F.; Li, J.P.; Mi, Y.M.; Tang, L.F.; Chen, Z.M. In Vitro Activity and Clinical Efficacy of Macrolides, Cefoperazone-Sulbactam and Piperacillin/Piperacillin-Tazobactam against Bordetella Pertussis and the Clinical Manifestations in Pertussis Patients Due to These Isolates: A Single-Centre Study in Zheji. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Y.M.; Hua, C.Z.; Fang, C.; Liu, J.J.; Xie, Y.P.; Lin, L.N.; Wang, G.L. Effect of Macrolides and β-Lactams on Clearance of Bordetella Pertussis in the Nasopharynx in Children with Whooping Cough. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-N.; Zhou, J.-S.; Hua, C.-Z.; Bai, G.-N.; Mi, Y.-M.; Zhou, M.-M. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Pertussis in Children and Their Close Contacts in Households: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Zhejiang Province, China. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, K.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, L.; Shi, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yao, K. High Prevalence of Macrolide-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis and PtxP1 Genotype, Mainland China, 2014–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Octavia, S.; Payne, M.; Lan, R. Genomic Epidemiology of Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.J.; Zou, J.; Yao, K.; Li, L.; Zhong, L. Analysis of Antibiotic Sensitivity and Resistance Genes of Bordetella Pertussis in Chinese Children. Medicine 2021, 100, e24090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Hu, N.; Lou, J.; Chen, K.; Kang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, N.; Liu, D.; et al. Characteristics of COVID-19 Infection in Beijing. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Du, Q.; Li, D.; Yuan, L.; Meng, Q.; Fu, Z.; Xu, H.; Yao, K.; Zhao, R. A Cross-Sectional Study Revealing the Emergence of Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis Carrying PtxP3 Alleles in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubů, V.; Zavadilová, J.; Fabiánová, K.; Urbášková, P. Trends in the Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, and Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole for Strains of Bordetella Pertussis Isolated in the Czech Republic in 1967–2015. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2017, 25, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lönnqvist, E.; Barkoff, A.M.; Mertsola, J.; He, Q. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Finnish Bordetella Pertussis Isolates Collected during 2006–2017. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, B.; Bameri, Z.; Babaei, R.; Shahcheraghi, F. Isolation of High Level Macrolide Resistant Bordetella Pertussis without Transition Mutation at Domain V in Iran. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, 18190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefanelli, P.; Buttinelli, G.; Vacca, P.; Tozzi, A.E.; Midulla, F.; Carsetti, R.; Fedele, G.; Villani, A.; Concato, C.; Carannante, A.; et al. Severe Pertussis Infection in Infants Less than 6 Months of Age: Clinical Manifestations and Molecular Characterization. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fry, N.K.; Duncan, J.; Vaghji, L.; George, R.C.; Harrison, T.G. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Historical and Recent Clinical Isolates of Bordetella Pertussis in the United Kingdom Using the Etest Method. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 1183–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzynski, T.A.; Boehm, D.M.; Rott-Petri, J.A.; Schell, R.F.; Allison, P.E. Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Bordetella Species Isolated in a Multicenter Pertussis Surveillance Project. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis—Yuma County, Arizona, May–October 1994. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1994, 43, 807–810. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, K.A.; Fusco, J.; Biedenbach, D.J.; Pfaller, M.A.; Jones, R.N. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Clinical Isolates of Bordetella Pertussis from Northern California: Report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3599–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, B.C.; Baker, C.N.; Tenover, F.C. A Simplified Method for Testing Bordetella Pertussisfor Resistance to Erythromycin and Other Antimicrobial Agents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartkus, J.M.; Juni, B.A.; Ehresmann, K.; Miller, C.A.; Sanden, G.N.; Cassiday, P.K.; Saubolle, M.; Lee, B.; Long, J.; Harrison, A.R.; et al. Identification of a Mutation Associated with Erythromycin Resistance in Bordetella Pertussis: Implications for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barkoff, A.M.; Mertsola, J.; Pierard, D.; Dalby, T.; Hoegh, S.V.; Guillot, S.; Stefanelli, P.; Van Gent, M.; Berbers, G.; Vestrheim, D.F.; et al. Surveillance of Circulating Bordetella Pertussis Strains in Europe during 1998 to 2015. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01998-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowden, K.E.; Williams, M.M.; Cassiday, P.K.; Milton, A.; Pawloski, L.; Harrison, M.; Martin, S.W.; Meyer, S.; Qin, X.; DeBolt, C.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of the Pertussis Epidemic in Washington State in 2012. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3549–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Heininger, U.; Hozbor, D.F.; Tan, T.Q.; von König, C.H.W. Emerging Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella Pertussis in Mainland China: Findings and Warning from the Global Pertussis Initiative. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2021, 8, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Kobayashi, R.; Inoue, N.; Iwata, S.; Kuroki, H.; Kawamura, N.; Nakayama, E.; Tajima, T.; Shimizu, K.; et al. Emergence of Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma Pneumoniae with a 23S RRNA Gene Mutation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2302–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisblum, B. Erythromycin Resistance by Ribosome Modification. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesingi, P.V.; Singh, B.R.; Pesingi, P.K.; Bhardwaj, M.; Singh, S.V.; Kumawat, M.; Sinha, D.K.; Gandham, R.K. MexAB-OprM Efflux Pump of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Offers Resistance to Carvacrol: A Herbal Antimicrobial Agent. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.; Timms, V.; Sim, E.; Pey, K.; Nguyen, T.; Sintchenko, V. Genomic and Transcriptomic Variation in Bordetella spp. Following Induction of Erythromycin Resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 3016–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, E.; Pupo, E.; Santana, H.; Guerra, M.; Castellanos-Serra, L.R. Elution of Lipopolysaccharides from Polyacrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 259, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimolai, N.; Zaher, A.; Trombley, C. Correlation of Erythromycin Agar Dilution Susceptibility Testing with Disc Diffusion Susceptibility for Bordetella Pertussis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1997, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, R.; Liu, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; He, Q.; Yan, Y. Direct Detection of Erythromycin-Resistant Bordetella Pertussis in Clinical Specimens by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3418–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassiday, P.K.; Tobin-D’Angelo, M.; Watson, J.R.; Wu, K.H.; Park, M.M.; Sanden, G.N. Co-Infection with Two Different Strains of Bordetella Pertussis in an Infant. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimolai, N. Pharmacotherapy for Bordetella Pertussis Infection. I. A Synthesis of Laboratory Sciences. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.M.; Liaw, G.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yen, M.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Mu, J.J.; Chiang, C.S. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bordetella Pertussis in Taiwan Prompted by a Case of Pertussis in a Paediatric Patient. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, S.A.; Bortolussi, R.; Langley, J.M.; Miller, B.; Eastwood, B.J. Seven Days of Erythromycin Estolate Is as Effective as Fourteen Days for the Treatment of Bordetella Pertussis Infections. Pediatrics 1997, 100, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, J.M.; Halperin, S.A.; Boucher, F.D.; Smith, B. Azithromycin Is as Effective as and Better Tolerated than Erythromycin Estolate for the Treatment of Pertussis. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e96–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlsson, R.M.; von Segebaden, K.; Bergström, J.; Kling, A.M.; Nilsson, L. Surveillance of Infant Pertussis in Sweden 1998–2012; Severity of Disease in Relation to the National Vaccination Programme. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winter, K.; Harriman, K.; Zipprich, J.; Schechter, R.; Talarico, J.; Watt, J.; Chavez, G. California Pertussis Epidemic, 2010. J. Pediatr. 2012, 161, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolussi, R.; Miller, B.; Ledwith, M.; Halperin, S. Clinical Course of Pertussis in Immunized Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1995, 14, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwantes, B.W.; Joynson, D.H.M.; Williams, W.O. Bordetella Pertussis Isolation in General Practice: 1977–79 Whooping Cough Epidemic in West Glamorgan. J. Hyg. 1983, 90, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahnmatz, M.; Richert, L.; al-Tawil, N.; Storsaeter, J.; Colin, C.; Bauduin, C.; Thalen, M.; Solovay, K.; Rubin, K.; Mielcarek, N.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Live Attenuated Intranasal Pertussis Vaccine BPZE1: A Phase 1b, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Dose-Escalation Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damron, F.H.; Barbier, M.; Dubey, P.; Edwards, K.M.; Gu, X.-X.; Klein, N.P.; Lu, K.; Mills, K.H.G.; Pasetti, M.F.; Read, R.C.; et al. Overcoming Waning Immunity in Pertussis Vaccines: Workshop of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivaska, L.; Barkoff, A.-M.; Mertsola, J.; He, Q. Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella pertussis: Current Situation and Future Challenges. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111570
Ivaska L, Barkoff A-M, Mertsola J, He Q. Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella pertussis: Current Situation and Future Challenges. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111570
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvaska, Lauri, Alex-Mikael Barkoff, Jussi Mertsola, and Qiushui He. 2022. "Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella pertussis: Current Situation and Future Challenges" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111570
APA StyleIvaska, L., Barkoff, A.-M., Mertsola, J., & He, Q. (2022). Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella pertussis: Current Situation and Future Challenges. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111570







