Infective Spondylitis in Adults: A Journey Through Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Vertebral Osteomyelitis
2.1. Overall
2.2. Epidemiology
2.3. Etiology
3. Discitis
3.1. Overall
3.2. Epidemiology
3.3. Etiology
4. Epidural Abscess
4.1. Overall
4.2. Epidemiology
4.3. Etiology
5. Subdural or Intradural Abscess
6. Paraspinal Muscle Abscess
6.1. Overall
6.2. Epidemiology
6.3. Etiology
7. Diagnosis of the Spinal Infection
7.1. Symptoms
7.2. Laboratory Tests
- Worsening local pain accompanied by fever;
- New or worsening local pain along with increased ESR or CRP levels;
- New or worsening local pain with sepsis or infective endocarditis;
- Fever combined with new neurological symptoms, with or without local pain;
- New local pain after a recent episode of sepsis caused by S. aureus.
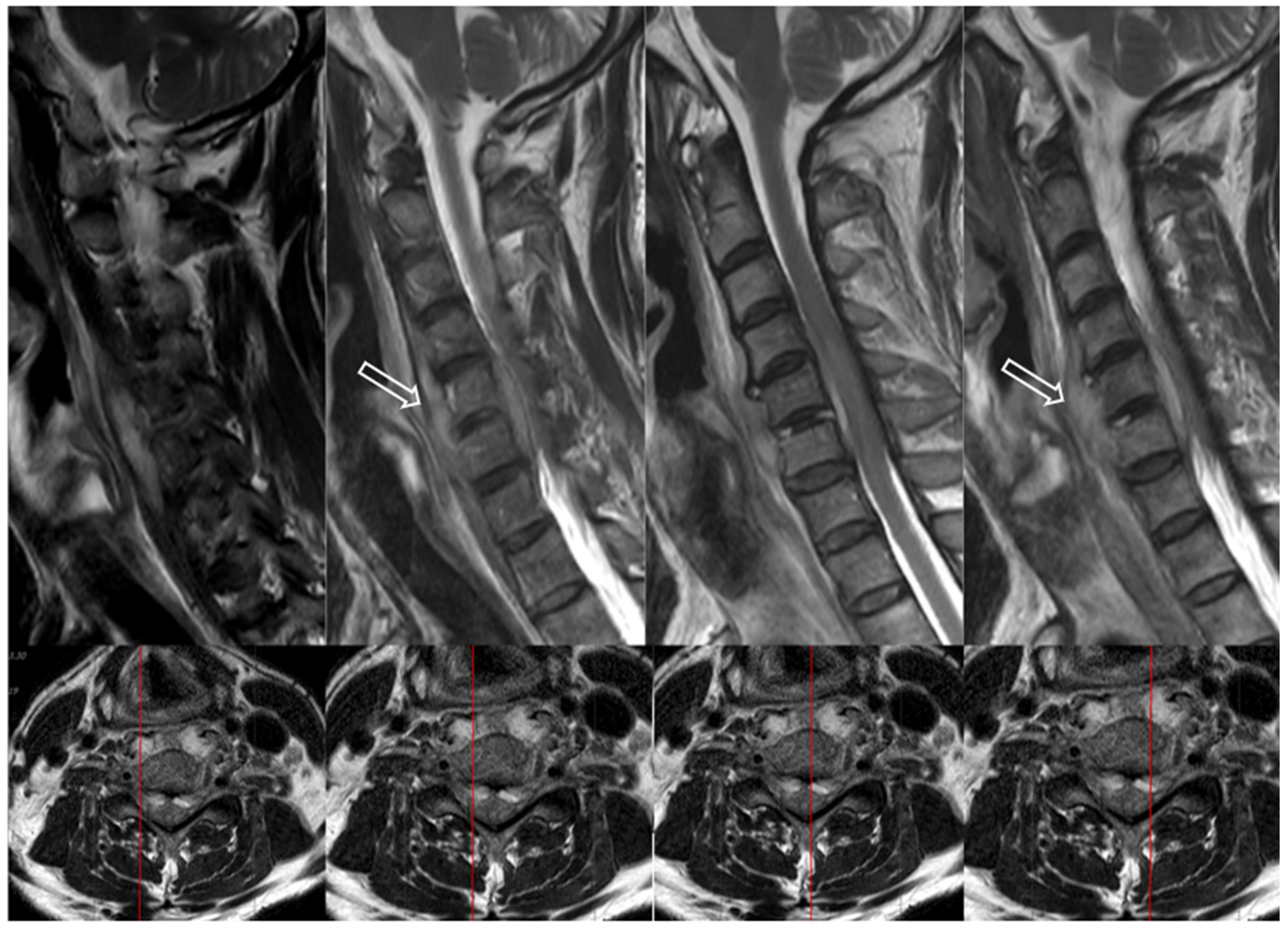
7.3. Imaging Tests
7.4. Bacteriological Tests
8. Postoperative Infection
8.1. Overall
8.2. Epidemiology
8.3. Etiology
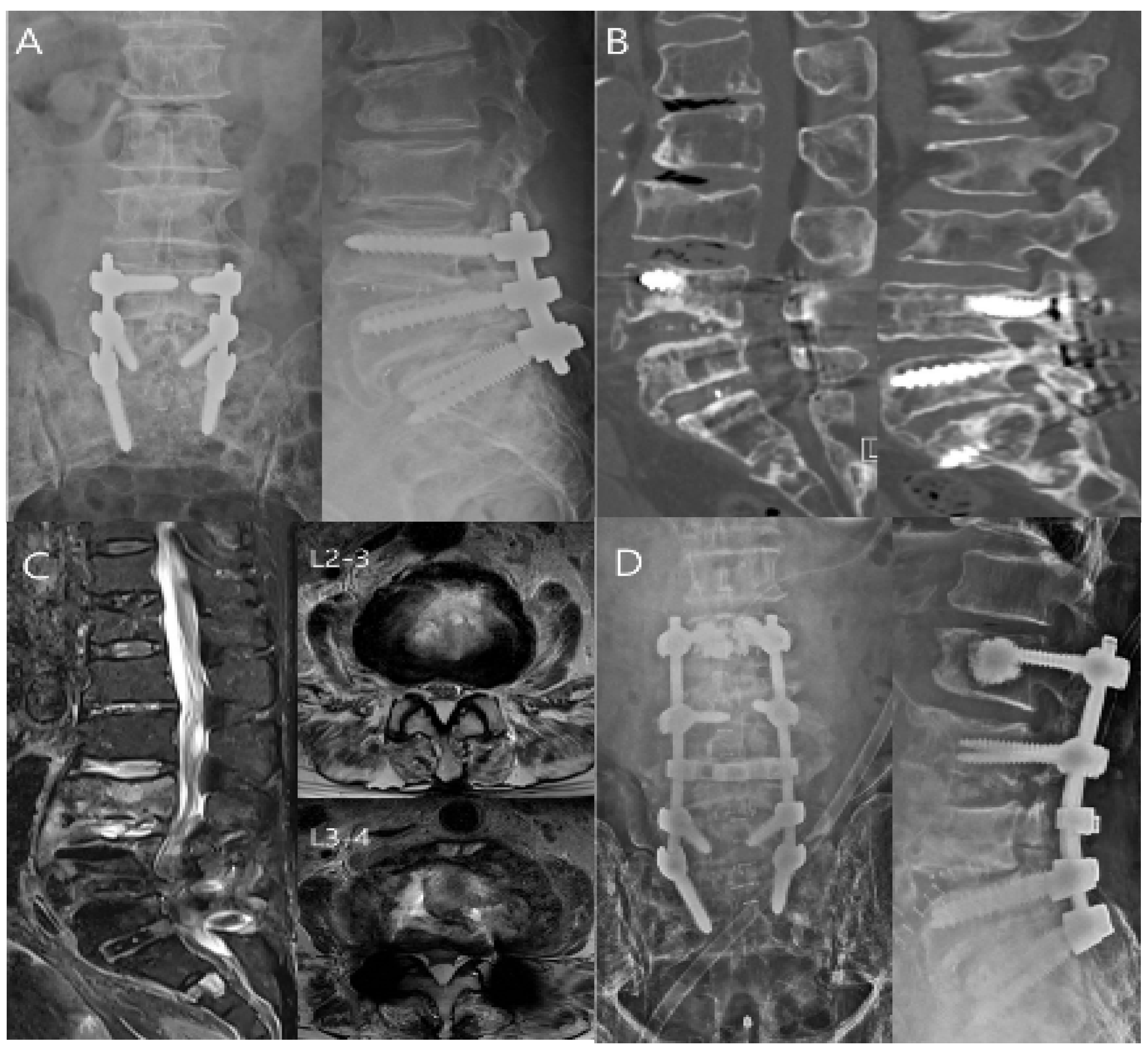
9. Treatment of the Spinal Infection
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Govender, S. Spinal infections. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2005, 87, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, E.; Samarkos, M.; Kakalou, E.; Fanourgiakis, P.; Skoutelis, A. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: A systematic review of clinical characteristics. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 39, pp. 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Skaf, G.S.; Domloj, N.T.; Fehlings, M.G.; Bouclaous, C.; Sabbagh, A.S.; Kanafani, Z.A.; Kanj, S. Pyogenic spondylodiscitis: An overview. J. Infect. Public Health 2010, 3, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunoki, M. A Comprehensive Review of Pyogenic Spondylitis Management for Neurosurgeons. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2023, 18, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W. Vertebral osteomyelitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Oh, J.-K.; Kim, Y.-W.; Park, M.S.; Kim, T.-H. Treatment outcomes in patients with pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis who have cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Kwon, J.W.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, E.H.; Jung, I.; Moon, S.H.; Suk, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, B.H. Effect of Preoperative Acupuncture and Epidural Steroid Injection on Early Postoperative Infection After Lumbar Spinal Fusion. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2024, 107, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Infectious discitis and spondylodiscitis in children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, K.; Diebo, B.G.; Faloon, M.; Naziri, Q.; Pourtaheri, S.; Paulino, C.B.; Emami, A. The Epidemiology of Vertebral Osteomyelitis in the United States From 1998 to 2013. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E102–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, E.K.; Sinha, R. Vertebral osteomyelitis in adults: An update. Br. Med. Bull. 2016, 117, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, E.F.; Kanj, S.S.; Kowalski, T.J.; Darouiche, R.O.; Widmer, A.F.; Schmitt, S.K.; Hendershot, E.F.; Holtom, P.D.; Huddleston, P.M., 3rd; Petermann, G.W.; et al. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, e26–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottle, L.; Riordan, T. Infectious spondylodiscitis. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani, M.; Ahmadvand, A.; Yazdanian, T.; Azimi, P.; Askariardehjani, N. Value of Spinal Infection Treatment Evaluation Score, Pola Classification, and Brighton Spondylodiscitis Score from Decision to Surgery in Patients with Spondylodiscitis: A Receiver-Operating Characteristic Curve Analysis. Asian Spine J. 2024, 18, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Carrol, C.L.; Baker, C.J. Discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis in children: An 18-year review. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, V.; Hughes, P.; Soni, B.; Oo, T. Discitis following urinary tract infection manifesting as recurrent autonomic dysreflexia related to truncal movements in a person with tetraplegia. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e238202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuo, C.-Y.; Fu, Y.-C.; Lu, Y.-M.; Chen, J.-C.; Shen, W.-J.; Yang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Spinal infection in intravenous drug abusers. Clin. Spine Surg. 2007, 20, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, D.A.; Gandham, S.; DeMatas, M. The diagnosis and management of discitis and spinal infection. Surgery 2021, 39, 540–546. [Google Scholar]
- Conaughty, J.M.; Chen, J.; Martinez, O.V.; Chiappetta, G.; Brookfield, K.F.; Eismont, F.J. Efficacy of linezolid versus vancomycin in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus discitis: A controlled animal model. Spine 2006, 31, E830–E832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, N.E. A review of complication rates for anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion (ACDF). Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Zhao, K.; Dong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Maimaiti, A.; Tian, P. Analysis of risk factors for surgical site infection in spinal surgery patients and study of direct economic losses. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, P.; Bregenzer, T.; Zimmerli, W. Spinal epidural abscess in clinical practice. QJM Int. J. Med. 2008, 101, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouiche, R.O. Spinal epidural abscess. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradilla, G.; Ardila, G.P.; Hsu, W.; Rigamonti, D. Epidural abscesses of the CNS. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reihsaus, E.; Waldbaur, H.; Seeling, W. Spinal epidural abscess: A meta-analysis of 915 patients. Neurosurg. Rev. 2000, 23, 175–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, M.; Panuncialman, I.; Lucas, P.; Palumbo, M. Spinal Epidural Abscess. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 39, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.S.; Ojemann, R.G.; Swartz, M.N.; Richardson, E.P., Jr. Spinal Epidural Abscess. N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 293, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, P. Spinal epidural abscesses: Conservative treatment for selected subgroups of patients. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 17, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszynski, A.E.; Hooten, W.M.; Huntoon, M.A. The incidence of spontaneous epidural abscess in Olmsted County from 1990 through 2000: A rare cause of spinal pain. Pain Med. 2007, 8, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.M.; Counsell, D.; Wildsmith, J.A. Major complications of central neuraxial block: Report on the Third National Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, R.; Smiley, R.M.; Riley, E.T.; Segal, S. Serious complications related to obstetric anesthesia: The serious complication repository project of the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, C.; Neundörfer, B.; Winterholler, M. Iatrogenic (para-) spinal abscesses and meningitis following injection therapy for low back pain. Pain 2005, 116, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Cho, O.H.; Jung, M.; Suk, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Ryu, K.N.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Choi, S.H.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of hematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis caused by gram-negative bacteria. J. Infect. 2014, 69, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, M.; Crum-Cianflone, N.F. Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Series of 101 Cases. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, H.; Andersen, S.; Andersen, O.; Gahrn-Hansen, B.; Siboni, K. Infections following epidural catheterization. J. Hosp. Infect. 1995, 30, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, E.S.; Rigamonti, D.; Standiford, H.; Numaguchi, Y.; Wolf, A.L.; Robinson, W.L. Spinal epidural abscess: A report of 40 cases and review. Surg. Neurol. 1992, 38, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.G.; Chu, G.; Fehlings, M.G. Pyogenic intradural abscess. Spine 2007, 32, E354–E357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.H.; de Jong, T.R.; Grotenhuis, J.A. Spinal subdural abscess. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 76, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velissaris, D.; Aretha, D.; Fligou, F.; Filos, K.S. Spinal Subdural Staphylococcus Aureus Abscess: Case report and review of the literature. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2009, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, H.; Alpers, B.J. Spinal subdural abscess. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1948, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorar, M.; Er, U.; Seçkin, H.; Ozturk, M.H.; Bavbek, M. Spinal subdural abscess: A rare cause of low back pain. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Blandino, A.; Romano, A.; Palizzi, S.; Moltoni, G.; Acqui, M.; Miscusi, M.; Bozzao, A. Intradural abscess: A challenging diagnosis. Case series and review of the literature. Radiol. Case Rep. 2023, 18, 4140–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, D.; Robinson, P.; Crowley, T.P. Iliopsoas abscess—A review and update on the literature. Int. J. Surg. 2012, 10, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, V.N.; Ramos, J.M.; Meseguer, V.; Pérez Arellano, J.L.; Serrano, R.; Ordóñez, M.A.G.; Peralta, G.; Boix, V.; Pardo, J.; Conde, A.; et al. Microbiology and outcome of iliopsoas abscess in 124 patients. Medicine 2009, 88, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapico, F.L.; Montgomerie, J.Z. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: Report of nine cases and review of the literature. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1979, 1, 754–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, H.; Tanishima, S.; Tanida, A. Diagnosis and management of spinal infections. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, C.E., III.; Wilkins, R.H.; Gallis, H.A.; Goldner, L.J.; Francis, R. Postoperative intervertebral disc space infection. Neurosurgery 1983, 13, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Yamada, K.; Yokosuka, K.; Yoshida, T.; Goto, M.; Matsubara, T.; Iwahashi, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Nagata, K.; Shiba, N. Pyogenic spondylitis: Clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. Kurume Med. J. 2018, 65, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeller, P.; Fazekas, F.; Krametter, D.; Koch, M.; Roob, G.; Schmidt, R.; Offenbacher, H. Pyogenic infectious spondylitis: Clinical, laboratory and MRI features. Eur. Neurol. 1997, 38, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemionow, K.; Steinmetz, M.; Bell, G.; Ilaslan, H.; McLain, R.F. Identifying serious causes of back pain: Cancer, infection, fracture. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2008, 75, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, A.D.; Carrol, E.D. Procalcitonin. Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2011, 96, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.-K.; Lee, H.-W.; Kwon, Y.-M. Clinical value of procalcitonin in patients with spinal infection. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2015, 58, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modic, M.T.; Feiglin, D.H.; Piraino, D.W.; Boumphrey, F.; Weinstein, M.A.; Duchesneau, P.M.; Rehm, S. Vertebral osteomyelitis: Assessment using MR. Radiology 1985, 157, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Igoumenou, V.G.; Panagopoulos, G.N.; Giannitsioti, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Papagelopoulos, P.J. Spondylodiscitis revisited. EFORT Open Rev. 2017, 2, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, N.; Faruch, M.; Lapègue, F.; Ponsot, A.; Chiavassa, H.; Railhac, J.J. Infections of the spinal column—Spondylodiscitis. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, H.S. Role of MR imaging in the management of spinal infections. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 158, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stäbler, A.; Reiser, M.F. Imaging Of Spinal Infection. Radiol. Clin. 2001, 39, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, D.; Solà, O.; Soriano, A.; Monegal, A.; Setoain, X.; Tomás, X.; Garcia, S.; Mensa, J.; Rubello, D.; Pons, F. A Prospective Study Comparing Whole-Body FDG PET/CT to Combined Planar Bone Scan With 67Ga SPECT/CT in the Diagnosis of Spondylodiskitis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, H.; Nanjo, Y.; Tanida, A.; Dokai, T.; Teshima, R. Clinical features of spinal infection in individuals older than eighty years. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lucas, E.M.; González Mandly, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Pellón, R.; Martín-Cuesta, L.; Izquierdo, J.; Sánchez, E.; Ruiz, E.; Quintana, F. CT-guided fine-needle aspiration in vertebral osteomyelitis: True usefulness of a common practice. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Currier, B.L.; Eismont, F.J. Infections of the Spine. In Rothman-Simeone the Spine, 6th ed.; Herkowitz, H.N., Garfin, S.R., Eismont, F.J., Bell, G.R., Balderston, R.A., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1513–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, K.; Gupta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, C.; Rao, P.S.; Bhat, S.S. PCR for M. tuberculosis in tissue samples. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2009, 3, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, V.; Barker, R.H., Jr. A simple method for diagnosing M. tuberculosis infection in clinical samples using PCR. Mol. Cell. Probes 1991, 5, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bible, J.E.; Biswas, D.; Devin, C.J. Postoperative infections of the spine. Am. J. Orthop. 2011, 40, E264–E271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.R.; Kwon, J.W.; Suk, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Moon, S.E.; Lee, B.H. Effectiveness of Toothbrushing Technique for Biofilm Removal and Postoperative Infection Control after Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Retrospective Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lener, S.; Hartmann, S.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Certo, F.; Thome, C.; Tschugg, A. Management of spinal infection: A review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.D.; Evangelisti, G.; Andreani, L.; Girardi, F.; Darren, L.; Sama, A.; Lisanti, M. Postoperative spine infections. Orthop. Rev. 2015, 7, 5900. [Google Scholar]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Oh, J.-K.; Kim, Y.-W.; Kim, T.-H. Outcomes of additional instrumentation in elderly patients with pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and previous spinal instrumentation. Spine J. 2019, 19, 1498–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartveldt, S.; Janssen, S.J.; Wood, K.B.; Cha, T.D.; Schwab, J.H.; Bono, C.M.; Jenis, L.G. Is there an association of epidural corticosteroid injection with postoperative surgical site infection after surgery for lumbar degenerative spine disease? Spine 2016, 41, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seavey, J.G.; Balazs, G.C.; Steelman, T.; Helgeson, M.; Gwinn, D.E.; Wagner, S.C. The effect of preoperative lumbar epidural corticosteroid injection on postoperative infection rate in patients undergoing single-level lumbar decompression. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooten, W.M.; Eberhart, N.D.; Cao, F.; Gerberi, D.J.; Moman, R.N.; Hirani, S. Preoperative Epidural Steroid Injections and Postoperative Infections After Lumbar or Cervical Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2023, 7, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.A.; Cheppalli, N.S.; Bhandarkar, A.W.; Patel, V.; Singla, A. Lumbar spinal steroid injections and infection risk after spinal surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnally, C.J., III.; Rush, A.J., III.; Rivera, S.; Vakharia, R.M.; Vakharia, A.M.; Massel, D.H.; Eismont, F.J. An epidural steroid injection in the 6 months preceding a lumbar decompression without fusion predisposes patients to post-operative infections. J. Spine Surg. 2018, 4, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, A.; Yang, S.; Werner, B.C.; Cancienne, J.M.; Nourbakhsh, A.; Shimer, A.L.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Shen, F.H. The impact of preoperative epidural injections on postoperative infection in lumbar fusion surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 26, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Issa, T.Z.; Kanhere, A.P.; Lambrechts, M.J.; Ciesielka, K.-A.; Kim, J.; Hilibrand, A.S.; Kepler, C.K.; Schroeder, G.D.; Vaccaro, A.R. Preoperative epidural steroid injections do not increase the risk of postoperative infection in patients undergoing lumbar decompression or fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 3251–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitz, T.M.; Mangan, J.; Schroeder, G.D.; Kepler, C.K.; Kurd, M.F.; Radcliff, K.E.; Woods, B.I.; Rihn, J.A.; Anderson, D.G.; Vaccaro, A.R. Do preoperative epidural steroid injections increase the risk of infection after lumbar spine surgery? Spine 2021, 46, E197–E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, S.; Kim, E.H.; Kwon, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.B.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, H.M.; Jung, I.; Lee, B.H. Invasive dental procedures as risk factors for postoperative spinal infection and the effect of antibiotic prophylaxis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Jabbar, A.; Berven, S.H.; Hu, S.S.; Chou, D.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Takemoto, S.; Ames, C.; Deviren, V.; Tay, B.; Weinstein, P.; et al. Surgical site infections in spine surgery: Identification of microbiologic and surgical characteristics in 239 cases. Spine 2013, 38, E1425–E1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Khoury, H.; Girgenti, D.; Welner, S.; Yu, H. Burden of surgical site infections associated with select spine operations and involvement of Staphylococcus aureus. Surg. Infect. 2017, 18, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Gunne, A.F.P.; Mohamed, A.S.; Skolasky, R.L.; Van Laarhoven, C.J.; Cohen, D.B. The presentation, incidence, etiology, and treatment of surgical site infections after spinal surgery. Spine 2010, 35, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiades, N.G.; Shao, B.; Ahn, E.S.; Blount, J.P.; Brockmeyer, D.L.; Hankinson, T.C.; Nesvick, C.L.; Sandberg, D.I.; Heuer, G.G.; Saiman, L. High prevalence of gram-negative and multiorganism surgical site infections after pediatric complex tethered spinal cord surgery: A multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2022, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramo, B.A.; Roberts, D.W.; Tuason, D.; McClung, A.; Paraison, L.E.; Moore, H.G., IV.; Sucato, D.J. Surgical site infections after posterior spinal fusion for neuromuscular scoliosis: A thirty-year experience at a single institution. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Papadopoulos, D.V.; Vrioni, G.; Sioutis, S.; Sapkas, G.; Benzakour, A.; Benzakour, T.; Angelini, A.; Ruggieri, P.; Mavrogenis, A.F. Spinal infections: An update. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, D.; Gottlieb, J.; Chan, S.; Martinez, O.; Eismont, F. Fungal infections of the spine. Spine 2015, 40, E719–E728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragee, E.J. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1997, 79, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courjon, J.; Lemaignen, A.; Ghout, I.; Therby, A.; Belmatoug, N.; Dinh, A.; Gras, G.; Bernard, L.; Group, D.S. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis of the elderly: Characteristics and outcomes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, T. Clinical characteristics of patients with pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and concurrent infections and their clinical outcomes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, X.; He, K.; Song, Q.; Yin, R. Current knowledge of vertebral osteomyelitis: A review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 44, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Bian, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, W.; Hou, C.; Zhu, L. Unilateral percutaneous endoscopic debridement and drainage for lumbar infectious spondylitis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, Z. A comprehensive clinical analysis of the use of percutaneous endoscopic debridement for the treatment of early lumbar epidural abscesses. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1215240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Liu, D.; Meng, F.-H.; Lu, J.-H.; Fan, Z. Full-Endoscopic Transforaminal Debridement and Decompression for Brucellar Thoracic Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Minimally Invasive Alternative to Open Surgery. Orthop. Surg. 2024, 16, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.-H. Treatment guideline for patients with native culture-negative pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2022, 480, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.Y.; Luk, K.D. Pyogenic spondylitis. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilinc, F.; Setzer, M.; Gessler, F.; Prinz, V.; Jussen, D.; Czabanka, M.; Freiman, T.; Behmanesh, B. Key Predictors of Treatment Failure in Conservatively Managed Spondylodiscitis: A Long-Term Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, M.; Walter, N.; Reinhard, J.; Pagano, S.; Szymski, D.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M.; Lang, S. Midterm survival and risk factor analysis in patients with pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: A retrospective study of 155 cases. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1357318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcellos, F.D.N.; Mashiach, E.; Bhanja, D.; Page, J.; Halalmeh, D.R. Outcomes, complications, and prognosis. In Osteomyelitis and Discitis of the Spine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 405–428. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, G.; Soliman, M.A.; Ali, A.M.; Aly, M.H. Spontaneous spondylodiscitis: Review, incidence, management, and clinical outcome in 44 patients. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Chikuda, H.; Yasunaga, H.; Horiguchi, H.; Fushimi, K.; Saita, K. Incidence and risk factors for mortality of vertebral osteomyelitis: A retrospective analysis using the Japanese diagnosis procedure combination database. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.-H. Clinical outcomes in older patients aged over 75 years who underwent early surgical treatment for pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.; Oh, J.; Park, M.; Chang, H.; Kim, T. The outcome following spinal instrumentation in haemodialyzed patients with pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.; von der Hoeh, N.H.; Zwingenberger, S.; Sauer, D.; Jung, N.; Pieroh, P.; Drange, S.; Pumberger, M.; Scheyerer, M.J.; Spine Section of the German Society for Orthopaedics and Trauma; et al. Spondylodiscitis in geriatric patients: What are the issues? Glob. Spine J. 2023, 13, 73S–84S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüer, C.; Stoffel, M.; Hecker, J.; Ringel, F.; Meyer, B. A staged treatment algorithm for spinal infections. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2013, 74, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipavlou, A.G.; Mader, J.T.; Necessary, J.T.; Muffoletto, A.J. Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine 2000, 25, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimar, J.R.; Carreon, L.Y.; Glassman, S.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Hartman, M.J.; Johnson, J.R. Treatment of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with anterior debridement and fusion followed by delayed posterior spinal fusion. Spine 2004, 29, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.C.; Wang, V.; Chou, D. The use of allograft or autograft and expandable titanium cages for the treatment of vertebral osteomyelitis. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.T.; Lee, Y.P.; Stimson, E.; Garfin, S.R. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) in the treatment of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Spine 2007, 32, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chang, H.-K.; Lu, M.-L.; Wegner, A.; Wu, R.-W.; Yin, T.-C. Transforaminal interbody debridement and fusion with antibiotic-impregnated bone graft to treat pyogenic discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis: A comparative study in Asian population. Asian Spine J. 2025, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Suk, K.S.; Kwon, J.W.; Moon, S.H.; Ju, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Abdou, M. Cervical transpedicular irrigation and drainage in a patient with cervical spondylodiscitis after hypopharyngeal cancer treatment: A case report. J. Clin. Med. Images 2023, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.H.; Lee, H.-M.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Moon, E.-S.; Park, J.-O.; Chong, H.-S.; Moon, S.-H. Transpedicular Curettage and Drainage of Infective Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Technique and Clinical Results. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2012, 4, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xing, W.; Xing, H.; Bai, Y.; Chang, Z. Safety and efficacy of negative pressure wound therapy in treating deep surgical site infection after lumbar surgery. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.A.; Butler, J.; Lieberman, I.; Schlenk, R. Negative-pressure wound therapy in the treatment of complex postoperative spinal wound infections: Complications and lessons learned using vacuum-assisted closure. J. Neurosurg. Spine SPI 2007, 6, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, Z. Case Report: A spinal infection with bilateral psoas abscesses was treated with NPWT to enhance the local infection by increasing the infiltration of neutrophil cells and draining the pus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1228376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeenko, M.O.; Korostelev, Y.M.; Shikhaleva, G.N.; Savin, M.D.; Filatov, Y.E.; Ryabykh, O.S. Negative pressure wound therapy in cases of spinal surgery and exposed dura: A case-based review. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavese, F.; Marengo, L.; Corradin, M.; Mansour, M.; Samba, A.; Andreacchio, A.; Rousset, M.; Dimeglio, A. Deep postoperative spine infection treated by negative pressure therapy in patients with progressive spinal deformities. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2018, 138, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ousey, K.J.; Atkinson, R.A.; Williamson, J.B.; Lui, S. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) for spinal wounds: A systematic review. Spine J. 2013, 13, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Yang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yu, X.; Chang, Z. A Comparison of Negative Pressure and Conventional Therapy in Spine Infections: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adogwa, O.; Fatemi, P.; Perez, E.; Moreno, J.; Gazcon, G.C.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Cheng, J.; Gottfried, O.; Bagley, C.A. Negative pressure wound therapy reduces incidence of postoperative wound infection and dehiscence after long-segment thoracolumbar spinal fusion: A single institutional experience. Spine J. 2014, 14, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolak, P.; König, M.A.; Osterhoff, G.; Wilzeck, V.; Simmen, H.P.; Jukema, G.N. Therapy of acute and delayed spinal infections after spinal surgery treated with negative pressure wound therapy in adult patients. Orthop. Rev. 2013, 5, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, K.; Takahashi, N.; Rikimaru, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Inoue, Y. New Continuous Negative-Pressure and Irrigation Treatment for Infected Wounds and Intractable Ulcers. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshian, J.; Dahdaleh, N.S.; Lam, S.K.; Savage, J.W.; Smith, Z.A. The use of vancomycin powder in modern spine surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical evidence. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, D.C.; Suk, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, J.W.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.H. Is Vancomycin More Effective than Taurolidine? Comparative Analysis of Their Preventive Effect against Spinal Infection in 1000 Patients with Spinal Fusion. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Meredith, D.S.; Kepler, C.K.; Huang, R.C. Management of postoperative spinal infections. World J. Orthop. 2012, 3, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Silvestre, M.; Bakaloudis, G.; Lolli, F.; Giacomini, S. Late-developing infection following posterior fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20 (Suppl. S1), S121–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedney, C.L.; Daffner, S.D.; Stefanko, J.J.; Abdelfattah, H.; Emery, S.E.; France, J.C. Fracture of fusion mass after hardware removal in patients with high sagittal imbalance. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhael, M.M.; Huddleston, P.M.; Nassr, A. Postoperative culture positive surgical site infections after the use of irradiated allograft, nonirradiated allograft, or autograft for spinal fusion. Spine 2009, 34, 2466–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowdell, J.; Brochin, R.; Kim, J.; Overley, S.; Oren, J.; Freedman, B.; Cho, S. Postoperative Spine Infection: Diagnosis and Management. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 37s–43s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, J.G. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1979, 1, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, L.V. Epidemiology, risk factors and treatments for antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Dig. Dis. 1999, 16, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Guo, L. Combined administration of antibiotics increases the incidence of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in critically ill patients. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.S. Antibiotic-induced increase in inflammatory markers in cured infectious spondylitis: Two case reports. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2019, 62, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignardi, G.E. Risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 1998, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimings, C.; Riley, T.V. Antibiotics and hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile infection: Update of systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensgens, M.P.; Goorhuis, A.; Dekkers, O.M.; Kuijper, E.J. Time interval of increased risk for Clostridium difficile infection after exposure to antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Kwon, J.-W.; Lee, S.-B.; Lee, H.-M.; Moon, S.-H.; Lee, B.H. Risk factors of clostridium difficile infection after spinal surgery: National health insurance database. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S.; Costerton, J.W. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, B.R.; Kurupati, R.B.; Shah, D.; Degulamadi, D.; Borgohain, N.; Krishnan, A. Outcome of percutaneous continuous drainage of psoas abscess: A clinically guided technique. Indian J. Orthop. 2014, 48, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mückley, T.; Schütz, T.; Kirschner, M.; Potulski, M.; Hofmann, G.; Bühren, V. Psoas Abscess: The Spine as a Primary Source of Infection. Spine 2003, 28, E106–E113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, W.N.; Sohn, H.J.; Chan, S.; Petrosyan, M.; Vermaire, H.M.; Kelso, R.L.; Towfigh, S.; Mason, R.J. Psoas abscess rarely requires surgical intervention. Am. J. Surg. 2008, 196, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.; Uusijärvi, J.; Lind, F.; Gustavsson, B.; Saraste, H. Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of postoperative infections in paediatric patients with neuromuscular spine deformity. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, W.-S.; Choi, S.-R.; Kwon, J.-W.; Suk, K.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Moon, S.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Shin, J.-W.; Lee, B.-H. Infective Spondylitis in Adults: A Journey Through Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040391
Jung W-S, Choi S-R, Kwon J-W, Suk K-S, Kim H-S, Moon S-H, Park S-Y, Shin J-W, Lee B-H. Infective Spondylitis in Adults: A Journey Through Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040391
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Woo-Seok, Sung-Ryul Choi, Ji-Won Kwon, Kyung-Soo Suk, Hak-Sun Kim, Seong-Hwan Moon, Si-Young Park, Jae-Won Shin, and Byung-Ho Lee. 2025. "Infective Spondylitis in Adults: A Journey Through Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040391
APA StyleJung, W.-S., Choi, S.-R., Kwon, J.-W., Suk, K.-S., Kim, H.-S., Moon, S.-H., Park, S.-Y., Shin, J.-W., & Lee, B.-H. (2025). Infective Spondylitis in Adults: A Journey Through Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions. Antibiotics, 14(4), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040391




