Prevalence of Variant GTRIStaphylococcus aureus Isolated from Dairy Cow Milk Samples in the Alpine Grazing System of the Aosta Valley and Its Association with AMR and Virulence Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacteriological Results
2.2. Genotyping
2.2.1. RS-PCR
2.2.2. MLST
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.4. Distribution of Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles Among Genotypic Clusters
2.5. Virulence and Antimicrobial Profiling
2.6. Association Between Phenotypic Resistance and Resistance Genes
3. Discussion
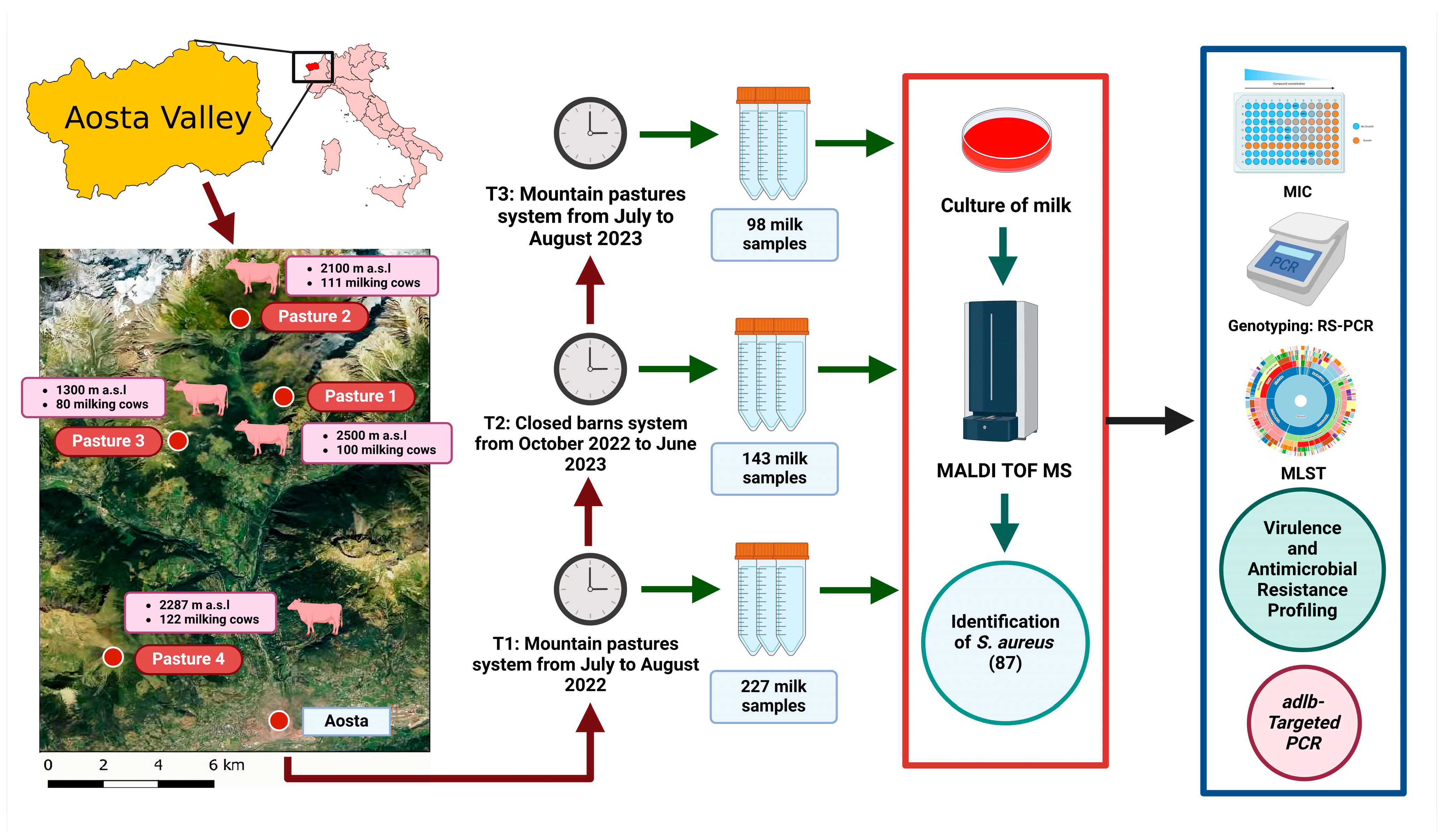
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statements
4.2. Herd Selection
4.3. Milk Sample Collection
4.4. Bacteriological Analysis and Staphylococcus Aureus Identification
4.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.6. Molecular Analysis
4.6.1. DNA Extraction
4.6.2. RS-PCR
4.6.3. MLST
4.6.4. Standard PCR
4.6.5. Adlb-Targeted PCR
4.7. β-Lactamase Detection
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pretolani, R.; Raffaelli, R. Differenziali Di Costo e Valorizzazione Delle Risorse Territoriali Nella Produzione Di Latte in Montagna. In Lavorare e Vivere in Montagna: Svantaggi Strutturali e Costi Aggiuntivi; Bononia University Press: Bologna, Italy, 2007; ISBN 8873952976. [Google Scholar]
- Halasa, T.; Huijps, K.; Østerås, O.; Hogeveen, H. Economic Effects of Bovine Mastitis and Mastitis Management: A Review. Vet. Q 2007, 29, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkema, H.W.; Schukken, Y.H.; Zadoks, R.N. Invited Review: The Role of Cow, Pathogen, and Treatment Regimen in the Therapeutic Success of Bovine Staphylococcus aureus Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1877–1895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bar-Gal, G.K.; Blum, S.E.; Hadas, L.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Leitner, G. Host-Specificity of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Intramammary Infections in Dairy Animals Assessed by Genotyping and Virulence Genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremonesi, P.; Pozzi, F.; Raschetti, M.; Bignoli, G.; Capra, E.; Graber, H.U.; Vezzoli, F.; Piccinini, R.; Bertasi, B.; Biffani, S.; et al. Genomic Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Associated with High Within-Herd Prevalence of Intramammary Infections in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6828–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.J.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus Sequence Typing for Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant and Methicillin-Susceptible Clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, N.; Nobrega, D.B.; Naqvi, S.A.; Barkema, H.W.; Jeroen, D.B. Genomic Analysis of Bovine Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Milk To Elucidate Diversity and Determine the Distributions of Antimicrobial and Virulence Genes and Their Association with Mastitis. mSystems 2020, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Commission Notice: Guidelines for the Prudent Use of Antimicrobials in Veterinary Medicine (2015/C 299/04). Off. J. Eur. Union. 2015, 58, 7–26.
- Monistero, V.; Graber, H.U.; Pollera, C.; Cremonesi, P.; Castiglioni, B.; Bottini, E.; Ceballos-Marquez, A.; Lasso-Rojas, L.; Kroemker, V.; Wente, N. Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Bovine Mastitis in Eight Countries: Genotypes, Detection of Genes Encoding Different Toxins and Other Virulence Genes. Toxins 2018, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals. 7th ed. CLSI Supplement Vet 01S. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/veterinary-medicine/documents/vet01s/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI Standard Vet 01; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CASFM Comité de l’antibiogramme de La Société Française de Microbiologie. Groupe de Travail Antibiogramme Vétérinaire. Recommandations 2024 V.1.0 Juin. Available online: https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/CASFM2024_V1.0.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Cosandey, A.; Boss, R.; Luini, M.; Artursson, K.; Bardiau, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Hehenberger, E.; Lam, T.; Mansfeld, M.; Michel, A.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Genotype B and Other Genotypes Isolated from Cow Milk in European Countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, C.; Boss, R.; Bodmer, M.; Leuenberger, A.; Ivanovic, I.; Graber, H.U. Sanitation of Staphylococcus aureus Genotype B-Positive Dairy Herds: A Field Study. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6897–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Borne, B.H.P.; Graber, H.U.; Voelk, V.; Sartori, C.; Steiner, A.; Haerdi-Landerer, M.C.; Bodmer, M. A Longitudinal Study on Transmission of Staphylococcus aureus Genotype B in Swiss Communal Dairy Herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 136, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Said, M.; Abbassi, M.S.; Bianchini, V.; Sghaier, S.; Cremonesi, P.; Romanò, A.; Gualdi, V.; Hassen, A.; Luini, M. V Genetic Characterization and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Milk in Tunisia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feil, E.J.; Cooper, J.E.; Grundmann, H.; Robinson, D.A.; Enright, M.C.; Berendt, T.; Peacock, S.J.; Smith, J.M.; Murphy, M.; Spratt, B.G. How Clonal Is Staphylococcus aureus? J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.M.-L.; Lloyd, D.H.; Lindsay, J.A. Staphylococcus aureus Host Specificity: Comparative Genomics of Human versus Animal Isolates by Multi-Strain Microarray. Microbiology 2008, 154, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Hasman, H.; Moodley, A.; Guardabassi, L.; Stegger, M.; Skov, R.L.; Aarestrup, F.M. Spa Type Distribution in Staphylococcus aureus Originating from Pigs, Cattle and Poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 141, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, E.; Kobatashi, H.; Nakajima, H.; Sshimizu, Y.; Eguchi, M. Epidemiological Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Cows and the Environment of a Dairy Farm in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, R.; Cosandey, A.; Luini, M.; Artursson, K.; Bardiau, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Hehenberger, E.; Lam, T.; Mansfeld, M.; Michel, A.; et al. Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: Subtyping, Evolution, and Zoonotic Transfer. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, A.; Maisano, A.M.; Bianchini, V.; Vezzoli, F.; Romanò, A.; Graber, H.U.; Cremonesi, P.; Zanardi, G.; Cappa, V.; Luini, M. Short Communication: Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from Bulk Tank Milk of Dairy Cattle in Lombardy (Northern Italy). J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemendaal, A.L.A.; Brouwer, E.C.; Fluit, A.C. Methicillin Resistance Transfer from Staphylocccus Epidermidis to Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in a Patient during Antibiotic Therapy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11841. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current Status and Future Prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitrus, A.A.; Zunita, Z.; Bejo, S.K.; Othman, S.; Nadzir, N.A.A. In Vitro Transfer of Methicillin Resistance Determinants MecA from Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to Methicillin Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus (MSSA). BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortimiglia, C.; Luini, M.; Bianchini, V.; Marzagalli, L.; Vezzoli, F.; Avisani, D.; Bertoletti, M.; Ianzano, A.; Franco, A.; Battisti, A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and of Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus Clonal Complexes in Bulk Tank Milk from Dairy Cattle Herds in Lombardy Region (Northern Italy). Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3046–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, S.A.; Lam, T.J.G.M.; Hoekstra, J.; Rutten, V.P.M.G.; Tessema, T.S.; Broens, E.M.; Riesebos, A.E.; Spaninks, M.P.; Koop, G. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Milk Samples of Dairy Cows in Small Holder Farms of North-Western Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antók, F.I.; Mayrhofer, R.; Marbach, H.; Masengesho, J.C.; Keinprecht, H.; Nyirimbuga, V.; Fischer, O.; Lepuschitz, S.; Ruppitsch, W.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; et al. Characterization of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Species Associated with Bovine Mastitis in Rwanda. Antibiotics 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndahetuye, J.B.; Persson, Y.; Nyman, A.-K.; Tukei, M.; Ongol, M.P.; Båge, R. Aetiology and Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Herds in Peri-Urban Areas of Kigali in Rwanda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Monistero, V.; Barberio, A.; Biscarini, F.; Cremonesi, P.; Castiglioni, B.; Graber, H.U.; Bottini, E.; Ceballos-Marquez, A.; Kroemker, V.; Petzer, I.M.; et al. Different Distribution of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Virulence Profiles of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Clinical Mastitis in Six Countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3431–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhagen, B.-A.; Köster, G.; Wallmann, J.; Heuwieser, W. Prevalence of Mastitis Pathogens and Their Resistance Against Antimicrobial Agents in Dairy Cows in Brandenburg, Germany. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, G.; Romanó, A.; Wahl, F.; Berger, T.; Rojo, L.V.; Graber, H.U. Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: A European Study of Contagiousness and Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1154550. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K.L.; Lyman, R.L.; Bodeis-Jones, S.M.; White, D.G. Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles among Mastitis-Causing Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Milk Samples. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; McClure, J.T.; Léger, D.; Dufour, S.; Sheldon, A.G.; Scholl, D.T.; Barkema, H.W. Antimicrobial Use on Canadian Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.D.; de Simoni Gouveia, J.J.; da Costa, M.M.; Soares, R.A.N.; Gouveia, G.V. Resistance and Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus by Whole-Genome Sequencing: A Comparative Approach in BlaZ-Positive Isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Marothi, Y.; Iyer, R.V.; Singh, B.; Sharma, M.; Eriksson, B.; Macaden, R.; Lundborg, C.S. Nasal Carriage and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus in Healthy Preschool Children in Ujjain, India. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibah, S.; Arzanlou, M.; Jannati, E.; Shapouri, R. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Strains Isolated from Clinical Specimens in Ardabil, Iran. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Didier, G.; Stephane, B.; John, S.B.; Philippe, W.; Sylvie, S.; Bruno, G.; Edouard, B.; Claude, C. Amoxicillin-Clavulanate Therapy Increases Childhood Nasal Colonization by Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Strains Producing High Levels of Penicillinase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4618–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.E.; Christensen, H.; Aarestrup, F.M. Diversity and Evolution of BlaZ from Staphylococcus aureus and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegg, P.L.; Oliveira, L.; Jin, W.; Okwumabua, O. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Occurrence of Selected Resistance Genes in Gram-Positive Mastitis Pathogens Isolated from Wisconsin Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4521–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveri, M.; Suominen, S.; Rantala, L.; Honkanen-Buzalski, T.; Pyörälä, S. Comparison of Phenotypic and Genotypic Detection of Penicillin G Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Intramammary Infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.; Kelman, T.; Pitesky, M. Overview of Quantitative Methodologies to Understand Antimicrobial Resistance via Minimum Inhibitory Concentration. Animals 2020, 10, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovic, I.; Boss, R.; Romanò, A.; Guédon, E.; Le-Loir, Y.; Luini, M.; Graber, H.U. Penicillin Resistance in Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: Genomic Evaluation of the Discrepancy between Phenotypic and Molecular Test Methods. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatermann, S.G.; Koschinski, T.; Friedrich, S. Distribution and Expression of Macrolide Resistance Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, C.; Boss, R.; Ivanovic, I.; Graber, H.U. Development of a New Real-Time Quantitative PCR Assay for the Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Genotype B in Cow Milk, Targeting the New Gene Adlb. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7834–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, H.; Frankenberger, S.; Zähringer, U.; Mack, D. Structure, Function and Contribution of Polysaccharide Intercellular Adhesin (PIA) to Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Formation and Pathogenesis of Biomaterial-Associated Infections. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gara, J.P. Ica and beyond: Biofilm Mechanisms and Regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 270, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A Review of Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Regulation Mechanism. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidelis, C.E.; Orsi, A.M.; Freu, G.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Santos, M.V. dos Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus uberis Isolates from Bovine Mastitis. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. Staphylococcus aureus α-Toxin: Nearly a Century of Intrigue. Toxins 2013, 5, 1140–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, G.; Biffani, S.; Minozzi, G.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Luini, M.; Piccinini, R. Virulence Genes of S. aureus from Dairy Cow Mastitis and Contagiousness Risk. Toxins 2017, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.L.; Malachowa, N.; Hammer, C.H.; Nardone, G.A.; Robinson, M.A.; Kobayashi, S.D.; DeLeo, F.R. Identification of a Novel Staphylococcus aureus Two-Component Leukotoxin Using Cell Surface Proteomics. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11634. [Google Scholar]
- DuMont, A.L.; Nygaard, T.K.; Watkins, R.L.; Smith, A.; Kozhaya, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Shopsin, B.; Unutmaz, D.; Voyich, J.M.; Torres, V.J. Characterization of a New Cytotoxin That Contributes to Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, F., III; Benson, M.A.; Chen, J.; Novick, R.P.; Shopsin, B.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus Leucocidin ED Contributes to Systemic Infection by Targeting Neutrophils and Promoting Bacterial Growth in Vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenesch, F.; Lina, G.; Henry, T. Staphylococcus aureus Hemolysins, Bi-Component Leukocidins, and Cytolytic Peptides: A Redundant Arsenal of Membrane-Damaging Virulence Factors? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Chavakis, T.; Preissner, K.T.; Herrmann, M. The Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, S.J.; Moore, C.E.; Justice, A.; Kantzanou, M.; Story, L.; Mackie, K.; O’Neill, G.; Day, N.P.J. Virulent Combinations of Adhesin and Toxin Genes in Natural Populations of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.R.; Foster, S.J. Surface Adhesins of Staphylococcus aureus. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Poole, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 51, pp. 187–224. ISBN 0065-2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveri, M.; Roslöf, A.; Rantala, L.; Pyörälä, S. Virulence Genes of Bovine Staphylococcus aureus from Persistent and Nonpersistent Intramammary Infections with Different Clinical Characteristics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkaik, N.J.; Benard, M.; Boelens, H.A.; de Vogel, C.P.; Nouwen, J.L.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Melles, D.C.; van Belkum, A.; van Wamel, W.J.B. Immune Evasion Cluster-Positive Bacteriophages Are Highly Prevalent among Human Staphylococcus aureus Strains, but They Are Not Essential in the First Stages of Nasal Colonization. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, C.; Abdelbary, M.; Layer, F.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. Prevalence of the Immune Evasion Gene Cluster in Staphylococcus aureus CC398. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Principles on Assignment of Defined Daily Dose for Animals (DDDvet) and Defined Course Dose for Animals (DCDvet) in Principles on Assignment of Defined Daily Dose for Animals (DDDA) and Defined Course Dose for Animals (DCDA), Veterinary Medicines Division, 2015, EMA/710019/2014. Available online: https://suivet.it/Data/Sites/1/media/farmaci/amr/amr-ddd-dcd-ema.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Adkins, P.R.F.; Middleton, J.R. Laboratory Handbook on Bovine Mastitis; National Mastitis Council, Incorporated: New Prague, MN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, L.P.; Lemma, F.; Koylass, M.; Rogers, J.; Ayling, R.D.; Worth, D.; Klita, M.; Steventon, A.; Line, K.; Wragg, P.; et al. Evaluation of MALDI-ToF as a Method for the Identification of Bacteria in the Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 101, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, J.R.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Grenfell, R.; Leite, R.F.; Juliano, L.; Santos, M. V Direct Identification of Bovine Mastitis Pathogens by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry in Pre-Incubated Milk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.C.d.A.; Brito, M.A.V.P.; Giambiagi-de Marval, M.; Vicentini, N.M.; Lange, C.C. Identification of Bovine Mastitis Pathogens Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in Brazil. J. Dairy Res. 2021, 88, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Antimicrobial Wild Type Distributions of Microorganisms. 2018. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2019–2020. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07209. [CrossRef]
- Haendiges, J.; Timme, R.; Kastanis, G.; Balkey, M. Manual DNA Extraction Using Qiagen DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit. Protocols.io 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syring, C.; Boss, R.; Reist, M.; Bodmer, M.; Hummerjohann, J.; Gehrig, P.; Graber, H.U. Bovine Mastitis: The Diagnostic Properties of a PCR-Based Assay to Monitor the Staphylococcus aureus Genotype B Status of a Herd, Using Bulk Tank Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 3674–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akineden, Ö.; Annemüller, C.; Hassan, A.A.; Lämmler, C.; Wolter, W.; Zschöck, M. Toxin Genes and Other Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Milk of Cows with Mastitis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salasia, S.I.O.; Khusnan, Z.; Lammler, C.; Zschock, M. Comparative Studies on Pheno- and Genotypic Properties of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Central Java in Indonesia and Hesse in Germany. JVS 2019, 5, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McClure, J.-A.; Conly, J.M.; Lau, V.; Elsayed, S.; Louie, T.; Hutchins, W.; Zhang, K. Novel Multiplex PCR Assay for Detection of the Staphylococcal Virulence Marker Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Genes and Simultaneous Discrimination of Methicillin-Susceptible from-Resistant Staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Zecconi, A.; Cesaris, L.; Liandris, E.; Daprà, V.; Piccinini, R. Role of Several Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Factors on the Inflammatory Response in Bovine Mammary Gland. Microb. Pathog. 2006, 40, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraud, S.; Mougel, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Lina, G.; Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Nesme, X.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus Genetic Background, Virulence Factors, Agr Groups (Alleles), and Human Disease. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 631–641. [Google Scholar]
- Monday, S.R.; Bohach, G.A. Use of Multiplex PCR to Detect Classical and Newly Described Pyrogenic Toxin Genes in Staphylococcal Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3411–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atshan, S.S.; Shamsudin, M.N.; Karunanidhi, A.; van Belkum, A.; Lung, L.T.T.; Sekawi, Z.; Nathan, J.J.; Ling, K.H.; Seng, J.S.C.; Ali, A.M.; et al. Quantitative PCR Analysis of Genes Expressed during Biofilm Development of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 18, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, J.; Grebe, T.; Tait-Kamradt, A.; Wondrack, L. Detection of Erythromycin-Resistant Determinants by PCR. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2562–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.B.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Aarestrup, F.M. Presence of erm Gene Classes in Gram-Positive Bacteria of Animal and Human Origin in Denmark. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, A.A.; Gillespie, B.E.; Oliver, S.P. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Species Isolated from Bovine Milk. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, G.K.; Larsen, A.R.; Robb, A.; Edwards, G.E.; Pennycott, T.W.; Foster, G.; Mot, D.; Hermans, K.; Baert, K.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. The Newly Described mecA Homologue, mecALGA251, Is Present in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from a Diverse Range of Host Species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Result | T1 | T2 | T3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus (single infection) | 24 (10.6%) | 6 (4.2%) | 10 (10.2%) | 40 (8.6%) |
| S. aureus (co-infection) | 25 (11%) | 17 (11.9%) | 5 (5.1%) | 47 (10%) |
| Others a | 126 (55.5%) | 104 (72.7%) | 69 (70.4%) | 299 (63.9%) |
| Contamination | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (8.2%) | 8 (1.7%) |
| Negative | 52 (22.9%) | 16 (11.2%) | 6 (6.1%) | 74 (15.8%) |
| Total | 227 (100%) | 143 (100%) | 98 (100%) | 468 (100%) |
| Cluster | Genotype | Number of Isolates (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CLR | GTRI | 50 (61.0) |
| GTRXIII | 2 (2.4) | |
| GTRIV | 4 (4.9) | |
| GTR | 2 (2.4) | |
| Total | 58 (70.7) | |
| CLB | GTB | 12 (14.6) |
| GTBIV | 1 (1.2) | |
| Total | 13 (15.9) | |
| CLBI | GTBI | 5 (6.1) |
| CLA | GTAII | 1 (1.2) |
| CLZ | GTZ | 1 (1.2) |
| CLC | GTC | 2 (2.4) |
| CLAP | GTAP | 1 (1.2) |
| CLJ | GTJI | 1 (1.2) |
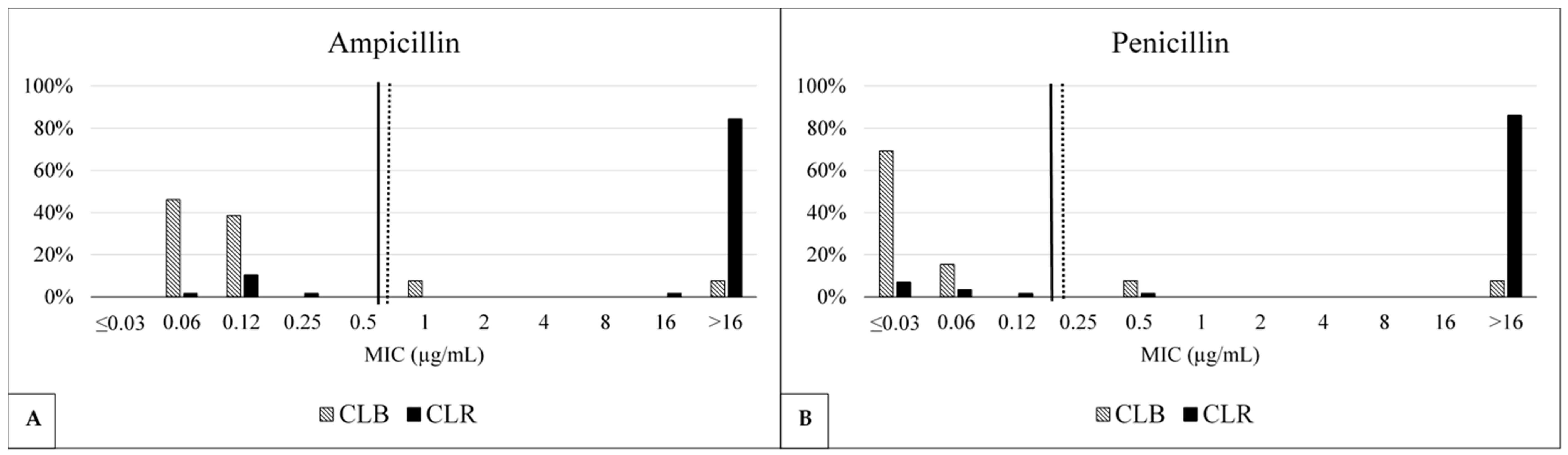
| Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobial (µg/mL) | (T)ECOFF (μg/mL) | Non-WT (%) | CBP (μg/mL) | References and Species | Isolate (n) | R (%) | MIC50 (μg/mL) | MIC90 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminopenicillins | Amoxicillin + clavulanate | >0.5/0.25 | 0 | ≥1/0.5 | [10] Dog | CLB (13) | 0 | ≤0.12/0.06 | 0.5/0.25 |
| 68.97 | CLR (58) | 68.97 | 1/0.5 | 1/0.5 | |||||
| (0.12/0.06–32/16) | 51.22 | All (82) | 51.22 | 1/0.5 | 1/0.5 | ||||
| Ampicillin | >0.5 | 15.38 | ≥1 | [10] Horse | CLB (13) | 15.38 | 0.12 | 1 | |
| 86.21 | CLR (58) | 86.21 | >16 | >16 | |||||
| (0.03–16) | 67.07 | All (82) | 67.07 | >16 | >16 | ||||
| 1st generation Cephalosporins | Cefazolin | >2 | 0 | ≥8 | [10] Dog | CLB (13) | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 1.72 | CLR (58) | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| (0.12–8) | 1.22 | All (82) | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 3rd generation Cephalosporins | Ceftiofur | na a | - | ≥8 | [10] Cattle | CLB (13) | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| - | CLR (58) | 0 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| (0.12–32) | - | All (82) | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Quinolones | Enrofloxacin | na a | - | ≥4 | [10,11] Cat | CLB (13) | 0 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| - | CLR (58) | 0 | ≤0.12 | 0.25 | |||||
| (0.12–4) | - | All (82) | 2.44 | ≤0.12 | 0.25 | ||||
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | >1 | 0 | ≥8 | [10] Human | CLB (13) | 0 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 3.45 | CLR (58) | 3.45 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | |||||
| (0.12–8) | 3.66 | All (82) | 3.66 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | ||||
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | >2 | 0 | ≥16 | [10] Human | CLB (13) | 0 | ≤2 | ≤2 |
| 3.45 | CLR (58) | 0 | ≤2 | ≤2 | |||||
| (2–32) | 4.88 | All (82) | 2.44 | ≤2 | ≤2 | ||||
| Kanamycin | na a | - | ≥16 | [12] b | CLB (13) | 0 | ≤4 | ≤4 | |
| - | CLR (58) | 3.75 | ≤4 | ≤4 | |||||
| (4–32) | - | All (82) | 4.88 | ≤4 | ≤4 | ||||
| Antistaphylococcal penicillins | Oxacillin | >2 | 0 | ≥4 | [10] Human | CLB (13) | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 0 | CLR (58) | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| (0.12–4) | 0 | All (82) | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Benzylpenicillins | Penicillin | >0.12 | 15.38 | ≥0.25 | [10] Human | CLB (13) | 15.38 | ≤0.03 | 0.5 |
| 87.93 | CLR (58) | 87.93 | >16 | >16 | |||||
| (0.03–16) | 69.51 | All (82) | 69.51 | >16 | >16 | ||||
| Rifamycins | Rifampin | na a | - | ≥0.12 | [12] b | CLB (13) | 7.60 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 |
| - | CLR (58) | 10.34 | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | |||||
| (0.06–2) | - | All (82) | 9.75 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ||||
| Sulfonamides | Trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole | >0.25/4.75 | 0 | ≥4/76 | [10] Human | CLB (13) | 0 | 0.25/4.75 | 0.25/4.75 |
| 0 | CLR (58) | 0 | 0.12/2.37 | 0.12/2.37 | |||||
| (0.12/2.37–4/76) | 2.44 | All (82) | 2.44 | 0.12/2.37 | 0.25/4.75 |
| Isolate (n) | Antimicrobial Resistance | Virulence Genes | Biofilm Formation | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaZ | clfA | lukE-lukD | chp | fmtB | cna | hla | hlb | icaA | icaB | icaC | icaD | |||||||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| GTRI (30) | 28 | 93.3 | 22 | 78.6 | 30 | 100 | 4 | 13.3 | 18 | 60 | 14 | 46.7 | 29 | 96.7 | 23 | 76.7 | 30 | 100 | 30 | 100 | 30 | 100 | 30 | 100 |
| GTB (8) | 5 | 62.5 | 7 | 87.5 | 8 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 62.5 | 5 | 55.6 | 8 | 100 | 7 | 87.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Year | 2022 | 2022 | 2021 2022 | 2021 2022 | 2021 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm | Parity (n) | SCC a (cells/mL) | DDDAit b | IMM c LCT d DDDAit b | IMM c DCT e DDDAit b |
| 1 | 3.6 | 70.000 | 3.78 1.47 | 1.63 0.66 | 1.84 0.16 |
| 2 | 2.8 | 409.000 | 2.34 2.14 | 0.69 0.83 | 0.0 0.0 |
| 3 | 3.4 | 124.000 | 13.89 5.61 | 3.29 2.84 | 5.03 0.25 |
| 4A f | 4.2 | 561.000 | 6.50 0.51 | 0.33 0.00 | 3.98 0.0 |
| 4B f | 4.2 | 561.000 | 3.03 3.54 | 0.20 0.00 | 1.57 1.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monistero, V.; Hossain, D.; Fusar Poli, S.; de Medeiros, E.S.; Cremonesi, P.; Castiglioni, B.; Biscarini, F.; Graber, H.U.; Mochettaz, G.; Ganio, S.; et al. Prevalence of Variant GTRIStaphylococcus aureus Isolated from Dairy Cow Milk Samples in the Alpine Grazing System of the Aosta Valley and Its Association with AMR and Virulence Profiles. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040348
Monistero V, Hossain D, Fusar Poli S, de Medeiros ES, Cremonesi P, Castiglioni B, Biscarini F, Graber HU, Mochettaz G, Ganio S, et al. Prevalence of Variant GTRIStaphylococcus aureus Isolated from Dairy Cow Milk Samples in the Alpine Grazing System of the Aosta Valley and Its Association with AMR and Virulence Profiles. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040348
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonistero, Valentina, Delower Hossain, Sara Fusar Poli, Elizabeth Sampaio de Medeiros, Paola Cremonesi, Bianca Castiglioni, Filippo Biscarini, Hans Ulrich Graber, Giulia Mochettaz, Sandra Ganio, and et al. 2025. "Prevalence of Variant GTRIStaphylococcus aureus Isolated from Dairy Cow Milk Samples in the Alpine Grazing System of the Aosta Valley and Its Association with AMR and Virulence Profiles" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040348
APA StyleMonistero, V., Hossain, D., Fusar Poli, S., de Medeiros, E. S., Cremonesi, P., Castiglioni, B., Biscarini, F., Graber, H. U., Mochettaz, G., Ganio, S., Gazzola, A., Addis, M. F., Roullet, C., Barberio, A., Deotto, S., Biasio, L., Ulloa, F., Galanti, D., Bronzo, V., & Moroni, P. (2025). Prevalence of Variant GTRIStaphylococcus aureus Isolated from Dairy Cow Milk Samples in the Alpine Grazing System of the Aosta Valley and Its Association with AMR and Virulence Profiles. Antibiotics, 14(4), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040348











