Screening of Anorectal and Oropharyngeal Samples Fails to Detect Bacteriophages Infecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
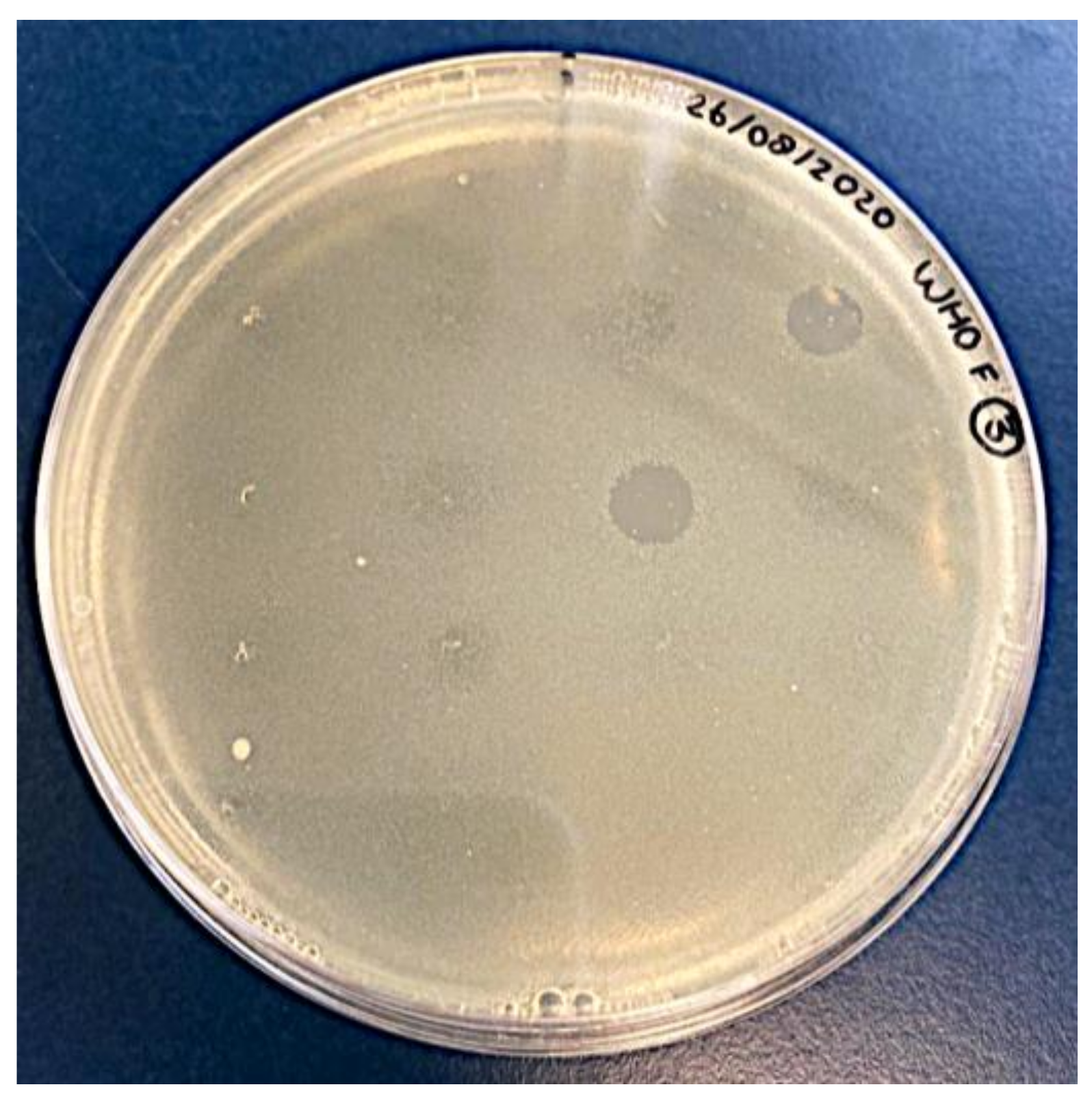
2.1. Isolation and Propagation of Potential Phages
2.2. Control Experiments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Potential Phage Containing Samples
4.3. Phage Enrichment Culture
4.4. Spot Test
4.5. Phage Isolation and Propagation
4.6. Control Experiments
4.7. Ethics Approval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kutter, E.; Sulakvelidze, A. Bacteriophages: Biology and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 0203491750. [Google Scholar]
- Chanishvili, N.; Chanishvili, T.; Tediashvili, M.; Barrow, P.A. Phages and their application against drug-resistant bacteria. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, D.D.; Pirnay, J.-P. Phage therapy: Could viruses help resolve the worldwide antibiotic crisis? Altern. Antibiot. 2015, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.M.; Koskella, B.; Lin, H.C. Phage therapy: An alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, S.; Rashel, M.; Uchiyama, J.; Sakurai, S.; Ujihara, T.; Kuroda, M.; Ikeuchi, M.; Tani, T.; Fujieda, M.; Wakiguchi, H.; et al. Bacteriophage therapy: A revitalized therapy against bacterial infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2005, 11, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unemo, M.; Shafer, W.M. Antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the 21st Century: Past, evolution, and future. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 587–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Xue, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wu, S.; Lv, H.; Yu, Y.; Van Der Veen, S. Increasing prevalence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone and resistance to azithromycin in Hangzhou, China (2015–2017). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, C.; Buyze, J.; Spiteri, G.; Cole, M.J.; Unemo, M. Population-Level Antimicrobial Consumption Is Associated with Decreased Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in 24 European Countries: An Ecological Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu Liu, C.; Green, S.I.; Min, L.; Clark, J.R.; Salazar, K.C.; Terwilliger, A.L.; Kaplan, H.B.; Trautner, B.W.; Ramig, R.F.; Maresso, A.W. Phage-Antibiotic Synergy is Driven by a Unique Combination of Antibacterial Mechanism of Action and Stoichiometry. MBio 2020, 11, e01462-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisette, T.; Lev, K.L.; Kebriaei, R.; Abdul-Mutakabbir, J.C.; Stamper, K.C.; Morales, S.; Lehman, S.M.; Canfield, G.S.; Duerkop, B.A.; Arias, C.A. Bacteriophage-antibiotic combinations for Enterococcus faecium with varying bacteriophage and daptomycin susceptibilities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00993-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, P. Phages for phage therapy: Isolation, characterization, and host range breadth. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadsworth, C.B.; Arnold, B.J.; Sater, M.R.A.; Grad, Y.H. Azithromycin resistance through interspecific acquisition of an epistasis-dependent efflux pump component and transcriptional regulator in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. MBio 2018, 9, e01419-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marri, P.R.; Paniscus, M.; Weyand, N.J.; Rendón, M.A.; Calton, C.M.; Hernández, D.R.; Higashi, D.L.; Sodergren, E.; Weinstock, G.M.; Rounsley, S.D.; et al. Genome sequencing reveals widespread virulence gene exchange among human Neisseria species. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratt, B.G.; Bowler, L.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.; Smith, J.M. Role of interspecies transfer of chromosomal genes in the evolution of penicillin resistance in pathogenic and commensal Neisseria species. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.V.; Pham, L.Q.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, M.X.B.; Nguyen, T.V.; May, F.; Le, G.M.; Klausner, J.D. Decreased Cephalosporin Susceptibility of Oropharyngeal Neisseria Species in Antibiotic-using Men Who Have Sex with Men in Hanoi, Vietnam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.L.; Culbertson, C.G.; Powell, H.M. Studies of a bacteriophage active against a chromogenic Neisseria. J. Bacteriol. 1956, 71, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelps, L.N. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteriophages for Neisseria. J. Gen. Virol. 1967, 1, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, V.I.; Hart, E.J.; Handley, J.; Goldberg, I.D. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage specific for Neisseria perflava. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1976, 4, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, S.G.; Hunter, D.H. Isolation of Bacteriophages Active against Neisseria meningitidis. J. Virol. 1967, 1, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aljarbou, A.N.; De Luca, A.A.M. Isolation of a New Neisseria Phage from the Oral Cavity of Healthy Humans. Open Access Sci. Reports 2012, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljarbou, A.N.; Aljofan, M. Genotyping, morphology and molecular characteristics of a lytic phage of Neisseria strain obtained from infected human dental plaque. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.A.; Short, H.B.; Young, F.E.; Clark, V.L. Autoplaquing in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 164, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alicja Niewiadomska, J.K.; Niewiadomska, A.; Klama, J. Analysis of the Filamentous Bacteriophage Genomes Integrated into Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA1090 Chromosome. Polish J. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Piekarowicz, A.; Klyz, A.; Majchrzak, M.; Szczesna, E.; Piechucki, M.; Kwiatek, A.; Maugel, T.K.; Stein, D.C. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Filamentous Phage Ngo 6 Is Capable of Infecting a Variety of Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piekarowicz, A.; Kłyz, A.; Majchrzak, M.; Adamczyk-Popławska, M.; Maugel, T.K.; Stein, D.C. Characterization of the dsDNA prophage sequences in the genome of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and visualization of productive bacteriophage. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachrach, G.; Leizerovici-Zigmond, M.; Zlotkin, A.; Naor, R.; Steinberg, D. Bacteriophage isolation from human saliva. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylenda, C.A.; Calvert, C.; Kolenbrander, P.E.; Tylenda, A. Isolation of Actinomyces bacteriophage from human dental plaque. Infect. Immun. 1985, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machuca, P.; Daille, L.; Vinés, E.; Berrocal, L.; Bittner, M. Isolation of a novel bacteriophage specific for the periodontal pathogen Fusobacterium nucleatum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7243–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitch, G.; Pratten, J.; Taylor, P.W. Isolation of bacteriophages from the oral cavity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Higashi, D.; Goytia, M.; Rendón, M.A.; Pilligua-Lucas, M.; Bronnimann, M.; McLean, J.A.; Duncan, J.; Trees, D.; Jerse, A.E.; et al. Commensal Neisseria Kill Neisseria gonorrhoeae through a DNA-Dependent Mechanism. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, E.L.; Ogle, J.M.; Finck, A.M. The Human Microbiome as a Focus of Antibiotic Discovery: Neisseria mucosa Displays Activity Against Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumen, J.G.E.; Van Dijck, C.; Abdellati, S.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S.; Baetselier De, I.; Martiny, D.; Crucitti, T.; Kenyon, C. Markedly Reduced Azithromycin and Ceftriaxone Susceptibility in Commensal Neisseria Species in Clinical Samples from Belgian Men Who Have Sex with Men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, A.; Alhanout, K.; Duval, R.E. Bacteriocins, antimicrobial peptides from bacterial origin: Overview of their biology and their impact against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, D.J.; Dajani, A.S. Interactions between Neisseria sicca and viridin B, a bacteriocin produced by Streptococcus mitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1978, 13, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rollins-Smith, L.A.; Smith, P.B.; Ledeczi, A.M.; Rowe, J.M.; Reinert, L.K. Caerin 1 antimicrobial peptides that inhibit HIV and neisseria may spare protective lactobacilli. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deasy, A.M.; Guccione, E.; Dale, A.P.; Andrews, N.; Evans, C.M.; Bennett, J.S.; Bratcher, H.B.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Gorringe, A.R.; Read, R.C. Nasal inoculation of the commensal neisseria lactamica inhibits carriage of neisseria meningitidis by young adults: A controlled human infection study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellati, S.; Laumen, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Basil, S.; Van Dijck, C.; De Block, T.; De Baetselier, I.; Martiny, D.; Kenyon, C. Circulating Isolates of Neisseria Mucosa do not Inhibit the Growth of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Preprints 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyen, S.A.; Dworkin, M. Autoplaquing in Myxococcus strains. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 158, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, E.P.F.; Vodstrcil, L.A.; Williamson, D.A.; Maddaford, K.; Hocking, J.S.; Ashcroft, M.; De Petra, V.; Bradshaw, C.S.; Fairley, C.K. Incidence and duration of incident oropharyngeal gonorrhoea and chlamydia infections among men who have sex with men: Prospective cohort study. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2020, 97, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbee, L.A.; Soge, O.O.; Khosropour, C.M.; Haglund, M.; Yeung, W.; Hughes, J.; Golden, M.R. The Duration of Pharyngeal Gonorrhea: A Natural History Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unemo, M.; Golparian, D.; Sánchez-Busó, L.; Grad, Y.; Jacobsson, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Lahra, M.M.; Limnios, A.; Sikora, A.E.; Wi, T.; et al. The novel 2016 WHO Neisseria gonorrhoeae reference strains for global quality assurance of laboratory investigations: Phenotypic, genetic and reference genome characterization. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3096–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unemo, M.; Fasth, O.; Fredlund, H.; Limnios, A.; Tapsall, J. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of the 2008 WHO Neisseria gonorrhoeae reference strain panel intended for global quality assurance and quality control of gonococcal antimicrobial resistance surveillance for public health purposes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijck, C.; Tsoumanis, A.; Rotsaert, A.; Vuylsteke, B.; Van den Bossche, D.; Paeleman, E.; Florence, E.; De Baetselier, I.; Brosius, I.; Laumen, J.; et al. Does an antibacterial mouthwash prevent sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men taking HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis? A randomised, placebo controlled, crossover trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabishvili, M.; de Vos, D.; Verbeken, G.; Kropinski, A.M.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Lavigne, R.; Wattiau, P.; Mast, J.; Ragimbeau, C.; Mossong, J.; et al. Selection and Characterization of a Candidate Therapeutic Bacteriophage That Lyses the Escherichia coli O104:H4 Strain from the 2011 Outbreak in Germany. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilcher, S.; Loessner, M.J. Engineering Bacteriophages as Versatile Biologics. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Batra, H.; Dong, J.; Chen, C.; Rao, V.B.; Tao, P. Genetic engineering of bacteriophages against infectious diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Condition | Oropharyngeal Swab | Anorectal Swab |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistogenicity study | Pre antibiotic use | 10 | 10 |
| Post antibiotic use | 10 | 8 | |
| PReGo study | Baseline | 64 | / |
| Post Listerine use | 54 | / | |
| Post placebo use | 54 | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laumen, J.G.E.; Abdellati, S.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S.; Van Dijck, C.; Van den Bossche, D.; De Baetselier, I.; de Block, T.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Soentjes, P.; Pirnay, J.-P.; et al. Screening of Anorectal and Oropharyngeal Samples Fails to Detect Bacteriophages Infecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020268
Laumen JGE, Abdellati S, Manoharan-Basil SS, Van Dijck C, Van den Bossche D, De Baetselier I, de Block T, Malhotra-Kumar S, Soentjes P, Pirnay J-P, et al. Screening of Anorectal and Oropharyngeal Samples Fails to Detect Bacteriophages Infecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(2):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020268
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaumen, Jolein Gyonne Elise, Saïd Abdellati, Sheeba Santhini Manoharan-Basil, Christophe Van Dijck, Dorien Van den Bossche, Irith De Baetselier, Tessa de Block, Surbhi Malhotra-Kumar, Patrick Soentjes, Jean-Paul Pirnay, and et al. 2022. "Screening of Anorectal and Oropharyngeal Samples Fails to Detect Bacteriophages Infecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae" Antibiotics 11, no. 2: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020268
APA StyleLaumen, J. G. E., Abdellati, S., Manoharan-Basil, S. S., Van Dijck, C., Van den Bossche, D., De Baetselier, I., de Block, T., Malhotra-Kumar, S., Soentjes, P., Pirnay, J. -P., Kenyon, C., & Merabishvili, M. (2022). Screening of Anorectal and Oropharyngeal Samples Fails to Detect Bacteriophages Infecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antibiotics, 11(2), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020268







