Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Syzygium aromaticum against the Five Most Common Microorganisms in the Oral Cavity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
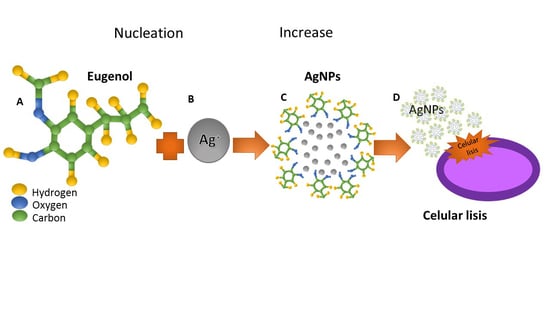
2.1. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles
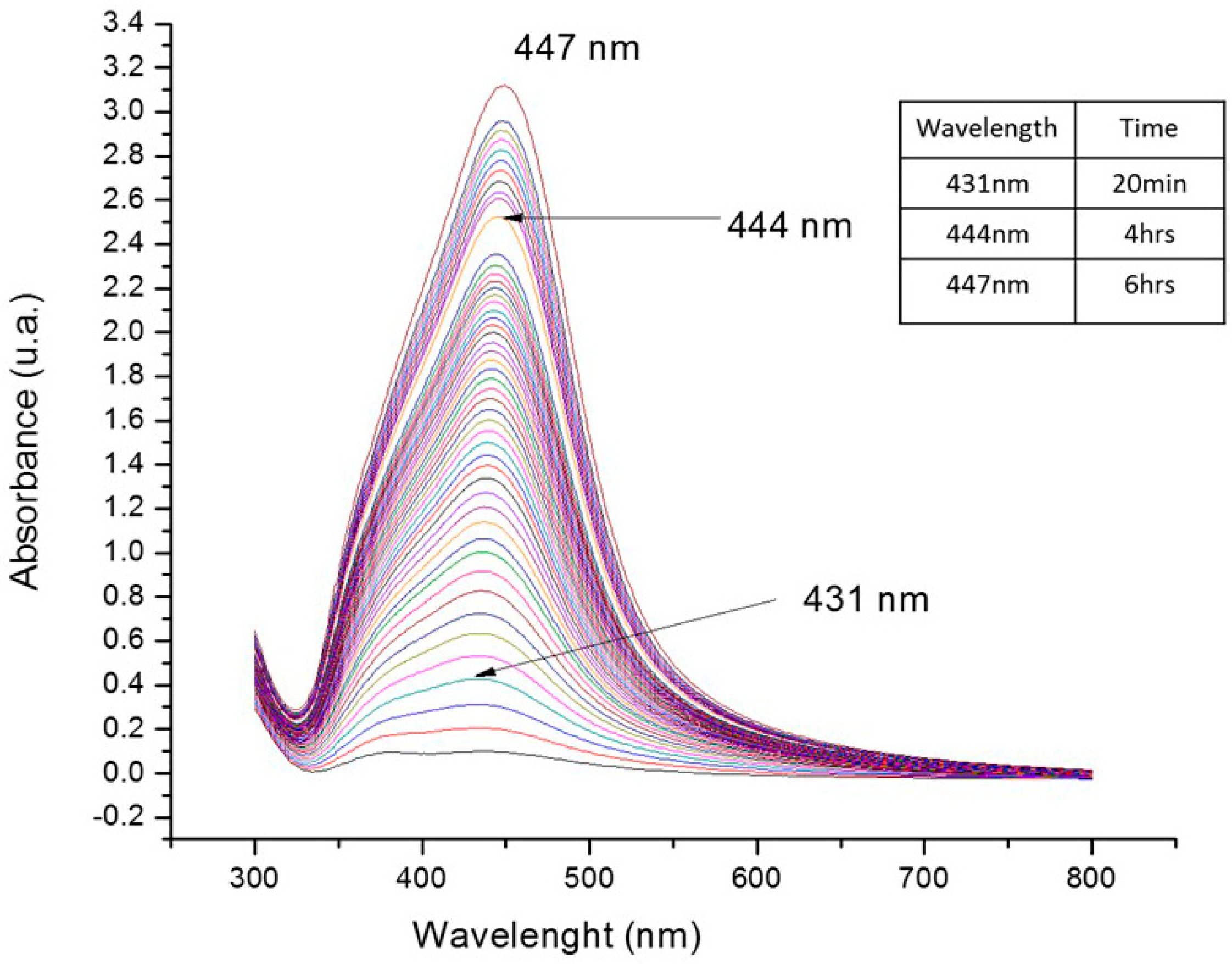
2.2.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
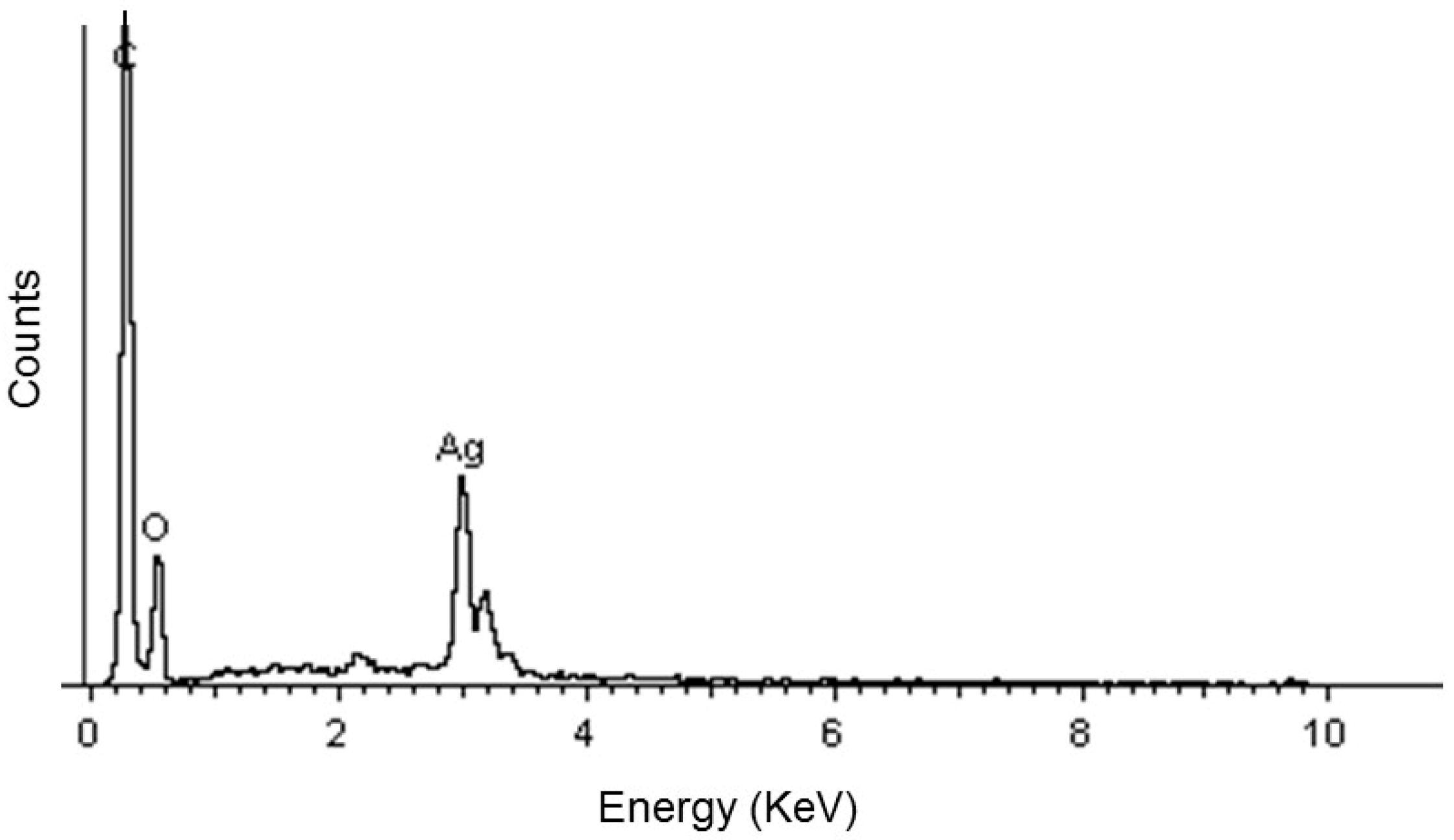
2.2.2. SEM-EDS Analysis
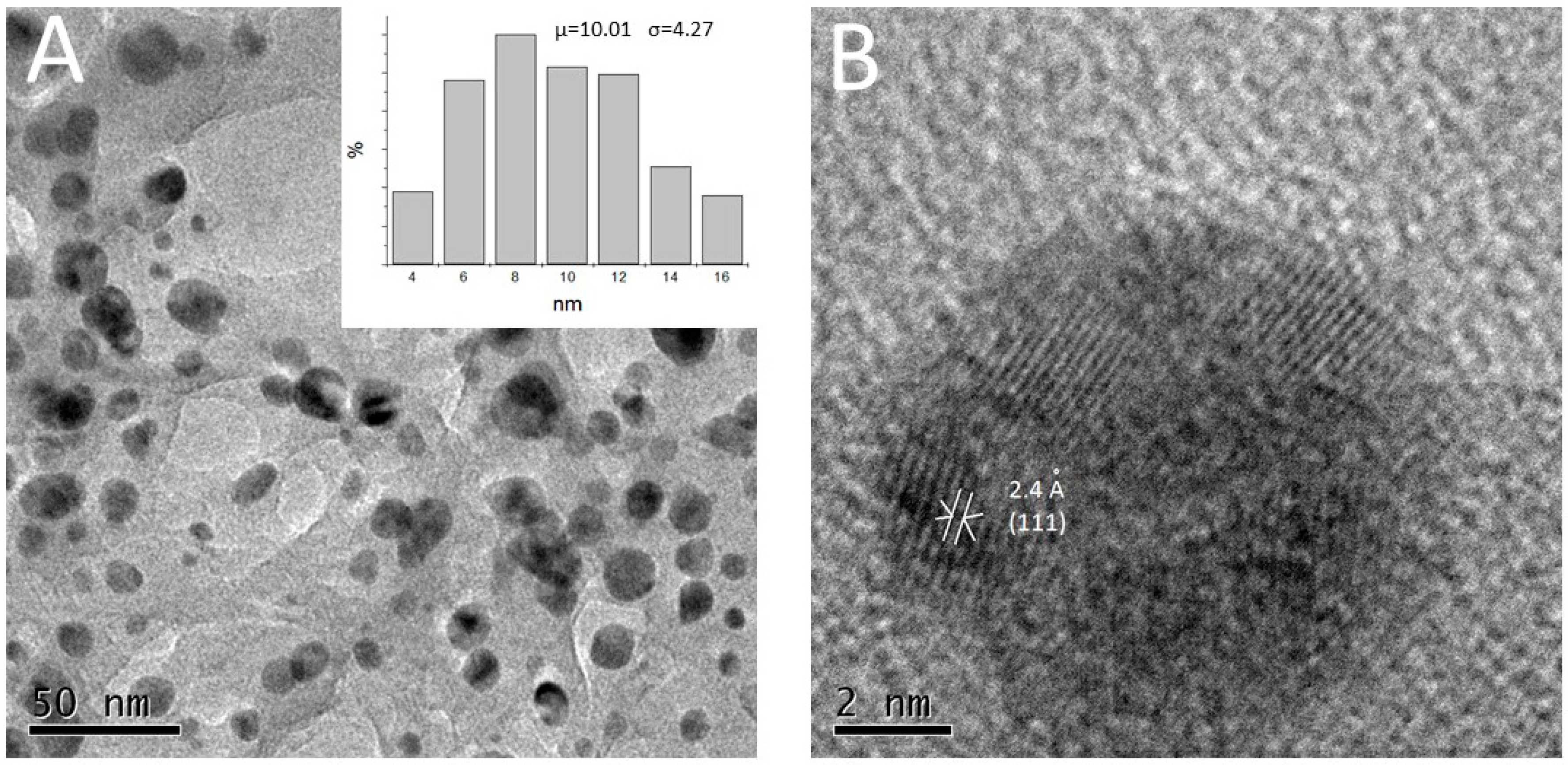
2.2.3. TEM
2.2.4. ζ Potential
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3.1. Disk Diffusion Test
2.3.2. Microdilution in Broth Test
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of AgNPs
4.2. Characterization of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles
4.2.1. Spectroscopy UV-Vis
4.2.2. SEM-EDS
4.2.3. TEM
4.2.4. Z Potential
4.3. Antimicrobial Activity
4.3.1. Disk Diffusion Test
4.3.2. Microdilution in Broth
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaloupka, K.; Malam, Y.; Seifalian, A.M. Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShan, D.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Ma, Q.; Cui, H.; Zhang, L. Application of Nanotechnology in Immunity against Infection. Coatings 2021, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent: A case study on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli as models for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barabadi, H.; Mojab, F.; Vahidi, H.; Marashi, B.; Talank, N.; Hosseini, O.; Saravanan, M. Green synthesis, characterization, antibacterial and biofilm inhibitory activity of silver nanoparticles compared to commercial silver nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 129, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Silva, G.F.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Zielinska, A.; Ventura, F.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Nanopharmaceutics: Part I—Clinical trials legislation and good manufacturing practices (GMP) of nanotherapeutics in the EU. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Souto, E.B.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Tewari, D.; Wang, D.; Atanasov, A.G.; Santini, A. Big impact of nanoparticles: Analysis of the most cited nanopharmaceuticals and nanonutraceuticals research. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2020, 2, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchooli, N.; Sanchooli, E.; Khandan Barani, H. Investigating the effect of water filter made using polyurethane foam containing silver nanoparticles on controlling Yersinia ruckeri in Oncorhynchus. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2022, 21, 500–515. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Pei, Y.; Tang, K. Soluble soybean polysaccharide films containing in-situ generated silver nanoparticles for antibacterial food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L.; Arias, J.; Molleda, P. Elaboración de nanopartículas de plata sintetizadas a partir de extracto de hojas de romero (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) y su uso como conservante. LA GRANJA Rev. Cienc. Vida 2022, 35, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangpraseurt, D.; You, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S. Biomimetic 3D living materials powered by microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, W.T.J.; Nyam, K.L. Evaluation of silver nanoparticles in cosmeceutical and potential biosafety complications. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.A.; Eid, A.M.; Elsheikh, T.M.Y.; Al-Faifi, Z.E.; Saad, N.; Sultan, M.H.; Selim, S.; Al-Khalaf, A.A.; Fouda, A. Mycosynthesis, Characterization, and Mosquitocidal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Fabricated by Aspergillus niger Strain. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchenko, V.; Kobylinskyi, S.; Iurzhenko, M.; Riabov, S.; Vashchuk, A.; Rybalchenko, N.; Zahorodnia, S.; Naumenko, K.; Demchenko, O.; Adamus, G. Nanocomposites based on polylactide and silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial and antiviral applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amooaghaie, R.; Saeri, M.R.; Azizi, M. Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Nigella sativa leaf extract in comparison with chemical silver nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, A.; Lee, J.H.; Yun, S.-I. Autoclave mediated one-pot-one-minute synthesis of AgNPs and Au–Ag nanocomposite from Melia azedarach bark extract with antimicrobial activity against food pathogens. Chem. Cent. J. 2016, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagtap, U.B.; Bapat, V.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, M.A.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Balusamy, S.R.; Akter, S. Green synthesis and potential antibacterial applications of bioactive silver nanoparticles: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, P.; Sreekanth, T.; Lee, J.-i.; Lee, K.D. Mycosynthesis: Antibacterial, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Inonotus obliquus (Chaga mushroom) extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 130, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.A.; Palanichamy, V.; Roopan, S.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alternanthera dentata leaf extract at room temperature and their antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 127, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Luckie, R.A.; Sanchez-Mendieta, V.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.A.; López-Castañares, R.; Perez-Mazariego, J.L.; Marquina-Fabrega, V.; Gómez, R.W. One-step aqueous synthesis of stoichiometric Fe–Cu nanoalloy. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4195–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaymat, T.M.; El Badawy, A.M.; Genaidy, A.; Scheckel, K.G.; Luxton, T.P.; Suidan, M. An evidence-based environmental perspective of manufactured silver nanoparticle in syntheses and applications: A systematic review and critical appraisal of peer-reviewed scientific papers. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; George, C.S. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pedroza, M.G.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; García-Contreras, R.; Jiménez-Martínez, Y.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; Navarro-Marchal, S.A.; Marchal, J.A.; Morales-Luckie, R.A.; Boulaiz, H. Silver nanoparticles from Annona muricata peel and leaf extracts as a potential potent, biocompatible and low cost antitumor tool. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystrioti, C.; Xanthopoulou, T.; Tsakiridis, P.; Papassiopi, N.; Xenidis, A. Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Dash, S.K.; Das, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, T.; Das, D.; Roy, S. Bio-fabricated silver nanoparticles preferentially targets Gram positive depending on cell surface charge. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokila, T.; Ramesh, P.; Geetha, D. Biosynthesis of AgNPs using Carica Papaya peel extract and evaluation of its antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.S.-L.; Khiew, P.-S.; Chiu, W.S.; Tan, Y.F.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Leong, C.-O. Green synthesis of graphene-silver nanocomposites and its application as a potent marine antifouling agent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, V.; Soumya, L.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chakra, S.; Bhatt, D.; Sreedhar, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama-Lara, S.A.; Morales-Luckie, R.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; Hinestroza, J.P.; García-Orozco, I.; Natividad, R. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity of platinum nanoparticles on bovine-bone powder: A novel support. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 6482186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreyra Maillard, A.P.V. Estudio del Efecto Antibacteriano de bio (Nano) Materiales Contra Microorganismos Patógenos Productores de Mastitis Bovina. 2019. Available online: https://ri.conicet.gov.ar/handle/11336/145722 (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Fonseca, M.S.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Sokolonski, A.R.; Stanisic, D.; Tomé, L.M.; Góes-Neto, A.; Azevedo, V.; Meyer, R.; Araújo, D.B.; Tasic, L. Activity of Fusarium oxysporum-Based Silver Nanoparticles on Candida spp. Oral Isolates. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, V.S.; Mudiam, M.K.R.; Kumar, M.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Singh, S.P.; Prasad, T. Silver nanoparticles induced alterations in multiple cellular targets, which are critical for drug susceptibilities and pathogenicity in fungal pathogen (Candida albicans). Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Revati, S.; Bipin, C.; Chitra, P.B.; Minakshi, B. In vitro antibacterial activity of seven Indian spices against high level gentamicin resistant strains of enterococci. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2015, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Liu, Y.; Wamer, W.G.; Yin, J.-J. Electron spin resonance spectroscopy for the study of nanomaterial-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xu, T.; Huang, G.; Jiang, S.; Gu, Y.; Chen, F. Oral microbiomes: More and more importance in oral cavity and whole body. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parahitiyawa, N.B.; Scully, C.; Leung, W.K.; Yam, W.C.; Jin, L.J.; Samaranayake, L.P. Exploring the oral bacterial flora: Current status and future directions. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; Stokes, L.N.; Olsen, I.; Dewhirst, F.E. Defining the normal bacterial flora of the oral cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuramitsu, H.K.; He, X.; Lux, R.; Anderson, M.H.; Shi, W. Interspecies interactions within oral microbial communities. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AlSheikh, R.; Albagieh, H.N.; Abdouh, I.; Zaki, H.; Alzahrani, A.M.; Halawany, H.S.; Al-Khalifa, K.S. In vitro activity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester against different oral microorganisms. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.O.; Garcia-Godoy, F. Primary Preventive Dentistry; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, S. Isolation and identification of the oral bacteria and their characterization for bacteriocin production in the oral cavity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Contreras, R.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; Mejía-Rubalcava, C.; Jiménez-Martínez, R.; Cuevas-Guajardo, S.; Sánchez-Reyna, P.A.; Mendieta-Zeron, H. Perspectives for the use of silver nanoparticles in dental practice. Int. Dent. J. 2011, 61, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Nyvad, B. The role of bacteria in the caries process: Ecological perspectives. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uju, D.E.; Obioma, N.P. Anticariogenic potentials of clove, tobacco and bitter kola. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeevika, A.; Shankaran, D.R. Seed-free synthesis of 1D silver nanowires ink using clove oil (Syzygium aromaticum) at room temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandan, D.; Bedre, M.D.; Basavaraja, S.; Sawle, B.; Manjunath, S.; Venkataraman, A. Rapid biosynthesis of irregular shaped gold nanoparticles from macerated aqueous extracellular dried clove buds (Syzygium aromaticum) solution. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.M.; Balaji, K.; Girilal, M.; Yadav, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Venketesan, R. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: A study against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mariri, A.; Safi, M. In vitro antibacterial activity of several plant extracts and oils against some gram-negative bacteria. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 39, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, I.S.; Rana, A.S.; Rajak, R.C. Evaluation of antifungal activity in essential oil of the Syzygium aromaticum (L.) by extraction, purification and analysis of its main component eugenol. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, J.H.; Castro, J.C.; Fenelon, V.C.; Garcia, F.P.; Nakamura, C.V.; Nogueira, A.C.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; de Souza, H.M.; Mangolim, C.S.; Moura-Costa, G.F. Essential oil characterization of Ocimum basilicum and Syzygium aromaticum free and complexed with β-cyclodextrin. Determination of its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and antitumoral activities. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2022, 102, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Rojas, D.F.; de Souza, C.R.F.; Oliveira, W.P. Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): A precious spice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajpai, S.; Kumari, M. A green approach to prepare silver nanoparticles loaded gum acacia/poly (acrylate) hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; DebMandal, M.; Saha, K.; Pal, N.K. In vitro antibacterial activity of three Indian spices against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Oman Med. J. 2011, 26, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Duhan, J.; Tewari, S.; Sangwan, P.; Yadav, A.; Singh, G.; Juneja, R.; Saini, H. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of Syzygium aromaticum, Ocimum sanctum and Cinnamomum zeylanicum plant extracts against Enterococcus faecalis: A preliminary study. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.N.; Ingale, A.G. Syzygium aromaticum extract mediated, rapid and facile biogenic synthesis of shape-controlled (3D) silver nanocubes. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Luckie, R.A.; Lopezfuentes-Ruiz, A.A.; Olea-Mejía, O.F.; Liliana, A.-F.; Sanchez-Mendieta, V.; Brostow, W.; Hinestroza, J.P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extracts of Heterotheca inuloides as reducing agent and natural fibers as templates: Agave lechuguilla and silk. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Cai, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Z.; Yu, C.-P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using tea leaf extract and evaluation of their stability and antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.-H. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of silky hairs of corn and investigation of its antibacterial and anticandidal synergistic activity and antioxidant potential. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, J.A.; Malaka, R.; Muthukumarasamy, N.P.; Sambandam, A.; Subramanian, S.; Sevanan, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Zea mays and exploration of its biological applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.M.E.; Luxton, T.P.; Silva, R.G.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Impact of environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Badawy, A.M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.; Tolaymat, T. The impact of stabilization mechanism on the aggregation kinetics of silver nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seil, J.T.; Webster, T.J. Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: Methods and literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2767. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The potential of silver nanoparticles for antiviral and antibacterial applications: A mechanism of action. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemlata, P.R.M.; Singh, A.P.; Tejavath, K.K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using cucumis prophetarum aqueous leaf extract and their antibacterial and antiproliferative activity against cancer cell lines. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniel, W.; Tholen, M. Protocols for Determination of Limits of Detection and Limits of Quantitation; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals: CLSI Supplement VET01S; Replaces VET01-S2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, P. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, Approved Standard; CLSI Document M27-A2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Anthony, B.F. Importance of bacterial growth phase in determining minimal bactericidal concentrations of penicillin and methicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 19, 1075–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

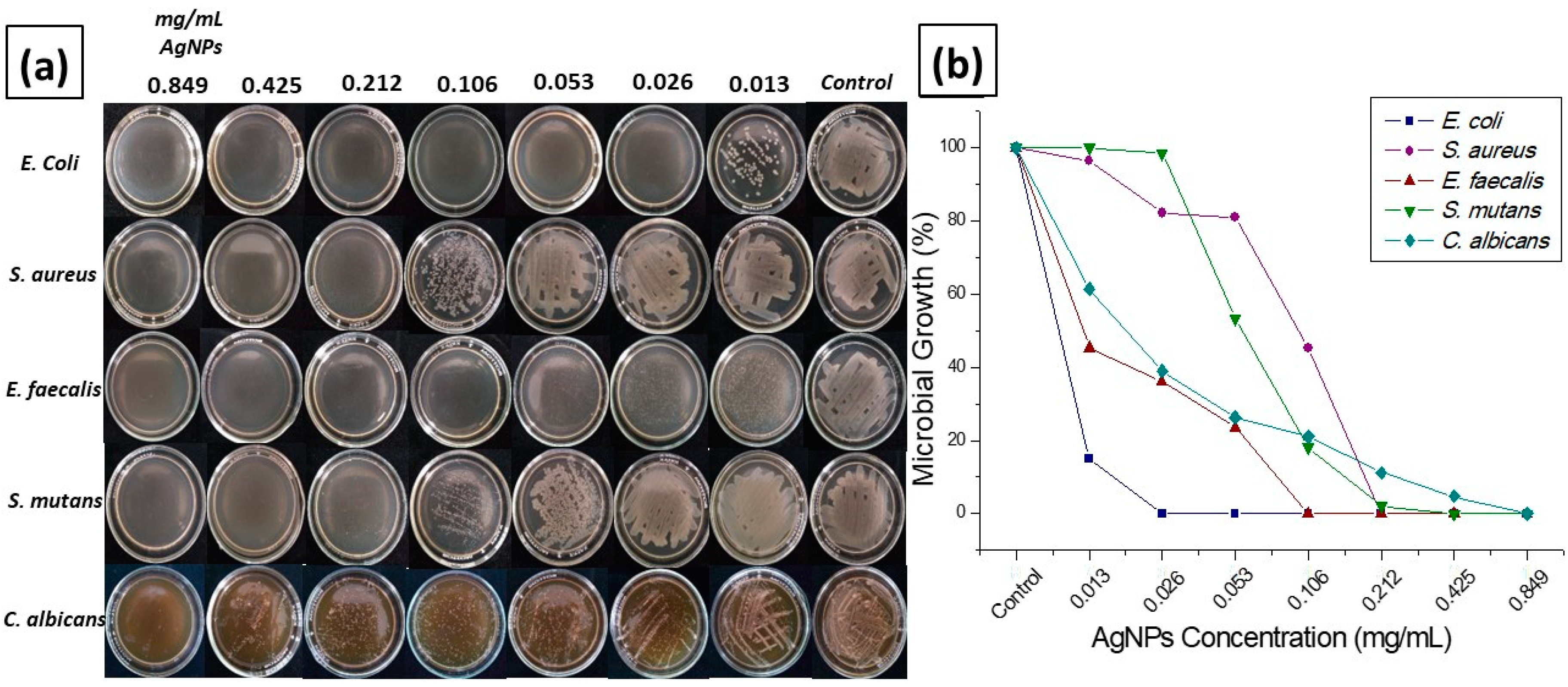
| AgNPs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs (mg/mL) | E. coli | S. aureus | E. faecalis | S. mutans | C. albicans |
| 0.849 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 0.425 | - | - | - | - | + |
| 0.212 | - | - | - | + | + |
| 0.106 | - | + | - | + | + |
| 0.053 | - | + | + | + | + |
| 0.026 | - | + | + | + | + |
| 0.013 | + | + | + | + | + |
| Control | + | + | + | + | + |
 MEC
MEC  .
.Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jardón-Romero, E.A.; Lara-Carrillo, E.; González-Pedroza, M.G.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Salmerón-Valdés, E.N.; Toral-Rizo, V.H.; Olea-Mejía, O.F.; López-González, S.; Morales-Luckie, R.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Syzygium aromaticum against the Five Most Common Microorganisms in the Oral Cavity. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070834
Jardón-Romero EA, Lara-Carrillo E, González-Pedroza MG, Sánchez-Mendieta V, Salmerón-Valdés EN, Toral-Rizo VH, Olea-Mejía OF, López-González S, Morales-Luckie RA. Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Syzygium aromaticum against the Five Most Common Microorganisms in the Oral Cavity. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(7):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070834
Chicago/Turabian StyleJardón-Romero, Erika Alejandra, Edith Lara-Carrillo, María G. González-Pedroza, Víctor Sánchez-Mendieta, Elías Nahum Salmerón-Valdés, Víctor Hugo Toral-Rizo, Oscar F. Olea-Mejía, Saraí López-González, and Raúl A. Morales-Luckie. 2022. "Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Syzygium aromaticum against the Five Most Common Microorganisms in the Oral Cavity" Antibiotics 11, no. 7: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070834
APA StyleJardón-Romero, E. A., Lara-Carrillo, E., González-Pedroza, M. G., Sánchez-Mendieta, V., Salmerón-Valdés, E. N., Toral-Rizo, V. H., Olea-Mejía, O. F., López-González, S., & Morales-Luckie, R. A. (2022). Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Syzygium aromaticum against the Five Most Common Microorganisms in the Oral Cavity. Antibiotics, 11(7), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070834