Intestinal and Extraintestinal Pathotypes of Escherichia coli Are Prevalent in Food Prepared and Marketed on the Streets from the Central Zone of Mexico and Exhibit a Differential Phenotype of Resistance Against Antibiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Fecal Coliform Bacteria from Food Samples
2.2. Pathogenic Genes Identification
2.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility
2.4. Antibiotic-Resistant Genotype
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Food Sampling and Bacterial Isolation
4.2. Biochemical Tests and Characterization of the Bacterial Wall by Gram Staining
4.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Cell Lysis
4.5. Colony PCR
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. Defining and Combating Antibiotic Resistance from One Health and Global Health Perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lv, C.; Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chang, Y.; et al. Global Antimicrobial Resistance: A System-Wide Comprehensive Investigation Using the Global One Health Index. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torumkuney, D.; de la Torre, C.; Langfeld, K.; Lopez-Turrent, N.P.; Ossaille Beltrame, C. Country Data on AMR in Mexico in the Context of Community-Acquired Respiratory Tract Infections: Links between Antibiotic Susceptibility, Local and International Antibiotic Prescribing Guidelines, Access to Medicine and Clinical Outcome. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, i43–i50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollner-Schwetz, I.; Krause, R. Therapy of Acute Gastroenteritis: Role of Antibiotics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretary of Health of Mexico State. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/761739/Mono20.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Palacio-Mejía, L.S.; Rojas-Botero, M.; Molina-Vélez, D.; García-Morales, C.; González-González, L.; Salgado-Salgado, A.L.; Hernández-Ávila, J.E.; Hernández-Ávila, M. Overview of Acute Diarrheal Disease at the Dawn of the 21st Century: The Case of Mexico. Salud Publica Mex. 2020, 62, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretary of Health of Mexico State. Twenty Main Causes of Disease in the State of Mexico; Secretary of Health of Mexico State: Mexico City, Mexico, 2021.
- Founou, R.C.; Founou, L.L.; Essack, S.Y. Clinical and Economic Impact of Antibiotic Resistance in Developing Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.M.; Wendt, A.; Coll, C.V.N.; Bohren, M.A.; Barros, A.J.D. E. coli Contamination of Drinking Water Sources in Rural and Urban Settings: An Analysis of 38 Nationally Representative Household Surveys (2014–2021). J. Water Health 2023, 21, 1834–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, J.; Yanez, F.; Sevillano, G.; Ortega-Paredes, D.; Paz y Miño, A. Ready To-Eat Street Food: A Potential Source for Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Epidemic Clones in Quito, Ecuador. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Nasrin, D.; Roose, A.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Levine, M.M. Global Burden of Diarrheal Diseases among Children in Developing Countries: Incidence, Etiology, and Insights from New Molecular Diagnostic Techniques. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6783–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, J.A.; Hatfield, K.M.; Wolford, H.; Nelson, R.E.; Olubajo, B.; Reddy, S.C.; McCarthy, N.; Paul, P.; McDonald, L.C.; Kallen, A.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infections in U.S. Hospitalized Patients, 2012–2017. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, K.; Voor In ’t Holt, A.F.; Vos, M.C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of the Clinical Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01730-17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dissasa, G.; Lemma, B.; Mamo, H. Isolation and Identification of Major Bacteria from Three Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes Live and Processed Fish, and Water Samples: Implications in Sanitary System of Fish Products. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, S.; Shimamoto, H.; Nukazawa, K.; Suzuki, Y. Growth and Decay of Fecal Indicator Bacteria and Changes in the Coliform Composition on the Top Surface Sand of Coastal Beaches during the Rainy Season. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Vidal, J.E.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; León-Sicairos, N. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Food Items in Northwestern Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Velazquez-Roman, J.; Valdez-Flores, M.A.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; Vidal, J.E.; Muro-Amador, S.; Guadrón-Llanos, A.M.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Medina-Serrano, J.; Tapia-Pastrana, G.; et al. Detection of Antimicrobial-Resistance Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Strains in Surface Water Used to Irrigate Food Products in the Northwest of Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 304, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Torres-Vitela, M.R.; Villarruel-López, A.; Gutiérrez-Alcántara, E.J.; Castro-Rosas, J. Presence of Multidrug-Resistant Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli, Enteropathogenic E. coli and Enterotoxigenic E. coli, on Raw Nopalitos (Opuntia ficus-indica L.) and in Nopalitos Salads from Local Retail Markets in Mexico. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vázquez, A.V.; Mandujano, A.; Cruz-Gonzalez, E.; Guerrero, A.; Vazquez, J.; Cruz-Pulido, W.L.; Rivera, G.; Bocanegra-García, V. Evaluation of Retail Meat as a Source of ESBL Escherichia coli in Tamaulipas, Mexico. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Hernandez, R.; Contreras-Rodriguez, A.; Hernandez-Velez, R.; Perez-Martinez, I.; Lopez-Merino, A.; Zaidi, M.B.; Estrada-Garcia, T. Mexican Unpasteurised Fresh Cheeses Are Contaminated with Salmonella Spp., Non-O157 Shiga Toxin Producing Escherichia coli and Potential Uropathogenic E. coli Strains: A Public Health Risk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua-Contreras, G.L.; Monroy-Pérez, E.; Díaz-Velásquez, C.E.; Uribe-García, A.; Labastida, A.; Peñaloza-Figueroa, F.; Domínguez-Trejo, P.; García, L.R.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Vaca, S. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Uropathogenic Strains of Escherichia coli from Mexico. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.Y.; Moreno-Flores, A.C.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Márquez-Díaz, F.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. An Evaluation of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates in Urinary Tract Infections from Aguascalientes, Mexico: Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Perales, C.; Ruiz de Chávez-Ramírez, D.; Valdez-Hibel, A. Calidad Higiénico-Sanitaria y Prácticas de Manufactura de Alimentos En Un Comedor Estudiantil En México. Univ. Salud 2024, 26, E17–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Ducoing, B.K.; Carrillo-Sanchez, A.K.; Rivera-Gutierrez, S.; Rios-Muñiz, D.; Estrada-Garcia, T.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F. In Mexico City, Fresh-Squeezed Street-Vended Orange Juice Is Contaminated with Fecal Coliforms, Escherichia coli, and Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli: A Potential Risk for Acquiring Foodborne Diseases. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e52022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Gonzalez, K.G.; Aguilar-Chairez, S.; Cerna-Cortes, J.; Soria-Herrera, R.J.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F. Microbiological Quality and Presence of Foodborne Pathogens in Fresh-Squeezed Orange Juice Samples Purchased from Street Vendors and Hygienic Practices in Morelia, Mexico. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Ramírez-Cruz, E.; Castro-Rosas, J. Presence of Indicator Bacteria, Salmonella and Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Pathotypes on Mung Bean Sprouts from Public Markets in Pachuca, Mexico. Food Control 2013, 31, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Torres-Vitela, M.d.R.; Villarruel-López, A.; Castro-Rosas, J. Presence of Some Indicator Bacteria and Diarrheagenic E. coli Pathotypes on Jalapeño and Serrano Peppers from Popular Markets in Pachuca City, Mexico. Food Microbiol. 2012, 32, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Segovia-Cruz, J.A.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Salas-Rangel, L.P.; Gutiérrez-Alcántara, E.J.; Castro-Rosas, J. Prevalence and Behavior of Multidrug-Resistant Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli, Enteropathogenic E. coli and Enterotoxigenic E. coli on Coriander. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa-Hernandez, M.C.; Cadena-Ramírez, A.; Téllez-Jurado, A.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Chávez-Urbiola, E.A.; Castro-Rosas, J. Presence of Multidrug-Resistant Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli, Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli on Fresh Cheeses from Local Retail Markets in Mexico. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, N.E.; Baumann, C.G.; Fascione, M.A. Developments in Mannose-Based Treatments for Uropathogenic Escherichia coli-Induced Urinary Tract Infections. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, T.J.; Kulesus, R.R.; Mulvey, M.A. Origins and Virulence Mechanisms of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2008, 85, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.J.; Zunino, P.; Scavone, P.; Robino, L. Selection of Effective Antibiotics for Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Intracellular Bacteria Reduction. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 542755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Sheikh, A. Emerging Themes in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, S813–S820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.M.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Velazquez-Roman, J.; Vidal, J.E.; Muro-Amador, S.; Alapizco-Castro, G.; Alberto Díaz-Quiñonez, J.; León-Sicairos, N. Surveillance of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Diarrhea Cases from Children, Adults and Elderly at Northwest of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiral, E.; Quiles, M.G.; Muñoz, L.; Moreno-Morales, J.; Alejo-Cancho, I.; Salvador, P.; Alvarez-Martinez, M.J.; Marco, F.; Vila, J. Emergence of Resistance to Quinolones and -Lactam Antibiotics in Enteroaggregative and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Causing Traveler’s Diarrhea. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huchin, C.; Briceño, M.A.; Mendoza, T.; Martínez, A.P.; Ramírez, M.A.; Torres, J.C. Prevalence and Drug-Resistance Patterns of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Shigella Species among Children with Diarrhea in Merida City, Mexico. J. Biosci. Med. 2018, 6, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Pastrana, G.; Rojas-Bautista, M.; Hernández-Pérez, P.; Santiago-Martínez, O.; Gómez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Terrazas-Luna, V.M.; Montes-Yedra, J.; Bautista-Avendaño, A.A.; García-López, E.S.; Leon-Sicairos, N.; et al. Virulence Genes, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, Phylotyping and Pathotyping of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Children in Southwest Mexico. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, M.S.; Dupont, H.L.; Connor, B.A. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Acute Diarrheal Infections in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.; Salinas, E.; Martínez, L.; Cruz-Còrdova, A.; Gonzàlez-Pedrajo, B.; Espinosa, N.; Amábile-Cuevas, C.F. Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates from an Urban Lake Receiving Water from a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Mexico City: Fecal Pollution and Antibiotic Resistance. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vázquez, A.V.; Rivera-Sánchez, G.; Lira-Méndez, K.; Reyes-López, M.Á.; Bocanegra-García, V. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes of Escherichia coli Isolated from Retail Meat in Tamaulipas, Mexico. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, C.; Clemente, L.; Moura, L.; Seyfarth, A.M.; Hansen, I.M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Amaro, A. Emergence and Clonal Spread of CTX-M-65 Producing Escherichia coli from Retail Meat in Portugal. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 653595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Rozo, J.; Pérez Pulido, R.; Grande, M.A.J.; Lucas, R.; Gálvez, A. Potentially pathogenic bacteria isolated from Paipa cheese and its susceptibility profiles to antibiotics and biocides. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Méndez, M.; Navarrete-Salazar, H.; Baltazar-Jiménez, F.; Muñoz-de la Paz, E.; Sánchez-Mawcinitt, M.F.; Gómez-Pardo, A.; Garza-González, E.; Ponce-De-León-Garduño, L.A.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Morfín-Otero, R.; et al. Emergence of Fosfomycin Resistance by Plasmid-Mediated Fos Genes in Uropathogenic ESBL-Producing E. coli Isolates in Mexico. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merida-Vieyra, J.; De Colsa- Ranero, A.; Arzate-Barbosa, P.; Arias-de la Garza, E.; Méndez-Tenorio, A.; Murcia-Garzón, J.; Aquino-Andrade, A. First Clinical Isolate of Escherichia coli Harboring Mcr-1 Gene in Mexico. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. In Virulence Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogens; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquito, S.; Ruiz, J.; Bauer, J.L.; Ochoa, T.J. Mecanismos Moleculares de Resistencia Antibiótica En Escherichia coli Asociadas a Diarrea. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2011, 28, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Environmental Factors Influencing the Development and Spread of Antibiotic Resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Islam, M.; Sharifuzzaman; Fakhruzzaman, M. Isolation and Identification of Escherichia coli and Salmonella from Poultry Litter and Feed. Isolation and Identification of Escherichia coli and Salmonella from Poultry Litter and Feed. Int. J. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2014, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Barrox, G.I.; Feltham, R.K.A. Cowan and Steel’s Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.C.; Hussey, M.A. Available online: https://asm.org/getattachment/5c95a063-326b-4b2f-98ce-001de9a5ece3/gram-stain-protocol-2886.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 13th ed.; CLSI Standard M02; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard, 9th ed.; CLSI Document M07-A9; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vineetha, N.; Sridhar, D.; Vignesh, R.A. Preparation, Standarization of Antibiotic Discs and Study of Resistance Pattern for First-Line Antibiotics in Isolates from Clinical Samples. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2015, 1, 624–631. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests; Approved Standard, 9th ed.; CLSI Document M2-A9; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- López-Saucedo, C.; Cerna, J.F.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Thompson, R.; Raul Velazquez, F.; Torres, J.; Tarr, P.I.; Estrada-García, T. Single Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction to Detect Diverse Loci Associated with Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Espinola, E.C. Identificar y Establecer La Prevalencia de Enterobacterias y Virus Entéricos Que Causan Diarrea, En Las Heces de Los Habitantes de Comunidades Indígenas de La Región de La Montaña, En El Estado de Guerrero. Bachelor’s Thesis, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, L.K.; Martin, I.; Alfa, M.; Mulvey, M. Multiplex PCR for the Detection of Tetracycline Resistant Genes. Mol. Cell Probes 2001, 15, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverstein-van Hall, M.A.; Paauw, A.; Box, A.T.A.; Blok, H.E.M.; Verhoef, J.; Fluit, A.C. Presence of Integron-Associated Resistance in the Community Is Widespread and Contributes to Multidrug Resistance in the Hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3038–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.T.H.; Chin, J.; Chapman, T.; Tran, L.T.; Coloe, P.J. Safety of Raw Meat and Shellfish in Vietnam: An Analysis of Escherichia coli Isolations for Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Genes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obe, T.; Nannapaneni, R.; Schilling, W.; Zhang, L.; Kiess, A. Antimicrobial Tolerance, Biofilm Formation, and Molecular Characterization of Salmonella Isolates from Poultry Processing Equipment. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2021, 30, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, P.; Haring, V.; Wittmann-Liehold, B.; Ashman, K.; Bagdasarian, M.; Scherzinger, E.; Scherzinger, E. Compiete Nucleotide Sequence and Gene Organization of the Broad-Host-Range Plasmid RSFlOlO. Gene 1989, 75, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.T.; Walsh, R.F.L.; Sheehan, A.E. Prebiotics and Probiotics for Depression and Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 102, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Kafle, S.; Dhungel, B.; Adhikari, N.; Shrestha, U.T.; Adhikari, B.; Banjara, M.R.; Rijal, K.R.; Ghimire, P. Detection of Oxa-48 Gene in Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Urine Samples. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndukui, J.G.; Gikunju, J.K.; Aboge, G.O.; Mwaniki, J.K.; Maina, J.N.; Mbaria, J.M. Molecular Characterization of ESBLs and QnrS Producers from Selected Enterobacteriaceae Strains Isolated From Commercial Poultry Production Systems in Kiambu County, Kenya. Microbiol. Insights 2022, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, O.B.; de Souza, E.M.; de Borba Dallagassa, C.; de Oliveira Pedrosa, F.; Klassen, G.; Irino, K.; Paludo, K.S.; de Assis, F.E.A.; Surek, M.; de Souza Santos Farah, S.M.; et al. Detection of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Using a Two-System Multiplex-PCR Protocol. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2013, 27, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna, J.F.; Nataro, J.P.; Estrada-Garcia, T. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Three Plasmid-Borne Genes of Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2138–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Terai, A.; Yuri, K.; Kurazono, H.; Takeda, Y.; Yoshida, O. Detection of Urovirulence Factors in Escherichia coli by Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1995, 12, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Meng, J.; Mcdermott, P.F.; Zhao, S. Escherichia coli from Retail Meats Carry Genes Associated with Uropathogenic Escherichia coli, but Are Weakly Invasive in Human Bladder Cell Culture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.; Bekal, S.; Sanschagrin, F.; Levesque, R.C.; Brousseau, R.; Masson, L.; Larivière, S.; Harel, J. Heterogeneity among Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Profiles of Extraintestinal Escherichia coli Isolates of Animal and Human Origin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5444–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, R.; Talavera, M.; Soriano, E.; Vázquez, J.; Gutiérrez, A. Presence of Class I Integrons in Escherichia coli from Meat Products in Federal Inspection Type(TIF) Plants in the Estado de Mexico. Vet.Méx 2013, 44, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cattoir, V.; Poirel, L.; Rotimi, V.; Soussy, C.J.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Qnr Genes in ESBL-Producing Enterobacterial Isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

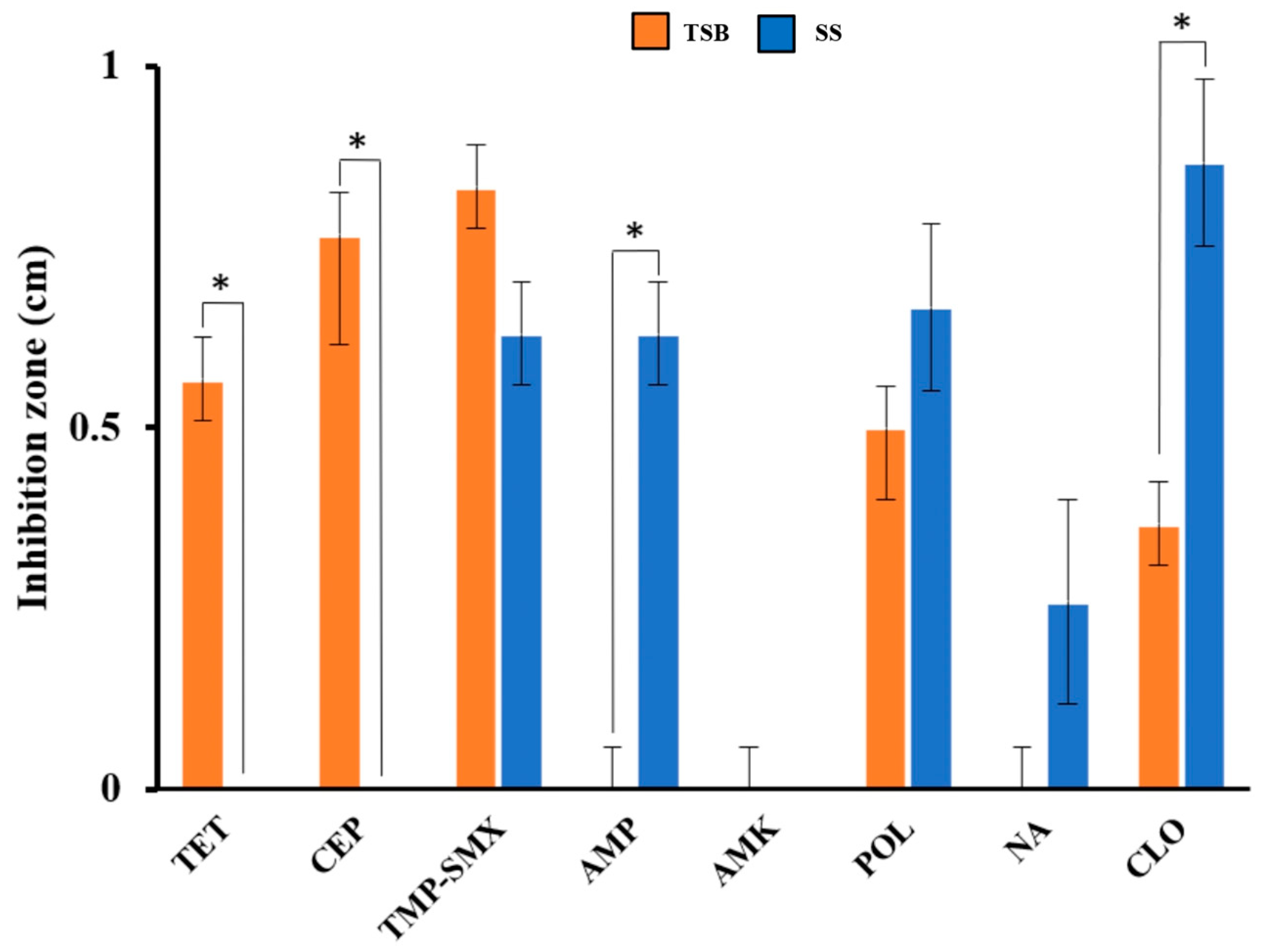
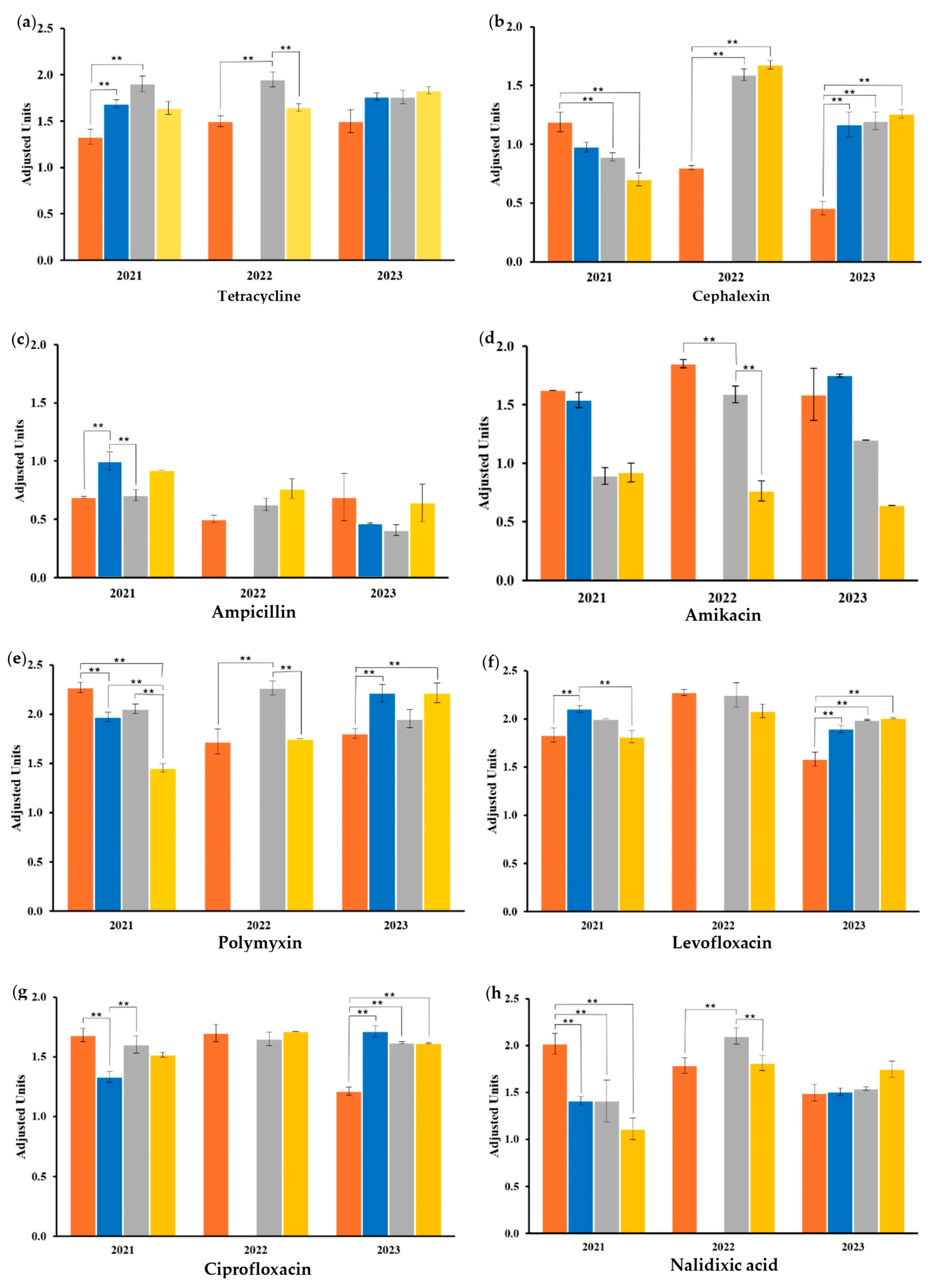
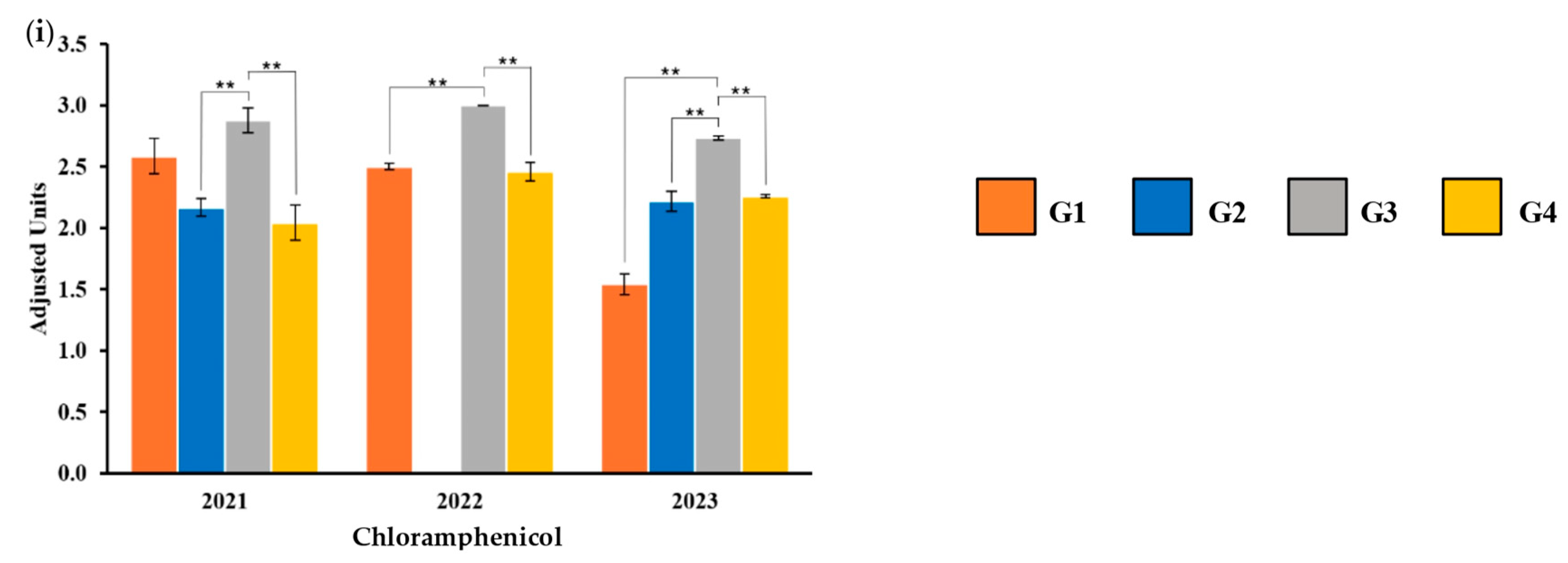


| Sample | E. coli Pathotypes | Pathogenic Genes | AR Genes | AR Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1-21 | ETEC, UPEC, DAEC | lt, afa, cnf1 | tetA, sul1, catA1 | R: AMP, NA, AMX I: CEP |
| G2-21 | UPEC, ETEC | lt, afa, vat | tetA, sul1, catA1 | R: CEP, AMP, AMX I: NA, GEN |
| G3-21 | ETEC, UPEC, DAEC | lt, cnf1, vat | tetA, sul1, catA1, strA | R: CEP, AMP, CIP I: NA |
| G4-21 | ETEC, UPEC, DAEC | lt, afa, cnf1, vat | tetA, sul1, catA1 | R: CEP, AMP, AMX I: NA, CLO, GEN |
| G1-22 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, cnf1, vat | tetA, sul1, catA1, qnrS | R: CEP, AMP, AMX |
| G3-22 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, hlyA, cnf1, vat | tetA, sul1, catA1, strA, floR | R: AMP, AMX I: CEP, AMK |
| G4-22 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, cnf1, vat | tetA, sul1, catA1, strA, floR, qnrS | R: AMP, AMX |
| G1-23 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, cnf1, vat | catA1, floR | R: CEP, AMP, AMX |
| G2-23 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, cnf1, vat | floR | R: AMP, AMX I: CEP |
| G3-23 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, cnf1, vat | R: AMP, AMX I: CEP | |
| G4-23 | ETEC, UPEC | lt, cnf1 | floR | R: AMP, AMX I: CEP |
| Antibiotic | G1-21 | G1-22 | G1-23 | G2-21 | G2-23 | G3-21 | G3-22 | G3-23 | G4-21 | G4-22 | G4-23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TET | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| CEP | I | R | R | R | I | R | I | I | R | S | I |
| TMP-SMX | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| AMP | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| AMK | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | S |
| POL | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| LEV | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| CIP | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| NA | R | S | S | I | S | I | S | S | I | S | S |
| CLO | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | S |
| AMX | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| GEN | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | I | S | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora-Coto, D.; Moreno-Vélez, P.; Luna-Muñoz, J.; Moreno-Campuzano, S.; Ontiveros-Torres, M.A. Intestinal and Extraintestinal Pathotypes of Escherichia coli Are Prevalent in Food Prepared and Marketed on the Streets from the Central Zone of Mexico and Exhibit a Differential Phenotype of Resistance Against Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040406
Mora-Coto D, Moreno-Vélez P, Luna-Muñoz J, Moreno-Campuzano S, Ontiveros-Torres MA. Intestinal and Extraintestinal Pathotypes of Escherichia coli Are Prevalent in Food Prepared and Marketed on the Streets from the Central Zone of Mexico and Exhibit a Differential Phenotype of Resistance Against Antibiotics. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040406
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora-Coto, Daniela, Pedro Moreno-Vélez, José Luna-Muñoz, Samadhi Moreno-Campuzano, and Miguel Angel Ontiveros-Torres. 2025. "Intestinal and Extraintestinal Pathotypes of Escherichia coli Are Prevalent in Food Prepared and Marketed on the Streets from the Central Zone of Mexico and Exhibit a Differential Phenotype of Resistance Against Antibiotics" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040406
APA StyleMora-Coto, D., Moreno-Vélez, P., Luna-Muñoz, J., Moreno-Campuzano, S., & Ontiveros-Torres, M. A. (2025). Intestinal and Extraintestinal Pathotypes of Escherichia coli Are Prevalent in Food Prepared and Marketed on the Streets from the Central Zone of Mexico and Exhibit a Differential Phenotype of Resistance Against Antibiotics. Antibiotics, 14(4), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040406







