Dissemination of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis Harboring Plasmids Encoding blaCTX-M-55 or blaCTX-M-14 Gene in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Information and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.2. Molecular Characteristics of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Isolates
2.3. Dissemination Characteristics of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Isolates
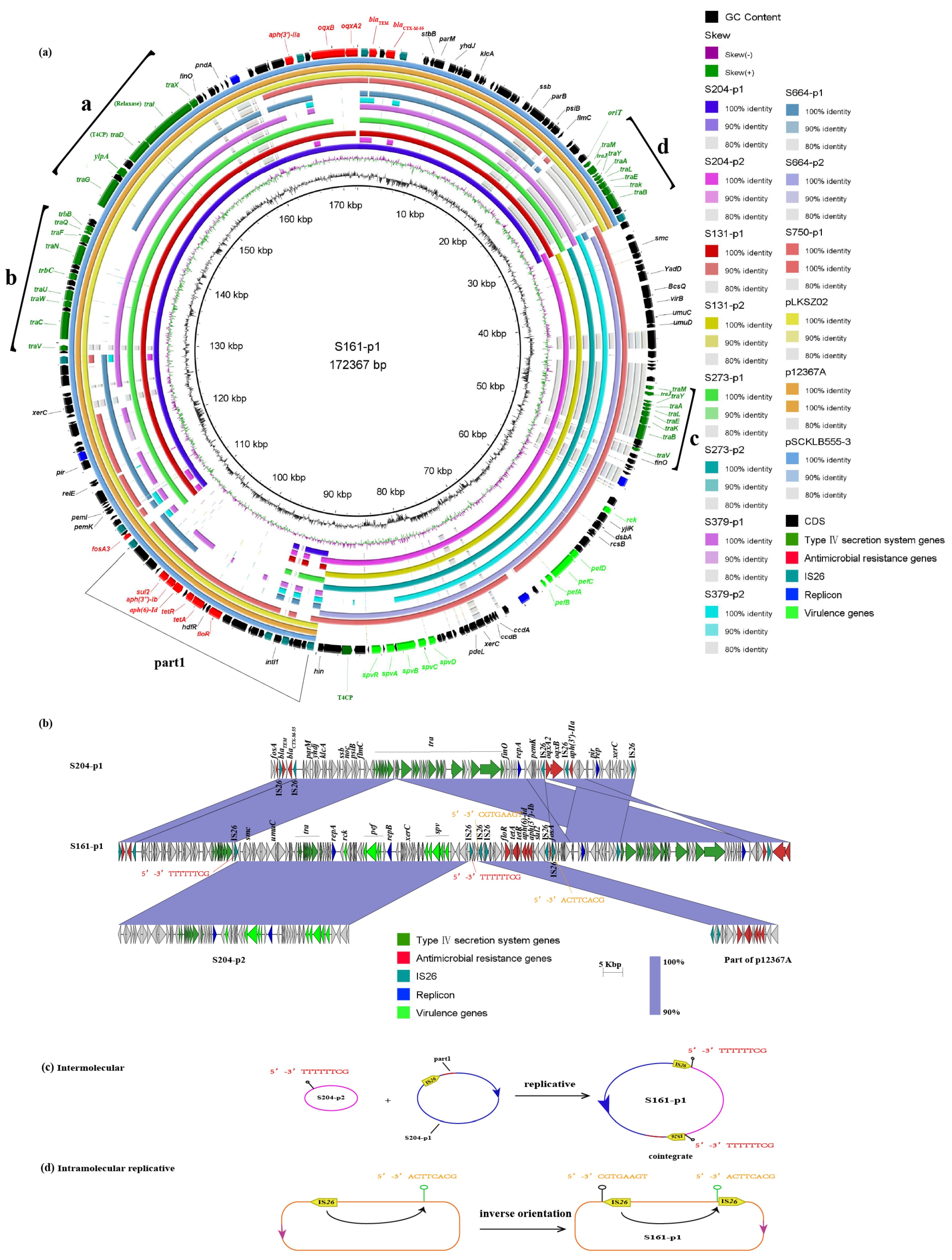
2.3.1. Analysis of Plasmid Structure Harboring blaCTX-M-55
2.3.2. Analysis of Plasmid Structure Harboring blaCTX-M-14
2.4. Plasmid Fusion Event of Two Plasmids
2.5. Plasmid Type Classification in This Study
2.6. Results of Plasmid Conjugation
2.7. Fitness Cost Analysis of Different Plasmids under Different Strain Backgrounds
2.8. Results of Plasmid Stability
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Isolates and Clinical Information
4.2. Bacterial Isolate Identification and Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
4.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing of CRO-RSE Strains
4.4. Genetic Structure Surrounding blaCTX-M-type Gene
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.6. Plasmid Transfer Assays
4.7. Bacterial Growth Curve Assay
4.8. Plasmid Stability Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guard-Petter, J. The chicken, the egg and Salmonella Enteritidis. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahramianfard, H.; Derakhshandeh, A.; Naziri, Z.; Khaltabadi Farahani, R. Prevalence, virulence factor and antimicrobial resistance analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis from poultry and egg samples in Iran. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.H.; Kan, B.; Chan, E.W.; Yan, M.; Chen, S. IncI1 Plasmids Carrying Various blaCTX-M Genes Contribute to Ceftriaxone Resistance in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, D.; McCusker, M.P.; Fanning, S.; Martins, M. Salmonella-host interactions—Modulation of the host innate immune system. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Mor, O. Persistent Infection and Long-Term Carriage of Typhoidal and Nontyphoidal Salmonellae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 00088-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.A.; Eade, C.R.; Wiedmann, M. Embracing Diversity: Differences in Virulence Mechanisms, Disease Severity, and Host Adaptations Contribute to the Success of Nontyphoidal Salmonella as a Foodborne Pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Duan, G.; Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Xi, Y.; Fan, Q. Transposition of ISEcp1 modulates blaCTX-M-55-mediated Shigella flexneri resistance to cefalothin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.; Simner, P.J.; Bradford, P.A. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases: An update on their characteristics, epidemiology and detection. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Coque, T.M. The CTX-M β-lactamase pandemic. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Hall, R.M. IS26-Mediated Formation of Transposons Carrying Antibiotic Resistance Genes. mSphere 2016, 1, 00038-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Poirel, L.; Sampaio, J.L.; Nordmann, P. Complete sequence of broad-host-range plasmid pRIO-5 harboring the extended-spectrum-β-lactamase gene blaBES-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Peng, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Mohsin, M.; Li, R.; Wang, Z. Distribution and genomic characterization of tigecycline-resistant tet(X4)-positive Escherichia coli of swine farm origin. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Olsen, R.H.; Xiao, J.; Meng, H.; Peng, S.; Shi, L. Genetic context of blaCTX–M–55 and qnrS1 genes in a foodborne Salmonella enterica serotype Saintpaul isolate from China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 899062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z. Emergence of a Hybrid IncI1-Iα Plasmid-Encoded bla(CTX-M-101) Conferring Resistance to Cephalosporins in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coipan, C.E.; Westrell, T.; van Hoek, A.; Alm, E.; Kotila, S.; Berbers, B.; de Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Ceyssens, P.J.; Borg, M.L.; Chattaway, M.; et al. Genomic epidemiology of emerging ESBL-producing Salmonella Kentucky bla (CTX-M-14b) in Europe. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2124–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Bai, J.; Liao, M.; Zhang, J. Fourth Generation Cephalosporin Resistance Among Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Isolates in Shanghai, China Conferred by bla (CTX-M-55) Harboring Plasmids. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Olsen, R.H.; Song, A.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C.; Meng, H.; Shi, L. First Report of a Foodborne Salmonella enterica Serovar Gloucester (4:i:l,w) ST34 Strain Harboring bla (CTX-M-) (55) and qnrS Genes Located in IS26-Mediated Composite Transposon. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 646101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; He, D.-D.; Zhang, M.-K.; Pan, Y.-S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.-H.; Hu, G.-Z. The Formation of Two Hybrid Plasmids Mediated by IS26 and Tn6952 in Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 676574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Zhuo, C.; Wu, A.; Chen, X.; Huang, L. Molecular Epidemiology and Characteristics of CTX-M-55 Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli From Guangzhou, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolund, A.; Sandegren, L. Characterization of ESBL disseminating plasmids. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djeghout, B.; Saha, S.; Sajib, M.S.I.; Tanmoy, A.M.; Islam, M.; Kay, G.L.; Langridge, G.C.; Endtz, H.P.; Wain, J.; Saha, S.K. Ceftriaxone-resistant Salmonella Typhi carries an IncI1-ST31 plasmid encoding CTX-M-15. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 12.0. 2022. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Seemann, T. Shovill: Faster SPAdes Assembly of Illumina Reads. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/shovill (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Vaser, R.; Šikić, M. Time-and memory-efficient genome assembly with Raven. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2021, 1, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Hawkey, J.; Méric, G.; Vezina, B.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Trycycler: Consensus long-read assemblies for bacterial genomes. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and In Silico pMLST: Identification and Typing of Plasmid Replicons in Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2075, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.-y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Snippy: Fast Bacterial Variant Calling from NGS Reads [Internet]. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/snippy (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Shi, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lan, P.; Xu, Q.; Hu, H.; Chen, Q.; Fan, J.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Opposite evolution of pathogenicity driven by in vivo wzc and wcaJ mutations in ST11-KL64 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Drug Resist. Updates 2023, 66, 100891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
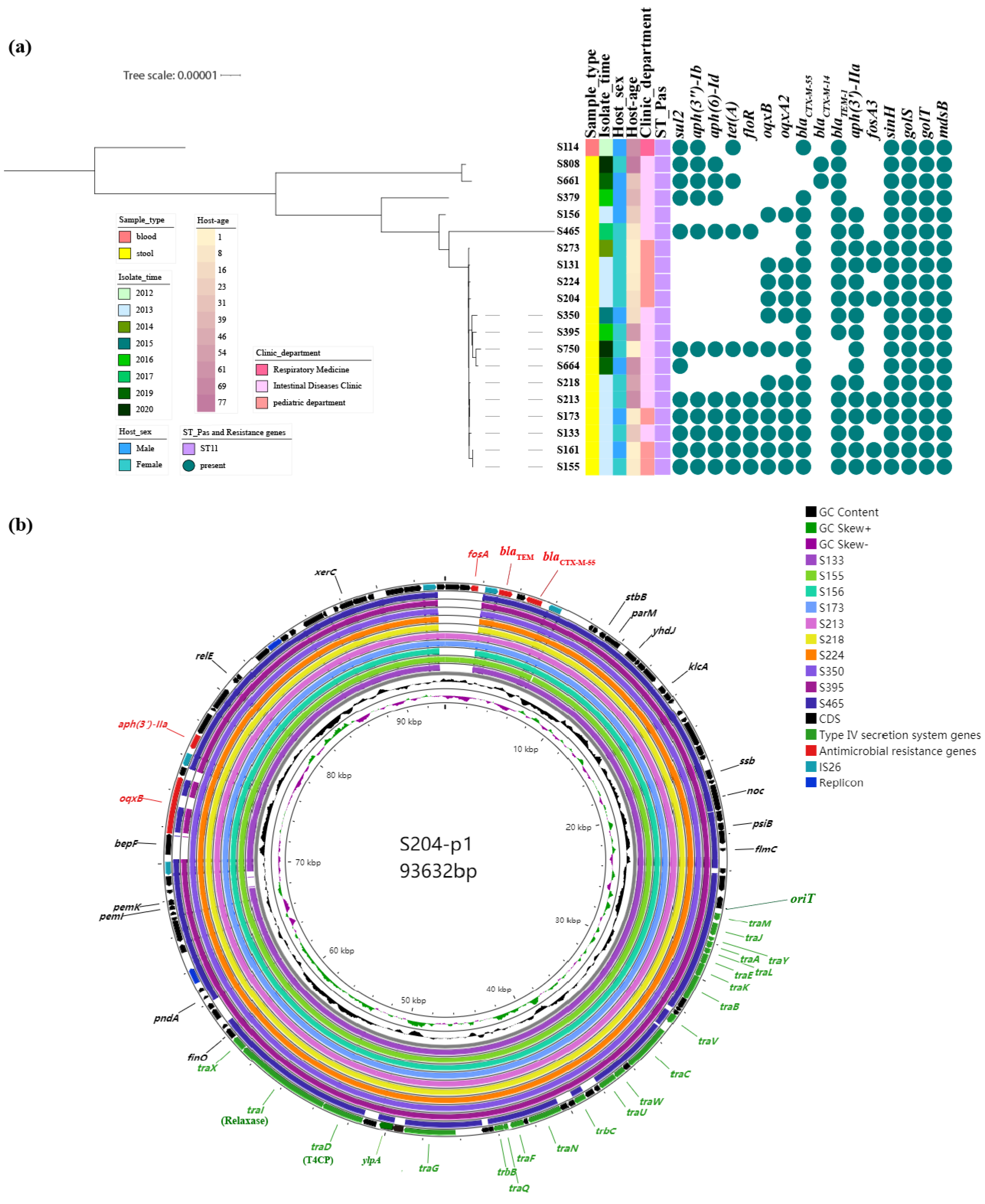

| * Location & (Plasmid_Type) | Size (bp) | GC (%) | blaCTX-M-type | Other Resistance Genes | Plasmid Replicons | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S273 | Chromosome | 4,679,990 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (A2) | 90,399 | 51.75 | blaCTX-M-55 | fosA3; aph(3′)-IIa; blaTEM | IncX1; IncFII(pHN7A8) | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 59,372 | 51.95 | - | - | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| S379 | Chromosome | 4,679,476 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (A2) | 113,301 | 49.97 | blaCTX-M-55 | blaTEM; aph(6)-Id; aph(3″)-Ib; sul2 | IncX1; IncFII(pHN7A8); IncN | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 57,128 | 51.85 | - | blaTEM | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| p3 | 3904 | 51.13 | - | - | Col156 | |
| S131 | Chromosome | 4,680,029 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (A2) | 93,985 | 52.01 | blaCTX-M-55 | fosA3; blaTEM; aph(3′)-IIa; oqxB; oqxA2 | IncX1; IncFII(pHN7A8) | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 59,372 | 51.95 | - | - | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| S204 | Chromosome | 4,679,989 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (A2) | 93,632 | 52.02 | blaCTX-M-55 | oqxA2; oqxB; aph(3′)-IIa; fosA3; blaTEM | IncX1; IncFII(pHN7A8) | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 59,372 | 51.95 | - | - | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| p3 | 52,891 | 43.83 | - | - | IncFII(p96A); IncFII(S) | |
| S161 | Chromosome | 4,679,615 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (A1) | 172,367 | 52.65 | blaCTX-M-55 | blaTEM; oqxA2; oqxB; aph(3′)-IIa; fosA3; sul2; aph(3″)-Ib; aph(6)-Id; tet(A); floR | IncX1; IncFII(pHN7A8); IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| S114 | Chromosome | 4,679,992 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (B) | 86,191 | 49.66 | blaCTX-M-55 | - | IncI1(Alpha) | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 64,327 | 51.76 | - | blaTEM | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| p3 | 29,336 | 47.22 | - | blaTEM; aph(6)-Id; aph(3″)-Ib; tet(A); aph(6)-Id; aph(3″)-Ib; sul2 | IncX1 | |
| p4 | 6647 | 48.52 | - | - | ColRNAI | |
| S808 | Chromosome | 4,679,741 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (B) | 93,230 | 49.88 | blaCTX-M-14 | - | IncI1(Alpha) | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 64,327 | 51.76 | - | blaTEM | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | |
| p3 | 24,484 | 44.75 | - | blaTEM; aph(6)-Id; aph(3″)-Ib; sul2 | IncX1 | |
| S664 | Chromosome | 4,679,298 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | - |
| p1 (A2) | 67,207 | 52.28 | blaCTX-M-55 | aph(3′)-IIa; sul2; blaTEM | IncFII(pHN7A8); IncX1 | |
| p2 (pSEV) | 59,323 | 51.95 | - | IncFIB(S); IncFII(S) | ||
| S750 | Chromosome | 4,680,774 | 52.18 | - | sinH; golS; golT; mdsB | |
| p1 (A1) | 116,054 | 53.10 | blaCTX-M-55 | blaTEM; oqxA2; oqxB; aph(3′)-IIa; aph(6)-Id; aph(3″)-Ib; sul2; tet(A); floR; | IncFII(S); IncX1 |
| Isolate Strain | The Plasmid Transferring | T4SS | blaCTX-M | Plasmid_Type | Recipient SL1344 | Recipient J53 | Recipient ATCC 13883 | Recipient ATCC 17978 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S273 | S273-p1 | a, b, d | 55 | A2 | + | + | + | – |
| S379 | S379-p1 | a, b, d | 55 | A2 | + | + | + | – |
| S131 | S131-p1 | a, b, d | 55 | A2 | – | – | – | – |
| S204 | S204-p1 | a, b, d | 55 | A2 | + | + | + | – |
| S664 | S664-p1 | a | 55 | A2 | – | + | – | – |
| S161 | S161-p1 | a, b, c, d | 55 | A1 | + | + | – | – |
| S750 | S750-p1 | c, d | 55 | A1 | + | – | – | – |
| S114 | S114-p1 | e | 55 | B | + | + | + | – |
| S808 | S808-p1 | e | 14 | B | + | + | + | + |
| Recipient (CRO_MIC) | S161-p1 | S114-p1 | S204-p1 | S808-p1 | S750-p1 | S273-p1 | S379-p1 | S664-p1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RrifSL1344 (0.125) | 1024 | 2048 | 2048 | 512 | 512 | 2048 | 1024 | - |
| RrifJ53 (0.06) | 2048 | 1024 | 1024 | 512 | - | 1024 | 512 | 512 |
| Rrif13883 (0.06) | - | 2048 | 2048 | 512 | - | 1024 | 1024 | - |
| Rrif17978 (8) | - | - | - | >2048 | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Fan, J.; Yu, L.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Hua, X. Dissemination of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis Harboring Plasmids Encoding blaCTX-M-55 or blaCTX-M-14 Gene in China. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050456
Yang S, Fan J, Yu L, He J, Zhang L, Yu Y, Hua X. Dissemination of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis Harboring Plasmids Encoding blaCTX-M-55 or blaCTX-M-14 Gene in China. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(5):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050456
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Siyuan, Jianzhong Fan, Lifei Yu, Jintao He, Linghong Zhang, Yunsong Yu, and Xiaoting Hua. 2024. "Dissemination of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis Harboring Plasmids Encoding blaCTX-M-55 or blaCTX-M-14 Gene in China" Antibiotics 13, no. 5: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050456
APA StyleYang, S., Fan, J., Yu, L., He, J., Zhang, L., Yu, Y., & Hua, X. (2024). Dissemination of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis Harboring Plasmids Encoding blaCTX-M-55 or blaCTX-M-14 Gene in China. Antibiotics, 13(5), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050456








