Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci as an Etiologic Agent of Ovine Mastitis, with a Focus on Subclinical Forms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
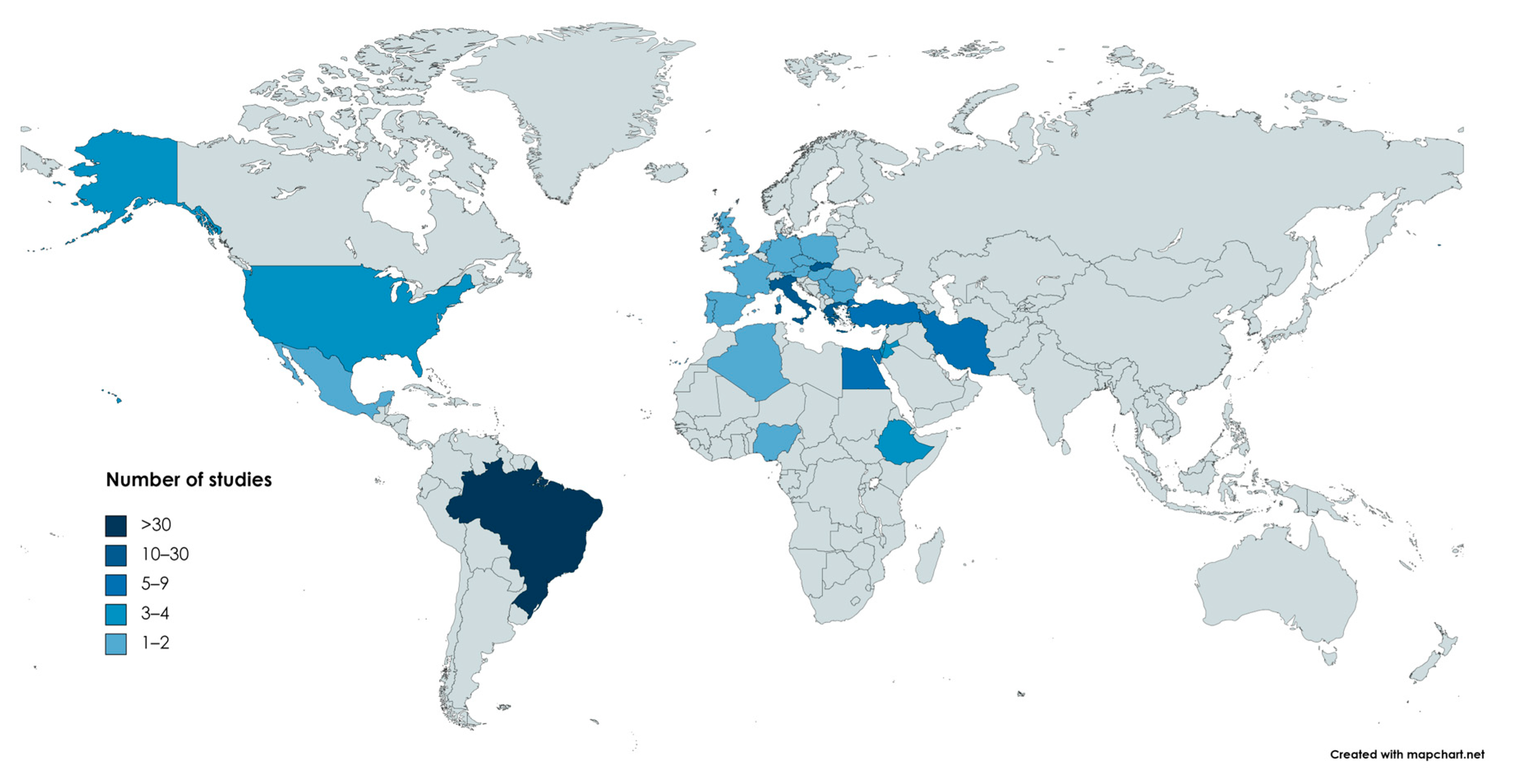
2.1. Geographical Distribution
- Europe: 67
- South America: 33
- Asia: 21
- Africa: 12
- North America: 5
- Europe and South America: 1
2.2. Relevant Findings of the Studies per Country
2.2.1. Brazil
2.2.2. Greece
2.2.3. Italy
2.2.4. Slovakia
2.2.5. Iran
2.2.6. Egypt
2.2.7. Turkey
2.2.8. USA
2.2.9. Ethiopia
2.2.10. Israel
2.2.11. Jordan
2.2.12. Other Countries
2.3. Breeds of Sheep Included in the Studies
2.4. Prevalence of Pathogens
2.5. Species of Identified CoNS
2.6. Antibiotic Resistance
2.7. Biofilm Production and Biofilm- and Toxin-Associated Genes
2.8. Procedures of Microbiological Examination in the Selected Studies
3. Discussion
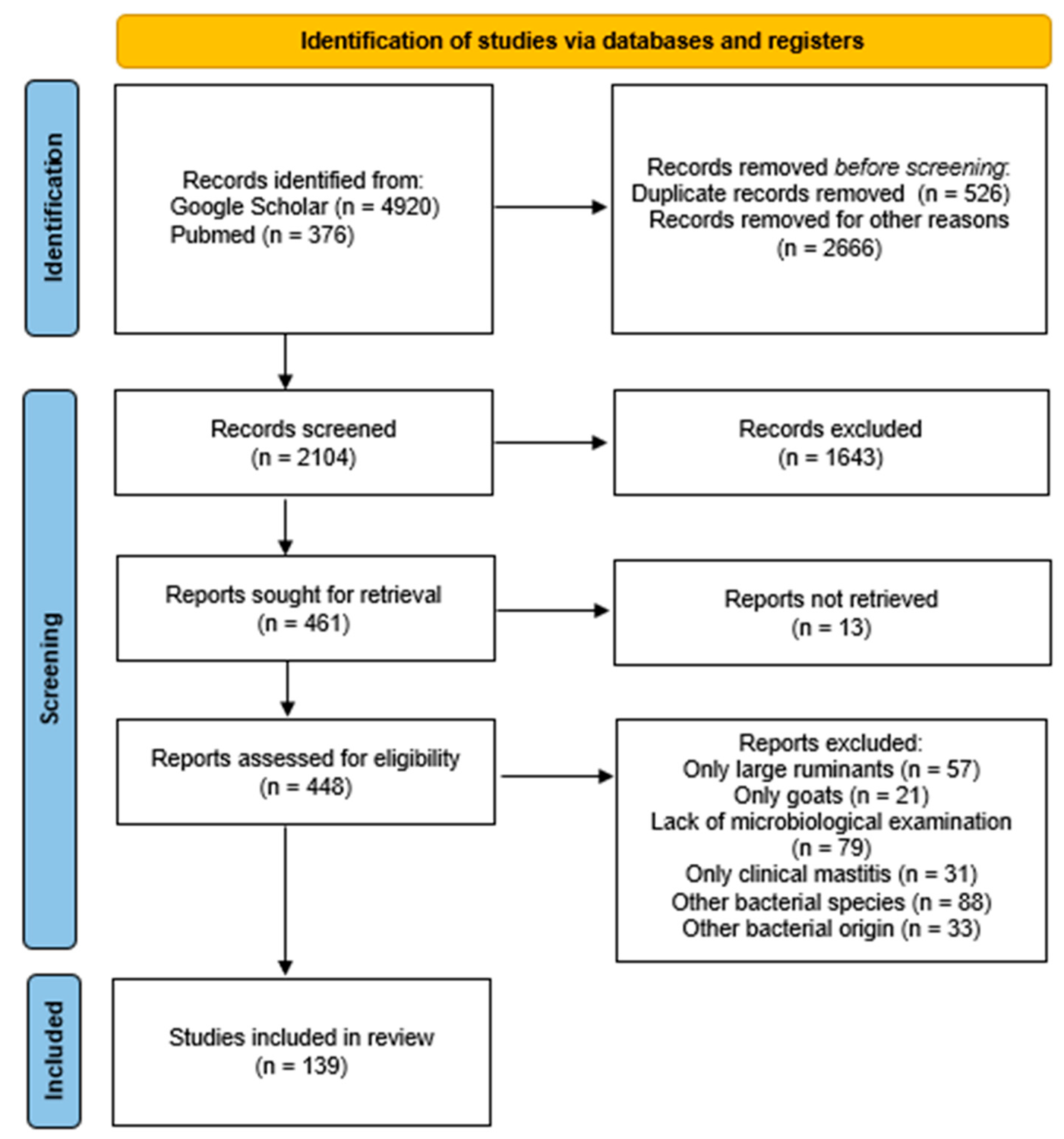
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selvaggi, M.; D’Alessandro, A.G.; Dario, C. Environmental and Genetic Factors Affecting Milk Yield and Quality in Three Italian Sheep Breeds. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Sarrou, S.; Fragkou, I.A.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Role of Staphylococci in Mastitis in Sheep. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelasakis, A.I.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petridis, I.G.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Fthenakis, G.C. Mastitis in Sheep—The Last 10 Years and the Future of Research. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libera, K.; Konieczny, K.; Grabska, J.; Smulski, S.; Szczerbal, I.; Szumacher-Strabel, M.; Pomorska-Mól, M. Potential Novel Biomarkers for Mastitis Diagnosis in Sheep. Animals 2021, 11, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkou, I.A.; Boscos, C.M.; Fthenakis, G.C. Diagnosis of Clinical or Subclinical Mastitis in Ewes. Small Rumin. Res. 2014, 118, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Romero, R.A.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E. Non-Aureus Staphylococci and Mammaliicocci as a Cause of Mastitis in Domestic Ruminants: Current Knowledge, Advances, Biomedical Applications, and Future Perspectives—A Systematic Review. Vet. Res. Commun. 2023, 47, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, F.; Bitrus, A.; Peter, I.; Chung, E.; Tukiran, N. Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis in Ruminants: A Review of Etiological Agents, Diagnosis, Clinical Management and Risk Factors. J. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 1, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaeghen, W.; Piepers, S.; Leroy, F.; Van Coillie, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Vliegher, S. Identification, Typing, Ecology and Epidemiology of Coagulase Negative Staphylococci Associated with Ruminants. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.Z.P.R.B.; Oliveira, L.G.L.; Afonso, J.A.B.; Lázaro, N.S.; Mendonça, C.L. Influence of Intrammary Infections on the Physical-Chemical Characteristics of Milk from Santa-Ines Ewes. Cienc. Anim. Bras. 2009, 10 (Suppl. S1), 760–765. [Google Scholar]
- Guaraná, E.D.S.; dos Santos, R.A.; Silva, N.D.; Campos, A.G.S.S.; Afonso, J.A.B.; de Mendonça, C.L. Influence of Subclinical Mastitis on the Physical-Chemical Characteristics of Milk from Santa Inês Ewes in Different Lactation Stages: A Preliminary Study. Ciênc. Anim. Bras. 2009, 10 (Suppl. S1), 754–759. [Google Scholar]
- Blagitz, M.G.; Batista, C.F.; Nunes, G.R.; Souza, F.N.D.; Gomes, V.; Azedo, M.R.; Sucupira, M.C.A.; Libera, A.M.M.P.D. Características físico-químicas, celulares e microbiológicas da secreção mamária de ovelhas Santa Inês no período lactante e pós-desmame. Rev. Ciênc. Agrar. 2010, 53, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucheis, S.B.; Hernandes, G.S.; Troncarelli, M.Z. Monitoramento Microbiológico da Mastite Ovina na Região de Bauru, SP. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2010, 77, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.D.S.E.; Silveira, J.A.S.D.; Pinheiro, C.P.; Sousa, M.G.S.D.; Oliveira, C.M.C.; Mendonça, C.L.D.; Duarte, M.D.; Barbosa, B.J.D. Etiologia e Perfil de Sensibilidade de Bactérias Isoladas de Ovelhas com Mastite na Região Nordeste do Estado do Pará. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2010, 30, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, C.J.; Zafalon, L.F.; Otsuk, I.P.; Nassar, A.F.C. Prejuízos Causados Pela Mastite em Ovelhas Santa Inês. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2010, 77, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaraná, E.L.D.S.; Santos, R.A.D.; Campos, A.G.S.S.; Silva, N.D.S.E.; Afonso, J.A.B.; Mendonça, C.L.D. Dinâmica celular e microbiológica do leite de ovelhas Santa Inês acompanhadas durante a lactação. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2011, 31, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, G.D.; Almeida, A.C.; Teixeira, L.M.; Xavier, T.R.; Souza, R.M.D.; Duarte, E.R. Caracterização da Mastite Ovina no Norte de Minas Gerais: Ocorrência, Etiologia e Epidemiologia. Rev. Caatinga 2011, 24, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zafalon, L.F.; Verissimo, C.J.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Martins, K.B.; Almeida, L.M.; Veschi, J.L.A. Estafilococos resistentes à oxacilina isolados em casos de mastite subclínica em ovinos. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2012, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.A.; Melo, C.B.; Seixas, L.; Azevedo, H.C.; Teixeira, K.M.; Melo, P.O. Mastitis and Milk Composition in First Partum Santa Ines Ewes. J. Vet. Adv. 2013, 3, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafalon, L.F.; Veschi, J.L.A.; Martins, K.B.; Santana, R.C.M. Occurrence of Ovine Subclinical Mastitis During Two Consecutive Lactations in a Santa Ines Breed Herd. Ciênc. Anim. Bras. 2015, 16, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.F.V.; Reway, A.P.; Félix, A.; Beutemmüller, E.A.; Pretto-Giordano, L.G.; Alfieri, A.A.; Lisbôa, J.A.N.; Müller, E.E. Mammary Gland Health of Santa Inês Ewes at the Drying and Puerperium and Evaluation of a Dry-off Terapy with Gentamicin. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura, G.S. Dinâmica da Infecção e Caracterização Molecular das Mastites Causadas por Staphylococcus spp. em Ovelhas da Raça Santa Inês. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal Rural de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, R.C.M.; Zafalon, L.F.; Esteves, S.N.; Tanaka, E.V.; Pilon, L.E.; Massa, R. Occurrence of Etiologic Agents Causing Subclinical Mastitis in Morada Nova and Santa Ines Ewes. Ars Vet. 2013, 29, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, R.C.M.; Zafalon, L.F.; Brandão, H.D.M.; Junior, G.A.F.; Pilon, L.E.; Junior, W.B.; Giglioti, R.; Mosqueira, V.C.F. Uso de Antimicrobiano Nanoparticulado para o Tratamento da Mastite Subclínica de Ovelhas de Corte no Período Seco. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2016, 36, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafalon, L.F.; Santana, R.C.M.; Pilon, L.E.; Júnior, G.A.F. Diagnosis of Subclinical Mastitis in Santa Inês and Morada Nova Sheep in Southeastern Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafalon, L.F.; Cunha, M.L.R.S.; Brandão, H.M.; Mosqueira, V.C.F.; Santana, R.C.M.; Barioni Júnior, W.; Martins, K.B.; Pilon, L.E. Relationship between Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus spp. and Failure of Antimicrobial Treatment of Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.B.; Faccioli, P.Y.; Bonesso, M.F.; Fernandes, S.; Oliveira, A.A.; Dantas, A.; Zafalon, L.F.; Cunha, M.D.L.R.S. Characteristics of Resistance and Virulence Factors in Different Species of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Milk of Healthy Sheep and Animals with Subclinical Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnol, A.M.D.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Franca, C.A.D.; Krewer, C.D.C.; Queiros, A.A.D.; Costa, M.M.D.; Braganca, J.F.M.; Girardini, L.K. Caracterização Fenotípica e Molecular de Isolados de Staphylococcus spp. Obtidos de Leite de Ovelhas do Município de Chapecó-SC. Semin. Ciênc. Agrár. 2013, 34, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.D.R. Contagem de Células Somáticas e Isolamento Bacteriano em Leite de Ovelhas no Estado do Rio Grande do Sul-Brasil. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Rio Grande, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, R.F.; Costa, P.T.; Fernandes, T.A.; Moreira, S.M.; Silveira, I.D.B.; De Moraes, R.E.; de Lima Gonzalez, H. Características Produtivas e Comportamentais de Ovelhas Lacaune em Diferentes Estádios de Lactação. REDVET Rev. Electrón. Vet. 2017, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Escopelli, K.S.; Lopes, E.J.C.; Pinto, A.T.; Schmidt, V. Diagnóstico de Mastite e Determinação da Composição do Leite de Ovelhas Laucane. Hig. Aliment. 2017, 31, 268–269. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, P.V.; Scapini, V.A.D.C.; Valentini, T.; Girardini, L.K.; De Souza, F.N.; Della Libera, A.M.M.P.; Heinemann, M.B.; Chande, C.G.; Cortez, A.; Collet, S.G.; et al. Milk Cellularity and Intramammary Infections in Primiparous and Multiparous Lacaune Ewes during Early Lactation. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 167, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, D.F.; Da Rosa, G.; Hanauer, D.; Saldanha, T.F.; Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Da Silva Dos Santos, D.; Piovezan, A.P.; Girardini, L.K.; Schafer Da Silva, A. Subclinical Mastitis in Lacaune Sheep: Causative Agents, Impacts on Milk Production, Milk Quality, Oxidative Profiles and Treatment Efficacy of Ceftiofur. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, B.V.; Da Costa, G.M.; Leite, R.F.; Lucas, F.A.; Custódio, D.A.D.C.; Lima, R.R.D.; Brighenti, C.R.G.; Alves, N.G. Relationship between Subclinical Mastitis and Reproduction in Lacaune Sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2022, 216, 106809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradieé, J.; da Rosa Moraes, C.; Gonçalves, M.; Vilanova, M.S.; Corrêa, G.F.; Lauz, O.G.; Osório, M.T.M.; Schmidt, V. Somatic cell count and California Mastitis Test as a diagnostic tool for subclinical mastitis in ewes. Acta Sci. Vet. 2012, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fim Junior, G.A.; Manieri, F.Z.; Lopes, N.S.D.S.; Pilon, L.E.; Zafalon, L.F. Occurrence of Subclinical Mastitis in Ewes of Different Breeds in the Same Production System. Rev. Bras. Hig. Sanid. Anim. 2014, 8, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fim Júnior, G.A. Contagem de Células Somáticas para o Diagnóstico da Mastite Subclínica Ovina em Diferentes Raças em Dois Períodos de Lactação. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Sao Paolo, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zafalon, L.F.; Santana, R.C.M.; Esteves, S.N.; Fim Júnior, G.A. Somatic Cell Count in the Diagnosis of Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep of Different Breeds. Semin. Ciênc. Agrár. 2018, 39, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, G.; Mattiello, S.P.; Peixoto, R.M.; Vargas, A.C.; Maciel, M.N.; Costa, M.M. Caracterização Bioquímica e Perfil de Sensibilidade aos Antimicrobianos de Agentes Bacterianos Isolados de Mastite Subclínica Ovina na Região Oeste de Santa Catarina. Ciênc. Anim. Bras. 2010, 11, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, C.A.; Peixoto, R.M.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Melo, N.F.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Veschi, J.L.A.; Mota, R.A.; Costa, M.M. Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. from Small Ruminant Mastitis in Brazil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2012, 32, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.V.D. Avaliação das Espécies e Perfil de Suscetibilidade aos Antimicrobianos de Staphylococcus Isolados de Leite de Ovelha. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal Rural do Rio De Janeiro, Sepetiba, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.D.S.; Lima, D.C.V.D.; Abad, A.C.A.; Oliveira, P.R.F.D.; Silva, J.G.D.; Moura, G.S.D.; Silva, A.T.F.; Amorim, V.D.S.; Costa, M.M.D.; Mota, R.A. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Non-Aureus Staphylococci Isolates from Buffalo, Goat and Sheep Mastitis in the Northeast Region of Brazil. J. Dairy Res. 2020, 87, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougoulis, D.A.; Kyriazakis, I.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Fragkou, I.A.; Skoufos, J.; Tzora, A.; Taitzoglou, I.A.; Kokoli, A.N.; Fthenakis, G.C. Patterns of Maternal-Offspring Behaviour of Dairy Sheep and Potential Association with Mammary Health. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 87, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougoulis, D.; Kyriazakis, I.; Tzora, A.; Taitzoglou, I.; Skoufos, J.; Fthenakis, G. Effects of Lamb Sucking on the Bacterial Flora of Teat Duct and Mammary Gland of Ewes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2007, 43, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiossis, E.; Brozos, C.N.; Petridou, E.; Boscos, C. Program for the Control of Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Chios Breed Ewes during Lactation. Small Rumin. Res. 2007, 73, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiossis, E.; Brozos, C.N.; Petridou, E.; Zdragas, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Boscos, C. Study on the Possible Survival of Staphylococcus Chromogenes through the Dry Period in Dairy Ewes. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 115, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sougaris, S.; Brozos, C.; Petridou, E.; Papadopoulos, T.; Kiossis, E. Abrupt and Gradual Drying-off Procedure and Intramammary Dry Treatment: Impact on Udder Health Status of Chios Breed Dairy Sheep. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2022, 73, 4031–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, I.G.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Fragkou, I.A.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Tzora, A.; Fotou, K.; Skoufos, I.; Amiridis, G.S.; Brozos, C.; Fthenakis, G.C. Effects of Drying-off Procedure of Ewes’ Udder in Subsequent Mammary Infection and Development of Mastitis. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 110, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogianni, V.S.; Papadopoulos, E.; Spanos, S.A.; Mitsoura, A.; Ptochos, S.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Barbagianni, M.S.; Kyriazakis, I.; Fthenakis, G.C. Trematode Infections in Pregnant Ewes Can Predispose to Mastitis during the Subsequent Lactation Period. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 96, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordalis, N.G.; Arsenopoulos, K.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Lianou, D.T.; Papadopoulos, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Field Evidence for Association between Increased Gastrointestinal Nematode Burden and Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 265, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulos, P.D.; Christodoulopoulos, G.; Minas, A.; Karatzia, M.A.; Pourliotis, K.; Kritas, S.K. The Role of Lactate Dehydrogenase, Alkaline Phosphatase and Aspartate Aminotransferase in the Diagnosis of Subclinical Intramammary Infections in Dairy Sheep and Goats. J. Dairy Res. 2010, 77, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumpas, A.T.; Giadinis, N.D.; Petridou, E.J.; Konstantinou, E.; Brozos, C.; Lafi, S.Q.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Karatzias, H. Consequences of Reduced Vitamin A Administration on Mammary Health of Dairy Ewes. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 110, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Malli, E.; Tsilipounidaki, K.; Sarrou, S.; Medvecky, M.; Hrabak, J.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Petinaki, E. First Description in Greece of mphC -Positive Staphylococci Causing Subclinical Mastitis in Ewes. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Cripps, P.J.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Sarrou, S.; Orfanou, D.C.; Politis, A.P.; Gonzalez-Valerio, T.C.; Argyros, S.; et al. Extensive Countrywide Field Investigation of Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep in Greece. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7297–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Riggio, V.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Association of Subclinical Mastitis Prevalence with Sheep Breeds in Greece. J. Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Sarrou, S.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Spyrou, V.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Slime-Producing Staphylococci as Causal Agents of Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 224, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Sarrou, S.; Papagiannitsis, C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Malli, E.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Antimicrobial Agent Susceptibility and Typing of Staphylococcal Isolates from Subclinical Mastitis in Ewes. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Cripps, P.J.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Chouzouris, T.M.; Lianou, D.T.; Gonzalez-Valerio, T.C.; Vallverdu, R.G.; Argyros, S.; et al. Evaluation of Efficacy of a Biofilm-Embedded Bacteria-Based Vaccine against Staphylococcal Mastitis in Sheep—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Field Study. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9328–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanidakis, N.; Brozos, C.N.; Voutzourakis, N.; Stefanakis, A.; Malama, E.; Zoller, D.; Zdragkas, A.; Hickford, J.; Sotiraki, S.; Kiossis, E. Effect of Abiotic and Biotic Factors on Subclinical Mastitis Occurrence in Low-Input Dairy Sheep Production Systems. Small Rumin. Res. 2021, 198, 106341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, E.I.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Giannoulis, T.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Kontou, P.I.; Lianou, D.T.; Mamuris, Z.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Michael, C.K.; et al. MLST-Based Analysis and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus Epidermidis from Cases of Sheep Mastitis in Greece. Biology 2021, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marogna, G.; Rolesu, S.; Lollai, S.; Tola, S.; Leori, G. Clinical Findings in Sheep Farms Affected by Recurrent Bacterial Mastitis. Small Rumin. Res. 2010, 88, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onni, T.; Sanna, G.; Cubeddu, G.P.; Marogna, G.; Lollai, S.; Leori, G.; Tola, S. Identification of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Ovine Milk Samples by PCR–RFLP of 16S rRNA and Gap Genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onni, T.; Sanna, G.; Larsen, J.; Tola, S. Antimicrobial Susceptibilities and Population Structure of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Associated with Ovine Mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, J.; Ceccarelli, D.; Spagnoletti, M.; Lollai, S.; Cappuccinelli, P.; Colombo, M.M. Molecular Characterization of Enterotoxigenic and Borderline Oxacillin Resistant Staphylococcus Strains from Ovine Milk. Food Microbiol. 2012, 32, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbondio, M.; Fois, I.; Longheu, C.; Azara, E.; Tola, S. Biofilm Production, Quorum Sensing System and Analysis of Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Collected from Sheep Milk Samples. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 174, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, B.; Bertelloni, F.; Marzoli, F.; Cerri, D.; Tola, S.; Azara, E.; Longheu, C.M.; Tassi, R.; Schiavo, M.; Cilia, G.; et al. Coagulase Negative Staphylococci from Ovine Milk: Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Susceptibility to Antibiotics, Disinfectants and Biofilm Production. Small Rumin. Res. 2020, 183, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.M.; Penati, M.; Fusar-Poli, S.; Addis, M.F.; Tola, S. Species Identification by MALDI-TOF MS and Gap PCR–RFLP of Non-Aureus Staphylococcus, Mammaliicoccus, and Streptococcus Spp. Associated with Sheep and Goat Mastitis. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azara, E.; Longheu, C.M.; Attene, S.; Sanna, S.; Sale, M.; Addis, M.F.; Tola, S. Comparative Profiling of Agr Locus, Virulence, and Biofilm-Production Genes of Human and Ovine Non-Aureus Staphylococci. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calarescu, G.; Leori, G.; Testa, C.; Marogna, G.; Secchi, L. Is the Doubling of Withdrawal Time a Sufficient Measure? Evaluations of Oxytetracyline Residue Persistence in Sheep Milk. In Proceedings of the 4th SAFO Workshop, Frick, Switzerland, 17–19 March 2005; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Cuccuru, C.; Meloni, M.; Sala, E.; Scaccabarozzi, L.; Locatelli, C.; Moroni, P.; Bronzo, V. Effects of Intramammary Infections on Somatic Cell Score and Milk Yield in Sarda Sheep. N. Z. Vet. J. 2011, 59, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, S.; Ferrini, A.M.; Appicciafuoco, B.; Massaro, M.R.; Sotgiu, G.; Liciardi, M.; Cannas, E.A. Efficacy of a Terpinen-4-Ol Based Dipping for Post-Milking Teat Disinfection in the Prevention of Mastitis in Dairy Sheep. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2019, 31, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, V.; Portolano, B.; Bovenhuis, H.; Bishop, S.C. Genetic Parameters for Somatic Cell Score According to Udder Infection Status in Valle Del Belice Dairy Sheep and Impact of Imperfect Diagnosis of Infection. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2010, 42, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolone, M.; Larrondo, C.; Yáñez, J.M.; Newman, S.; Sardina, M.T.; Portolano, B. Assessment of Genetic Variation for Pathogen-Specific Mastitis Resistance in Valle Del Belice Dairy Sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, S.; Liciardi, M.; Amatiste, S.; Bergagna, S.; Bolzoni, G.; Caligiuri, V.; Cerrone, A.; Farina, G.; Montagna, C.O.; Saletti, M.A.; et al. Survey on Small Ruminant Bacterial Mastitis in Italy, 2013–2014. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 141, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignacca, S.A.; Dore, S.; Spuria, L.; Zanghì, P.; Amato, B.; Duprè, I.; Armas, F.; Biasibetti, E.; Camperio, C.; Lollai, S.A.; et al. Intramammary Infusion of a Live Culture of Lactococcus Lactis in Ewes to Treat Staphylococcal Mastitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1798–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spuria, L.; Biasibetti, E.; Bisanzio, D.; Biasato, I.; De Meneghi, D.; Nebbia, P.; Robino, P.; Bianco, P.; Lamberti, M.; Caruso, C.; et al. Microbial Agents in Macroscopically Healthy Mammary Gland Tissues of Small Ruminants. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipčincová, I.; Bhide, M.; Dudriková, E.; Trávniček, M. Genotypic Characterization of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Sheep Milk in Slovakia. Acta Vet. Brno 2010, 79, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigo, F.; Vasiľ, M.; Elečko, J.; Lapin, M.; Farkašova, Z. Production of Enterotoxins of Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Samples of Sheep Milk. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2014, 8, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigo, F.; Vasiľ, M.; Takáč, L.; Zigová, M.; Elečko, J. Mastitis Pathogens Isolated from Raw Milk Samples on Sheep Farms Situated in Marginal Parts of Slovakia. Folia Vet. 2018, 62, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiľ, M.; Elečko, J.; Farkašová, Z.; Zigo, F. Development of Resistance to Antibiotics in Bacteria Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Milk Samples in the Sheep Breedings on East of Slovakia. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2018, 12, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiľ, M.; Farkašová, Z.; Elečko, J.; Zigo, F. Occurrence of Resistance to Antibiotics Therapy in Coagulase-Positive and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Sheep´s Milk in Holding in Slovakia. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2020, 14, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holko, I.; Tančin, V.; Tvarožková, K.; Supuka, P.; Supuková, A.; Lucia, M. Occurence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Common Udder Pathogens Isolated from Sheep Milk in Slovakia. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2019, 13, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vašíček, J.; Tvarožková, K.; Uhrinčať, M.; Mačuhová, L.; Hleba, L.; Tančin, V. Distribution of Leucocytes and Epithelial Cells in Sheep Milk in Relation to the Somatic Cell Count and Bacterial Occurrence: A Preliminary Study. Slovak J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 52, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Pikhtirova, A.; Bujok, J.; Pecka-Kiełb, E.; Zachwieja, A.; Vasil, M.; Elečko, J.; Zigo, F. Fatty Acid Profile of Ewe’s Milk Infected with Staphylococcus spp. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 21, 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Tvarožková, K.; Tančin, V.; Uhrinčať, M.; Hleba, L.; Mačuhová, L. Mastitis Pathogens and Somatic Cell Count in Ewes Milk. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2020, 14, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvarožková, K.; Vašíček, J.; Uhrinčať, M.; Mačuhová, L.; Hleba, L.; Tančin, V. The Presence of Pathogens in Milk of Ewes in Relation to the Somatic Cell Count and Subpopulations of Leukocytes. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 66, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigo, F. Sheep Mastitis Caused by Staphylococci and Streptococci and Their Influence on Oxidative Status. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2021, 24, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigo, F.; Farkašová, Z.; Farag Mohammed Rehan, I.; Sayed-Ahmed, A. Occurrence of Mastitis in Dairy Herds and the Detection of Virulence Factors in Staphylococci. In Infectious Diseases; Bustos-Martínez, J., José Valdez-Alarcón, J., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023; Volume 17, ISBN 978-1-83769-985-8. [Google Scholar]
- Batavani, R.A.; Mortaz, E.; Falahian, K.; Dawoodi, M.A. Study on Frequency, Etiology and Some Enzymatic Activities of Subclinical Ovine Mastitis in Urmia, Iran. Small Rumin. Res. 2003, 50, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Lotfalian, S.; Karimi, S. Drug Resistance in Isolated Bacteria from Milk of Sheep and Goats with Subclinical Mastitis in Shahrekord District. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 8, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Soleimani, F.; Moatamedi, A.; Shams, N.; Lotfalian, S. Study on Some Characteristics of Staphylococci Isolated from Sheep Subclinical Mastitis Milk in Shahrekord, Iran. Biol. J. Microorg. 2014, 2, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshti, R.; Shaieghi, J.; Eshratkhah, B.; Ghalehkandi, J.G.; Maheri-Sis, N. Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Ewes of the Tabriz Region, Iran. Glob. Vet. 2010, 4, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Arighi Sareh, A.; Hadavi, E.; Abdi, K. Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Ghezel Ewes in Nagadeh District, Iran. J. Vet. Clin. Res. 2012, 3, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Narenji Sani, R.; Mahdavi, A.; Moezifar, M. Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Ewes in Two Seasons in Semnan Province, Iran. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narenji Sani, R.; Hajigolikhani, B.; Ahmadi-Hamedani, M.; Kafshdouzan, K. Diagnostic Evaluation of Milk Lactate Dehydrogenase and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities by Receiver Operating Characteristic Analysis Curve in Early Lactation of Ewes with Subclinical Mastitis. Vet. Res. Forum 2018, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, B.; Ownagh, A.; Mardani, K.; Ardebili, F.F. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Staphylococci Isolated from Sheep with Subclinical Mastitis in West-Azerbaijan Province, Iran. Vet. Res. Forum 2016, 7, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Moawad, A.A.; Osman, S.A. Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Ewes at Fayoum Governorate, Egypt. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2005, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, Y.R. Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Ewes at Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt and Observation on Bacteria Associated with it. Kafrelsheikh Vet. Med. J. 2007, 5, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassiony, T.; El-Prince, E.; Abdel-hameed, K.; Abdel-haleem, A.; Sadek, O. Prevalence and Public Health Hazard of Subclinical Mastitis in Goats and Sheep in Assiut Governorate. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2008, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.-S.; Eissa, M.; Menaze, A. The Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep and Goats. Zagazig Vet. J. 2018, 46, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalhamed, A.M.; Zeedan, G.S.G.; Abou Zeina, H.A.A. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria Causing Mastitis in Small Ruminants and Their Susceptibility to Antibiotics, Honey, Essential Oils, and Plant Extracts. Vet. World 2018, 11, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggag, Y.; Nossair, M.; Habib, H.; Naggar, A.; Abdallah, M.; Farag, H. Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis in Small Ruminants and Role of Staphylococcus Species in Such Infection. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 62, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergün, Y.; Aslantaş, Ö.; Doğruer, G.; Ki̇Reçci̇, E.; Saribay, M.K.; Ateş, C.T.; Ülkü, A.; Demi̇r, C. Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Awassi Dairy Ewes in Southern Turkey. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2009, 33, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergün, Y.; Aslantaş, Ö.; Ki̇Reçci̇, E.; Öztürk, F.; Ceylan, A.; Boyar, Y. Antimicrobial Susceptibility, Presence of Resistance Genes and Biofilm Formation in Coagulase Negative Staphlococci Isolated from Subclinical Sheep Mastitis. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2012, 18, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirecci, E.; Ergun, Y.; Dogruer, G.; Saribay, M.K. Usefulness of the E-test for the Determination of the Susceptibility of Staphylococcus sp. Isolated from Milk of Sheep and Goats with Subclinical Mastitis to Amikacin and Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2009, 53, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ünal, N.; Askar, Ş.; Macun, H.C.; Sakarya, F.; Altun, B.; Yıldırım, M. Panton–Valentine Leukocidin and Some Exotoxins of Staphylococcus Aureus and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Staphylococci Isolated from Milks of Small Ruminants. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, N.; Çinar, O.D. Detection of Stapylococcal Enterotoxin, Methicillin-Resistant and Panton–Valentine Leukocidin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Cows and Ewes with Subclinical Mastitis. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şeker, E.; Özenç, E.; Baki Acar, D.; Yilmaz, M. Prevalence of Methicillin Resistance and Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Genes in Staphylococci Isolated from Pirlak Sheep with Subclinical Mastitis in Turkey. Kocatepe Vet. J. 2019, 12, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, C.; Berger, Y.M.; Thomas, D.L.; Ruegg, P.L. Impact of Intramammary Antimicrobial Dry Treatment and Teat Sanitation on Somatic Cell Count and Intramammary Infection in Dairy Ewes. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 97, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, R.M.; Woodruff, K.L.; Hummel, G.L.; Williams, J.D.; Stewart, W.C.; Cunningham-Hollinger, H.C.; Bisha, B. Post-Weaning Management Strategies and Impacts on Ewe Subclinical Mastitis and Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2021, 5, S80–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, R.M.; Stewart, W.C.; Taylor, J.B.; Bisha, B.; Yeoman, C.J.; Van Emon, M.L.; Murphy, T.W. Relationships among Intramammary Health, Udder and Teat Characteristics, and Productivity of Extensively Managed Ewes. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, R.M.; Woodruff, K.L.; Hummel, G.L.; Williams, J.D.; Austin, K.J.; Stewart, W.C.; Cunningham-Hollinger, H.C.; Bisha, B. Effects of Management Strategies during Early Lactation and Weaning on Etiological Agents of Ovine Subclinical Mastitis and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Milk-Derived Bacterial Isolates. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrewahid, T.; Abera, B.; Menghistu, H. Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Small Ruminants of Tigray Regional State, North Ethiopia. Vet. World 2012, 5, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, S.; Abraha, A. Prevalence of Bacteria Associated with Subclinical Mastitis in Haramaya University Dairy Cattle, Goat and Sheep Farms. East Afr. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2017, 1, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hayle, W.A.; Ahmed, R.; Uddin, M.E. Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis among Small Ruminants and Isolation of Some Etiological Bacterial Pathogens in Jimma Town, Ethiopia. Eur. J. Med. Health Sci. 2020, 2, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.; Chaffer, M.; Shamay, A.; Shapiro, F.; Merin, U.; Ezra, E.; Saran, A.; Silanikove, N. Changes in Milk Composition as Affected by Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwimmer, A.; Kenigswald, G.; Van Straten, M.; Lavi, Y.; Merin, U.; Weisblit, L.; Leitner, G. Dry-off Treatment of Assaf Sheep: Efficacy as a Management Tool for Improving Milk Quantity and Quality. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 74, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.; Merin, U.; Krifucks, O.; Blum, S.; Rivas, A.L.; Silanikove, N. Effects of Intra-Mammary Bacterial Infection with Coagulase Negative Staphylococci and Stage of Lactation on Shedding of Epithelial Cells and Infiltration of Leukocytes into Milk: Comparison among Cows, Goats and Sheep. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 147, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Majali, A.M.; Jawabreh, S. Period Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Awassi Sheep in Southern Jordan. Small Rumin. Res. 2003, 47, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekish, M.O.; Alshehabat, M.A.; Abutarbush, S.M. The Prevalence and Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Awassi Sheep; Emphasis on the Relationship Between the Isolated Organisms and the Somatic Cell Count. Eur. J. Vet. Med. 2014, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hawari, A.D.; Obeidat, M.; Awaisheh, S.S.; Al-Daghistani, H.I.; Al-Abbadi, A.A.; Omar, S.S.; Qrunfleh, I.M.; Al-Dmoor, H.M.; El-Qudah, J. Prevalence of Mastitis Pathogens and their Resistance Against Antimicrobial Agents in Awassi Sheep in Al-Balqa Province of Jordan. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2014, 9, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, B.A.A.; Kheira, B.; Bettache, G.; Habib, A.; Mebrouk, K. Evaluation of Microbiological and Sanitary Quality of Ewe’s Raw Milk in Western of Algeria and Detection of Antibiotic Residue by Delvotest. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2013, 7, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Smaali, S. Etude de l’Έtiologie Βactérienne des Mammites Subcliniques des Ovins à l’Est de l’Algérie. Afr. Sci. Rev. Int. Sci. Technol. 2014, 10, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, P.; Miny, M.; Fuchs, K.; Baumgartner, W. The Potential of Measuring Serum Amyloid A in Individual Ewe Milk and in Farm Bulk Milk for Monitoring Udder Health on Sheep Dairy Farms. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourakas, M.; Wurm, A.; Hess, C.; Urbantke, V.; Wittek, T.; Baumgartner, M. Untersuchungen zu Speziesverteilung, Pathogenität und Resistenzprofil von Staphylokokken aus aseptisch entnommenen Schaf- und Ziegenmilch-proben. Wien Tierärztl. Monatsschr. 2021, 108, 214–225. [Google Scholar]
- Stoimenov, A.; Popova, T.; Stoimenov, G.; Hristov, K. Microbiological Status of the Mammary Gland in Lactating Sheeps. Tradit. Mod. Vet. Med. 2022, 7, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Stoimenov, A.; Popova, T.; Stoimenov, G.; Hristov, K. Antibiotic Sensitivity of the Causative Microorganisms of Subclinical Mastitis in Lactating Sheep. Zhivotnov. Nauki 2022, 59, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Vyletělová, M.; Hanuš, O.; Karpíšková, R.; Šťástková, Z. Occurrence and Antimicrobial Sensitivity in Staphylococci Isolated from Goat, Sheep and Cow’s Milk. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2014, 59, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyletělová, M.; Vlková, H.; Manga, I. Occurrence and Characteristics of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Raw Milk Manufacturing. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, X.; Lagriffoul, G.; Concordet, D.; Barillet, F.; Bergonier, D. Physiological and Pathological Thresholds of Somatic Cell Counts in Ewe Milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2006, 62, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, R.; Bergonier, D.; Dion, S.; Hygonenq, M.C.; Aurel, M.R.; Robert-Granié, C.; Foucras, G. Response to Somatic Cell Count-Based Selection for Mastitis Resistance in a Divergent Selection Experiment in Sheep. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1203–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, K.; Burow, E.; Knappstein, K. EC and CMT Detect Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Sheep but Less Sensitive than in Dairy Cows. Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2008, 58, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Tonamo, A.; Komlósi, I.; Varga, L.; Kačániová, M.; Peles, F. Identification of Ovine-Associated Staphylococci by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Acta Aliment. 2021, 50, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, R.A.P.; Jiménez, I.B.; Ramírez, J.M.T. Frecuencia de Mastitis Subclínicas en Ovejas en Ordeña y Sensibilidad Antibiótica de los Agentes Etiológicos Responsables. In Proceedings of the 5th Congreso Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología Agropecuaria, Roque, Celaya, Mexico, 21–23 March 2018; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Danmallam, F.A.; Pimenov, N.V.; Ngulukun, S.S.; Mwankon, S.E. Prevalence and Bacterial Etiology of Mastitis in Small Ruminants in Toro Local Government Area, Bauchi State of Nigeria. Russ. J. Agric. Soc.-Econ. Sci. 2018, 79, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwan, G.; Abusafieh, D.; Aref, R.; Omar, J.A. Prevalence Of Microorganisms Associated with Intramammary Infection in Cows and Small Ruminants in the North of Palestine. IUG J. Nat. Stud. 2005, 13, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Świderek, W.P.; Charon, K.M.; Winnicka, A.; Gruszczyńska, J.; Pierzchała, M. Physiological Threshold of Somatic Cell Count in Milk of Polish Heath Sheep and Polish Lowland Sheep. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2016, 16, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mot, D.; Mot, T. Clinical, Microbiological and Hematological Findings in Ovine Subclinical Mastitis. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 49, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, N.C.; Laranjo, M.; Costa, M.M.; Queiroga, M.C. Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus Associated with Small Ruminant Mastitis: Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroga, M.C. Prevalence and Aetiology of Sheep Mastitis in Alentejo Region of Portugal. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 153, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroga, M.C.; Duarte, E.L.; Laranjo, M. Sheep Mastitis Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm Effects on Cell Adhesion and Inflammatory Changes. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 168, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakanjac, S.; Todorovic, I. Subclinical mastitis in sheep: Causes and their sensitivity to antibiotics. Vet. Glas. 2010, 64, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, C.; Tardáguila, J.A.; De La Fuente, L.F.; San Primitivo, F. Effects of Selective and Complete Dry Therapy on Prevalence of Intramammary Infection and on Milk Yield in the Subsequent Lactation in Dairy Ewes. J. Dairy Res. 2004, 71, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovai, M.; Caja, G.; Salama, A.A.K.; Jubert, A.; Lázaro, B.; Lázaro, M.; Leitner, G. Identifying the Major Bacteria Causing Intramammary Infections in Individual Milk Samples of Sheep and Goats Using Traditional Bacteria Culturing and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5393–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Crommenacker, L.W.J.H. Mastitis in Sheep. Master’s Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Crommenacker-Konings, L.W.J.H.; Van Dam, P.; Everts, R.; Shittu, A.; Nielen, M.; Lam, T.J.G.M.; Koop, G. Dynamics of Intramammary Infections in Suckler Ewes during Early Lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 5979–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, H.; Donachie, W.; Macaldowie, C.; Keefe, G. Bacteriology and Somatic Cell Counts in Milk Samples from Ewes on a Scottish Farm. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 68, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zadoks, R.N.; Tassi, R.; Martin, E.; Holopainen, J.; McCallum, S.; Gibbons, J.; Ballingall, K.T. Comparison of Bacteriological Culture and PCR for Detection of Bacteria in Ovine Milk—Sheep Are Not Small Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6326–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Garch, F.; Youala, M.; Simjee, S.; Moyaert, H.; Klee, R.; Truszkowska, B.; Rose, M.; Hocquet, D.; Valot, B.; Morrissey, I.; et al. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Nine Udder Pathogens Recovered from Bovine Clinical Mastitis Milk in Europe 2015–2016: VetPath Results. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T.; Andam, C.P. Extensive Horizontal Gene Transfer within and between Species of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, P.D.C.; Ferreira, L.M.; Nader Filho, A.; Zafalon, L.F.; Vicente, H.I.G.; Souza, V.D. Comparison of Methods for the Detection of Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deka, N. Comparison of Tissue Culture Plate Method, Tube Method and Congo Red Agar Method for the Detection of Biofilm Formation by Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus Isolated from Non-Clinical Isolates. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 810–815. [Google Scholar]
- Banaszkiewicz, S.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Schubert, J.; Tabiś, A.; Król, J.; Stefaniak, T.; Węsierska, E.; Bania, J. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—Stability, Expression, and Genomic Context. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piette, A.; Verschraegen, G. Role of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Human Disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.F.S.; Do Prado Paim, T.; De Abreu Cardoso, C.; Stéfano Lima Dallago, B.; De Melo, C.B.; Louvandini, H.; McManus, C. Mastitis Detection in Sheep by Infrared Thermography. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country | Number of Studies |
|---|---|
| Brazil | 33 |
| Greece | 18 |
| Italy | 16 |
| Slovakia | 12 |
| Iran | 8 |
| Egypt, Turkey | 6 |
| USA | 4 |
| Ethiopia, Israel, Jordan | 3 |
| Algeria, Austria, Bulgaria, France, Portugal, Spain, The Netherlands, UK | 2 |
| Czech Republic, Czech Republic and Slovakia, Germany, Hungary, Mexico, Nigeria, Palestine, Poland, Portugal and Brazil, Romania, Serbia | 1 |
| Breed | Number of Studies |
|---|---|
| Assaf | 5 |
| Awassi | 8 |
| Chios | 6 |
| Friesian | 6 |
| Lacaune | 26 |
| Santa Ines | 21 |
| Sarda | 5 |
| Texel | 6 |
| Tsigai | 9 |
| Valachian | 10 |
| Prevalent Pathogen | Number of Studies |
|---|---|
| CoNS | 95 |
| S. aureus | 11 |
| E. coli | 3 |
| Bacillus spp. | 2 |
| CoPS | 1 |
| Enterococci | 1 |
| Mycoplasma spp. | 1 |
| NaS | 1 |
| S. hyicus | 1 |
| Staphylococci | 1 |
| Mixed infections | 1 |
| Identified CoNS Species | Number of Total Isolations | Number of Respective Studies | % of Total Identified CoNS |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. arlettae | 45 | 5 | 0.86 |
| S. auricularis | 199 | 15 | 3.82 |
| S. capitis | 50 | 16 | 0.96 |
| S. caprae | 249 | 25 | 4.78 |
| S. carnosus | 5 | 2 | 0.10 |
| S. caseolyticus | 3 | 1 | 0.06 |
| S. chromogenes | 782 | 44 | 15.00 |
| S. cohnii | 29 | 12 | 0.56 |
| S. condimenti | 1 | 1 | 0.02 |
| S. devriesei | 8 | 4 | 0.15 |
| S. epidermidis | 2046 | 61 | 39.25 |
| S. equorum | 145 | 14 | 2.78 |
| S. haemolyticus | 167 | 26 | 3.20 |
| S. gallinarum | 6 | 2 | 0.12 |
| S. hominis | 21 | 5 | 0.40 |
| S. jettensis | 1 | 1 | 0.02 |
| S. kloosii | 11 | 3 | 0.21 |
| S. lentus | 79 | 16 | 1.52 |
| S. lugdunensis | 19 | 5 | 0.36 |
| S. microti | 8 | 2 | 0.15 |
| S. muscae | 5 | 4 | 0.10 |
| S. pasteuri | 5 | 2 | 0.10 |
| S. petrasii | 3 | 1 | 0.06 |
| S. piscifermentans | 11 | 1 | 0.21 |
| S. rostri | 1 | 1 | 0.02 |
| S. saccharolyticus | 2 | 2 | 0.04 |
| S. saprophyticus | 33 | 12 | 0.63 |
| S. sciuri | 74 | 12 | 1.42 |
| S. simulans | 497 | 42 | 9.53 |
| S. vitulinus | 7 | 5 | 0.13 |
| S. warneri | 121 | 26 | 2.32 |
| S. xylosus | 361 | 40 | 6.92 |
| S. hyicus 1 | 64 | 5 | 1.23 |
| S. intermedius 1 | 21 | 4 | 0.40 |
| S. schleiferi 1 | 134 | 9 | 2.57 |
| Total | 5213 | 77 | 100% |
| Class | Antibiotic 1 | Resistant (R) Isolates/Tested CoNS per Study | Total R/ Total CoNS | Resistance Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 0/7, 1/45, 6/78, 0/9, 0/7, 2/131, 0/1, 2/56, 0/24, 9/106, 5/75, 0/70, 0/11, 1/11, 1/112, 1/72, 0/4, 3/73, 0/20, 2/17, 0/8 | 33/937 | 3.52% |
| Streptomycin | 0/7, 17/56, 54/106, 4/11, 2/22, 2/24, 2/108, 0/4, 4/137 | 85/475 | 17.89% | |
| Kanamycin | 0/7, 2/131, 3/56, 6/24, 2/73, 4/8 | 17/299 | 5.69% | |
| Neomycin | 15/45, 0/7, 4/56, 0/11, 6/11, 1/24, 7/108, 36/99, 0/4, 8/137, 0/20 | 77/522 | 14.75% | |
| Ansamycins | Rifampicin | 0/1, 0/46, 0/24, 12/106, 1/112, 1/73 | 14/362 | 3.87% |
| Β-lactams | Amoxicillin | 40/45, 0/7, 63/106, 10/24, 49/72, 1/108, 0/137, 0/17, 5/8 | 168/524 | 32.06% |
| Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid | 0/20, 2/78, 0/1, 1/39, 0/70, 0/11, 11/11, 15/99 | 29/329 | 8.81% | |
| Ampicillin | 1/7, 33/78, 56/131, 13/56, 3/24, 20/39, 30/70, 2/11, 11/11, 1/11, 10/30, 13/24, 31/72, 4/108, 21/115, 29/73, 0/4, 6/137, 0/20, 11/33 | 295/1054 | 27.99% | |
| Cephalothin | 0/7, 2/56, 0/70, 0/11, 0/30, 0/73 | 2/247 | 0.81% | |
| Cefoxitin | 0/7, 0/1, 0/56, 2/72, 0/108, 3/115, 0/73, 1/137, 1/33 | 7/602 | 1.16% | |
| Oxacillin | 0/7, 2/131, 0/1, 7/56, 0/24, 19/106, 16/75, 0/70, 1/11, 1/30, 7/72, 3/108, 0/4, 1/137, 0/17, 1/6 | 58/855 | 6.78% | |
| Penicillin | 1/7, 40/45, 8/73, 9/9, 44/78, 56/131, 1/1, 14/46, 20/56, 5/24, 22/39, 23/75, 30/70, 3/11, 11/11, 8/11, 9/30, 23/24, 19/112, 29/72, 7/108, 29/115, 0/4, 7/137, 11/33, 7/8 | 436/1330 | 32.78% | |
| Fluoro- quinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 0/7, 0/1, 8/106, 0/39, 1/75, 0/24, 1/112, 0/4, 0/17, 0/8 | 10/393 | 2.54% |
| Enrofloxacin | 9/9, 4/78, 0/7, 1/46, 6/106, 0/70, 0/11, 3/99, 0/4, 0/73, 0/17, 0/8 | 23/528 | 4.36% | |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin | 0/1, 0/46, 7/24, 0/112, 2/72 | 9/255 | 3.53% |
| Lincosamides | Clindamycin | 0/1, 0/39, 6/75, 14/115, 6/73, 1/33, 0/14, 0/4 | 27/354 | 7.63% |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | 8/78, 1/131, 0/1, 3/46, 5/56, 17/24, 46/106, 0/39, 3/75, 4/70, 2/11, 5/11, 2/22, 1/30, 3/112, 9/108, 10/115, 7/137, 2/33 | 128/1205 | 11.28% |
| Phenicols | Chloramphenicol | 0/7, 0/1, 0/24, 0/75, 0/24, 2/73, 0/17, 0/6 | 2/227 | 0.88% |
| Pholate pathway inhibitor | Sulphamethoxazole–Trimethoprim | 2/78, 0/46, 6/56, 1/115, 0/99, 0/4, 0/73, 0/33, 2/8 | 11/512 | 2.15% |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 1/7, 0/7, 33/45, 9/9, 19/78, 13/131, 0/1, 4/46, 9/56, 48/106, 1/39, 2/75, 8/70, 3/11, 1/11, 17/30, 3/24, 12/112, 12/72, 1/108, 24/115, 27/99, 0/4, 8/73, 0/137, 16/33, 0/4 | 271/1503 | 18.03% |
| Antibiotic 1 | Resistant Isolates/Tested CoNS per Continent (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | South America | Asia | Total Rate | Chi-Square | |
| Ampicillin | 141/632 (22.31%) | 76/232 (32.76%) | 78/190 (41.05%) | 27.99% | p < 0.00001 |
| Cefoxitin | 5/467 (1.07%) | 2/135 (1.48%) | ne | 1.16% | p = 0.694939. |
| Gentamicin | 7/263 (2.67%) | 18/463 (3.89%) | 7/166 (4.21%) | 3.52% | p = 0.617974 |
| Enrofloxacin | 12/206 (5.83%) | 6/128 (4.69%) | 5/194 (2.58%) | 4.36% | p = 0.276063 |
| Erythromycin | 51/560 (9.10%) | 60/429 (13.99%) | 15/216 (6.94%) | 11.28% | p = 0.008058 |
| Oxacillin | 7/424 (1.65%) | 51/361 (14.13%) | ne | 6.78% | p < 0.00001 |
| Penicillin | 151/650 (23.23%) | 125/399 (31.33%) | 120/236 (50.85%) | 32.78% | p < 0.00001 |
| Tetracycline | 98/717 (13.69%) | 104/505 (20.59%) | 36/236 (15.25%) | 18.03% | p = 0.004888 |
| Phenotypic Test for Biofilm Production | Detection of Biofilm-Associated Genes in CoNS | Detection of Toxin-Associated Genes in CoNS | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/39 (CRA) | 13/39 (icaD) | --- | [39] |
| 1/36 (CRA) | 2/36 (icaD) | --- | [27] |
| 33/53 (PA) 2 | 10/112 (icaABCD), 16/112 (bap), 3/112 (bhp) | 56/112 (sea), 19/112 (seb), 15/112 (sec), 1/112 (tsst) | [26] |
| --- | 4/127 (icaA), 37/127 (icaC), 53/127 (icaD), 3/127 (bap), 0/57 (bhp) | 35/127 (sec), 0/127 (sea, seb, sed, tsst) | [25] |
| --- | --- | 6/13 4 (sea, seb), 0/13 (sec-see, tsst) | [21] |
| 194/620 (CRA and PA) | 43/116 (icaA), 28/116 (icaC), 30/116 (icaD), 40/116 (bap), 58/116 (eno), 20/116 (clfa) | --- | [55] |
| 149/222 (CRA and PA) | --- | --- | [57] |
| --- | --- | 0/24 (sea-see, seg-sel, seq, tsst) | [63] |
| 2/199 (CRA) | 6/199 (icaA), 5/199 (icaD), 113/199 (bhp), 11/199 (aap), 199/199 (embp) | 0/199 (sea-see, tsst) | [64] |
| 0/73 (CRA) | 15/73 (icaA), 20/73 (icaD), 0/73 (bap), 49/73 (embp), 45/73 (eno, fbe), 6/73 (aap) | --- | [65] |
| 41/125 (PA) | 3/125 (icaA), 1/125 (icaD), 37/125 (bhp), 22/125 (aap), 63/125 (embp) | 0/125 (sea-see, tsst) | [67] |
| 8/109 (CRA), 26/327 (PA) | --- | --- | [140] |
| 74/102 3 (PA) | 1/24 (bap), 2/24 (icaA), 15/24 (icaD) | --- | [138] |
| --- | --- | 1/102 (sea, sec), 2/102 (seb, sed), 0/102 (see) | [77] |
| 8/44 (CRA) | --- | --- | [87] |
| --- | --- | 13/40 (sea-see, seg-sej) 1, 0/40 (eta, etb, tsst) 2/40 (plv) | [106] |
| 28/70 (CRA) | 42/70 (icaA and icaD) | --- | [103] |
| --- | --- | 4/27 (plv) | [107] |
| Total 5 | |||
| CRA:48/570 (8.4%) PA:174/607 (28.7%) | aap: 39/397 (9.8%), bap: 60/452 (13.3%), bhp: 153/493 (31%), embp: 311/397 (78.3%), icaA: 115/734 (15.7%), icaD: 181/809 (22.4%) | sea-see, seg-sel, seq 6: 129/742 (17.4%) tsst: 1/640 (0.002%) | |
| Microbiological Examination Procedure | Number of Respective Studies |
|---|---|
| Conventional phenotypic tests for identification 1 | 116 |
Inoculation in both non-selective and selective media
| 71 47 23 25 |
| Inoculation only in non-selective media 2 | 66 |
Commercial biochemical identification kit (total)
| 44 25 5 9 13 |
| Molecular assays | 37 |
| MALDI-TOF MS | 14 |
| VITEK II | 10 |
| Susceptibility estimated through disc diffusion | 39 |
| Susceptibility estimated through MIC 4 | 16 |
| Country/Region | Breed | Total Milk Samples Tested | Total Number of Isolated CoNS | Prevalent Isolated Pathogen | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algeria/Oran, Mascara, Relizane | Ouled-Djellal | 105 | 15 | Enterococci | [121] |
| Algeria/eastern | Ouled-Djellal | 214 | 34 | CoNS | [122] |
| Austria | na | 267 | 75 | CoNS | [123] |
| Austria | na | 908 | 130 | CoNS | [124] |
| Brazil/Pernambuco | Santa Ines | 244 | 80.2% * | CoNS | [9] |
| Brazil | Santa Ines | na | 79.2% * | CoNS | [10] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | Santa Ines | 48 | 23 | CoNS | [11] |
| Brazil/Bauru | Santa Ines | 309 | 85 | CoNS | [12] |
| Brazil/Para | Santa Ines | 352 | 7 | CoNS | [13] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | Santa Ines | 125 | 18 | CoNS | [14] |
| Brazil/Santa Catarina | na | 164 | 25 | NaS | [38] |
| Brazil/northeast | Santa Ines | 340 | 56 | CoNS | [15] |
| Brazil/Montes Claros | Santa Ines | 286 | 64 | CoNS | [16] |
| Brazil/Pernambuco, Bahia | na | na | 106 | na | [39] |
| Brazil/Pernambuco | na | na | 39 | CPS | [40] |
| Brazil/Capao do Leao | Corriedale, Texel | 176 | 15 | CoNS | [34] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | Santa Ines | 448 | 75 | CoNS | [17] |
| Brazil/Chapeco SC | Lacaune-Ile de France, Lacaune-Texel | na | 11 | CoNS | [27] |
| Brazil/Sergipe State | Santa Ines | 330 | 85 | CoNS | [18] |
| Brazil/Sao Carlos | variable | 911 | 92 | CoNS | [35] |
| Brazil/Sao Carlos | Santa Ines, Morada Nova | 393 | 39 | CoNS | [22] |
| Brazil/Sao Carlos | Santa Ines | 1081 | 122 | CoNS | [19] |
| Brazil/Sao Carlos | variable | 1457 | 118 | CoNS | [36] |
| Brazil/Rio Grande do Sul | Lacaune | 315 | 55 | CoNS | [28] |
| Brazil/Sao Carlos | Santa Ines, Morada Nova | 584 | 57 | CoNS | [23] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | Santa Ines, Morada Nova | 907 | 134 | CoNS | [24] |
| Brazil/Rio Grande do Sul | Lacaune | 71 | 39 | CoNS | [29] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | Santa Ines, Bergamacia | 484 | 53 | na | [26] |
| Brazil/Santa Catarina | Lacaune | 179 | 22 | CoNS | [30] |
| Brazil/Santa Catarina | Lacaune | 492 | 68 | CoNS | [31] |
| Brazil/northeast | na | na | 72 | na | [41] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | variable | 1457 | 123 | CoNS | [37] |
| Brazil/Sao Paolo | Santa Ines, Morada Nova | na | 57 | na | [25] |
| Brazil/Parana State | Santa Ines | 256 | 36 | CoNS | [20] |
| Brazil/Chapeco SC | Lacaune | 30 | 4 | S. hyicus | [32] |
| Brazil | Santa Ines | 532 | 68 | CoNS | [21] |
| Brazil/Minas Gerais | Lacaune | 109 | 41 | CoNS | [33] |
| Bulgaria | Lacaune | 30 | 17 | CoNS | [125] |
| Bulgaria | variable | 120 | 8 | CoNS | [126] |
| Czech Republic | Tsigai | 60 | 1 | S. aureus | [127] |
| Czech Republic/Slovakia | Tsigai | 89 | 3 | S. aureus | [128] |
| Egypt/Fayoum Governorate | Balady | 196 | 38 | CoNS | [96] |
| Egypt/Kafr El Seikh Governorate | Native breeds | 245 | 66 | CoNS | [97] |
| Egypt/Assiut Governorate | na | 198 | 9 | CoNS | [98] |
| Egypt/El-Fayoum, Beni-Suef, Giza | na | 189 | 8 | S. aureus | [100] |
| Egypt/Sharkia Governorate | na | 216 | 9 | Mixed infections | [99] |
| Egypt | na | 455 | 18 | S. aureus | [101] |
| Ethiopia/Kafta Humera | Begayd, Abergelle | 135 | 11 | CoNS | [112] |
| Ethiopia/Haramaya | Native breeds | 24 | 2 | Staphylococci | [113] |
| Ethiopia/Jimma | Native breeds | 372 | 19 | S. epidermidis | [114] |
| France/southwest | na | 3758 | na | CoNS | [129] |
| France/Roquefort | Lacaune | 1122 | 325 | CoNS | [130] |
| Germany/middle, northern | East Friesian, Lacaune, mixbreeds | 328 | 24 | CoNS | [131] |
| Greece | Karagouniko | 480 | 2 | CoNS | [42] |
| Greece | Karagouniko | 924 | 11 | CoNS | [43] |
| Greece | Chios | 916 | 73 | CoNS | [44] |
| Greece | na | 206 | 41 | CoNS | [50] |
| Greece | Mytilene | 461 | 91 | CoNS | [51] |
| Greece/Giannitsa | Chios | 94 | 11 | CoNS | [45] |
| Greece/central Greece | Lacaune cross | 186 | 13 | CoNS | [47] |
| Greece/central Greece | Lacaune | na | 7 | CoNS | [48] |
| Greece/throughout country | na | na | 90 | CoNS | [52] |
| Greece/throughout country | variable | 2198 | 454 | CoNS | [53,54,55,56] |
| Greece/Thessaly | variable | 3637 | 272 | CoNS | [57] |
| Greece/southern | na | 240 | 44 | CoNS | [49] |
| Greece/Crete | Sfakia | 9624 | 652 | CoNS | [58] |
| Greece/throughout country | variable | na | 33 | na | [59] |
| Greece/Central Macedonia | Chios | na | 60 | CoNS | [46] |
| Hungary/eastern | na | 62 | 4 | S. aureus | [132] |
| Iran/Urmia Province | na | 209 | 44 | CoNS | [88] |
| Iran/Shahrekord Region | Native breeds | 400 | 7 | Mycoplasma spp. | [89] |
| Iran/Tabriz | na | 260 | 18 | CoNS | [91] |
| Iran/Nagadeh | Ghezel | 146 | 5 | E. coli | [92] |
| Iran/Shahrekord Region | Native breeds | 600 | 22 | S. aureus | [90] |
| Iran/Semnan Region | na | 1192 | 87 | CoNS | [93] |
| Iran/West Azerbaijan Province | Makui, Ghezel, crossbreds | 900 | 24 | na | [95] |
| Iran/Semnan Province | Sangsari | 196 | 50 | CoNS | [94] |
| Israel | Israeli-Assaf | na | 36 | na | [115] |
| Israel | Israeli-Assaf | 318 | 134 | CoNS | [116] |
| Israel | Assaf | 61 | 29 | na | [117] |
| Italy/Sardinia | na | 42 | 10 | CoNS | [68] |
| Italy/Sardinia | Sarda | 2198 | 61 | CoNS | [60] |
| Italy/Sicily | Valle del Belice | 8843 | 2316 | CoNS | [71] |
| Italy/Sardinia | Sarda | 2201 | 226 | na | [61,62] |
| Italy/Sardinia | Sarda | 2828 | 820 | CoNS | [69] |
| Italy/Sardinia | Sarda | na | 24 | CoNS | [63] |
| Italy/Sardinia, Lazio, Sicily, Tuscany | na | 23,040 | 4162 | CoNS | [73] |
| Italy | Valle del Belice | 20,519 | 7951 | CoNS | [72] |
| Italy/Sardinia, Sicily | Sarda, Valle del Belice, Comisana | 123 | 75 | CoNS | [74] |
| Italy/Piedmont | Variable | 41 | 32 | CoNS | [75] |
| Italy/Sardinia | Sarda | 1498 | 134 | CoNS | [70] |
| Italy/Sardinia | na | na | 199 | na | [64] |
| Italy/Tuscany, Lazio | na | 120 | 73 | na | [65] |
| Italy/Sardinia | na | na | 190 | na | [66] |
| Italy/Sardinia | na | na | 124 | na | [67] |
| Jordan/Southern | Awassi | 1147 | 10 | S. aureus | [118] |
| Jordan/Al Balqa | Awassi | 220 | 11 | S. aureus | [120] |
| Jordan/Northern | Awassi | 279 | 38 | CoNS | [119] |
| Mexico/Pajacuaran | Rambouillet, Criolla, Friesian | 150 | 11 | CoNS | [133] |
| Nigeria/Bauchi State | na | 108 | 2 | E. coli, S. aureus | [134] |
| Palestine | Awassi | 40 | 12 | CoNS | [135] |
| Poland/Zelazna | Native breeds | 634 | 108 | Staphylococci | [136] |
| Portugal/Evora, Alentejo | Variable | 414 | 249 | CoNS | [139] |
| Portugal/Alentejo | na | na | 109 | na | [140] |
| Portugal-Brazil | na | 138 | 20 | S. aureus | [138] |
| Romania/western | Merinos of Transylvania, Turcana | 30 | 1 | na | [137] |
| Serbia | na | 13,218 | 25 | E. coli | [141] |
| Slovakia/eastern | Tsigai, Valachian, Tsigai-Merino | 540 | 214 | CoNS | [76] |
| Slovakia | Valaska | 820 | 31 | CoNS | [77] |
| Slovakia/eastern | Improved Valaska | 3466 | 288 | na | [79] |
| Slovakia/Gelnica, Trebisov | Improved Valaska, Tsigai, Lacaune | 494 | 76 | CoNS | [78] |
| Slovakia | Variable | 310 | 99 | CoNS | [81] |
| Slovakia | Tsigai | 20 | 8 | CoNS | [82] |
| Slovakia/northern | Valaska | 40 | 9 | CoNS | [83] |
| Slovakia | Improved Valaska, mixbreeds | 3466 | 158 | S. aureus | [80] |
| Slovakia | Tsigai, Lacaune, Improved Valachian | 407 | 104 | CoNS | [84] |
| Slovakia | Lacaune | 98 | 31 | CoNS | [85] |
| Slovakia/eastern and northern | Lacaune, improved Valachian, crossbreeds | 981 | na | CoNS | [86] |
| Slovakia/eastern | Improved Valachian, Tsigai, Lacaune | 940 | 44 | CoNS | [87] |
| Spain | Churra | 2022 | 361 | CoNS | [142] |
| Spain/Barcelona | Manchega, Lacaune | 216 | na | CoNS | [143] |
| The Netherlands | Texel | 388 | 131 | CoNS | [144] |
| The Netherlands | Texel | 920 | 251 | CoNS | [145] |
| Turkey/Hatay | Awassi | 1458 | 75 | CoNS | [102] |
| Turkey/Hatay | Awassi | na | 50 | na | [104] |
| Turkey/Kirikalle | na | 1604 | 41 | CoNS | [105] |
| Turkey/Kirikalle | na | na | 40 | na | [106] |
| Turkey/Hatay | Awassi | na | 70 | na | [103] |
| Turkey/Afyonkarahisar | Pirlak | 464 | 31 | na | [107] |
| UK/Midlothian | Blackface cross Border Leicester | 492 | 33 | CoNS | [146] |
| UK/Penicuik | Scottish Blackface cross Leicester | 219 | 21 | CoNS | [147] |
| USA/Wisconsin | Variable 1 | 214 | 73 | CoNS | [108] |
| USA/Wyoming | Rambouillet | 22 | 4 | Bacillus spp. | [109] |
| USA/Montana, Idaho | Variable | 243 | 25 | Bacillus spp. | [110] |
| USA/Wyoming | na | 174 | na | CoNS | [111] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lysitsas, M.; Spyrou, V.; Billinis, C.; Valiakos, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci as an Etiologic Agent of Ovine Mastitis, with a Focus on Subclinical Forms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121661
Lysitsas M, Spyrou V, Billinis C, Valiakos G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci as an Etiologic Agent of Ovine Mastitis, with a Focus on Subclinical Forms. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(12):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLysitsas, Marios, Vassiliki Spyrou, Charalambos Billinis, and George Valiakos. 2023. "Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci as an Etiologic Agent of Ovine Mastitis, with a Focus on Subclinical Forms" Antibiotics 12, no. 12: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121661
APA StyleLysitsas, M., Spyrou, V., Billinis, C., & Valiakos, G. (2023). Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci as an Etiologic Agent of Ovine Mastitis, with a Focus on Subclinical Forms. Antibiotics, 12(12), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121661









