Safety and Tolerability of ShigActive™, a Shigella spp. Targeting Bacteriophage Preparation, in a Phase 1 Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Enrollment and Demographics
2.2. Safety and Tolerability
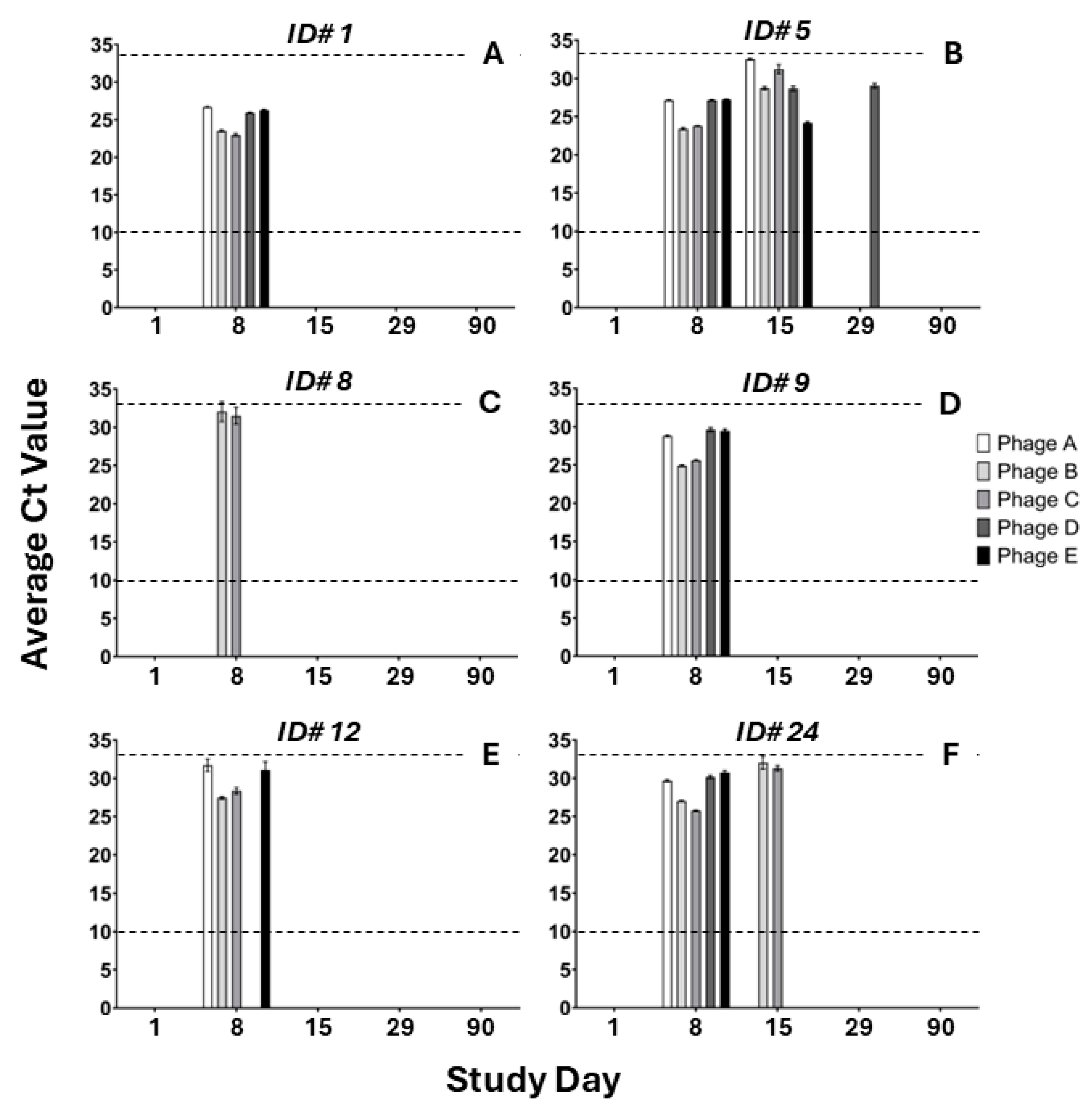
2.3. Pharmacokinectics
2.4. Intestinal Inflammation
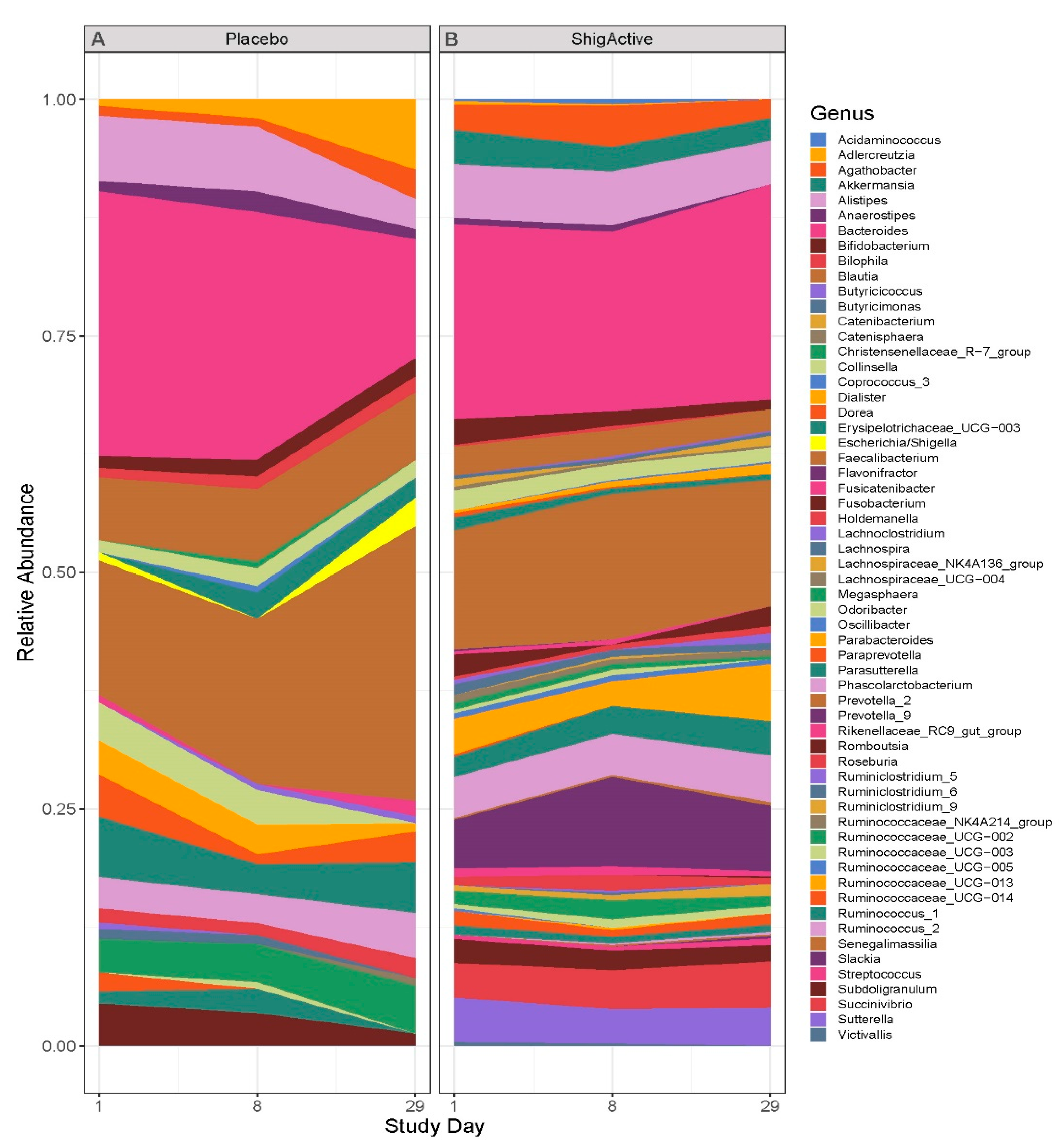
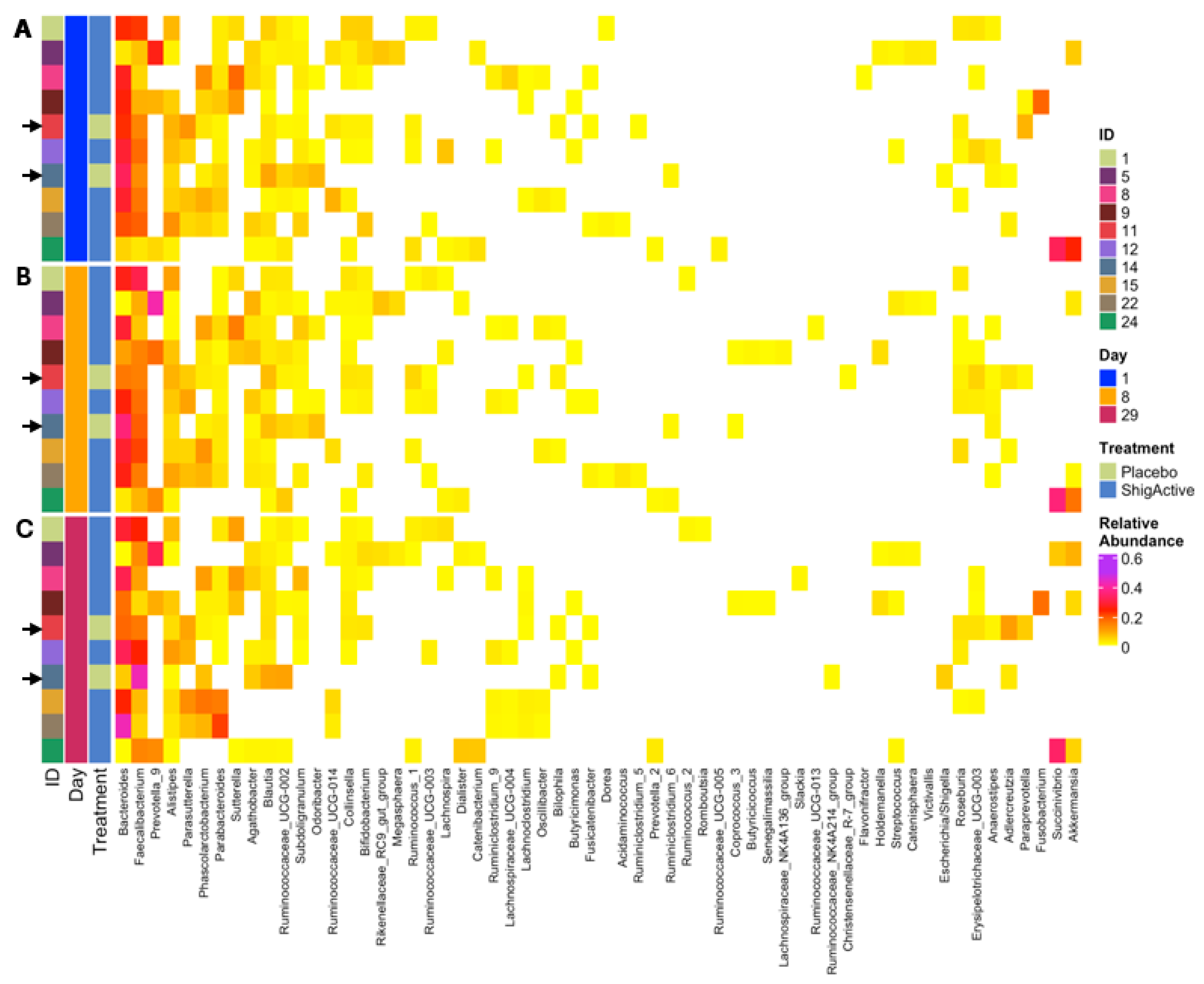
2.5. Changes in Microbiome Composition
2.5.1. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Output
2.5.2. Alpha Diversity Did Not Change from Baseline through Day 29
2.5.3. Variable Microbial Communities Observed among Participants with Greater Shifts at Later Timepoints
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
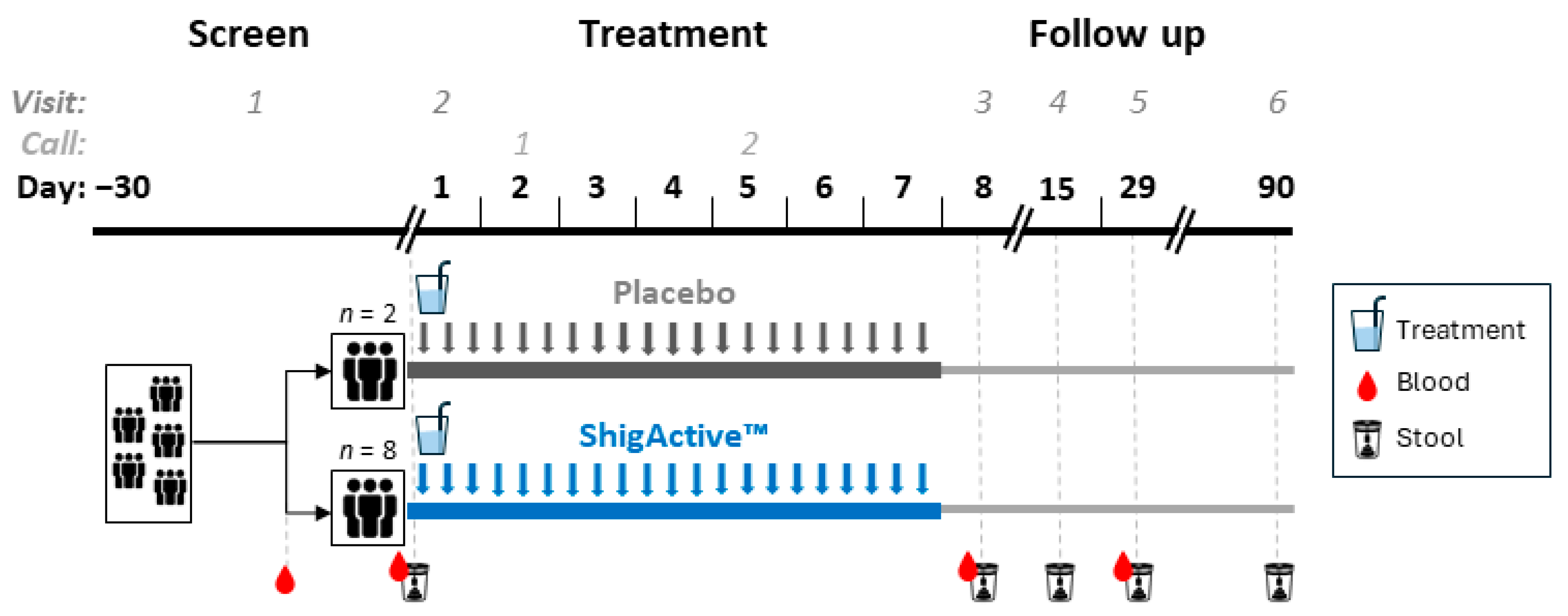
4.1. Trial Design and Participants
4.2. Interventions and Randomization
4.3. Study Procedures
4.4. Bacteria
4.5. Stool Extracts
4.6. Phage Enumeration
4.7. Inflammatory Mediators
4.8. Microbiome Analyses
4.8.1. Microbial DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.8.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analyses
4.9.1. Demographics and Safety Analyses
4.9.2. Biomarker and Phage Statistical Analyses
4.9.3. Microbiome Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotloff, K.L.; Winickoff, J.P.; Ivanoff, B.; Clemens, J.D.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Adak, G.K.; Levine, M.M. Global burden of Shigella infections: Implications for vaccine development and implementation of control strategies. Bull. World Health Organ. 1999, 77, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Riddle, M.S.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Pavlinac, P.; Zaidi, A.K.M. Shigellosis. Lancet 2018, 391, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, P.; Faruque, A.S.; Naheed, A.; Sack, D.A. Decrease in shigellosis-related deaths without Shigella spp.-specific interventions, Asia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Polyak, C.S.; Bishop, R.D.; Sobel, J.; Mintz, E.D. Laboratory-confirmed shigellosis in the United States, 1989–2002: Epidemiologic trends and patterns. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States--major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; p. 114.
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978 92 4 156474 8. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS) Report: Early Implementation 2017–2018; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9789241515061. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Shimamoto, T. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Shigella spp. of food origin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 194, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.; Grass, J.; Bicknese, A.; Campbell, D.; Hurd, J.; Kirkcaldy, R.D. Elevated risk for antimicrobial drug-resistant Shigella infection among men who have sex with men, United States, 2011–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1613–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyreva, V.K.; Jospin, G.; Greninger, A.L.; Watt, J.P.; Eisen, J.A.; Chaturvedi, V. Recent Outbreaks of Shigellosis in California Caused by Two Distinct Populations of Shigella sonnei with either Increased Virulence or Fluoroquinolone Resistance. mSphere 2016, 1, e00344-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, S.; Cohen, D. An update on vaccines against Shigella. Ther. Adv. Vaccines 2013, 1, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Wierzba, T.; Walker, R.I. Status of vaccine research and development for Shigella. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulakvelidze, A. Challenges of bacteriophage therapy. In Industrial Pharmaceutical Microbiology; Hodges, N., Hanlon, G., Eds.; Euromed Communications, Ltd.: Passfield, UK, 2012; pp. S13.11–S13.20. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki, J.; Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, T.; Iwano, H. Fitness Trade-Offs between Phage and Antibiotic Sensitivity in Phage-Resistant Variants: Molecular Action and Insights into Clinical Applications for Phage Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, W.C. Bacteriophage therapy. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, L.D. Bacteriophages for managing Shigella in various clinical and non-clinical settings. Bacteriophage 2013, 3, e25098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulakvelidze, A.; Kutter, E. Bacteriophage therapy in humans. In Bacteriophages: Biology and Application; Kutter, E., Sulakvelidze, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 381–436. [Google Scholar]
- Gorski, A.; Borysowski, J.; Miedzybrodzki, R. Phage Therapy: Towards a Successful Clinical Trial. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, T.; Salabarria, A.-C.; Edwards, R.A.; Roach, D.R. Standardized bacteriophage purification for personalized phage therapy. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2867–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, L.; Prazak, J.; Que, Y.A.; Cameron, D.R. Progress and Pitfalls of Bacteriophage Therapy in Critical Care: A Concise Definitive Review. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, G.A.; Lodise, T.P.; Tamma, P.D.; Knisely, J.M.; Alexander, J.; Aslam, S.; Barton, K.D.; Bizzell, E.; Totten, K.M.C.; Campbell, J.L.; et al. Considerations for the Use of Phage Therapy in Clinical Practice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0207121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbellino, M.; Kieffer, N.; Kutateladze, M.; Balarjishvili, N.; Leshkasheli, L.; Askilashvili, L.; Tsertsvadze, G.; Rimoldi, S.G.; Nizharadze, D.; Hoyle, N.; et al. Eradication of a Multidrug-Resistant, Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolate Following Oral and Intra-rectal Therapy With a Custom Made, Lytic Bacteriophage Preparation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, N.; Zhvaniya, P.; Balarjishvili, N.; Bolkvadze, D.; Nadareishvili, L.; Nizharadze, D.; Wittmann, J.; Rohde, C.; Kutateladze, M. Phage therapy against Achromobacter xylosoxidans lung infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis: A case report. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczynski, P.; Weber-Dabrowska, B.; Kohutnicka, M.; Łuczak, M.; Gorecki, A.; Górski, A. Successful eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) intestinal carrier status in a healthcare worker—case report. Folia Microbiol. 2006, 51, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruttin, A.; Brussow, H. Human volunteers receiving Escherichia coli phage T4 orally: A safety test of phage therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febvre, H.P.; Rao, S.; Gindin, M.; Goodwin, N.D.M.; Finer, E.; Vivanco, J.S.; Lu, S.; Manter, D.K.; Wallace, T.C.; Weir, T.L. PHAGE Study: Effects of Supplemental Bacteriophage Intake on Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallin, S.; Alam Sarker, S.; Barretto, C.; Sultana, S.; Berger, B.; Huq, S.; Krause, L.; Bibiloni, R.; Schmitt, B.; Reuteler, G.; et al. Safety analysis of a Russian phage cocktail: From metagenomic analysis to oral application in healthy human subjects. Virology 2013, 443, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.A.; Brüssow, H. From bench to bed and back again: Phage therapy of childhood Escherichia coli diarrhea. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1372, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, V.; Ukhanova, M.; Li, M.; Reinhard, M.; Sulakvelidze, A. Bacteriophage administration significantly reduces Shigella colonization and shedding by Shigella-challenged mice without deleterious side effects and altering the gut microbiota. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 5, e1088124. [Google Scholar]
- Howden, C.W. Review article: Immediate-release proton-pump inhibitor therapy--potential advantages. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22 (Suppl. S3), 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratha, V.S.; McGraw, T.; Tobin, W. A randomized, crossover pharmacodynamic study of immediate-release omeprazole/sodium bicarbonate and delayed-release lansoprazole in healthy adult volunteers. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2016, 4, e00238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorohan, B.M.; Obrisca, B.; Jurubita, R.; Lupusoru, G.; Achim, C.; Andronesi, A.; Fratila, G.; Berechet, A.; Micu, G.; Ismail, G. Sodium citrate versus sodium bicarbonate for metabolic acidosis in patients with chronic kidney disease: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2024, 103, e37475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordtran, J.S.; Morawski, S.G.; Santa Ana, C.A.; Rector, F.C., Jr. Gas production after reaction of sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric acid. Gastroenterology 1984, 87, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Jung, Y.S. Comparative Efficacy of Tegoprazan vs Esomeprazole/Sodium Bicarbonate for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, e00632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, S.; Kredo-Russo, S.; Valdes-Mas, R.; Kviatcovsky, D.; Weinstock, E.; Matiuhin, Y.; Silberberg, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Furuichi, M.; Oka, A.; et al. Targeted suppression of human IBD-associated gut microbiota commensals by phage consortia for treatment of intestinal inflammation. Cell 2022, 185, 2879–2898 e2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.A.; Sultana, S.; Reuteler, G.; Moine, D.; Descombes, P.; Charton, F.; Bourdin, G.; McCallin, S.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Neville, T.; et al. Oral Phage Therapy of Acute Bacterial Diarrhea With Two Coliphage Preparations: A Randomized Trial in Children From Bangladesh. EBioMedicine 2016, 4, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.A.; McCallin, S.; Barretto, C.; Berger, B.; Pittet, A.C.; Sultana, S.; Krause, L.; Huq, S.; Bibiloni, R.; Bruttin, A.; et al. Oral T4-like phage cocktail application to healthy adult volunteers from Bangladesh. Virology 2012, 434, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowska, K. Phage therapy: What factors shape phage pharmacokinetics and bioavailability? Systematic and critical review. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2000–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusiak-Szelachowska, M.; Weber-Dabrowska, B.; Jonczyk-Matysiak, E.; Wojciechowska, R.; Gorski, A. Bacteriophages in the gastrointestinal tract and their implications. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Adler, J.; Chachu, K.A.; Nguyen, N.H.; Siddique, S.M.; Weiss, J.M.; Sultan, S.; Velayos, F.S.; Cohen, B.L.; Singh, S.; et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Role of Biomarkers for the Management of Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1367–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buskirk, A.D.; Ndungo, E.; Shimanovich, A.A.; Lam, D.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Ikumapayi, U.N.; Ma, B.; Powell, H.; Antonio, M.; Nataro, J.P.; et al. Mucosal Immune Profiles Associated with Diarrheal Disease Severity in Shigella- and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-Infected Children Enrolled in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study. mBio 2022, 13, e0053822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Nguyen, N.H.; Cohen, B.L.; Velayos, F.S.; Weiss, J.M.; Sultan, S.; Siddique, S.M.; Adler, J.; Chachu, K.A.; et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Role of Biomarkers for the Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 344–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.K. Calprotectin or Lactoferrin: Do They Help. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, V.; Ukhanova, M.; Visone, L.; Abuladze, T.; Sulakvelidze, A. Bacteriophage Administration Reduces the Concentration of Listeria monocytogenes in the Gastrointestinal Tract and Its Translocation to Spleen and Liver in Experimentally Infected Mice. Int. J. Microbiol. 2010, 2010, 624234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffer, N.; Woolston, J.; Li, M.; Das, C.; Sulakvelidze, A. Bacteriophage preparation lytic for Shigella significantly reduces Shigella sonnei contamination in various foods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.H. Methods of study bacterial viruses. In Bacteriophages; Interscience Publishers, Ltd.: London, UK, 1959; pp. 443–519. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, J.B.; Humphrys, M.S.; Robinson, C.K.; Settles, M.L.; Ott, S.; Fu, L.; Yang, H.; Gajer, P.; He, X.; McComb, E.; et al. Ultrahigh-Throughput Multiplexing and Sequencing of >500-Base-Pair Amplicon Regions on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 Platform. mSystems 2019, 4, e00029-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochazkova, P.; Roubalova, R.; Dvorak, J.; Kreisinger, J.; Hill, M.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H.; Tomasova, P.; Pelantova, H.; Cermakova, M.; Kuzma, M.; et al. The intestinal microbiota and metabolites in patients with anorexia nervosa. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
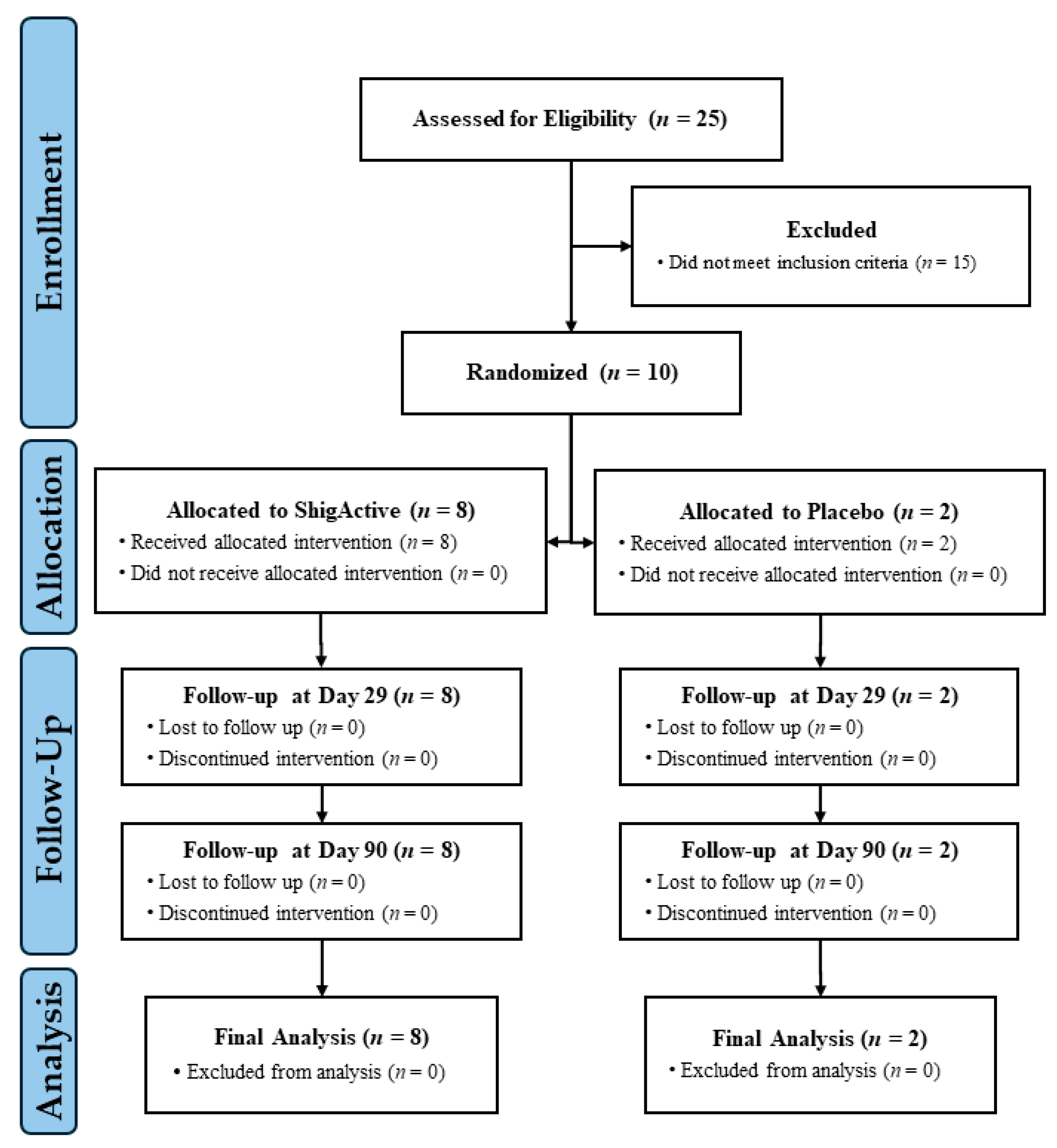



| Subject Demographics | Total (n = 10) | ShigActive (n = 8) | Placebo (n = 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Male | 5 (50.0) | 4 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) |
| Female | 5 (50.0) | 4 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Non-Hispanic | 9 (90.0) | 7 (87.5) | 2 (100.0) |
| Hispanic or Latino | 1 (10.0) | 1 (12.5) | - |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 1 (10.0) | - | 1 (50.0) |
| Black/African American | 1 (10.0) | 1 (12.5) | - |
| White | 8 (80.0) | 7 (87.5) | 1 (50.0) |
| Age (year) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 32.9 (6.74) | 32.5 (7.59) | 34.4 (0.28) |
| Median [Q1, Q3] | 34.4 [25.5, 38.1] | 32.8 [25.4, 39] | 34.4 [34.2, 34.6] |
| Min, Max | 23.7, 42.1 | 23.7, 42.1 | 34.2, 34.6 |
| All Subjects (n = 10) | ShigActive™ (n = 8) | Placebo (n = 2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. AEs (% Total) | No. Subjects (% Total) | No. AEs (% Total) | No. Subjects (% Total) | No. AEs (% Total) | No. Subjects (% Total) | |
| Any Adverse Event | 9 (100) | 4 (40) | 9 (100) | 4 (50) | - | - |
| Mild (Grade 1) | 8 (88.9) | 4 (40) | 8 (88.9) | 4 (50) | - | - |
| Moderate (Grade 2) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (10) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (12.5) | - | - |
| Severe (Grade 3) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Treatment-emergent * | 8 (88.9) | 4 (40) | 8 (88.9) | 4 (50) | - | - |
| Any Serious Adverse Event | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solicited Adverse Events (Day 1–7) | 6 (100) | 3 (30) | 6 (100) | 3 (37.5) | - | - |
| Diarrhea | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Fever | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vomiting | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nausea | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Abdominal Pain/Cramping | 1 (16.7) | 1 (10) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (12.5) | - | - |
| Bloating | 3 (50) | 2 (20) | 3 (50) | 2 (25) | - | - |
| Tenesmus | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Anorexia/Loss of Appetite | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Excessive Gas | 2 (33.3) | 2 (20) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (25) | - | - |
| Headache | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Unsolicited Adverse Events (Day 1–29; listed by MedDRA SOC) | 3 (100) | 3 (30) | 3 (100) | 3 (37.5) | - | - |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 1 (33.3) † | 1 (10) † | 1 (33.3) † | 1 (12.5) † | - | - |
| Gastrointestinal | 2 (66.7) ‡ | 2 (20) ‡ | 2 (66.7) ‡ | 2 (25) ‡ | - | - |
| Treatment-emergent * | 2 (66.7) | 2 (20) | 2 (66.7) | 2 (25) | - | - |
| Event of Special Interest § | 1 | 1 (10) | 1 | 1 (12.5) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.H.; Woolston, J.; Grant-Beurmann, S.; Robinson, C.K.; Bansal, G.; Nkeze, J.; Permala-Booth, J.; Fraser, C.M.; Tennant, S.M.; Shriver, M.C.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of ShigActive™, a Shigella spp. Targeting Bacteriophage Preparation, in a Phase 1 Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090858
Chen WH, Woolston J, Grant-Beurmann S, Robinson CK, Bansal G, Nkeze J, Permala-Booth J, Fraser CM, Tennant SM, Shriver MC, et al. Safety and Tolerability of ShigActive™, a Shigella spp. Targeting Bacteriophage Preparation, in a Phase 1 Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(9):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090858
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wilbur H., Joelle Woolston, Silvia Grant-Beurmann, Courtney K. Robinson, Garima Bansal, Joseph Nkeze, Jasnehta Permala-Booth, Claire M. Fraser, Sharon M. Tennant, Mallory C. Shriver, and et al. 2024. "Safety and Tolerability of ShigActive™, a Shigella spp. Targeting Bacteriophage Preparation, in a Phase 1 Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial" Antibiotics 13, no. 9: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090858
APA StyleChen, W. H., Woolston, J., Grant-Beurmann, S., Robinson, C. K., Bansal, G., Nkeze, J., Permala-Booth, J., Fraser, C. M., Tennant, S. M., Shriver, M. C., Pasetti, M. F., Liang, Y., Kotloff, K. L., Sulakvelidze, A., & Schwartz, J. A. (2024). Safety and Tolerability of ShigActive™, a Shigella spp. Targeting Bacteriophage Preparation, in a Phase 1 Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial. Antibiotics, 13(9), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090858







