Frequency, Distribution, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus sciuri Isolated from Dogs and Their Owners in Rio de Janeiro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distribution of Staphylococci and M. sciuri Amongst Owners and Dogs
2.2. Identification of MRS and MRMs
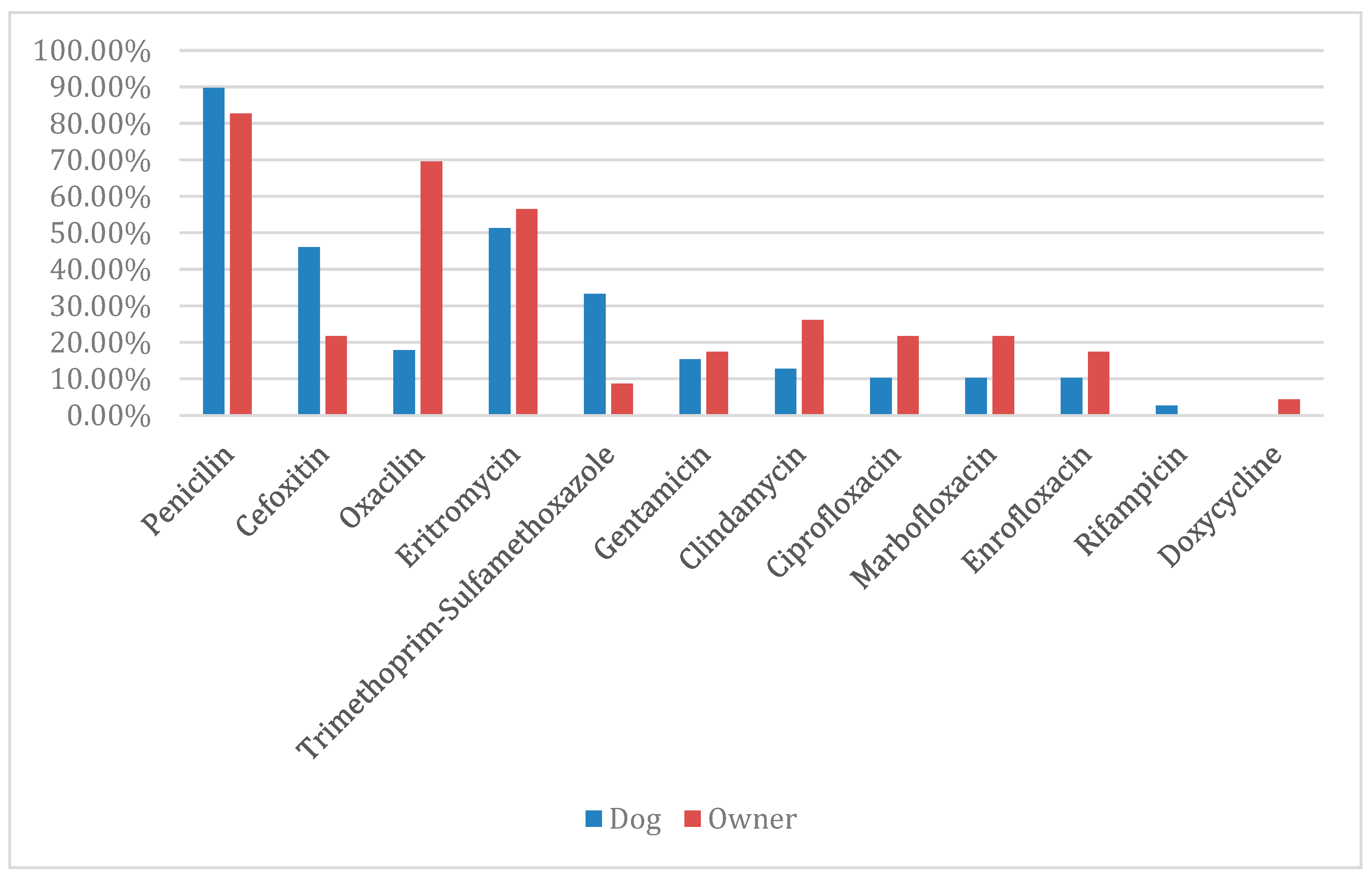
2.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of MRS and MRMs
2.4. Comparative Study Between Dog–Owner Pairs MRS and MRMs
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Study Area, Population, and Samples
4.2. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococci and M. sciuri
4.3. Identification of the mecA Gene
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of MRS and MRM Strains
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prado, R.; Freitas, E.; Júnior, E.V.; Costa, P.; Siqueira, M.; Rossi, D. Staphylococcus spp.: Importantes riscos à saúde pública. Pubvet 2015, 9, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List of Prokariotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature—LPSN. Available online: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Urbaneja, M.E. Implicações da resistência bacteriana por Staphylococcus spp. na medicina veterinária. Pubvet 2024, 18, e1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.R.; Rosenthal, K.S.; Pfaller, M.A. Medical Microbiology, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.P.L.; da Cunha, M.d.L.R.d.S. Avaliação da colonização nasal por Staphylococcus spp. resistenteà oxacilina em alunos de enfermagem. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2009, 45, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.A.; Vancanneyt, M.; Baele, M.; Vaneechoutte, M.; De Graef, E.; Snauwaert, C.; Cleenwerck, I.; Dawyndt, P.; Swings, J.; Decostere, A.; et al. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius sp. nov., a coagulase-positive species from animals. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howden, B.P.; Giulieri, S.G.; Lung, T.W.F.; Baines, S.L.; Sharkey, L.K.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Hachani, A.; Monk, I.R.; Stinear, T.P. Staphylococcus aureus host interactions and adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.L.; Santos, D.O.; de Freitas, C.C.; Ferreira, B.L.A.; Afonso, I.F.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Castro, H.C. Staphylococcus aureus: Visitando uma cepa de importância hospitalar. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2007, 43, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Aqib, A.I.; Muzammil, I.; Majeed, N.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Kulyar, M.F.-E.; Fatima, M.; Zaheer, C.-N.F.; Muneer, A.; Murtaza, M.; et al. MRSA compendium of epidemiology, transmission, pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention within one health framework. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1067284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botoni, L.S.; Filho, N.P.R.; Scherer, C.B.; Braga, L.; Leme, F.O.P.; Bicalho, A.C.P.V. Superficial pyoderma due to meticillin resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP). Medvep Derm.—J. Contin. Educ. Dermatol. Vet. Allergol. 2014, 3, 270–277. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, I.M.; Assumpção, Y.D.M.; Paletta, A.C.C.; Aguiar, L.; Guimarães, L.; da Silva, I.T.; Côrtes, M.F.; Botelho, A.M.N.; Jaeger, L.H.; Ferreira, R.F.; et al. Investigation of antimicrobial susceptibility and genetic diversity among Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from dogs in Rio de Janeiro. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Wirth, J.S.; Saravanan, V.S. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. Nov., and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Prem, A.; Tjokrosurjo, J.; Sary, M.; Van Bel, M.A.; Rodrigues-Hoffmann, A.; Kavanagh, M.; Wu, G.; Van Eden, M.E.; Krumbeck, J.A. The canine skin and ear microbiome: A comprehensive survey of pathogens implicated in canine skin and ear infections using a novel next-generation-sequencing-based assay. Veter Microbiol. 2020, 247, 108764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, A.; Giambiagi-Demarval, M.; Rossi, C.C. Mammaliicoccus sciuri’s Pan-Immune System and the Dynamics of Horizontal Gene Transfer Among Staphylococcaceae: A One-Health CRISPR Tale. J. Microbiol. 2024, 62, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacramento, A.G.; Fuga, B.; Monte, D.F.; Cardoso, B.; Esposito, F.; Dolabella, S.S.; Barbosa, A.A.; Zanella, R.C.; Cortopassi, S.R.; da Silva, L.C.; et al. Genomic features of mecA-positive methicillin-resistant Mammaliicoccus sciuri causing fatal infections in pets admitted to a veterinary intensive care unit. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 171, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.A. S. pseudintermedius e S. aureus Resistant Isolates from Dogs with Superficial Pyoderma. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Goiás, Goiás, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, C.C.S.; de Oliveira, A.S.; de Almeida, S.P.; de Oliveira, C.M.S. Importância do Uso Racional de Antimicrobianos em Ambiente Hospitalar. Arquivos 2023, 9, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S.F. Manual de Terapêutica Veterinária, 2nd ed.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Loureiro, R.J.; Roque, F.; Rodrigues, A.T.; Herdeiro, M.T.; Ramalheira, E. O uso de antibióticos e as resistências bacterianas: Breves notas sobre a sua evolução. Rev. Port. Saúde Pública 2016, 34, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial resistance: Risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeghaire, S.; Argudín, M.A.; Feßler, A.T.; Hauschild, T.; Schwarz, S.; Butaye, P. The ecological importance of the Staphylococcus sciuri species group as a reservoir for resistance and virulence genes. Veter Microbiol. 2014, 171, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Torres, C.; Lozano, C.; Zarazaga, M. High diversity of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius lineages and toxigenic traits in healthy pet-owning household members. Underestimating normal household contact? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 36, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suepaul, S.; Georges, K.; Unakal, C.; Boyen, F.; Sookhoo, J.; Ashraph, K.; Yusuf, A.; Butaye, P. Determination of the frequency, species distribution and antimicrobial resistance of staphylococci isolated from dogs and their owners in Trinidad. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, L.; Teixeira, I.M.; da Silva, I.T.; Antunes, M.; Pesset, C.; Fonseca, C.; Santos, A.L.; Côrtes, M.F.; Penna, B. Epidemiologic case investigation on the zoonotic transmission of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius among dogs and their owners. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K.C.; Burnham, C.D.; Westblade, L.F. From canines to humans: Clinical importance of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, L.A.; Kania, S.A.; Kirzeder, E.M.; Eberlein, L.C.; Bemis, D.A. Risk of colonization or gene transfer to owners of dogs with meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Vet. Dermatol. 2009, 20, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matins, C. Staphylococcal Infections in Dogs: Prevalence, Antibacterial Resistance, Risk and Virulence Factors. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Uberlândia, Uberlândia, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, E.M. Occurrence and Characterization of Staphylococcus spp. Methicillin-Resistant Isolates from Dogs and Their Human Contacts in Municipalities in Rio de Janeiro. Master’s Thesis, Federal Fluminense University, Niterói, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dotto, E.K. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococcus Isolated from Dogs, Cats and Humans: Meta-Analysis. Bachelor’s Thesis (Residency in Preventive Veterinary Medicine), Federal University of Santa Maria, Santa Maria, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Weese, J.S.; van Duijkeren, E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in veterinary medicine. Veter Microbiol. 2010, 140, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Osman, M.; Green, B.A.; Yang, Y.; Ahuja, A.; Lu, Z.; Cazer, C.L. Evidence for the transmission of antimicrobial resistant bacteria between humans and companion animals: A scoping review. One Health 2023, 17, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunon, G.I.L.; Silva, E.P.; Faierstein, C.C. Isolation of multiresistant staphylococci from canine otitis and its importance for public health. Bepa 2008, 5, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, M.F.A.; Chaves, L.K.M.; Pereira, G.E.S.; Albuquerque, D.L.; Miranda, M.L.A.F.; Zorzi, L.R.M.; Waterloo, M.M.L. Emergence of antimicrobial resistance in pets: A narrative review of the literature and its implications for Public Health. Res. Soc. Dev. 2024, 13, e45131047090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.S.; Metzger, D.A.; Higuvhi, R. Chelex 100 as a Medium for Simple Extraction of DNA for PCR-Based Typing from Forensic Material. BioTechniques 1991, 10, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; McClure, J.-A.; Elsayed, S.; Louie, T.; Conly, J.M. Novel Multiplex PCR Assay for Characterization and Concomitant Subtyping of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec Types I to V in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5026–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Supplement Document, M100-ed 32; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Malvern, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Second Informational Supplement. VET01-S02; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Malvern, PA, USA, 2018; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Isolated from Dogs % (N) | Isolated from Owners % (N) | TOTAL % (N) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nostrils | Perineum | Nostrils | General | |
| S. pseudintermedius | 22.2 (16) | 27.3 (15) | 6.9 (4) | 18.9 (35) |
| M. sciuri | 19.4 (14) | 20 (11) | 8.6 (5) | 16.2 (30) |
| S. epidermidis | 9.7 (7) | 9.1 (5) | 50 (29) | 22.1 (41) |
| S. urealyticus | 6.9 (5) | 10.9 (6) | 3.5 (2) | 7 (13) |
| S. saprophyticus | 11.1 (8) | 3.6 (2) | 8.6 (5) | 8.1 (15) |
| S. aureus | 8.3 (6) | 5.4 (3) | 13.8 (8) | 9.1 (17) |
| S. hominis | 6.9 (5) | 7.3 (4) | 3.5 (2) | 5.9 (11) |
| S. schleiferi | 1.4 (1) | 9.1 (5) | 0 | 3.2 (6) |
| S. warneri | 5.6 (4) | 1.8 (1) | 1.7 (1) | 3.2 (6) |
| S. haemolyticus | 4.2 (3) | 1.8 (1) | 1.7 (1) | 2.7 (5) |
| S. arlettae | 2.8 (2) | 1.8 (1) | 0 | 1.6 (3) |
| S. xylosus | 1.4 (1) | 1.8 (1) | 0 | 1 (2) |
| S. intermedius | 0 | 0 | 1.7 (1) | 0.5 (1) |
| Total % (N) | 56.7 (72) | 43.3 (55) | 100 (58) | 100 (185) |
| Species | mecA Gene (%) |
|---|---|
| S. epidermidis | 33.9 |
| S, saprophyticus | 16.1 |
| M. sciuri | 14.5 |
| S. hominis | 9.7 |
| S. urealyticus | 6.4 |
| S. haemolyticus | 6.4 |
| S. aureus | 4.8 |
| S. pseudintermedius | 3.2 |
| S. warneri | 3.2 |
| S. schleiferi | 1.6 |
| Pairs | Sample Identification | Bacterial Species | mecA Gene | Site | CFO | PEN | OXA | GEN | CIP | ENO | MBF | ST | ERI | CLI | RIF | DOX | Multidrug-Resistant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 (D) | S. warneri | + | N | 34 | 18 | ---- | 28 | 30 | 30 | 32 | 22 | R | R | 42+ | 36 | * |
| 333 (O) | S. warneri | + | N | 24 | 16 | ---- | 24 | 28 | 32 | 30 | 26 | R | R | 38 | 14 | * | |
| 2 | 33.1 (D) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 18 | 12 | 30 | 34 | 34 | 30 | 22 | 12 | 30 | 42 | 24 | |
| 340 (O) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 34 | 12 | 24 | 32 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 28 | 40 | 30 | ||
| 3 | 83.2 (D) | S. epidermidis | + | P | ---- | 14 | 14 | 30 | 34 | 36 | 34 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 42 | 30 | |
| 353 (O) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 10 | 14 | 24 | 36 | 32 | 34 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 42 | 34 | ||
| 4 | 107.1 (D) | S. saprophyticus | + | P | 26 | 14 | ---- | 30 | 32 | 34 | 30 | 36 | 30 | 26 | 38 | 34 | |
| 358.2 (O) | S. saprophyticus | + | N | 18 | 10 | ---- | 32 | 32 | 36 | 30 | 34 | 30 | 26 | 40 | 38 | ||
| 5 | 316.2 (D) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 36 | 14 | 30 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 24 | 34 | 34 | 42+ | 30 | |
| 410 (O) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 36 | 18 | 26 | 34 | 36 | 36 | 24 | 32 | 32 | 42 | 30 | ||
| 6 | 99 (D) | S. hominis | + | N | 28 | R | ---- | 8 | R | R | 12 | R | 12 | 36 | 42 | 36 | * |
| 347 (O) | S. hominis | + | N | 22 | R | ---- | 10 | R | R | 10 | R | R | 28 | 42 | 32 | * | |
| 7 | 144 (D) | S. pseudintermedius | + | N | ---- | 10 | 16 | 12 | R | R | 8 | R | 10 | 18 | 42 | 36 | * |
| 367 (O) | S. pseudintermedius | + | N | ---- | 10 | 24 | R | R | R | R | R | R | 16 | 36 | 34 | * | |
| 8 | 23 (D) | S. haemolyticus | + | N | 10 | R | ---- | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | 42+ | 28 | * |
| 338 (O) | S. haemolyticus | + | N | 12 | 12 | ---- | R | 26 | 24 | 30 | 24 | R | 20 | 40 | 22 | * | |
| 9 | 216 (D) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 16 | 12 | 16 | 30 | 36 | 34 | 24 | 28 | 30 | 12 | 22 | |
| 387 (O) | S. epidermidis | + | N | ---- | 16 | 14 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 28 | 20 | 10 | 28 | 42 | 32 | ||
| 10 | 223.2 (D) | S. saprophyticus | + | P | 16 | 10 | ---- | 28 | 30 | 28 | 26 | 30 | 28 | 30 | 38 | 34 | |
| 388 (O) | S. saprophyticus | + | N | 20 | 12 | ---- | R | 32 | 34 | 32 | 28 | R | 24 (D) | 42 | 16 | * | |
| 11 | 173 (D) | S. aureus | - | P | 34 | 20 | ---- | 14 | 26 | 30 | 26 | 32 | 6 | 26 | 36 | 34 | |
| 365 (O) | S. aureus | - | N | 36 | 18 | ---- | 12 | 28 | 30 | 26 | 30 | 6 | 26 | 36 | 30 | * | |
| 12 | 319 (D) | S. aureus | - | N | 30 | 18 | ---- | 22 | 28 | 26 | 26 | 30 | 6 | 26 | 34 | 34 | |
| 412 (O) | S. aureus | - | N | 34 | 16 | ---- | 22 | 22 | 28 | 28 | 30 | R | 26 (D) | 32 | 30 | * | |
| 13 | 420 (D) | S. aureus | - | N | 32 | 14 | ---- | 10 | 28 | 24 | 28 | 30 | 6 | 26 (D) | 38 | 30 | * |
| 416 (O) | S. aureus | - | N | 36 | 18 | ---- | 24 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 32 | R | 30 (D) | 38 | 30 | * | |
| 14 | 126 (D) | M. sciuri | - | P | 26 | 28 | ---- | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 18 | 32 | 30 | |
| 130 (D) | M. sciuri | + | N | 26 | 28 | ---- | 26 | 26 | 26 | 24 | 26 | 26 | 20 | 32 | 30 | ||
| 356 (O) | M. sciuri | - | N | 26 | 30 | ---- | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 26 | 26 | 18 | 30 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonnard, F.C.; Guimarães, L.; Teixeira, I.M.; Freire, S.M.; Maia, A.; Pinto, P.C.d.C.A.; Blanchart, T.V.; Penna, B. Frequency, Distribution, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus sciuri Isolated from Dogs and Their Owners in Rio de Janeiro. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040409
Bonnard FC, Guimarães L, Teixeira IM, Freire SM, Maia A, Pinto PCdCA, Blanchart TV, Penna B. Frequency, Distribution, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus sciuri Isolated from Dogs and Their Owners in Rio de Janeiro. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040409
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonnard, Fernanda Cruz, Luciana Guimarães, Izabel Mello Teixeira, Sandryelle Mercês Freire, Alessandra Maia, Patrícia Câmara de Castro Abreu Pinto, Thais Veiga Blanchart, and Bruno Penna. 2025. "Frequency, Distribution, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus sciuri Isolated from Dogs and Their Owners in Rio de Janeiro" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040409
APA StyleBonnard, F. C., Guimarães, L., Teixeira, I. M., Freire, S. M., Maia, A., Pinto, P. C. d. C. A., Blanchart, T. V., & Penna, B. (2025). Frequency, Distribution, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus sciuri Isolated from Dogs and Their Owners in Rio de Janeiro. Antibiotics, 14(4), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040409






